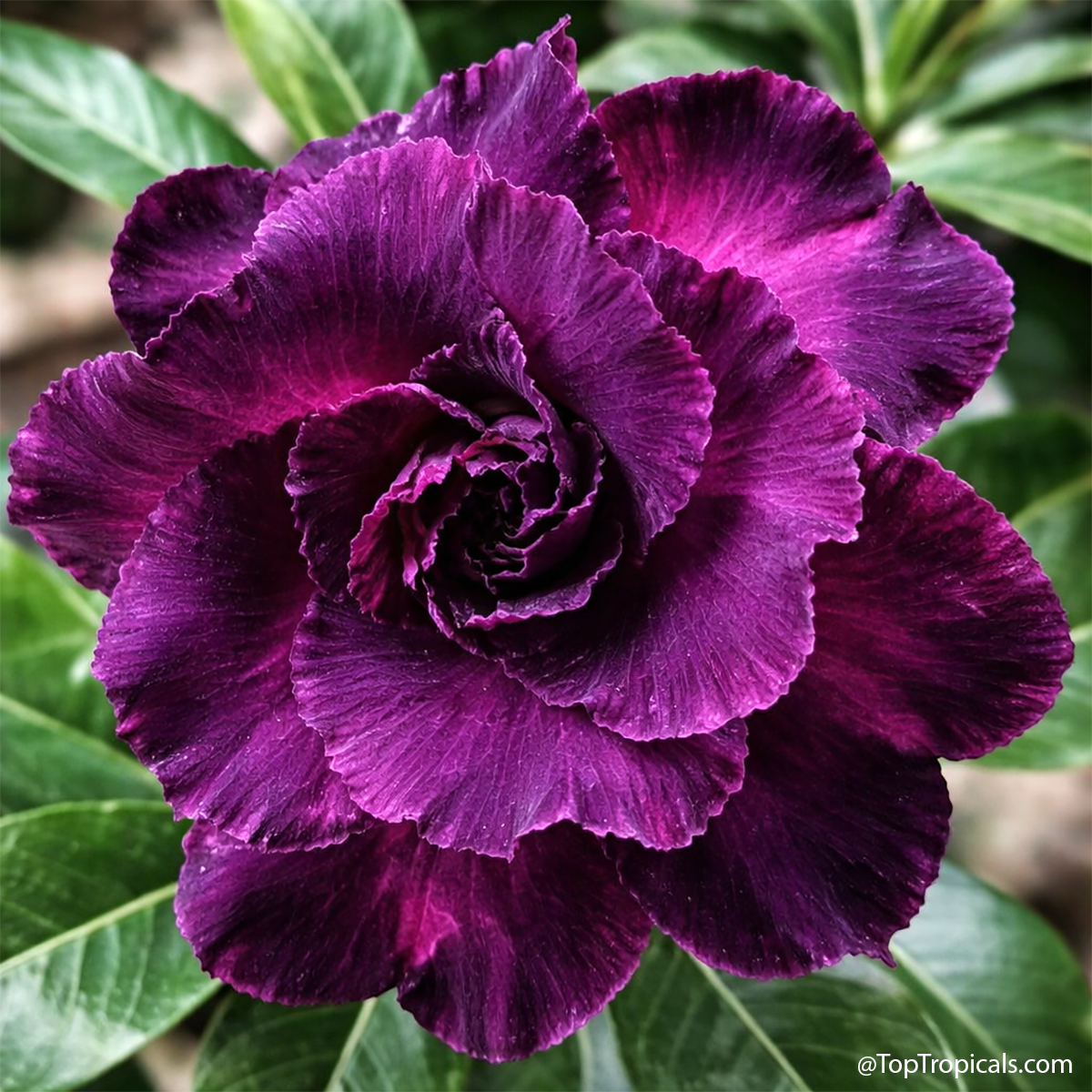
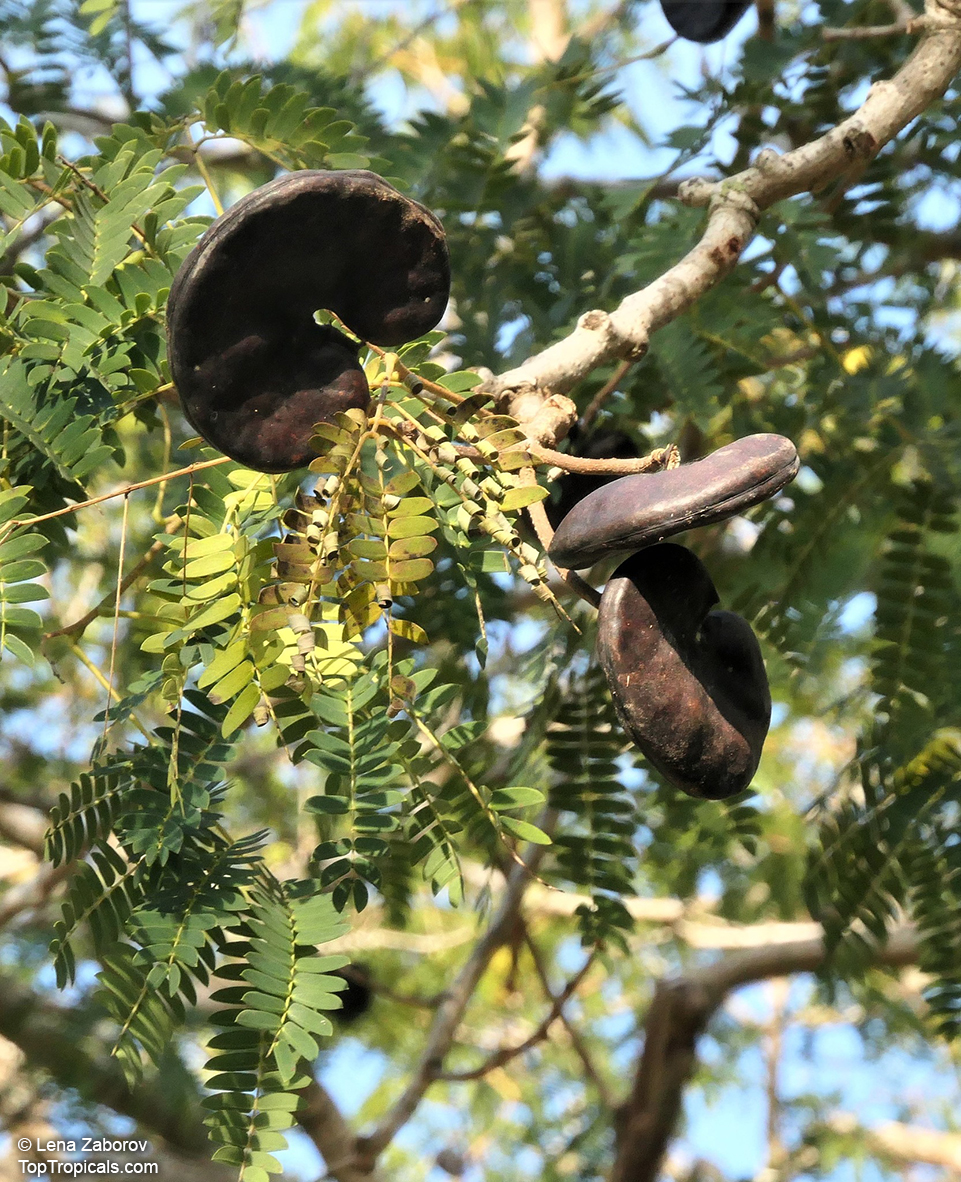
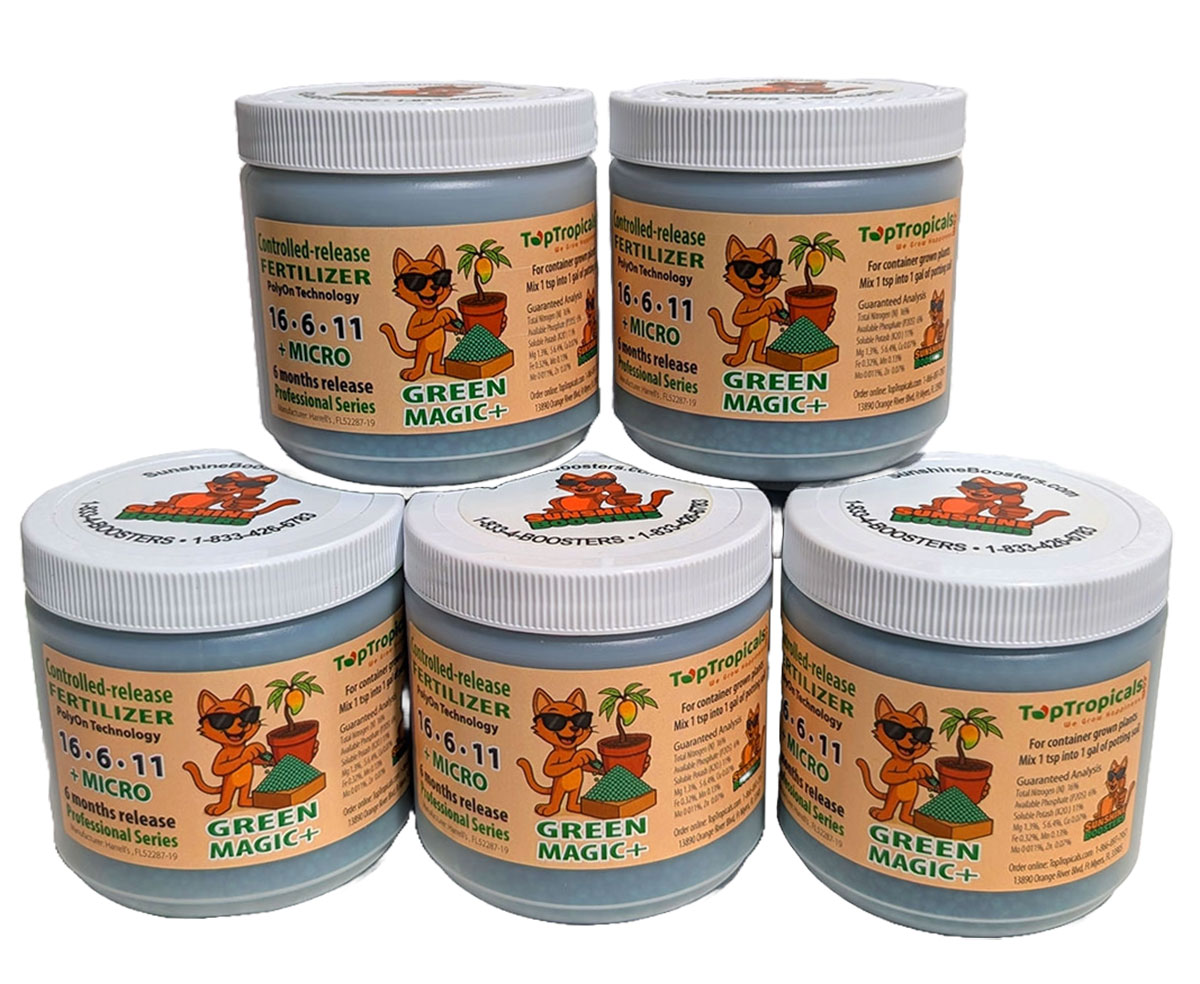
SEARCH RESULTS: NASHIA
| Number of items: 215 |
 Next page | Go to page: 1 2 3 4 5 Last |
Nothing found per your request: nashia. Here are some suggestions
CHECK OUT OUR FLASH DEALS:
BOGO - buy one get one free
Secret Garden - Half price limited time
Discounted items - what's on sale today
See all specials and limited time offers
To stay on top of our deals and be the first one to receive discount coupons - sign up for our Newsletter!
BOGO - buy one get one free
Secret Garden - Half price limited time
Discounted items - what's on sale today
See all specials and limited time offers
To stay on top of our deals and be the first one to receive discount coupons - sign up for our Newsletter!






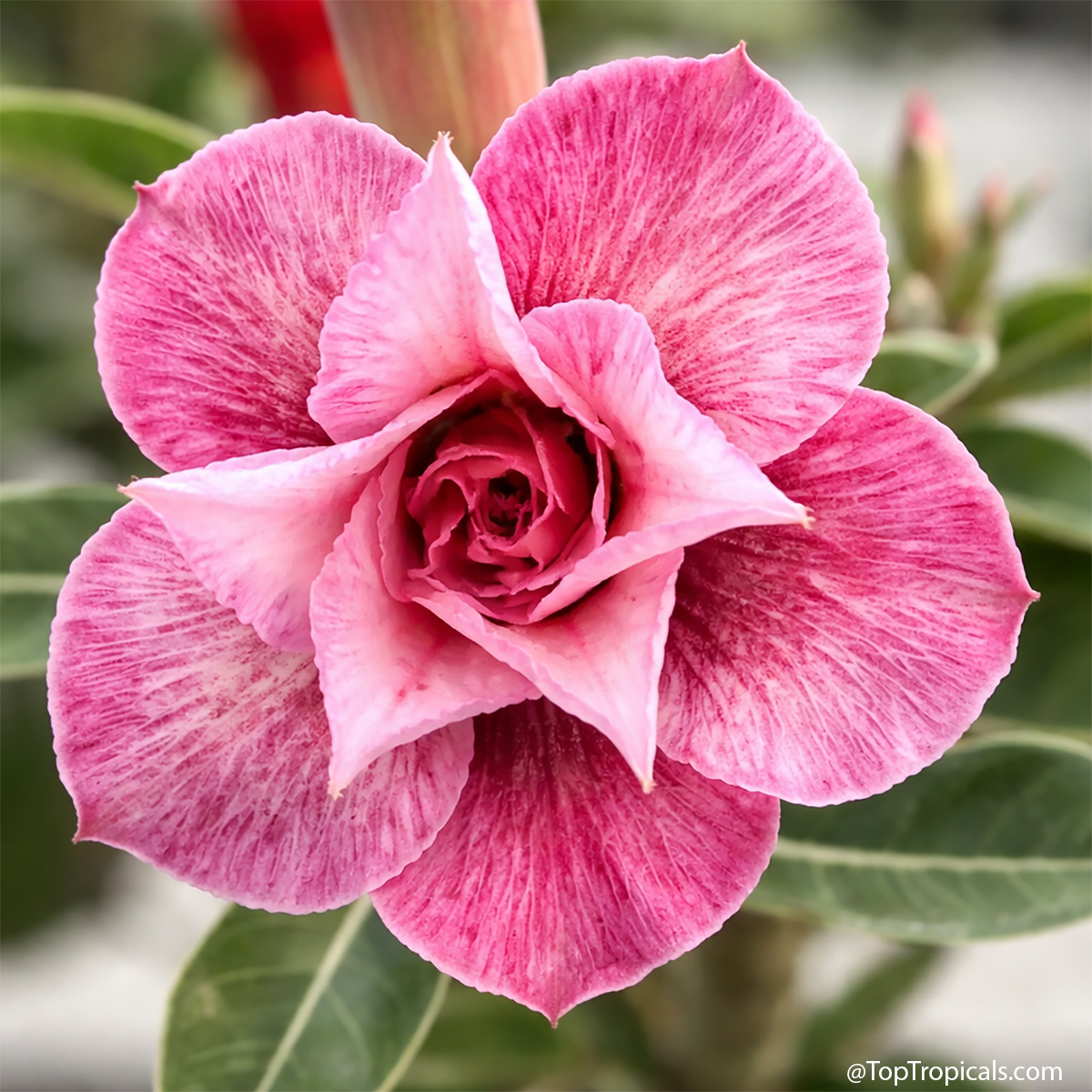
Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE C-Cibus - Crop Nutrition Booster
SUNSHINE-Honey - sugar booster
Grown in
10"/3 gal pot
8 plants in stock
$89.95






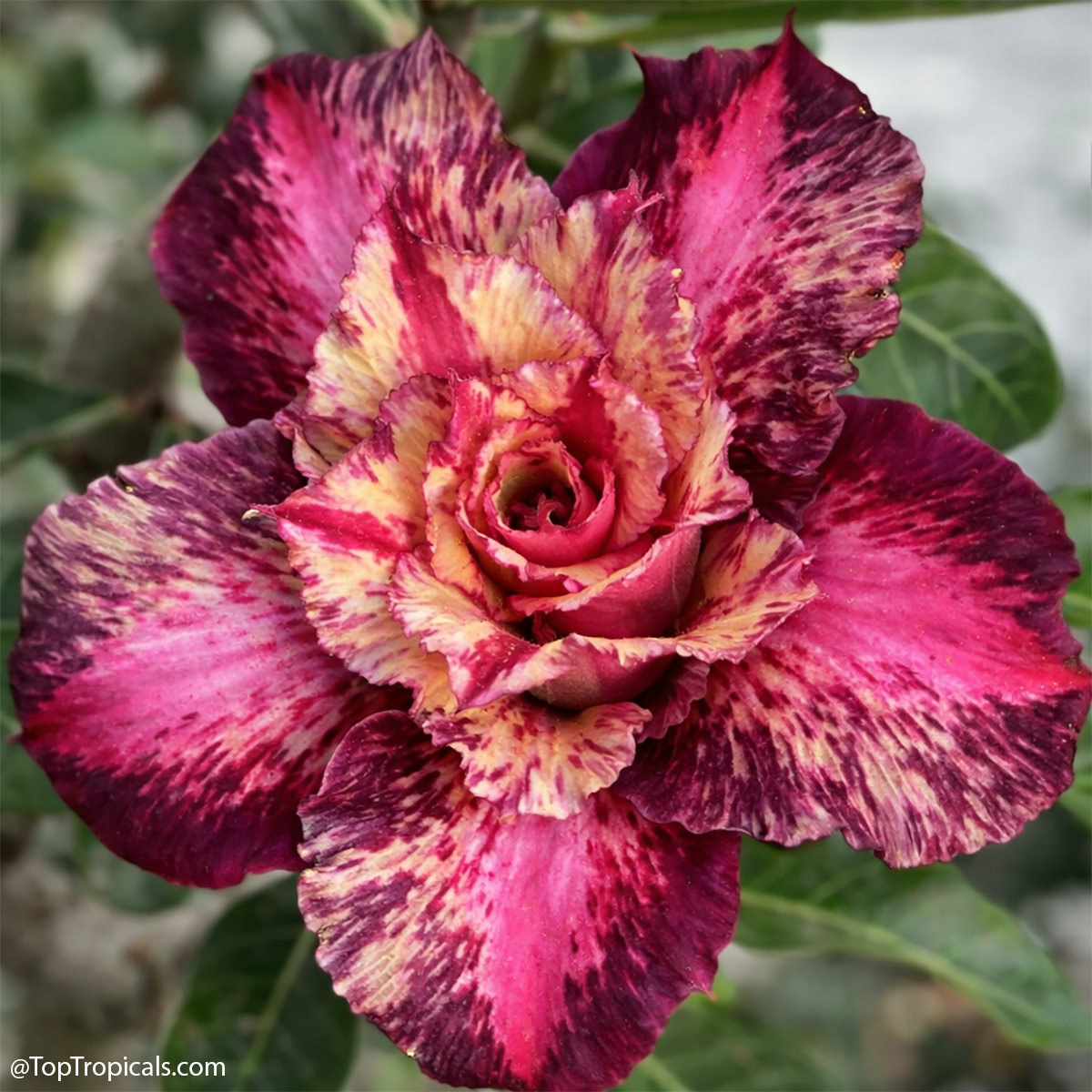
Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE C-Cibus - Crop Nutrition Booster
SUNSHINE-Honey - sugar booster
Grown in
10"/3 gal pot
5 plants in stock
$89.95






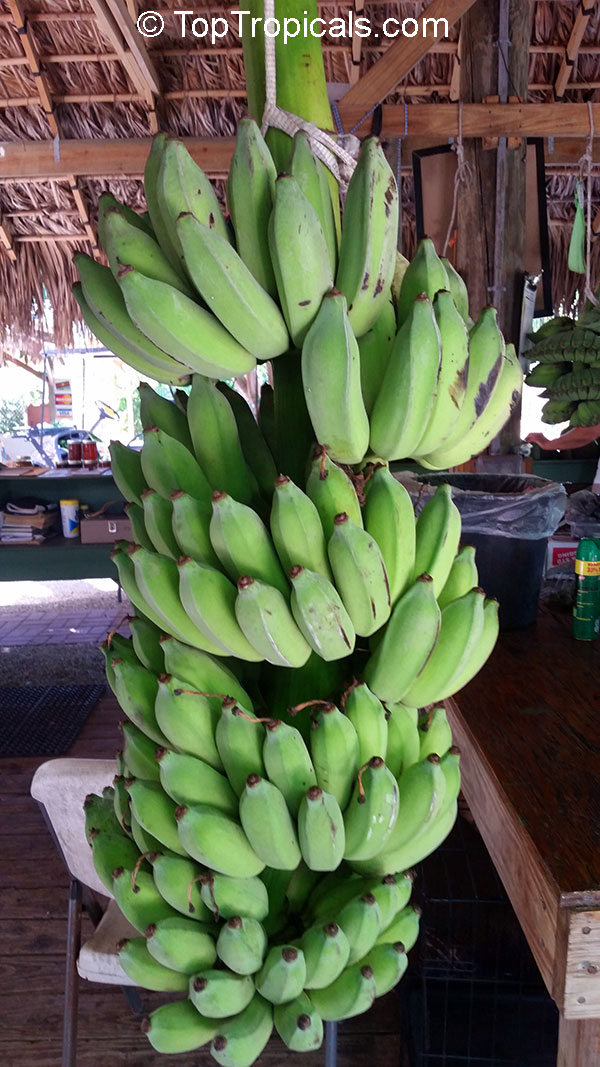
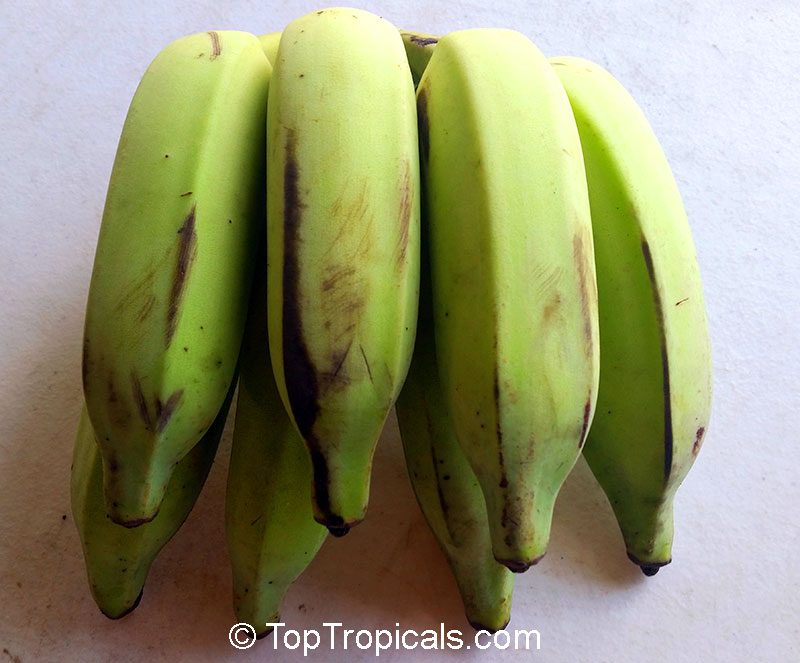
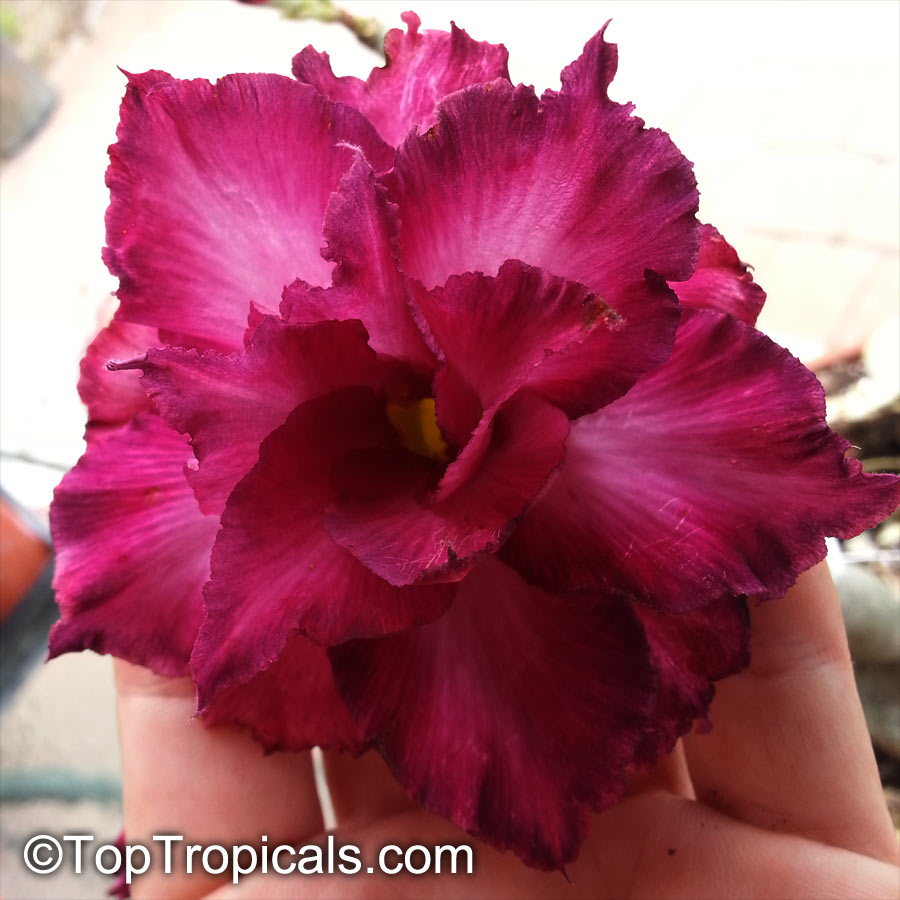
Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Robusta - Rapid Growth Booster
Local pickup only. This item is not available for shipping. Local delivery may be available in Ft. Myers or Sebring, Florida. Contact us for an estimate. Non-pickup orders are subject to restocking fees.
Grown in
10"/3 gal pot, large plant, pick up only
2 Plants in stock
$49.95
Sale $29.95
Max purchase qty: 2






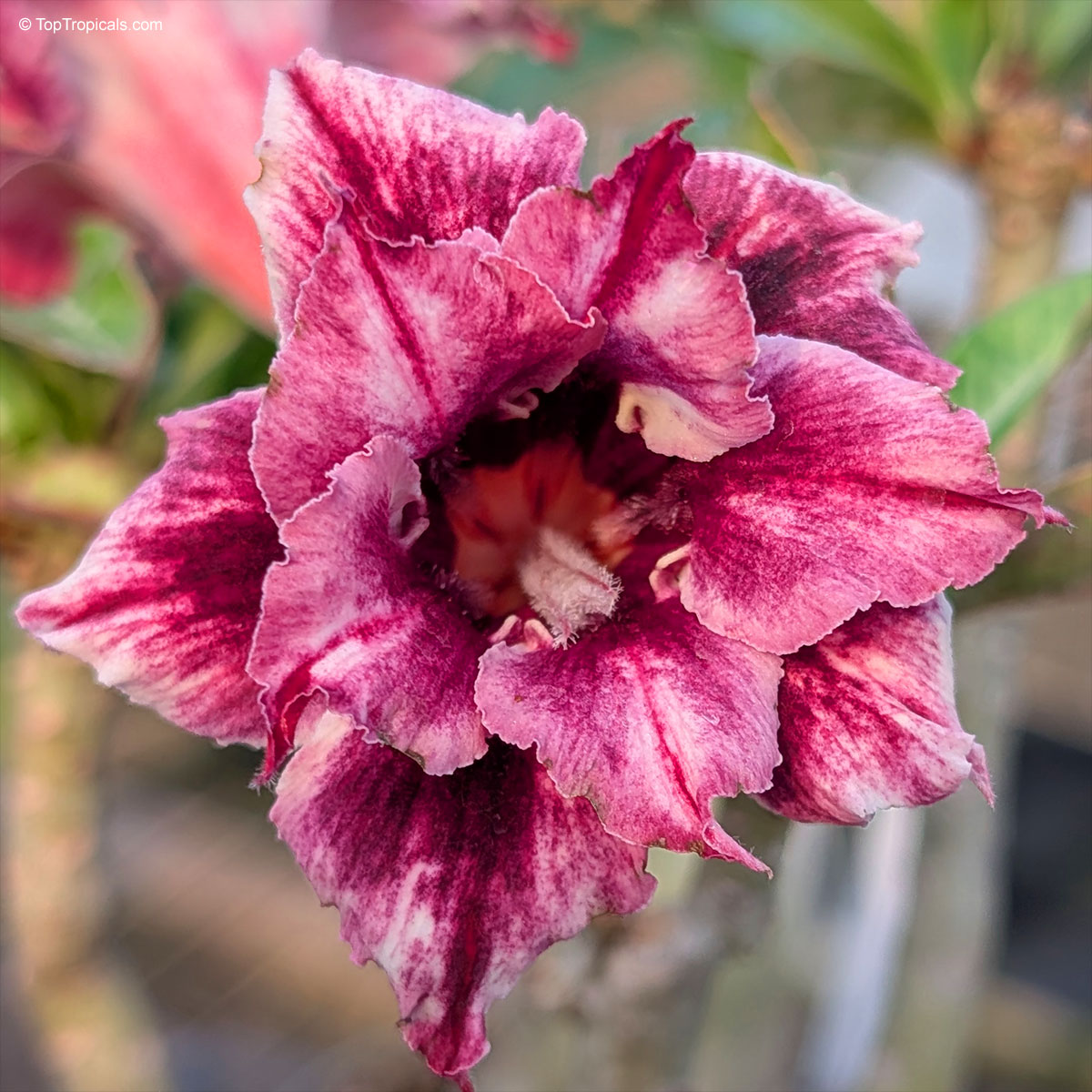
Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Robusta - Rapid Growth Booster
Local pickup only. This item is not available for shipping. Local delivery may be available in Ft. Myers or Sebring, Florida. Contact us for an estimate. Non-pickup orders are subject to restocking fees.
Grown in
10"/3 gal pot, large plant, pick up only
5 Plants in stock
$49.95
Sale $29.95





Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Robusta - Rapid Growth Booster
Grown in
10"/3 gal pot, very large plant, topped for shipping
4 plants in stock
$49.95





Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Robusta - Rapid Growth Booster
Grown in
10"/3 gal pot, large plant, topped for shipping
4 plants in stock
$49.95





Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Robusta - Rapid Growth Booster
Grown in
10"/3 gal pot
6 plants in stock
$69.95





Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Robusta - Rapid Growth Booster
Grown in
10"/3 gal pot, topped for shipping
4 plants in stock
$49.95








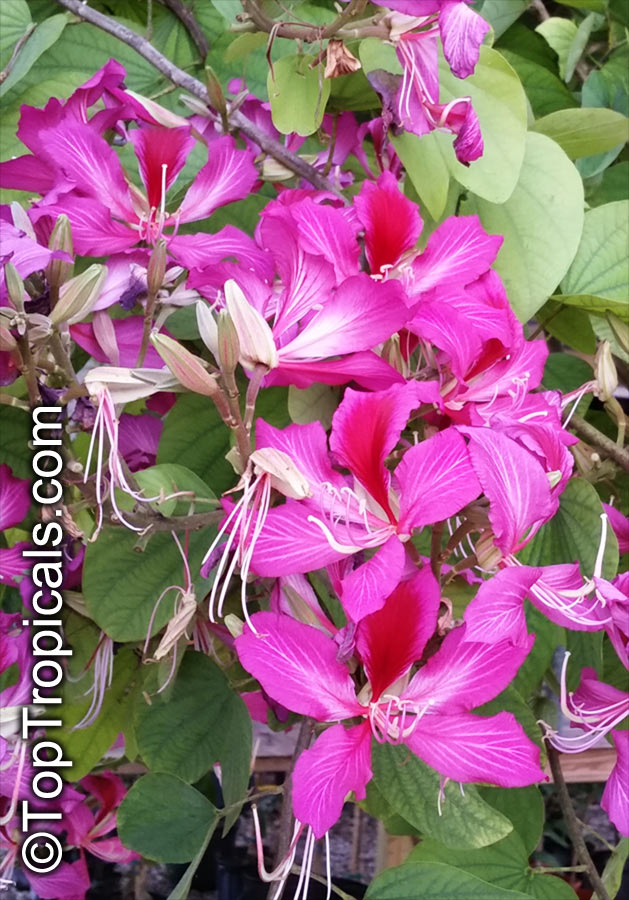
Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Megaflor - Bloom Nutrition Booster
Grown in
6"/1 gal or larger pot
In stock
$69.95









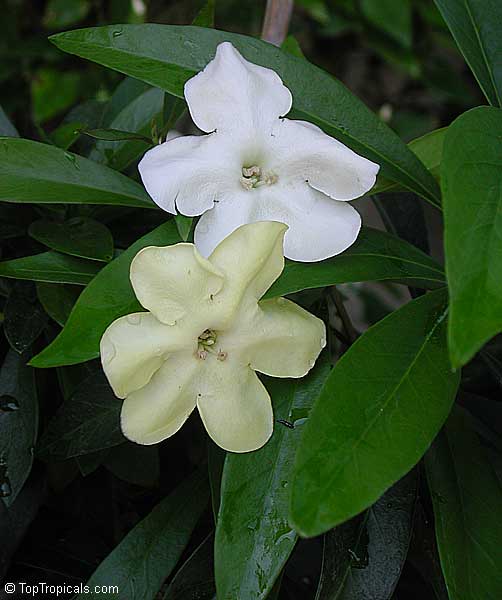
Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Pikake - Fragrant Flower Booster
Grown in
10"/3 gal pot
3 Plants in stock
$49.95






Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Megaflor - Bloom Nutrition Booster
Grown in
10"/3 gal pot, large plant
In stock
$39.95
Sale $29.95






Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Megaflor - Bloom Nutrition Booster
Grown in
14"/7 gal pot, large plant
7 Plants in stock
$79.95








Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Robusta - Rapid Growth Booster
Grown in
6"/1 gal pot
In stock
$39.95








Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Megaflor - Bloom Nutrition Booster
Grown in
10"/3 gal pot
4 plants in stock
$59.95










Recommended Supplies: SUNSHINE Megaflor - Bloom Nutrition Booster
SUNSHINE-Epi - Caudex booster
Adenium Soilless Mix
Succulent Care. This plant is shipped bare-rooted. Plant it in well-drained soil mix, water and keep in warm (75-80F) place in filtered light. Let soil dry between waterings.
Grown in
6"/1 gal pot, shipped barerooted
In stock
$49.95













Recommended Supplies: SUNSHINE Megaflor - Bloom Nutrition Booster
SUNSHINE-Epi - Caudex booster
Adenium Soilless Mix
Succulent Care. This plant is shipped bare-rooted. Plant it in well-drained soil mix, water and keep in warm (75-80F) place in filtered light. Let soil dry between waterings.
Grown in
6"/1 gal pot, shipped barerooted
10 plants in stock
$49.95













Recommended Supplies: SUNSHINE Megaflor - Bloom Nutrition Booster
SUNSHINE-Epi - Caudex booster
Adenium Soilless Mix
Succulent Care. This plant is shipped bare-rooted. Plant it in well-drained soil mix, water and keep in warm (75-80F) place in filtered light. Let soil dry between waterings.
Grown in
6"/1 gal pot, shipped barerooted
10 plants in stock
$49.95









Recommended Supplies: SUNSHINE Megaflor - Bloom Nutrition Booster
SUNSHINE-Epi - Caudex booster
Adenium Soilless Mix
Succulent Care. This plant is shipped bare-rooted. Plant it in well-drained soil mix, water and keep in warm (75-80F) place in filtered light. Let soil dry between waterings.
Grown in
6"/1 gal pot, shipped barerooted
7 plants in stock
$49.95









Recommended Supplies: SUNSHINE Megaflor - Bloom Nutrition Booster
SUNSHINE-Epi - Caudex booster
Adenium Soilless Mix
Succulent Care. This plant is shipped bare-rooted. Plant it in well-drained soil mix, water and keep in warm (75-80F) place in filtered light. Let soil dry between waterings.
Grown in
6"/1 gal pot, shipped barerooted
5 plants in stock
$49.95










Recommended Supplies: SUNSHINE Megaflor - Bloom Nutrition Booster
SUNSHINE-Epi - Caudex booster
Adenium Soilless Mix
Succulent Care. This plant is shipped bare-rooted. Plant it in well-drained soil mix, water and keep in warm (75-80F) place in filtered light. Let soil dry between waterings.
Grown in
6"/1 gal pot, shipped barerooted
5 plants in stock
$49.95













Recommended Supplies: SUNSHINE Megaflor - Bloom Nutrition Booster
SUNSHINE-Epi - Caudex booster
Adenium Soilless Mix
Succulent Care. This plant is shipped bare-rooted. Plant it in well-drained soil mix, water and keep in warm (75-80F) place in filtered light. Let soil dry between waterings.
Grown in
6"/1 gal pot, shipped barerooted
9 plants in stock
$49.95










Recommended Supplies: SUNSHINE Megaflor - Bloom Nutrition Booster
SUNSHINE-Epi - Caudex booster
Adenium Soilless Mix
Succulent Care. This plant is shipped bare-rooted. Plant it in well-drained soil mix, water and keep in warm (75-80F) place in filtered light. Let soil dry between waterings.
Grown in
6"/1 gal pot, shipped barerooted
10 plants in stock
$49.95






Grown in
6"/1 gal or larger pot
In stock
$29.95
Professional-grade, balanced, controlled-release granulated...
more
This item may be shipped separately from plants.
This item may be shipped separately from plants.
1 lb (1 jar)
In stock
$14.95
| Number of items: 215 |
 Next page | Go to page: 1 2 3 4 5 Last |


























