Garden Blog - Top Tropicals
Date:
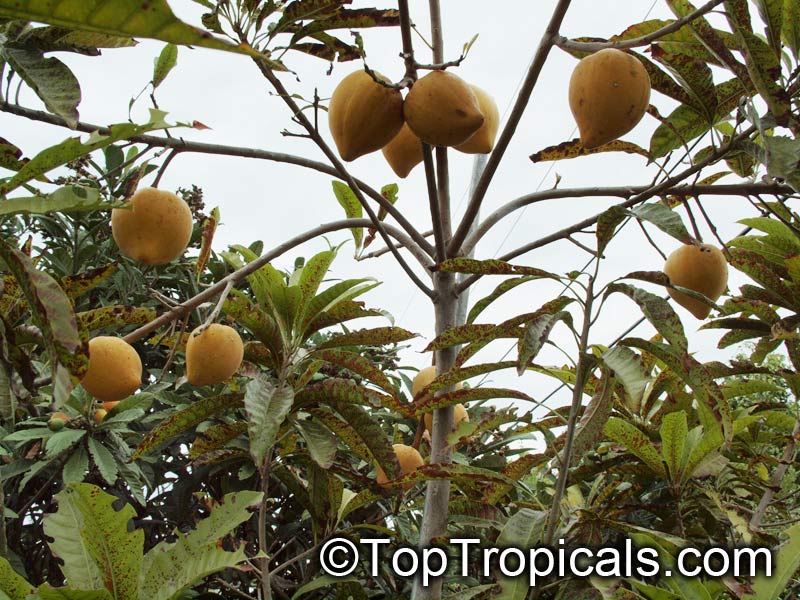
What is Akee?
Grow Your Own Food
Q: What is Akee and how do you eat it? Is it a fruit or a vegetable?
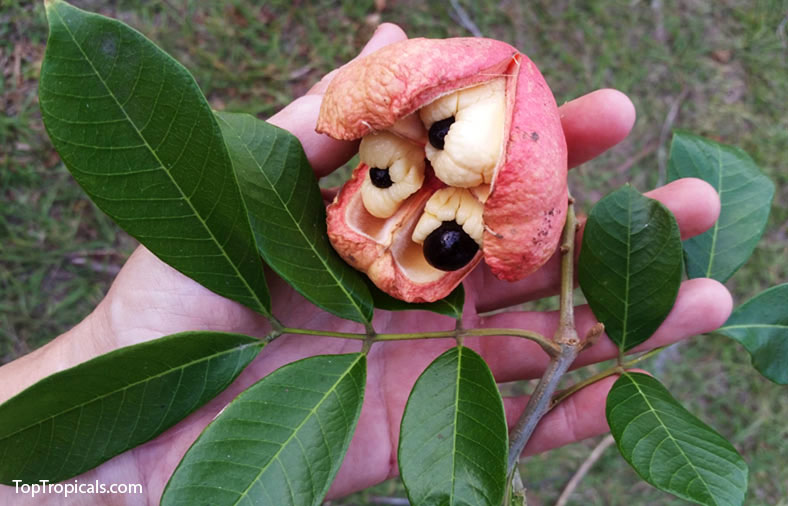
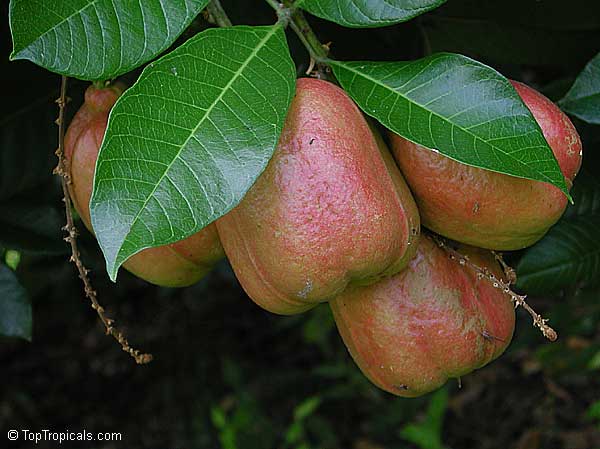
A: Blighia sapida, commonly known as Akee, holds a special place as the Jamaican National Fruit. The fruit of this medium size, fast growing subtropical tree is used as a vegetable, is renowned for its delicious taste, vibrant red pods, and creamy texture. Akee is primarily grown in Jamaica and is an integral part of Jamaican cuisine. Its unique ripening process and the need for careful preparation make it distinctive.
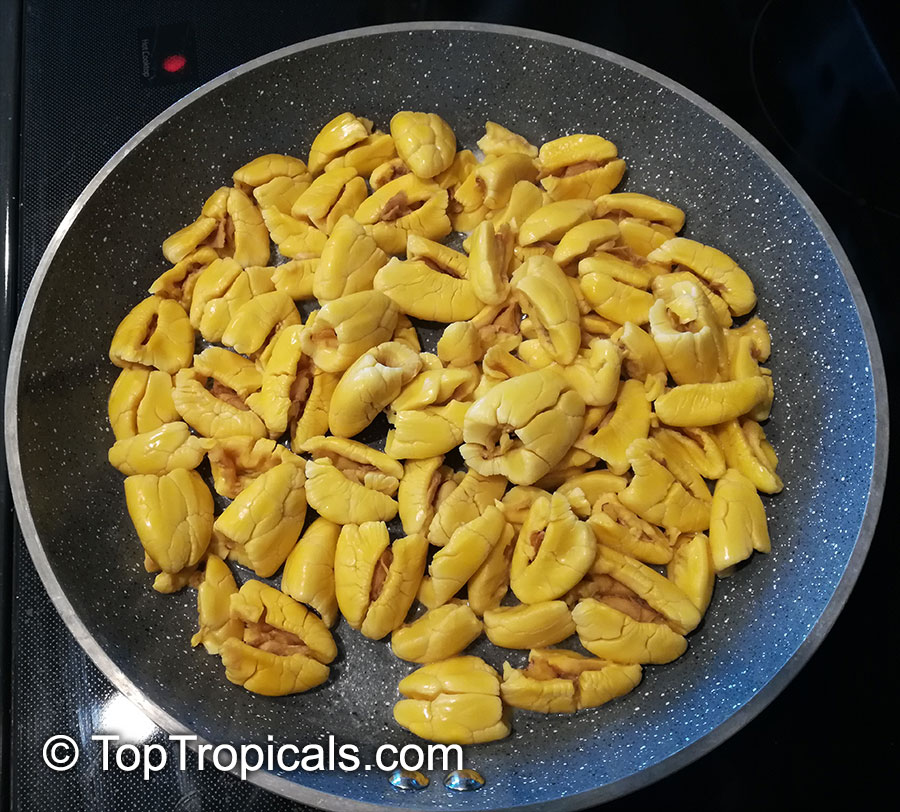
The fruit starts off green and gradually transforms into a vibrant red hue when it matures. To enjoy Akee, the pods must be harvested when fully ripe, and the skin should be orange to red. They are then carefully opened, revealing three distinct sections: the creamy white or yellow flesh, the central seed, and a thin, dark membrane. The seed and the membrane are not edible, only the ripe yellow flesh is consumed, which has a soft, buttery consistency and a mild, nutty flavor.
Akee is often cooked and served in various traditional Jamaican dishes. It is famously paired with salted codfish, creating the popular national dish known as "Ackee and Saltfish." This dish is a flavorful combination of sauteed Akee with flaked salted codfish, onions, peppers, tomatoes, and spices. Akee is also used in stews, curries, and salads, adding a rich and distinct taste to the culinary preparations.
Beyond its culinary significance, Akee holds cultural and historical importance in Jamaica. It is believed to have been brought to the Caribbean region from West Africa during the transatlantic slave trade era. Today, Akee symbolizes national pride and is a source of cultural identity for Jamaicans.
Akee tree is fast growing and easy to grow. It will start producing within 2-3 years after planting.
Date:
Repotting tropical plants
By Alex Butova, the Witch of Herbs and Cats
Q: When is the best time to repot tropical plants?
A: Repotting tropical plants is vital for their overall health and growth. The best time to repot them is during the Spring through early Summer, when they start active growth.
Start by selecting a well-draining soil mix that consists of equal parts potting soil, peat moss, and perlite. Gather the necessary supplies, including a slightly larger pot, the soil mix, and a good fertilizer
Carefully remove the plant from its current pot, trim any damaged branches, and place it in the new pot with fresh soil mix. Be sure to position the plant with the growth point slightly above the soil level. Water the plant thoroughly but avoid overwatering. After repotting, find an appropriate location with suitable lighting conditions for your plant. Monitor the moisture levels and water when the top inch of the soil feels dry.
Additionally, apply the appropriate Sunshine Boosters fertilizer according to the instructions on the packaging. Use Sunshine Boosters fertilizers for specific plant needs (Robusta for foliage, Megaflor for flowering, Ananas for pineapples, etc.). It is safe to apply Sunshine Boosters all year around. Keep a close eye on the plant for any signs of stress or issues and adjust your care routine as needed. Help the plant to cope with stress by spraying with solution of Sunshine Epi.
Enjoy the beauty of your thriving indoor tropical garden!
Date:
NEW
VIDEO:
ABC7 Fort Myers News:
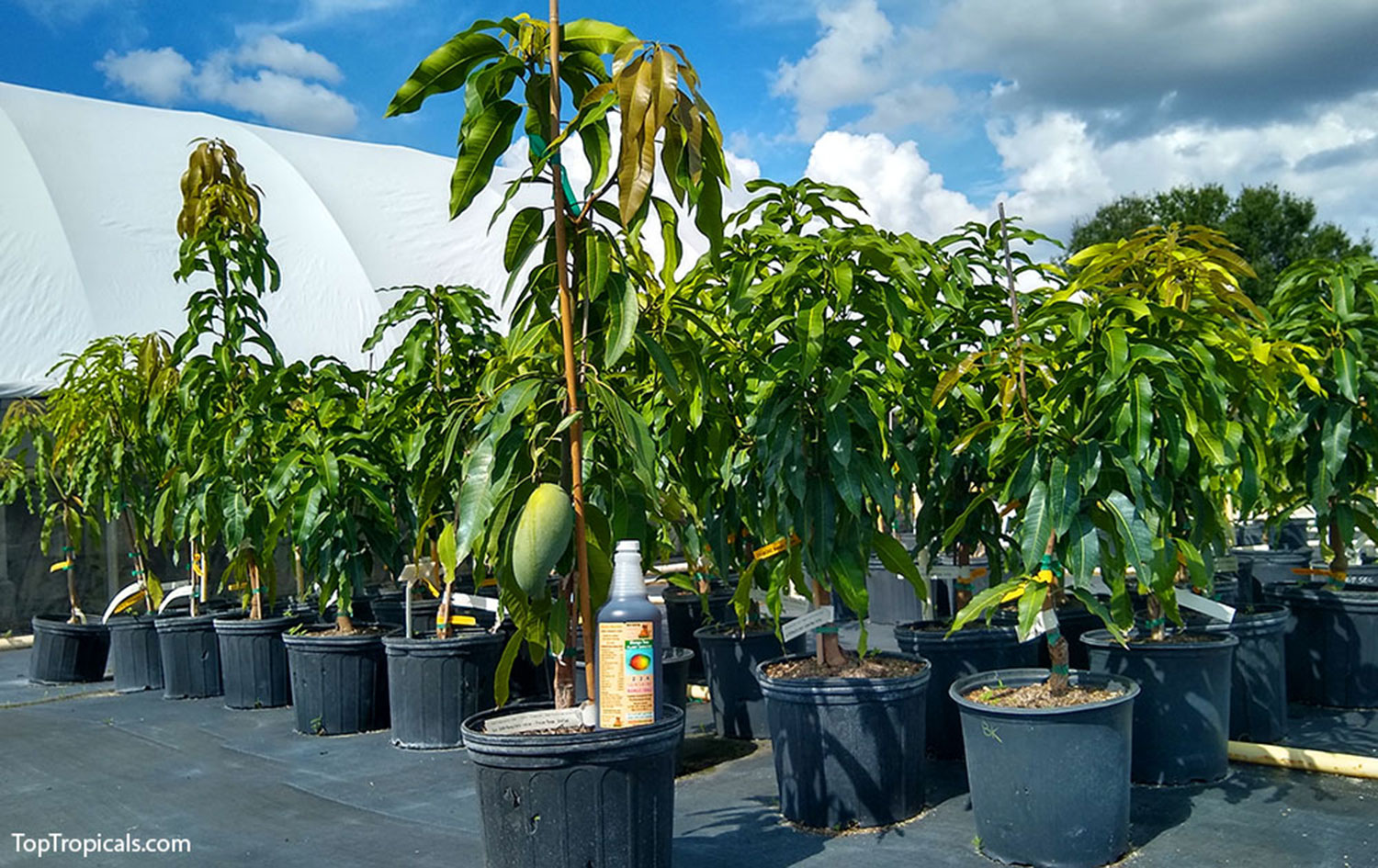
Mango Varieties at Top Tropicals
We continue the series of ABC-7 News on Top Tropicals selections. Previously, we showed you segments about Butterfly Plants and Rare Fruit Trees. Today's video will show you how to pick the best mango tree and how to take care of it.
At Top Tropicals, we have over a hundred varieties of mango, from Dwarf "Condo" mangoes to large upright trees, from colorful fruit to green Asian varieties. We have them all! And we can ship them to your door. Top Tropicals is open seven days a week, and their staff can answer all of your questions.
Watch the news segment by Rachel Anderson for ABC-7:
Mango Varieties at Top Tropicals
.
Subscribe to our Channel:
Stay updated with TopTropicals Videos by subscribing to our channel at YouTube.com/TopTropicals and get our latest video news of what is fruiting and blooming!
Date:
PeopleCats of the month:
Cat Brothers
Photo above: You've met before Georgie and Philemon but you probably
didn't know they were brothers. Not twins, because they were from litters
following each other, so Georgie is the older brother. But they both are very
smart, maybe their mother taught them the same tricks.
Photo below: Wesley and Marco are actually real twins... but they are so
different! Fat and skinny, lazy and crazy, quiet and loud, velvet and fluffy.
But they are both very sweet and loving!
Gemini Cats and their Zodiac
5/21-6/20
By Alex Butova, the Witch of Herbs and Cats
Today's story is about Gemini cats.
They are known for their exceptional communication skills. They are
undoubtedly quite the chatty felines! With a diverse repertoire of meows, and it's
up to us humans to decipher their messages. These cats possess remarkable
intelligence, capable of uttering words like 'hello' and posing 'why?' questions,
even when they are just kittens. If you happen to leave paint around, be
prepared for Gemini cats to step in it and leave paw print messages around the
house. It's their way of communicating in a feline code that may elude our
comprehension.
CONTINUE READING >>
Date:
Top
Tropicals TikTok Reels:
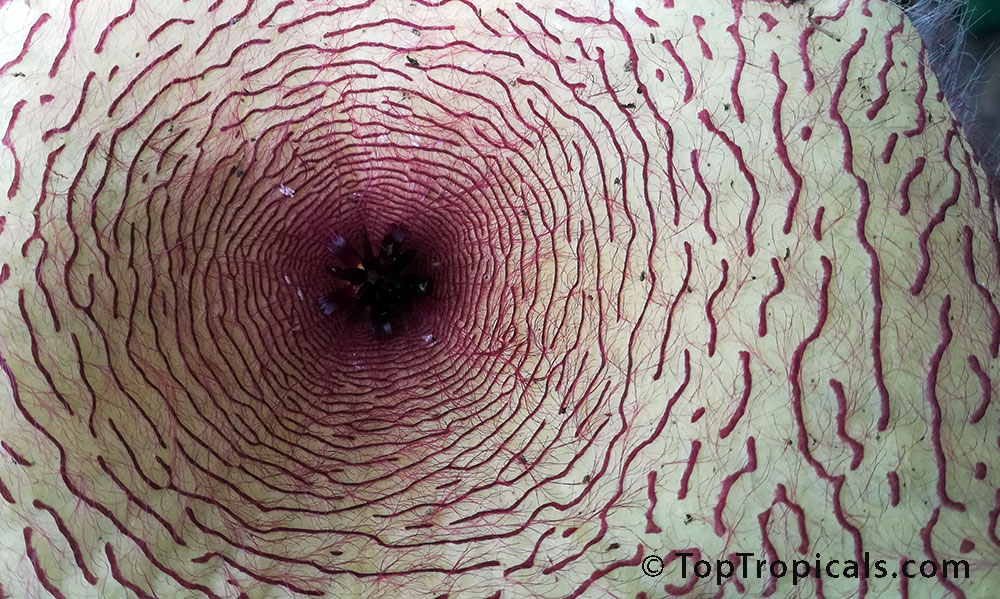
Starfish Flower - Stapelia gigantea
Calling all Exotic Gardeners!
Discover a botanical amusement on our TikTok channel! Unearth rare plants, bizarre and strange flowers, and hidden treasures from around the globe. Join our passionate community and let's explore the extraordinary together. Follow us at tiktok.com/@toptropicals and unlock a world of captivating green wonders!
Our first reel is introducing Stapelia gigantea - Starfish Flower, Giant Toad Flower, Carrion Flower... This is one of the largest flowers in the plant world!...
Subscribe to our TikTok Channel:
Stay updated with TopTropicals Videos by subscribing to our channel at tiktok.com/@toptropicals and get our latest video news of what is fruiting and blooming!
Date:
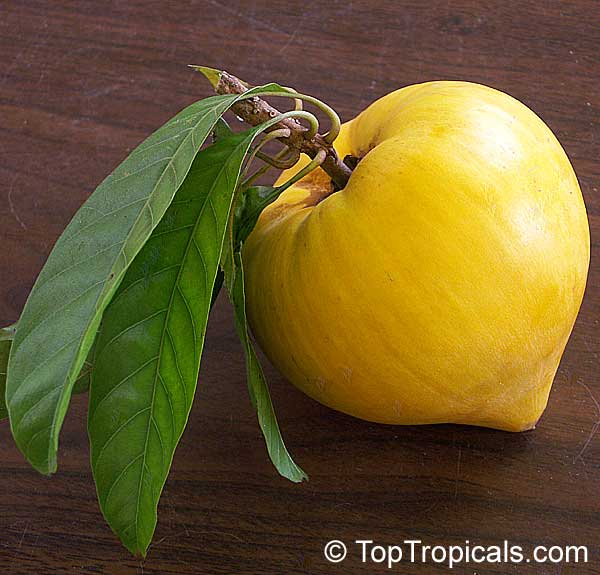
Benefits of Canistel tree and fruit
Q: What is so good about Canistel fruit? Should I plant a Canistel tree in my garden?
A: Canistel fruit, also known as Eggfruit, has several appealing qualities. It is highly regarded for its sweet, custard-like flavor and smooth, creamy texture. Additionally, canistel fruit is a good source of essential nutrients such as vitamin A, vitamin C, and dietary fiber, making it a nutritious choice for those seeking a unique and tasty fruit experience.
Planting a Canistel tree can be beneficial for a few reasons. Firstly, it allows you to enjoy the delectable fruit it produces right in your own backyard, providing a fresh and unique addition to your homegrown produce.
Secondly, Canistel trees are relatively low-maintenance and can thrive in warm climates, making them a suitable choice for tropical or subtropical regions.
Finally, by planting a Canistel tree, you contribute to the preservation and diversity of fruit-bearing trees, enriching the ecosystem and potentially attracting wildlife to your garden.
To learn more about Canistel tree, fruit, tasty recipes, and more - see this article:
Pouteria campechiana - Canistel, the curious heart-shaped Egg Super-Fruit
Date:
Horoscope for Guanabana tree?
By Alex Butova, the Witch of Herbs and Cats
Q: What is the ruling planet of Guanabana? I have searched the internet, but can't find anything. Thought maybe you might know?
A: Annona muricata is native to the Caribbean and Central America, which falls under the patronage of the Pisces constellation. The planets that rule the house for this constellation are the Moon, Jupiter, and Neptune, with Water being a key element of its essence. These planets can be considered the ruling planets for the Guanabana plant...
Date:
NEW
VIDEO:
ABC7 Fort Myers News:
Rare Tropical Fruit Trees at Top Tropicals
We received lots of orders from our customers for butterfly attracting plants after our recent . We are glad you liked the story and the plants!
Today's topic is on tropical fruit. Enjoy this quick tour and learn more about different varieties of rare tropical fruit and what can be grown in your yard. We have them all! And we can ship them to your door.
Fruit and plants introduced in the video:
Persimmon
Coffee
Sapodilla
Sapote
Vanilla
Pomegranate
Yellow Dragon
fruit
Litchi
Tamarind
Chocolate
Tree
Raspberry
Grape
Watch the news segment by Rachel Anderson for ABC-7: Rare fruit trees at Top Tropicals.
Subscribe to our Channel:
Stay updated with TopTropicals Videos by subscribing to our channel at YouTube.com/TopTropicals and get our latest video news of what is fruiting and blooming!
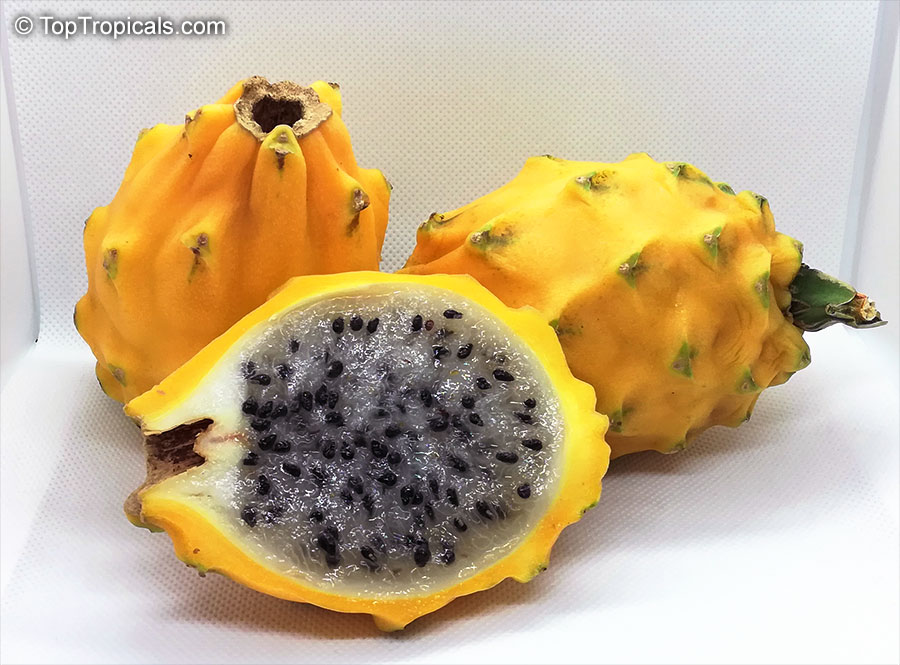
In the photo: Yellow Dragon Fruit, Selenicereus megalanthus, the sweetest and the most flavorful rare Yellow Pitaya. The taste is said to be superior to most cactus fruits.
Date:
NEW
VIDEO:
ABC7 Fort Myers News:
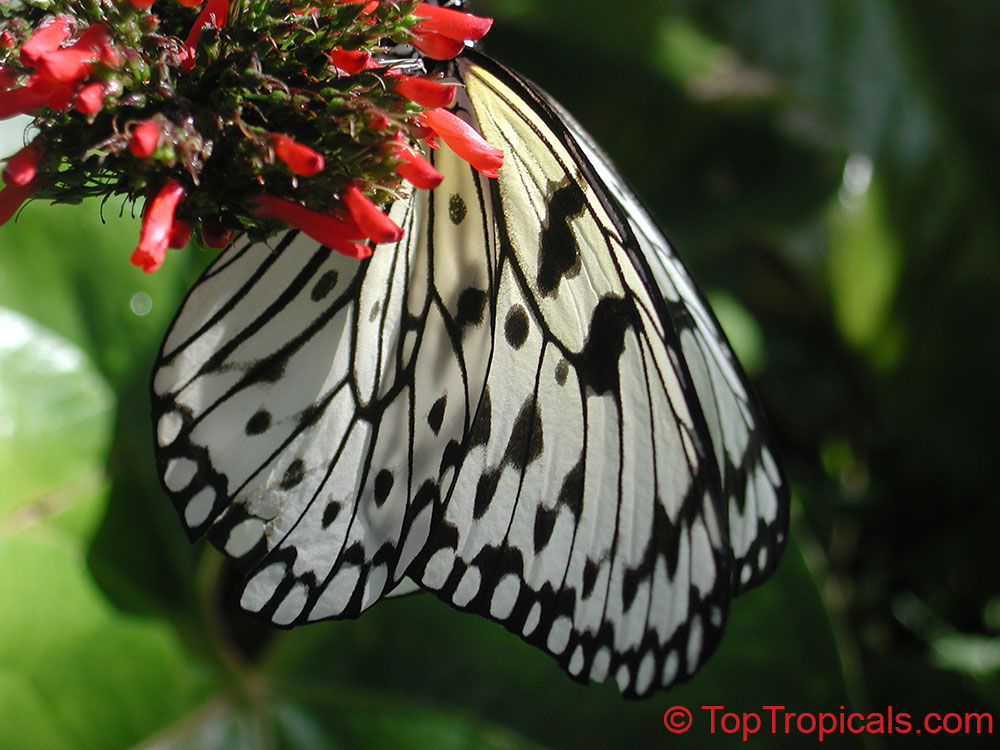
Butterfly plants at Top Tropicals
Butterfly plants... what can be more romantic and sweet in your garden!
Watch the news segment by Rachel Anderson for ABC-7: Butterfly plants at Top Tropicals.
"...Spring has sprung, and if you're looking to spruce up your
garden, Top Tropicals in Fort Myers has you covered! They have hundreds of exotic
plants, fruit trees, fragrant flowers and plants that will attract
butterflies to your garden!
If you're looking for a Mother's Day gift, plants are gifts that keep
on giving!.."
In the photo: Butterfly plants display in Top Tropicals office. Come and see our large selection of butterfly attractors in the nursery!
Subscribe to our Channel:
Stay updated with TopTropicals Videos by subscribing to our channel at YouTube.com/TopTropicals and get our latest video news of what is fruiting and blooming!
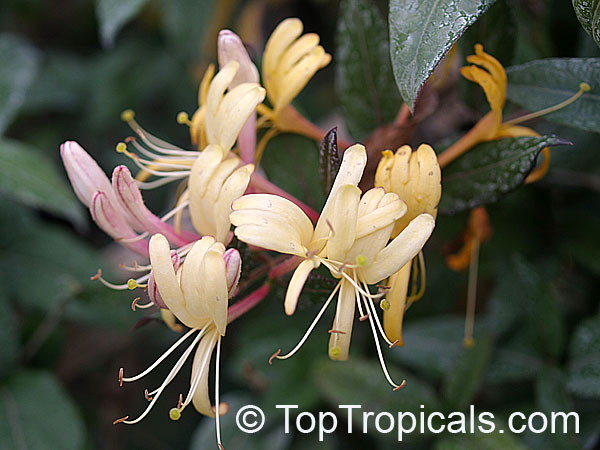
In the photo: Lonicera japonica - Japanese Honeysuckle - a garden favorite, hardy, fast growing vine. Jasmine-sweet scented flowers attract butterflies, and hummingbirds, and berries attract birds!
Date:
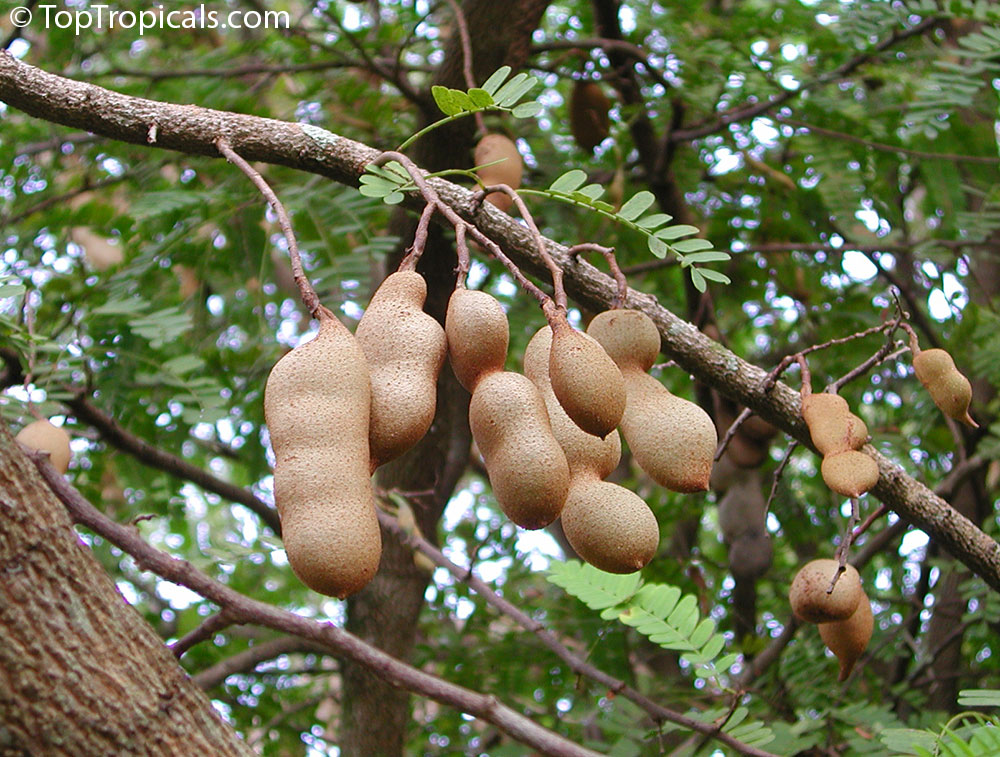
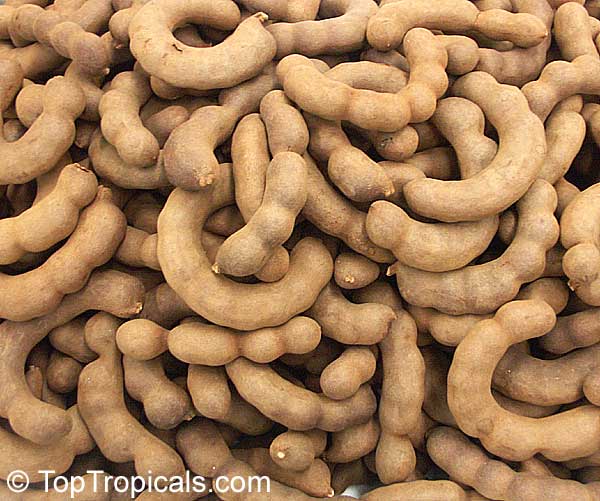
The
Wonderful World of Tamarind:
from Planting to Plating
Q: I use a lot of tamarind in my cooking. Can I grow my own Tamarind fruit? Can Tamarind tree grow in North Florida? Will Tamarind grow well outside or should I keep it in a pot?
A: Originating from tropical Africa, the Tamarind - Tamarindus indica - is a tropical tree that is highly appreciated for its ornamental beauty, delightful shade, and soft texture.
Tamarind is a highly valued culinary ingredient, with its tangy and sweet-sour flavor profile making it a popular addition to many dishes. It is frequently used in South Asian, Latin American, Caribbean, and African cuisines to add a touch of acidity and sweetness. Tamarind paste, made from the fruit's pulp, is a key ingredient in Worcestershire sauce, tamarind chutney, and many curry dishes. The seeds, when roasted and ground, can be used as a coffee substitute or as a thickening agent in sauces and stews....
Tamarind tree is prized for its versatile fruits and numerous health
benefits. The tree can be grown outside in warm climates, as well as in pots and
indoors... even as bonsai!
CONTINUE READING >>