Cucurbitaceae - Botanical Family
| Number of plants found: 36 | Next | 
|
Go to page: | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
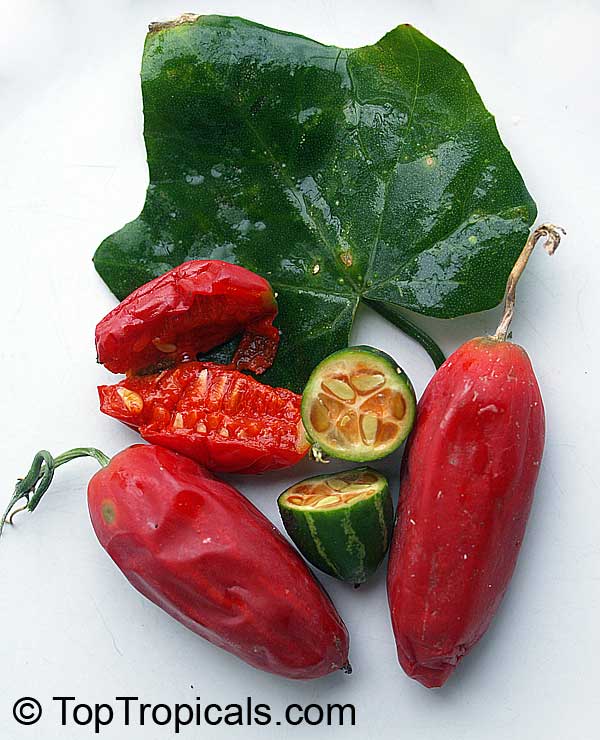
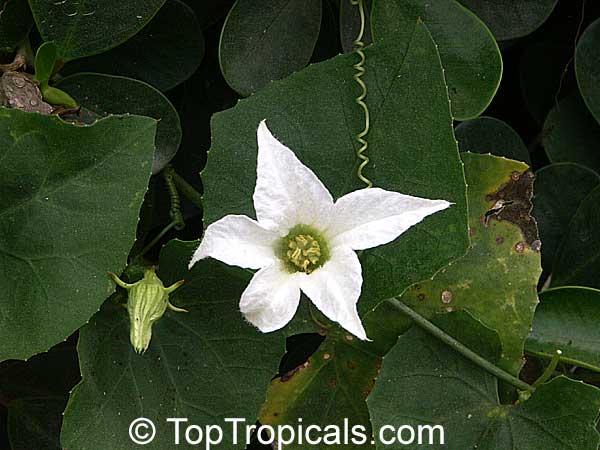
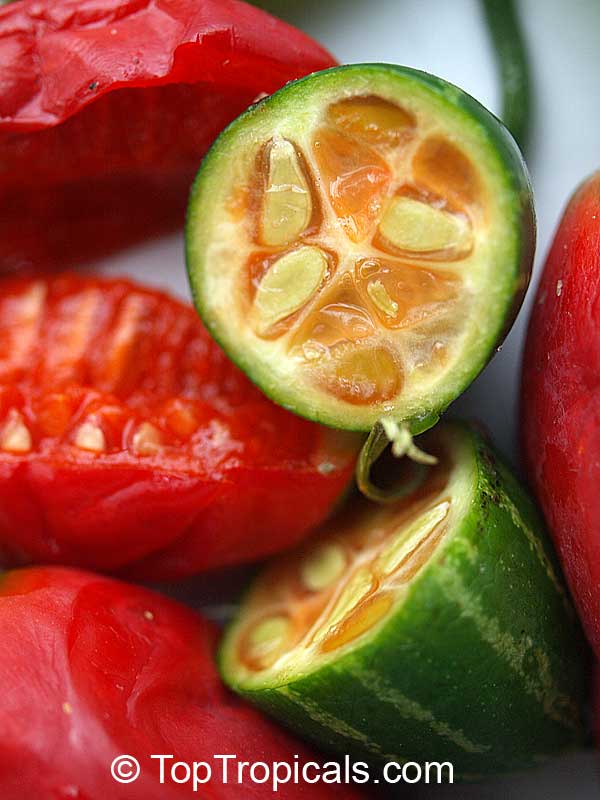
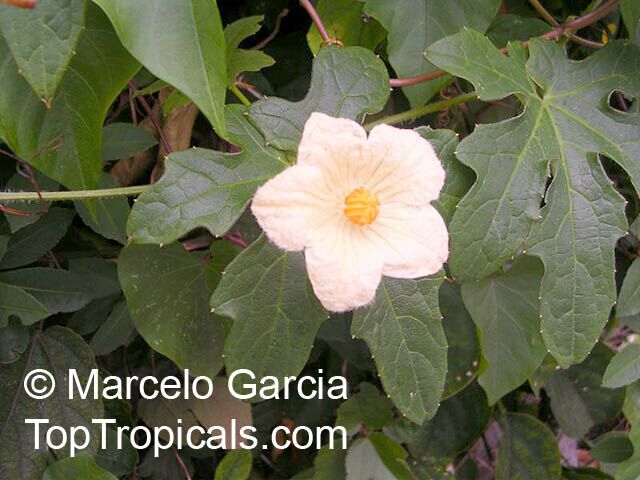
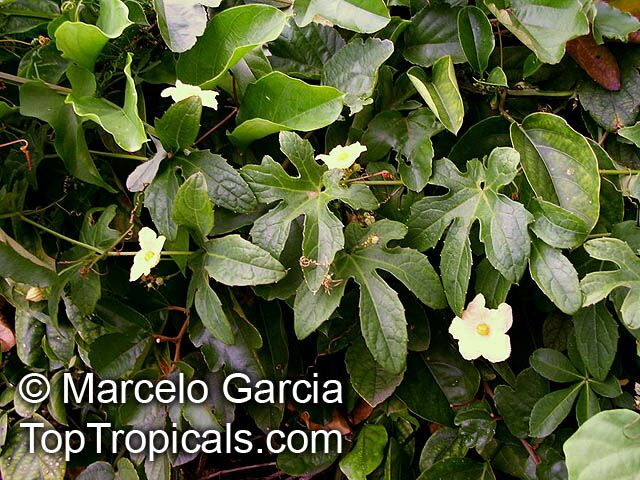
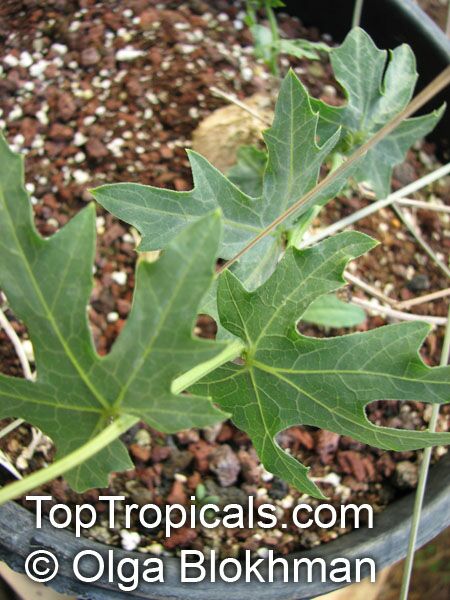
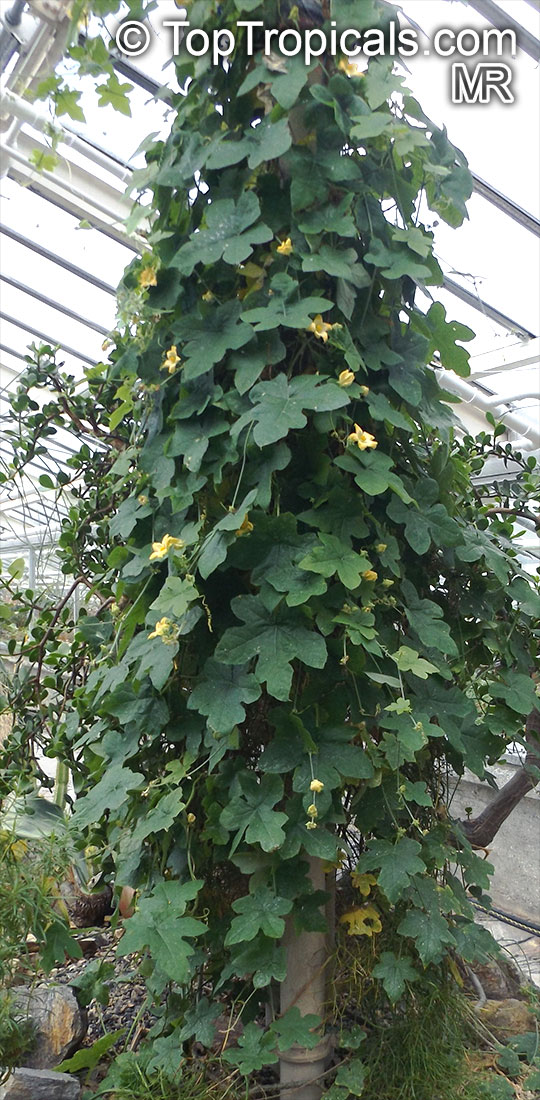
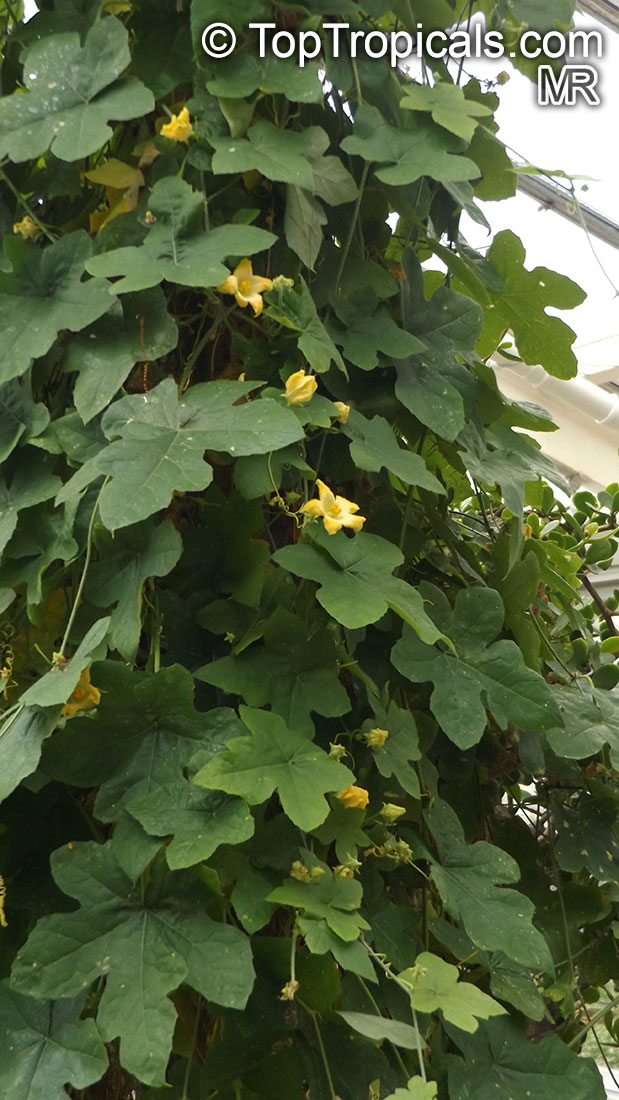
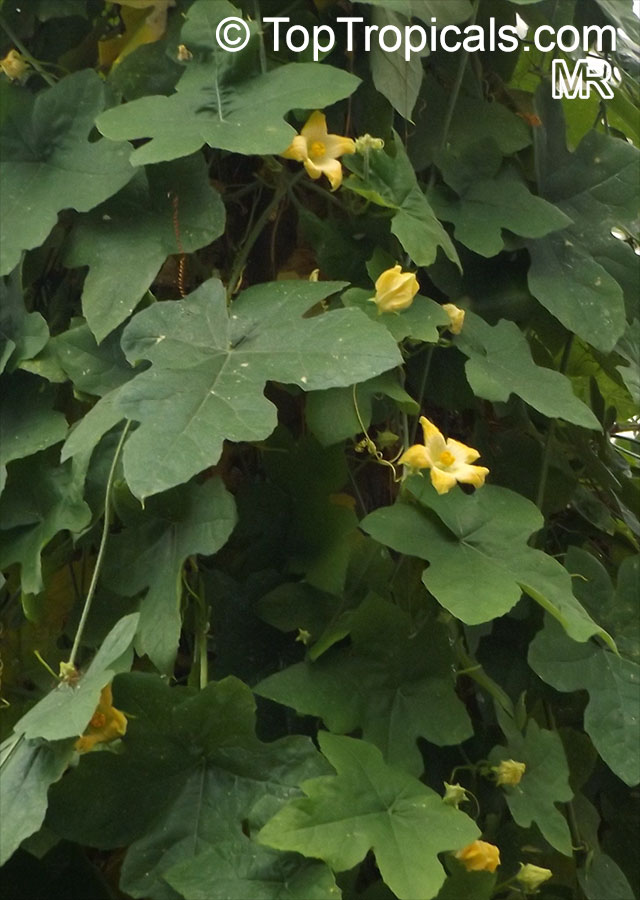
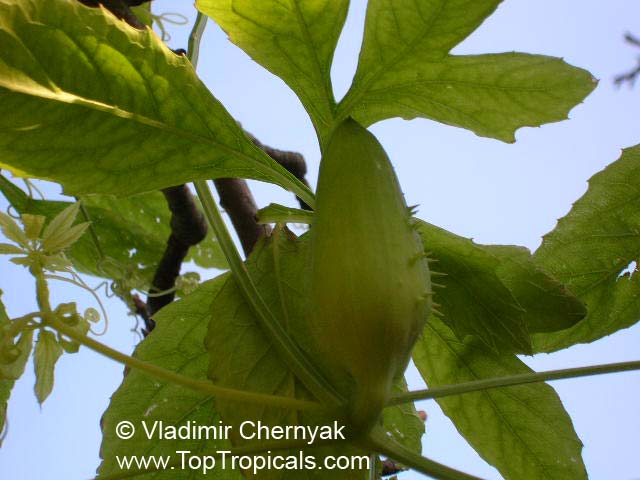
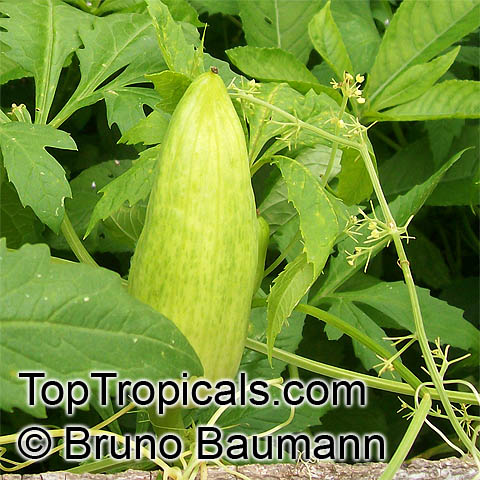
Botanical name: Coccinia grandis
Common names: Ivy Gourd, Scarlet Gourd, Tindora
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Origin: Africa, Asia and Australia







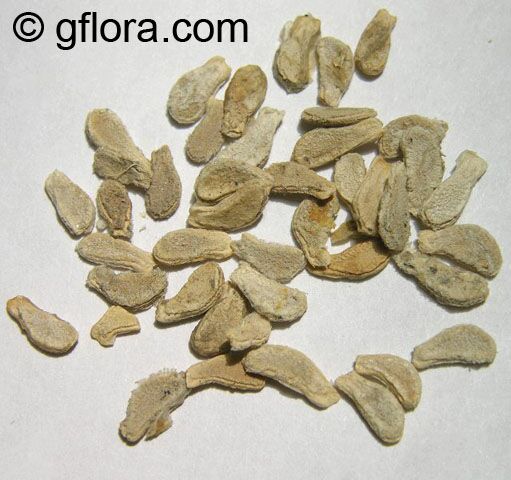
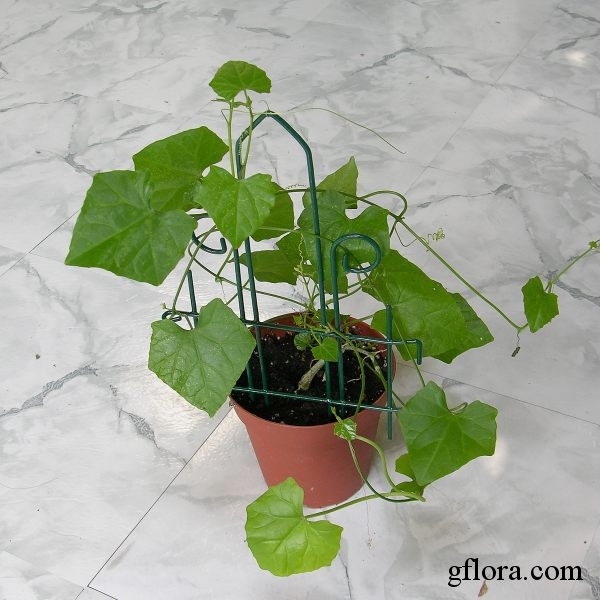
Native to Africa, Asia and Australia, Coccinia grandis (Ivy Gourd) is an attractive yet invasive vine or creeper that's also known for its ethnomedical properties. It grows well in full sun to semi-shade and requires moderate watering on a regular basis. It is cultivated in USDA Hardiness Zones 9-11 and blooms from the beginning of summer to the middle of autumn.
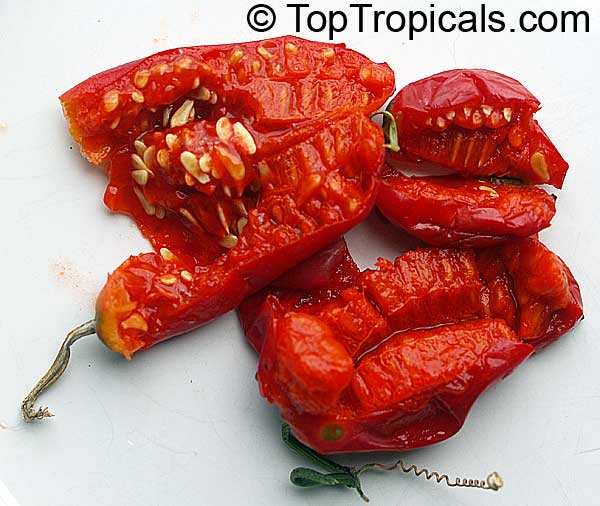
In addition to its beauty and ethnomedical functions, Coccinia grandis is also an edible fruit that is sweet and sour in taste. Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, Ivy Gourd can be used for consuming either raw as a salad or for making jams, juices, and sauces. It is believed to have several health benefits such as improving digestion, regulating blood sugar levels and even reducing chronic pain. In some parts of India, this plant is used to treat common colds, fever, bruises, and so on.
Coccinia grandis can produce a good amount of fruits during the season. Usually, they start to appear in late summer and autumn. The diet should be balanced when consuming Ivy Gourd fruit as it tends to be a heavyweight food item.
When it comes to caring for the plant, Ivy Gourd does not require much attention and can even be grown in a pot if preferred. It should be watered moderately and the soil should not be allowed to dry out. For cold climates, it should be covered with straw mulch to ensure insulation during winter. Winter protection may be needed in USDA Hardiness Zones lower than 9.
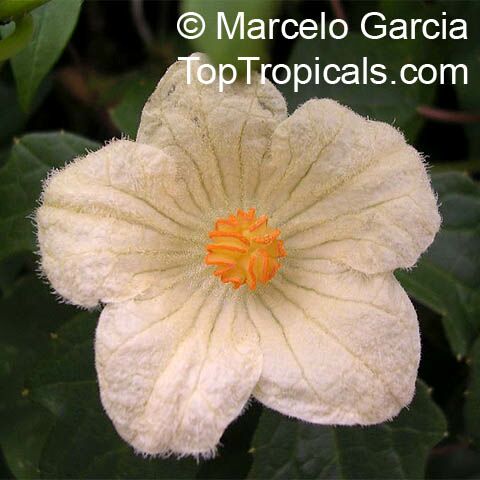
Botanical name: Coccinia indica
Common names: Donda, Bimbika
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Origin: India







Rambling vine from a fast growing caudex. Ripe fruit eaten.
Botanical name: Coccinia sessilifolia
Common name: Borobohlolo
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Origin: Southern Africa






Botanical names: Coccinia trilobata, Coccinia kilimandjarica, Peponia trilobata
Common name: Coccinia
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Origin: Tropical Africa




Coccinia trilobata is a herbaceous, perennial climbing plant, with stems reaching up to 4 metres in length growing from a tuberous rootstock. It is adorned with dark green, three-lobed leaves, as well as innumerable small, yellow-orange, lightly fragrant flowers - more noticeable in the evening. Additionally, oblong, yellow-orange fruits, measuring approx. 5cm appear after the flowers have faded.
Originally native to Tropical Africa, Coccinia trilobata thrives in places with warm climates. Specifically, USDA Zones 9-11 are the ideal environment, with full sun and moderate water requirements. It makes for a great addition to any garden as its abundant fruits and flowers exude a vibrant yellow-orange hue.
In colder regions where winter can be unforgiving, Coccinia trilobata can still be grown in a pot. To protect the plant from extreme frost, bring the pot indoors, and give it a suitable spot in a sunny window- sill or a balcony. During warmer months, it can respectfully be placed in the garden, requiring adequate watering - not too much nor too little - to ensure healthy growth and flowering. With the right level of care, Coccinia trilobata can be admired by any gardener in any location.
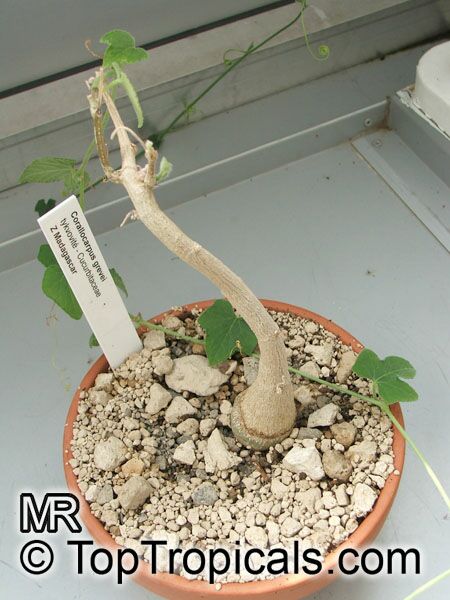
Botanical name: Corallocarpus grevei
Common name: Corallocarpus
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Origin: Madagascar






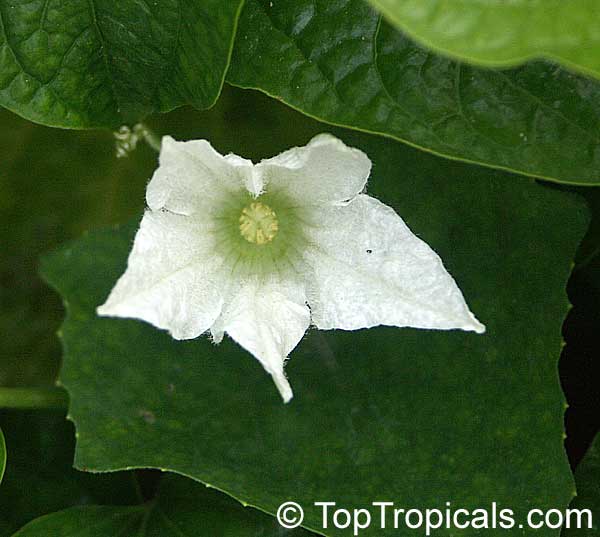
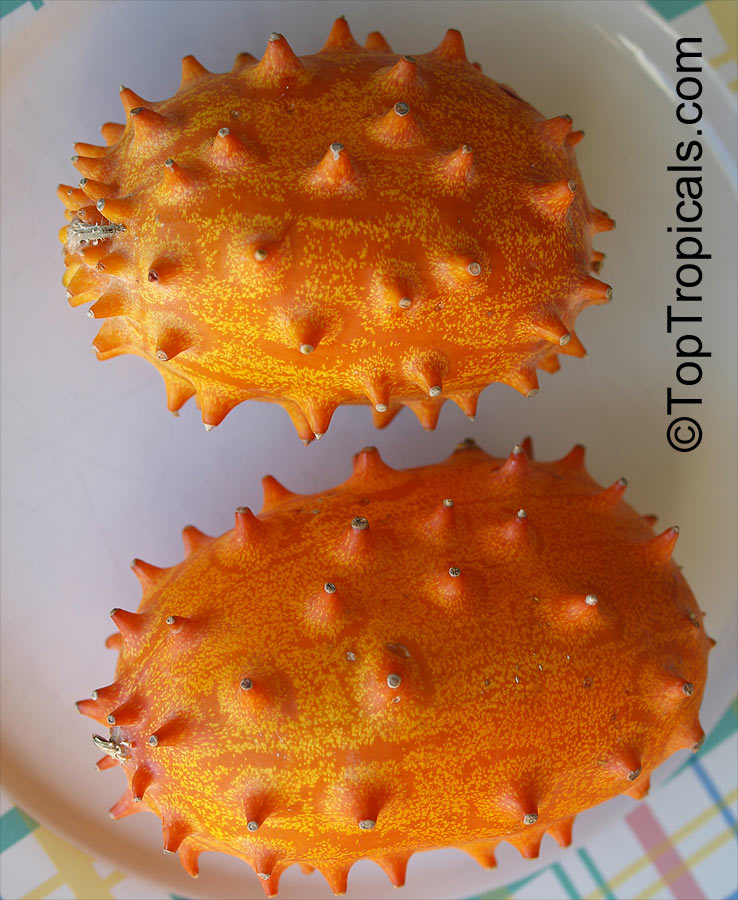
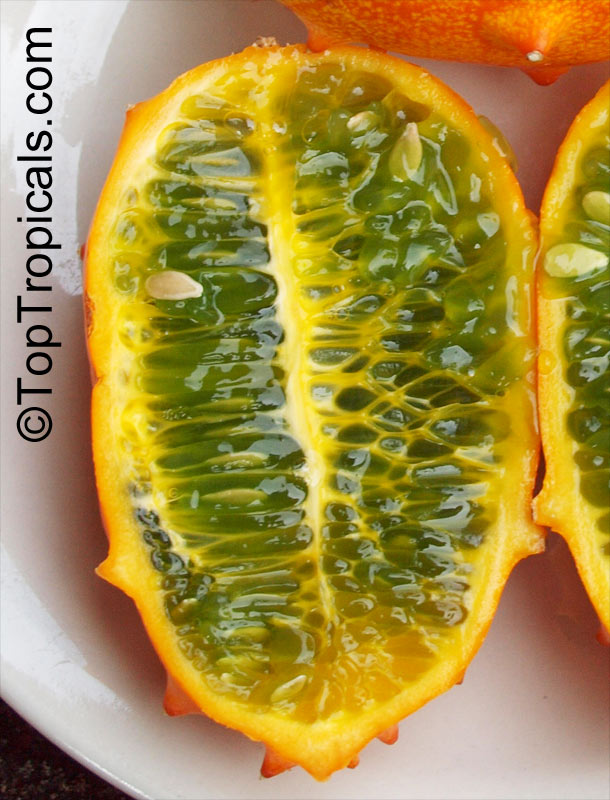
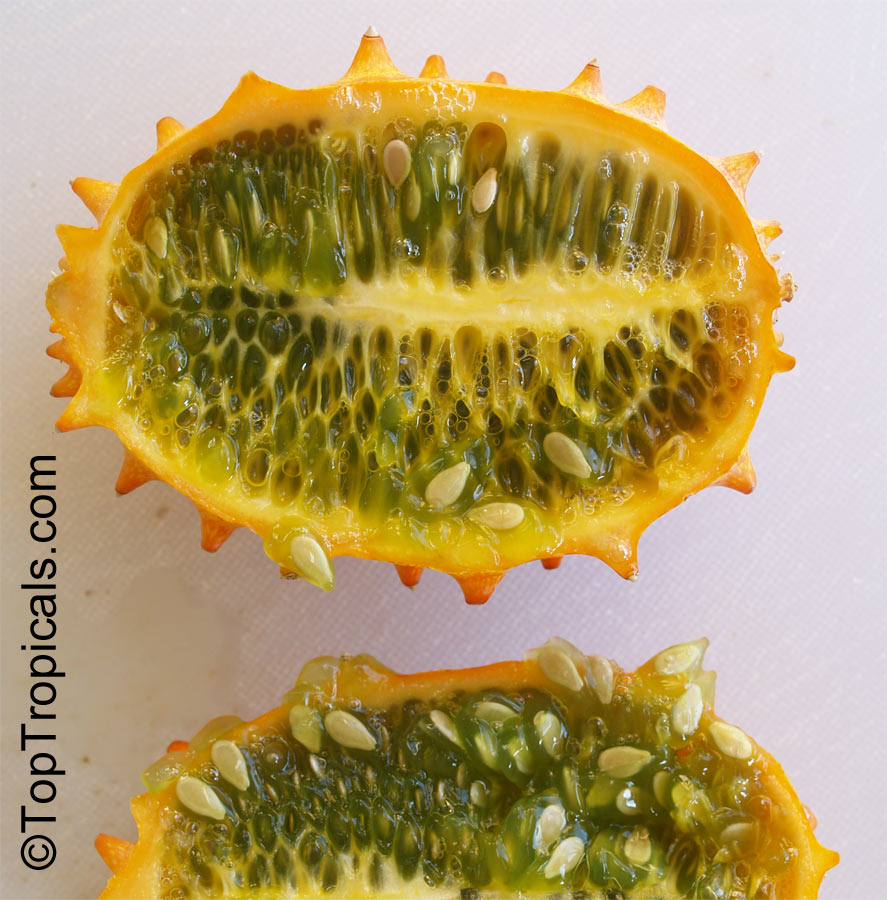
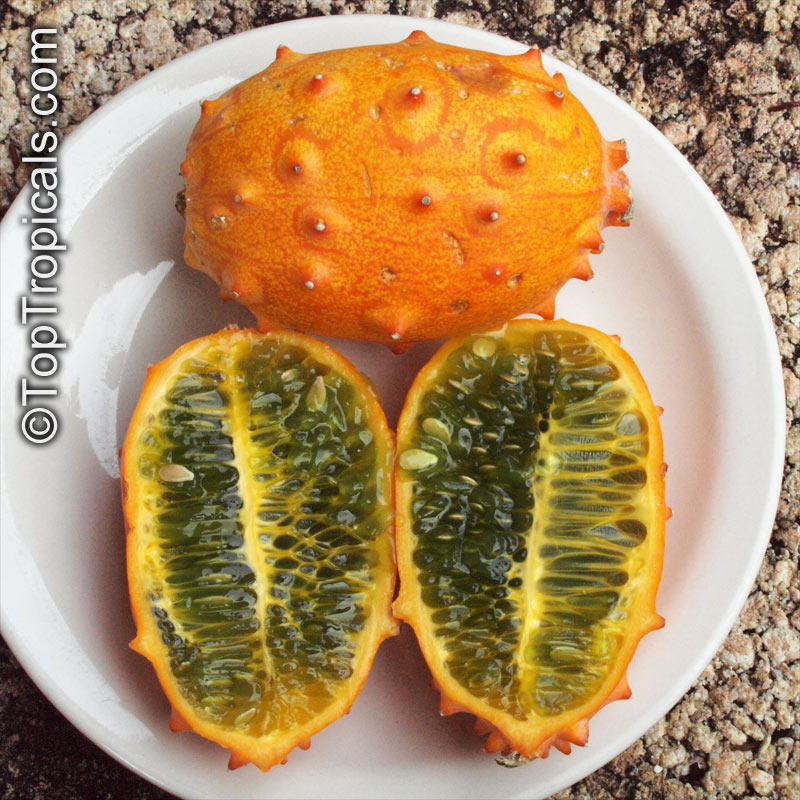
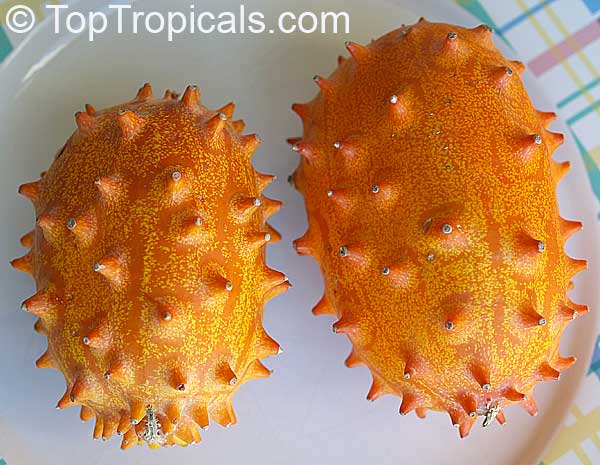
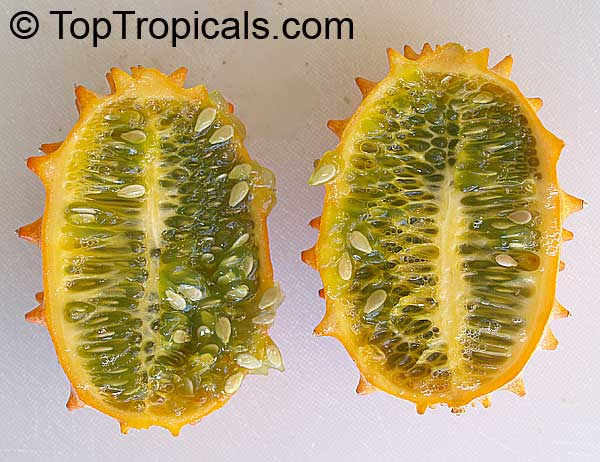
Botanical name: Cucumis metuliferus
Common names: African Horned Cucumber, Kiwano
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Origin: Africa






It is a vining annual that can be grown practically anywhere, provided a warm season. Bright orange, ovaloid fruit with numerous prominent spines. Flesh is bright green, watery, and with a slight sweetness. Plants can produce up to 100 fruits on a single vine. Provide support for the tendrils to grab. Grow much like pumpkins or watermelons, in full sun, provide regular water.
Fruit eaten raw. Cut open the ripe fruit and sprinkle with sugar, which enhances the flavor considerably. The seeds are edible.
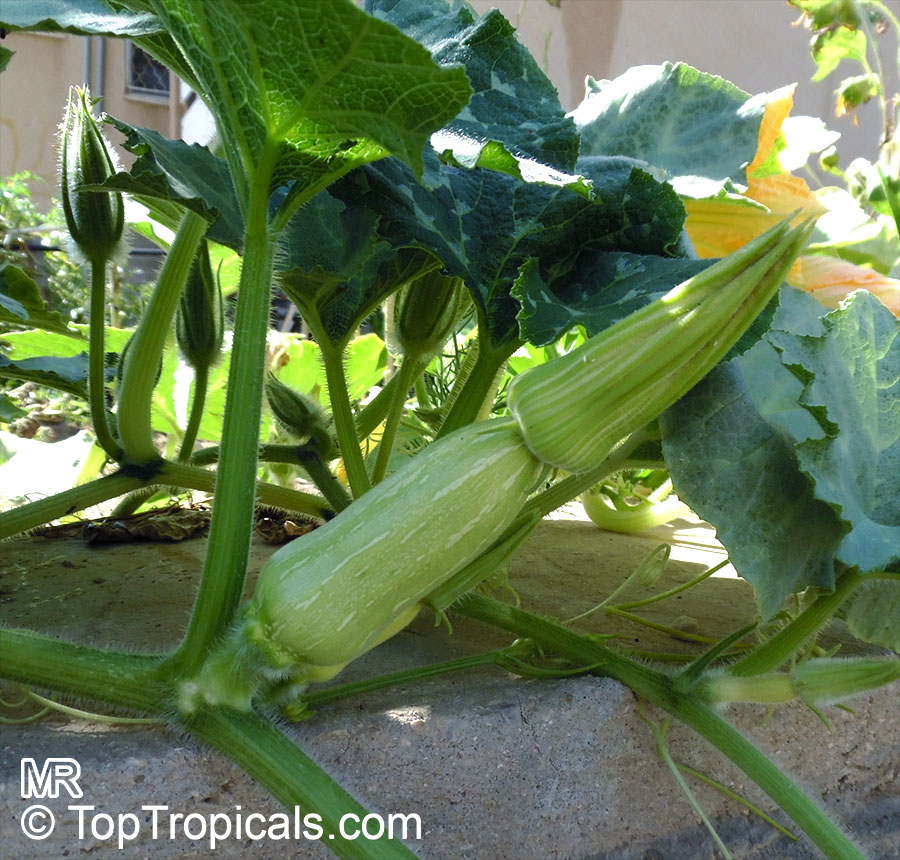
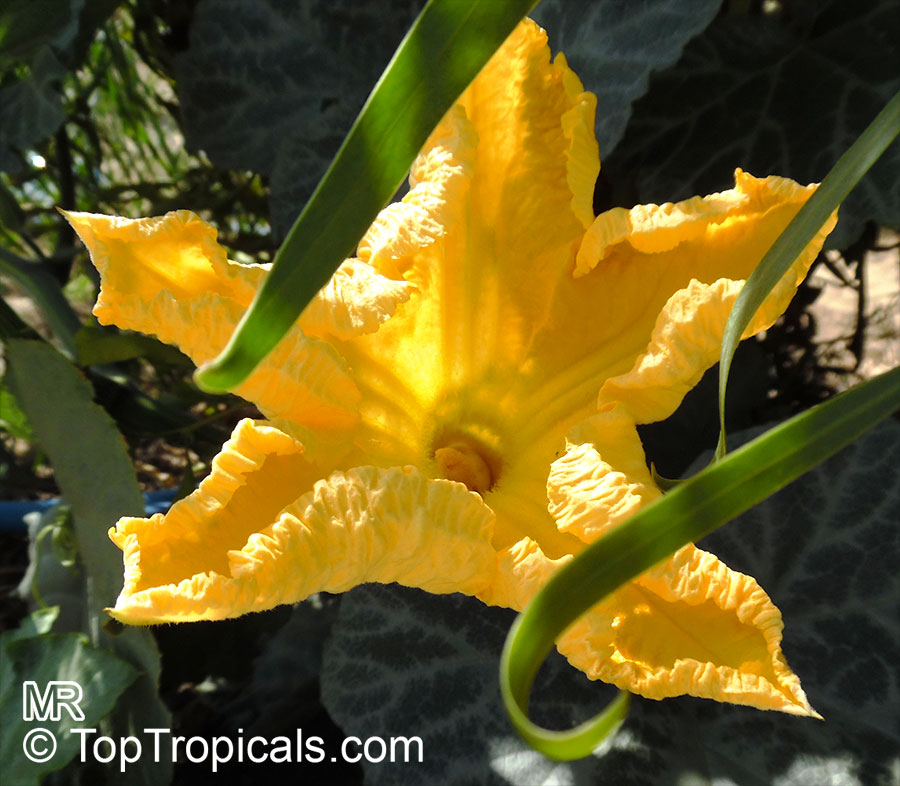
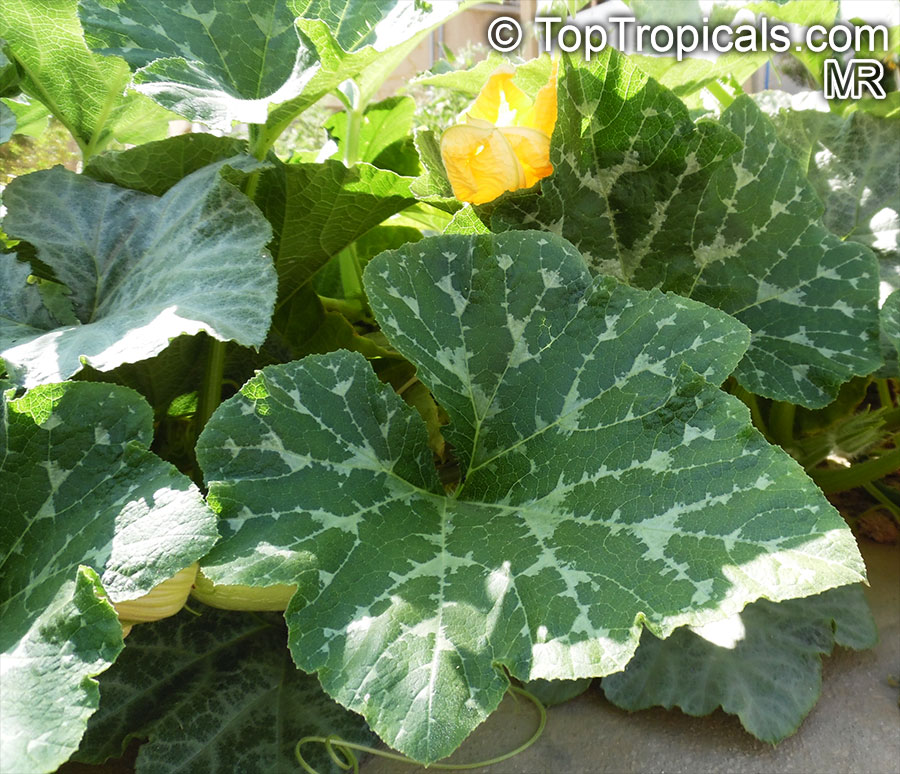
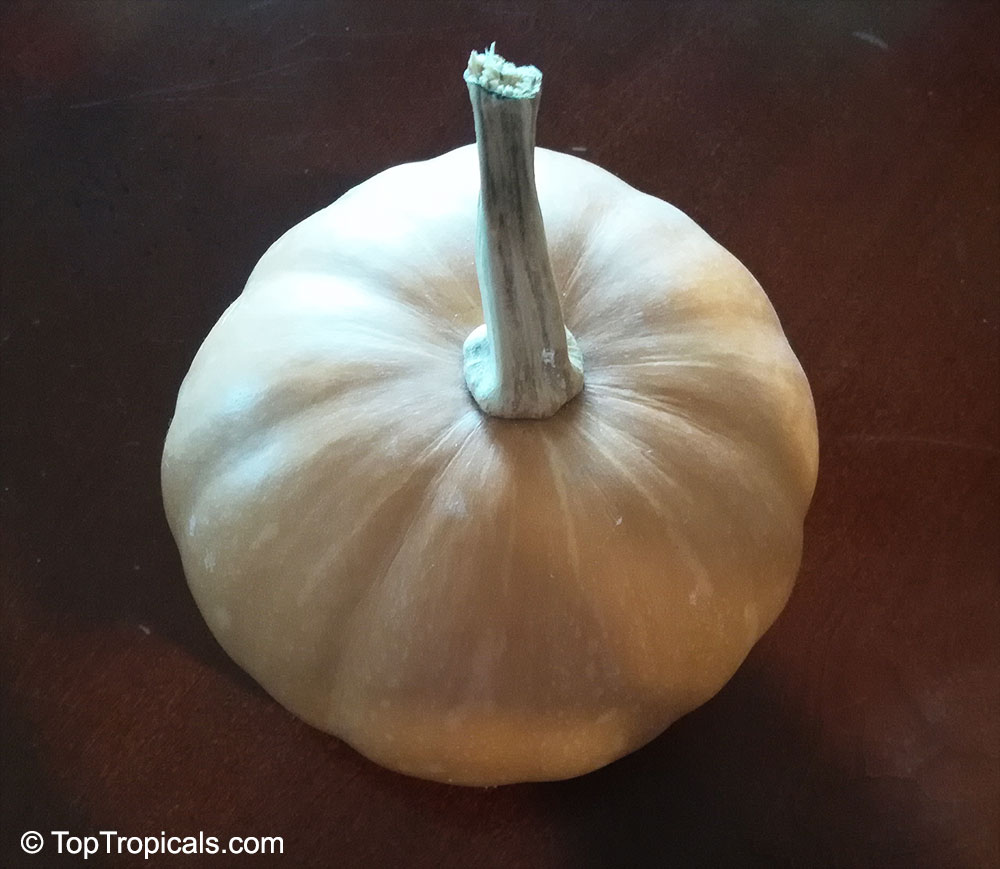
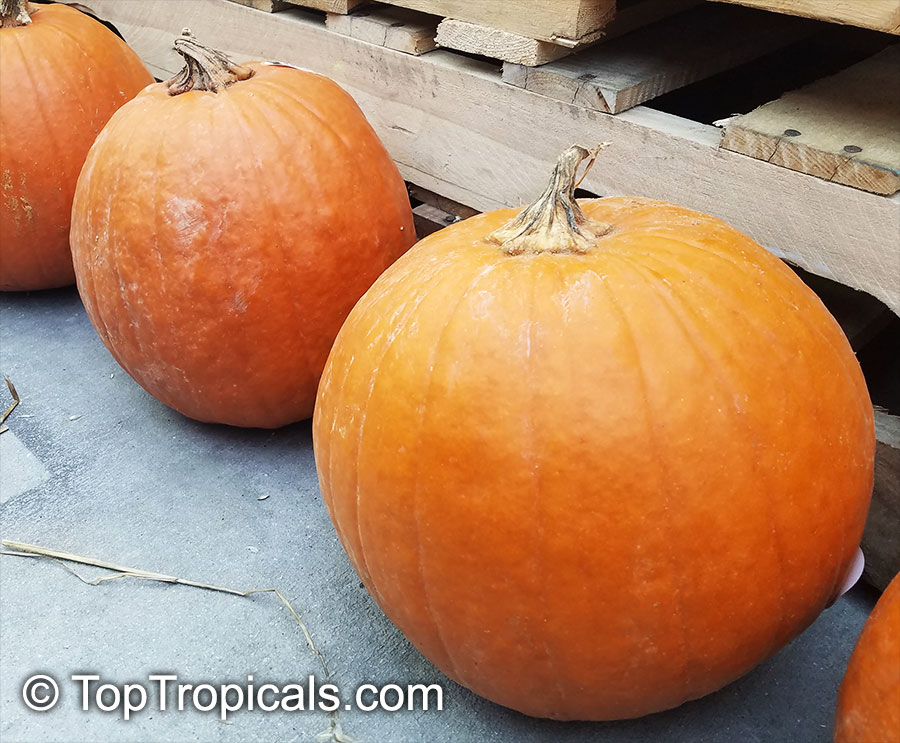
Botanical name: Cucurbita pepo
Common names: Pumpkin, Scallop, Zucchini, Ornamental gourds
Family: Cucurbitaceae










Cucurbita pepo, commonly known as Pumpkin, is a creeper of the Cucurbitaceae family. This plant is native to the western Americas and is commonly grown in the USDA Zone 3-11. Its flower is of yellow and orange colors and can bloom during the summer and autumn.
Pumpkin is not only an ornamental plant, but it has also ethnomedical and edible uses. Its oil is an important part of Ayurvedic medicine, and its leaves and fruits are used to make sauces and as a spice in many parts of the world. This plant is also used in many dishes as it is an excellent source of Vitamin A, Vitamin C, and Vitamin E.
This plant loves full sun and loves to be watered regularly but with moderate water.
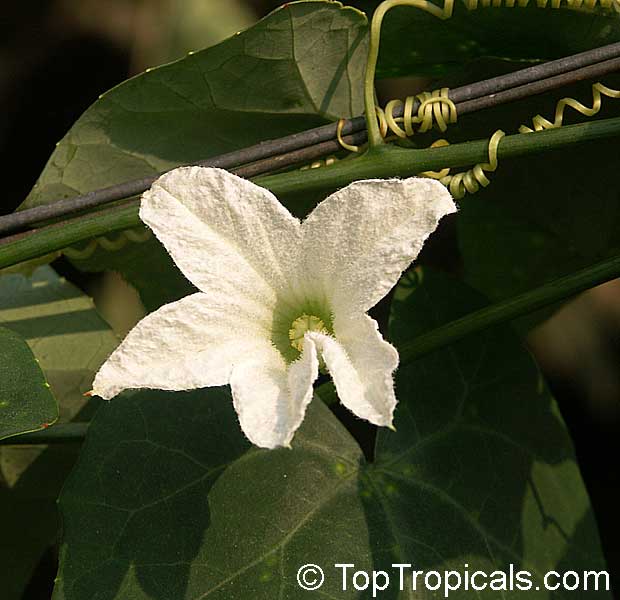
Botanical names: Cyclanthera pedata, Momordica pedata
Common names: Caigua, Wild Cucumber, Stuffing Cucumber
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Origin: South America









Cyclanthera pedata (Caigua) is a fast-growing vine or creeper that is native to South America. It thrives in full sun, with semi-shade in warmer climates. It can tolerate regular, moderate water and is an ethnomedical plant, used for many ailments. The Caigua produces white to off-white flowers, followed by small fruits. It is a versatile plant, with the leaves, flowers, young fruits and young shoots all edible; the mature fruit can be used in a dish similar to stuffed peppers.
This plant grows best in USDA Zone 6-10 and is fairly cold hardy, able to withstand temperatures at least to 30s F for a short period of time. When grown in a pot, it may need some protection from cold weather or frost. It can be grown in colder regions as an annual and is often seen in markets in Peru and Ecuador. If grown in a climate that suits it, the large mature fruits may produce up to 15 fruits per plant.
The fruit of the Caigua is rich in vitamins A, E and C and is also full of antioxidants and proteins. It can be eaten raw, pickled, boiled, or fried, and is often added to salads and sauces. It can also be used as a side dish, similar to a stuffed pepper, with ingredients like meat, fish, or cheese. Additionally, it is featured in popular Andean dishes, such as locro, a dish made using maize, pork, and caigua.
Overall, the Cyclanthera pedata is a versatile and healthy plant native to South America, with many nutritional benefits. Easily grown in warmer climates, the fruit of the caigua can be eaten in different ways, making it an interesting addition to any garden.
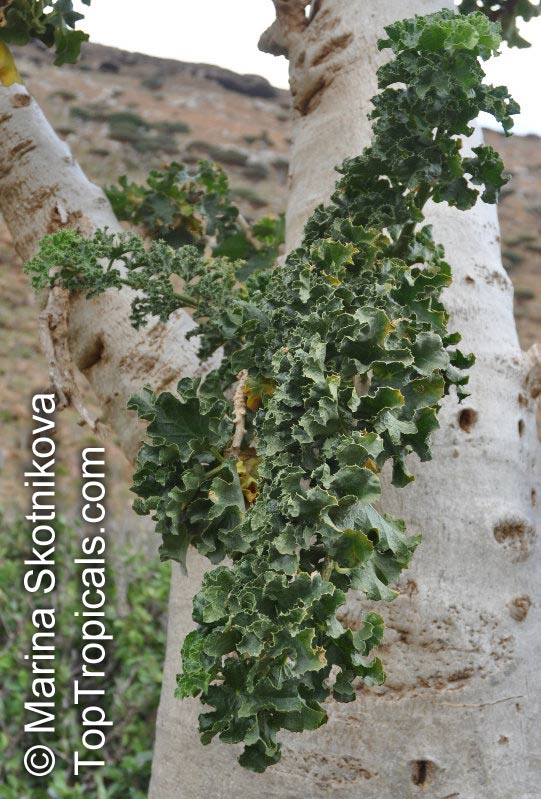
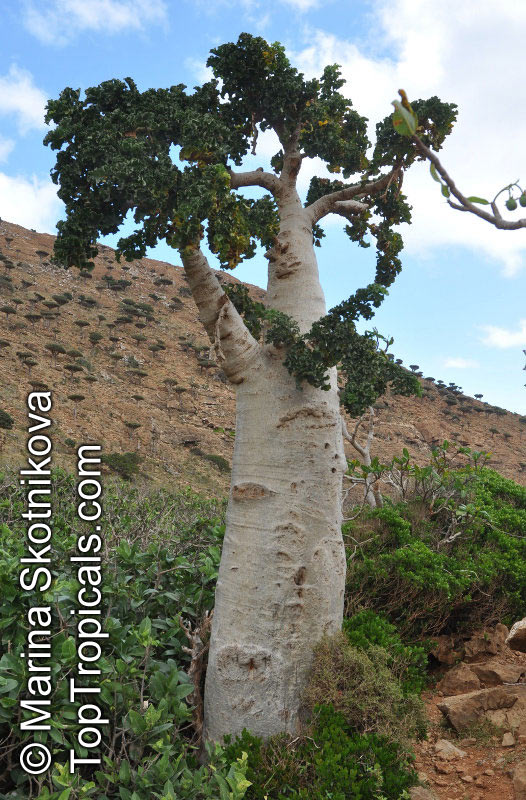
Botanical name: Dendrosicyos socotranus
Common name: Cucumber Tree
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Origin: Socotra




Dendrosicyos socotranus, commonly known as the Cucumber Tree, is native to Socotra, a small archipelago off the coast of Yemen. It is a small tree, typically growing to a height of 10 to 20 feet, with many branches and a shallow, fibrous root system.
This plant is best suited to full sun and moderate water, although it prefers dry conditions once established. The Cucumber Tree is ideal for xeriscaping in USDA Zone 9-11, and it can survive without supplemental water in these areas. It is also relatively easy to grow in pots, especially in areas where winter temperatures can occasionally drop below freezing.
The Cucumber Tree has a large and stout caudex, making it an attractive focal point in any garden or landscape. It is a slow-growing tree but is very tolerant of pruning and can be shaped for many different horticultural purposes. The plant also has a naturally dense and shrub-like habit, and it is often used in either formal or informal hedging.
When planting the Cucumber Tree in a pot, it is important to allow for plenty of drainage. The soil should be well-draining, slightly acidic, and enriched with organic matter. If this tree is grown in a cold region, it is best to bring the plant indoors during winter, as temperatures below freezing can damage the roots and leaves.
It is also important to fertilize the plant regularly, especially when it is young. A light, balanced fertilizer should be applied at least once a month, as this will encourage healthy growth and encourage bright, vibrant foliage. If the Cucumber Tree is planted in a pot, however, it is best to refrain from fertilization altogether.
In summary, Dendrosicyos socotranus is an attractive and low-maintenance tree, suitable for both indoor and outdoor gardens. It can thrive in full sun and moderate water, as well as in dry conditions, and it makes a great addition to any landscape. This plant is also perfect for xeriscaping in USDA Zone 9-11 and is easy to care for in pots in cold regions.
| Next |  |
Use link to repeat this search:
https://toptropicals.com/cgi-bin/garden_catalog/cat.cgi?search_op=and&keyword_op=and&language=e&family=Cucurbitaceae
&number=10&no_change_lang=1&user=tt&sale=1&first=0










































