Toxic or Poisonous - Plant Encyclopedia Results
Top Tropicals Plant Encyclopedia
| Number of plants found: 159 | Next | 
|
Go to page: | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Last |
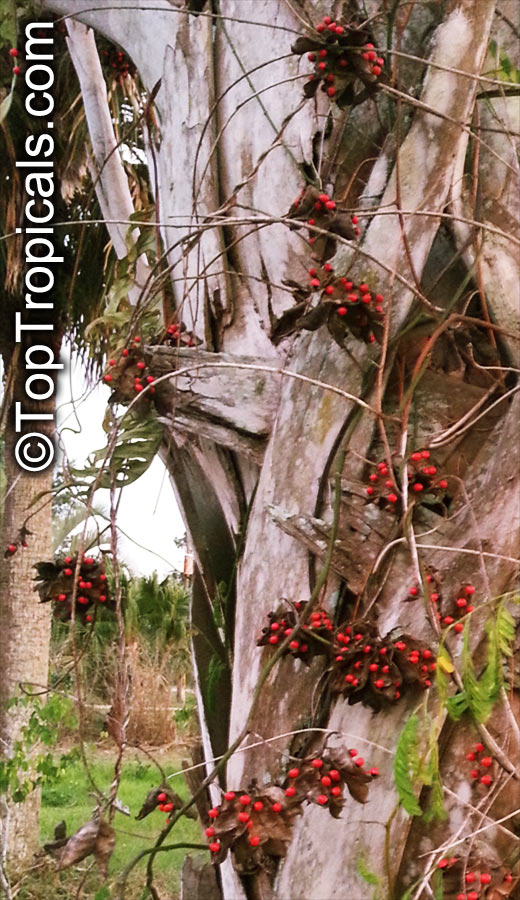
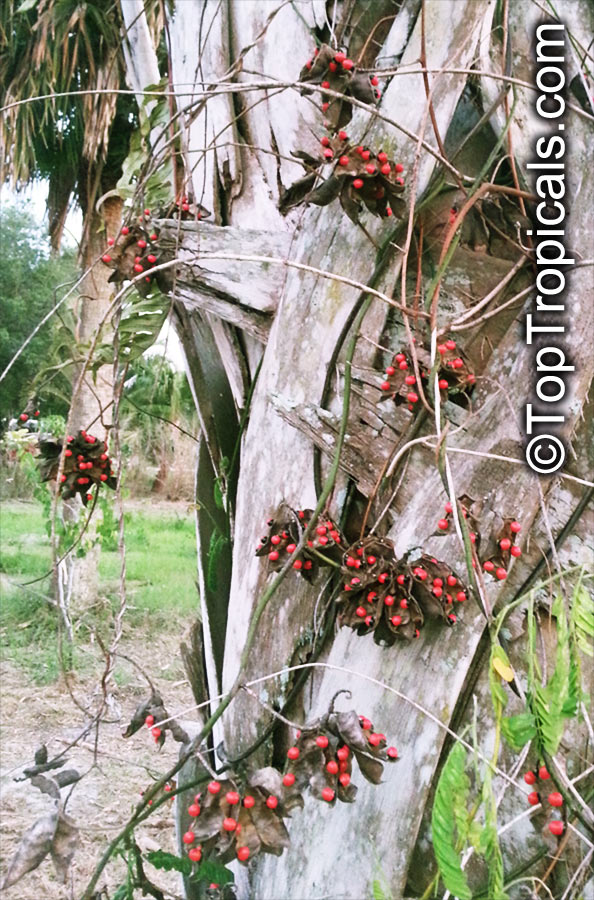
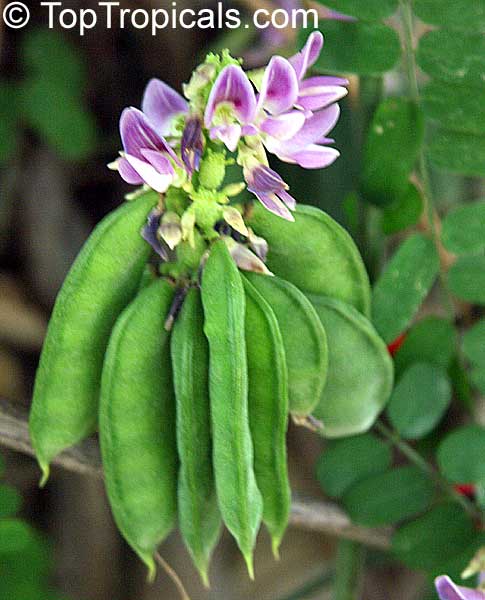
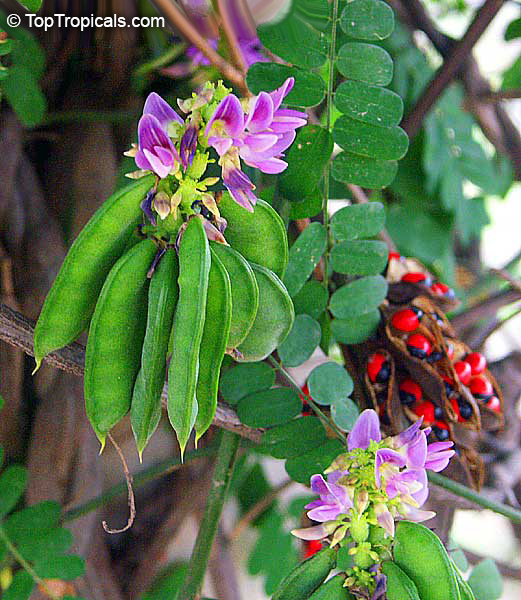
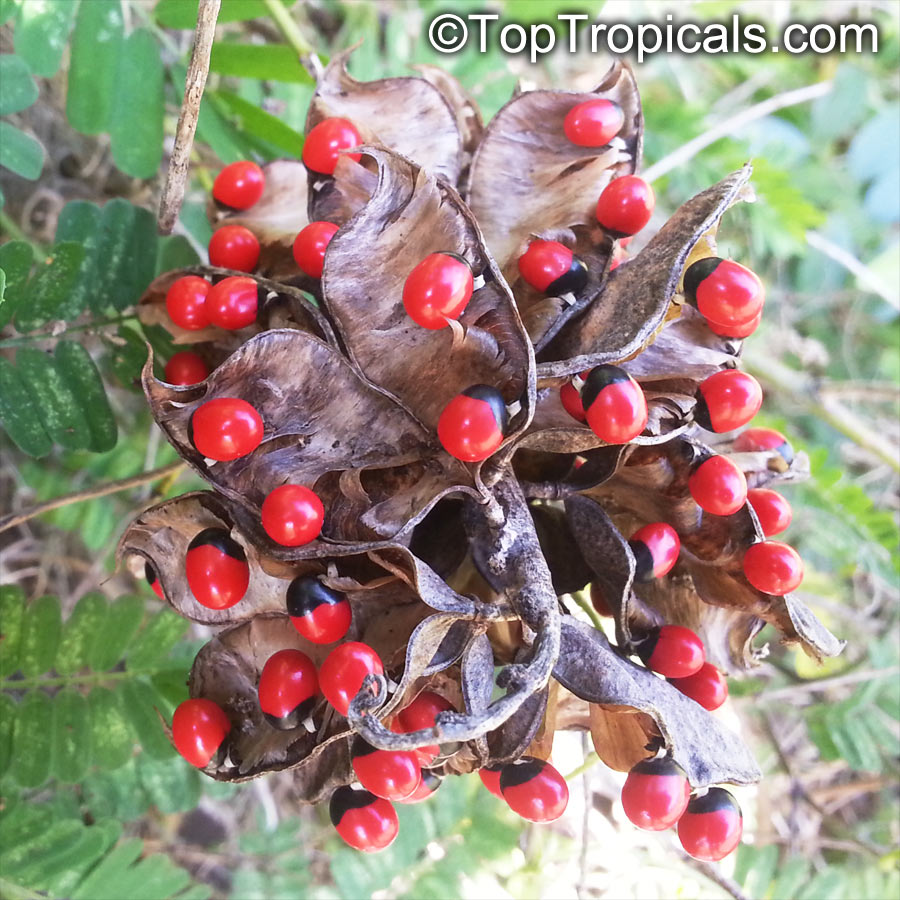
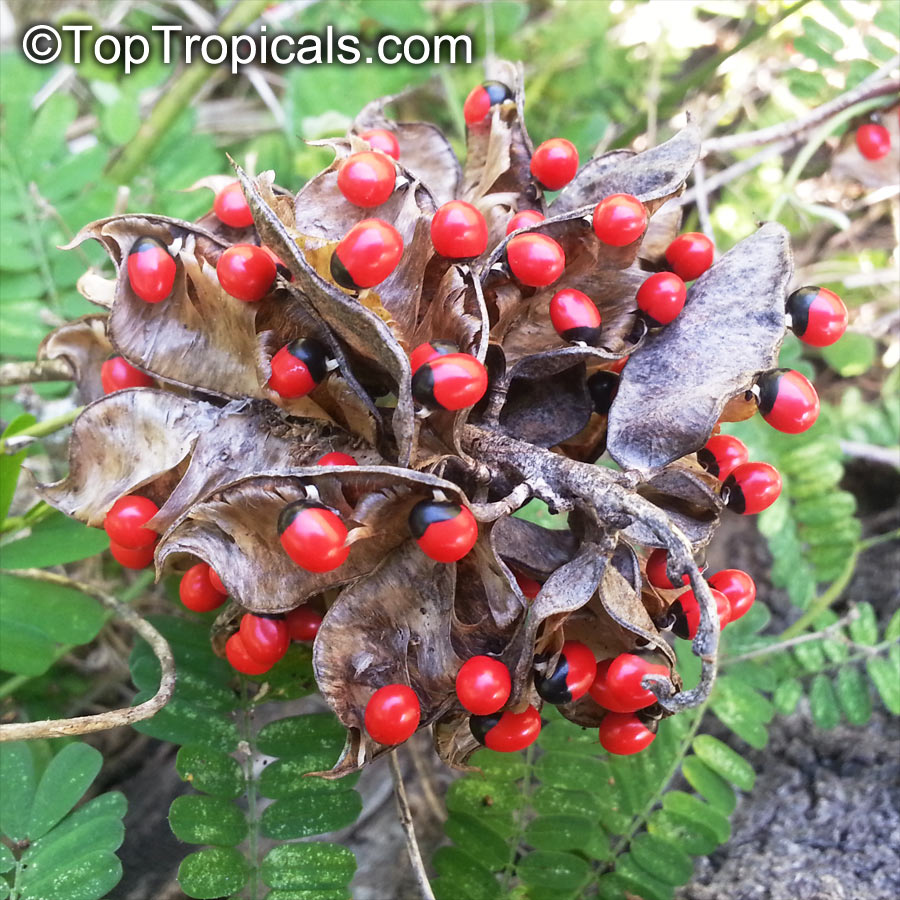
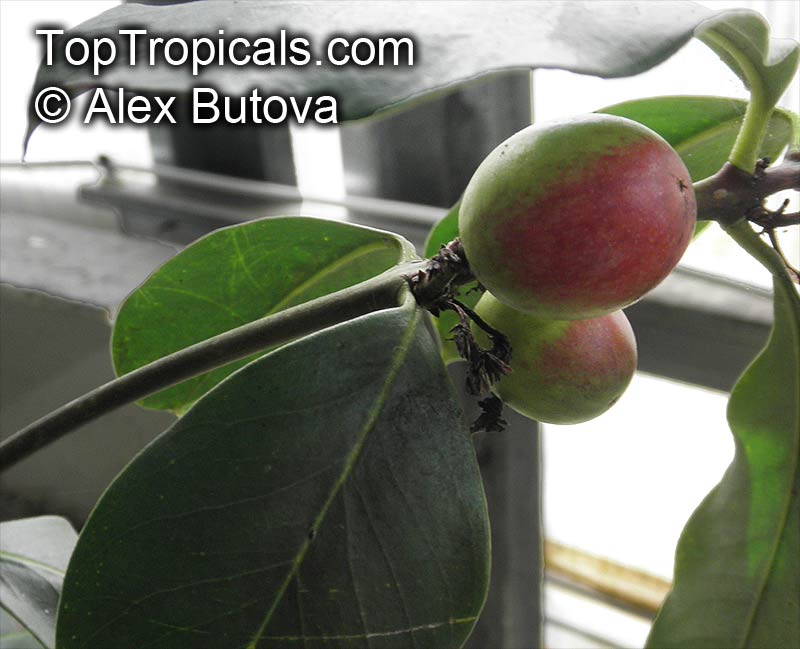
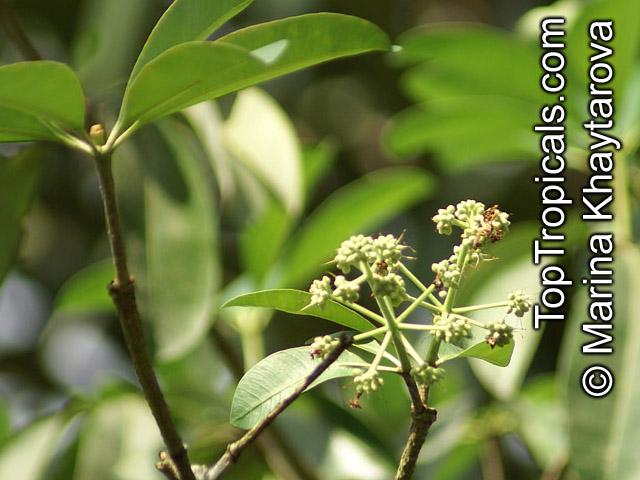
Botanical name: Abrus precatorius
Common names: Buddhist rosary bead, Rosary pea vine, Carolina muida, Deadly crab's eye, Lucky bean, Prayer beads, Weather plant, Wild liquorice
Family: Fabaceae
Subfamily: Faboideae
Origin: India, Sri Lanka, Thailand



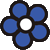



Abrus precatorius has small pretty purple flowers located at the end of the stalks. Fruits are short, inflated pods, splitting open when mature to reveal the round; hard and shiny seeds which are scarlet, but black at the base. Seeds contain abrin, one of the most toxic plant poisons known.
Botanical names: Acokanthera oblongifolia, Acokanthera spectabilis, Carissa spectabilis
Common names: Bushman's Poison, Wintersweet
Family: Apocynaceae
Origin: South Africa
Hardiness: 35°F







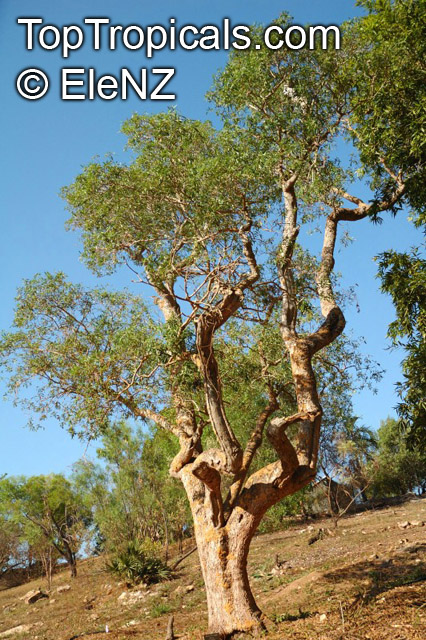
This shrub is one of three members of the genus, Acokanthera. It belongs to the same family as many popular subtropical ornamental plants such as frangipani, allamanda and oleander, as well as the impala lily and num-num. This family is characterized by having sweetly scented flowers and sticky, milky sap which is very poisonous. The Bushman's poison is a hardy drought. It's a frost resistant, evergreen shrub that tolerates full sun but prefers shade, it also does well as a container plant.
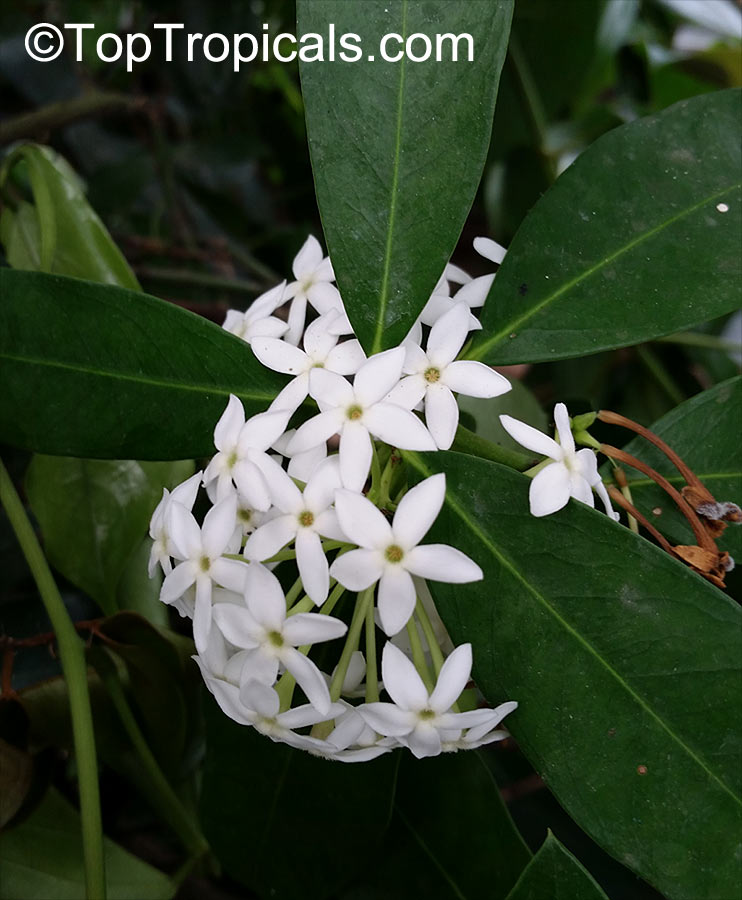
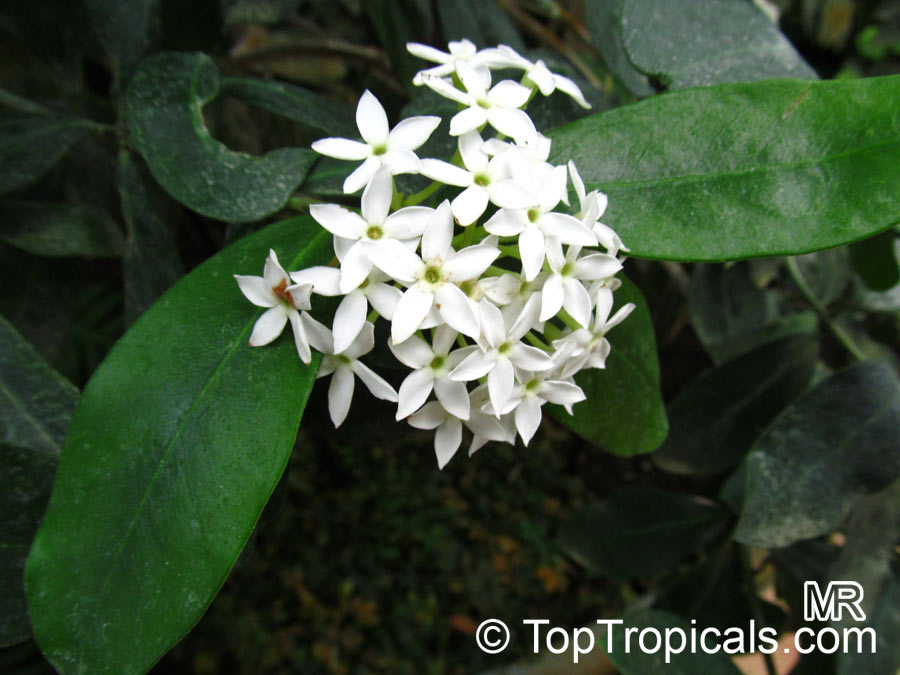
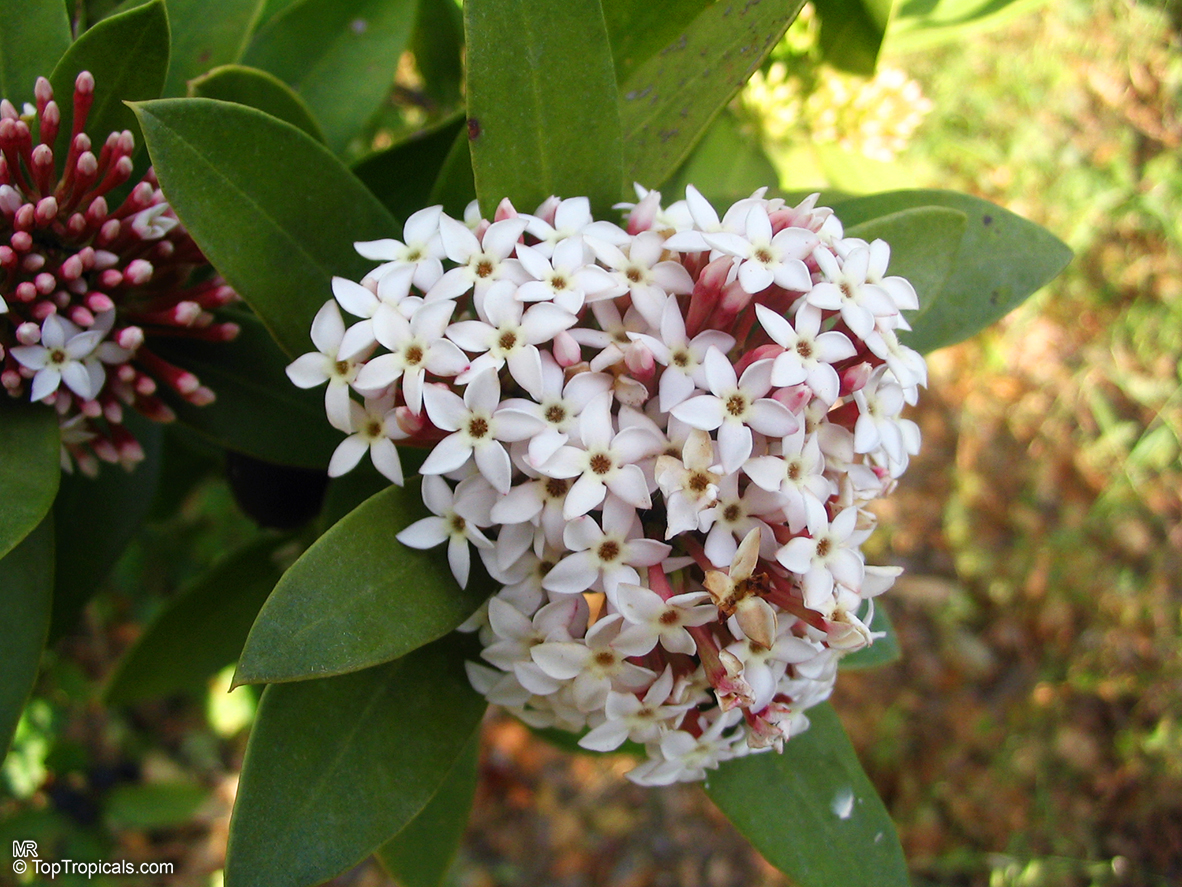
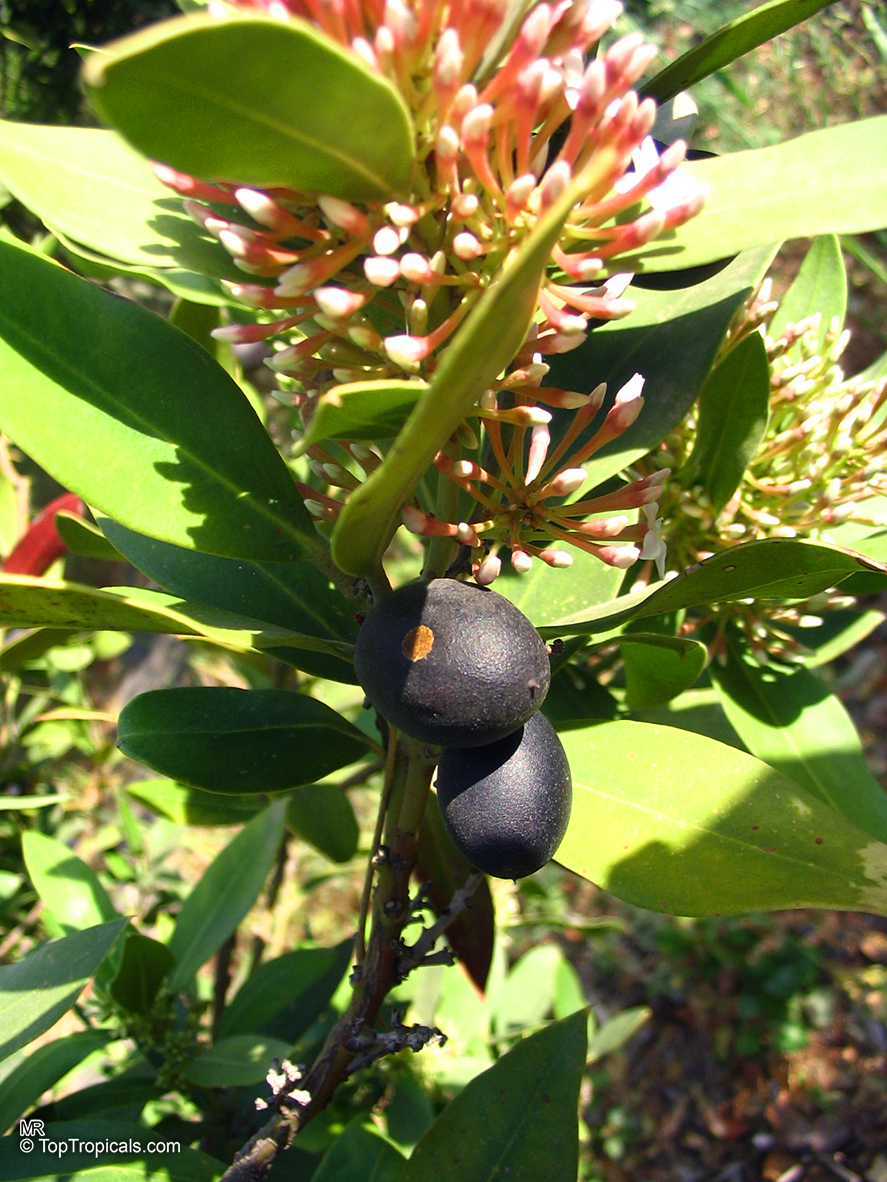
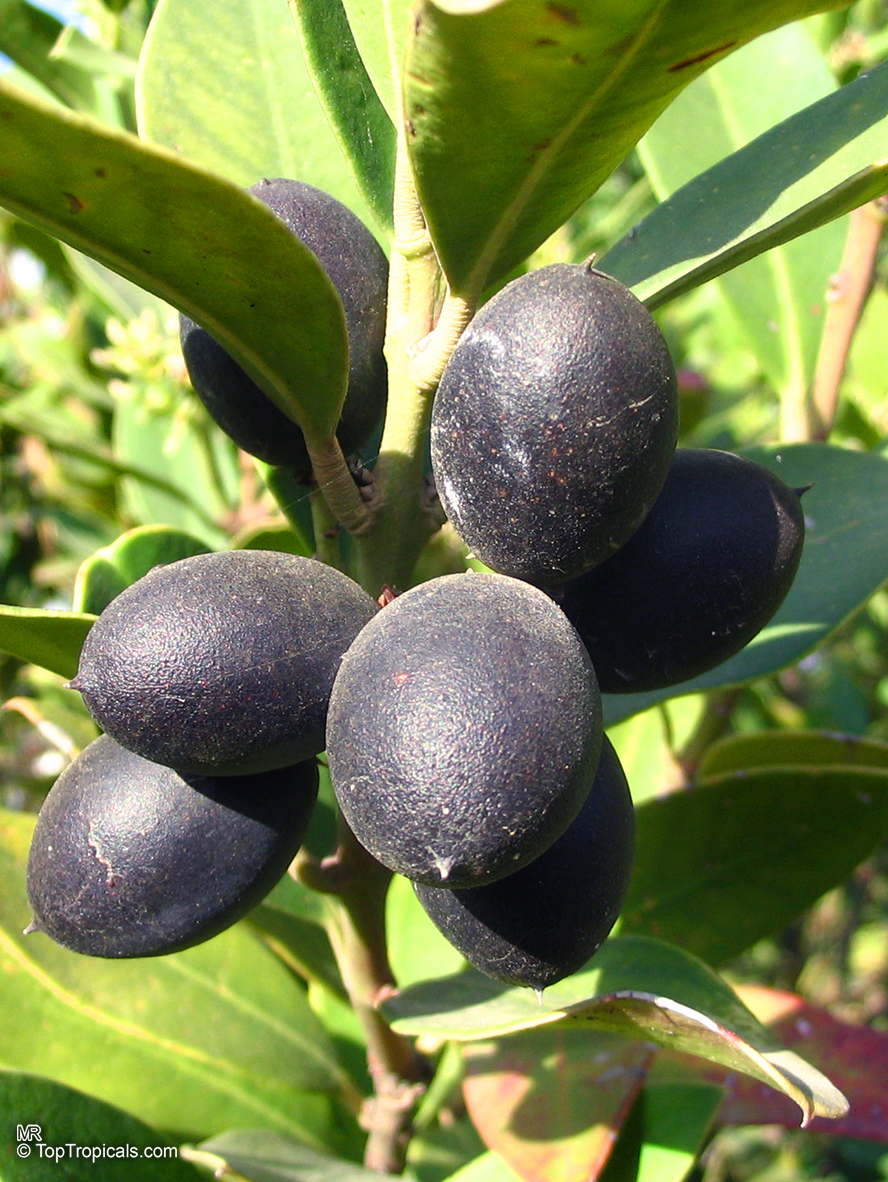
Botanical name: Acokanthera oppositifolia
Common name: Bushman's Poison
Family: Apocynaceae
Origin: South Africa








Acokanthera oppositifolia (Bushman's Poison) is a large shrub, typically growing 5-10 feet tall. It has glossy dark green leaves that are opposite and grow up to 3-4 inches long. In the spring and summer months, the Bushman's Poison flowering shrub is adorned with white, off-white flowers which have a strong, sweet, perfume-like scent.
In its native habitat, the Acokanthera oppositifolia is mainly used for its ethnomedical applications, such as treatment for headaches, inflammations, fever and even malaria. However, it should be noted that the milky sap is considered to be poisonous or toxic and should not be ingested.
As an ornamental plant, the Bushman's Poison works well in well-drained soil in full sun or partial shade and requires moderate amounts of water. It is suitable for growing in regions with USDA Hardiness Zones 9-11 and a mature plant can tolerate short periods of time in temperatures as low as 30°F. When growing in a pot, it is advisable to move the container to a protected area during cold winters and to protect the roots from the frost.
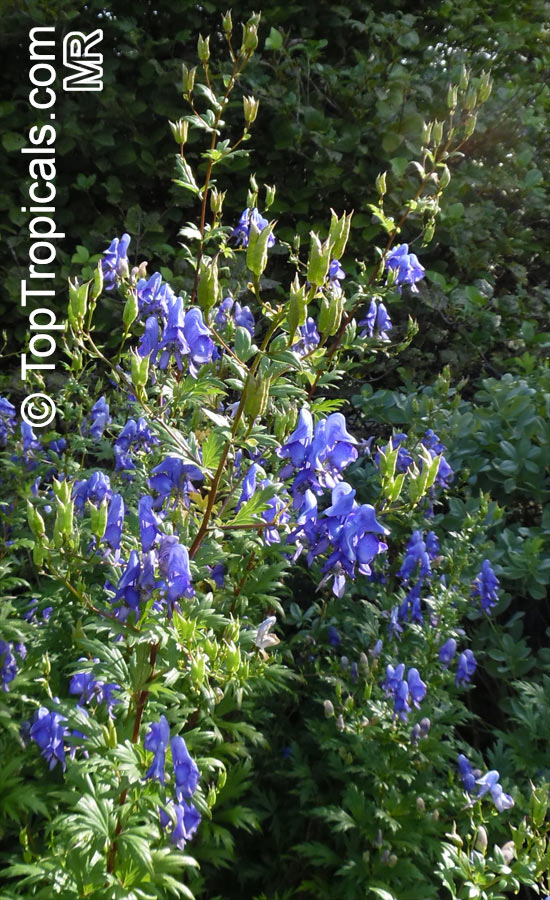
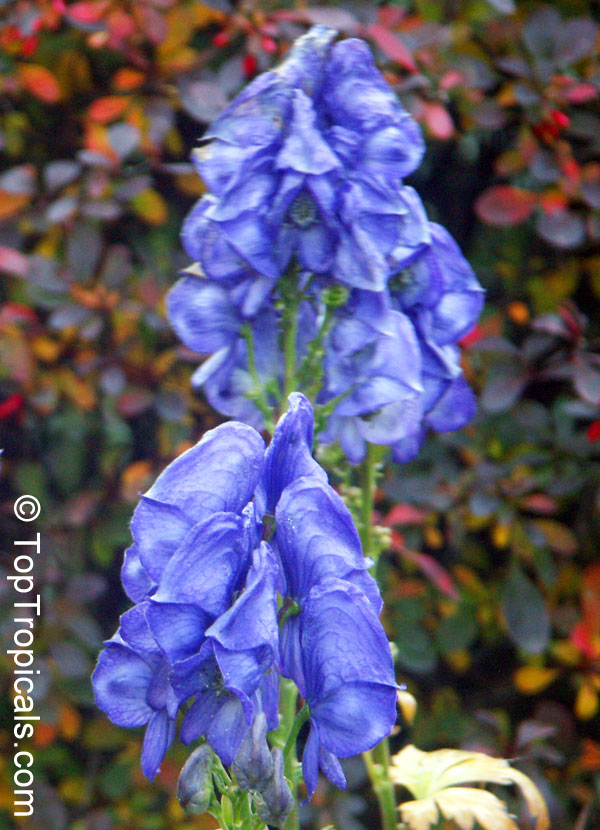
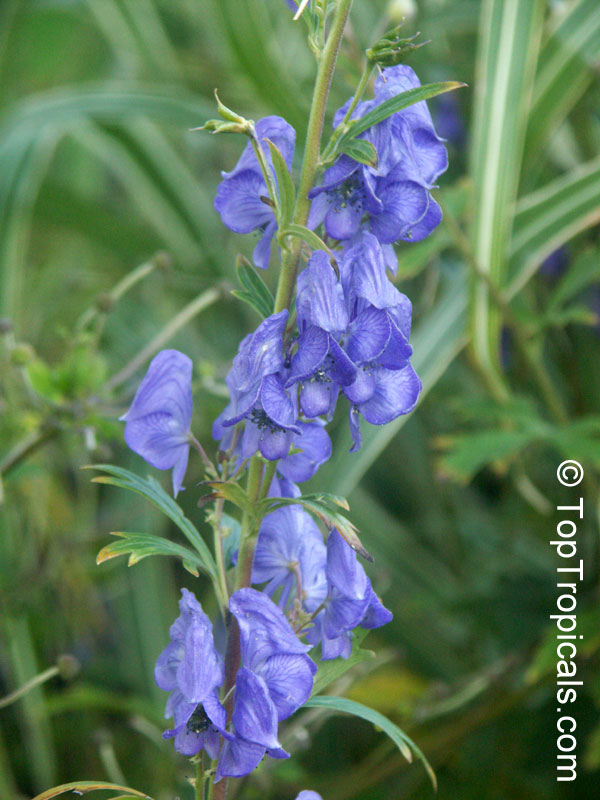
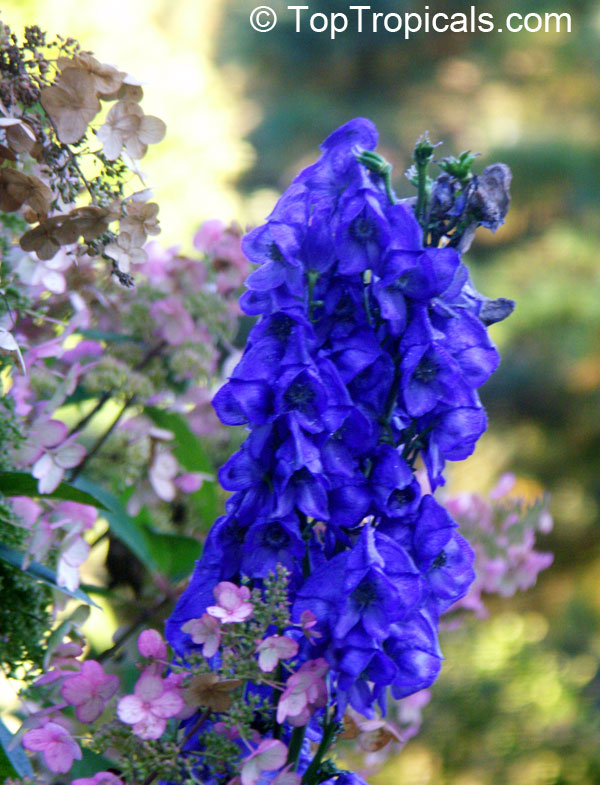
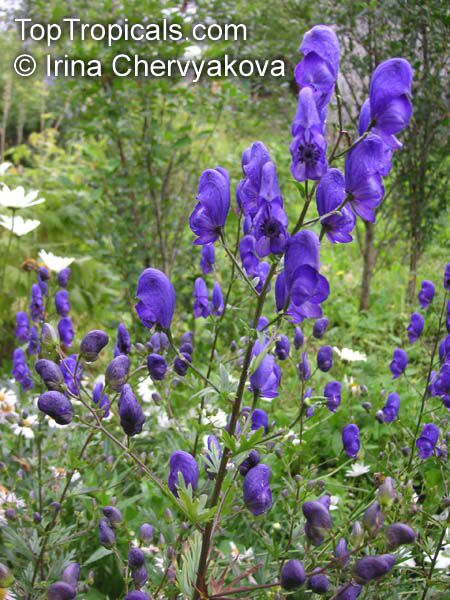
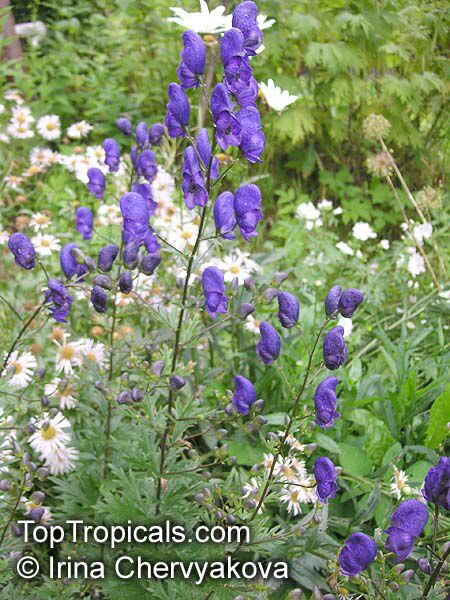
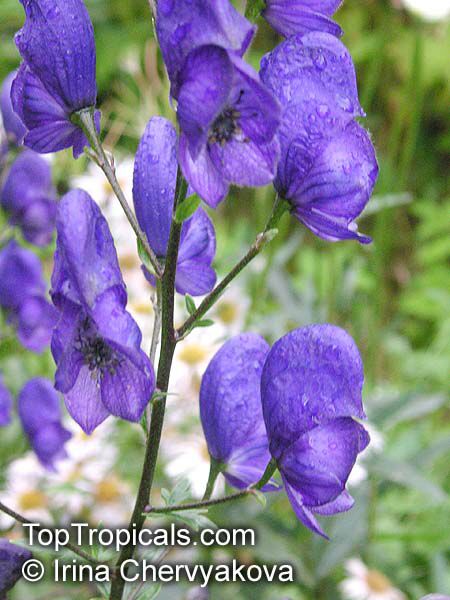
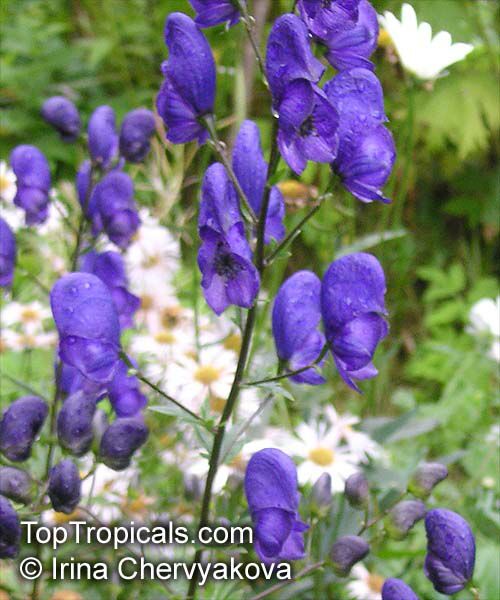
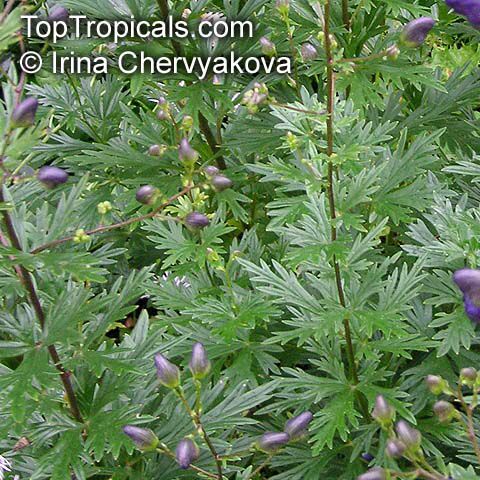
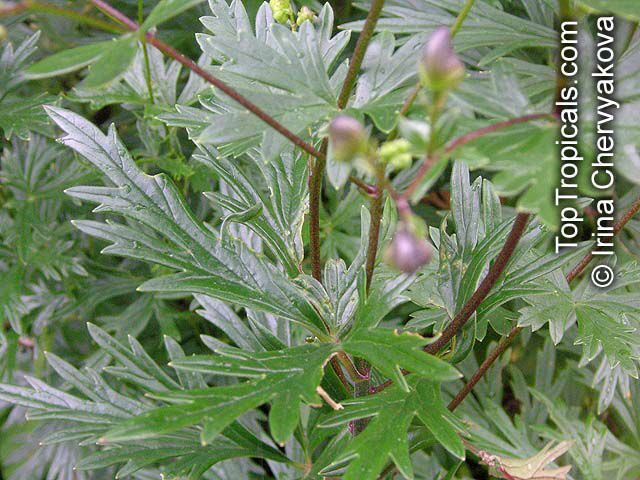
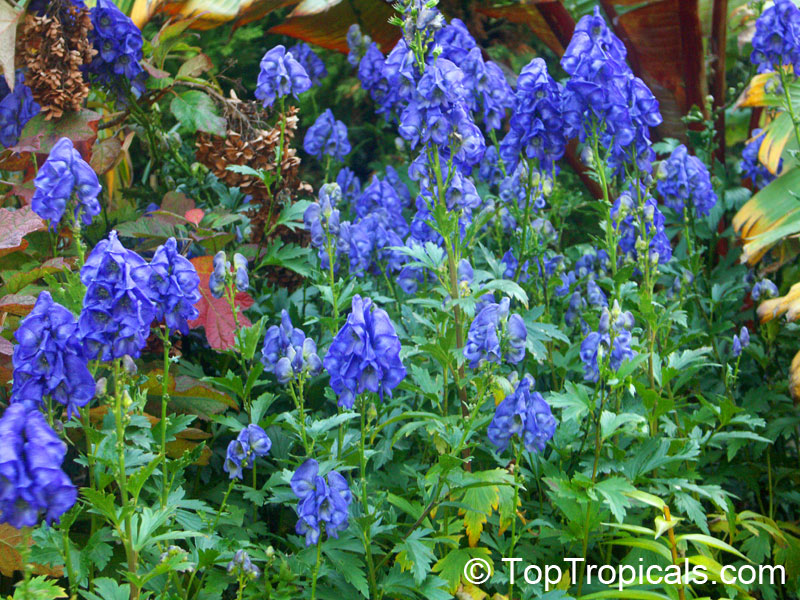
Botanical name: Aconitum sp.
Common names: Monkshood, Wolfsbane
Family: Ranunculaceae














Different Aconitum species (and their varieties) scattered across temperate regions of globe.
These are handsome plants, the tall, erect stem being crowned by racemes of large and eye-catching blue, purple, white, yellow or pink zygomorphic flowers. Aconitum is grown in gardens for its attractive spike like inflorescences and showy flowers.
All Aconitum plants contain poisonous alkaloids that can, in sufficient quantity, be deadly. Man has used Aconitum as a medicine and poison for thousands of years. Outside Europe it was widely used for its medical properties.
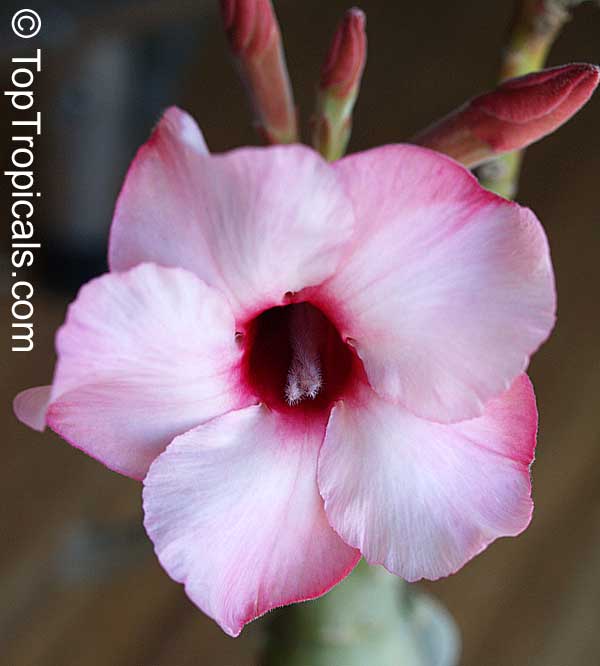
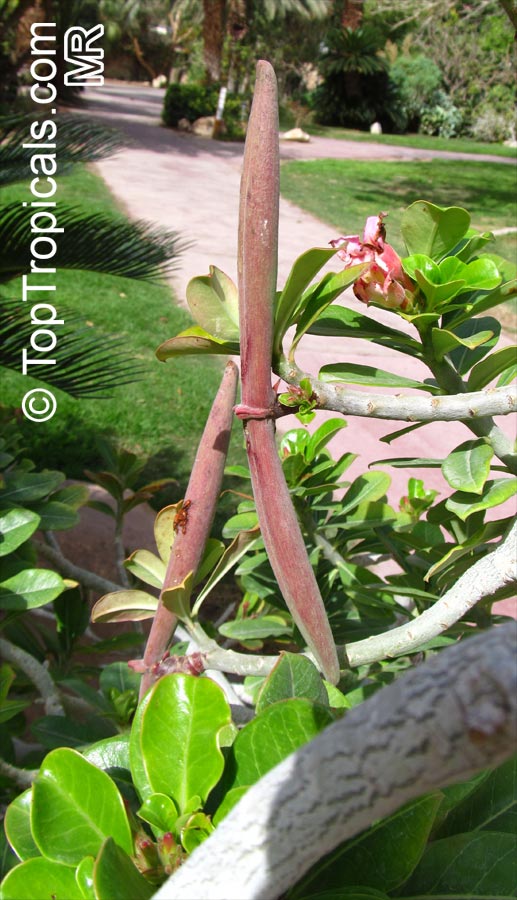
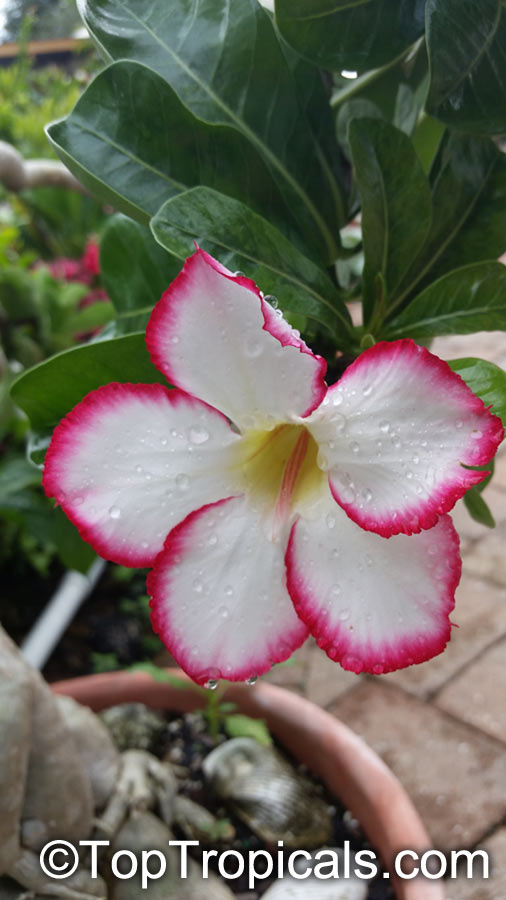
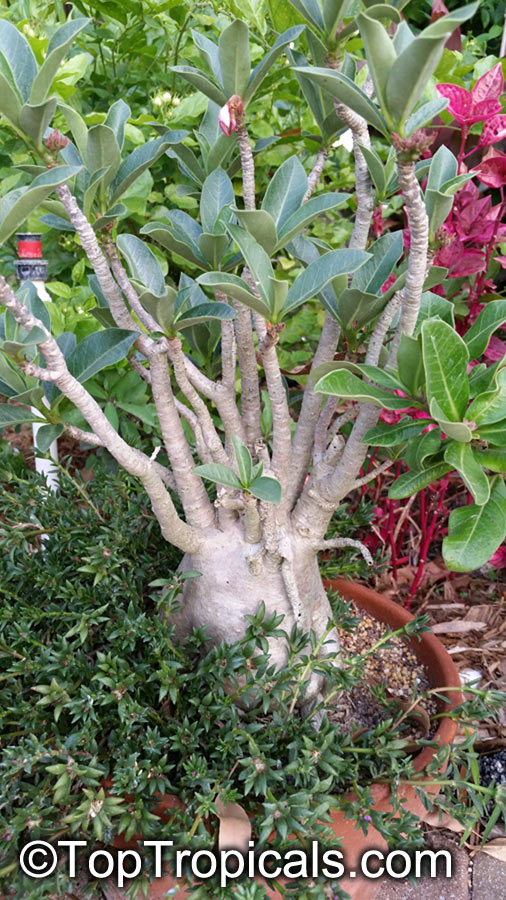
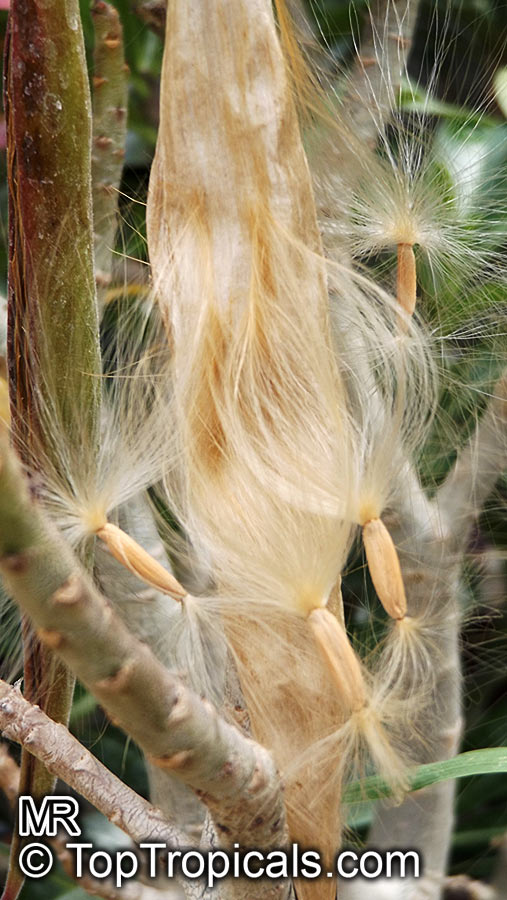
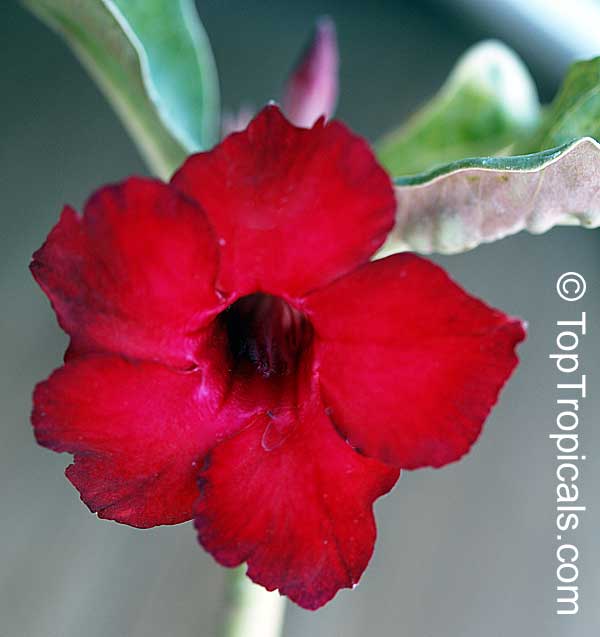
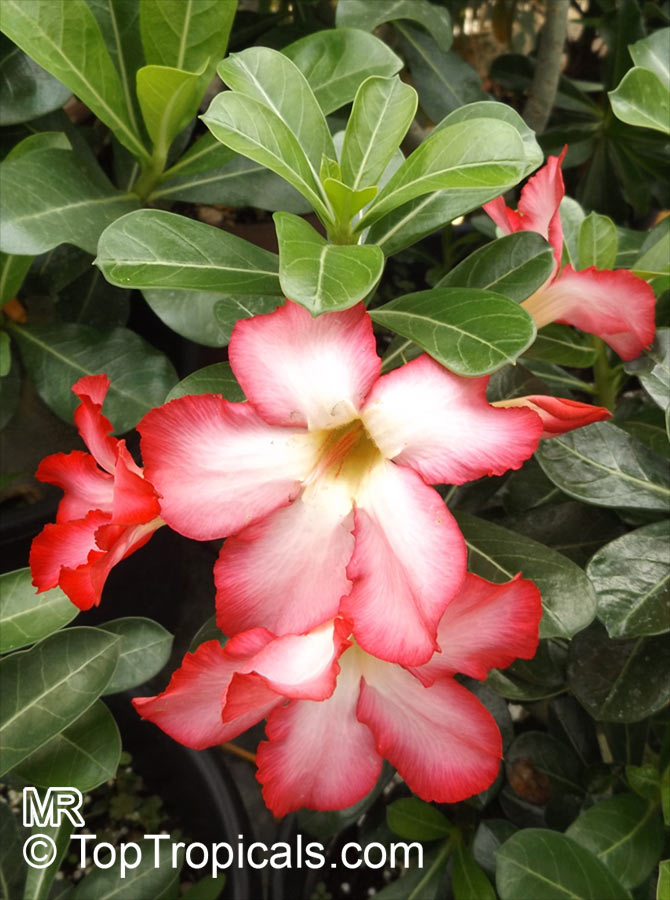
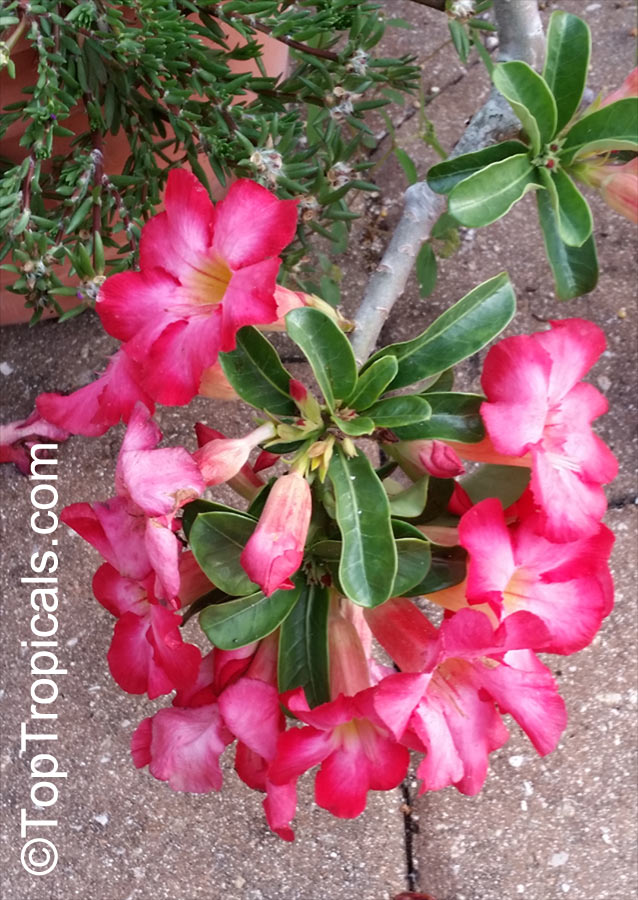
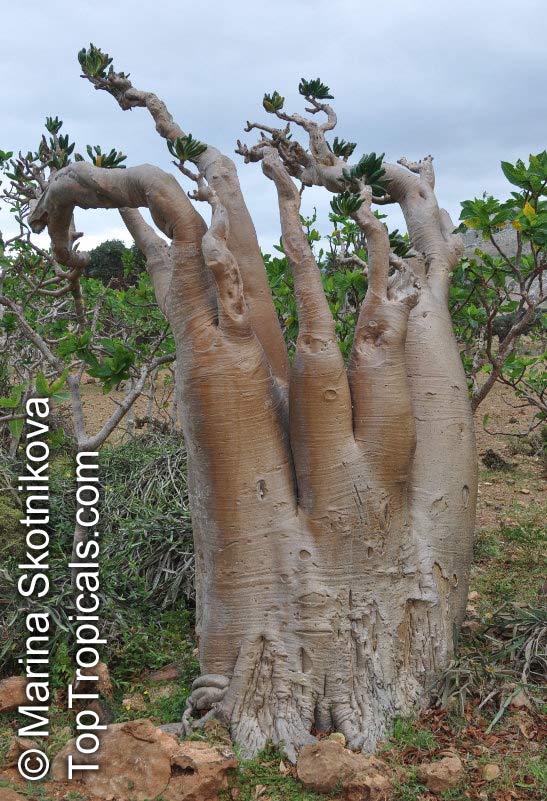
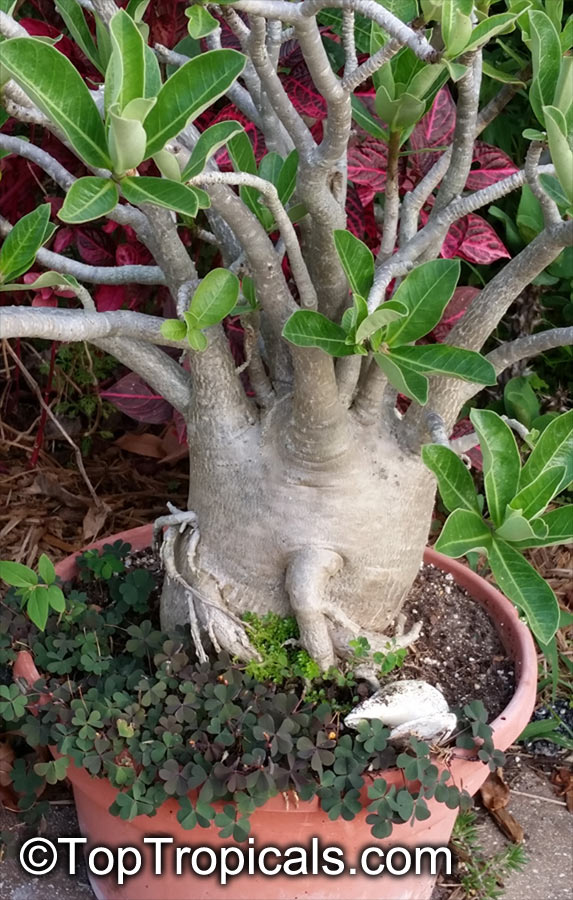
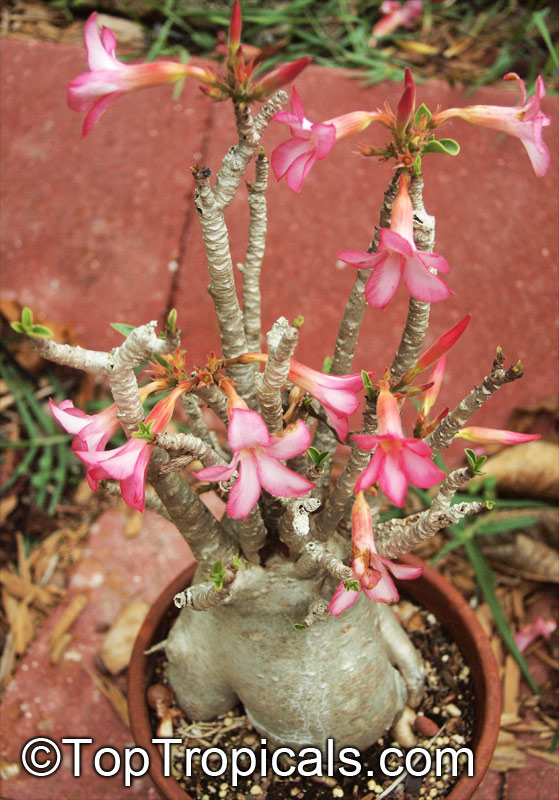
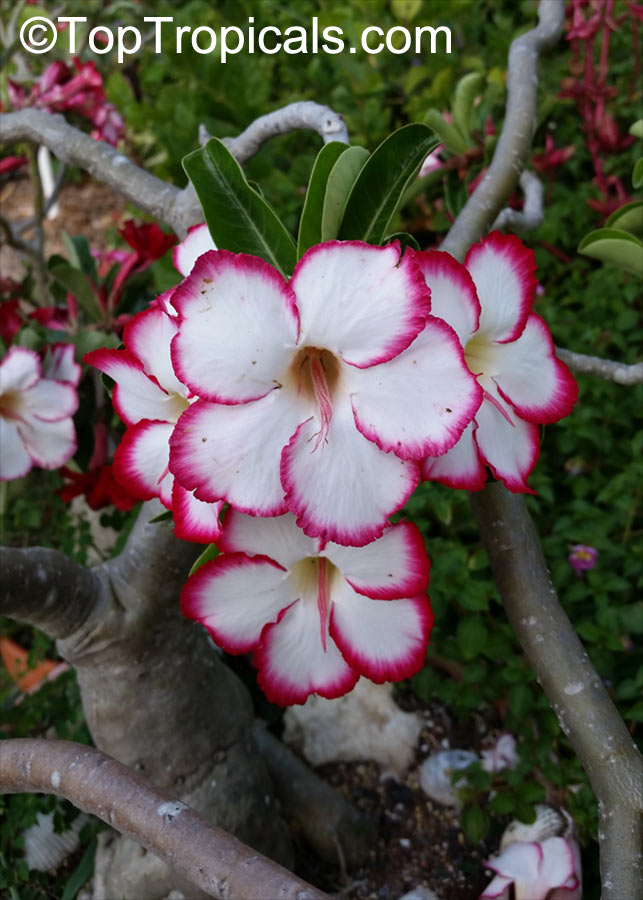
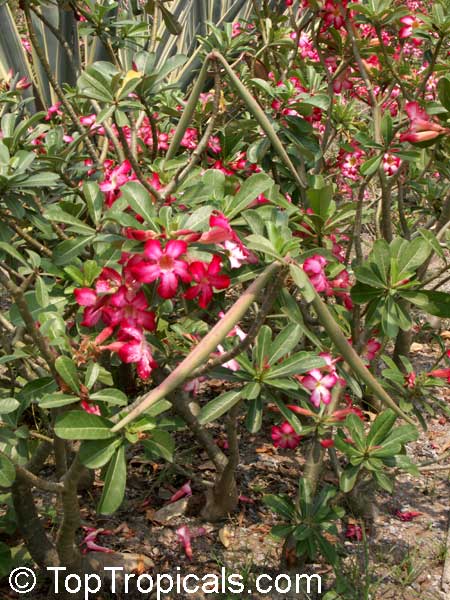
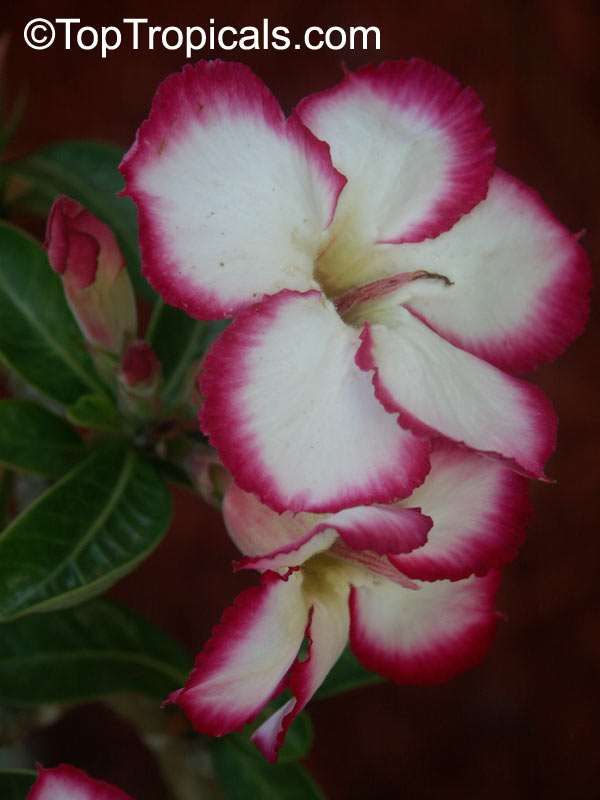
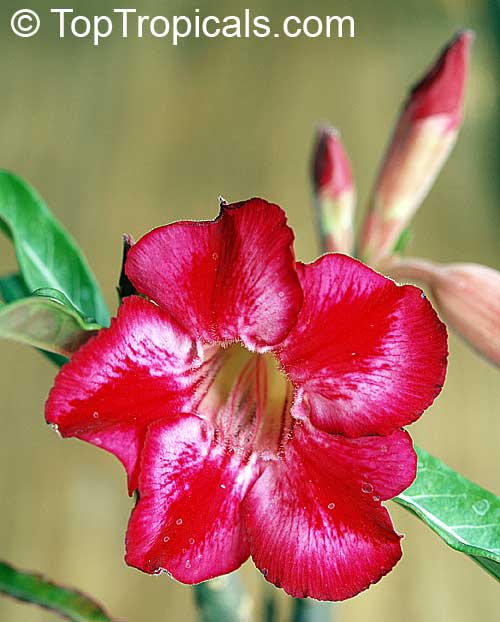
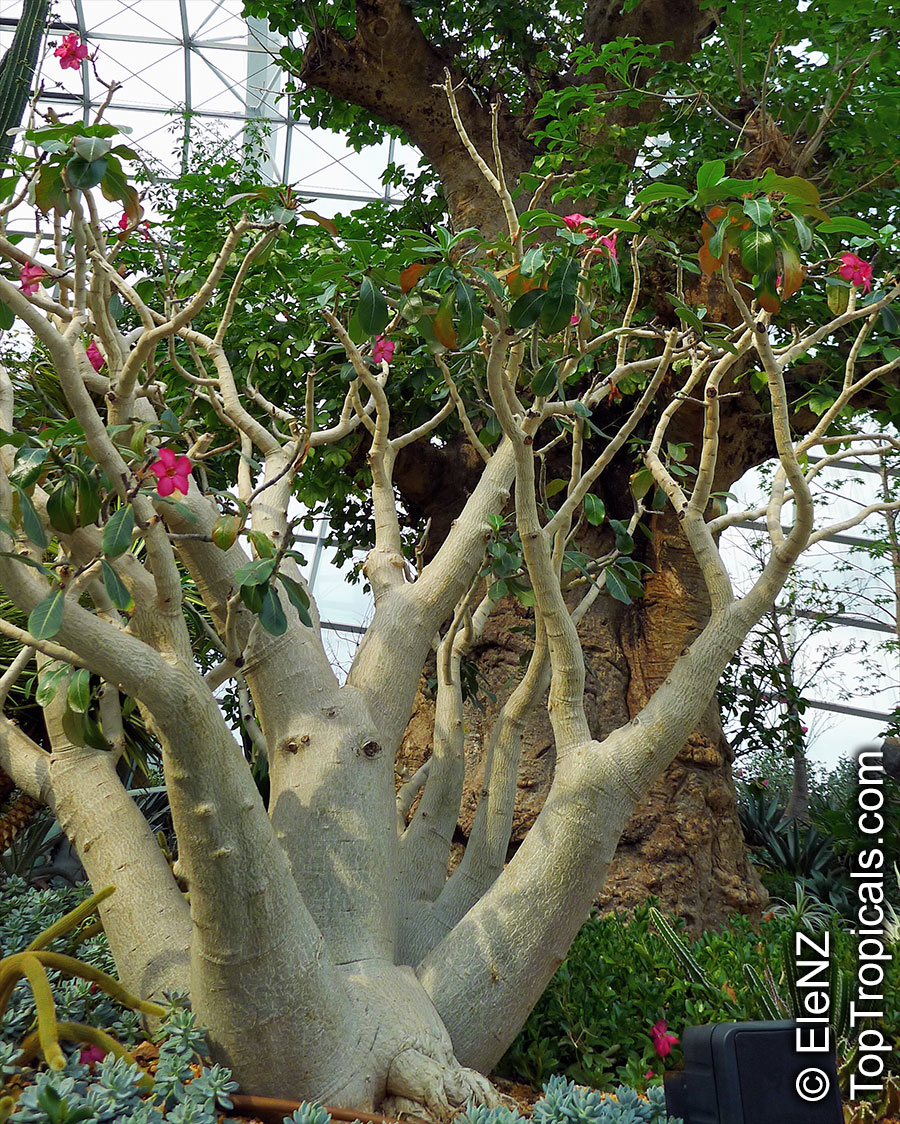
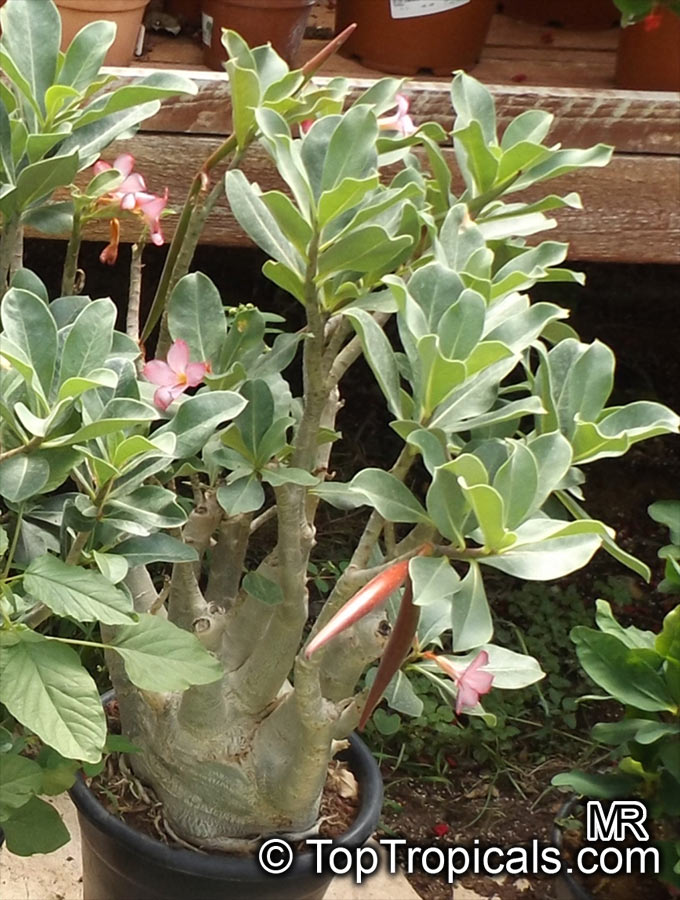
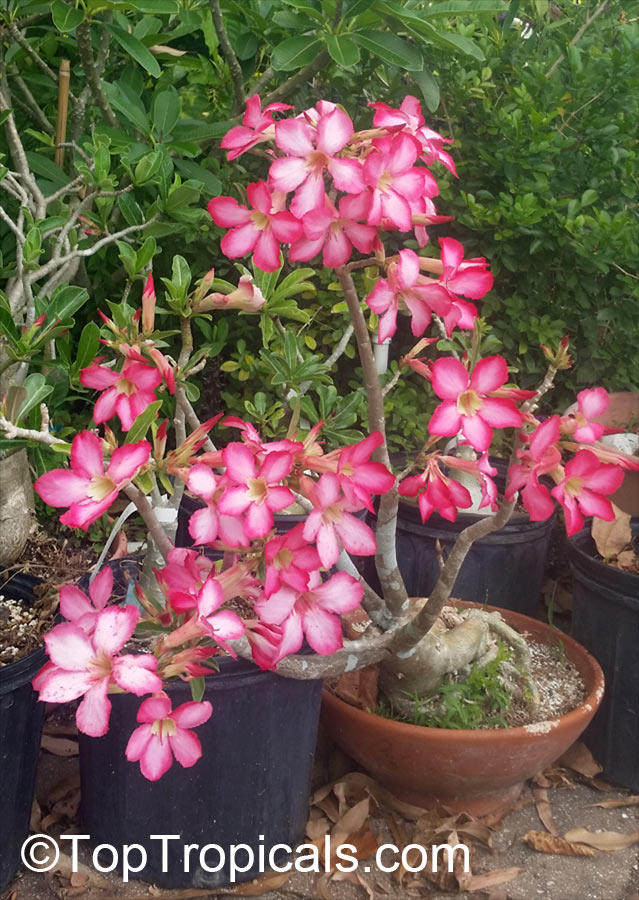
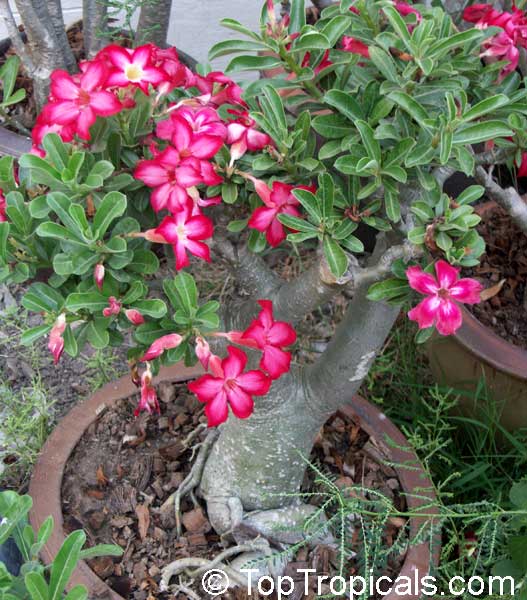
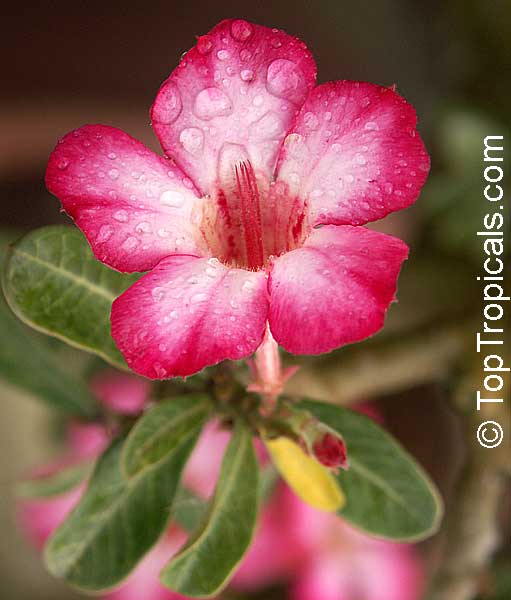
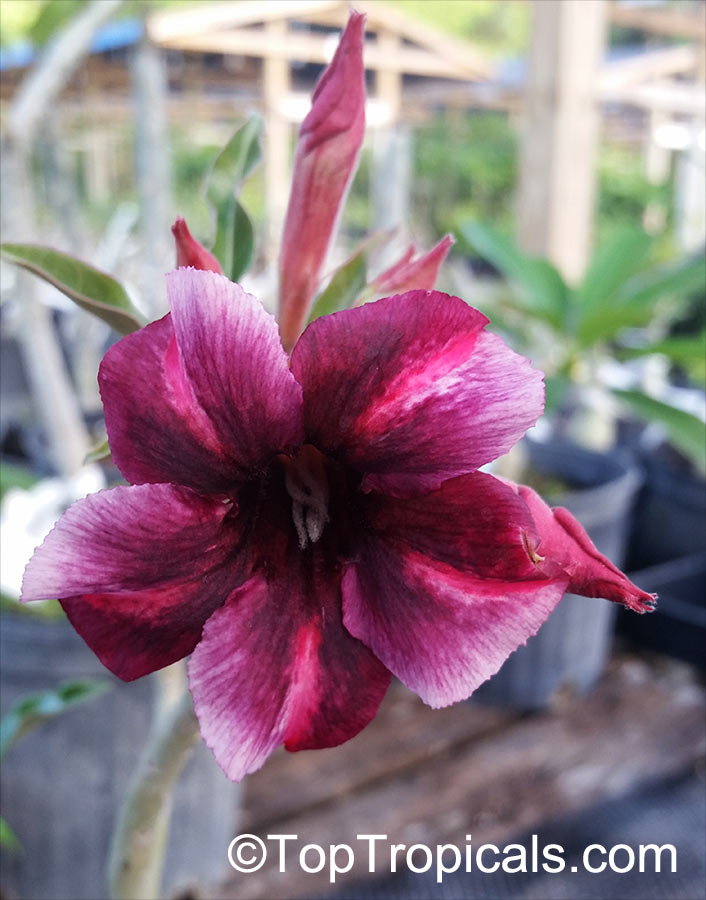
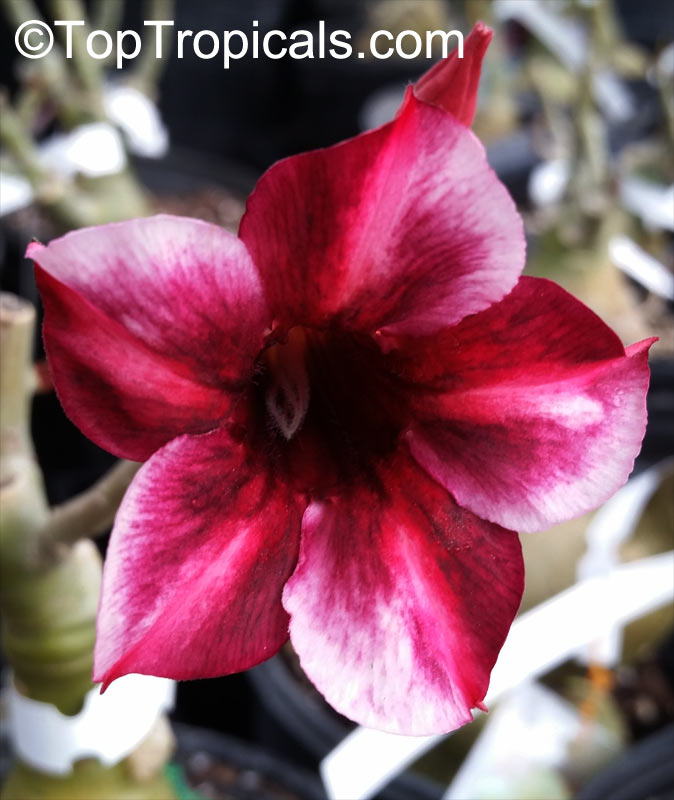
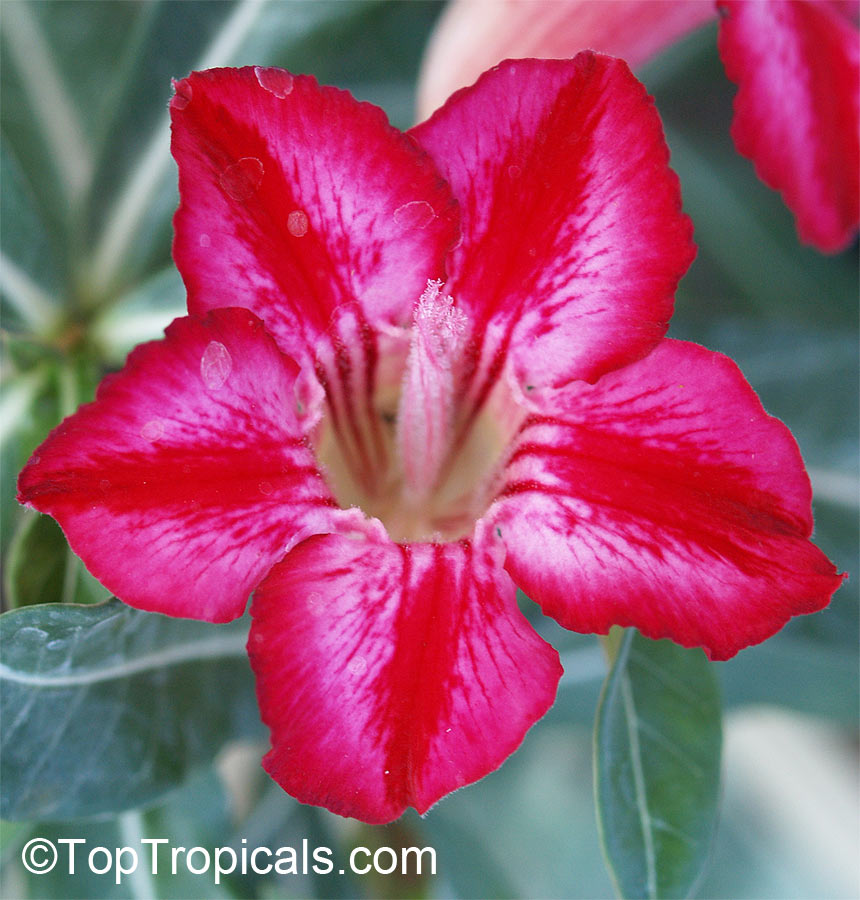
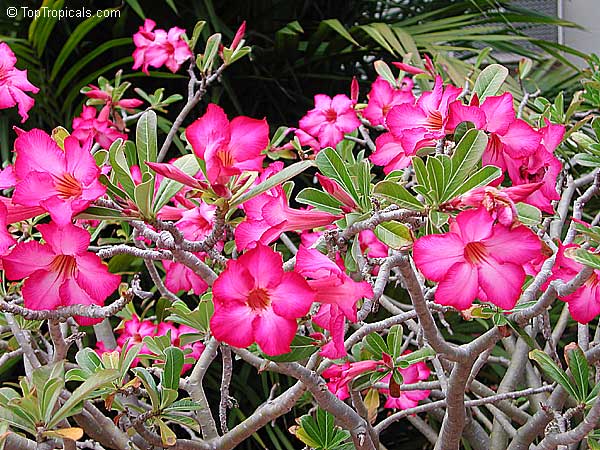
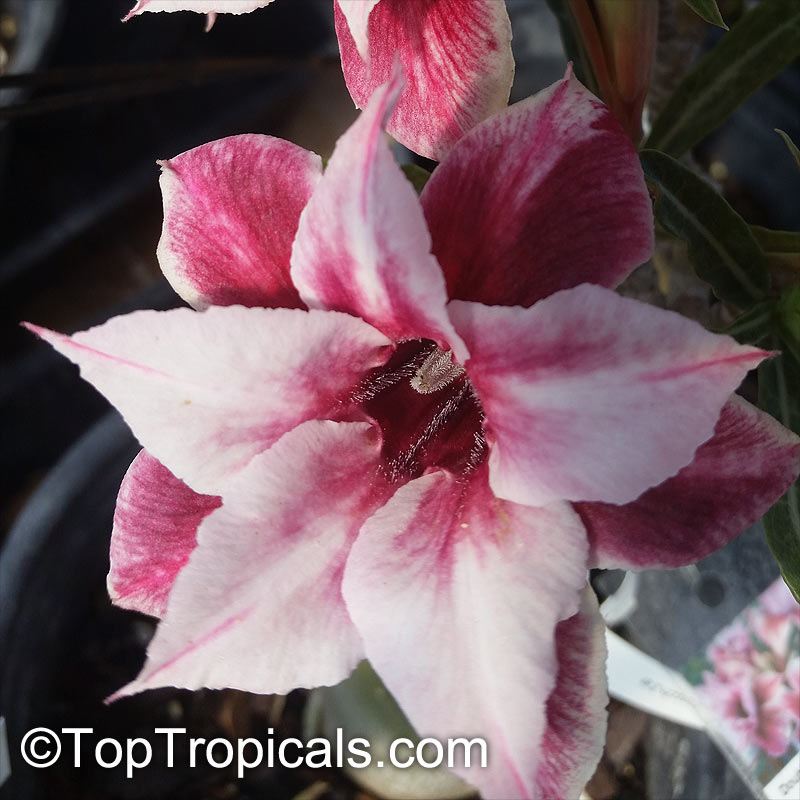
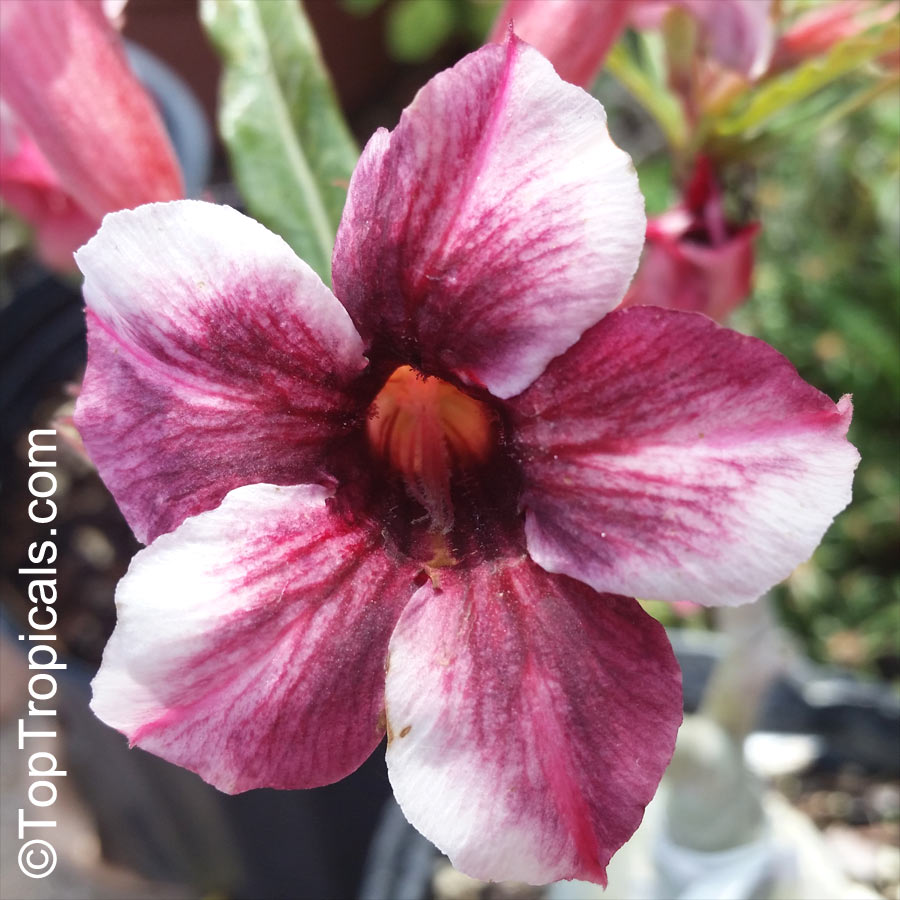
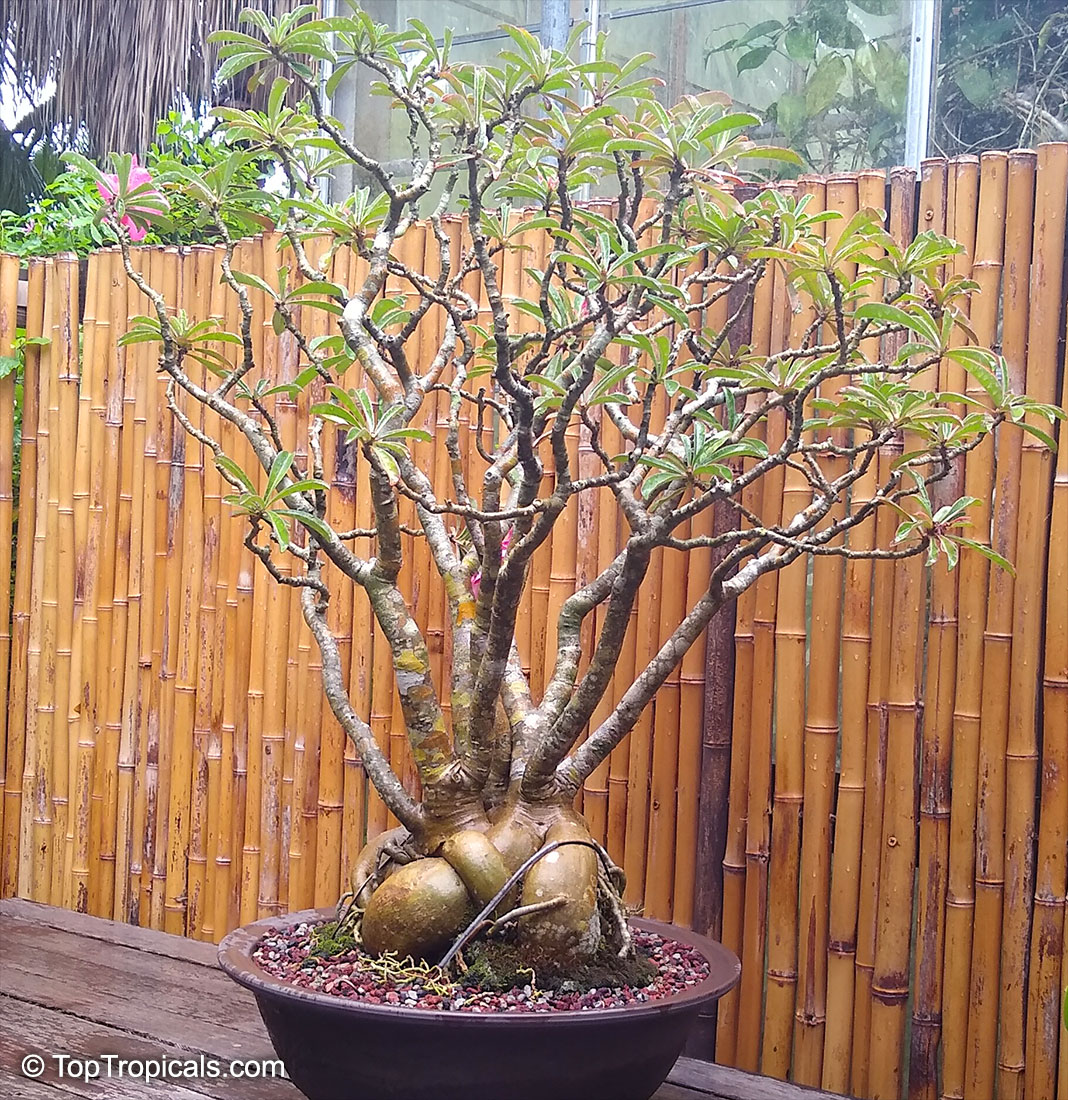
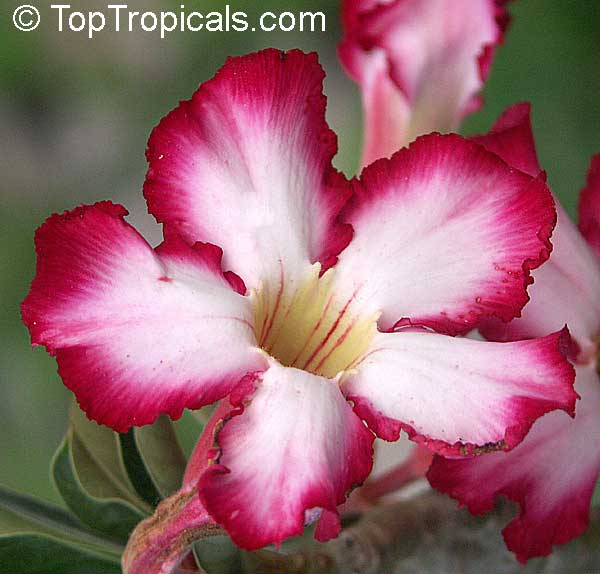
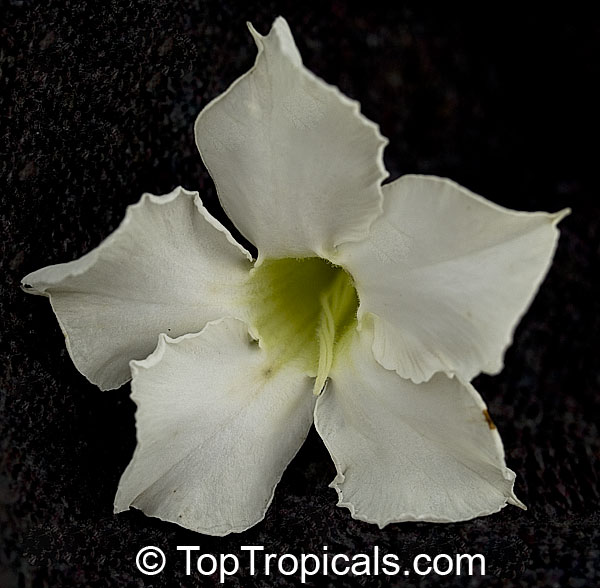
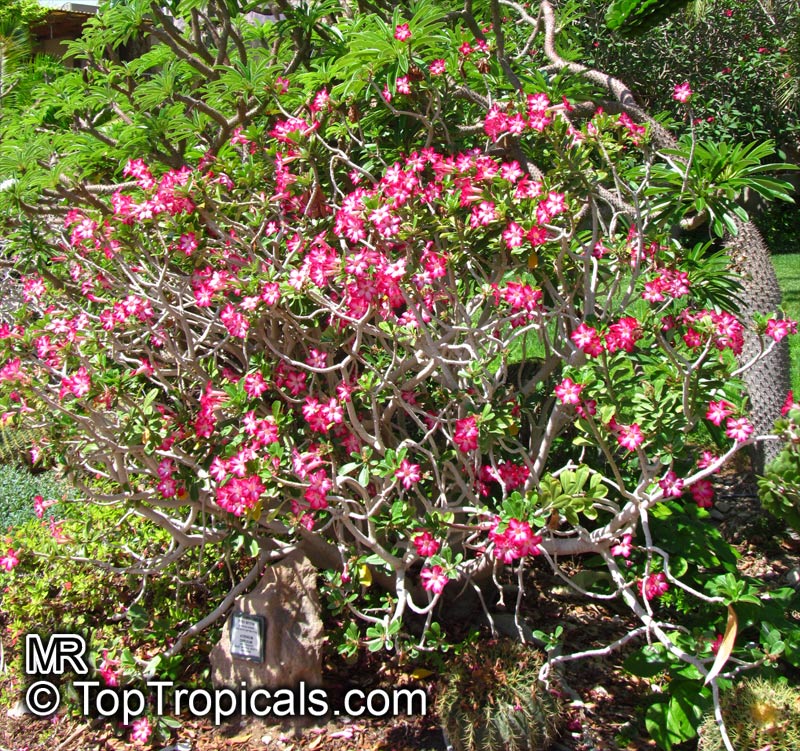
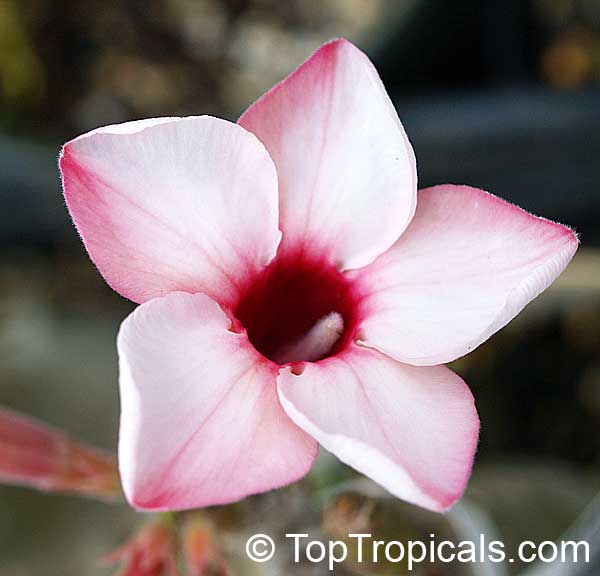
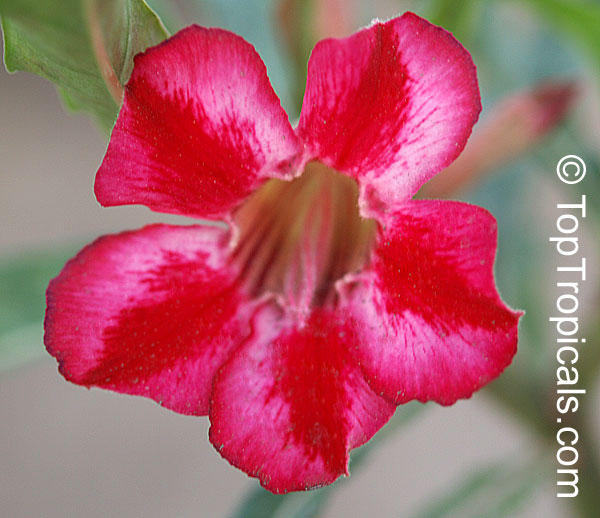
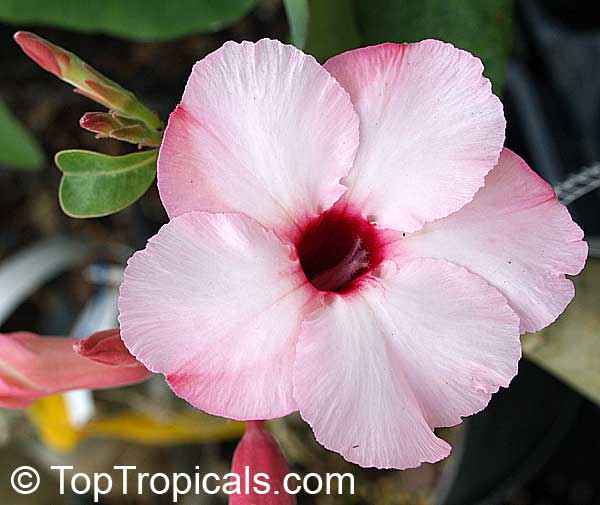
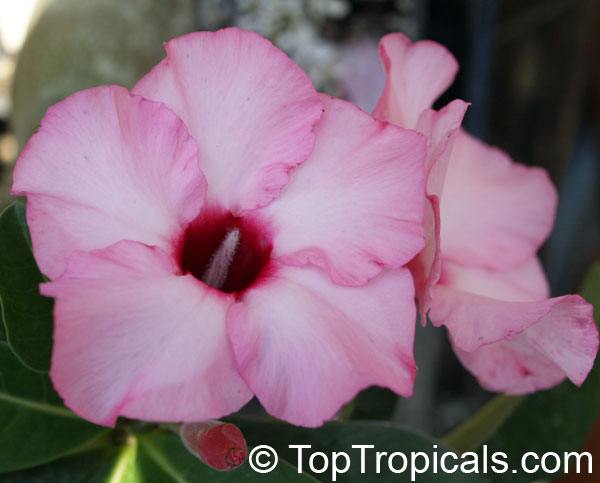
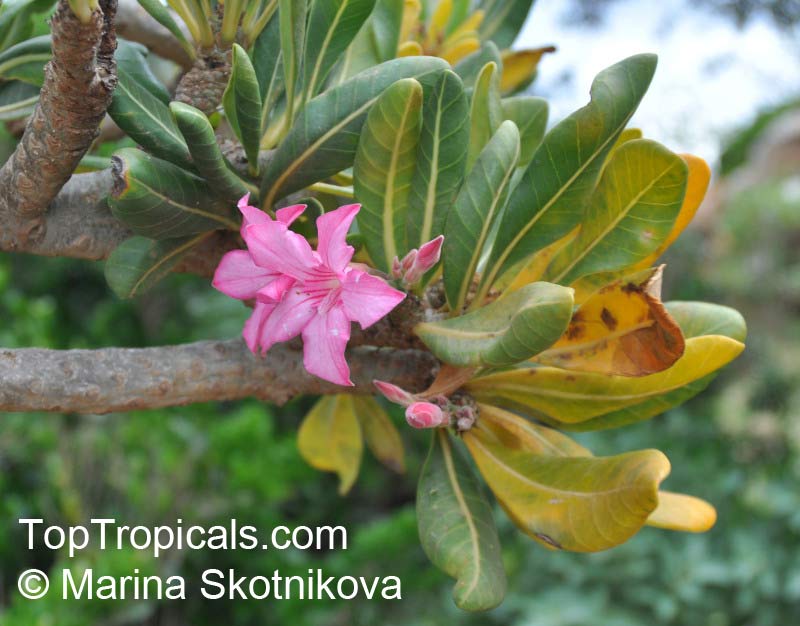
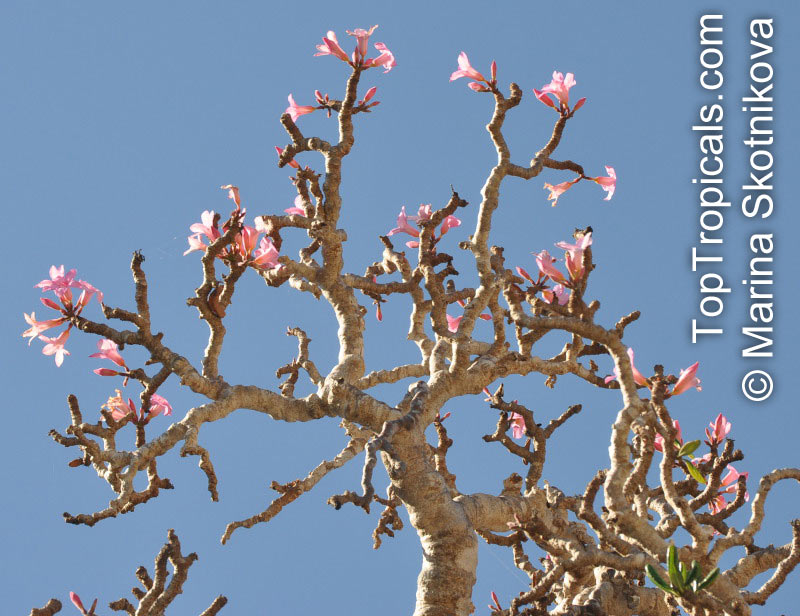
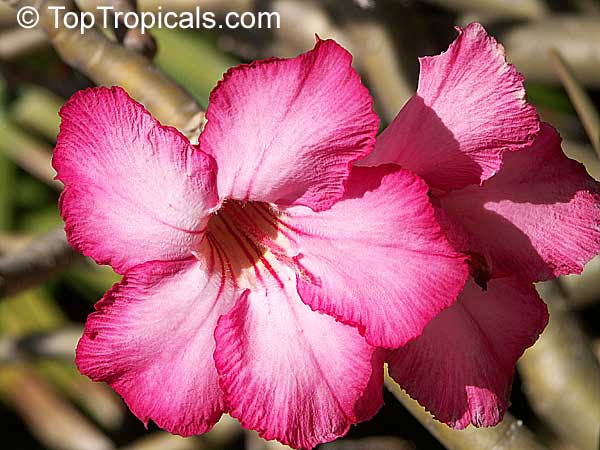
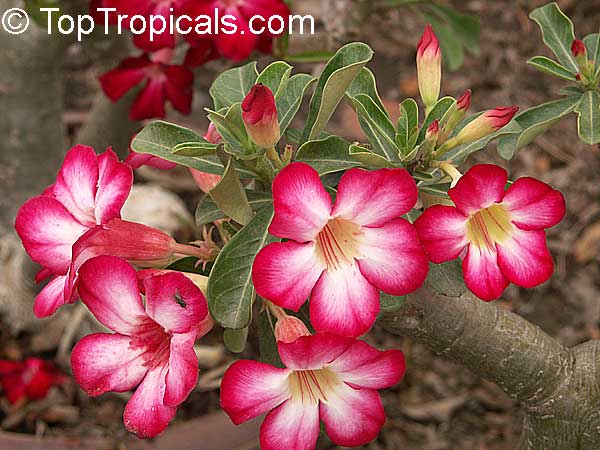
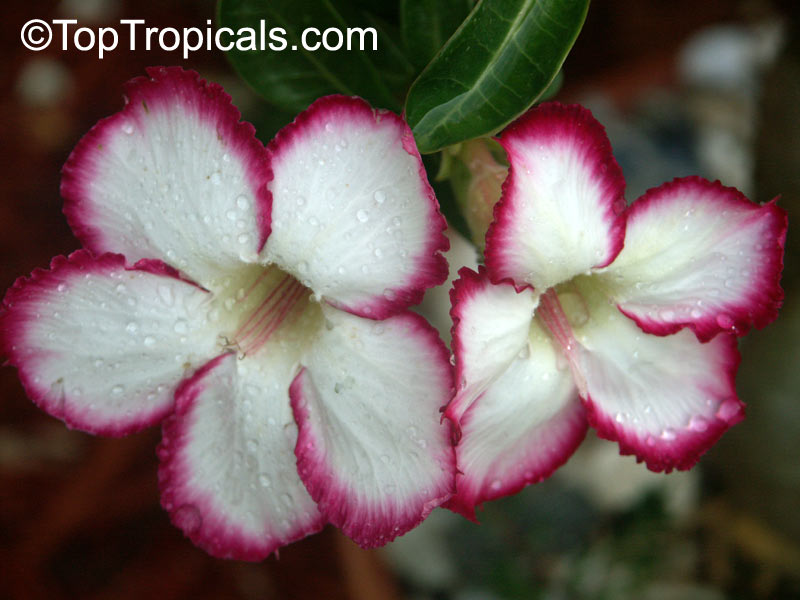
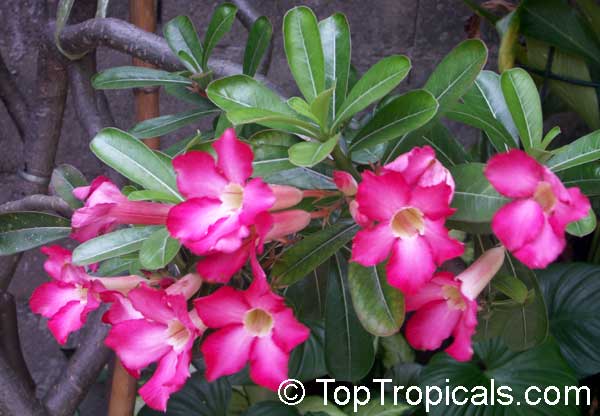
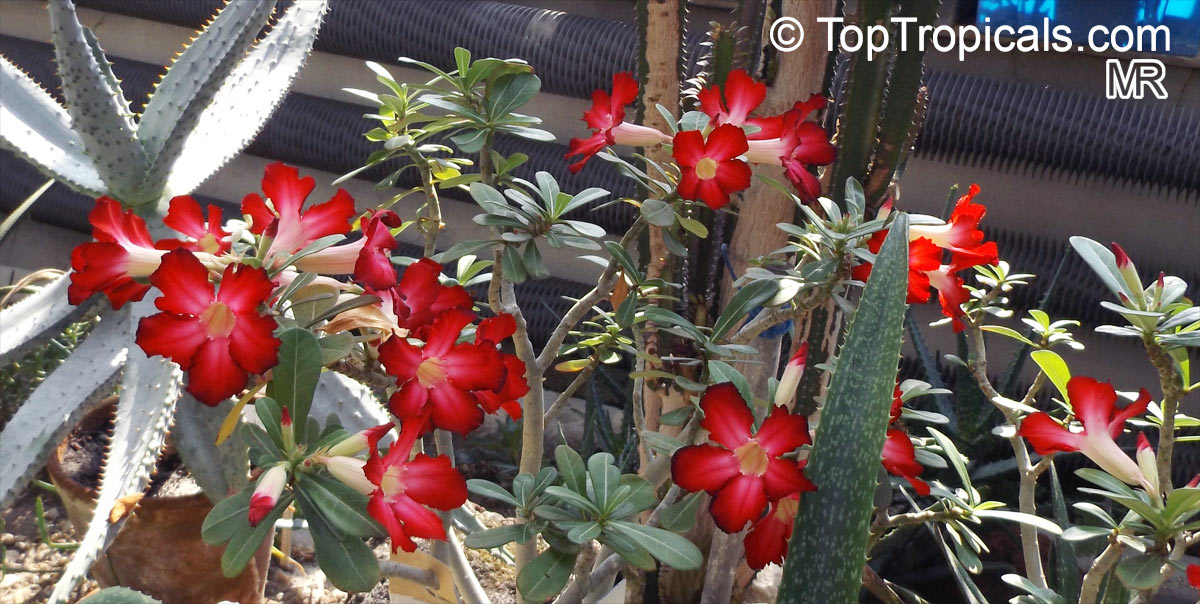
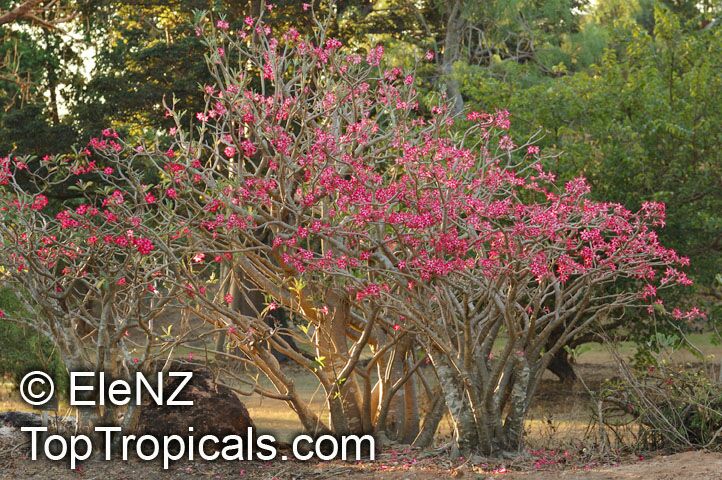
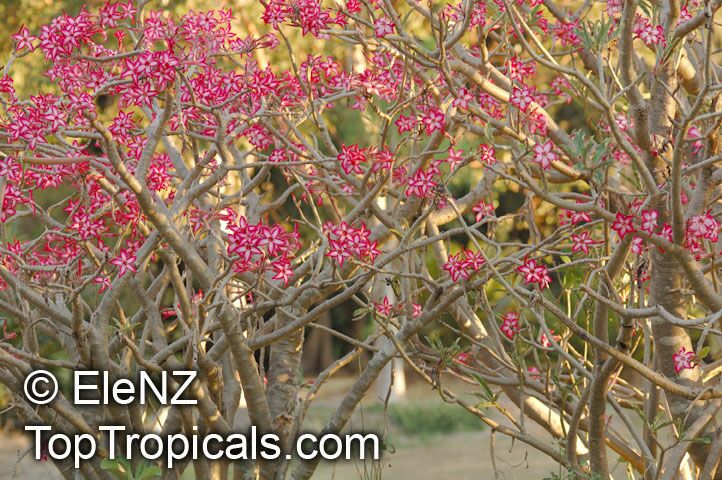
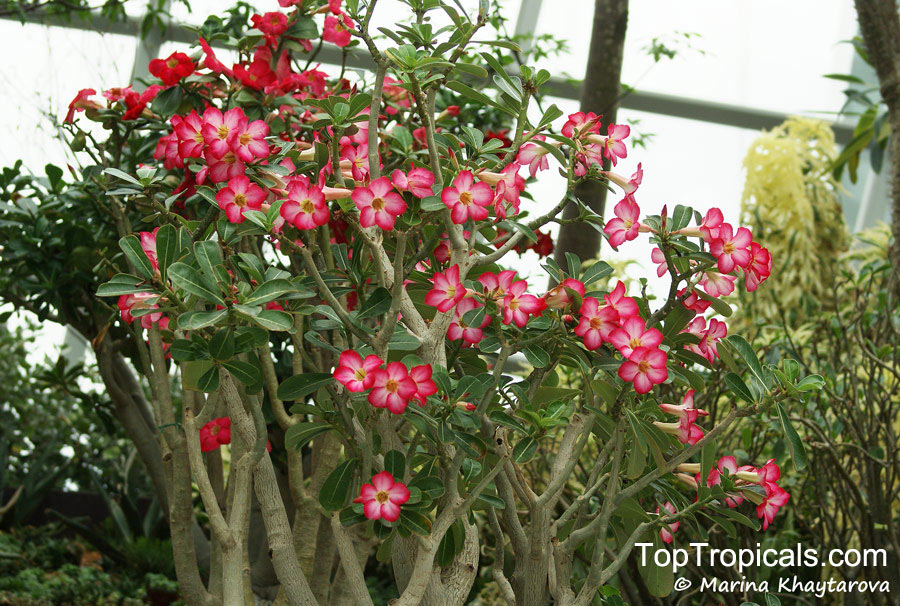
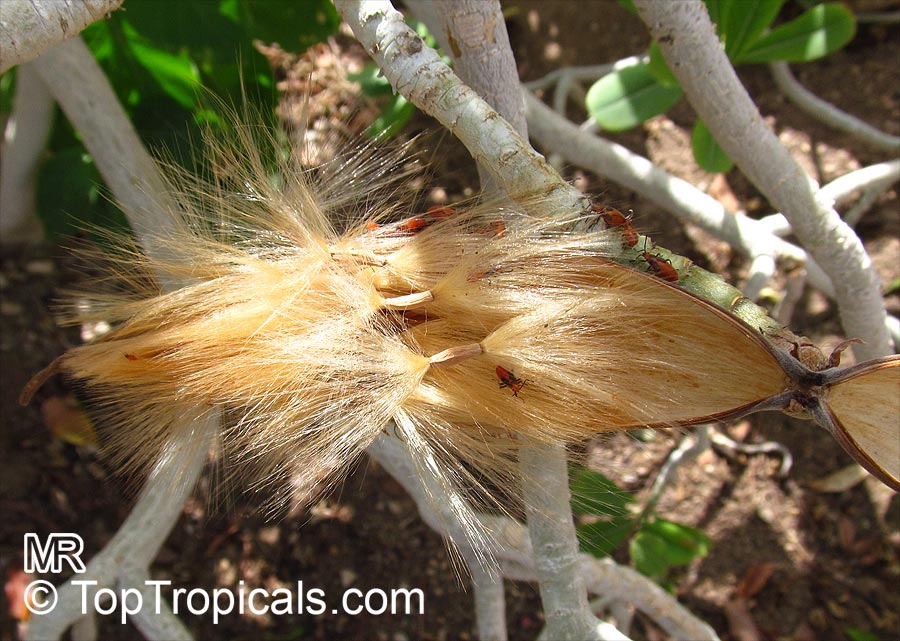
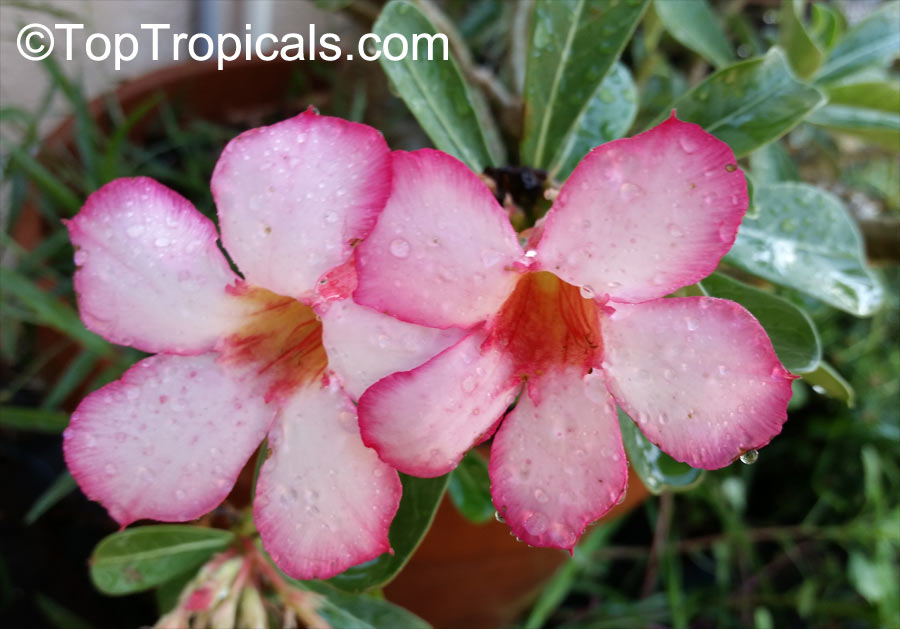
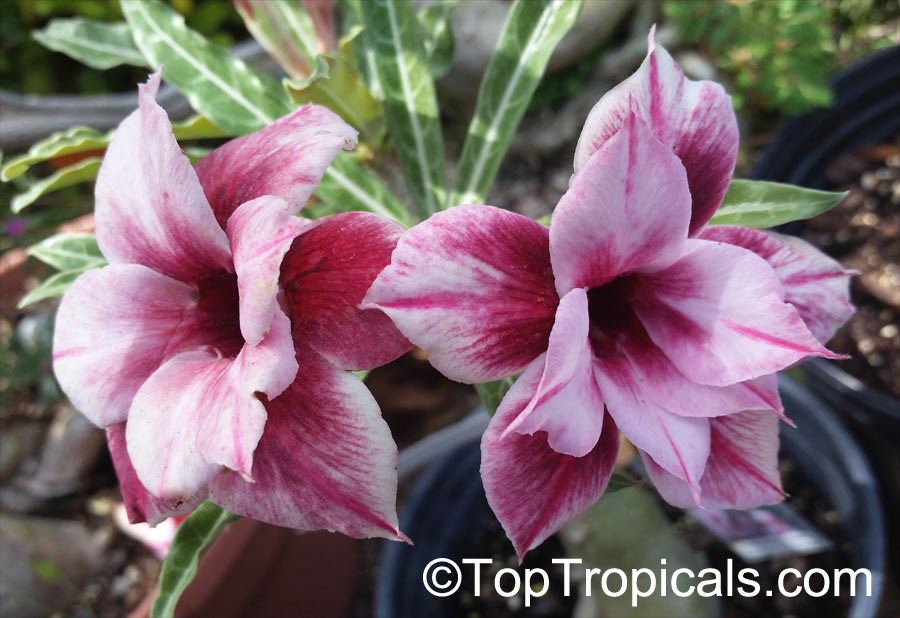
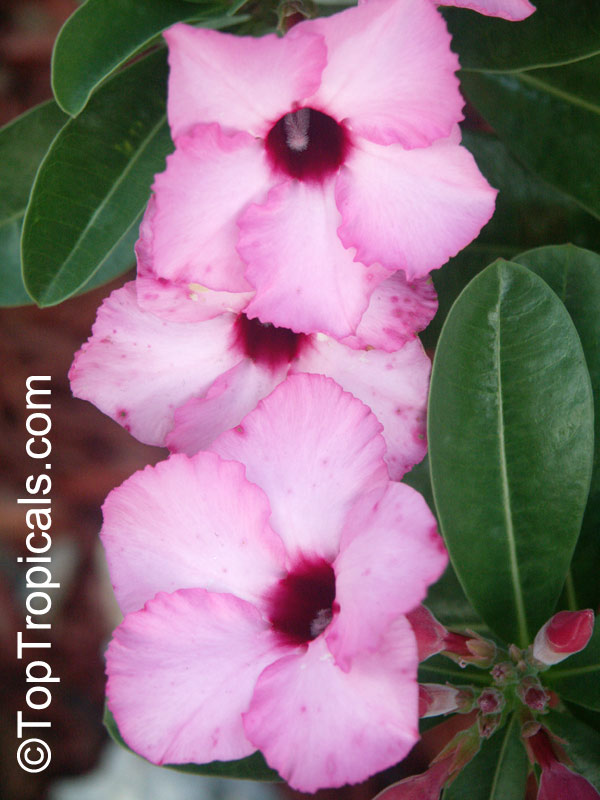
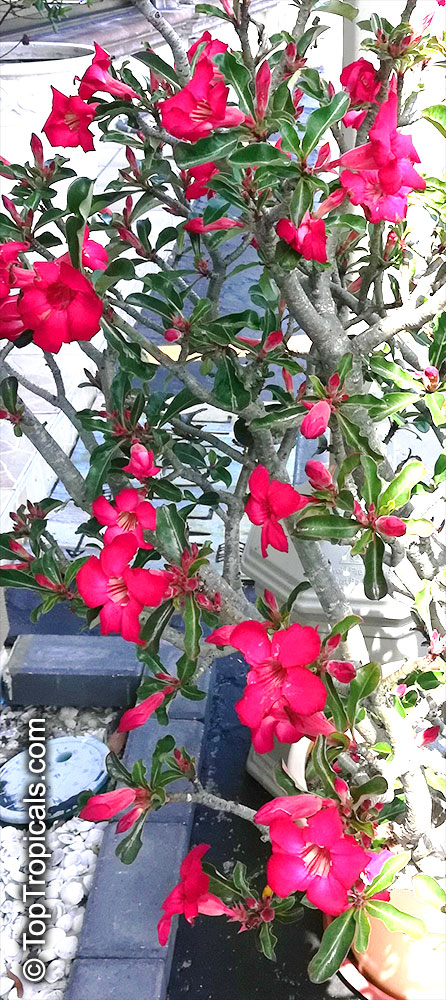
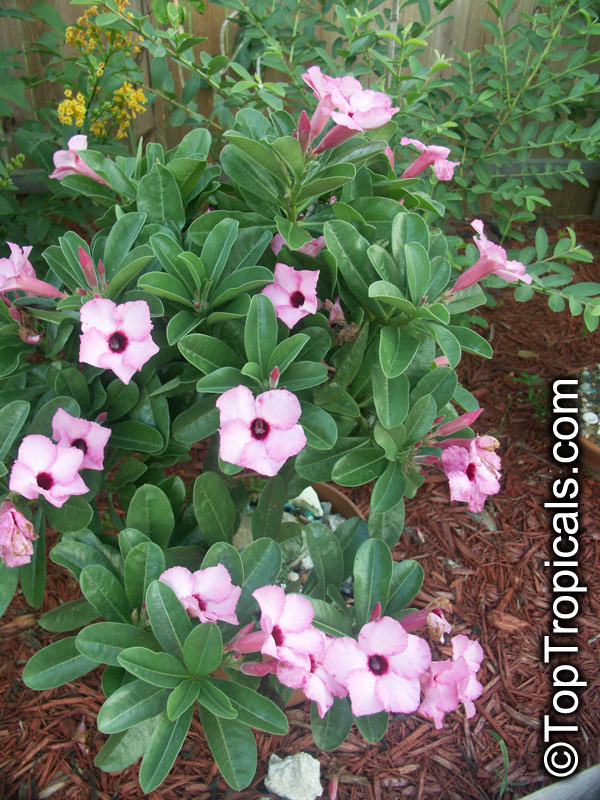
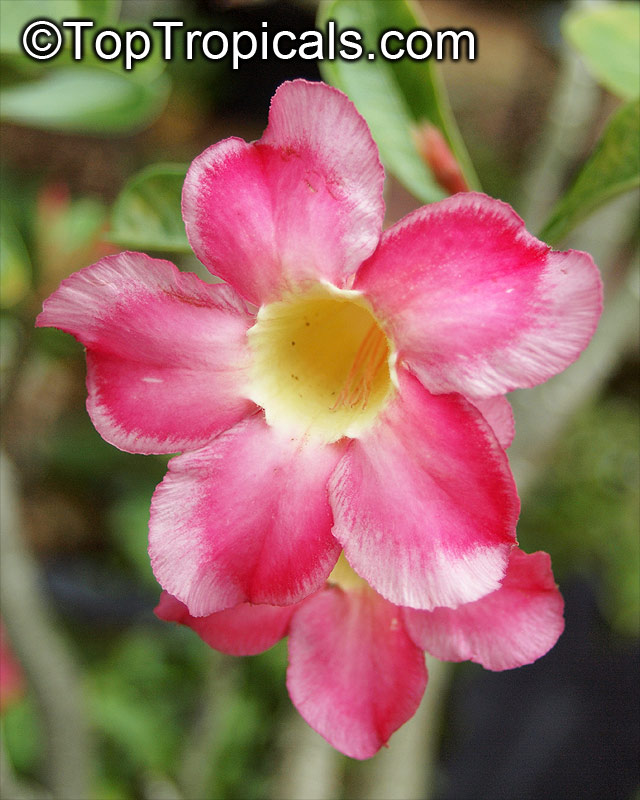
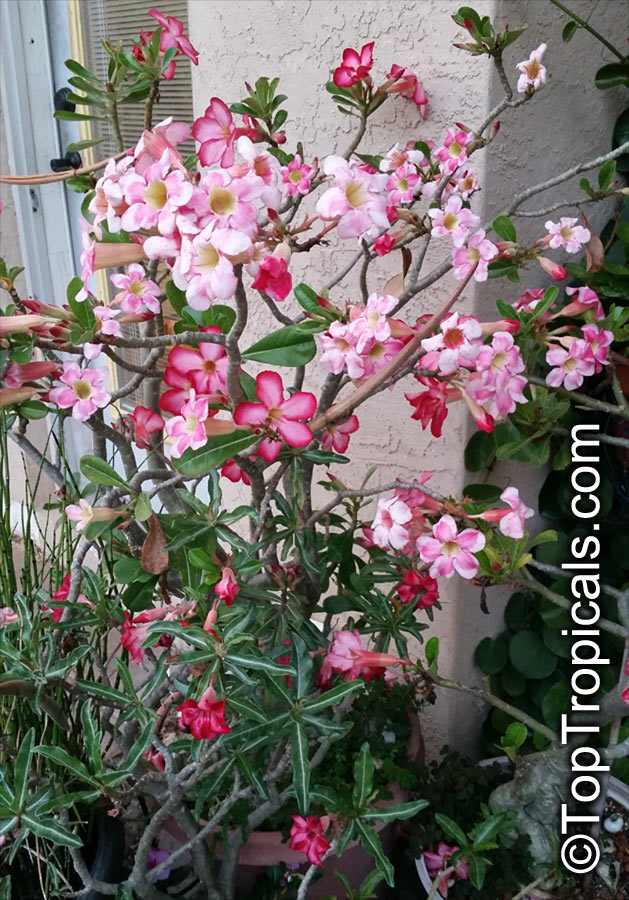
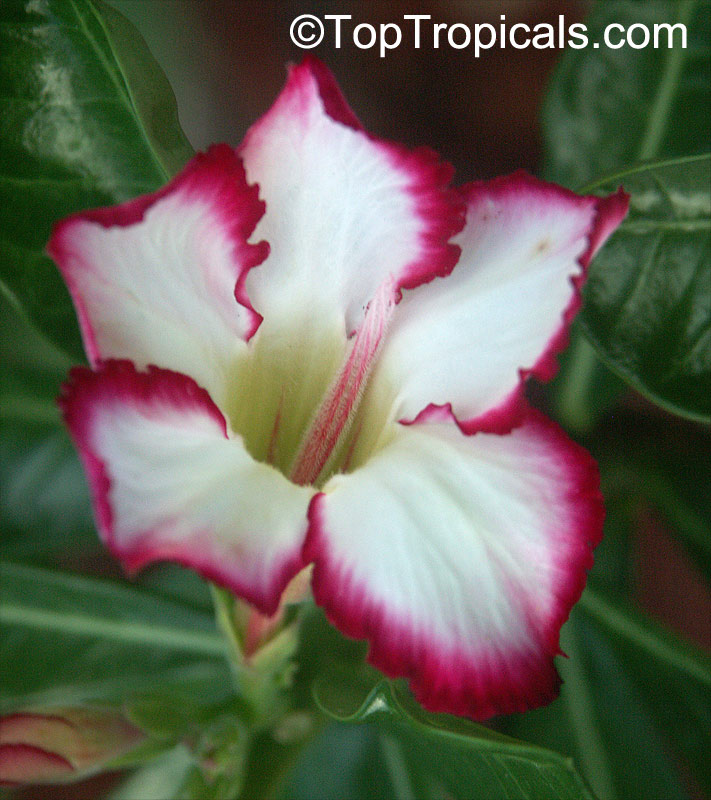
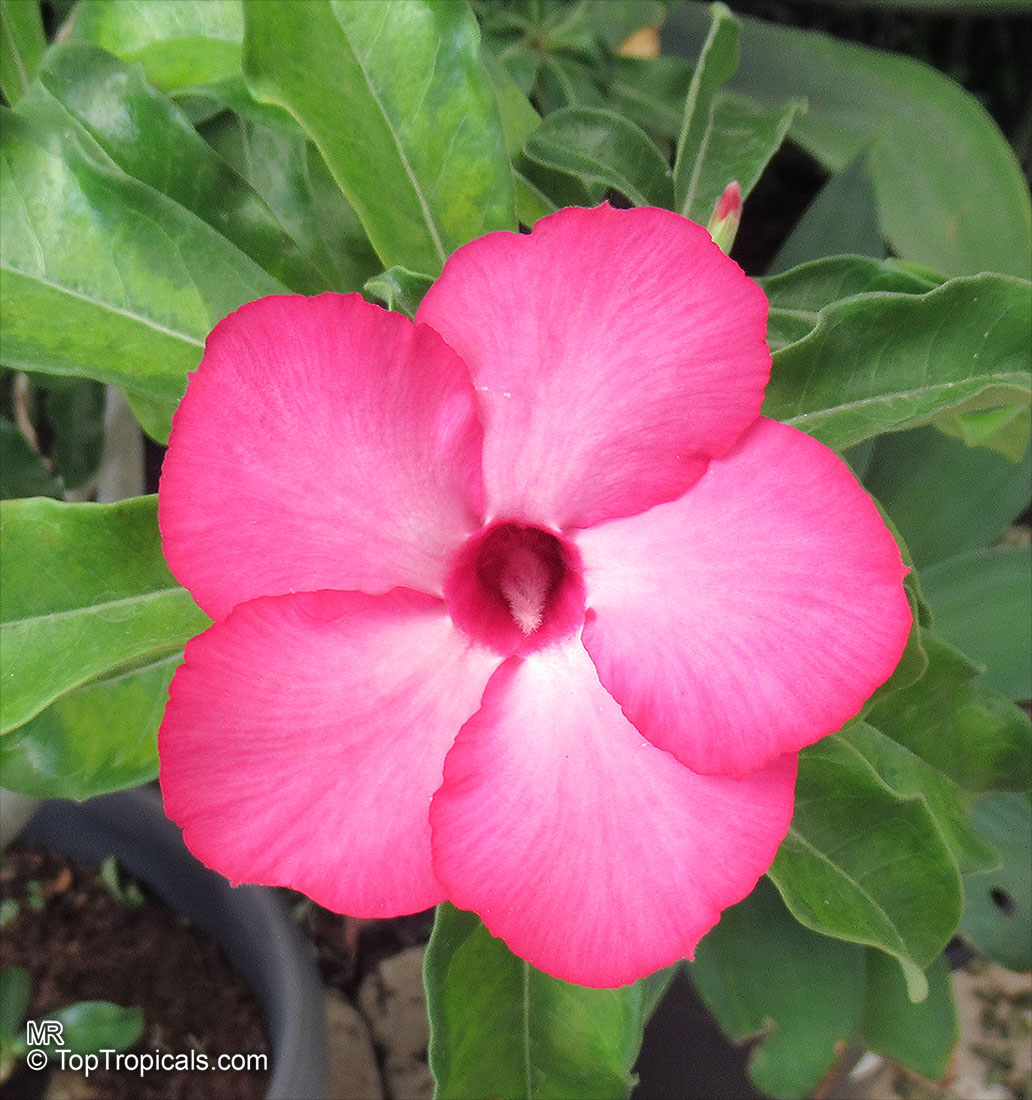
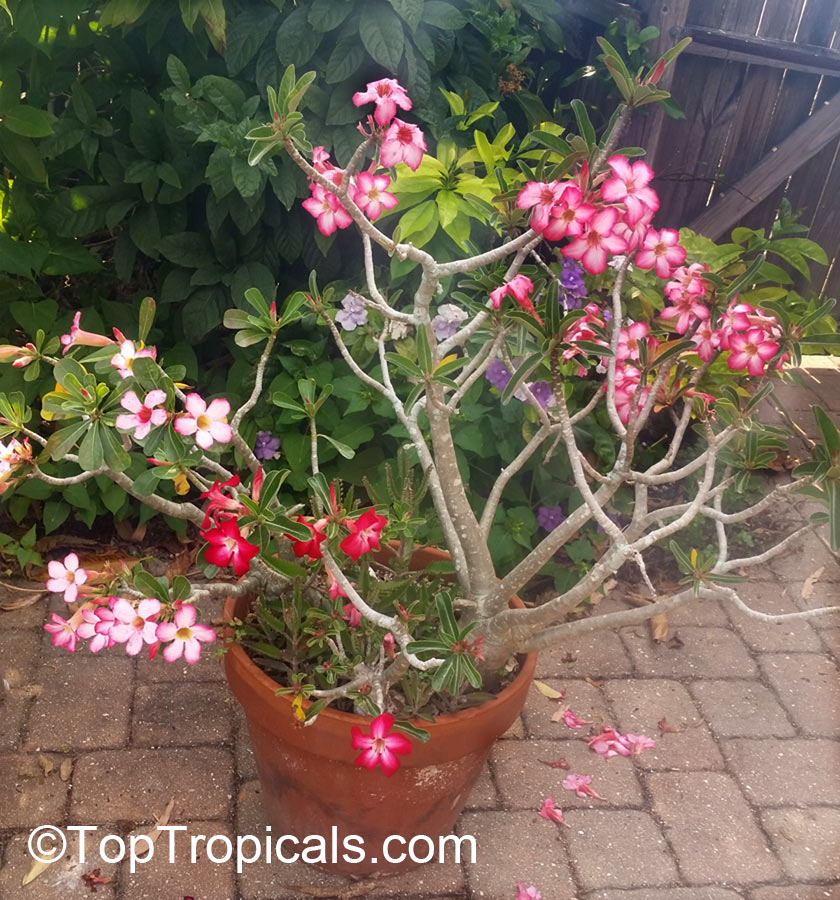
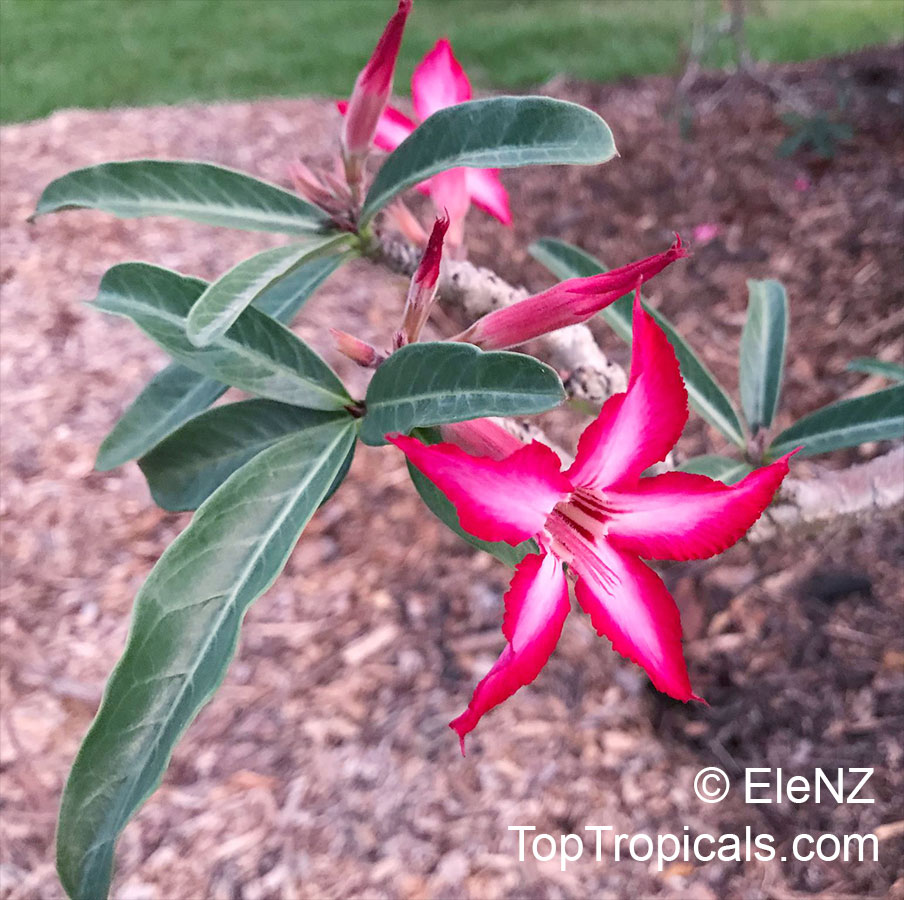
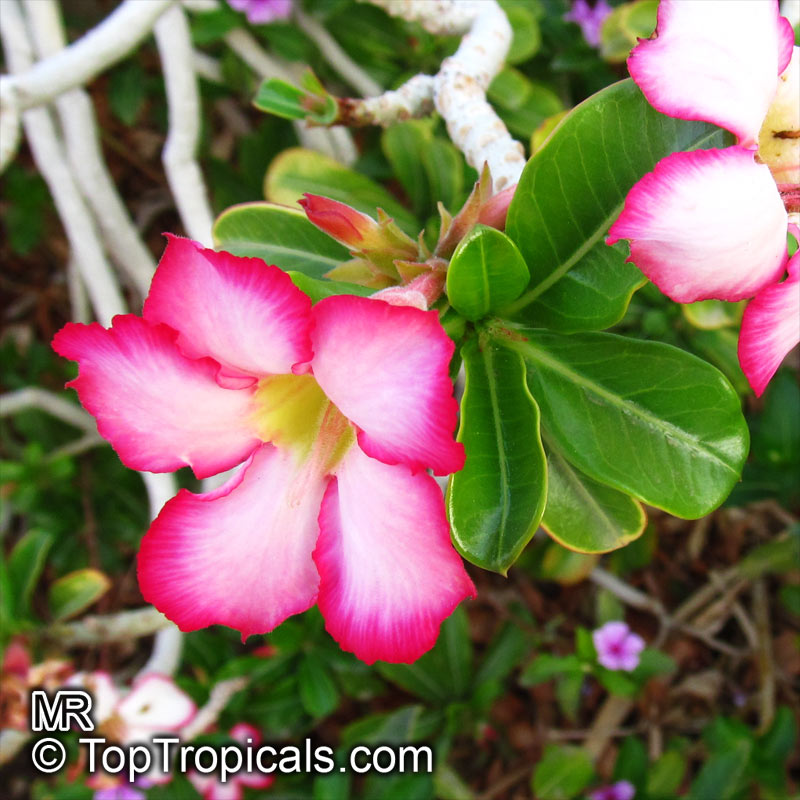
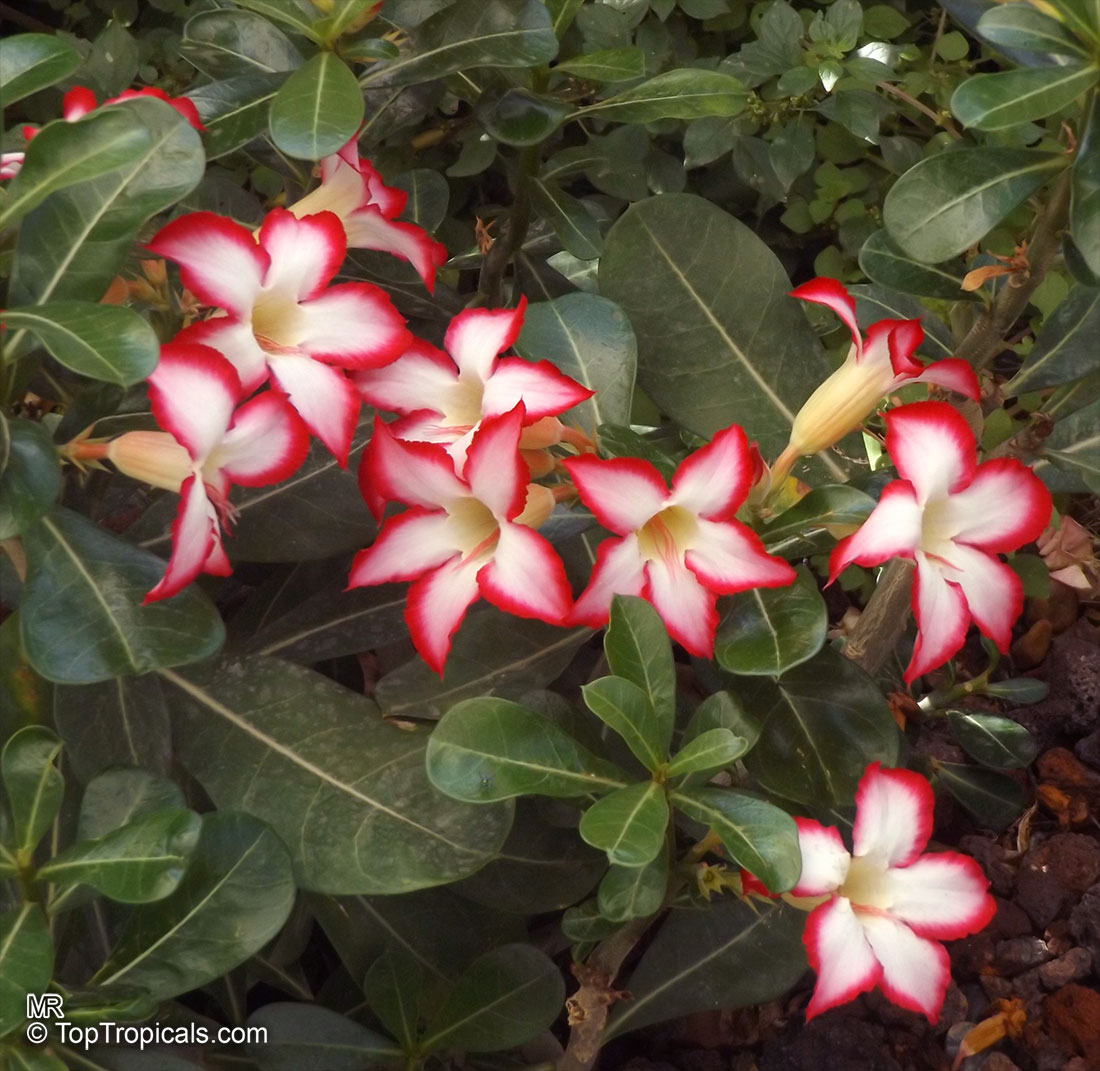
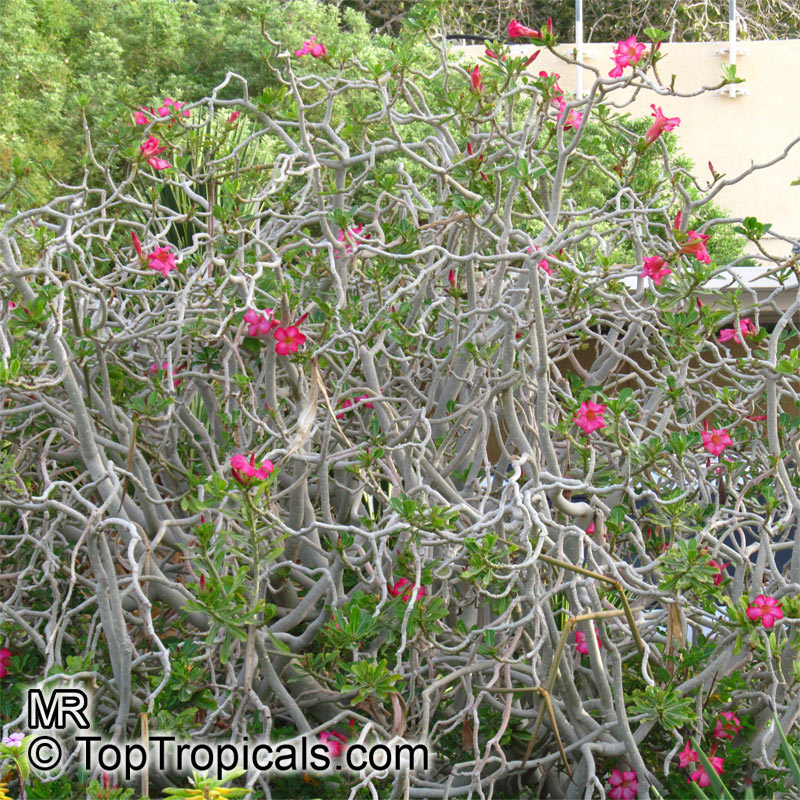
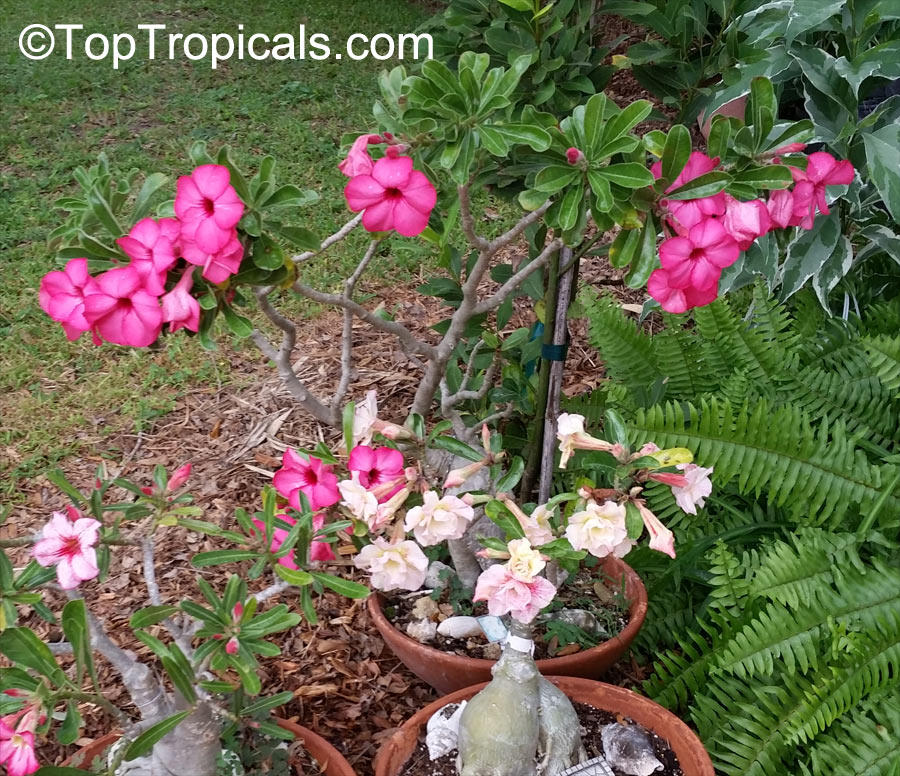
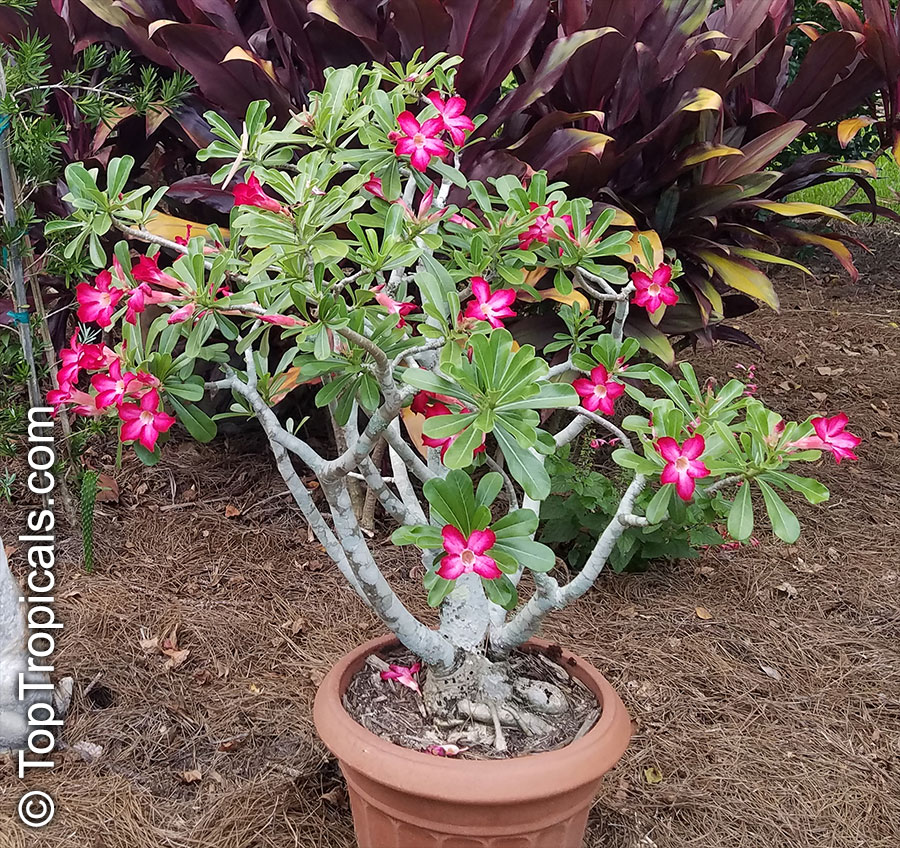
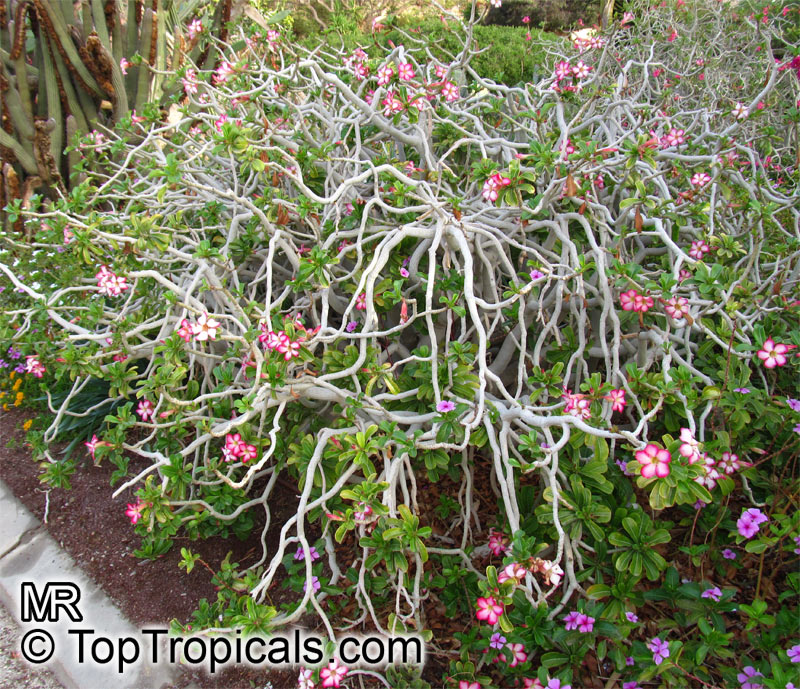
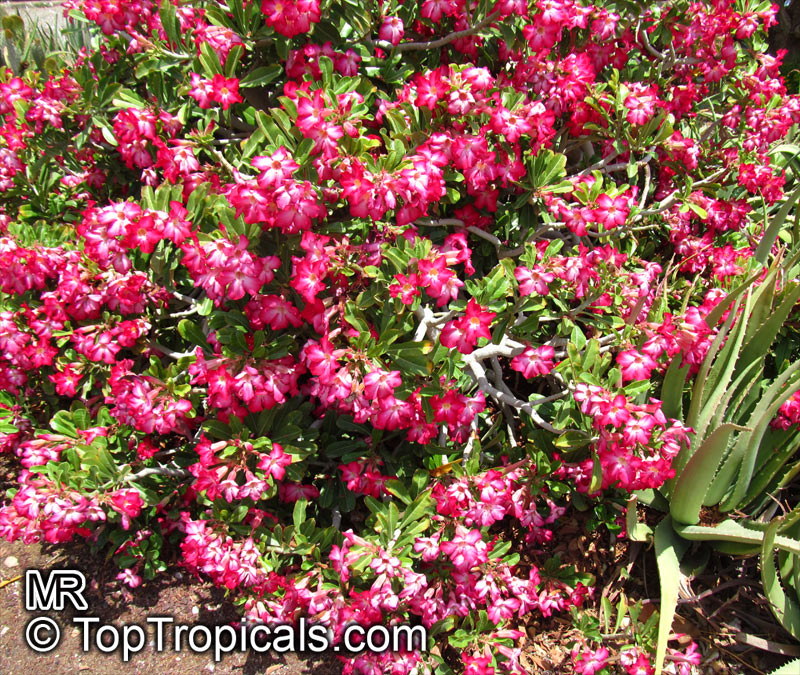
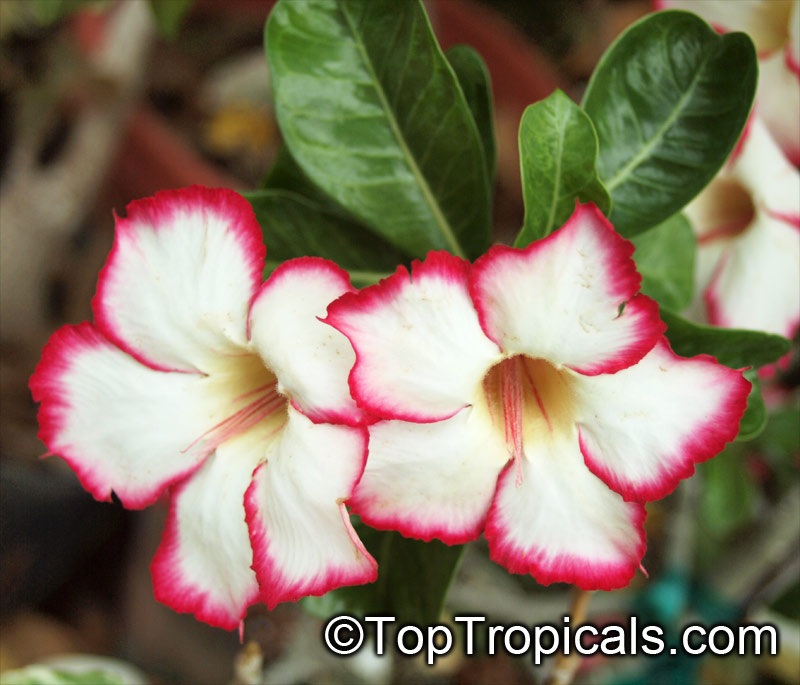
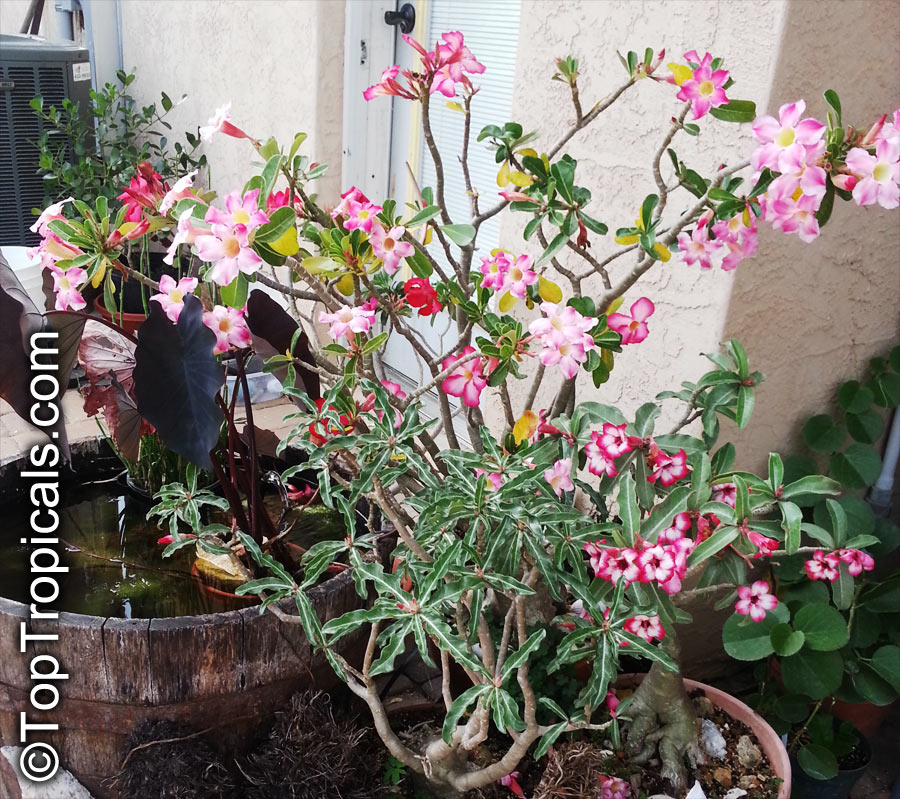
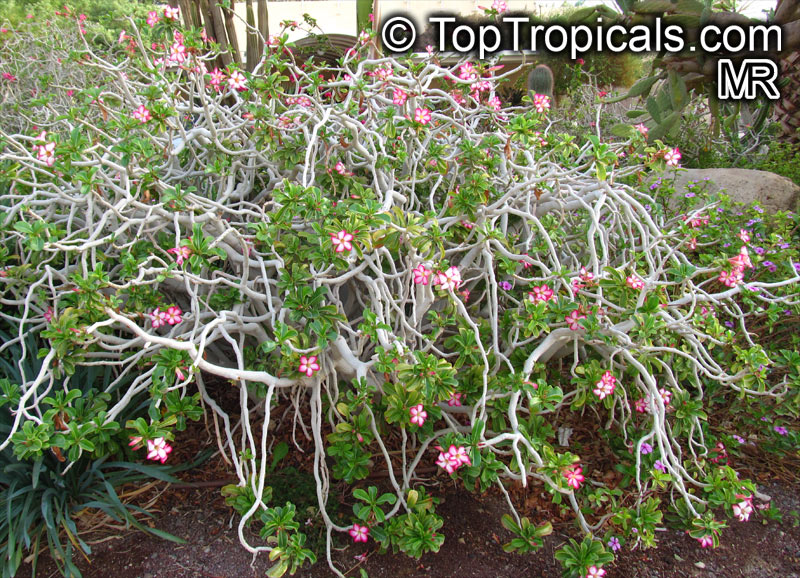
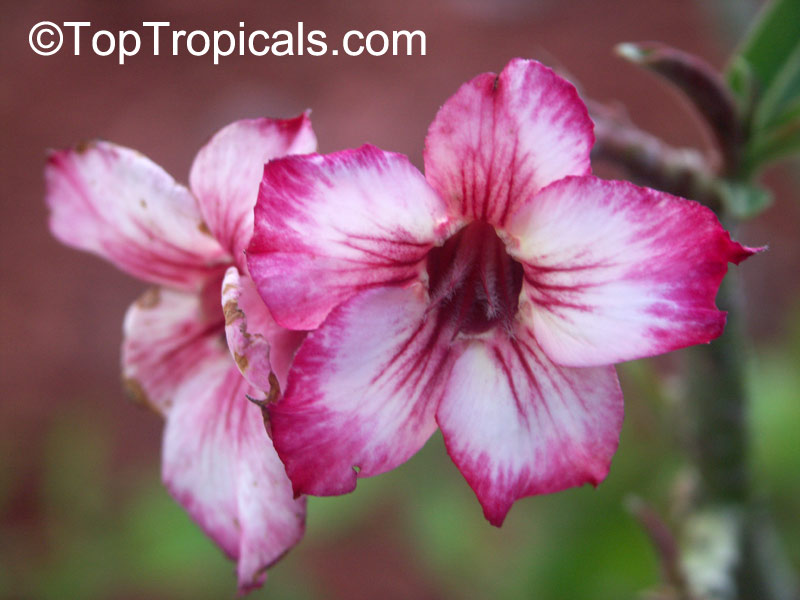
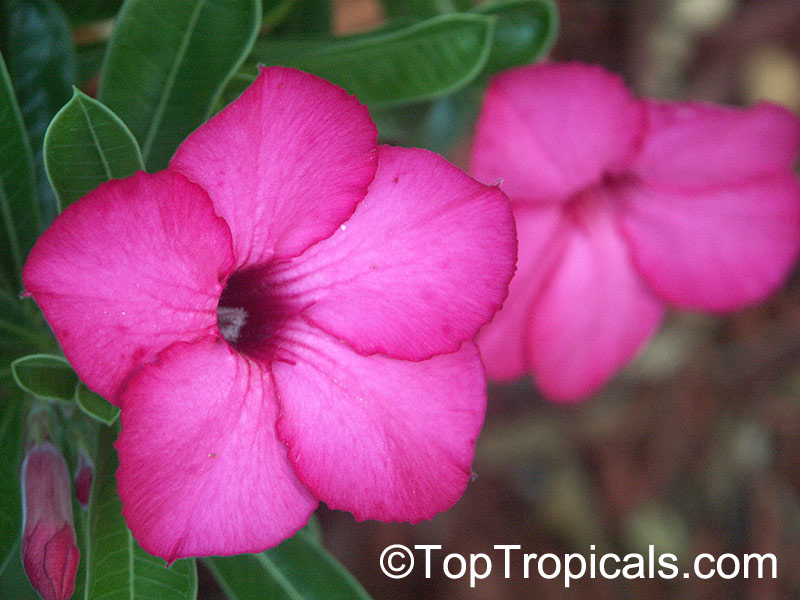
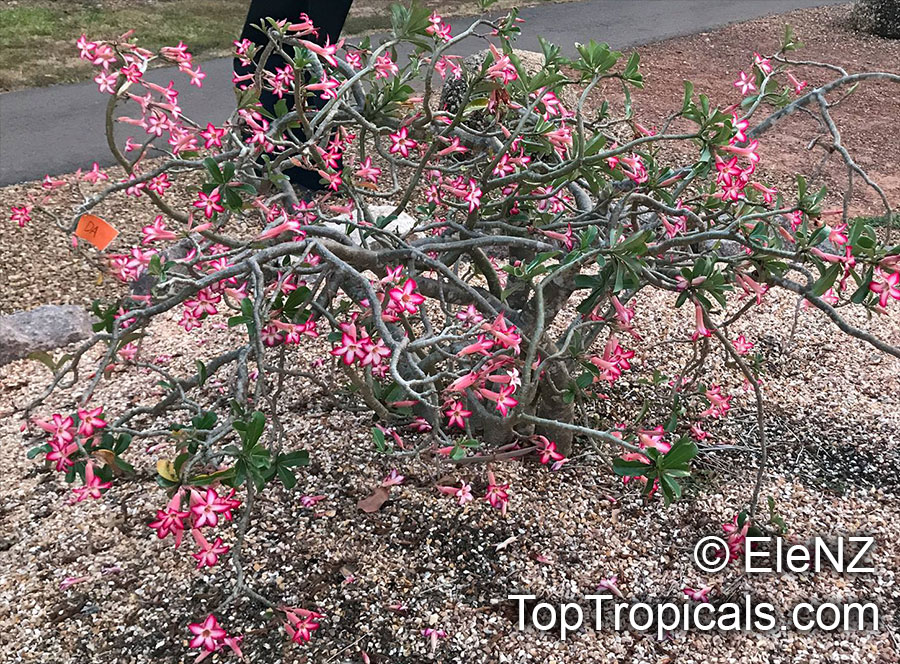
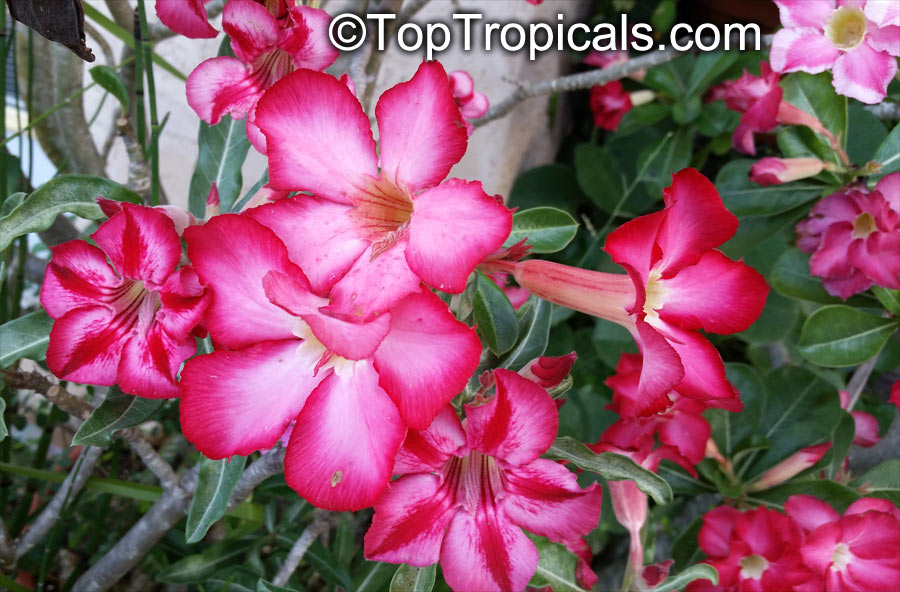
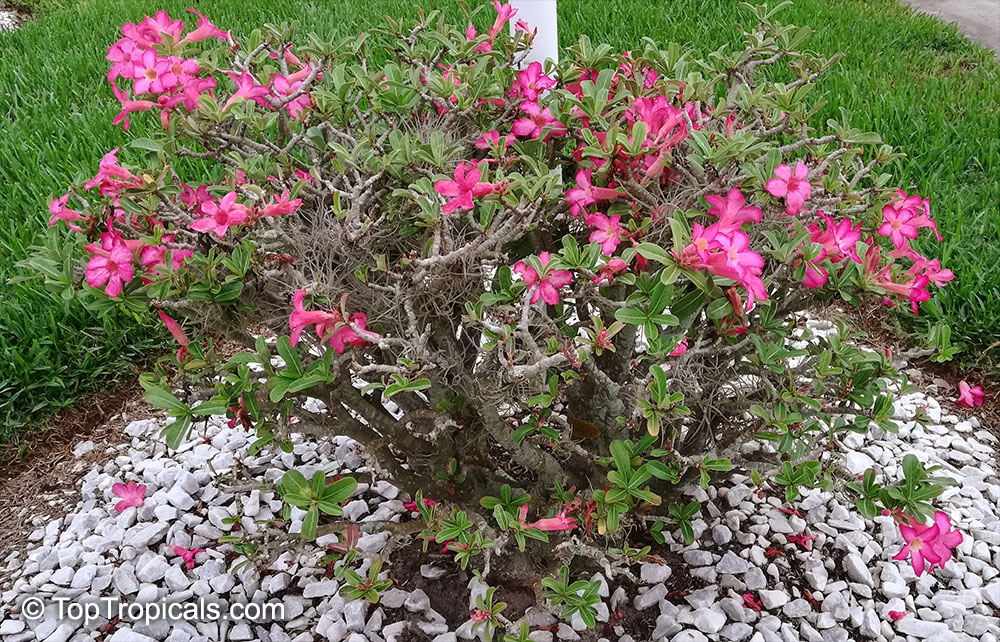
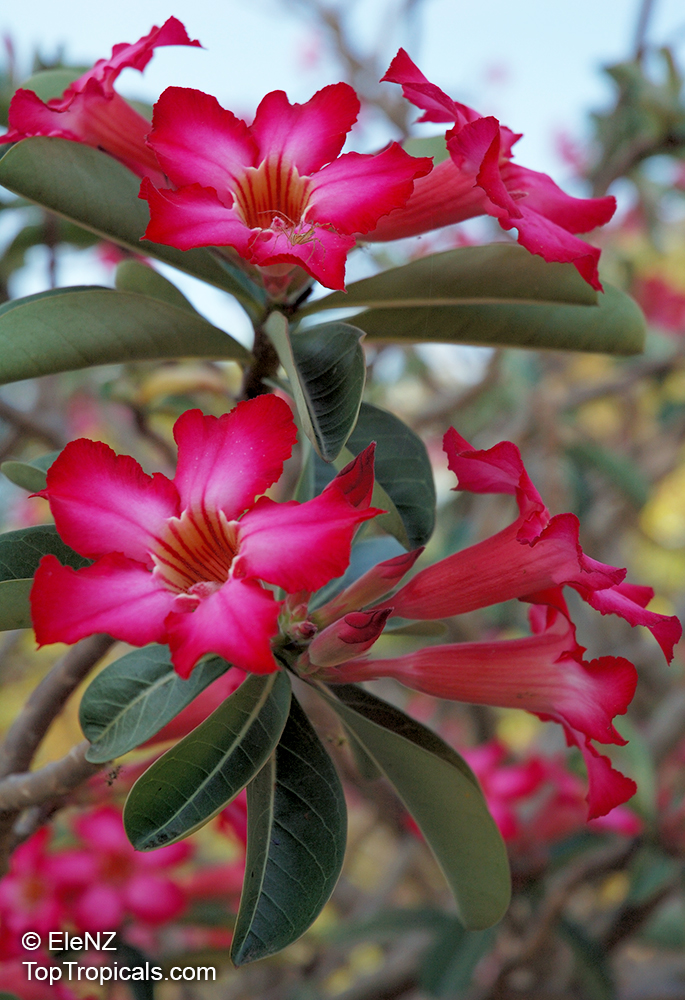
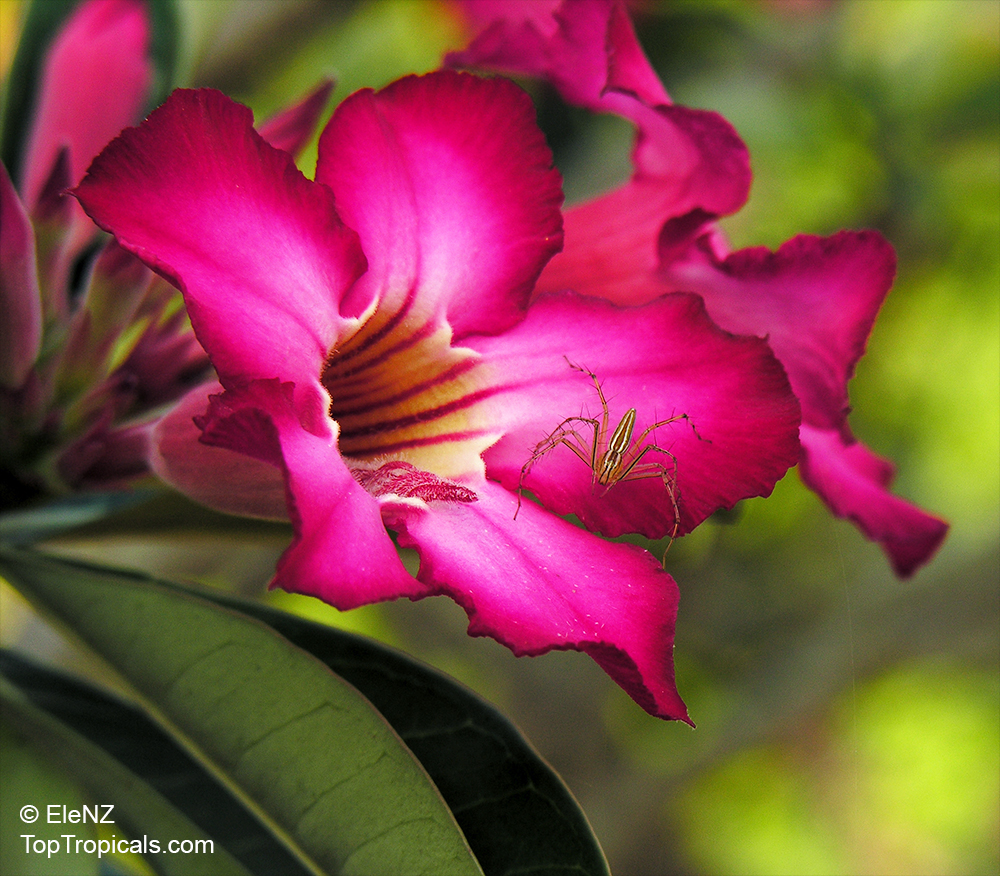
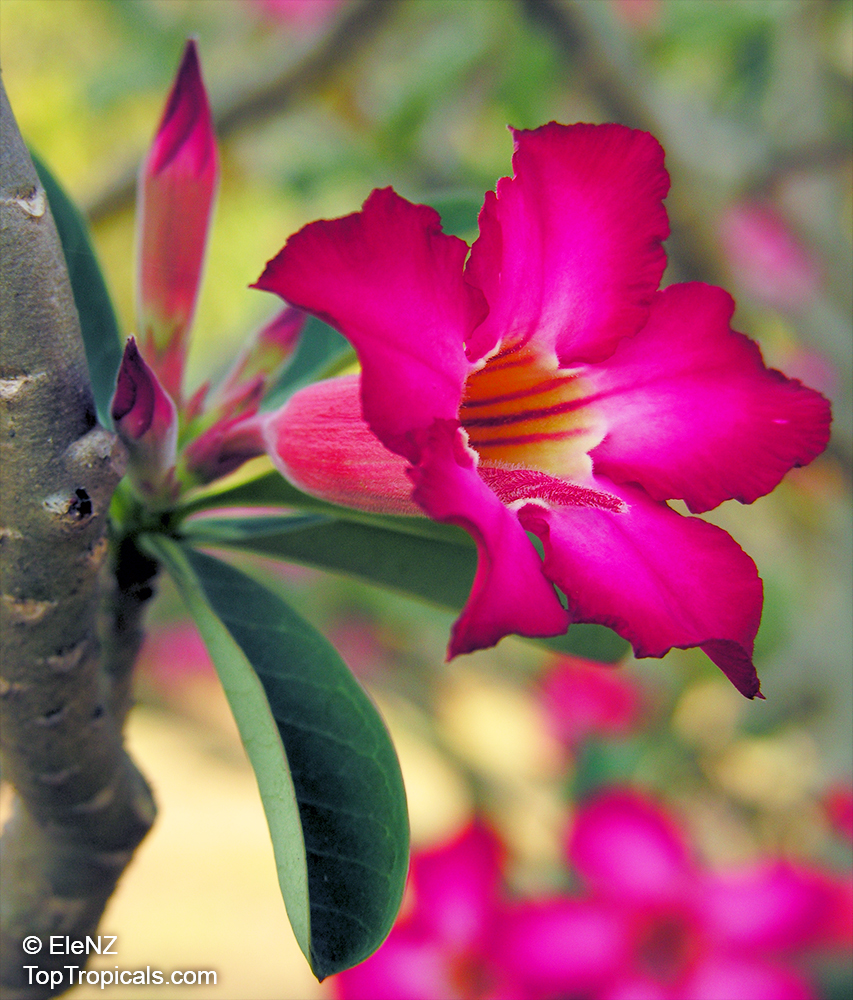
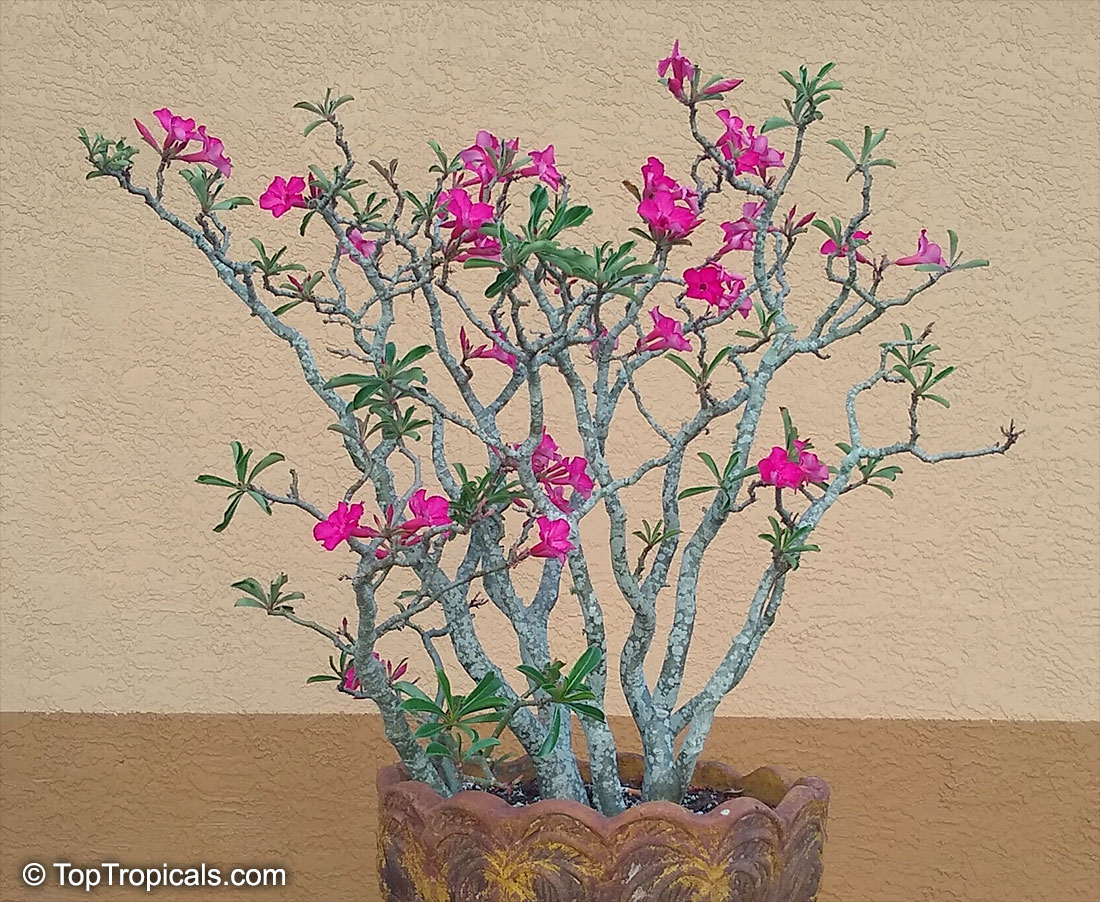
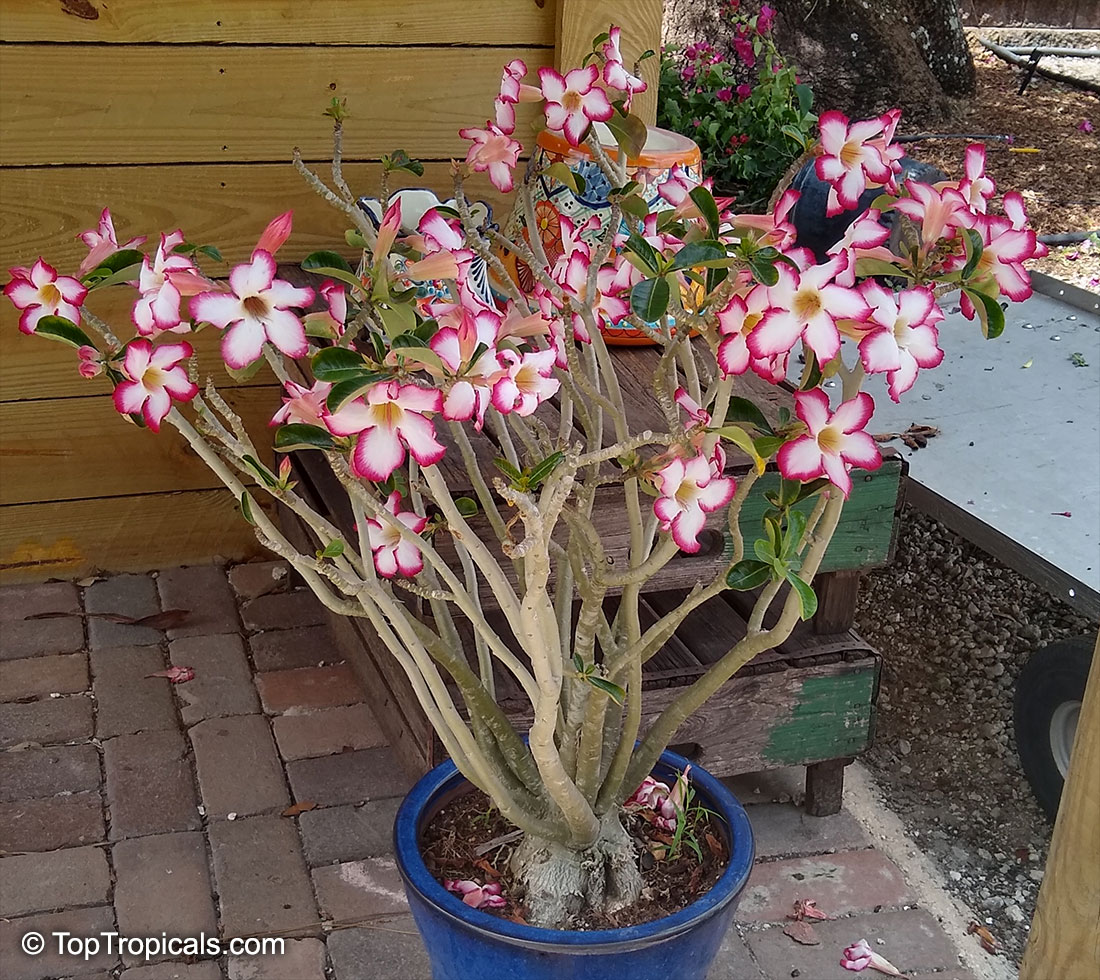
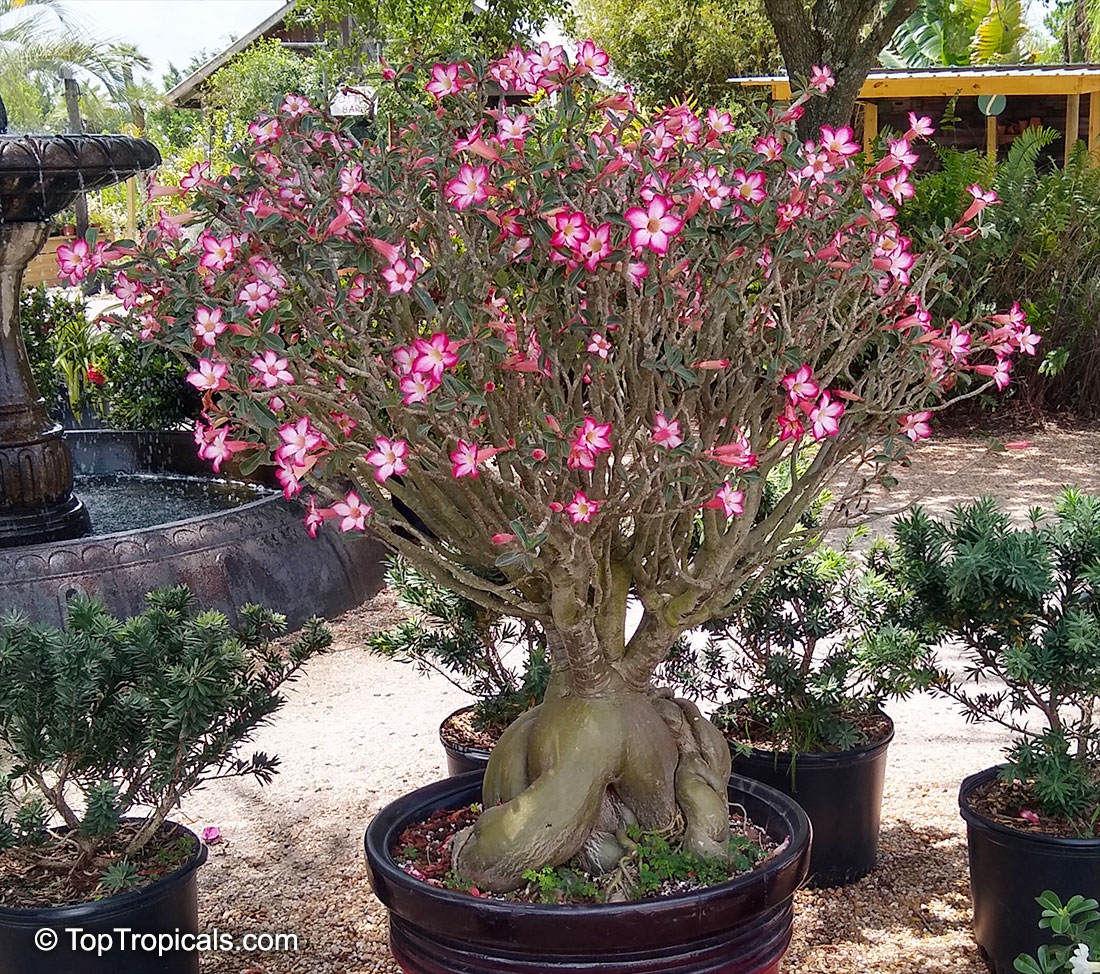
Botanical name: Adenium obesum
Common names: Desert Rose, Impala Lily
Family: Apocynaceae
Origin: Arabia and East Africa
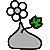










Growing to a height of about 4-5ft, this succulent plant is a member of the same family as Plumeria. Its swollen, often twisted trunk, is pale grey. The leaves are glossy, and club-shaped. The flowers appear almost continuously, are trumpet-shaped and range from white and bright pink to crimson, red. It exudes a highly toxic sap, which in some places is used as a poison for arrows. Adeniums are not generally grown in moist tropical gardens but are often seen as a decorative pot plants. They may also be used in rock gardens.They need full sun and a well-drained potting mixture. Exotic multi-color varieties can be grafted onto the same plant. See other exotic species of Adenium, photo gallery of exotic varieties and Thai Adeniums - milti-colored, multi-grafted.
See article about Adenium.
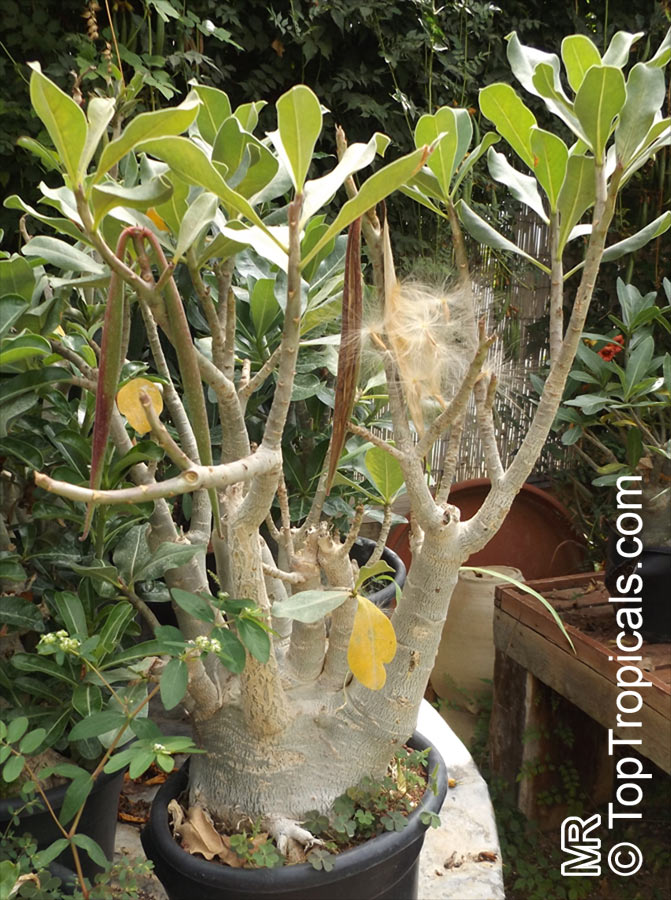
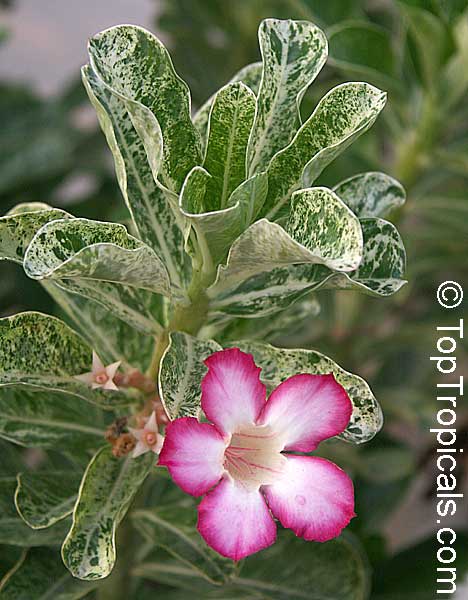
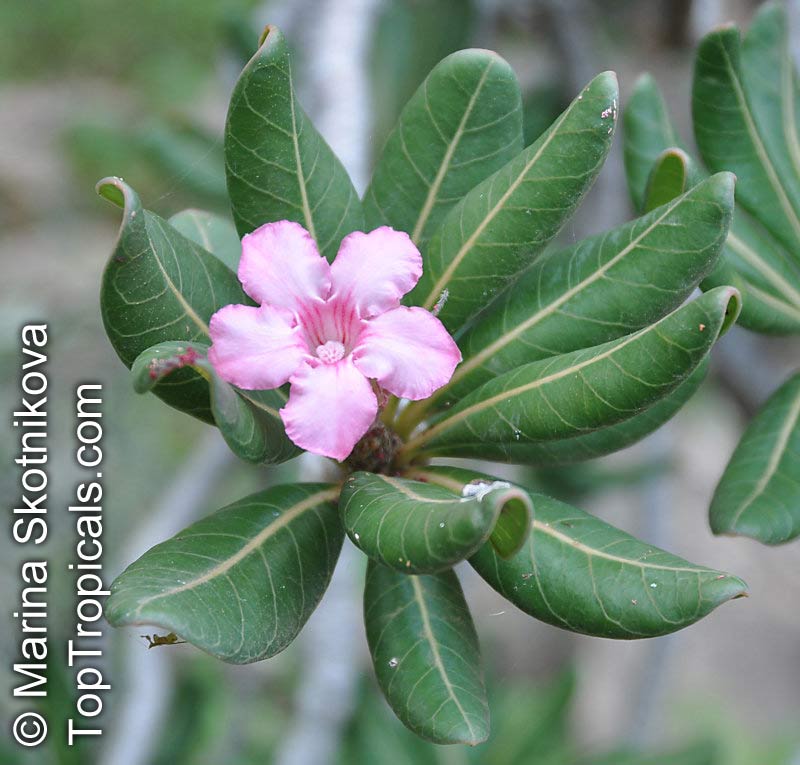
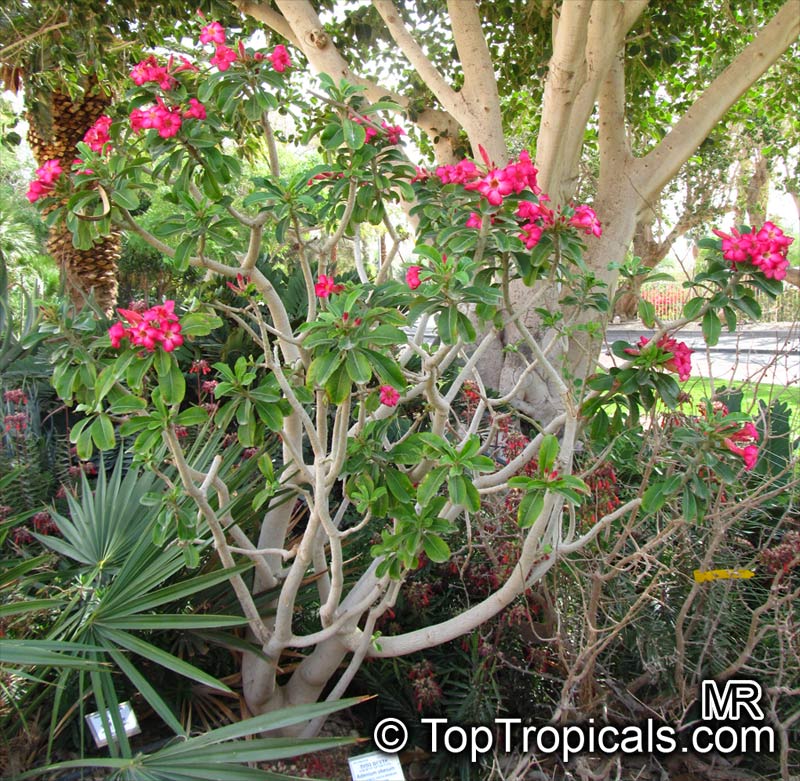
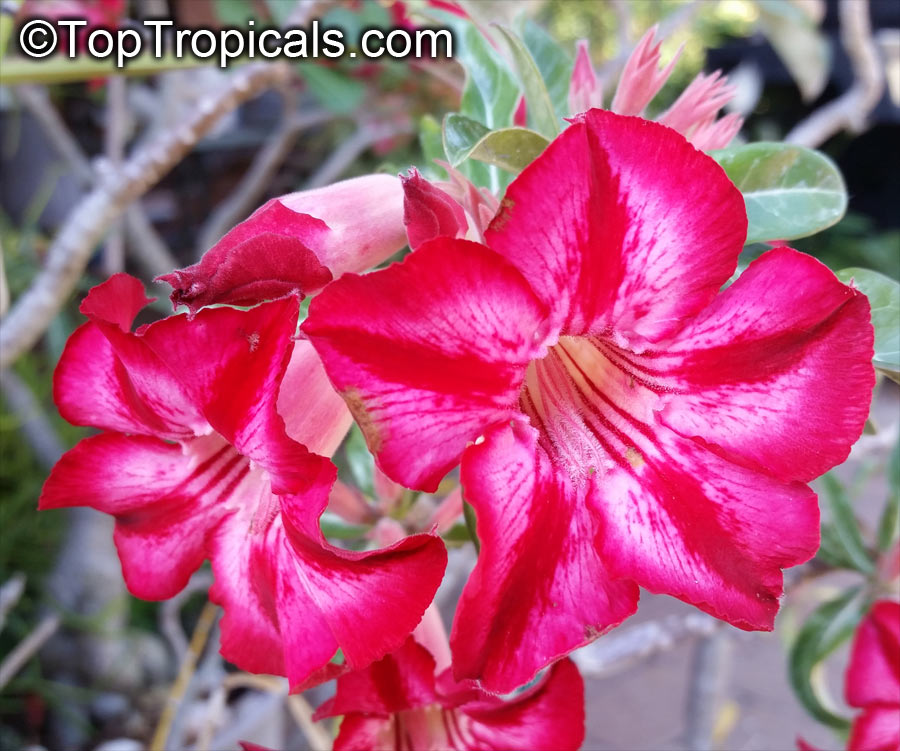
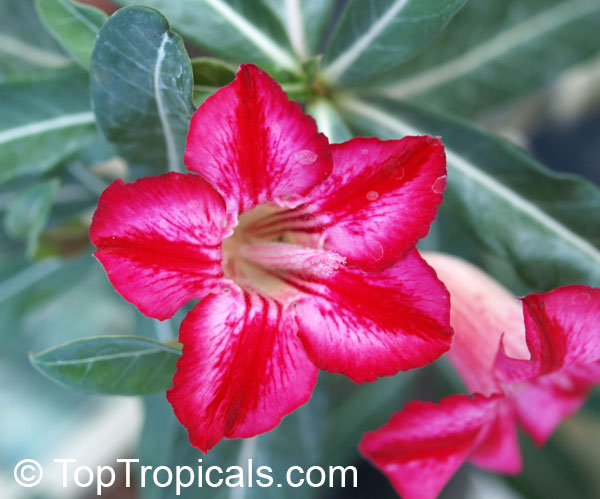
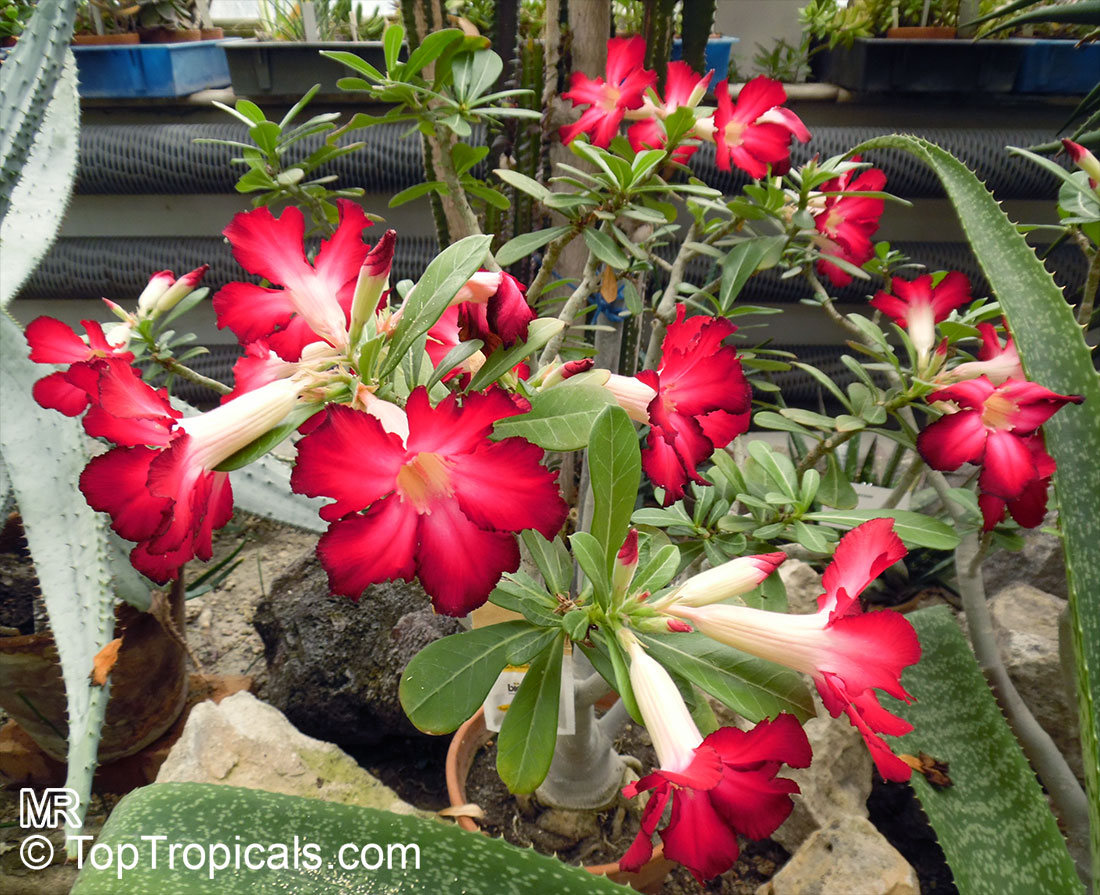
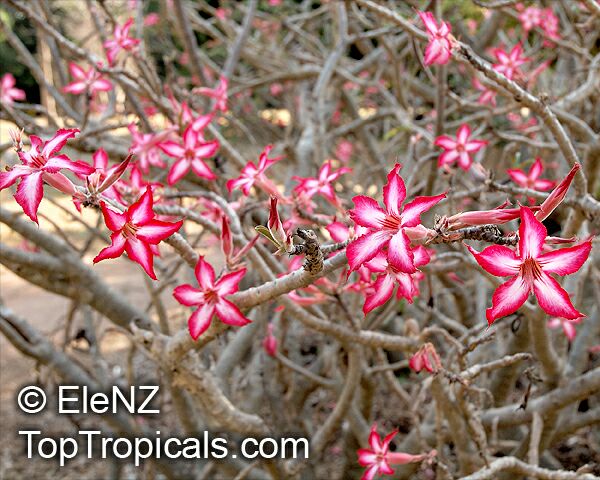
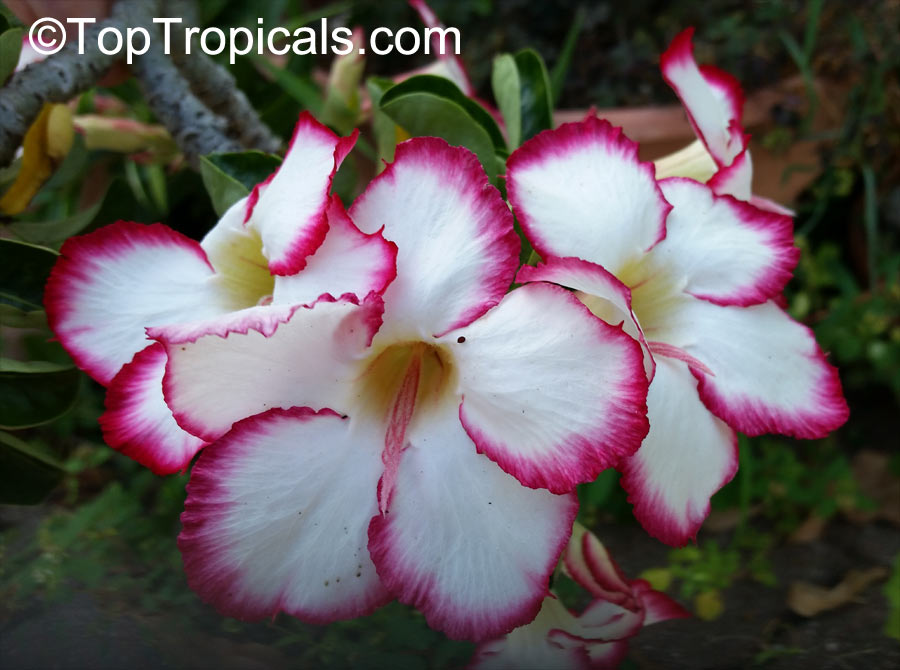
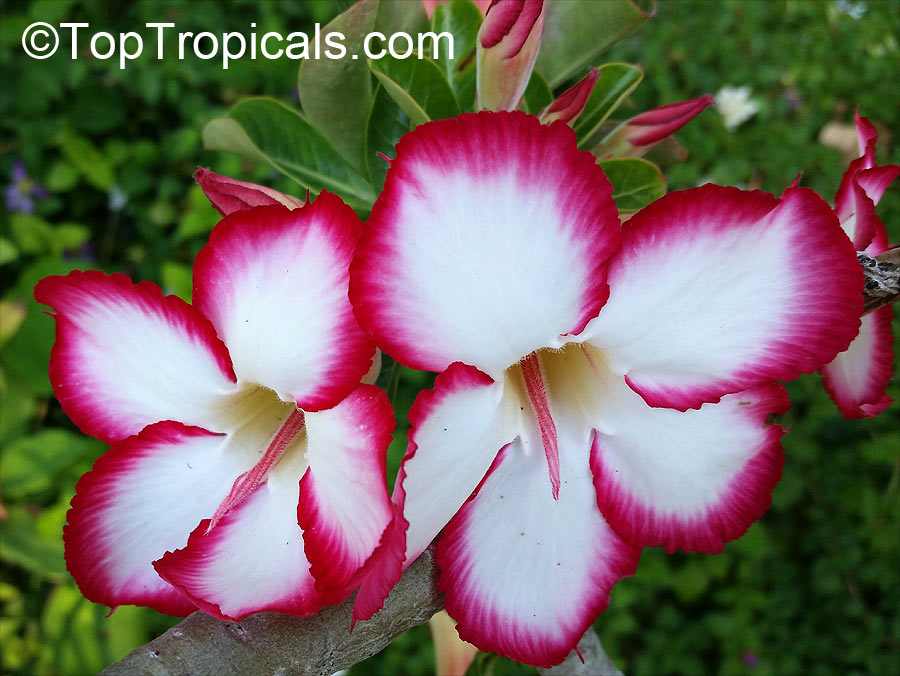
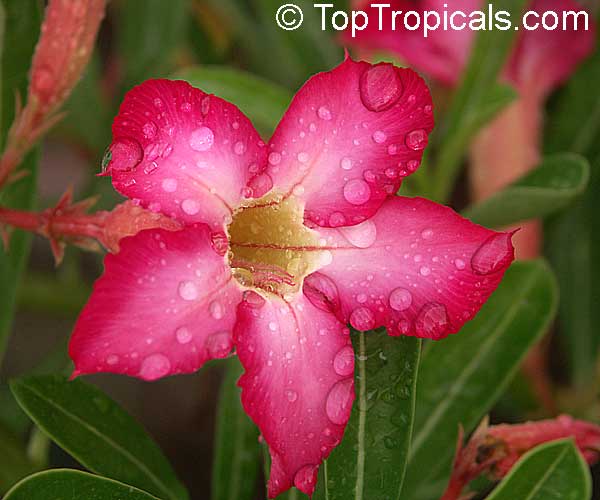
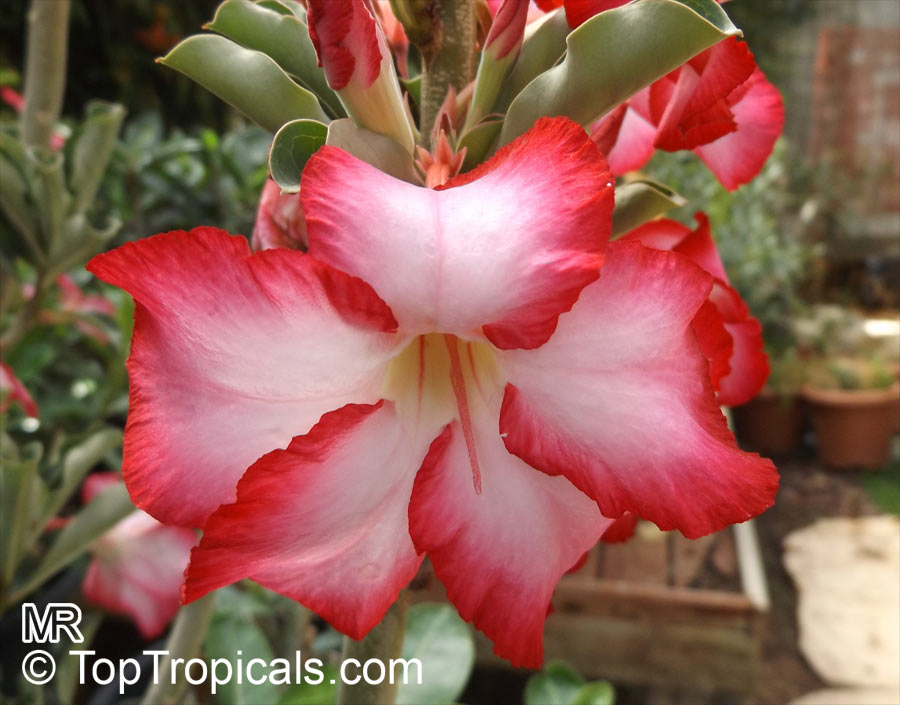
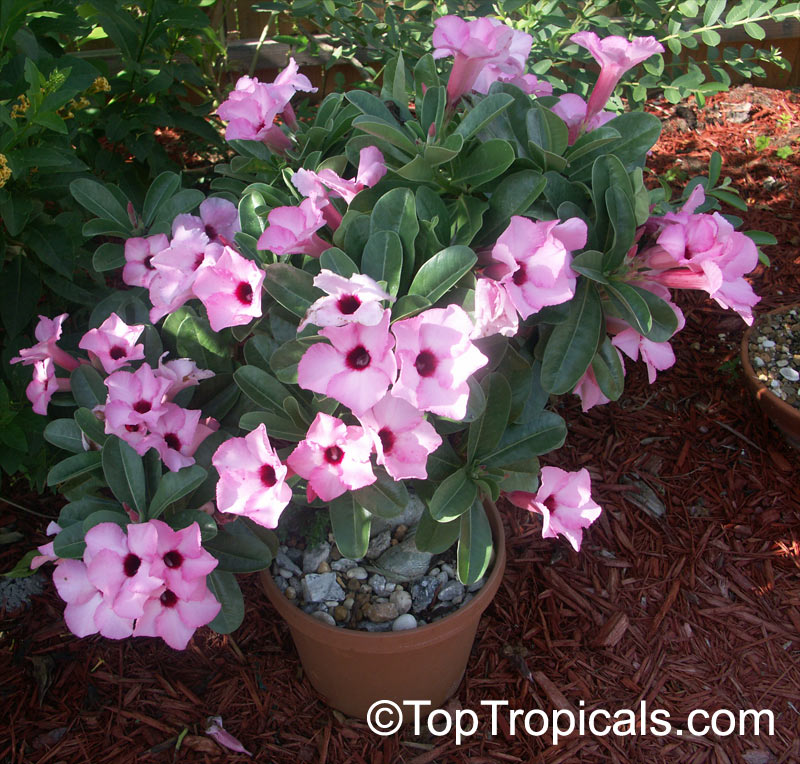
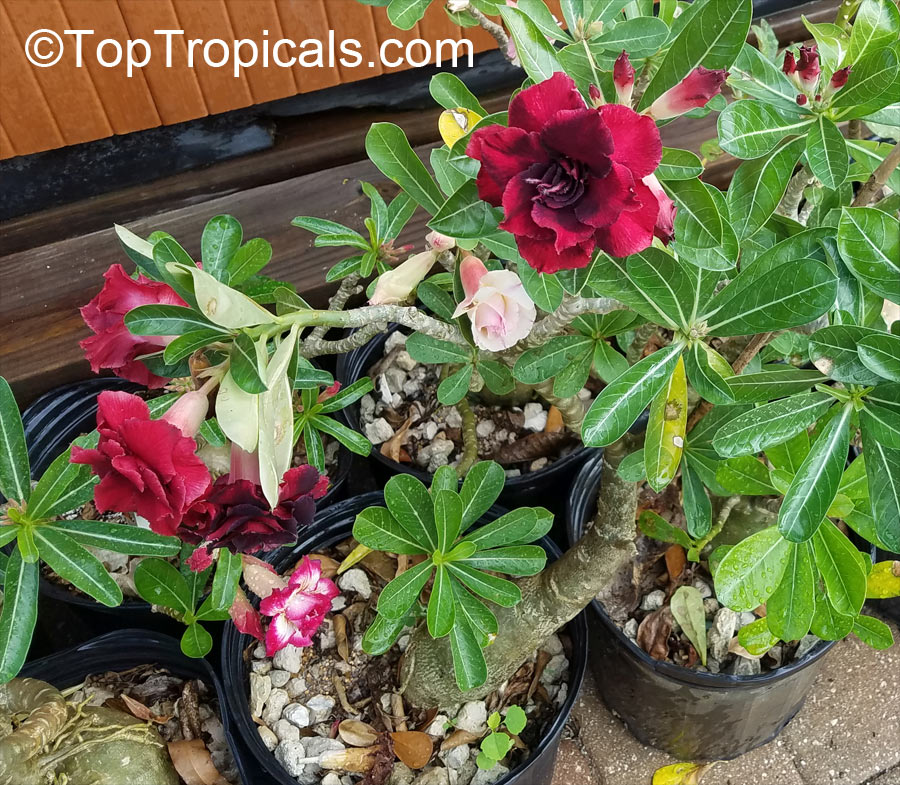
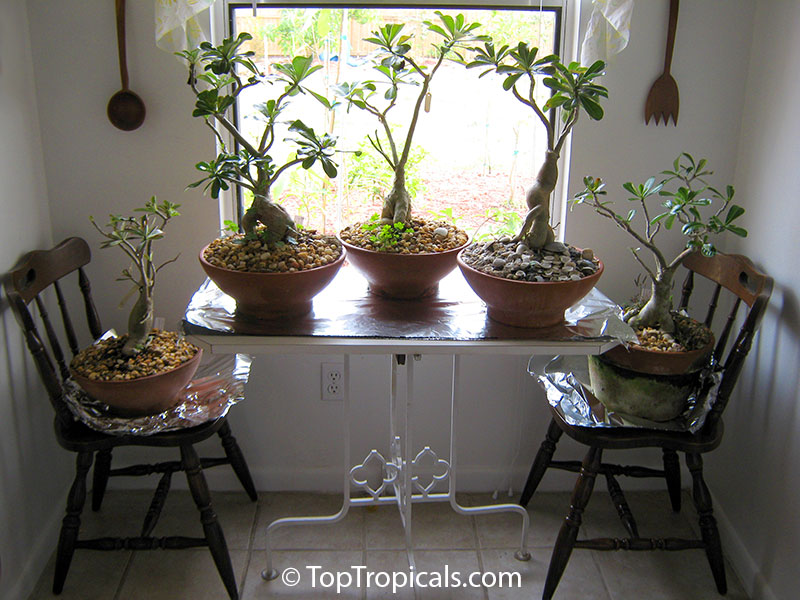
Botanical name: Adenium sp.
Common names: Adenium, Desert Rose, Impala Lily
Family: Apocynaceae













See other exotic species of Adenium, photo gallery of exotic varieties and Thai Adeniums - milti-colored, multi-grafted.
See article about Adenium.
Botanical name: Aesculus californica
Common names: California Buckeye, California Horse-chestnut
Family: Sapindaceae
Origin: California









Aesculus californica is a large deciduous shrub or small tree, up to 4�"12 m (13�"39 ft) tall, with gray bark often coated with lichens and mosses. It is used as an ornamental plant for its striking leaf buds, lime green foliage, fragrant white flowers, red-brown foliage in mid to late summer, and architectural silver branches through fall. The tree also acts as a soil binder, which prevents erosion in hilly regions.
The seeds are poisonous. The nectar and pollen of the flowers is toxic to honeybees, so the trees should not be planted near apiaries.
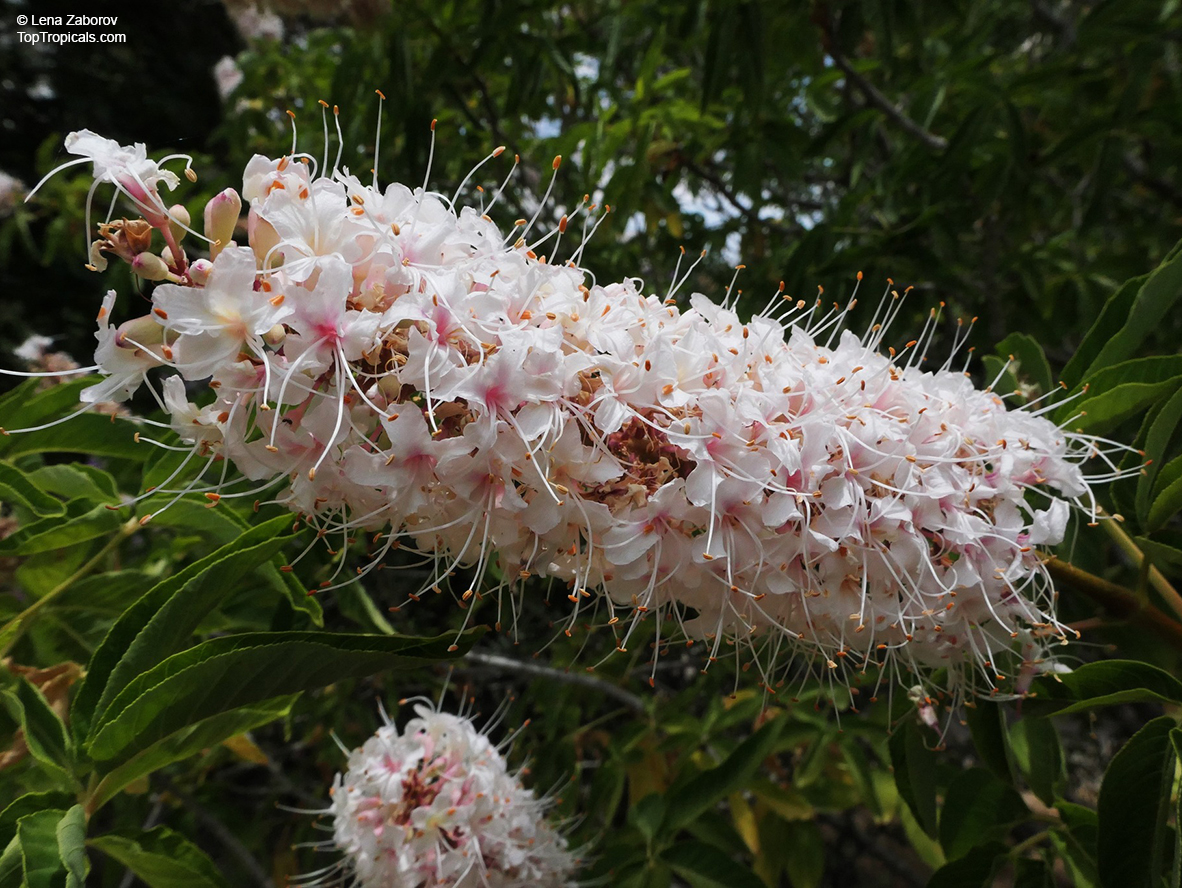
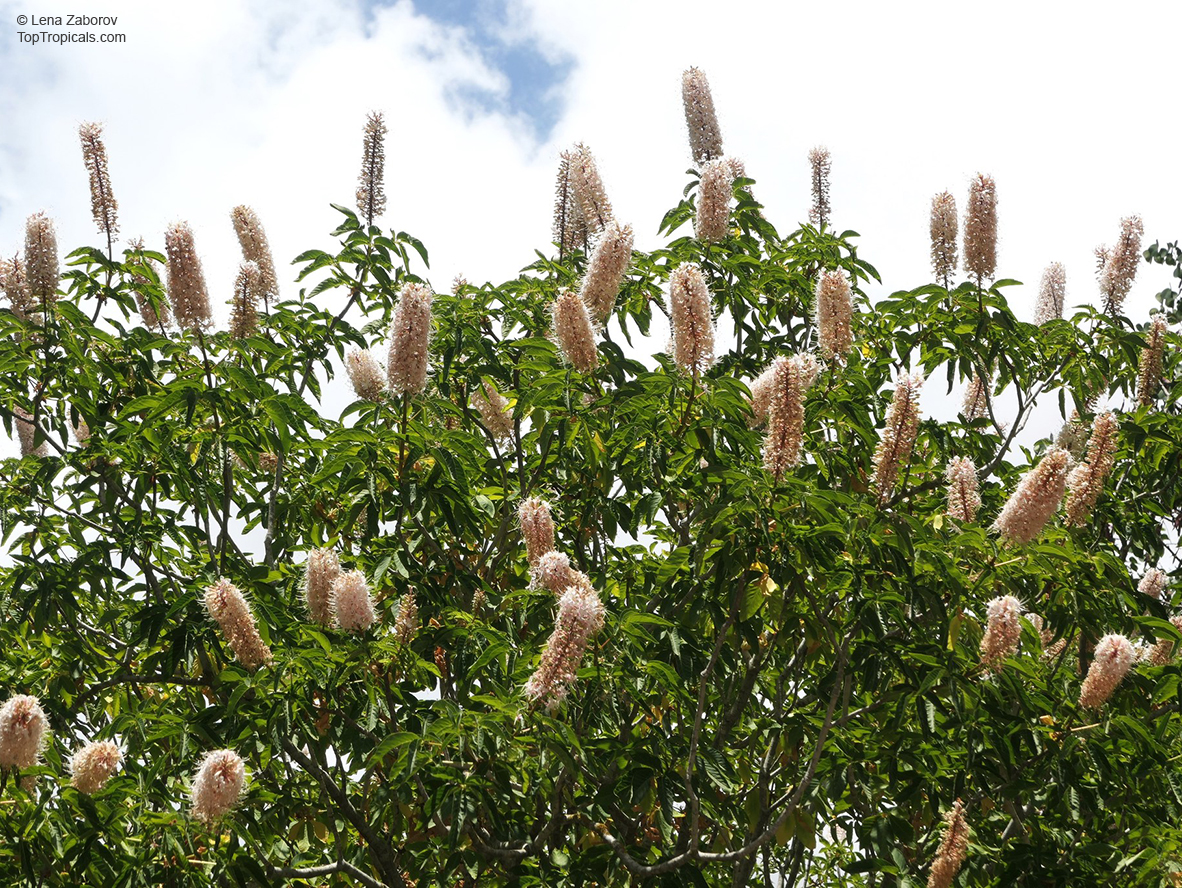
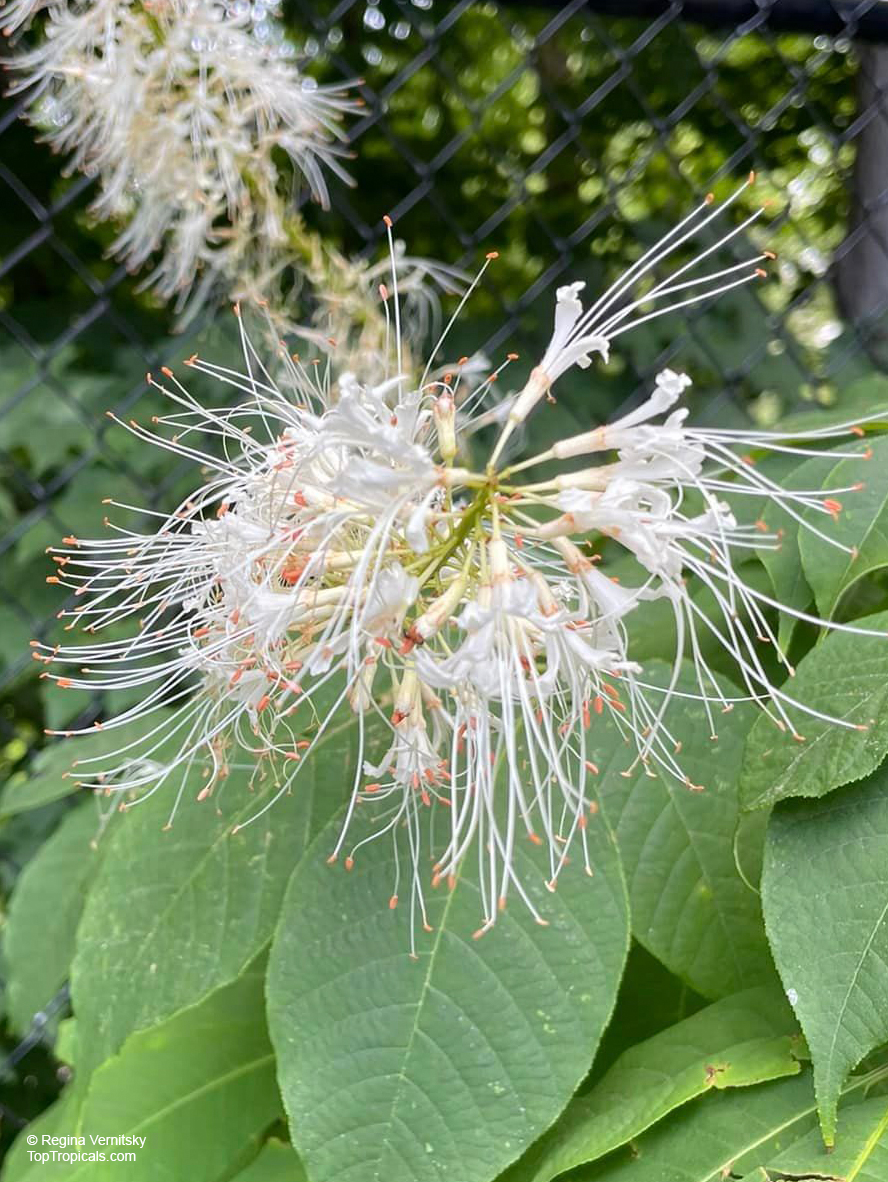
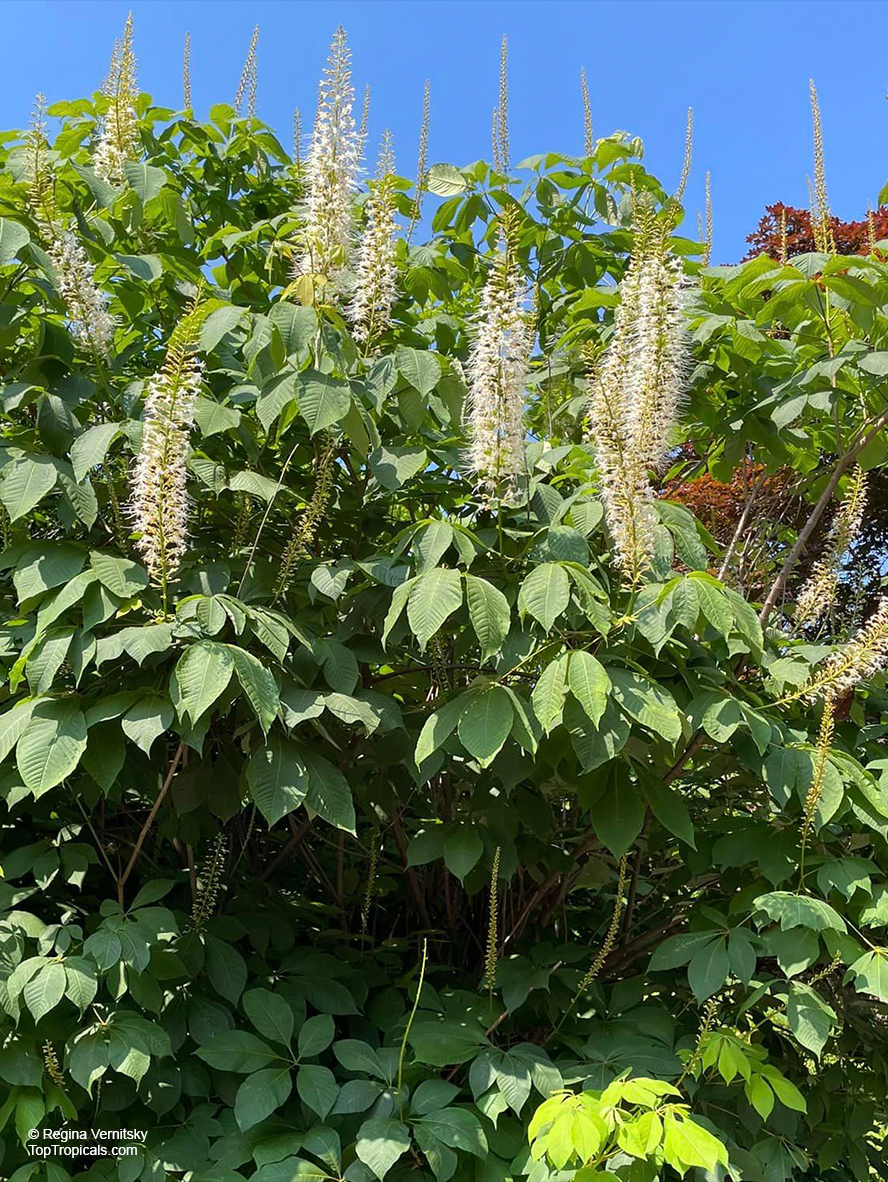
Botanical name: Aesculus parviflora
Common names: Bottlebrush Buckeye, Small-flowered Buckeye
Family: Sapindaceae
Origin: Southeastern United States








Aesculus parviflora is grown as an ornamental plant in gardens, where its August flowering attracts butterflies. It prefers moist, well-drained soils in part shade to full shade.
This plant is highly poisonous to humans IF EATEN.
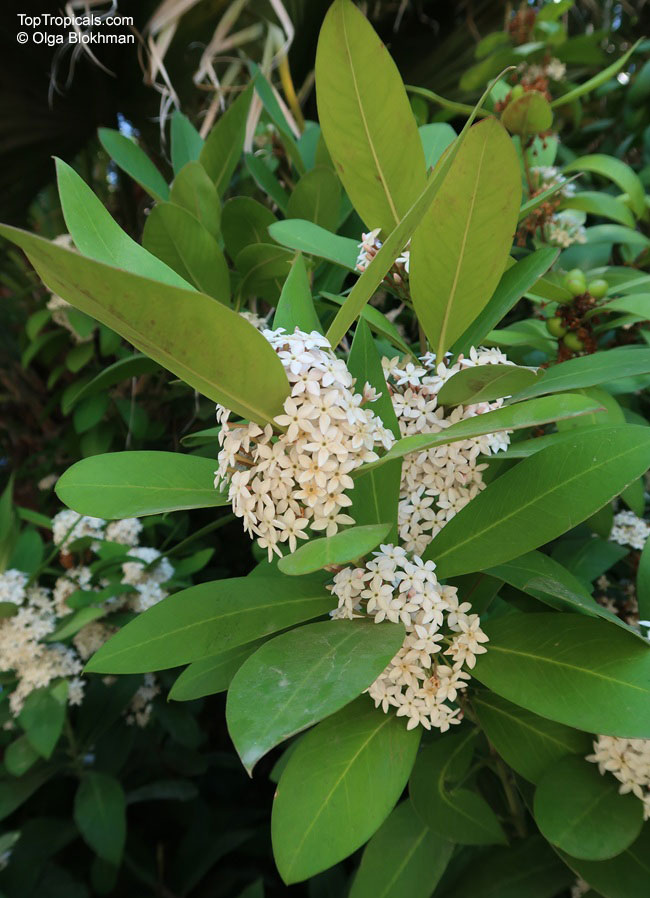
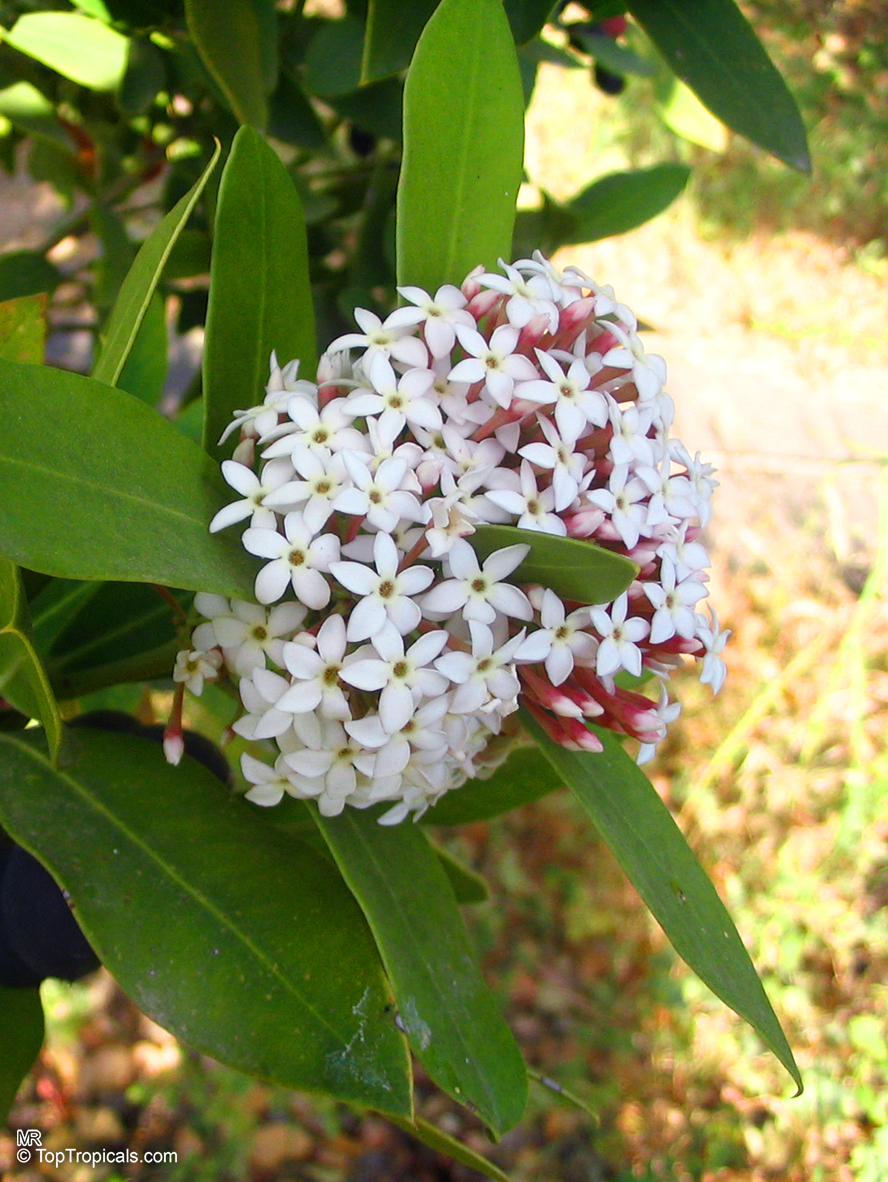
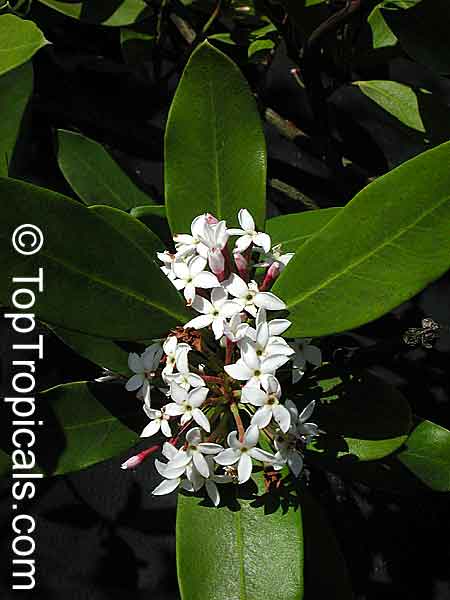
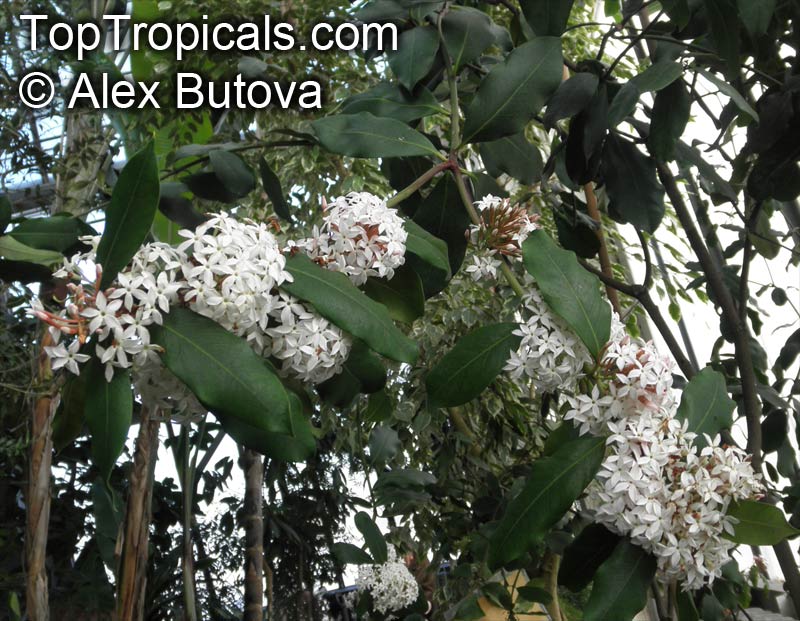
Botanical name: Alstonia angustiloba
Common name: Pulai Tree
Family: Apocynaceae
Origin: Southeastern Asia










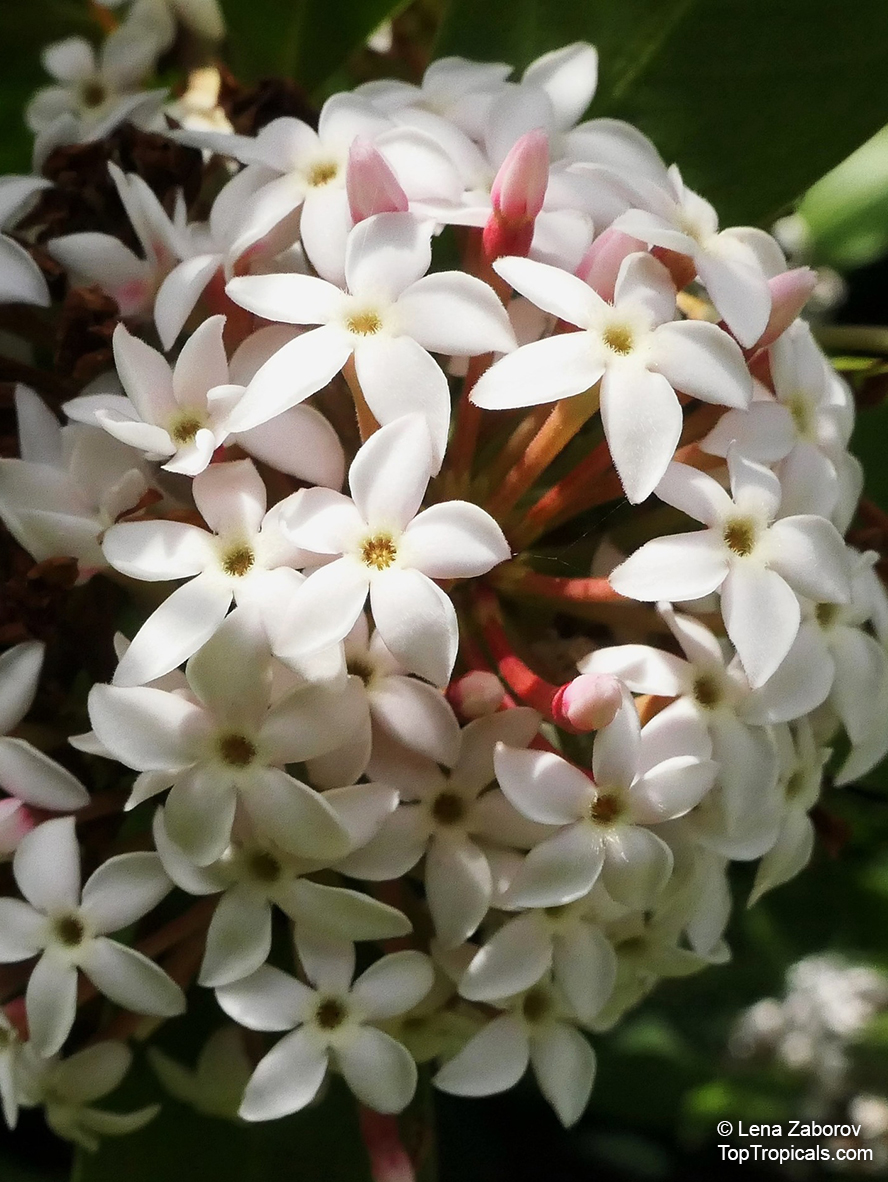
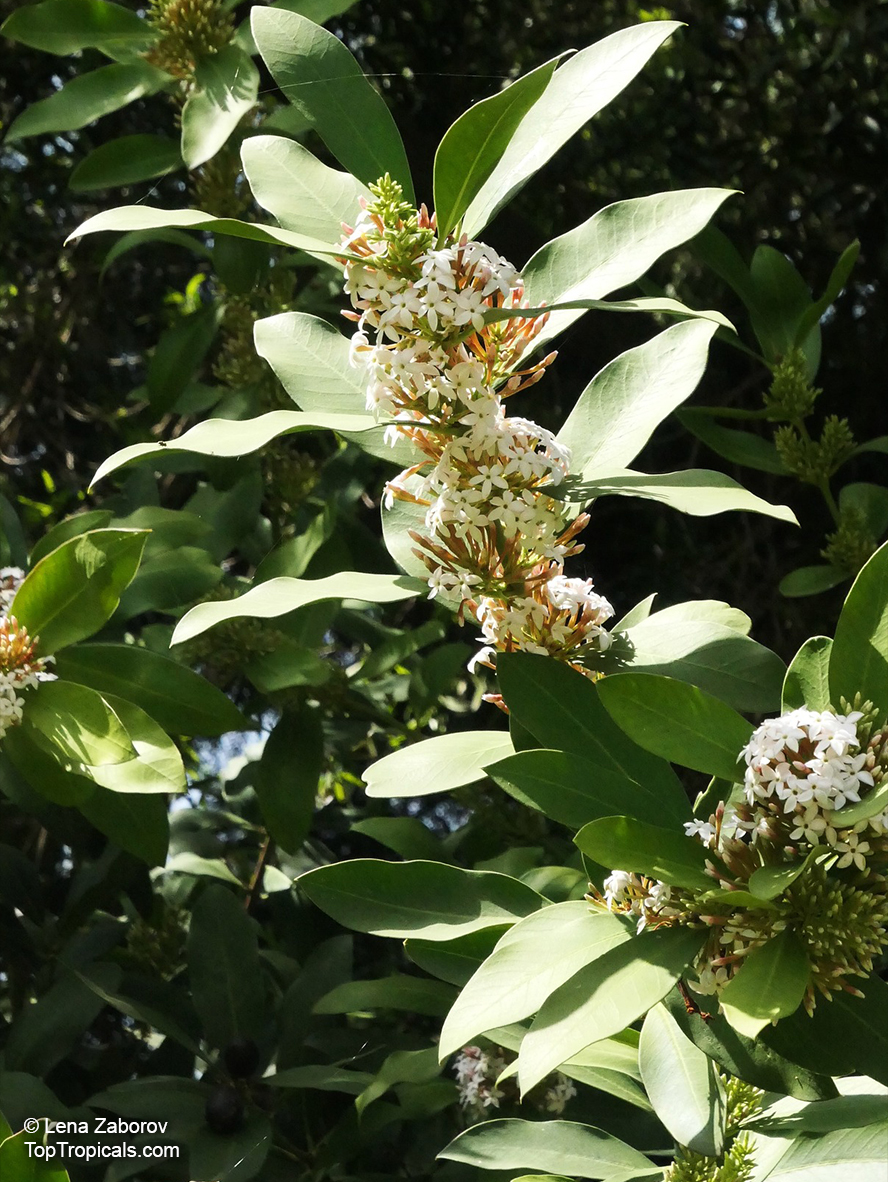
The Pulai Tree is a native to Southeastern Asia, and is widely cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions. It can grow to a big tree, typically taller than 20 feet, or a smaller tree, which is 10-20 feet in height. This hardwood evergreen tree prefers full sun or semi-shade and a soil that is evenly moist but can tolerate some drought. It also prefers an acidic soil with a pH of 5.5 to 6.5.
The Pulai Tree produces fragrant white or off-white flowers throughout the year, making it a popular ornamental plant in many regions. It attracts butterflies, hummingbirds, and other pollinators. An ethnomedical plant, it has various medicinal benefits. The latex is used against shingles, boils, abcesses, and ringworm and is an ingredient in chewing gum. The leaves and roots of the tree also possess antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties.
When grown in pots, the Pulai Tree needs regular and even watering and is best placed in a sheltered spot away from cold winds. In areas located in USDA Zones 9-11, the tree can be grown outdoors, otherwise it must be placed over winter in a protected location. However, it is important to note that the plant is potentially poisonous or toxic when taken internally, so it should be kept away from children. With regular care and maintenance, the Pulai Tree can bring year-round beauty and fragrance to any garden or home.
| Next |  |
Use link to repeat this search:
https://toptropicals.com/cgi-bin/garden_catalog/cat.cgi?search_op=and&keyword_op=and&language=e&number=10&no_change_lang=1
&v1=poi&user=tt&sale=1&first=0












































































































































