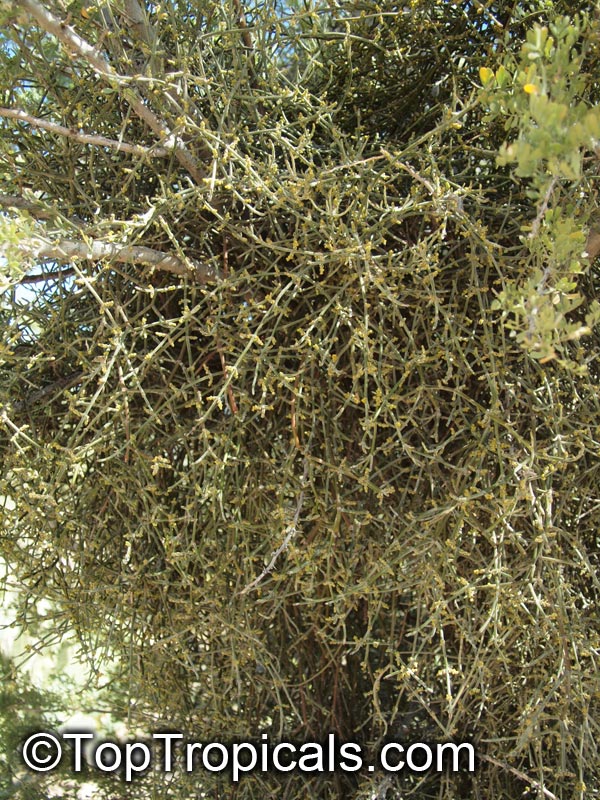
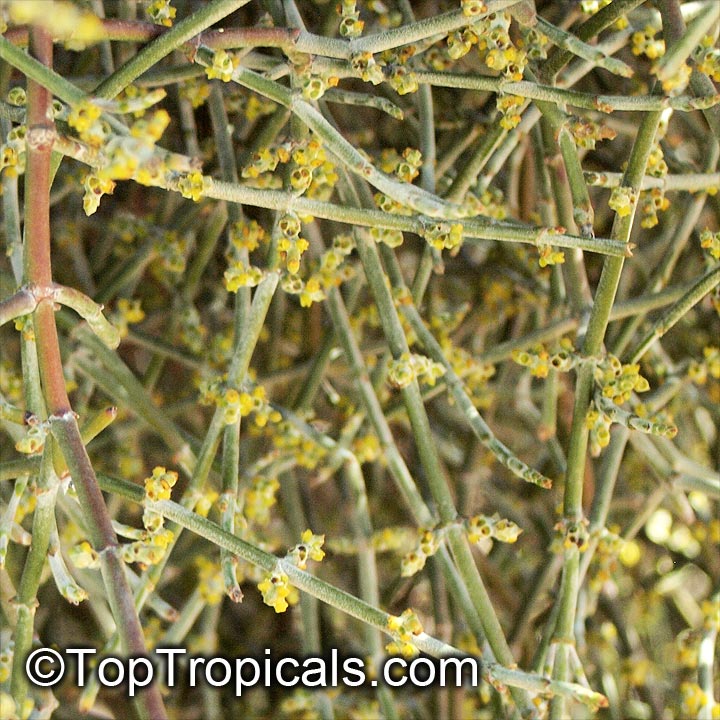
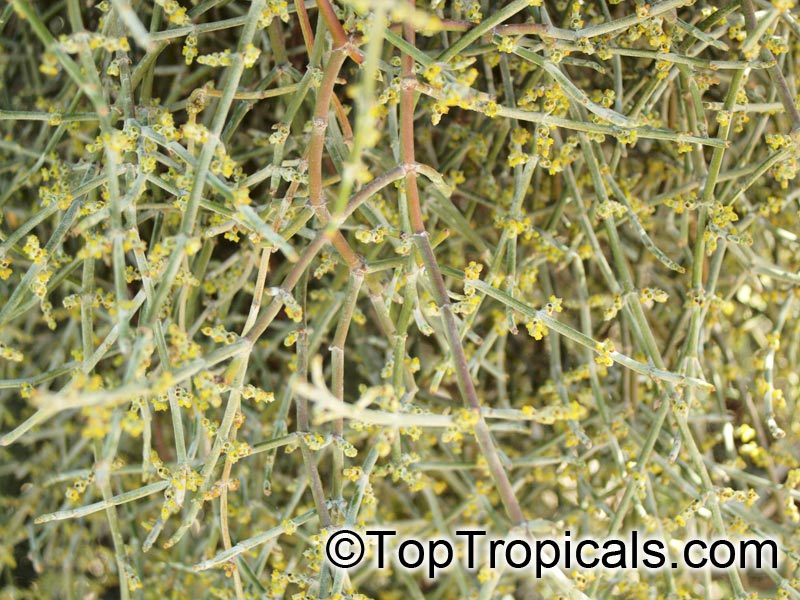
Phoradendron californicum (Desert Mistletoe)
Botanical name: Phoradendron californicum
Common names: Desert Mistletoe, Mesquite Mistletoe
Family: Santalaceae
Origin: California, Arizona







Phoradendron californicum is a leafless plant that attaches to host plants, often leguminous woody desert trees such as Cercidium and Prosopis.
The plants are dioecious with tiny, inconspicuous, yellowish flowers. The female plants produce numerous, spherical, translucent, white, pink, or red berries that are adored by fruit-eating birds.
Desert Mistletoe plants, but not the berries, contain phoratoxins which can easily lead to death. The white to reddish fruits are edible, but native tribes ate only the fruits of mistletoes growing on Prosopis, Olneya tesota or Acacia greggii.
Link to this plant:
https://toptropicals.com/catalog/uid/phoradendron_californicum.htm


