Salicaceae - Botanical Family
| Number of plants found: 14 | Next | 
|
Go to page: | 1 | 2 |
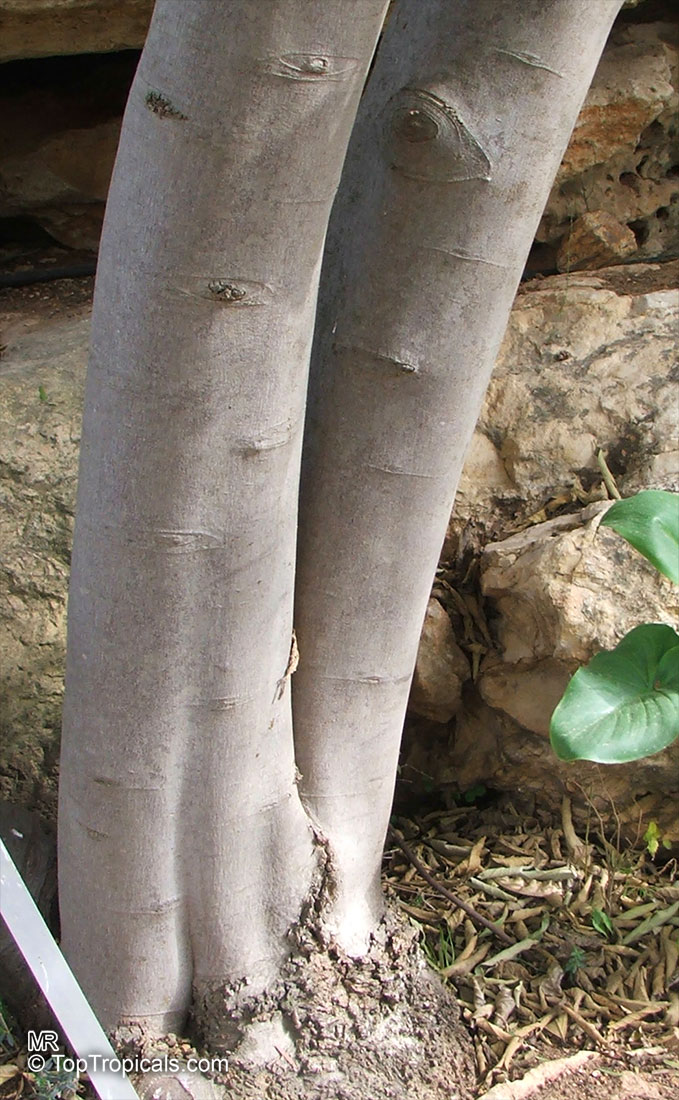
Botanical name: Banara vanderbiltii
Common name: Palo de Ramon
Family: Salicaceae
Origin: Puerto Rico




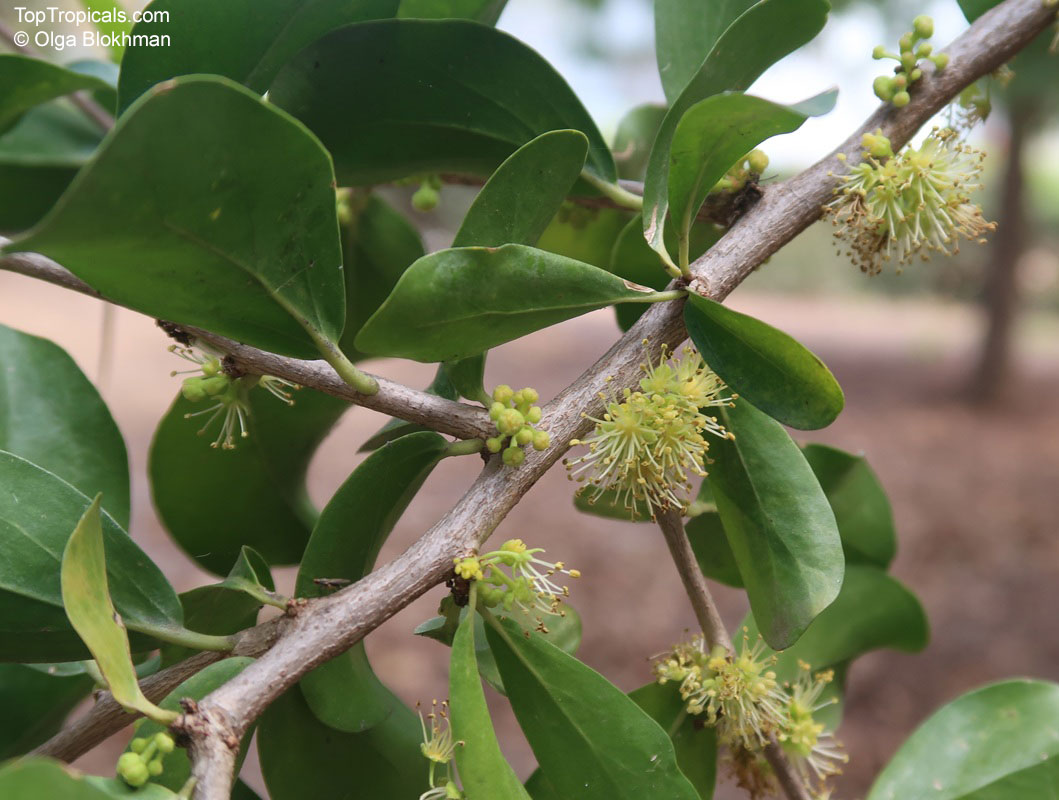
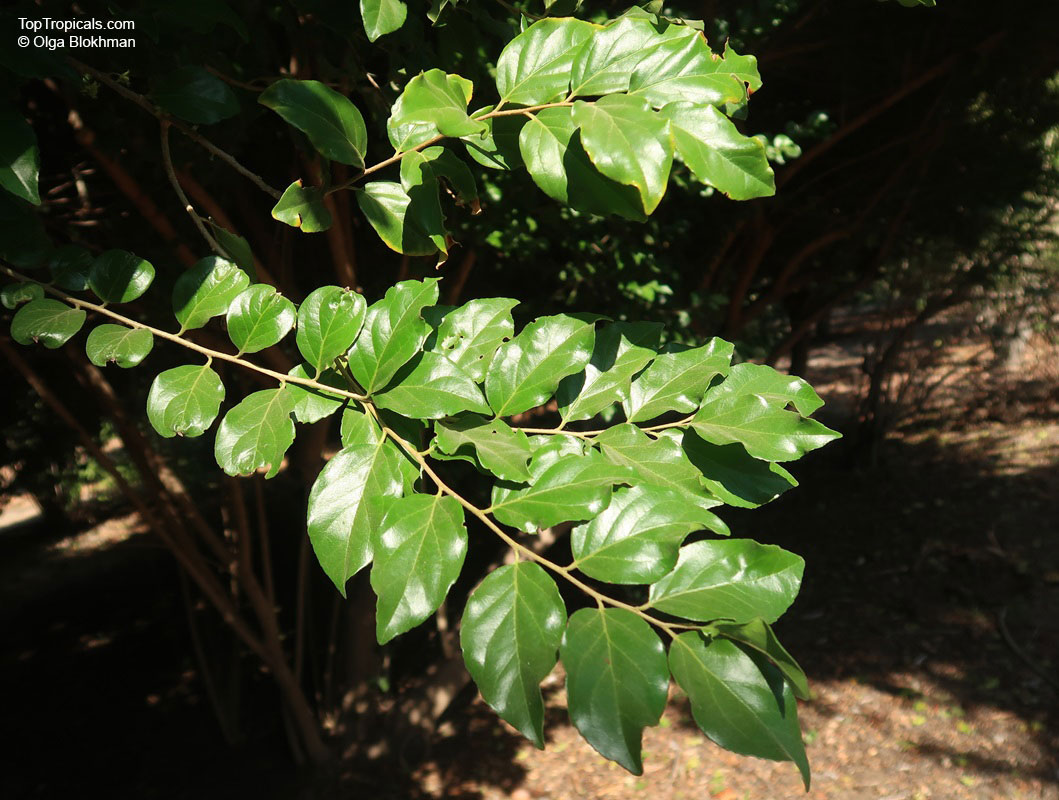
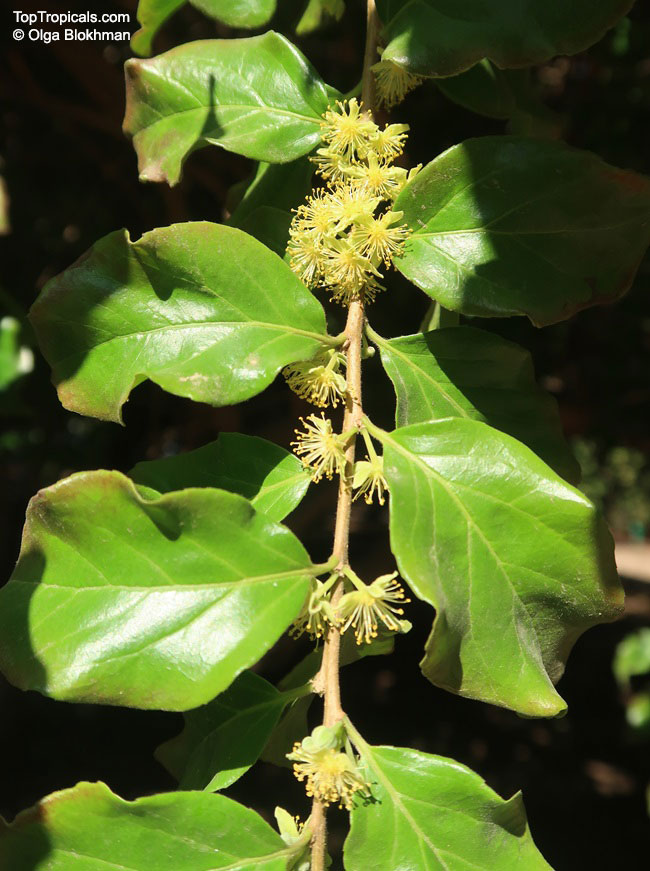
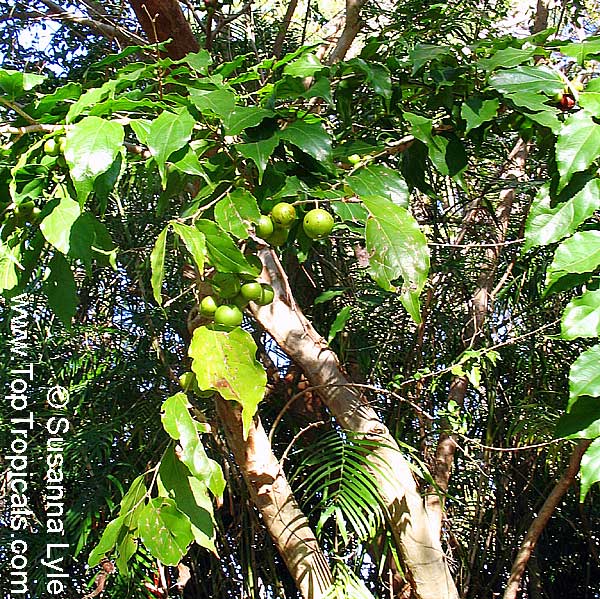
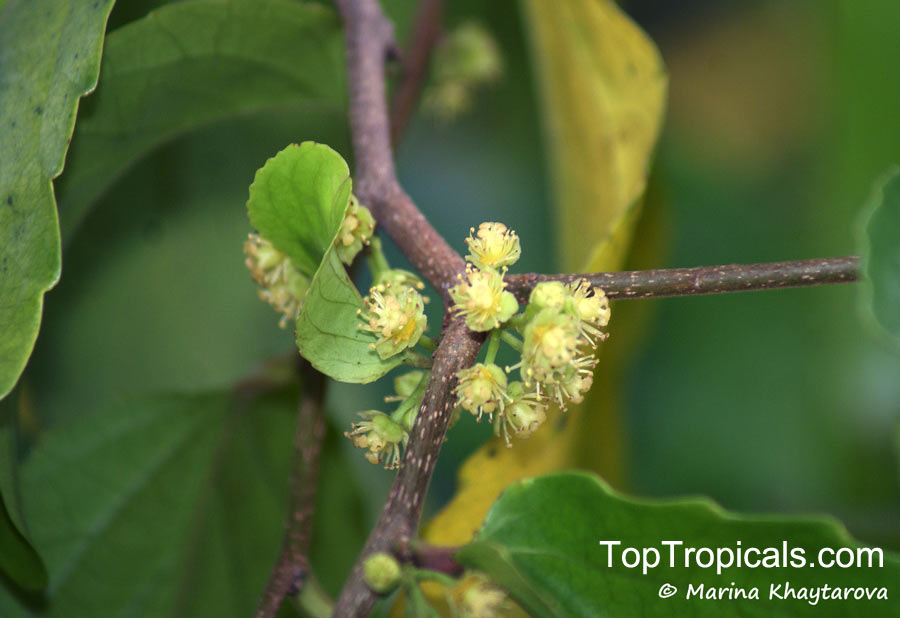
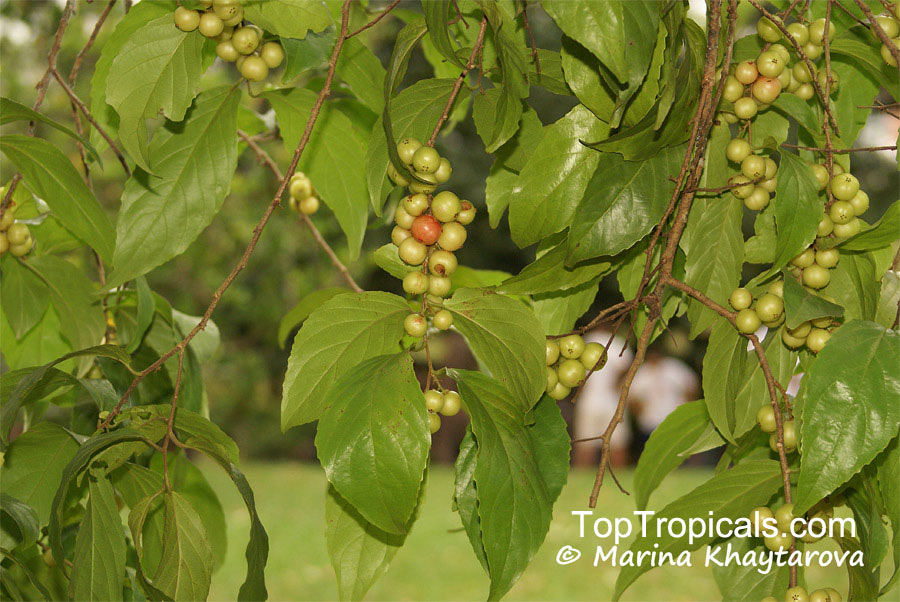
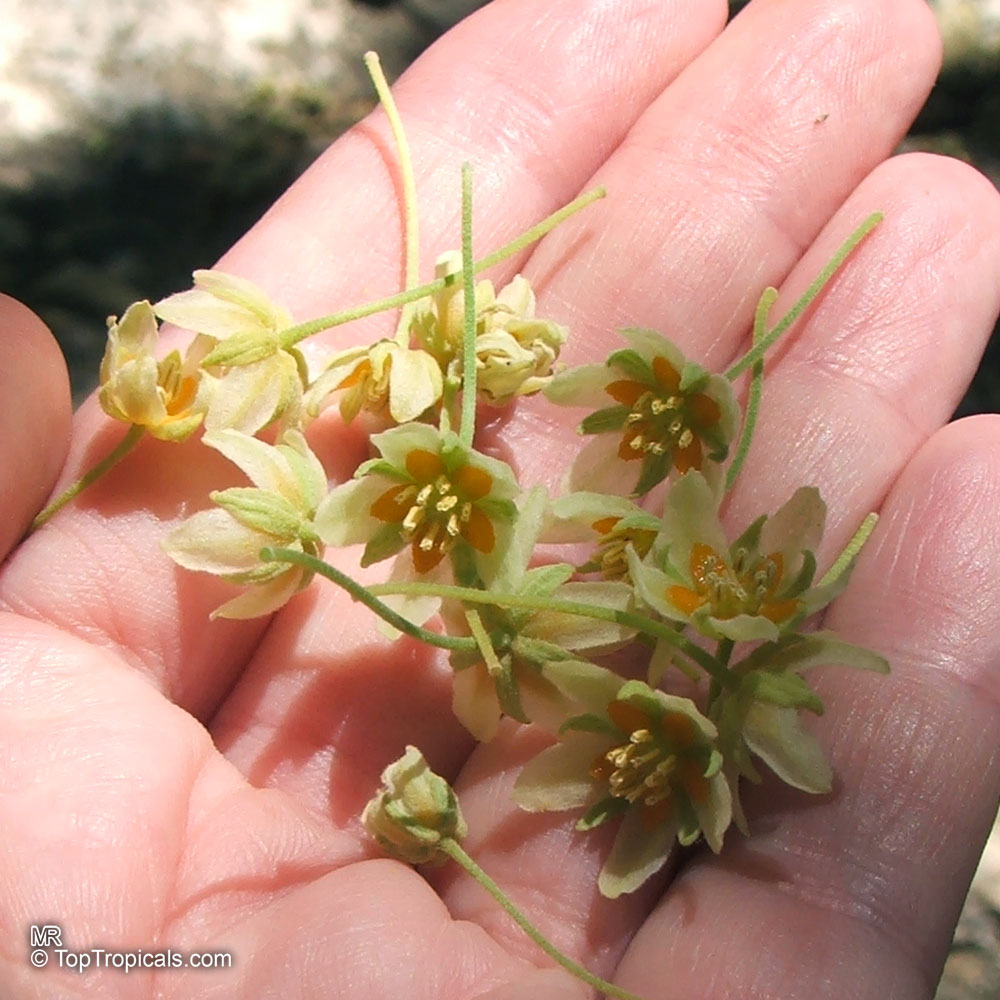
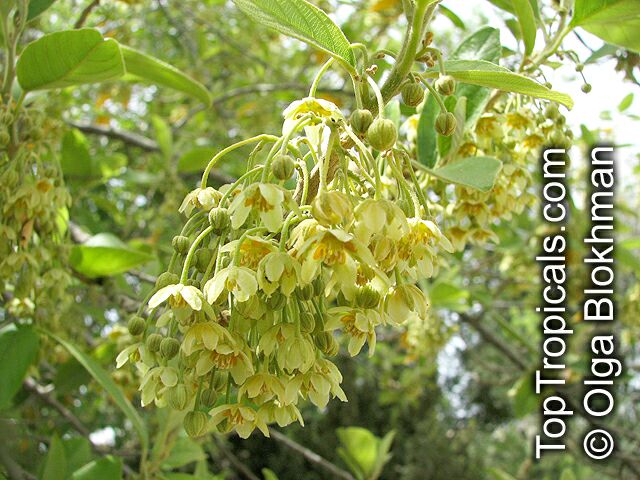
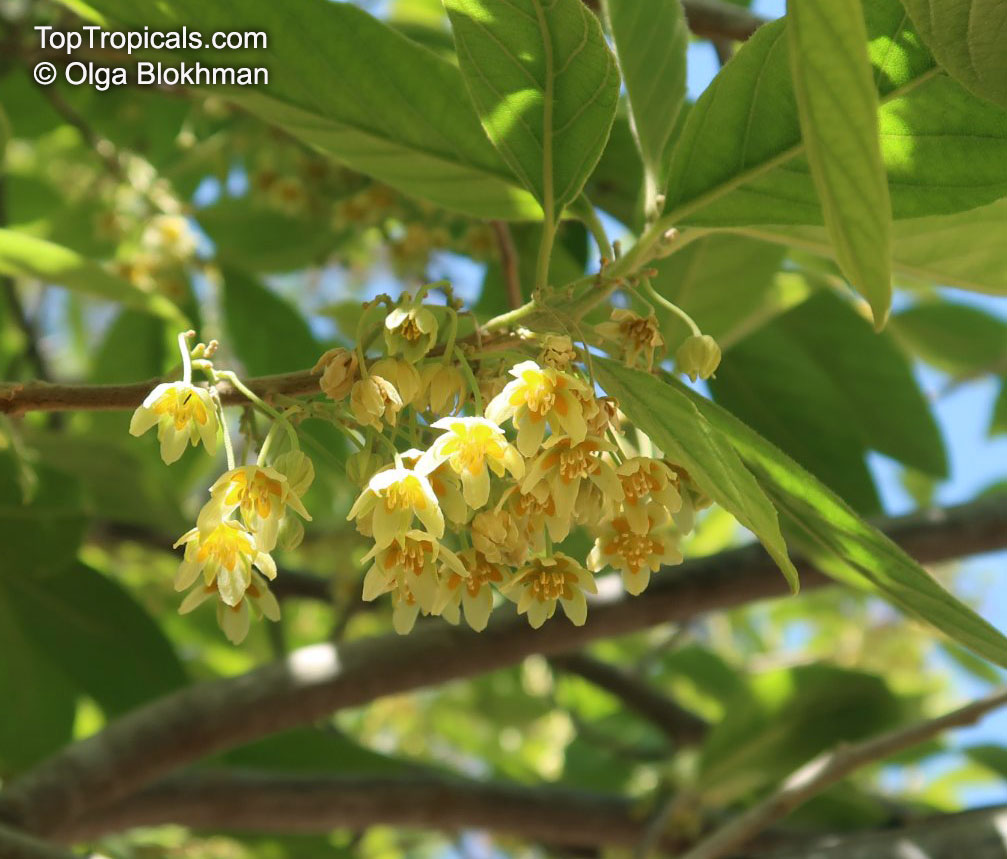
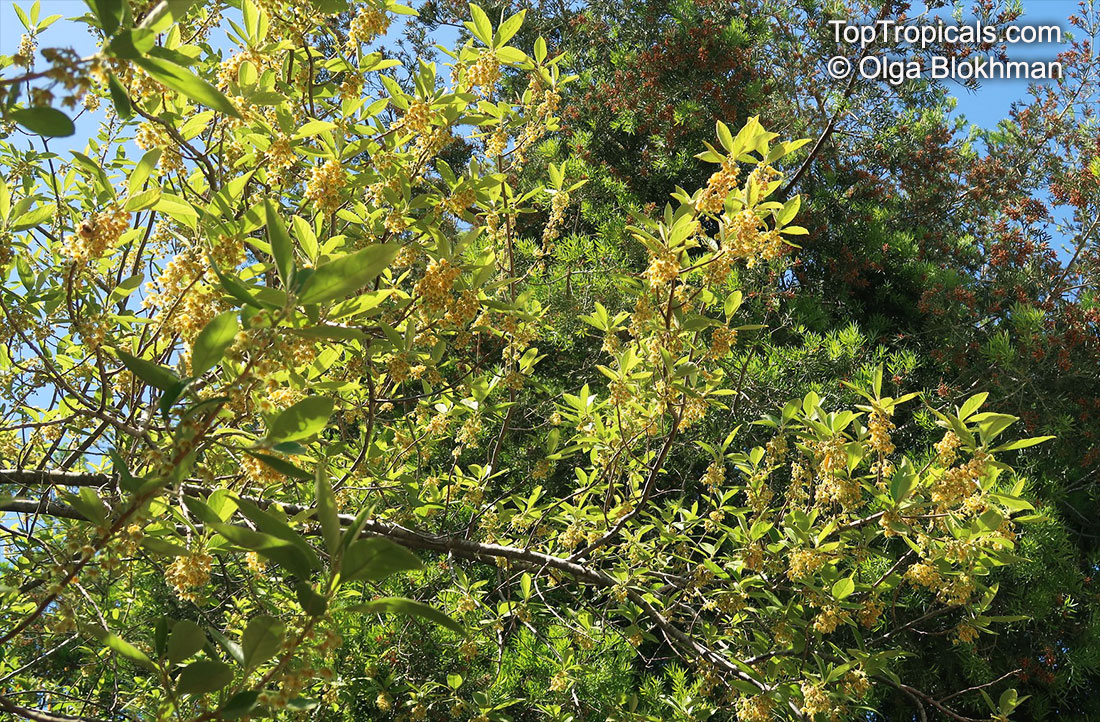
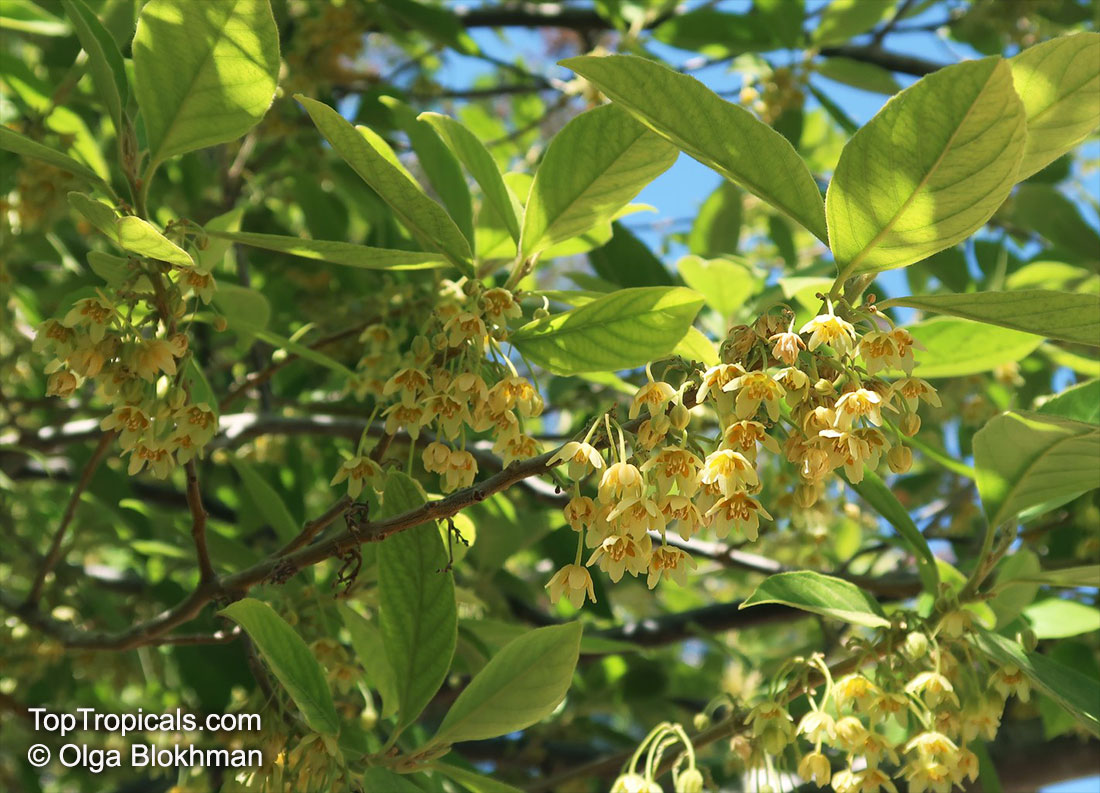
Botanical name: Casearia corymbosa
Common name: Casearia
Family: Salicaceae (Formerly:Flacourtiaceae)
Origin: Central and South America






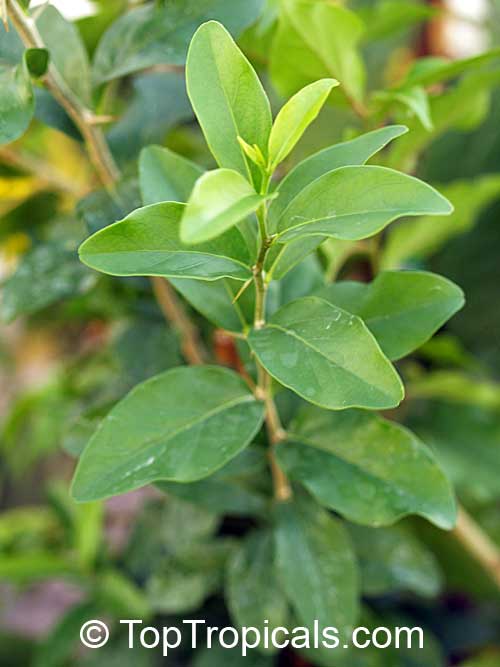
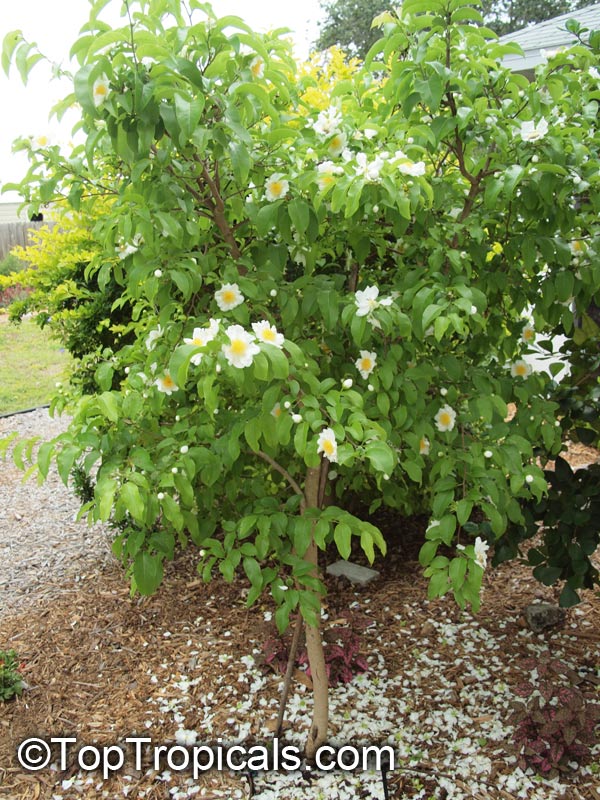
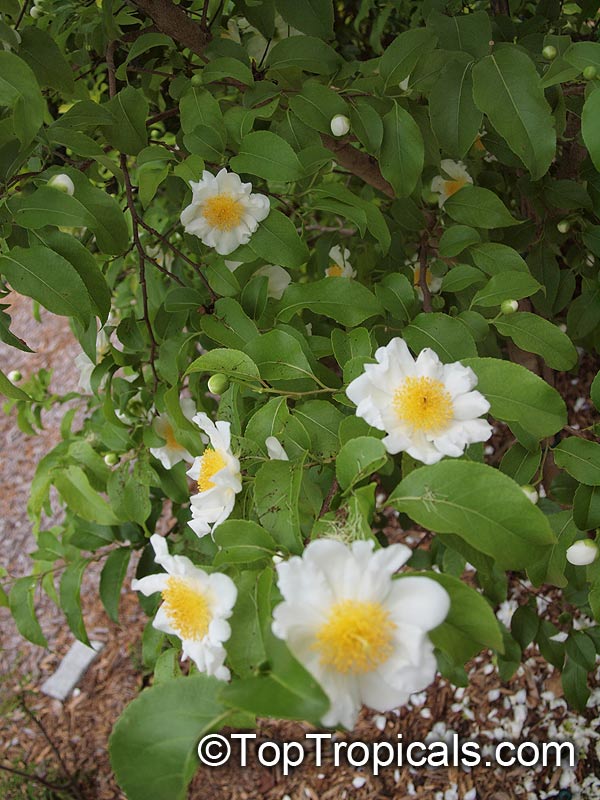
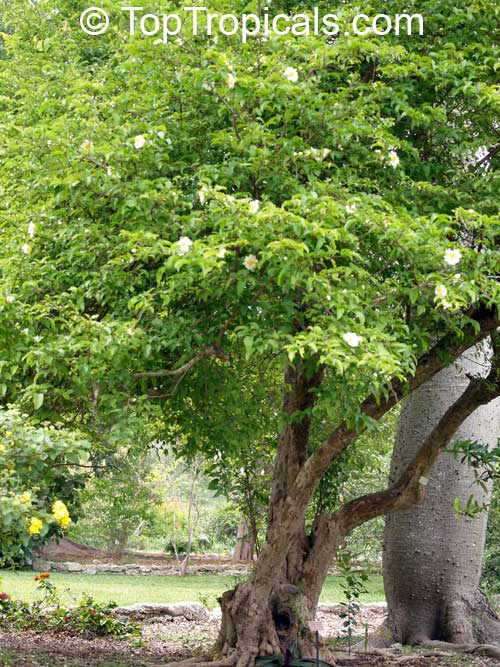
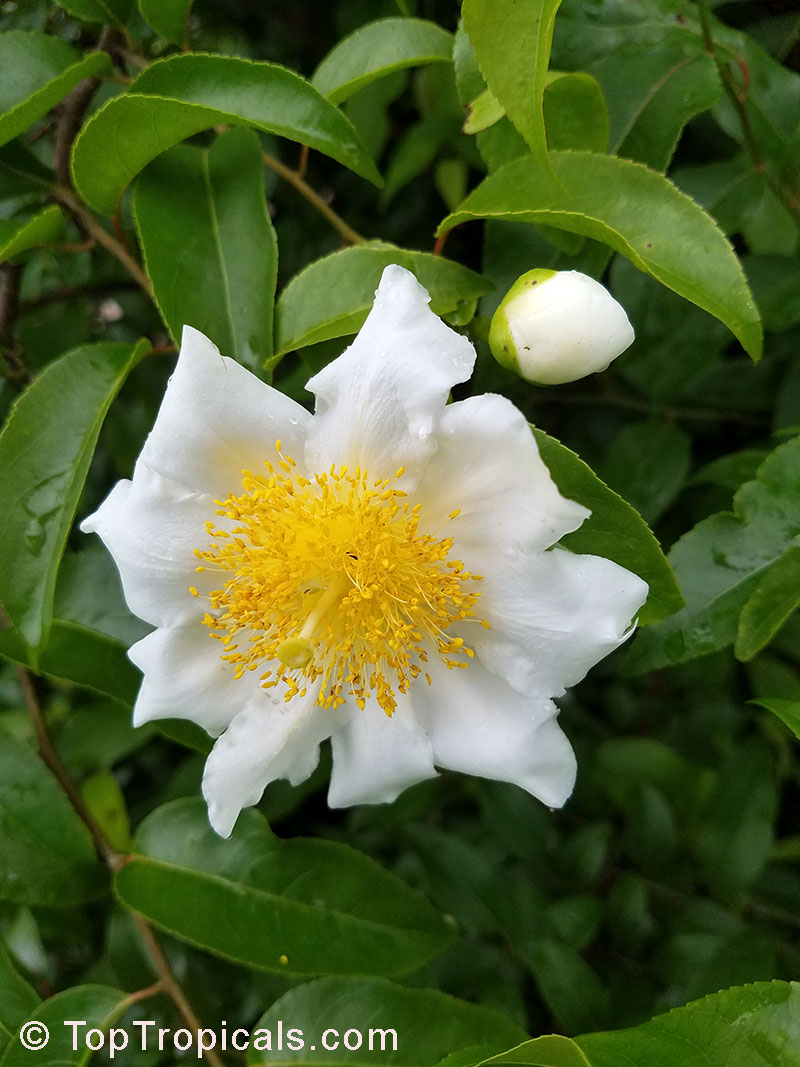
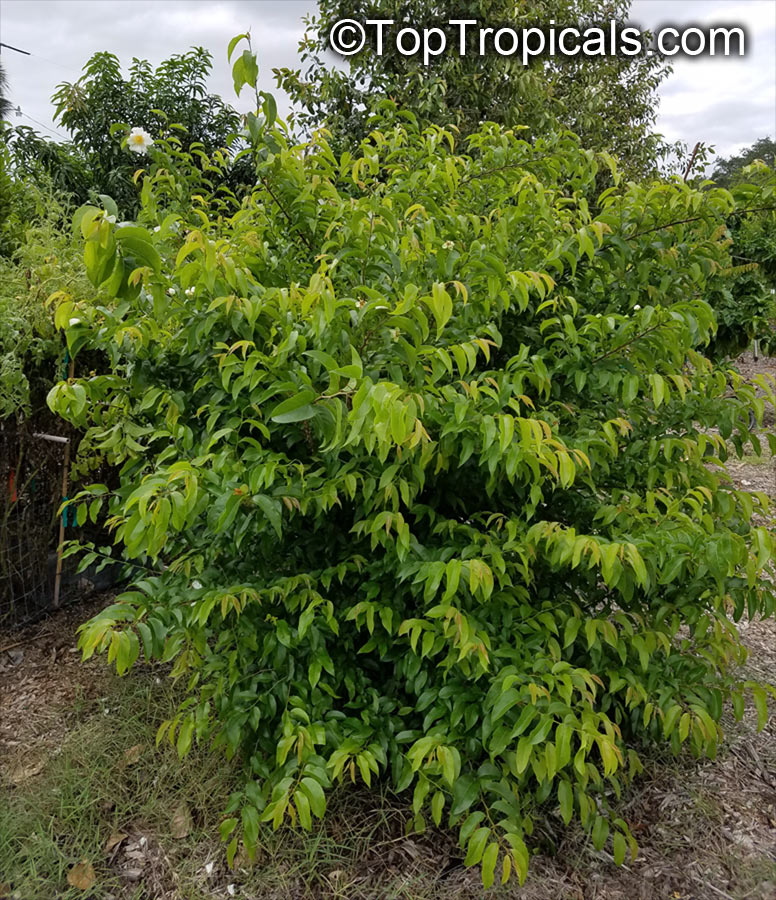
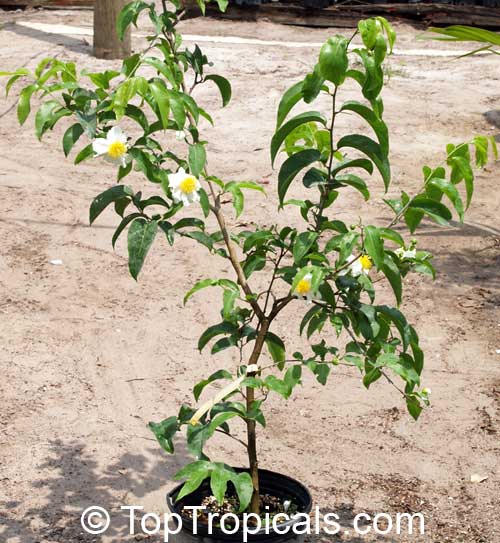
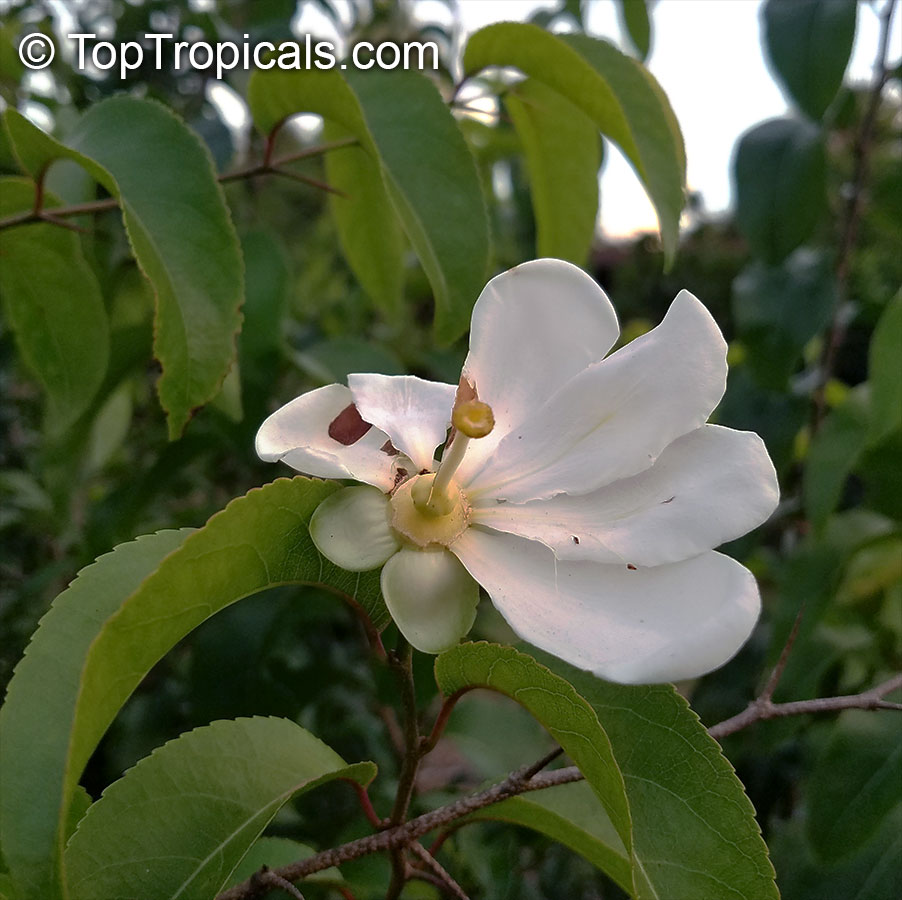
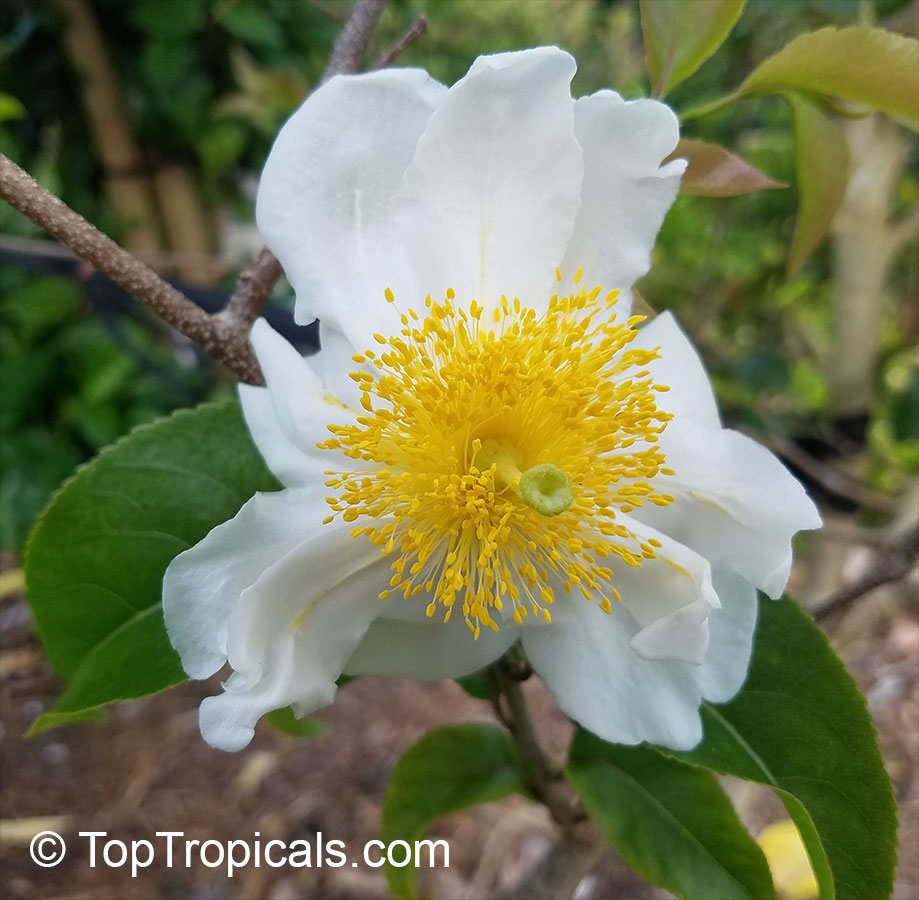
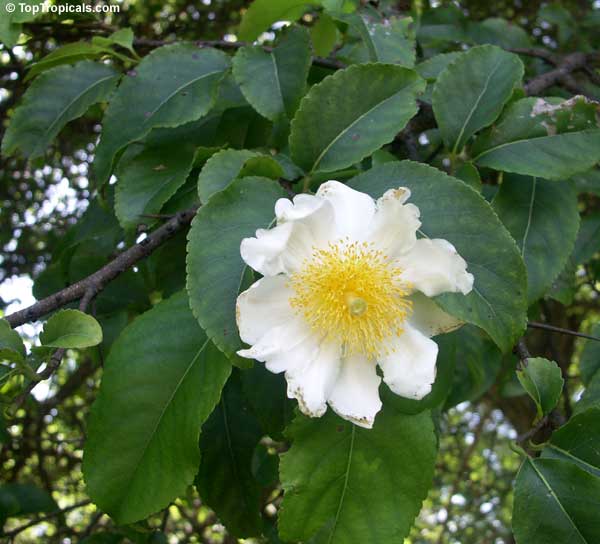
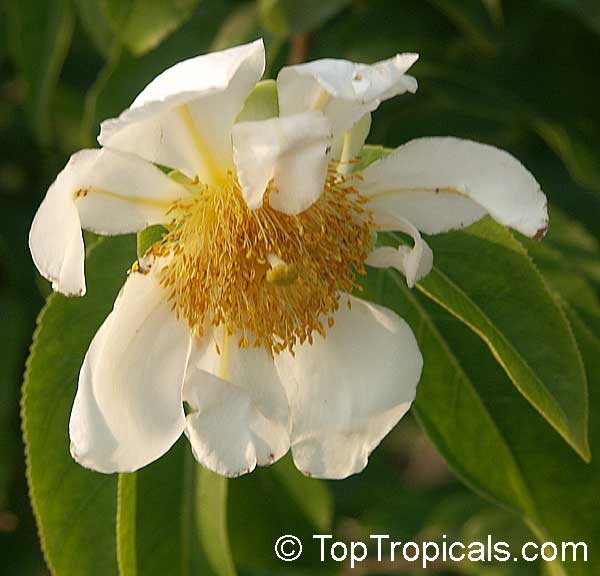
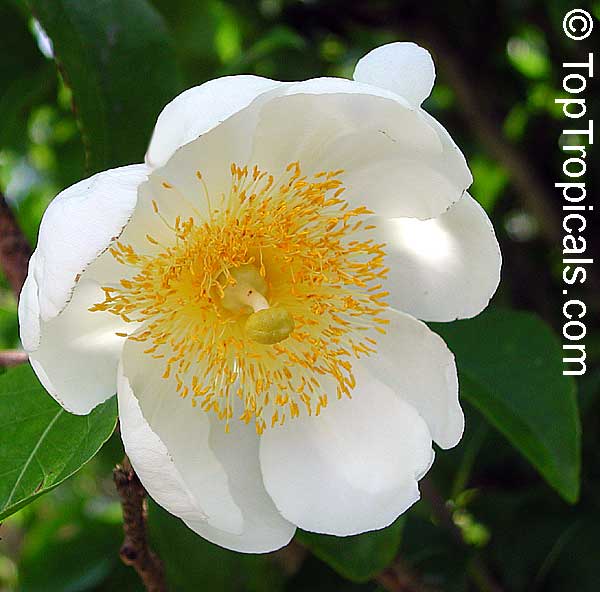
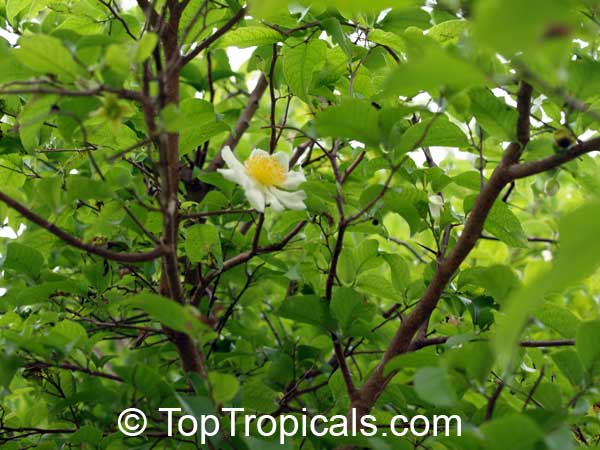
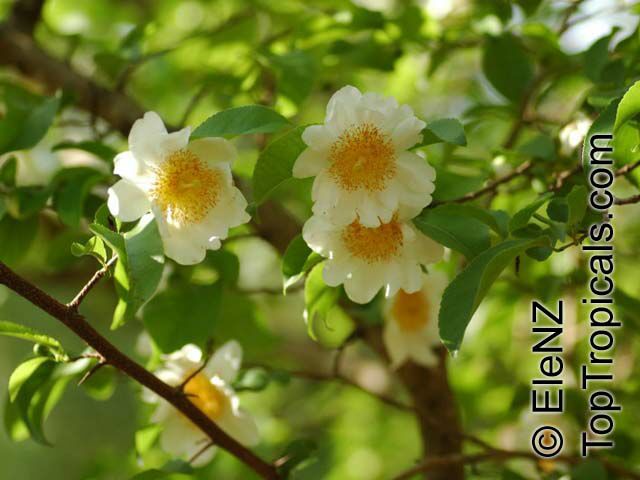
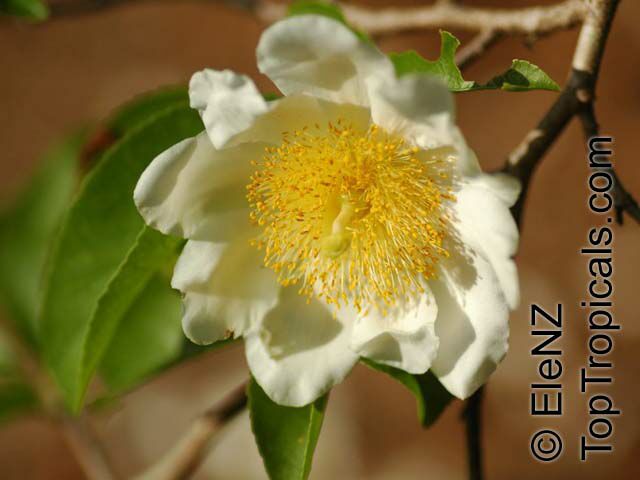
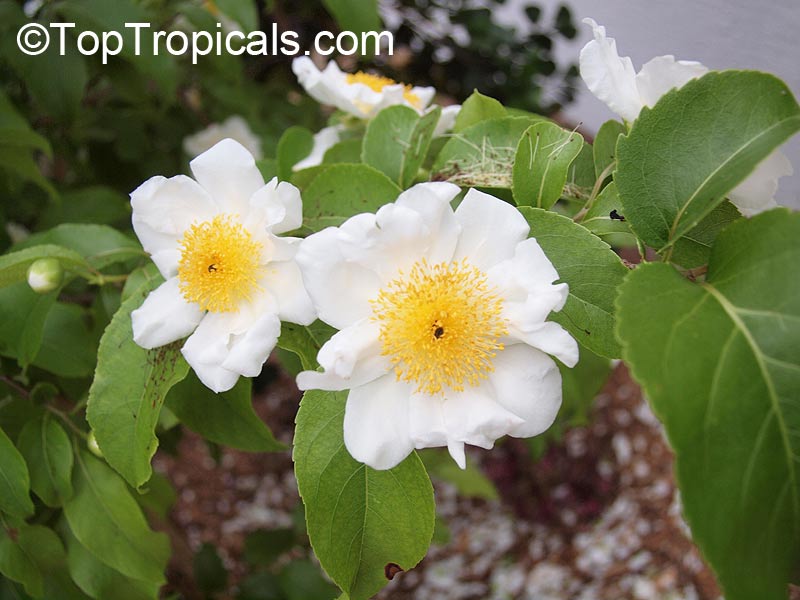
Commonly known as Silverbush, this small tree can reach a height of 10 to 20 feet with alternate, simple leaves attached to the branches (normally 3 to 5 inches long with a width of 1.5 to 2.5 inches). Distributed in Central and South America from Mexico to Argentina, the Casearia corymbosa is an evergreen shrub with a moderate growth rate that is cultivated for its attractive white to off-white flowers.
When planting Casearia corymbosa, it's best to choose a location with full sun to partial shade. Its soil should also be kept moderately moist. A regular watering schedule is recommended to encourage the plant growth and health, while allowing the soil to dry out in between. Fertilizers, although not necessary, can provide additional benefits to the shrub, including promoting growth and brightening its foliage.
In colder temperate regions, Casearia corymbosais often grown in containers or pots and brought inside in the winter months. If a potted shrub is kept outdoors, it needs to be stored in a sheltered location to protect it from strong winds, cold temperatures and heavy precipitation.
The Casearia corymbosaenjoys attracting a variety of wildlife, especially butterflies and hummingbirds. Its white to off-white blossoms are incredibly fragrant and bloom for 4 to 6 weeks during summertime. Pruning is also beneficial for keeping its shape and size in check, as well as reducing its problem with branch dieback. All in all, this evergreen shrub is perfect for bringing a hint of exoticism to any garden or landscape.
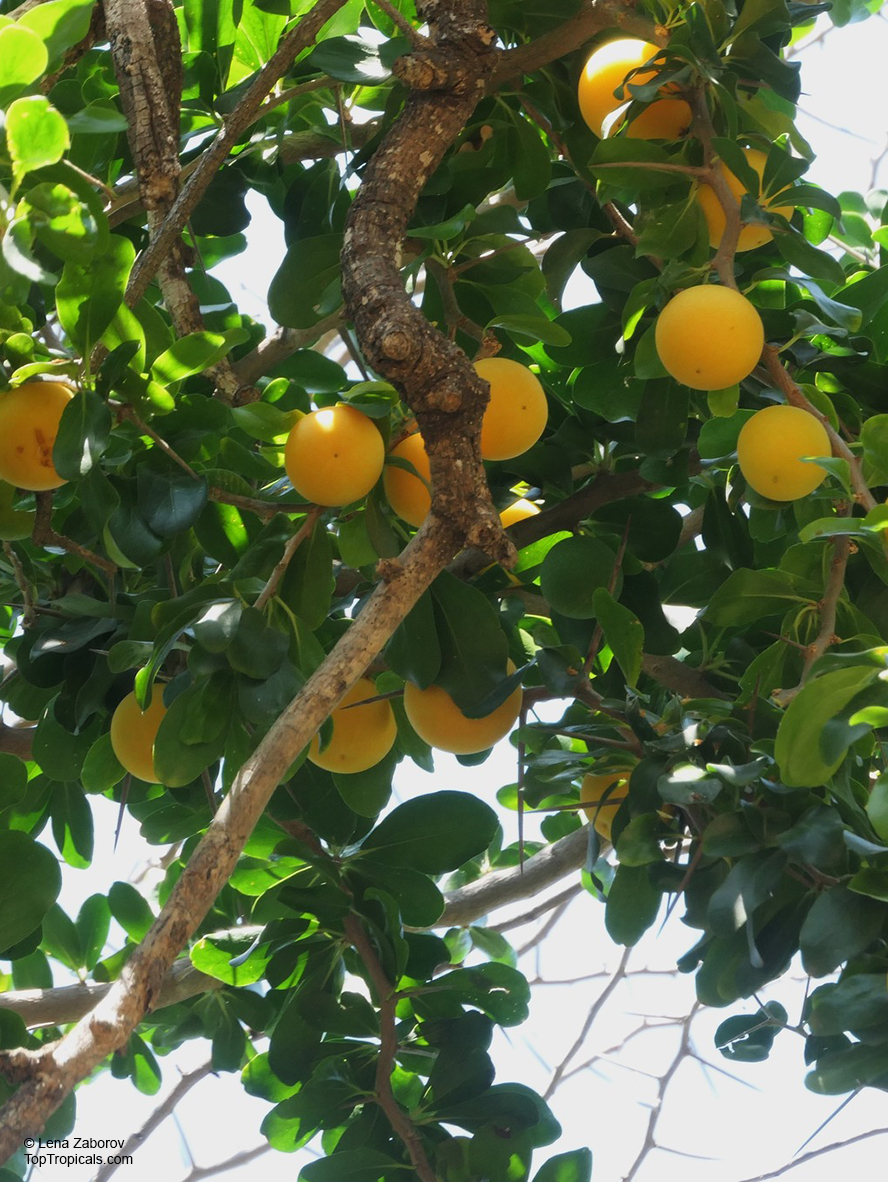
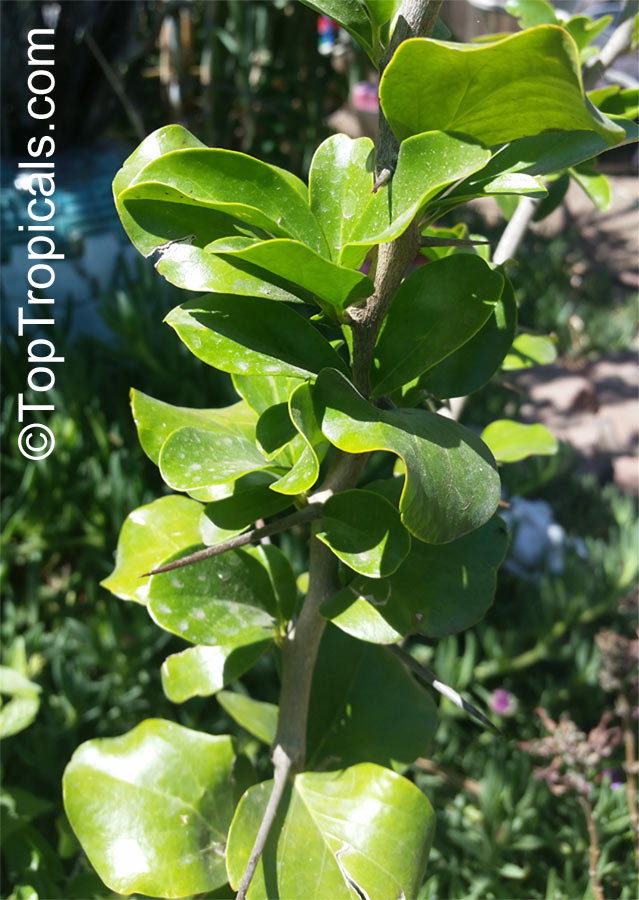
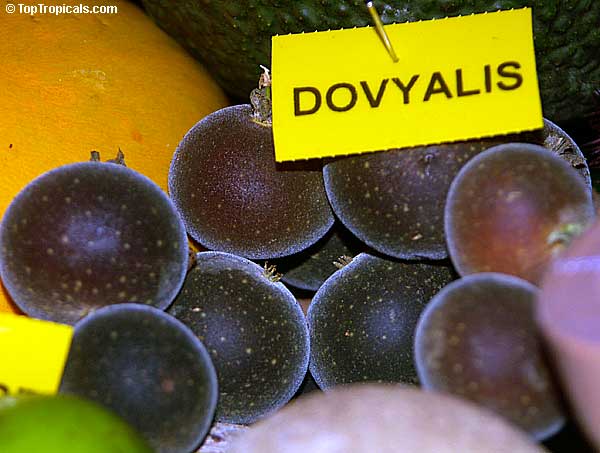
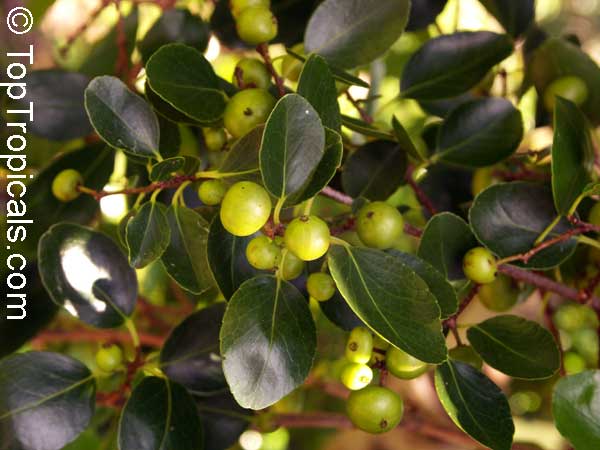
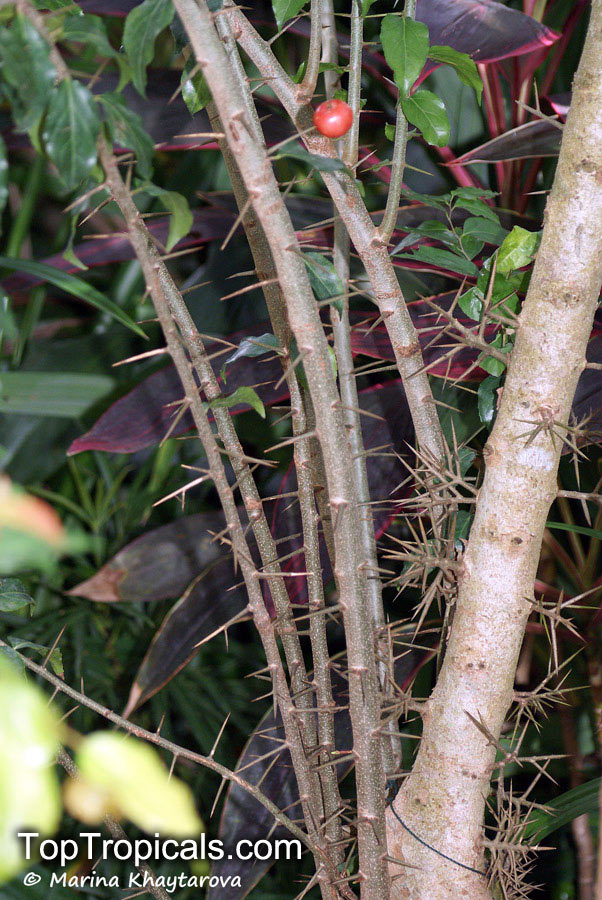
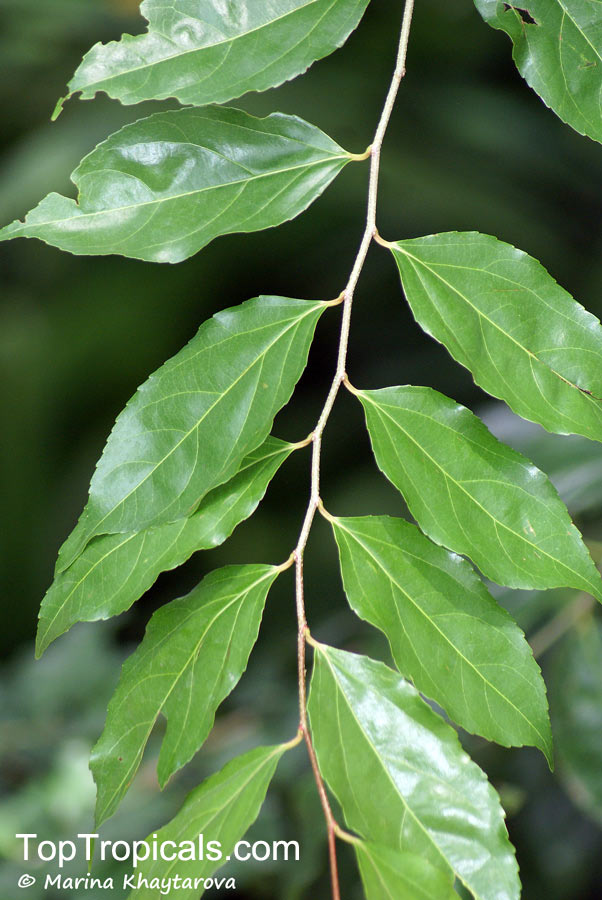
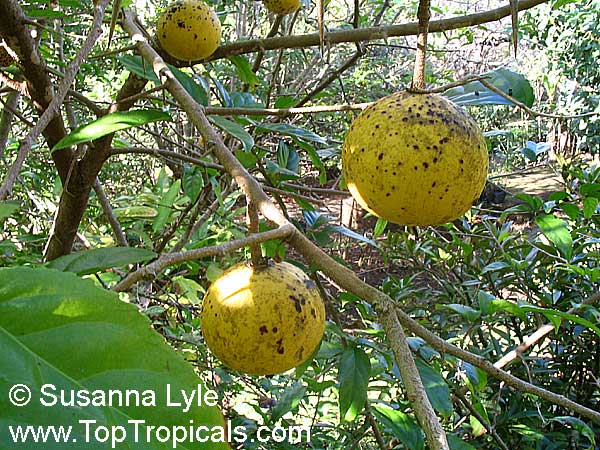
Botanical name: Dovyalis caffra
Common name: Kei Apple
Family: Salicaceae (Formerly:Flacourtiaceae)
Origin: Southwest Africa










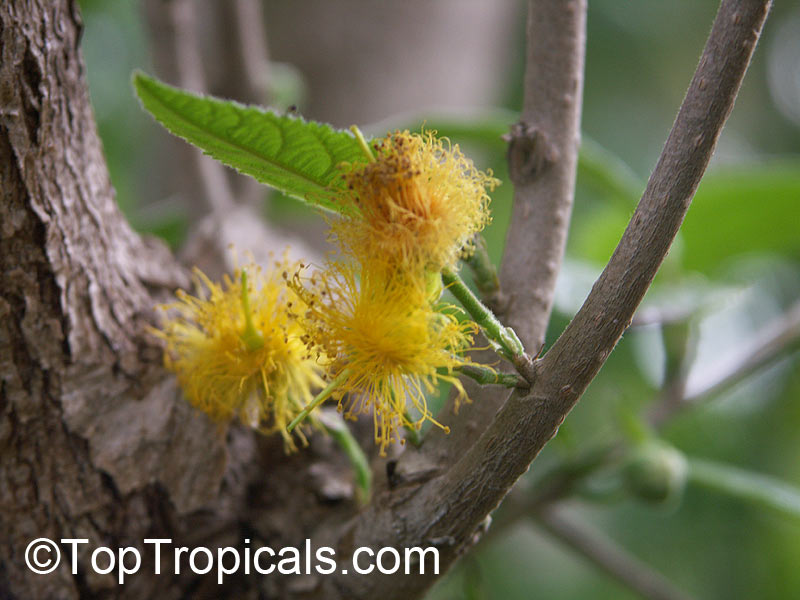
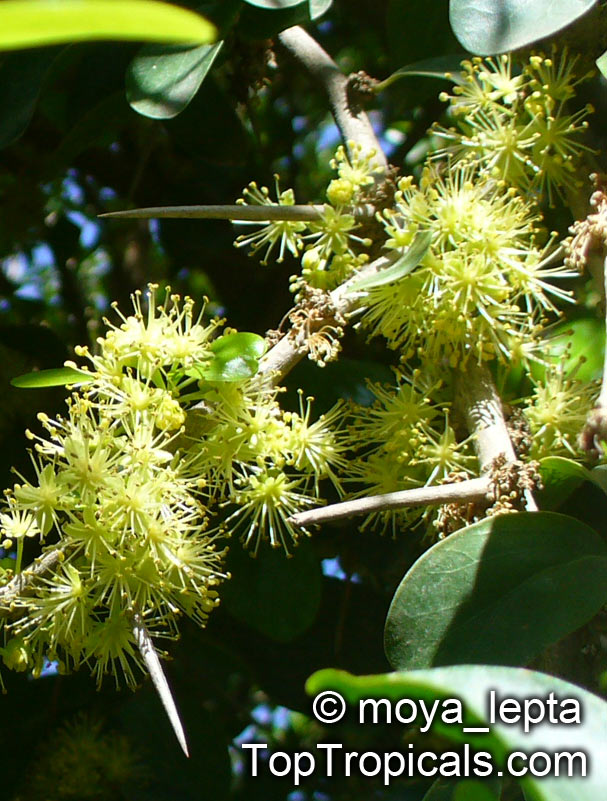
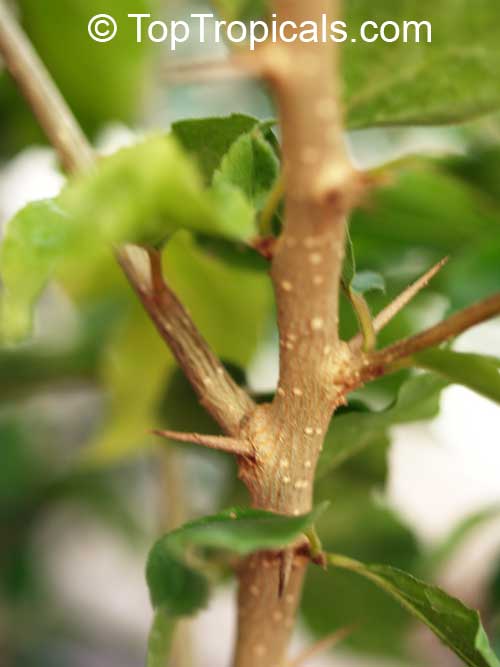
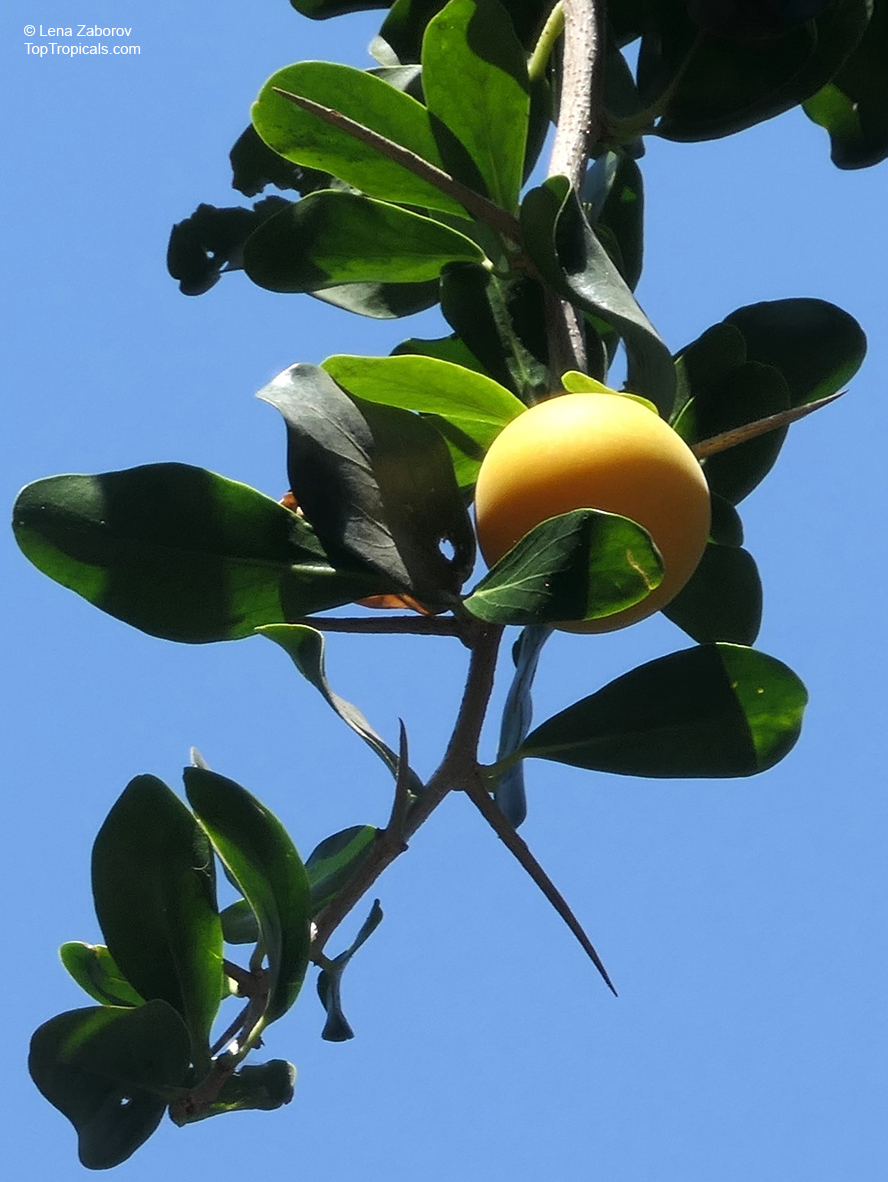
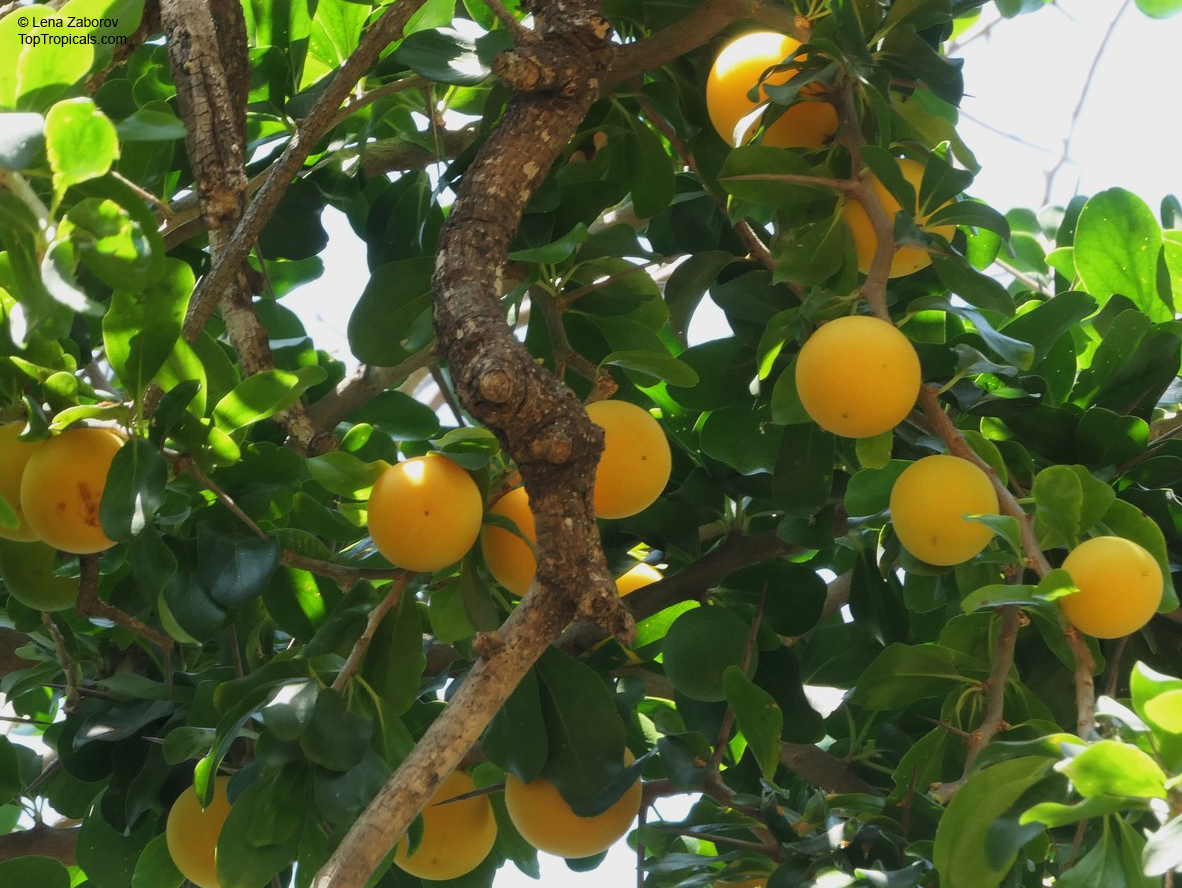
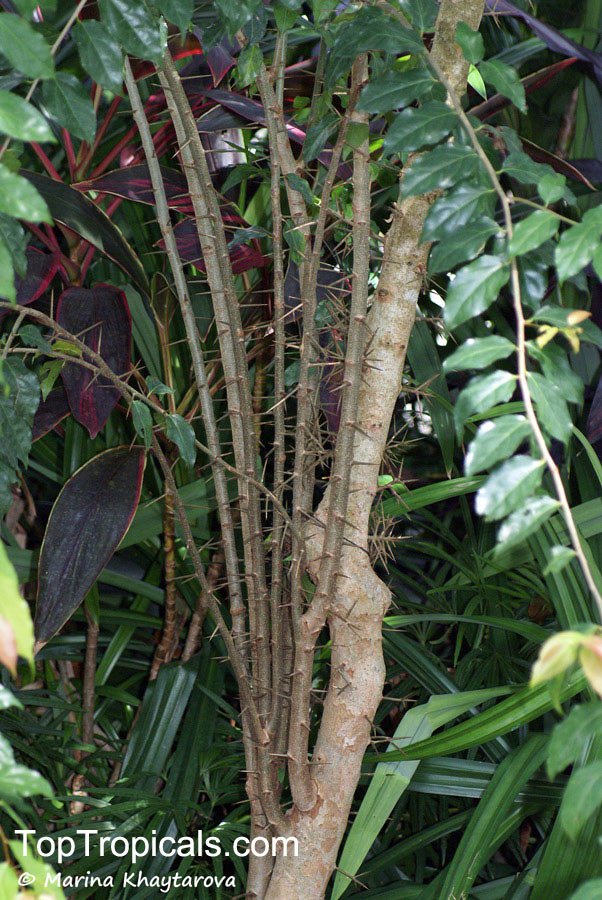
Kei Apple plants (Dovyalis caffra) are evergreen shrubs or small trees that produce thorny or spiny branches. Native to Southwest Africa, they can grow up to 5-20 feet tall and wide and are salt tolerant, making them suitable for coastal gardens and seaside plantings. They are also often used as impenetrable hedges to keep unwanted animals away.
Kei Apples produce yellow and orange flowers that attract pollinators and fruits high in dietary fiber and antioxidants. The fruits have a slightly acidic flavor and can be eaten fresh or used in desserts. They are often sprinkled with sugar. The plant can yield up to two hundred fruits per season.
The plant is hardy to at least 30°F, but young plants should be kept healthy and nourished in the winter. When grown in cold areas, the plant does well in a pot and must be brought indoors before temperatures drop below freezing. It should be planted in well-draining soil with plenty of organic matter and provided with full sun. Regular watering is required, and moderate water is needed in periods of warmth.
The plant can form allelopathic relationships, inhibiting the growth of other plants nearby. For the most part, both male and female plants are required for fruit set, although there are some female trees that can bear fruit without a male.
In conclusion, Kei Apples are a versatile and useful plant that can provide edible fruits, form impenetrable hedges, and thrive in coastal areas. With proper care and maintenance, they can be a valuable addition to any garden or landscape.
Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE C-Cibus - Crop Nutrition Booster
SUNSHINE-Honey - sugar booster
Last one
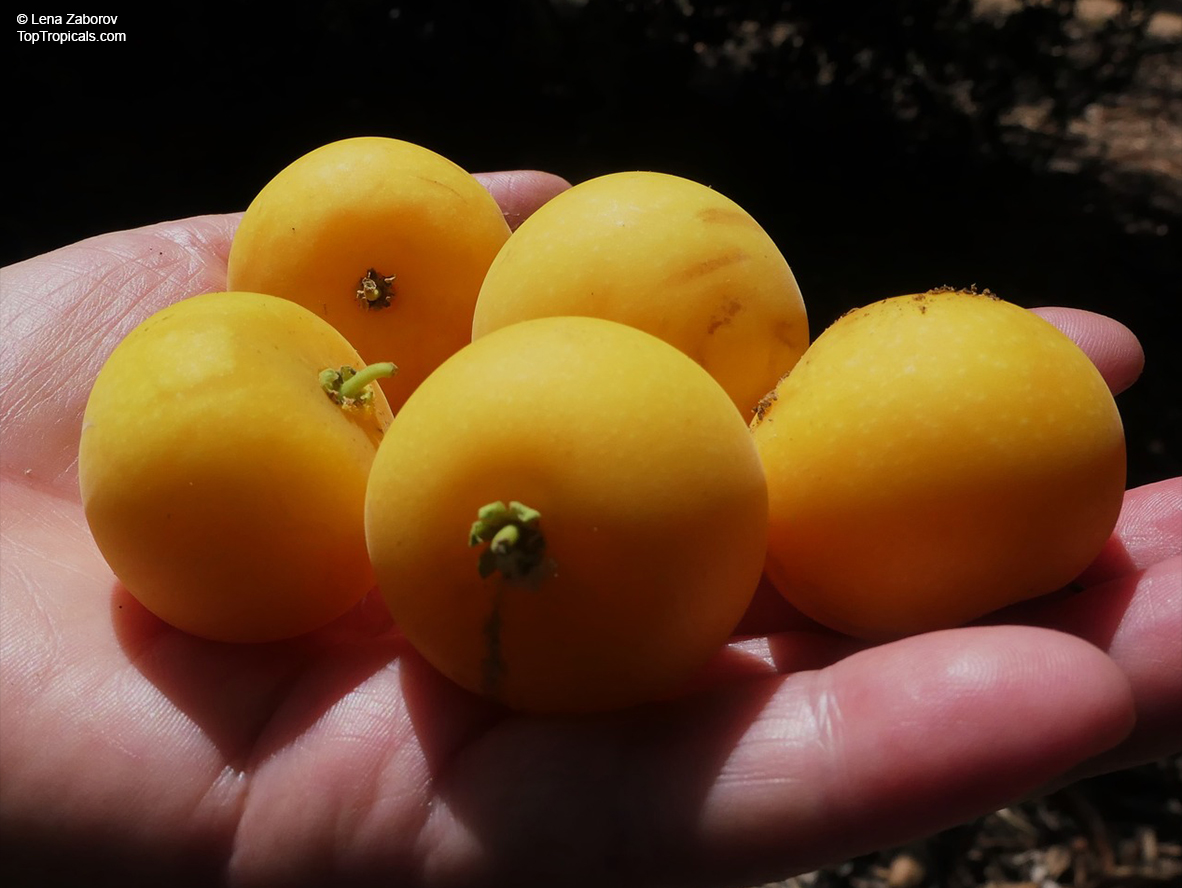
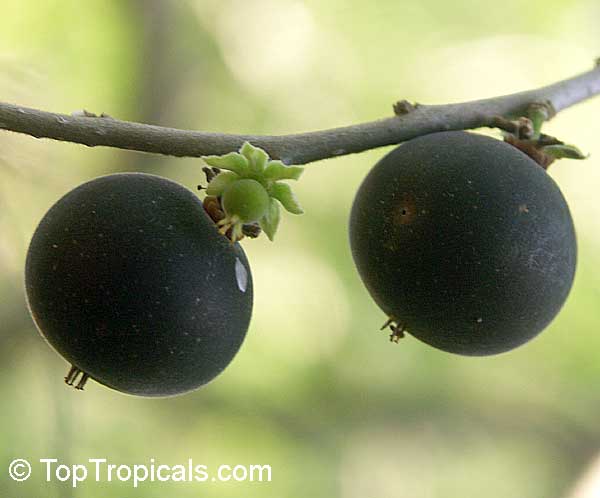
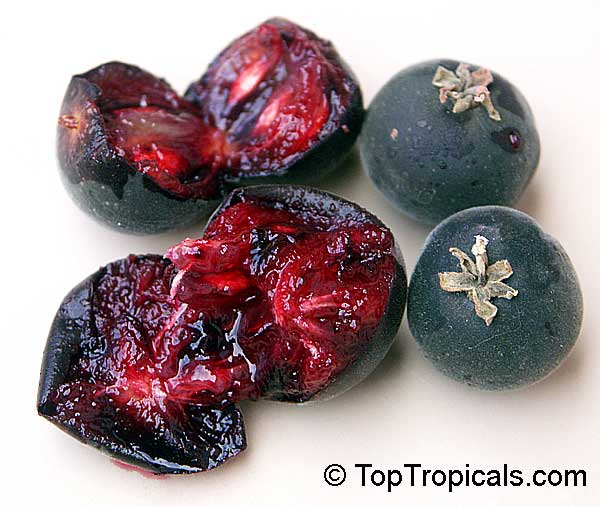
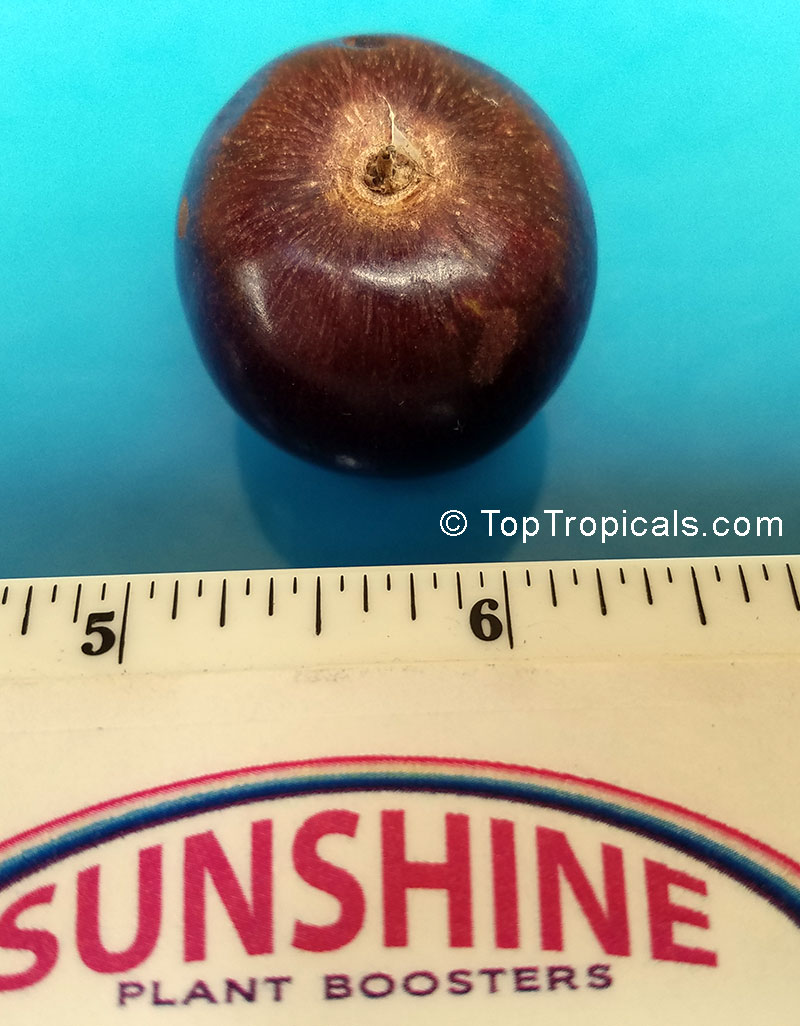
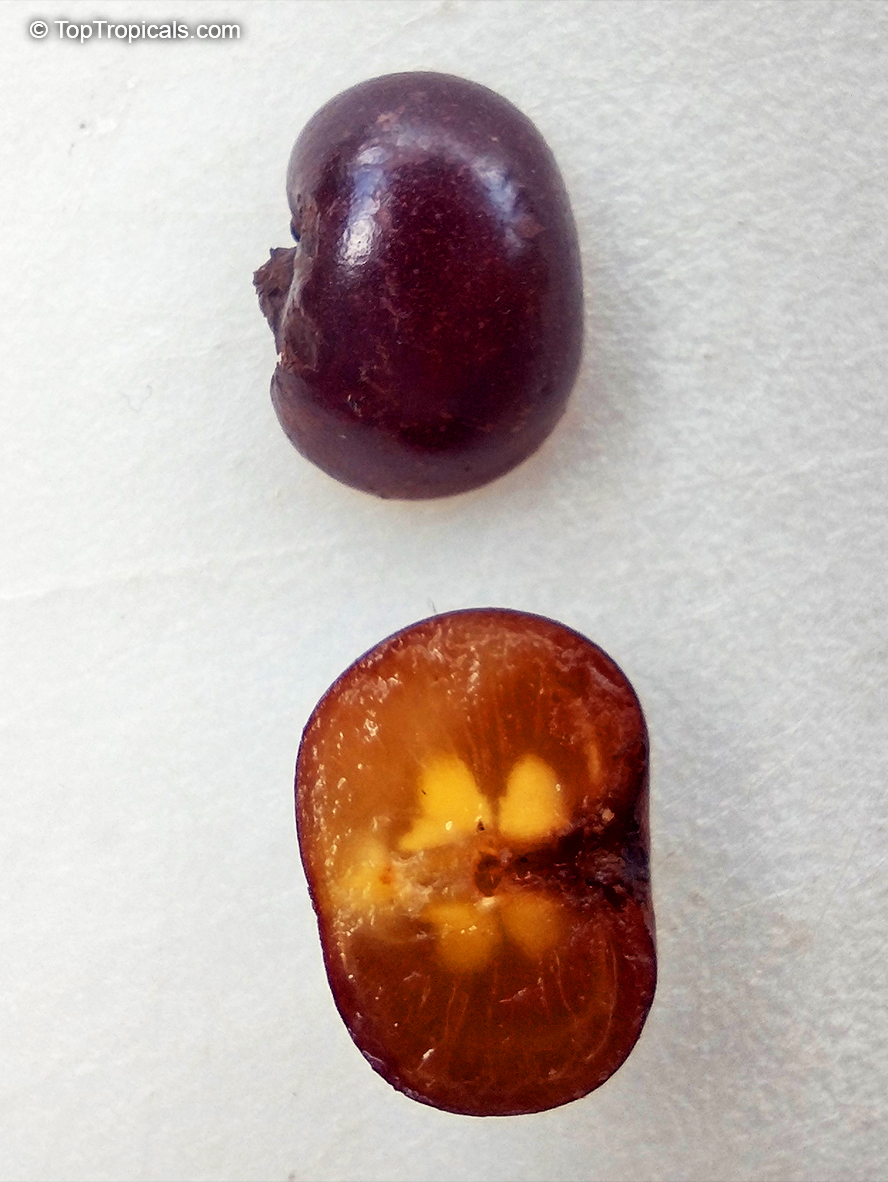
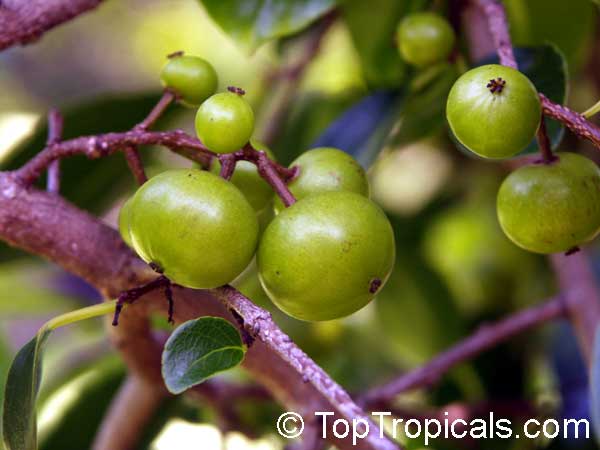
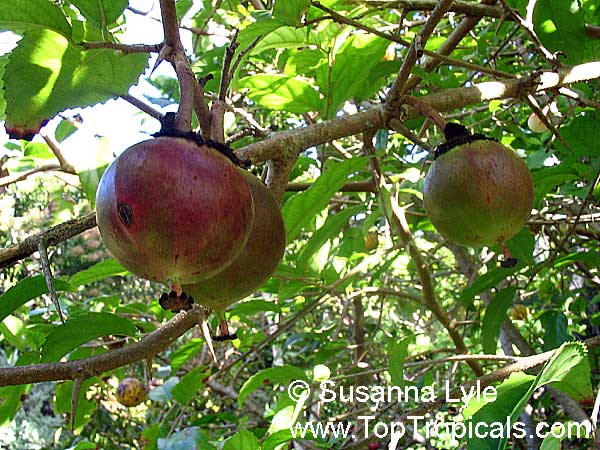
Botanical name: Dovyalis hebecarpa
Common names: Tropical Apricot, Ceylon Gooseberry, Ketembilla
Family: Salicaceae (Formerly:Flacourtiaceae)
Origin: South Africa






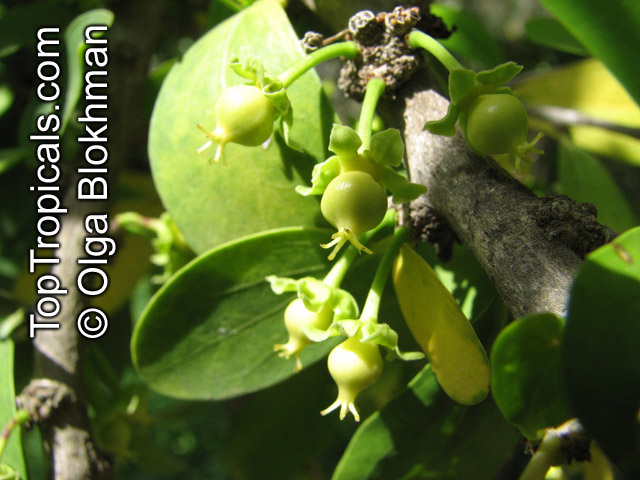
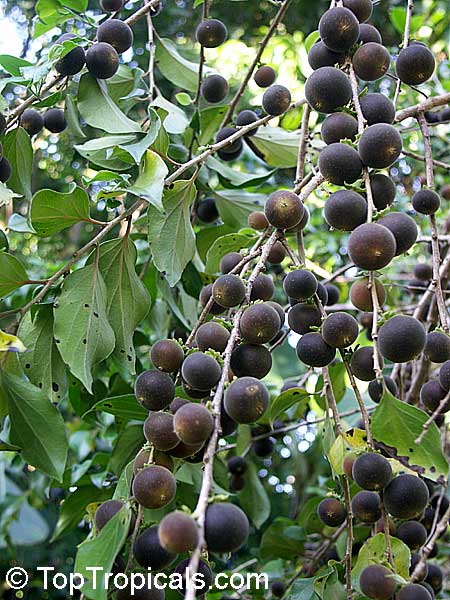
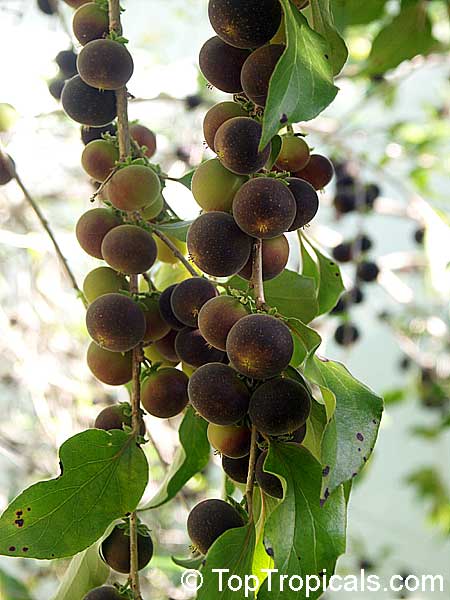
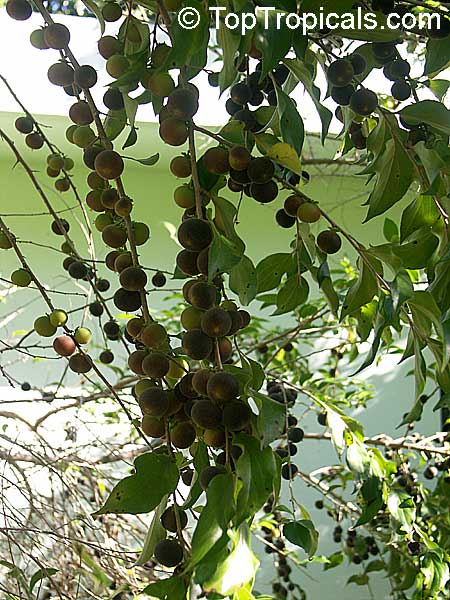
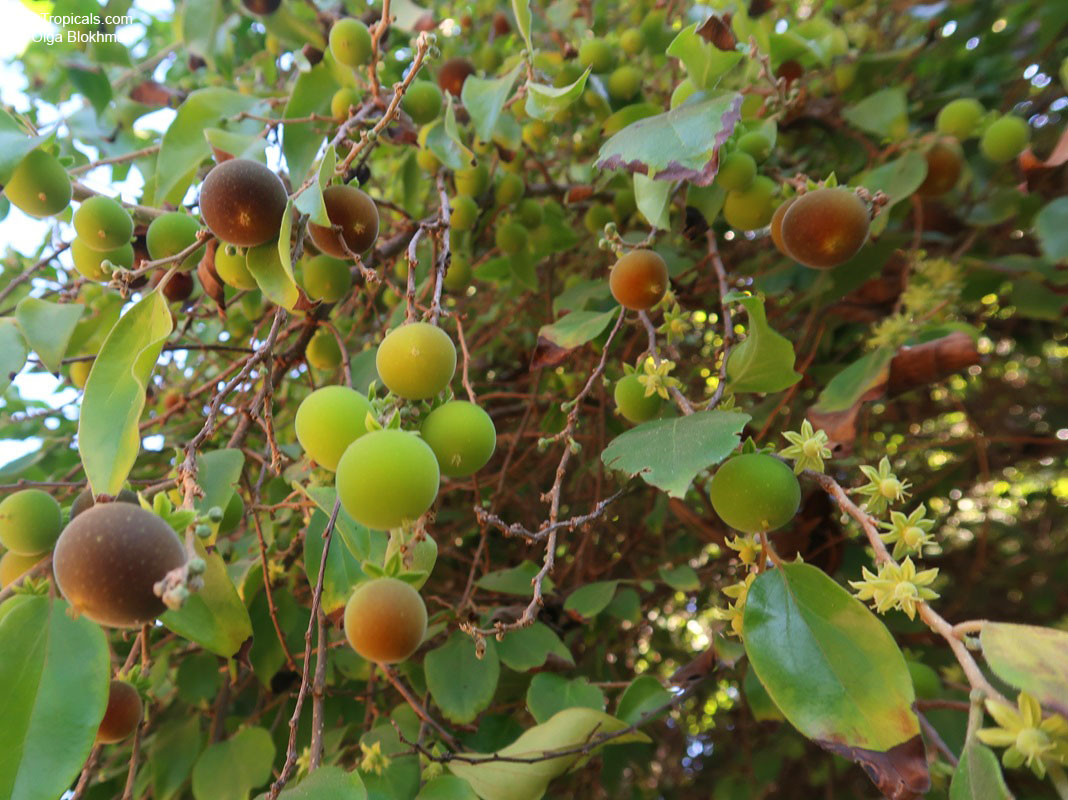
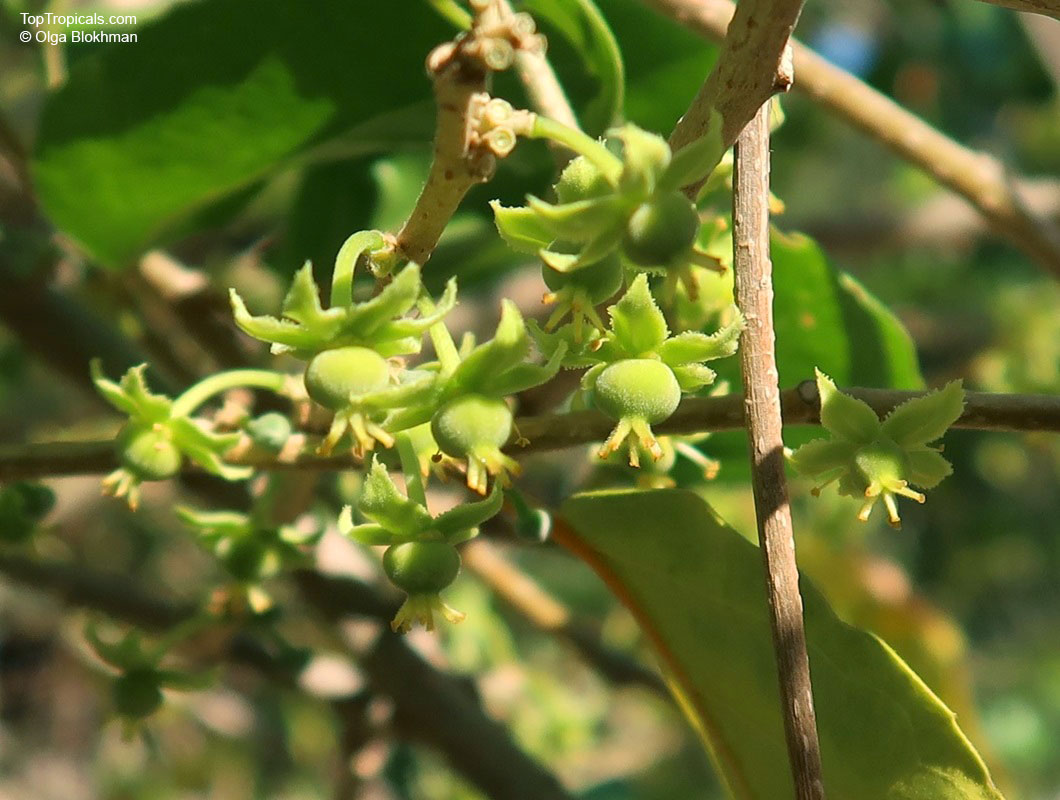
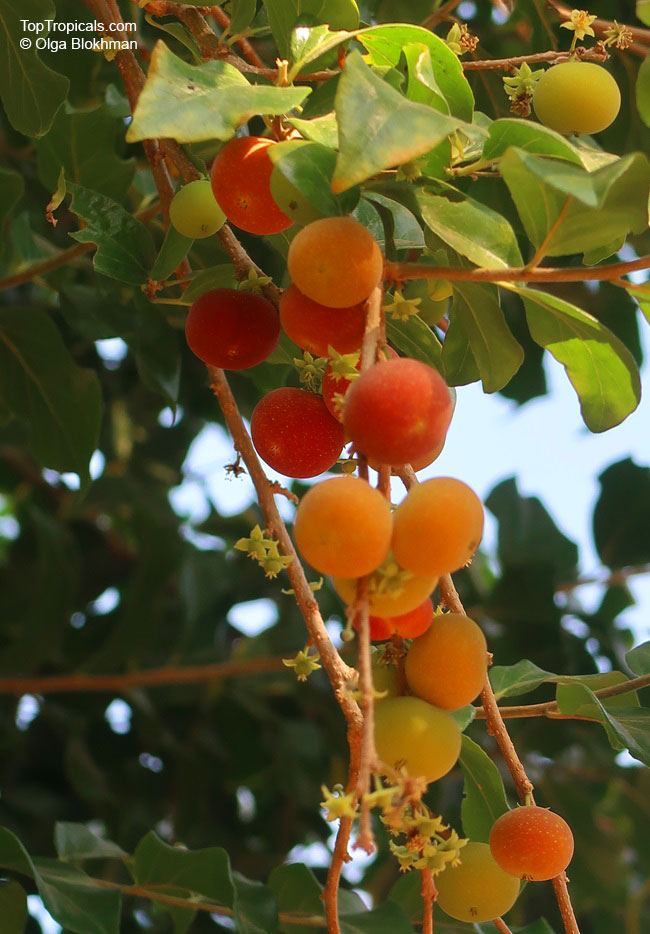
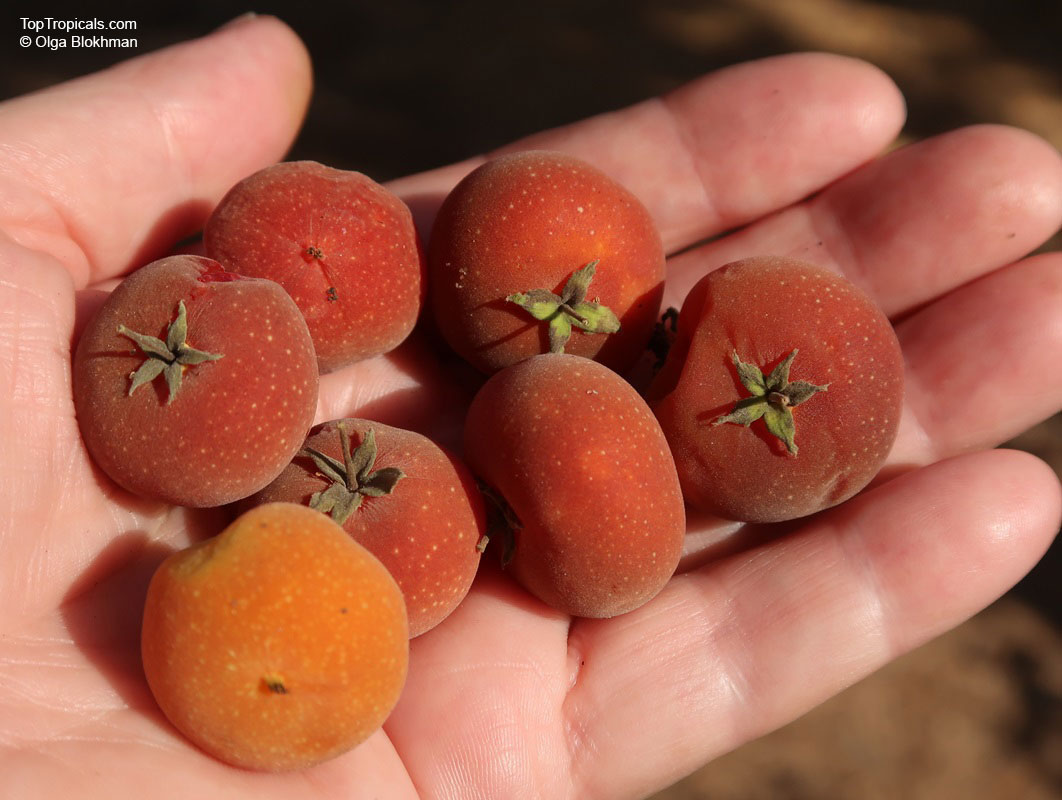
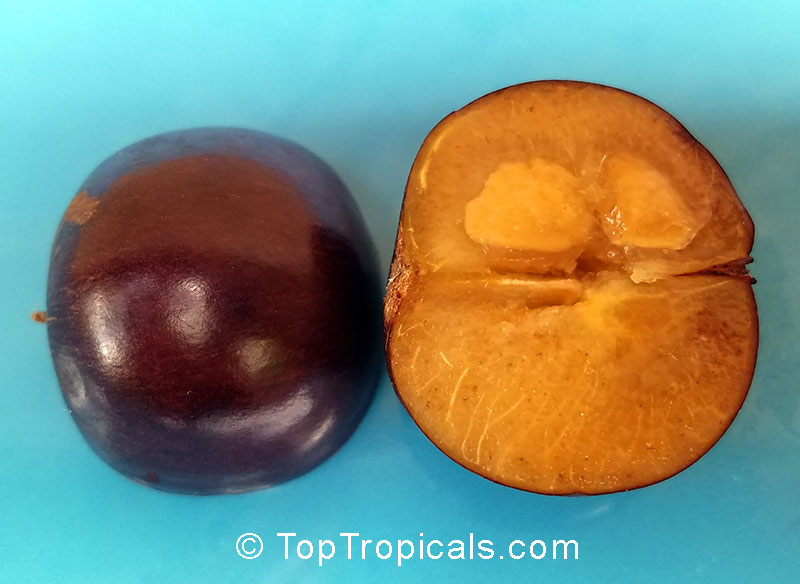
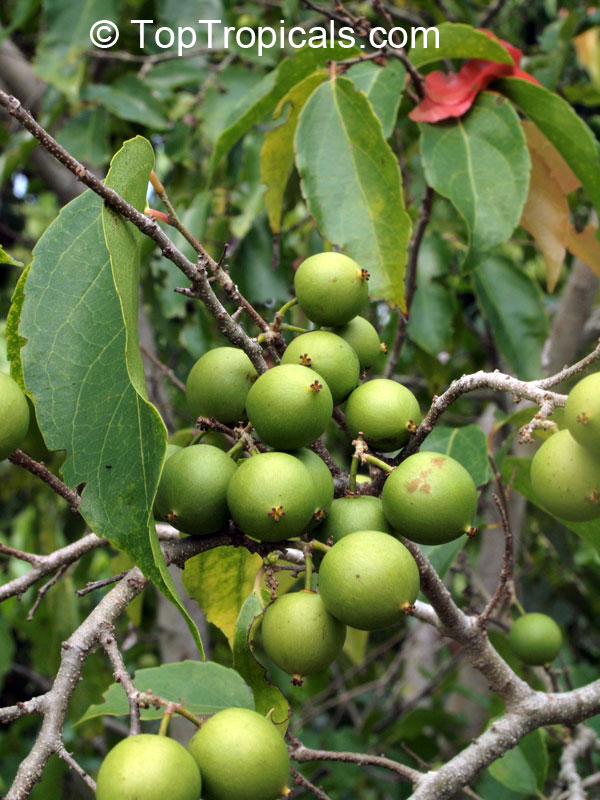
A small shrubby spiny tree to 15-20ft cultivated for its maroon-purple fruit with acid pulp tasking like gooseberries. Much less thorny than other members of the family. Grows very quickly under ideal conditions. Trees bear fruits in great quantities. Small juicy fruit to 1" around with brown to deep purple velvet skin and deep red acidic pulp, resembling small grape tomatoes in shape. The fruit is usually used in drinks, fresh, either as a flavoring for beverages, or in preserves. Fruits can be eaten out of hand but are usually not for the pulp is very acidic. Plants will tolerate dry and wet soils, although lots of moisture is necessary for proper fruit development. Fruiting occurs from spring to early summer. In some areas tree will bear multiple crops throughout the year. Propagation by seed. Dovyalis abyssinica has the color and flavor of astingent apricot, hence the common name. Cultivated hybrids available.
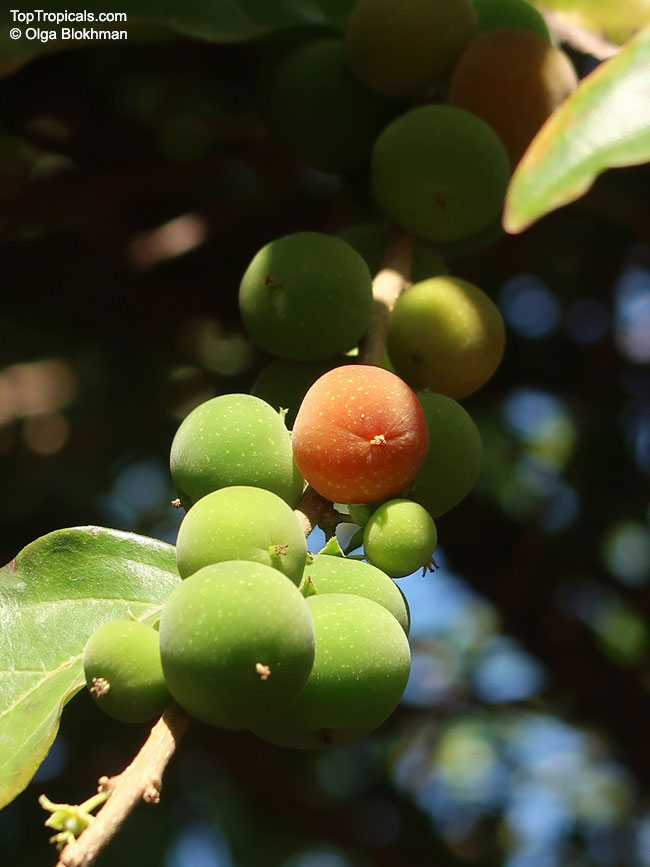
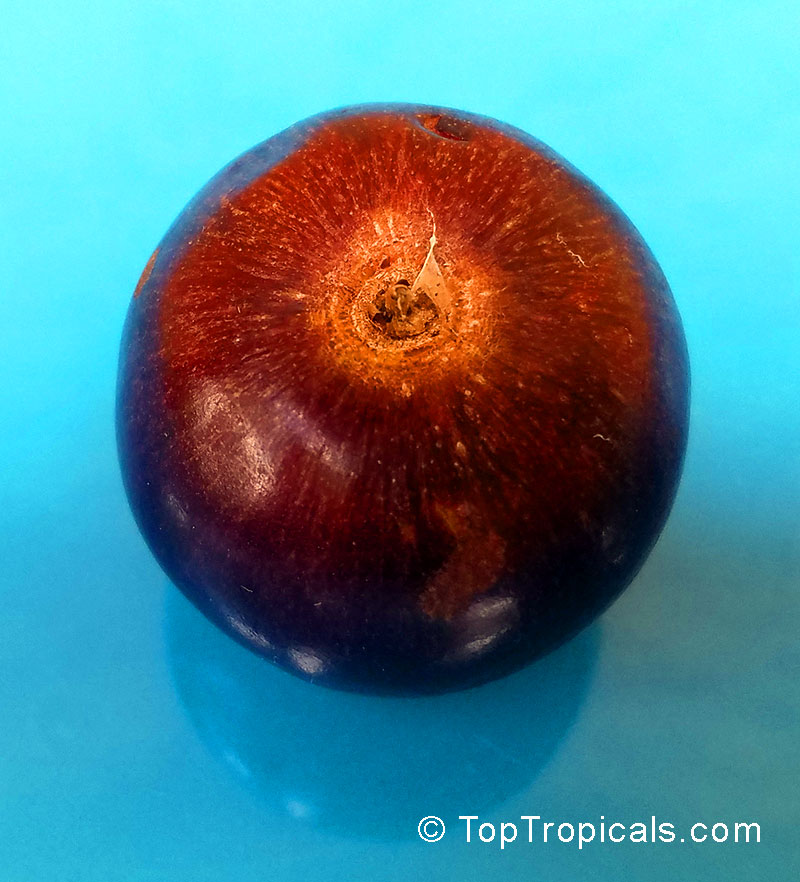
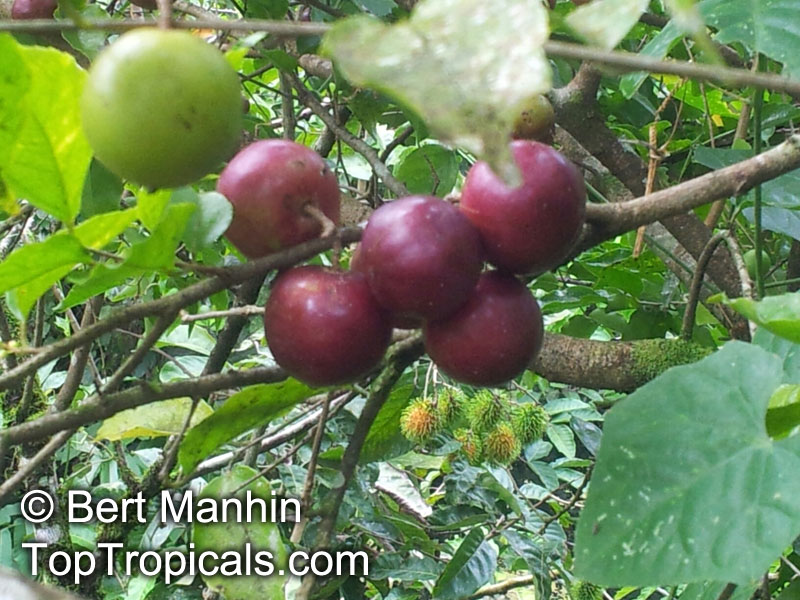
Botanical name: Flacourtia indica
Common names: Governors plum, Madagascar Plum, Batoko palm
Family: Salicaceae (Formerly:Flacourtiaceae)
Origin: Tropical Africa, Madagascar and Asia







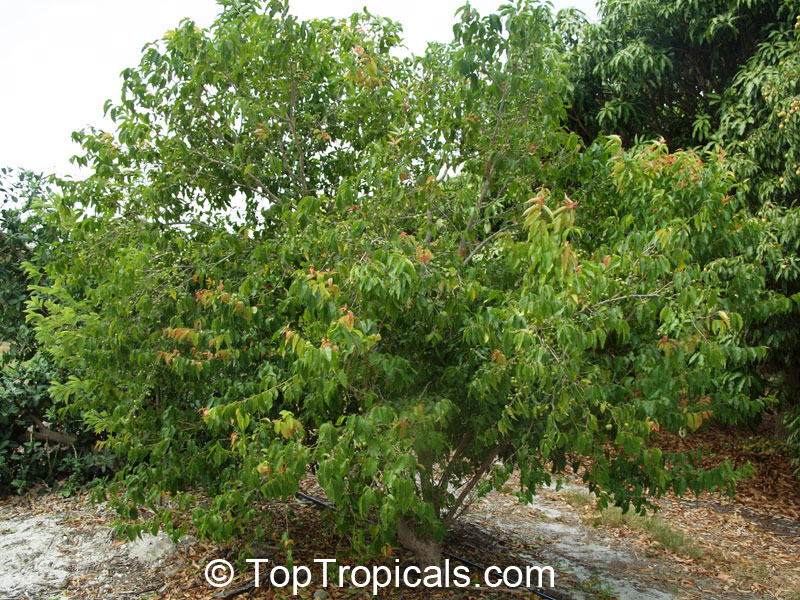
Flacourtia indica or Governors plum is a very hardy plant, able to tolerate temperatures in cold regions to 30s °F (USDA Zone: 10-11) for a short time. It can grow 5 to 10 feet tall as a shrub or 10 to 20 feet tall as a small tree. Full sun and regular watering will keep this plant at its best, with occasional deep watering to simulate natural wet periods in its native areas. It is a large shrub or small tree with a wide crown, dark and glossy leaves and either thorny or spiny branchlets, depending on the cultivar.
Governors plum produces one to two harvests of fruit a year. The fruits, when ripe, are red, deep-red, or purple, resembling a plum. They are about one inch wide and contain one or two seeds. They are sweet and sour, with a texture and flavor similar to a plum. Besides having delicious fruits, Governors Plum is packed with vitamins and minerals, like vitamin C and magnesium, and is full of antioxidants, which greatly helps in fighting inflammation, cholesterol, and diabetes. It can be eaten fresh, dried, or made into preserves and jellies.
The tree is easy to grow, self-fertile and doesn't require much care, not fussy about soil and very forgiving if you forget to water it.
Seeds germinate readily, but it takes a while until the seedling is ready to be transplanted into a big pot or in the ground, a few months.
Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE C-Cibus - Crop Nutrition Booster
SUNSHINE-Honey - sugar booster
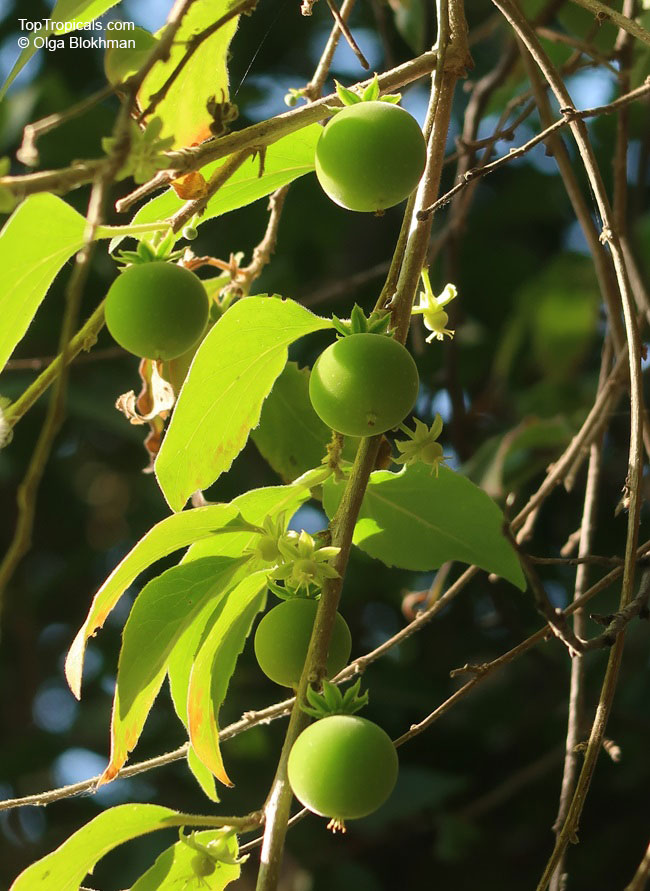
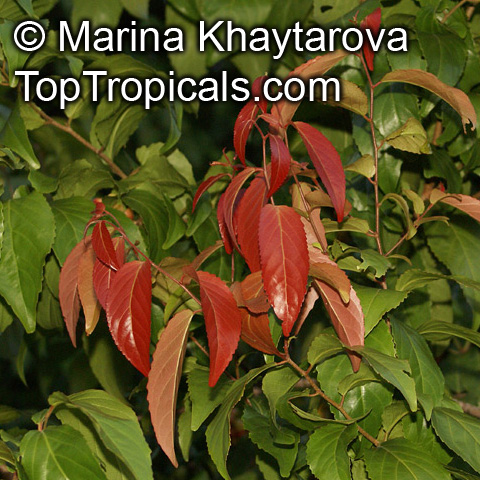
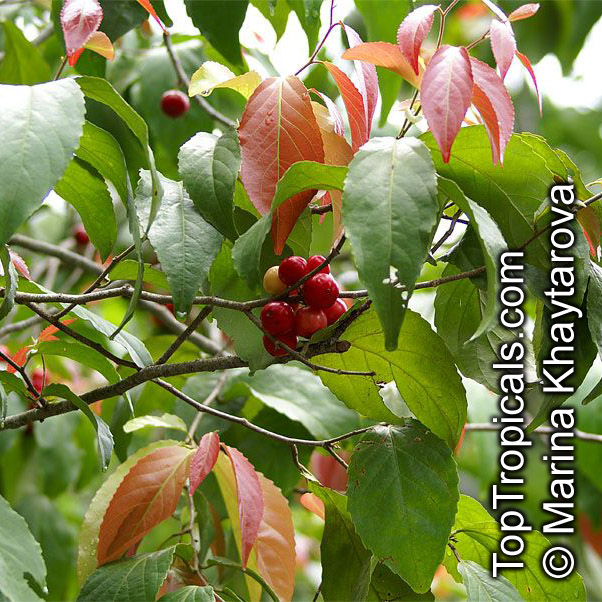
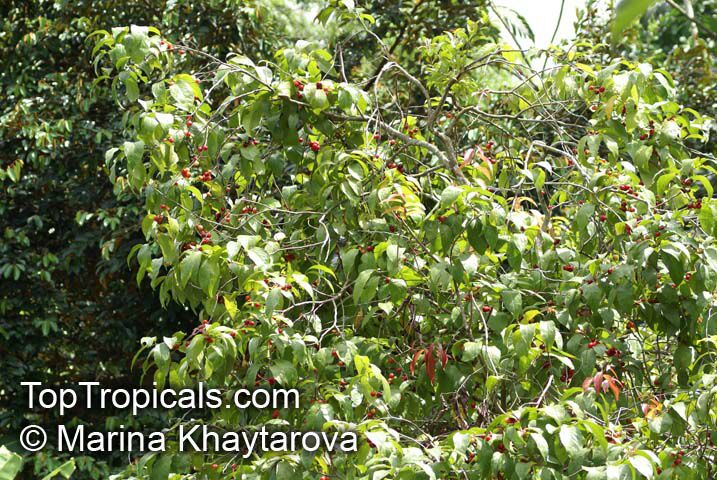
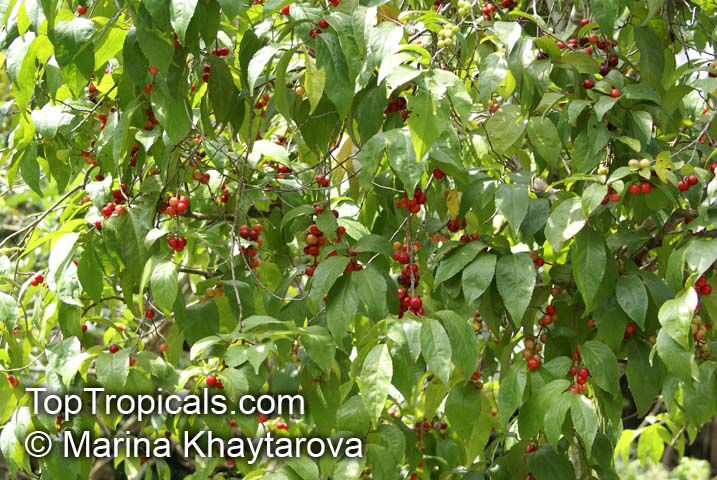
Botanical name: Flacourtia inermis
Common names: Rukam, Batoko Plum, Lori-Lori
Family: Salicaceae (Formerly:Flacourtiaceae)
Origin: Malesia





Botanical names: Flacourtia jangomas, Flacourtia cataphracta, Stigmarota jangomas
Common names: Indian Coffee Plum, Indian Cherry, Runealma Plum
Family: Salicaceae (Formerly:Flacourtiaceae)
Origin: Southeast Asia











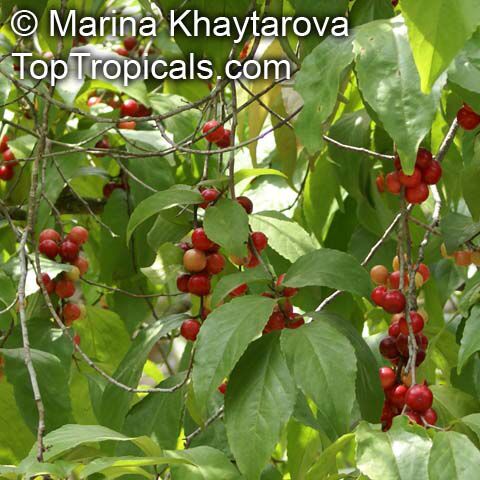
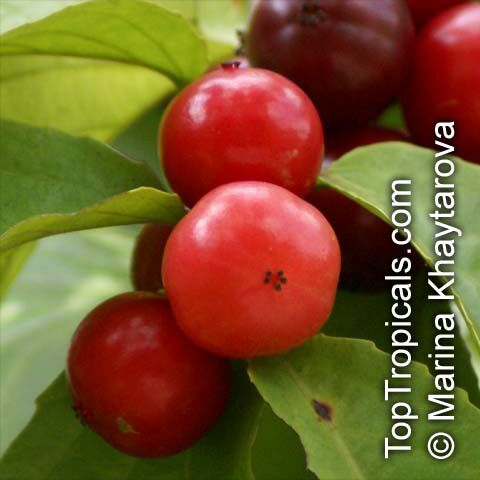
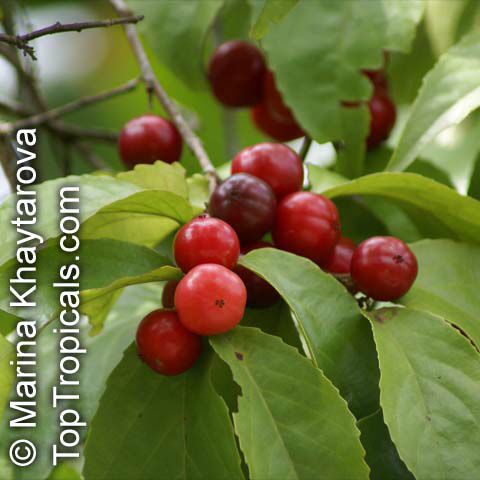
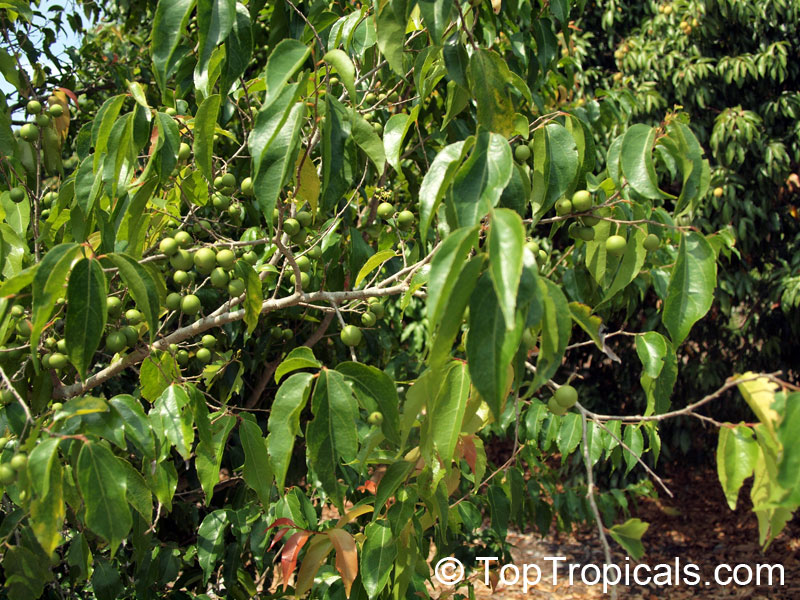
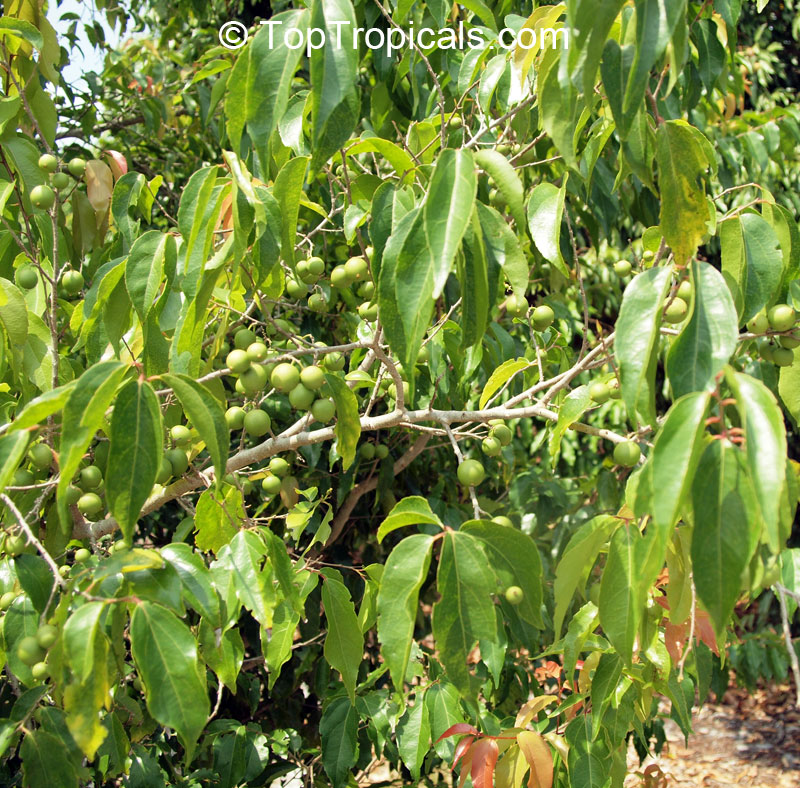
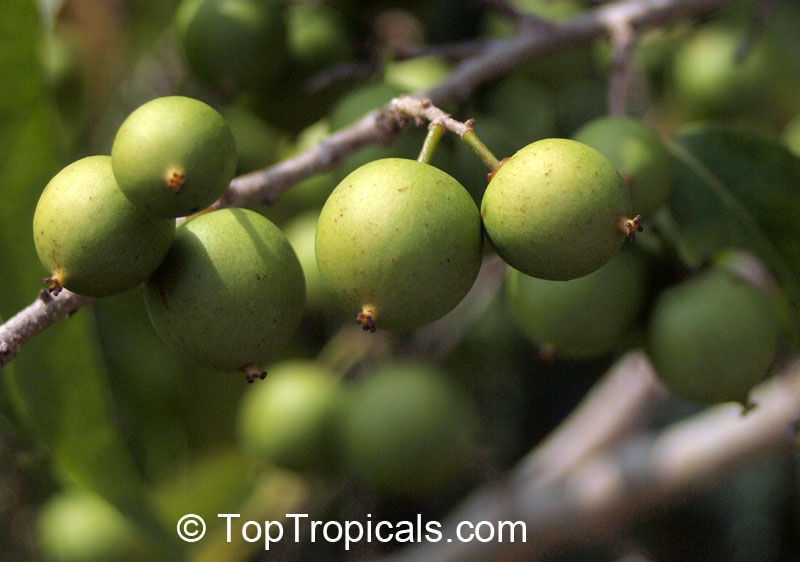
Flacourtia jangomas (Indian Coffee Plum), native to Southeast Asia, is a hardy plant that can take full sun or semi-shade and requires regular to moderate water. It takes on a large shrub form, reaching 5-10 feet in height, or a small tree of 10-20 feet. It produces small, white to off-white flowers which give way to juicy fruits that are round, pink to dark red and approximately 1 inch in width. These fruits are edible and are often used in jams, as well as for their ethnomedical uses.
This deciduous plant is cold hardy, thriving in USDA plant hardiness zones 9-11. Its versatile nature makes it a perfect addition to many landscapes, and it is believed to bring a long lifespan of beauty and usefulness. It can also be grown in pots in colder regions.
Health wise, Flacourtia jangomas is packed with many vitamins, minerals, and electrolytes that are essential for a healthy diet. It has significant amounts of vitamin A and C and notable levels of minerals such as calcium, iron, and dietary fiber. In addition to the vitamins and minerals, Flacourtia jangomas has a high content of antioxidants, said to reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and diabetes.
The fruits are easily harvested from the branches when ripe and are a delicious, juicy treat. The fruit can be eaten raw or cooked, and can also be used to make jams, jellies, and juices. All of the parts of the tree have medicinal uses, yet the bark has the highest potency.
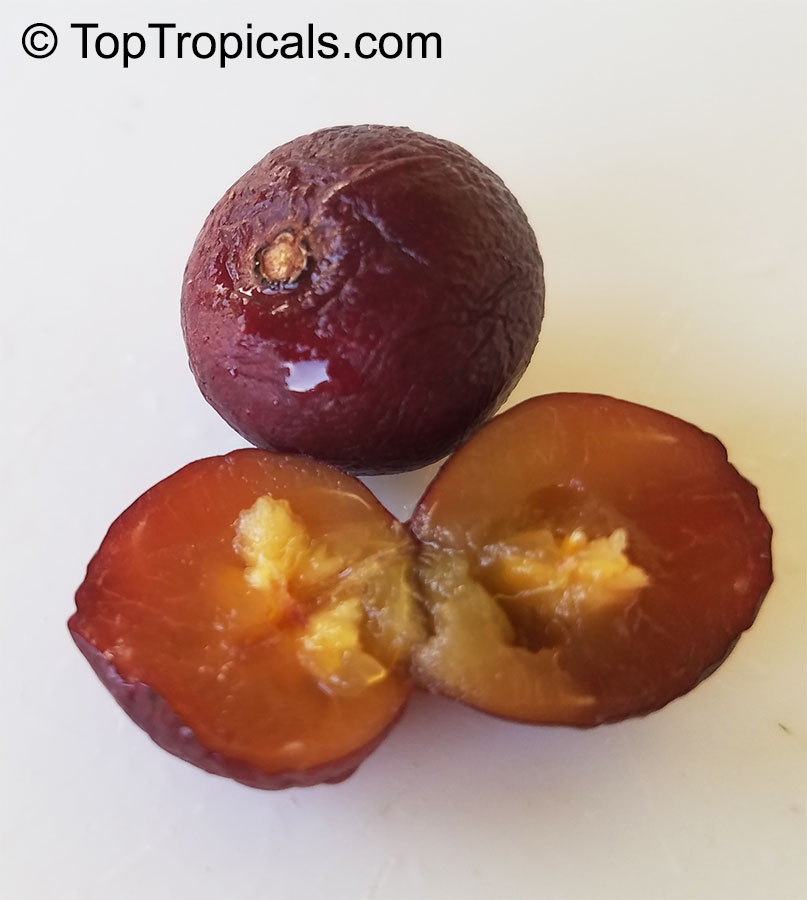
Botanical names: Flacourtia rukam, Flacourtia euphlebia
Common name: Rukam
Family: Salicaceae (Formerly:Flacourtiaceae)
Origin: Malaysia








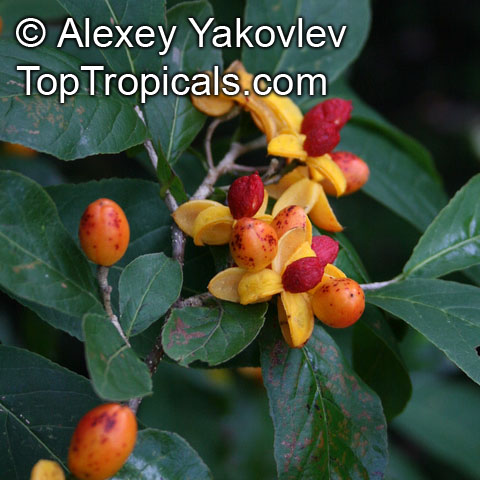
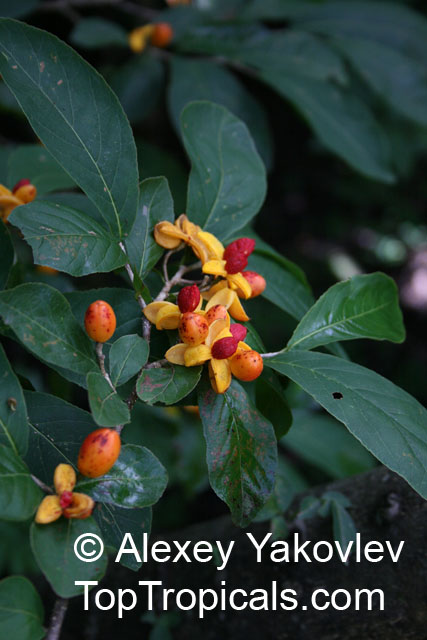
Rukam (Flacourtia rukam) is a tropical fruit tree that is native to Southeast Asia, but has also been introduced to Thailand and India. It grows best in USDA Zone 9-11 and thrives in humid conditions. The tree can be grown in a container and should be placed in a location with full sun or partial shade, and given regular watering. It is recommended to fertilize the tree with a slow-release fertilizer twice a year in the spring and summer, and to prune it selectively to control its shape and size. The tree can reach a height of 10-20 feet when fully mature.
Rukam is known for its abundant yellow and orange flowers which attract butterflies and hummingbirds. The tree also produces an edible fruit that is light green to pink or purplish-green to dark red in color, with a whitish, juicy, and acidic pulp. The ripe fruit can be eaten raw or used in dishes such as rujak (a fruit salad with spicy sauce), pickled, or made into jam or confectionaries. The young leaves of the tree are also edible and can be eaten raw in side dishes.
In addition to being an ornamental plant, Rukam is also used in traditional medicine. The young leaves, fruits, and roots of the tree are used to treat a variety of ailments. A root decoction is taken by women after childbirth, and the juice of the leaves is applied to inflamed eye lids. Rukam trees can produce a large amount of fruit, with some varieties producing up to 500 fruits in a season. These fruit are not only tasty, but are also rich in vitamins and minerals.
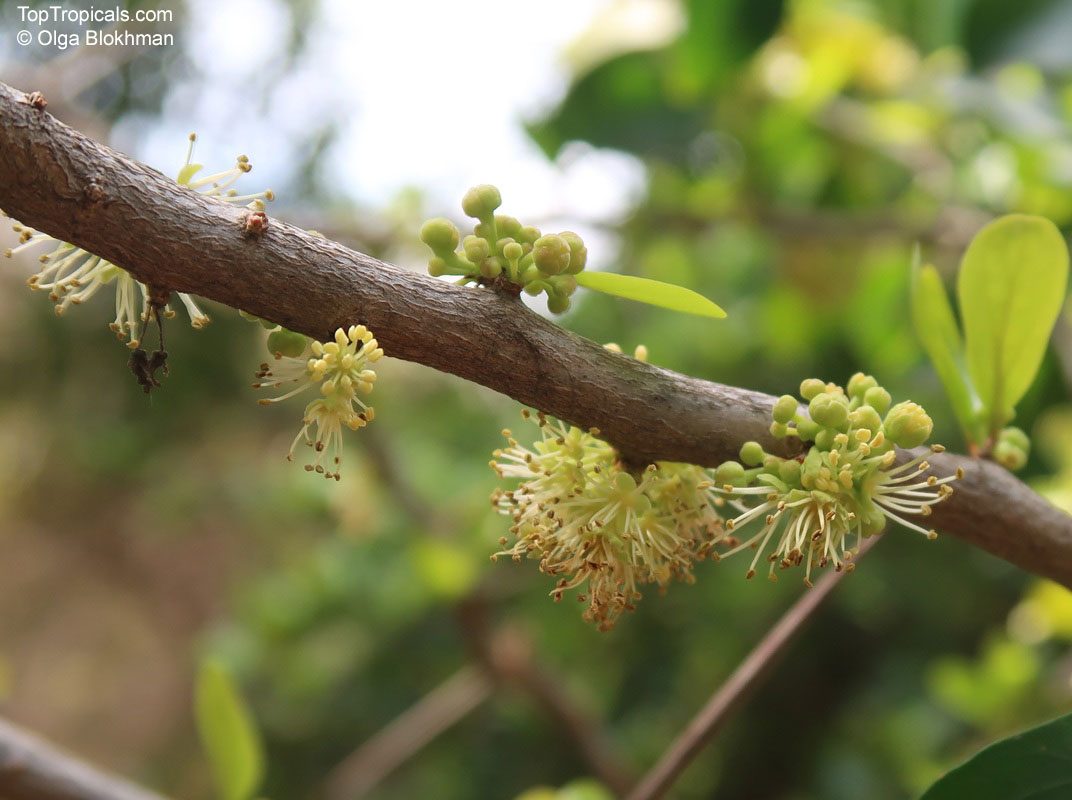
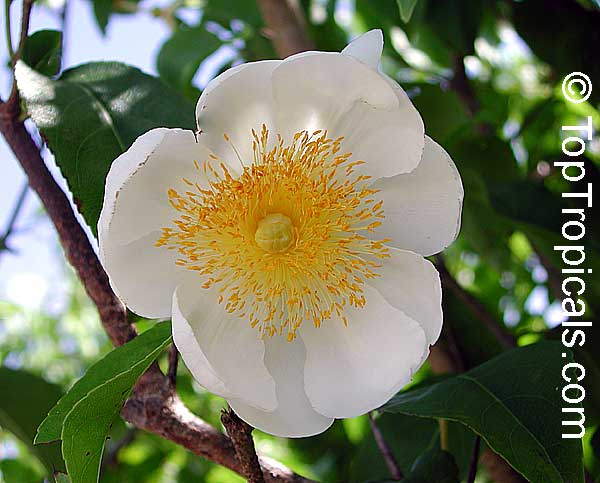
Botanical name: Kiggelaria africana
Common name: Wild peach
Family: Salicaceae (Formerly:Flacourtiaceae)
Origin: South Africa








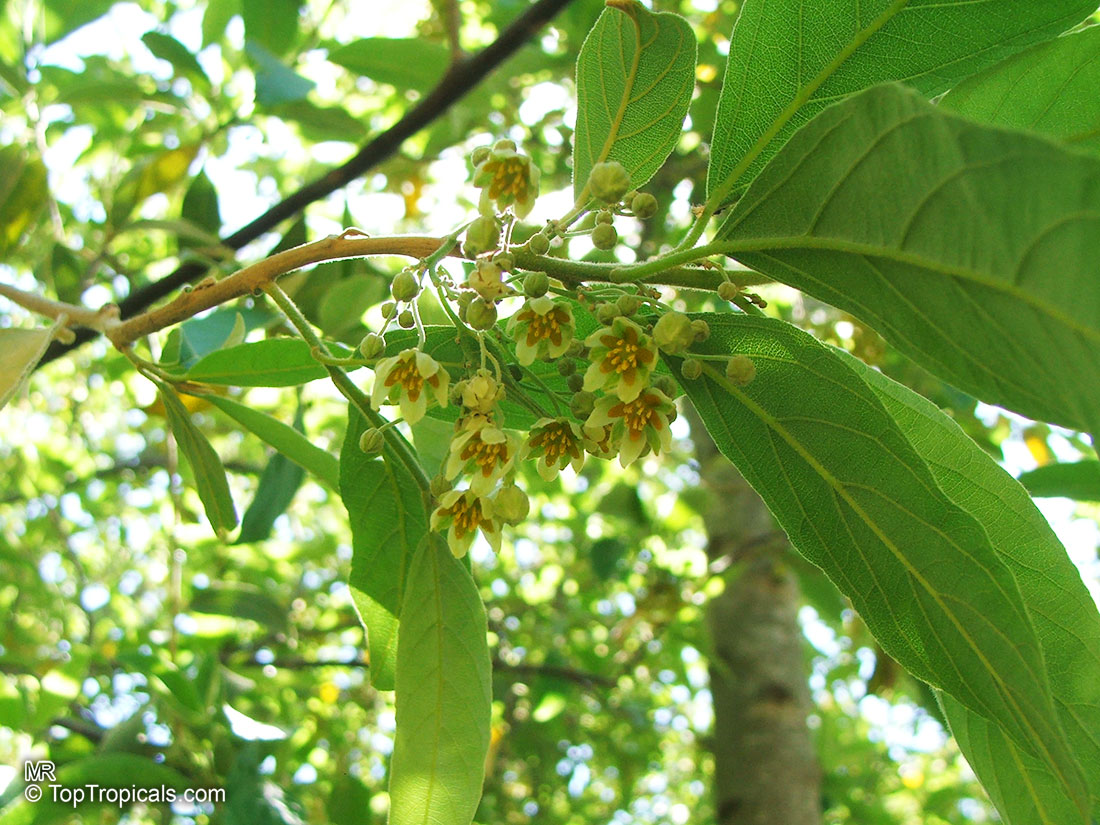
Well-shaped and reasonably robust, the low-branching, wild peach has smooth, pale grey bark that becomes rough with age. The variable leaves of this evergreen tree may resemble those of the peach. The tiny, bell-shaped flowers which bloom from August to January (spring to summer), are yellow-green, with male and female flowers on separate trees. The hard, round, knobbly, greenish yellow capsule which forms in February to July (late summer to mid-winter) splits to expose shiny black seeds, enclosed in an oily, sticky, bright orange-red coat.
The hardish, pink-brown wood is a useful general purpose timber (beams, floorboards, furniture).
Reasonably frost-hardy, it likes a moderate amount of water, and a place in the sun. Always add plenty of compost to the soil when planting, and apply a thick mulch layer (organic material, e.g. dried leaves) to protect the surface of the soil. This tree grows in both summer and winter rainfall areas. It tolerates temperatures ranging from about - 2 C to +36C.
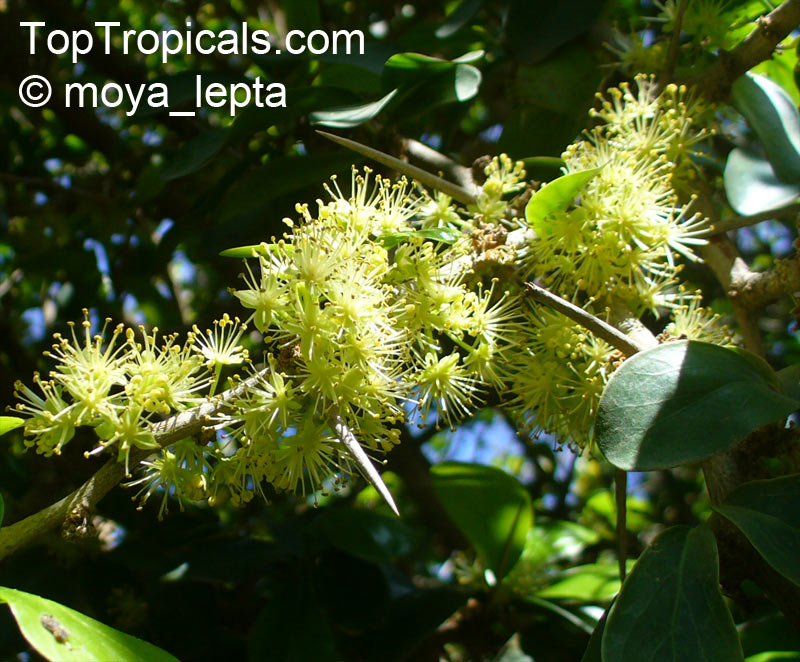
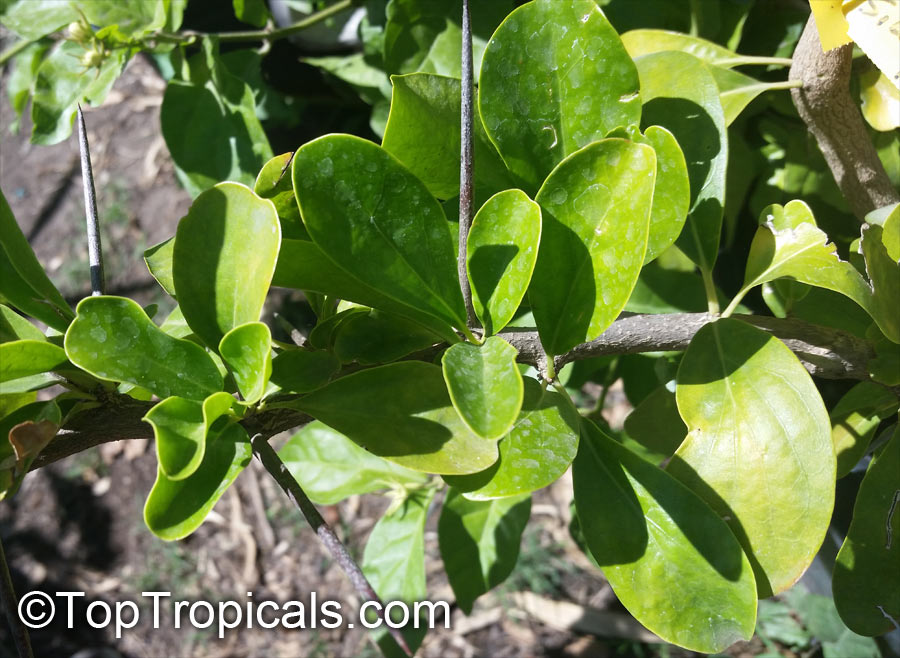
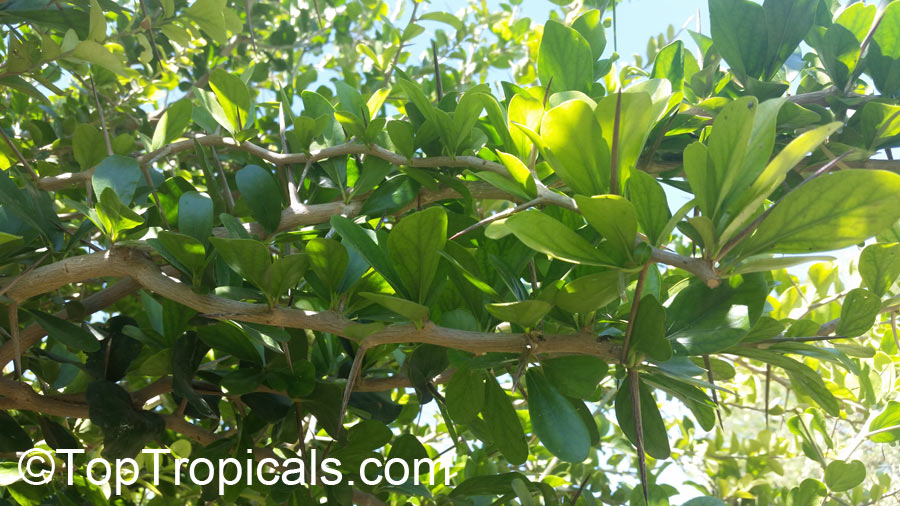
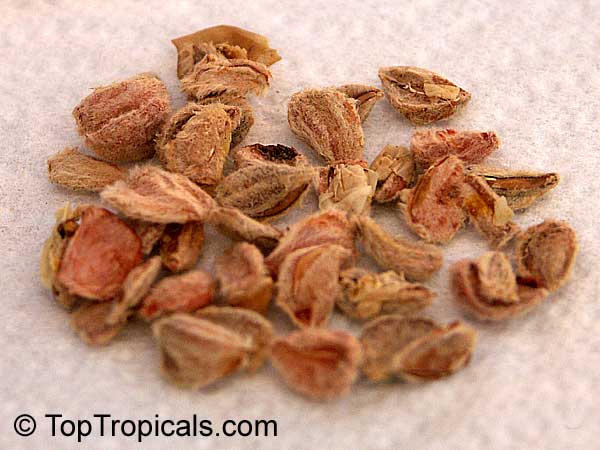
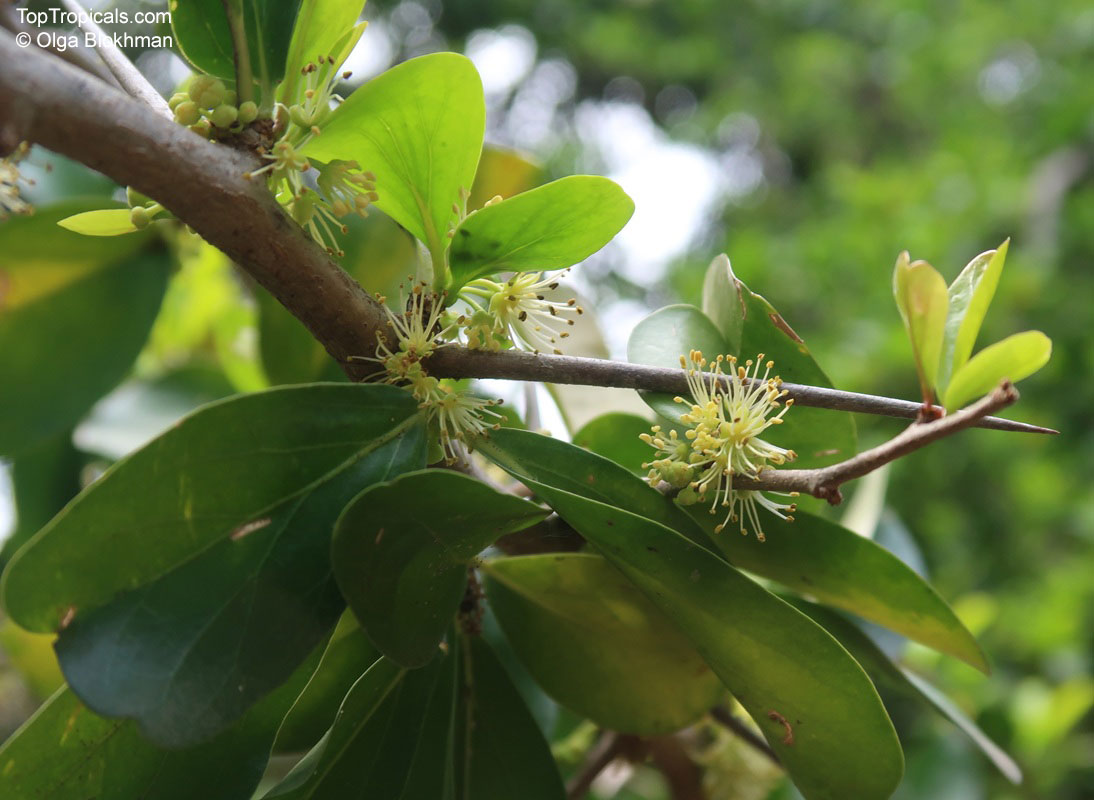
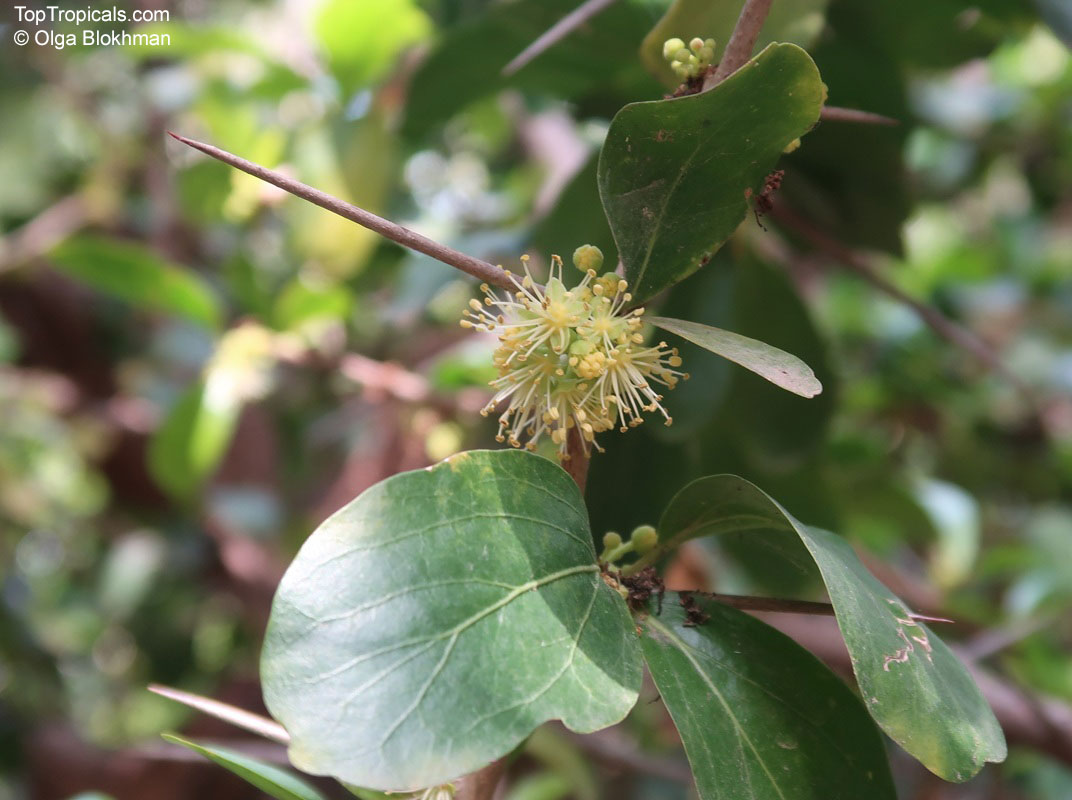
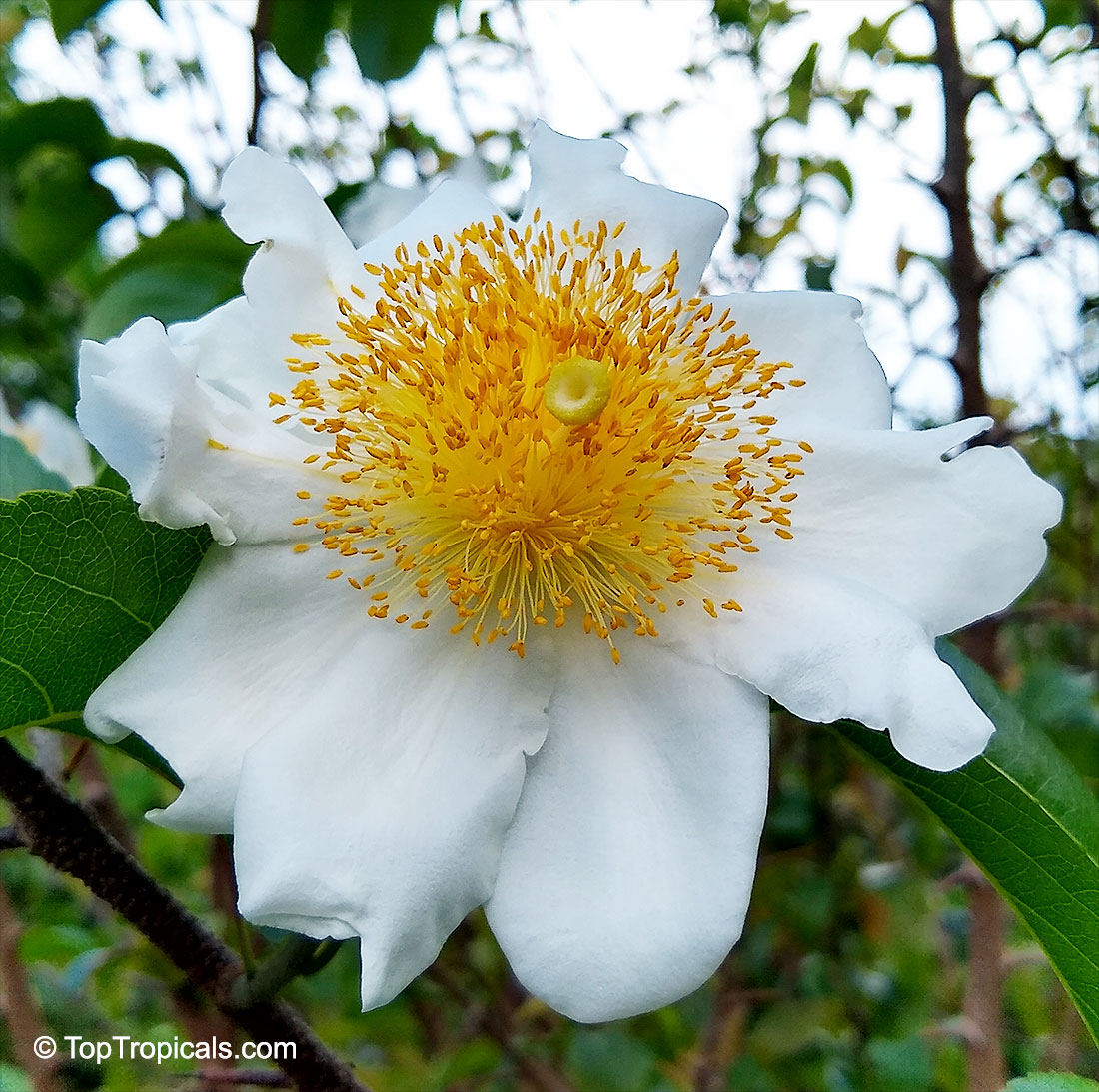
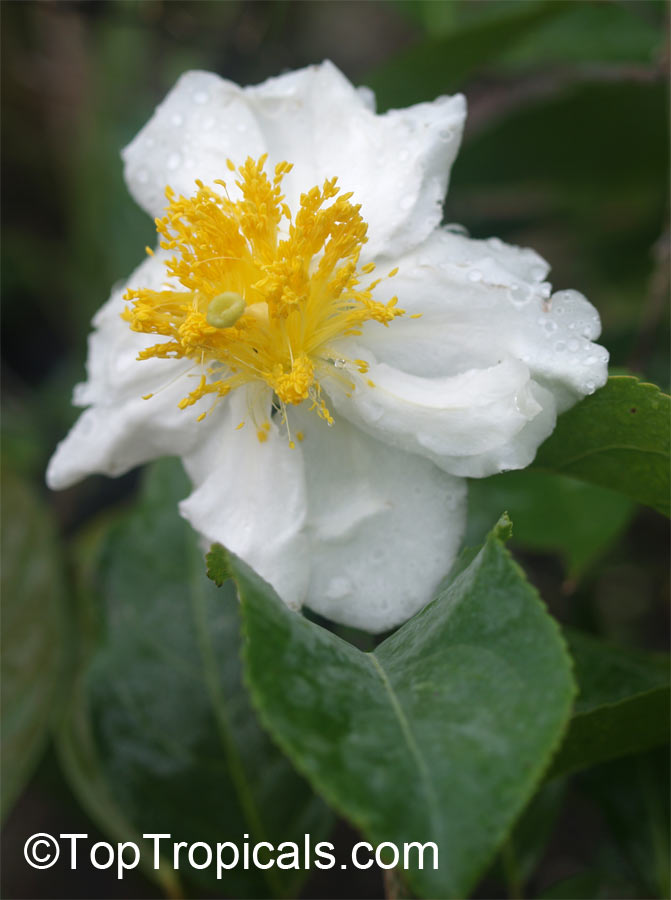
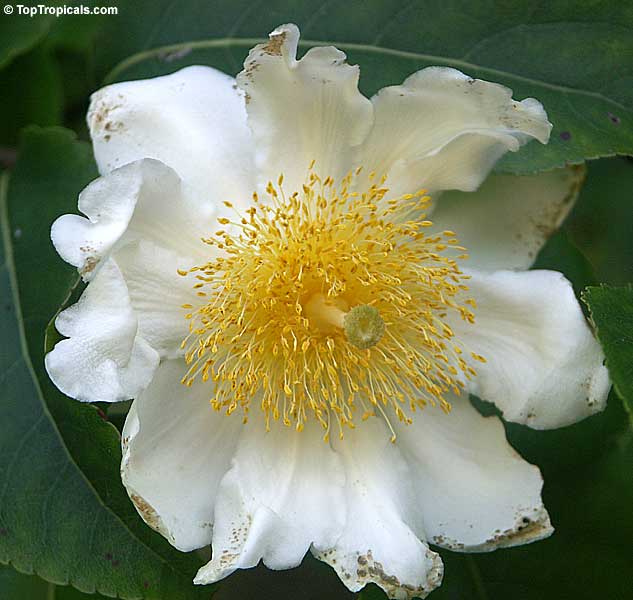
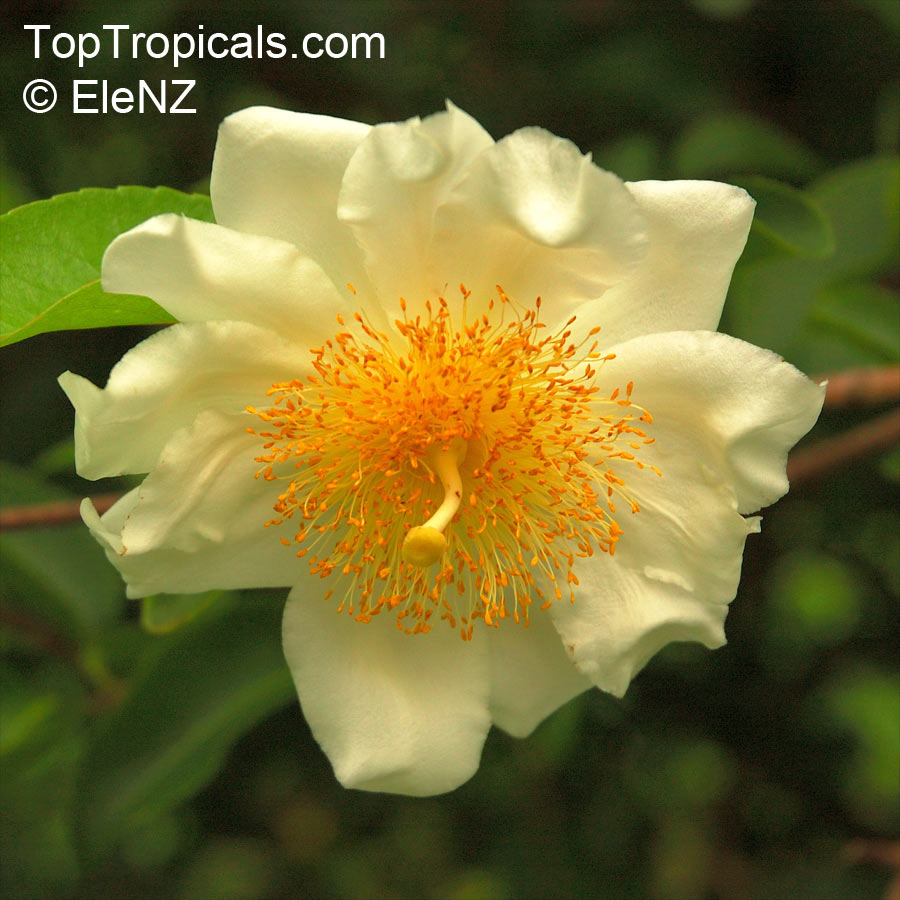
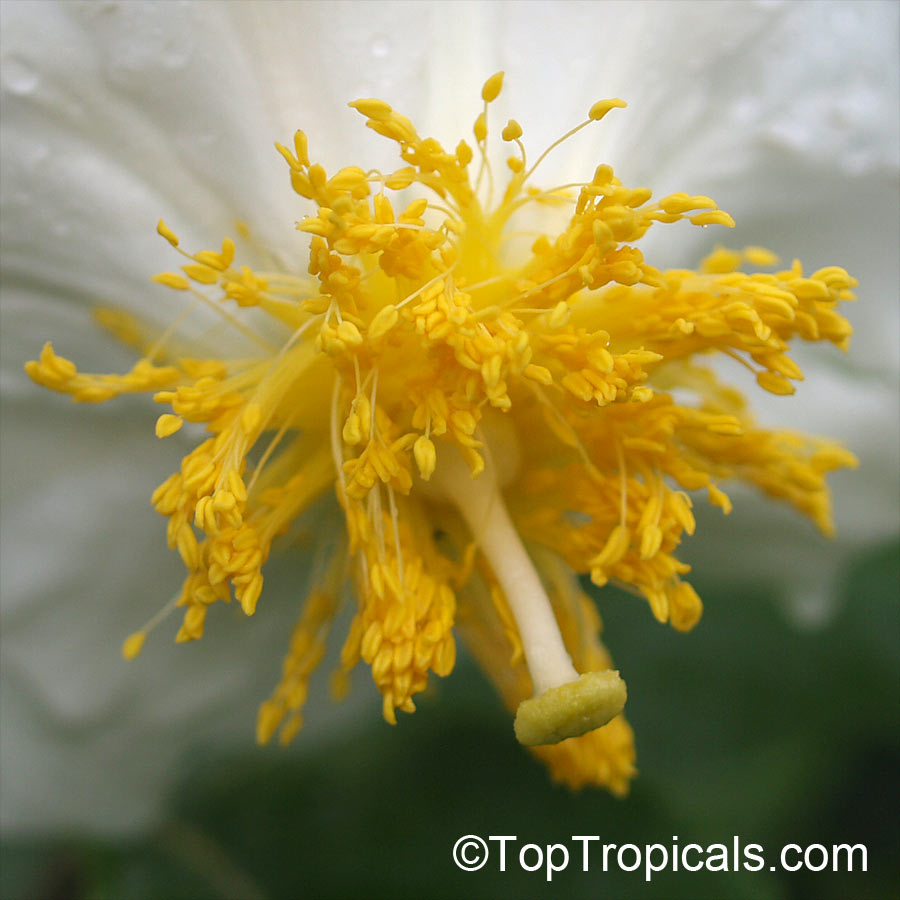
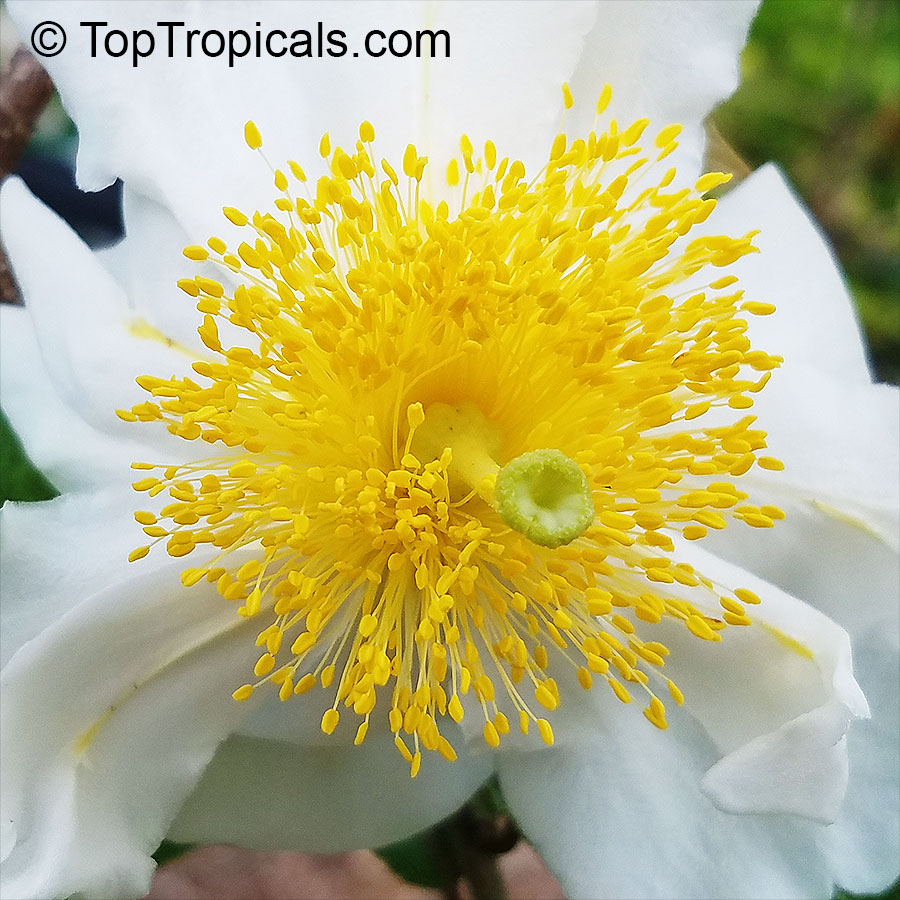
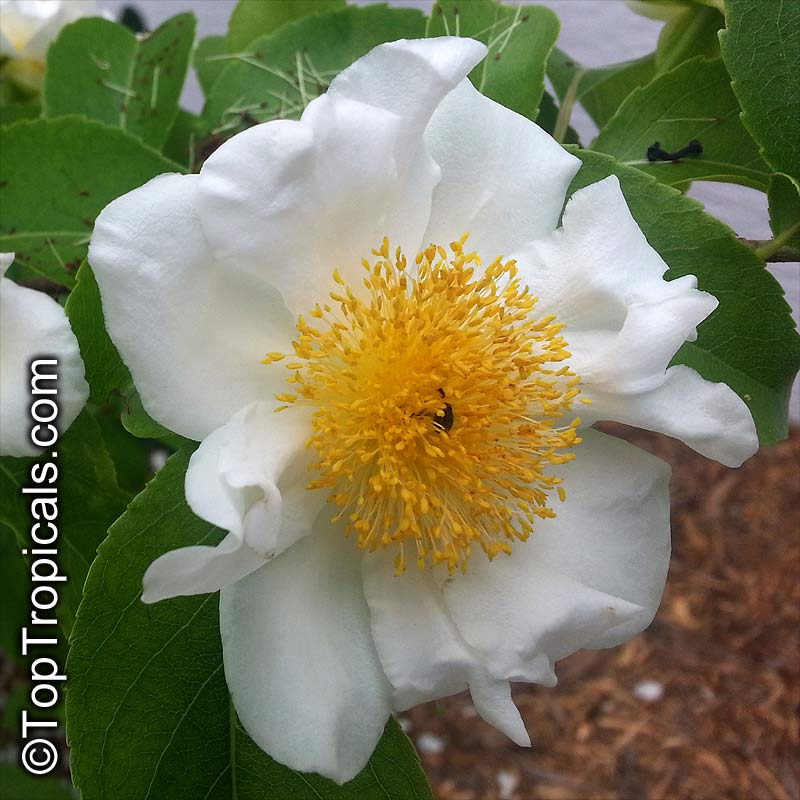
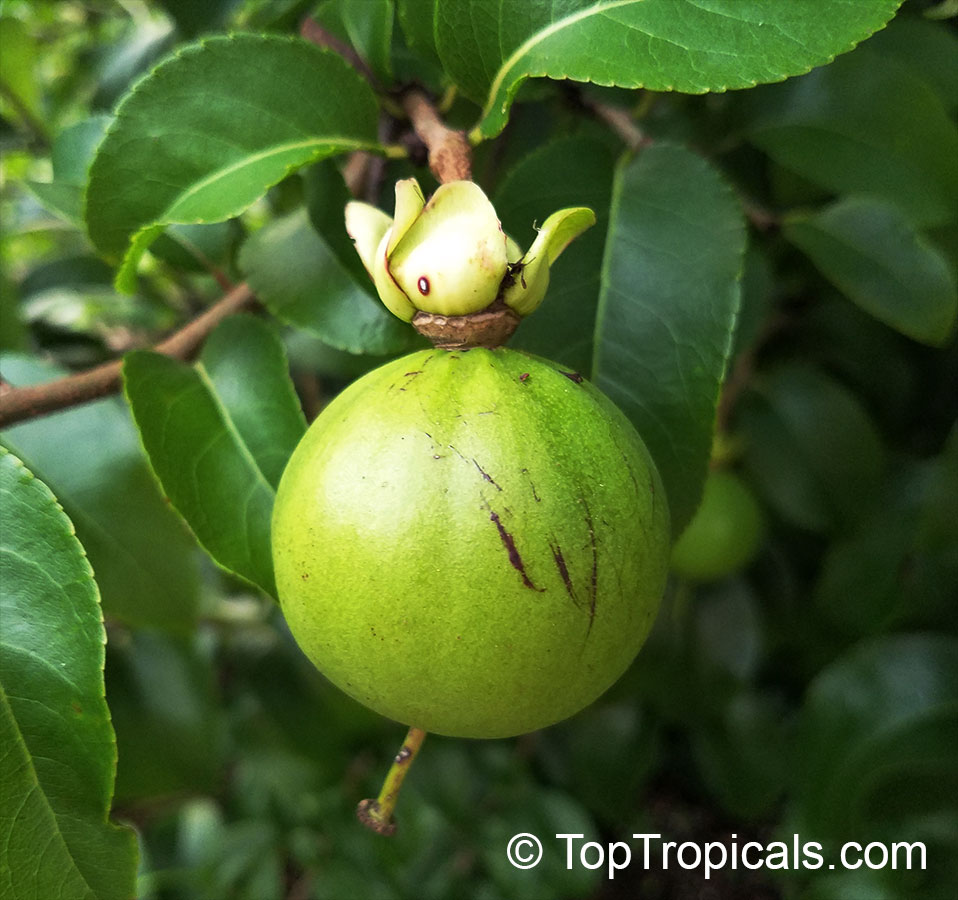
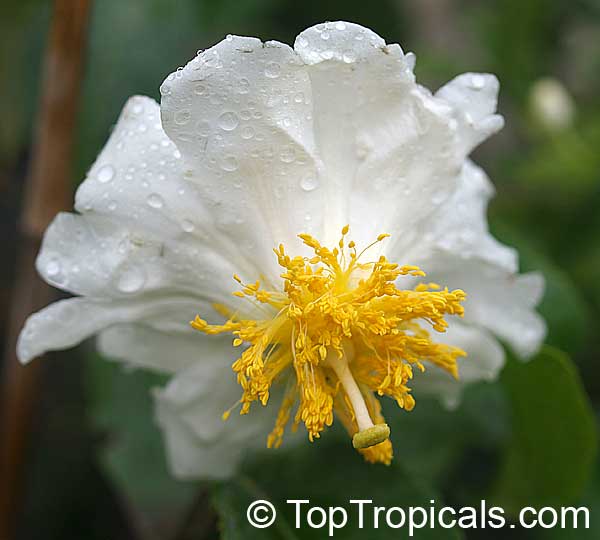
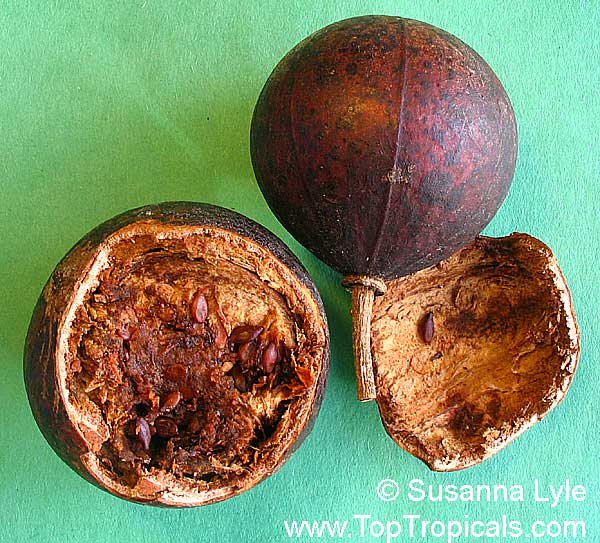
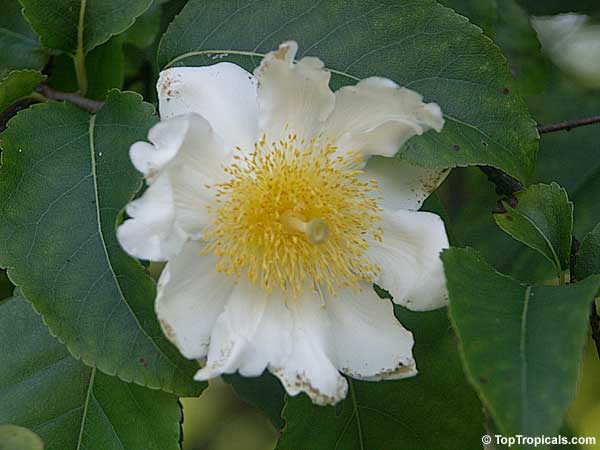
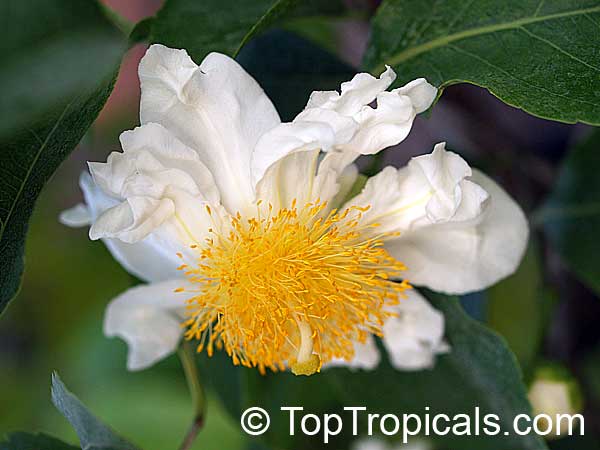
Botanical name: Oncoba spinosa
Common names: Fried Egg Tree, Snuff-box Tree
Family: Salicaceae (Formerly:Flacourtiaceae)
Origin: South Africa, Arabia












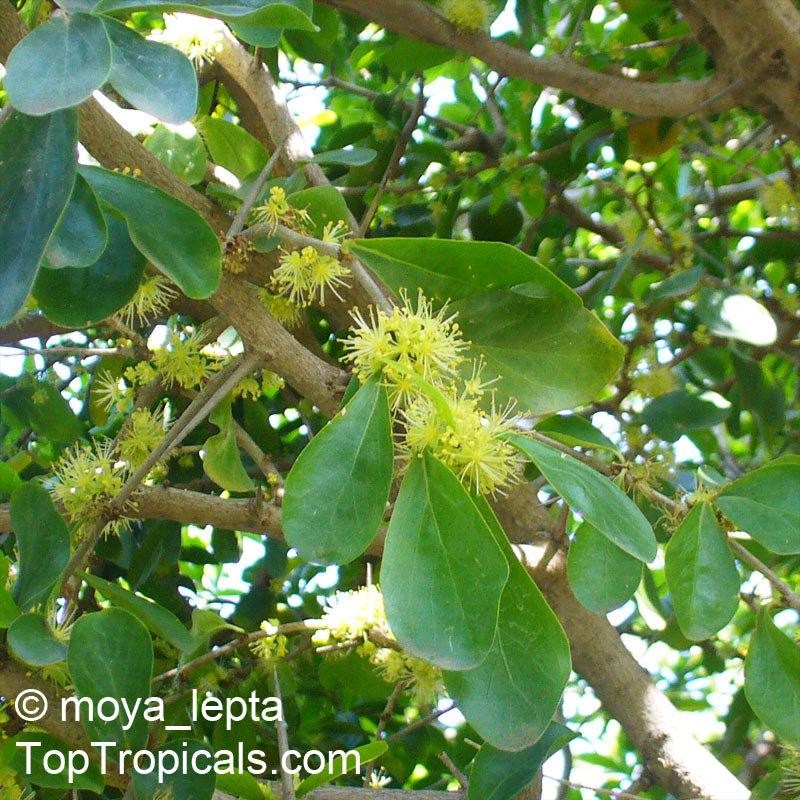
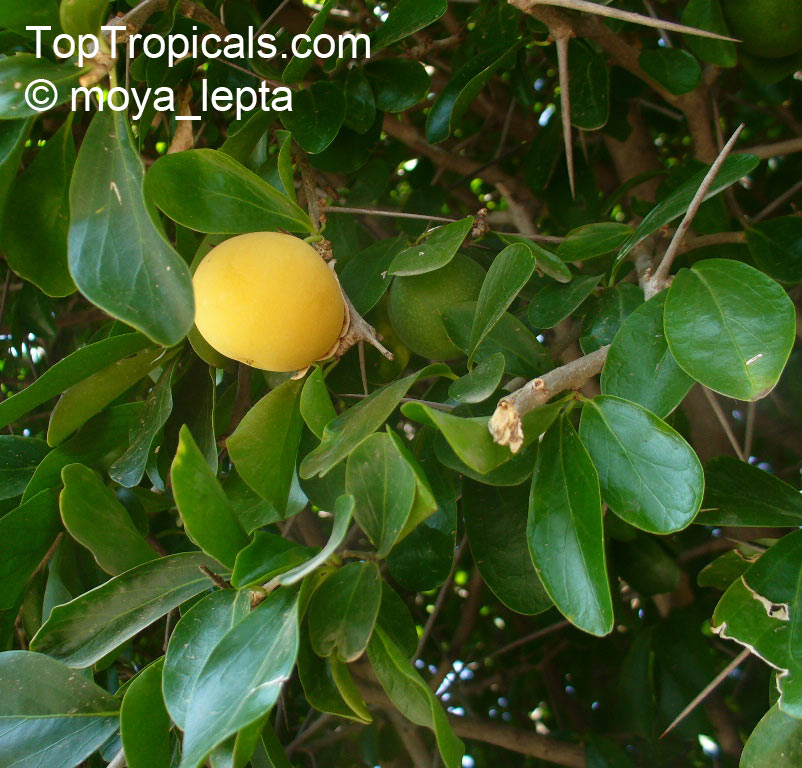
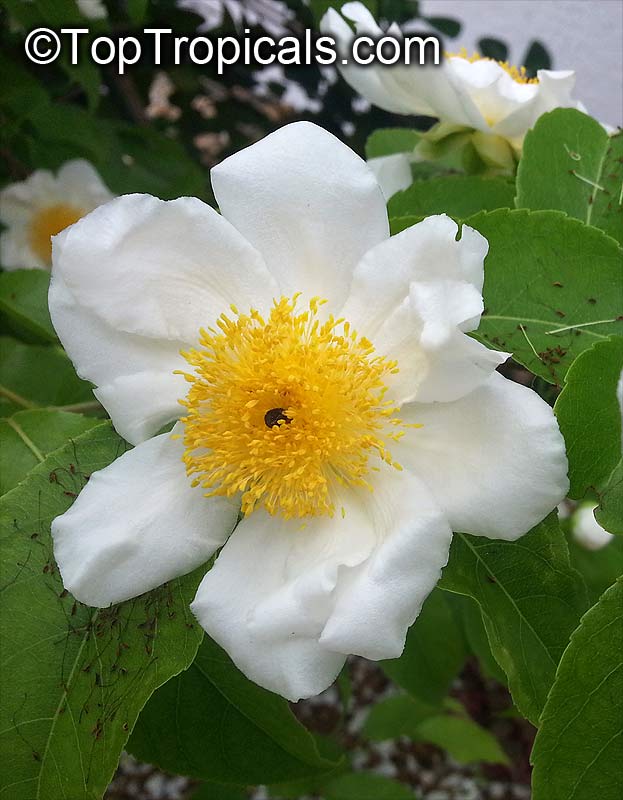
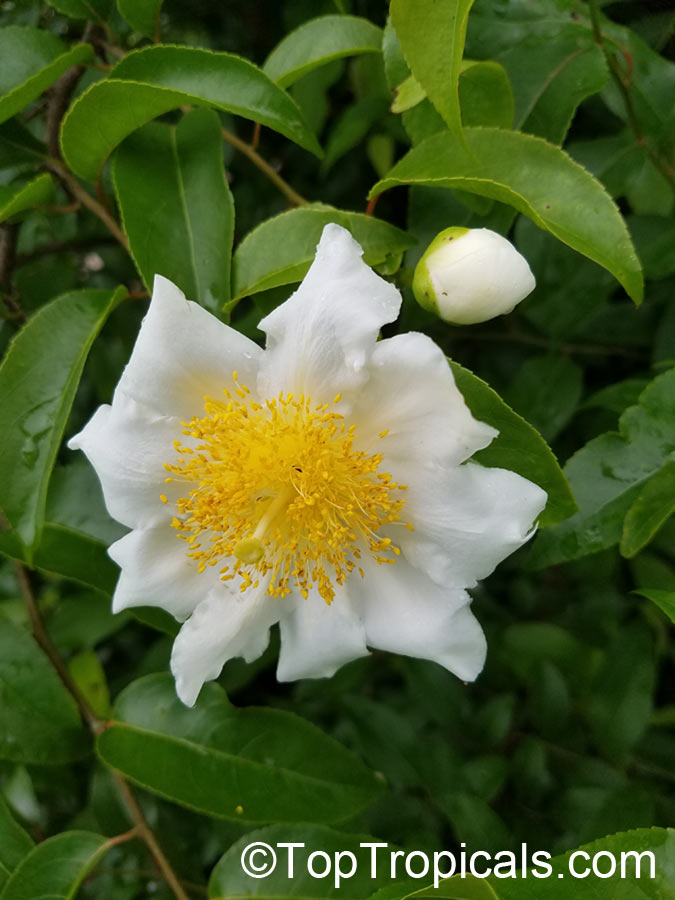
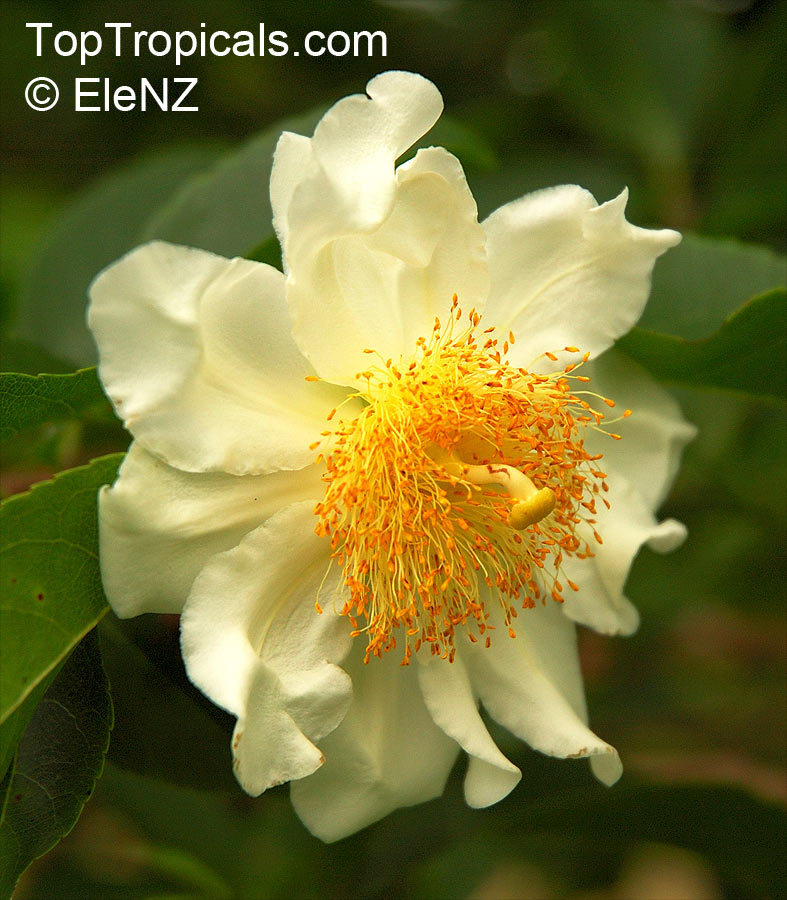
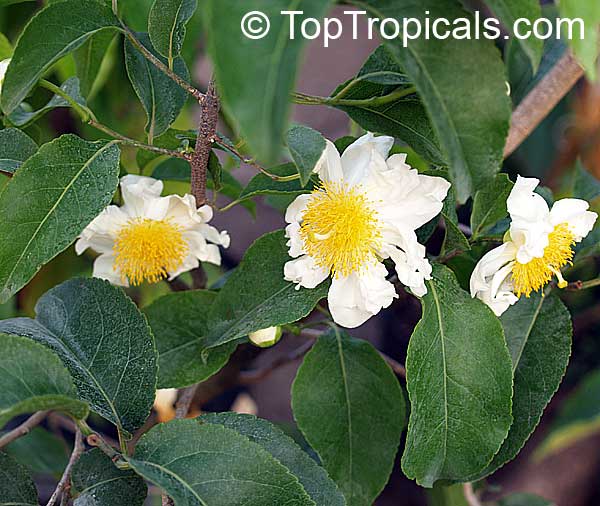
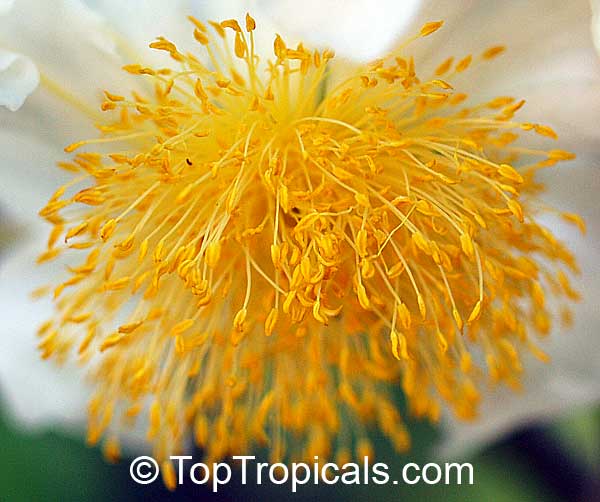
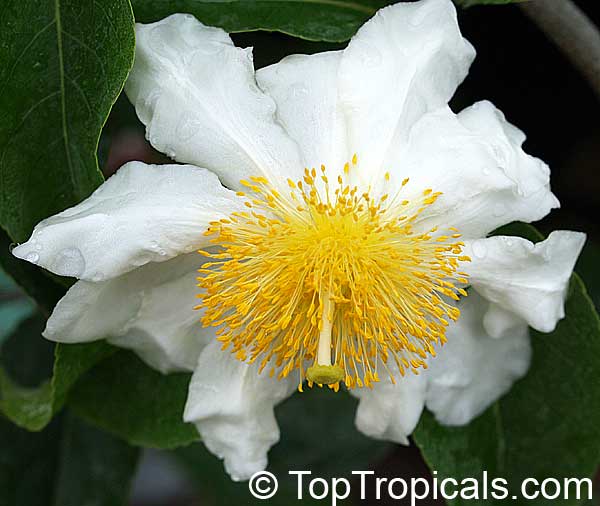
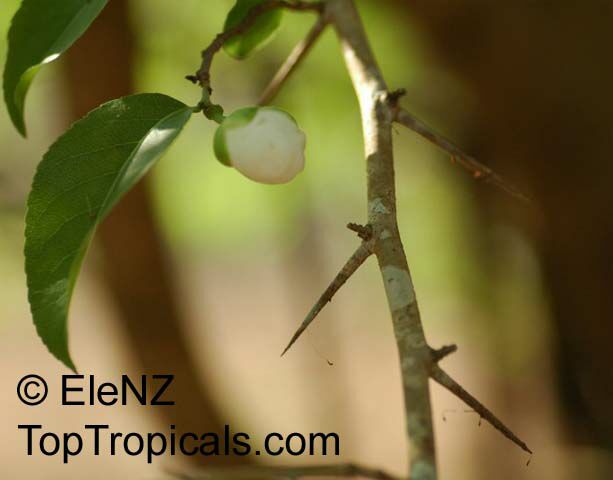
A spiny shrub or small tree. The flowers are white, honey-fragrant and solitary (3" across). The fruits have a sour, edible pulp. Beautiful white and yellow camellia-like flowers look like 'fried eggs' when they drop off and fall on the ground with their yellow stamens facing upwards. Light tip pruning promotes bushy growth. Flowers attract butterflies. Blooms late spring to summer. The hard-shelled fruits are used as snuff boxes. If the fruit are left to dry with the seeds inside they it make amusing rattles for children and are also used as anklets and armlets for dancers to add rhythm when performing. The pulp of the fruit is edible, but is seldom used for that purpose. In African medicine the roots are used in the treatment of dysentery and bladder complaints. It is said that the seeds contain a drying oil that is suitable for varnish, but it is too difficult to extract to be of any commercial significance. The wood is light brown in color and can take a good polish, but the pieces are seldom large enough to be of any commercial value.
Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Megaflor - Bloom Nutrition Booster
| Next |  |
Use link to repeat this search:
https://toptropicals.com/cgi-bin/garden_catalog/cat.cgi?search_op=and&keyword_op=and&language=e&family=Salicaceae&number=10
&no_change_lang=1&user=tt&sale=1&first=0































 SUNSHINE C-Cibus (NPK 2-2-4) - Crop Booster for every watering.
SUNSHINE C-Cibus (NPK 2-2-4) - Crop Booster for every watering.  SUNSHINE C-Cibus (NPK 2-2-4) - Crop Booster for every watering.
SUNSHINE C-Cibus (NPK 2-2-4) - Crop Booster for every watering.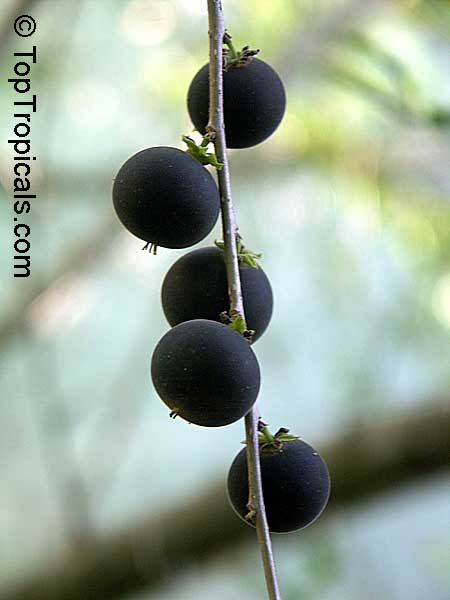 
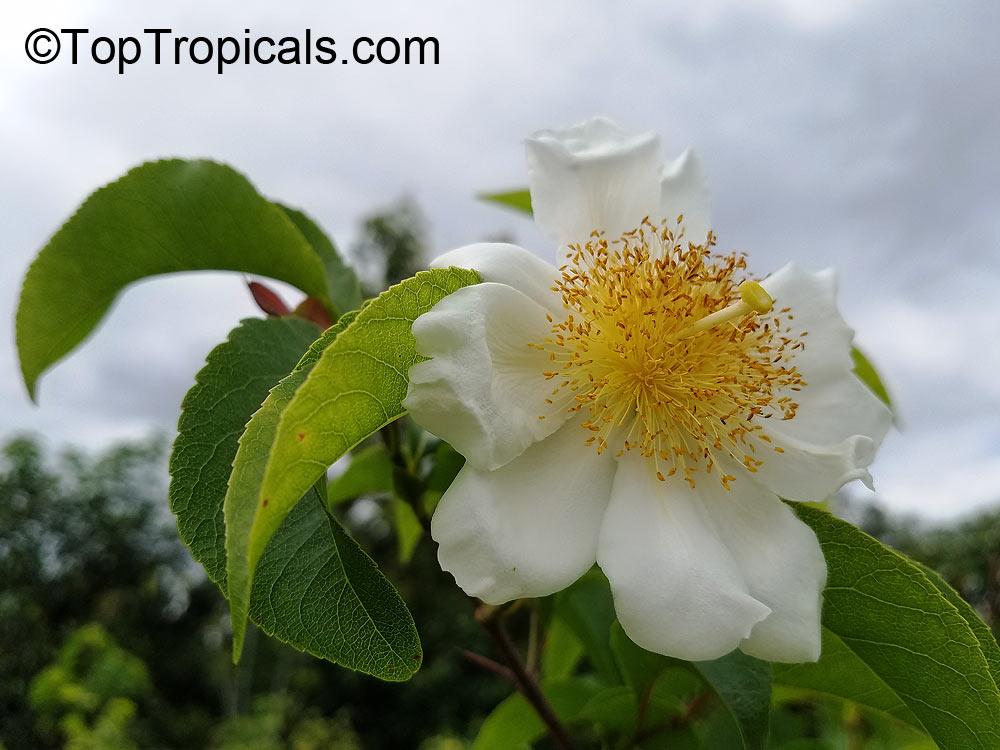
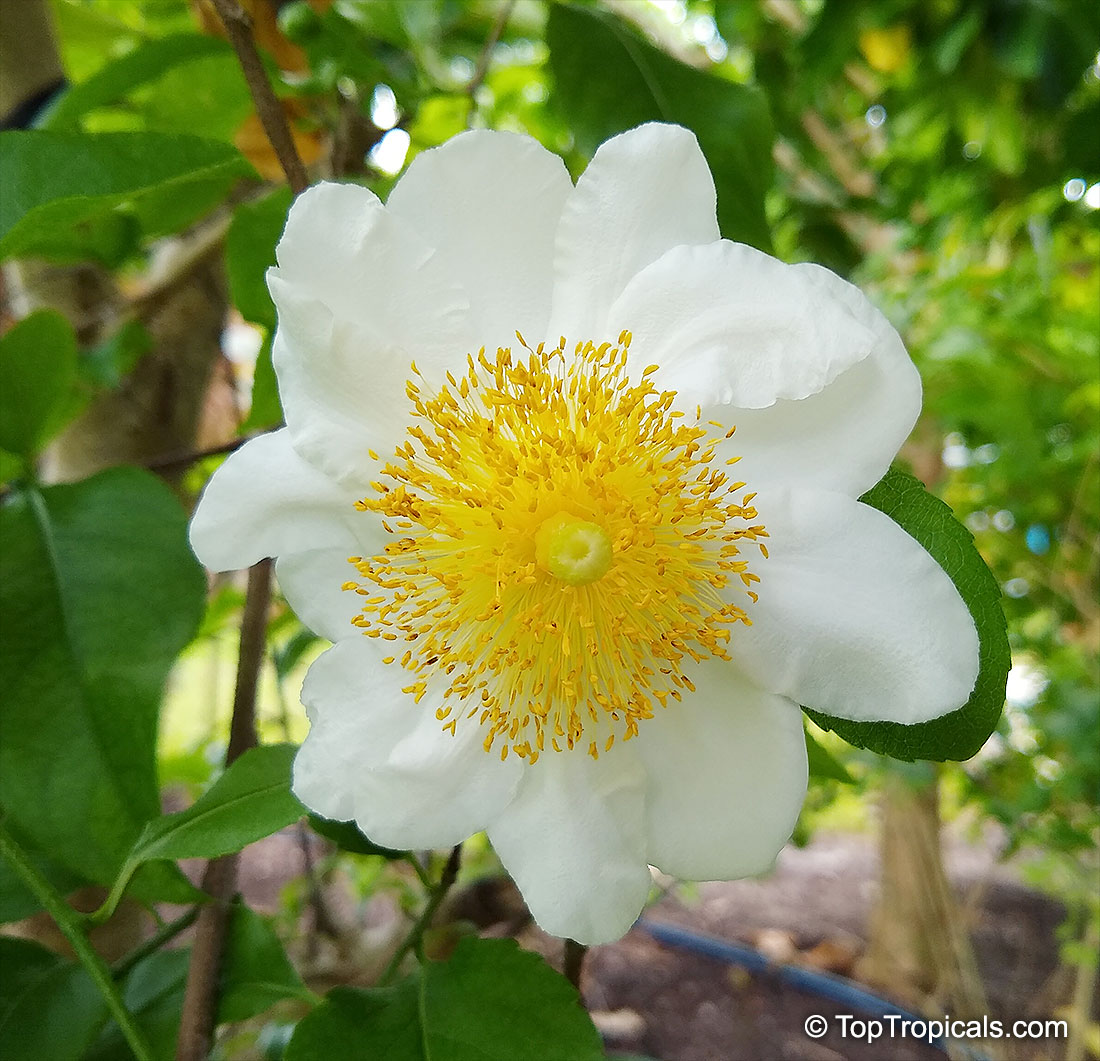






























































































 SUNSHINE Pikake (NPK 2-2-4) - eco-friendly concentrated nutrition booster for fragrant flowers. Improves quantity and quality of flowers. Encourages profuse blooming. Increases flower fragrance intensity. Can be used with every watering. For best results, use in combination with
SUNSHINE Pikake (NPK 2-2-4) - eco-friendly concentrated nutrition booster for fragrant flowers. Improves quantity and quality of flowers. Encourages profuse blooming. Increases flower fragrance intensity. Can be used with every watering. For best results, use in combination with