Featured plant - a special for your collection
Syzygium jambos, Rose Apple - a Sacred Tree of Enlightenment from the Land of Jambudvipa
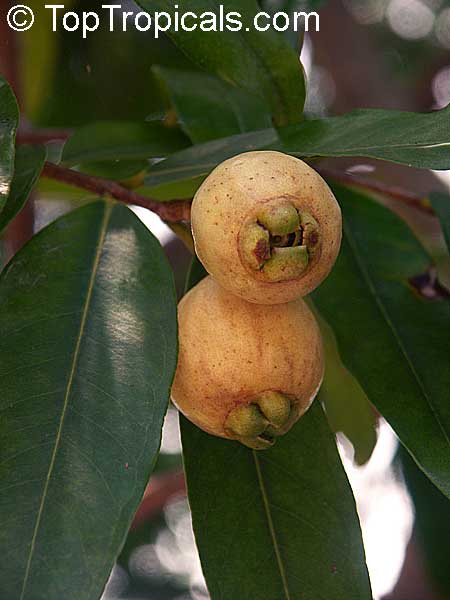

Scientific names and synonyms: Syzygium jambos, Eugenia jambos, Jambosa jambos, Jambosa vulgaris, Caryophyllus jambos.
Family: Myrtaceae
Common
names: Rose Apple, Malabar Plum, Jambu, Chom pu, Chom-phu, Pomme
Rosa, Pomme Rose, Pommier Rose, Poma Rosa, Pomarrosa, Manzana
Rosa, Manzanita de Rosa, Bodhi Tree
Alternate names: Jambosier by French-speaking
people, Plum Rose or Malabar Plum in the English-speaking West Indies,
Pommeroos or Appelroos in Surinam, and Jambeiro or Jambo Amarelo in
Brazil; Jaman in India, and Yambo in the Philippines.
Origin: SE Asia and Malaya
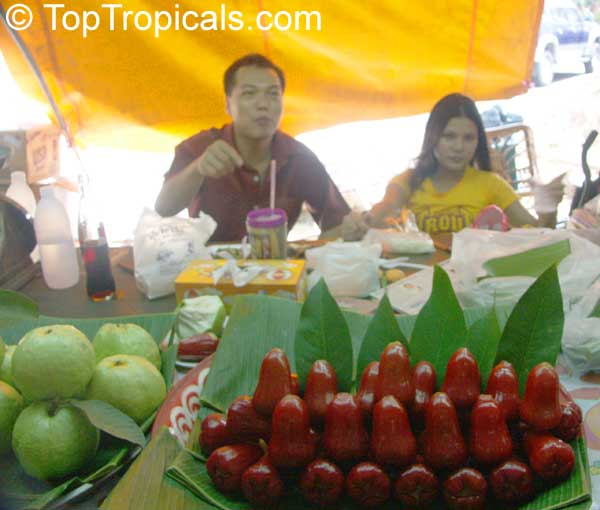
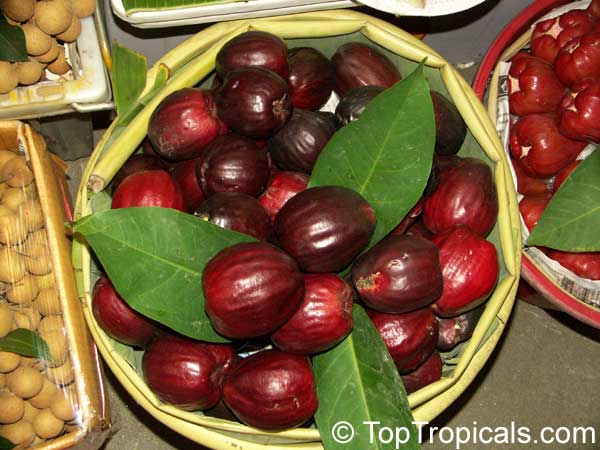
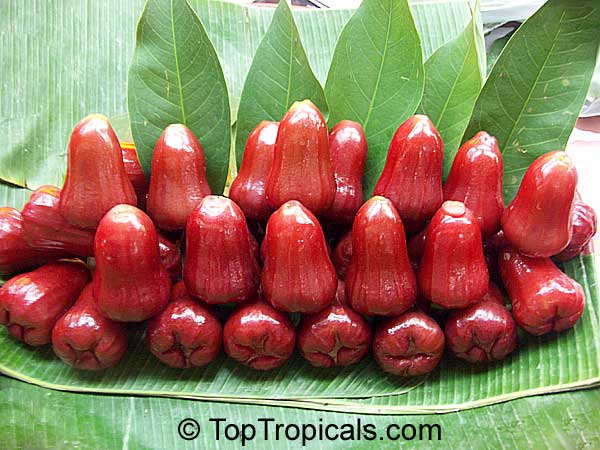
Rose apple is a popular fruit native to Southeast Asia. The beautiful blossoms contain hundreds of showy stamens. The crisp and juicy fruits are very distinctly rose scented and highly prized for jellies and confections. The plant is easy to grow, moderately cold hardy and tolerates poor soils. Makes an attractive, wide-spreading shade tree as well as compact and bushy contaner fruiting plant.
 Many
visitors of Southeast Asia have seen, and perhaps tasted, the rose
apple as it
is available there at fruit markets. More popularly
known in Thailand as the Jambu (or Chom-poo) Tree, it is a
multibranched attractive tropical evergreen tree that grows
approximately 25ft, with juicy, rose scented fruit.
Many
visitors of Southeast Asia have seen, and perhaps tasted, the rose
apple as it
is available there at fruit markets. More popularly
known in Thailand as the Jambu (or Chom-poo) Tree, it is a
multibranched attractive tropical evergreen tree that grows
approximately 25ft, with juicy, rose scented fruit. The flesh is a bit softer than that of an apple. It tastes like a cross between apple and watermelon, with a very mild rose scent and aftertaste. Its decorative appearance guarantees it a prominent place on any fruit platter during the peak season between June and September.
Rose Apple Tree (Jambu Tree, Enlightenment Tree) is sacred to Buddhism

Under the Tree of Enlightenment
In ancient Sanskrit, the land now called India was referred to by the
ancient Indians themselves as Jambudvipa, which means Rose-apple-land
(jambud = rose apple; vipa = land).
With its thick, leathery leaves and great span of branches, the Jambu
Tree offers great shade and coolness against the sun. Story tell that Lord Buddha sat in the shade of a Jambu Tree. He was watching men and oxen as they
ploughed the land in readiness for a new crop and meditating on the burdens we all must carry in this
life. There he sat under the tree determined that he would either reach enlightenment or
die where he sat. Later the tree to be called the Bodhi Tree (Tree of
Enlightenment).
And
then it happened! He got an enlightenment experience seing his previous births and realized that people are born and reborn
into different states according to their deeds.
The Plant
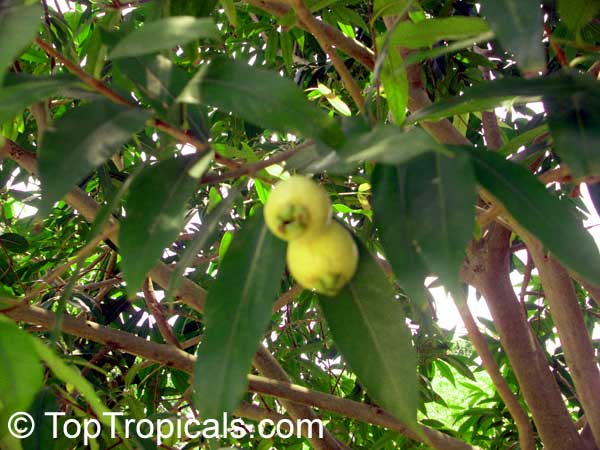
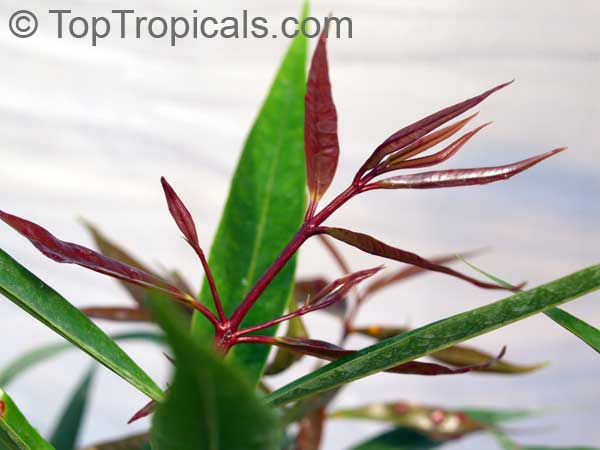
Like many other fruits to which the word "apple" has been attached, the rose apple in no way resembles an apple, neither in the tree nor in its fruit. The rose apple tree may be a shrub but is generally a tree in nature reaching 25 or even 40 ft in height, and has a dense crown of slender, wide-spreading branches, often the overall width exceeding the height.The glossy, leathery, shiny leaves are about six to eight inches in length and about two inches in width. New leaves, as they appear, are dark wine colored and gradually turn dark green as they mature.

The Flower
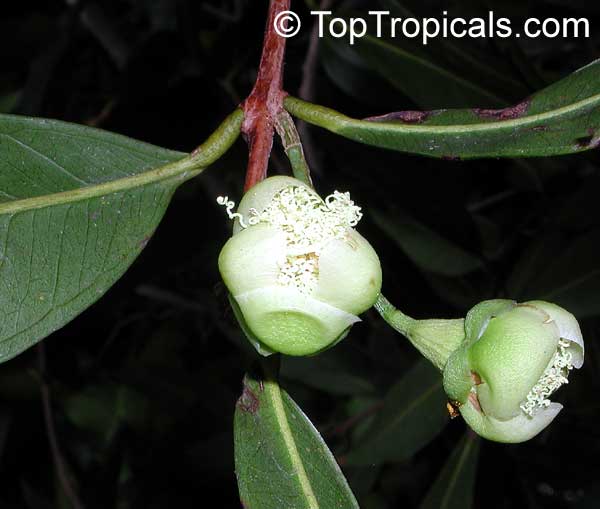
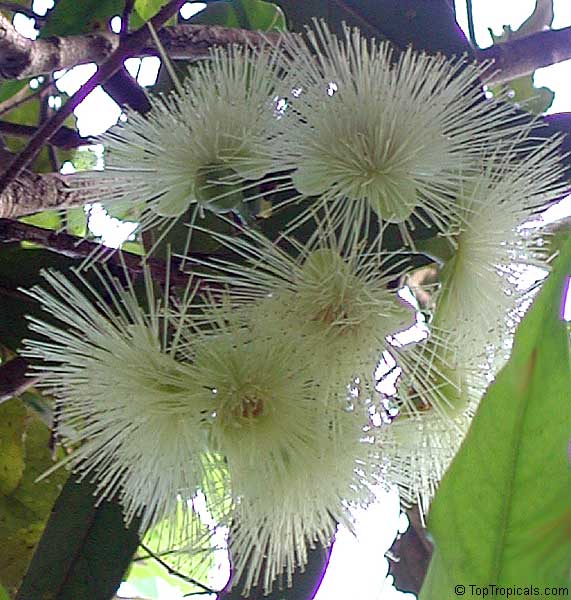 The
beautiful flowers are generally
produced in short terminal racemes on new growth. They are very showy, almost 2" in diameter,
white to pale cream and sweetly scented, consisting of very many
conspicuous long stamens. Flowers produced from late
winter through the spring and early summer.
The
beautiful flowers are generally
produced in short terminal racemes on new growth. They are very showy, almost 2" in diameter,
white to pale cream and sweetly scented, consisting of very many
conspicuous long stamens. Flowers produced from late
winter through the spring and early summer. Often the tree will have fruit maturing while it is still producing additional flowers. In tropics the rose apple trees bloom and fruit sporadically nearly all year. The main season in the Bahamas and in Florida is May through July. In South India, blooming usually occurs in January, with fruit ripening in March and April.

The Fruit
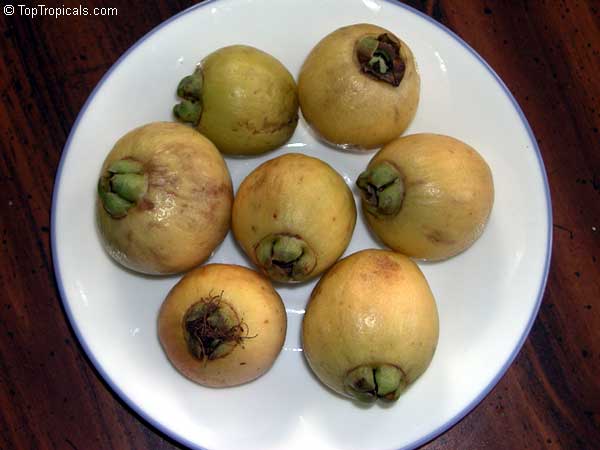
The round or oval fruits are up to 2" in diameter and are pale yellow with sometimes a faint, pink blush. Fruits have a thin layer of pale yellowish flesh and a hollow central cavity containing 1-3 large brown seeds which loosen from the inner wall and rattle when the fruit is shaken. The flesh is very distinctly rose scented, with distinctive rose-water flavor and is generally crisp and juicy.
Rose apples bruise easily and are highly perishable. Fruits spoil very quickly so they should be used soon after picking. In India, they say that a mature Rose Apple Tree will yield 5 lbs of fruit each season. The fruits are, of course, very light in weight because they are hollow.
Care and Cultivation History
The tree is moderately resistant to winds and tolerates cool and seaside conditions, although it is not highly salt tolerant so should not be planted on direct salt exposed locations. In India, Rose Apple does best on the banks of canals and streams and yet tolerates semi-arid conditions.
For optimum fruiting rose apples should be fertilized two or three times a year with a general complete fertilizer containing all micronutrients. On high pH soils some micronutrient deficiencies might develop which would require treatment with nutritional sprays.
Rose apples are easily propagated by seeds, with only about 3 years for seedlings to start flower and fruit production. Young trees start to grow slowly, but once well established require very little maintenance. They can be grown as container plants and will easily fruit in pots.
The Rose Apple is cultivated and naturalized in many parts of tropics, including India, SE Asia, and the Pacific Islands. It was introduced into Jamaica in 1762 and became well distributed in Bermuda, the Bahamas, the West Indies and, at low and medium elevations, from southern Mexico to Peru.In 1825 few young trees were taken from Brazil to Hawaii by ship. The rose apple became naturalized on the islands of Kauai, Molokai, Oahu, Maui and Hawaii. In 1893, it was reported as already cultivated in Ghana. It is semi-naturalized in some areas of West Tropical Africa and on the islands of Zanzibar, Pemba and Reunion. It is believed to have been first planted in Queensland, Australia, about 1896. A tree obtained from an Italian nursery has grown and borne well on the coastal plain of Israel.
The Rose Apple was introduced into Florida, at Jacksonville, around 1877. In California, it is planted as far north as San Francisco. It flourishes in the tropical and subtropical climates and grows from sea level to 3000 ft elevation in its native range. In Jamaica, it is naturalized from near sea-level up to an altitude of 3,000 ft; in Hawaii, from sea-level to 4,000 ft. In India, it ranges up to 4,400 ft; in Ecuador, to 7,500 ft. At the upper limits the tree grows vigorously but may not bear fruit.Uses
Food
Around the tropical world, many people, especially children, like to eat rose apples as an out of hand fruit, and also use them to make stewes, preserves, jellies and jams. The jellies and preserves made from Rose Apple retain the distinctive rose flavor.
The fruit can be stewed with some sugar and served as dessert.
The fruit is made into jam or jelly with lemon juice added, or more frequently preserved in combination with other fruits of more pronounced flavor. It is also made into a syrup for use as a sauce or to flavor cold drinks.
In Jamaica, the halved or sliced fruits are candied by stewing them in very heavy sugar sirup with cinnamon.
Other usesFruit extract can be used to make a sweet smelling rose water. The ripe fruits, with seeds removed, could be distilled to make a "rosewater" equal to the best obtained from rose petals.
The flexible branches have been employed in Puerto Rico to make hoops for large sugar casks, and also are valued for weaving large baskets.
The bark has been used for tanning and yields a brown dye.
The sapwood is white. The heartwood is dark-red or brown, fibrous, close-grained, medium-heavy to heavy, strong; and has been used to make furniture, beams for construction, frames for musical instruments (violins, guitars, etc.).
A yellow essential oil, distilled from the leaves, used in the perfume industry.
The flowers are a rich source of nectar for honeybees and the honey is a good amber color. Much comes from the San Cristobal River Valley in Cuba.
Medicinal Uses
In India, the fruit is regarded as a tonic for the brain and liver. An infusion of the fruit acts as a diuretic.
A sweetened preparation of the flowers is believed to reduce fever. The seeds are employed against diarrhea, dysentery and catarrh. In Nicaragua, it has been claimed that an infusion of roasted, powdered seeds is beneficial to diabetics. They say in Colombia that the seeds have an anesthetic property; Cuban people believe that the root is an effective remedy for epilepsy. However, according to scientific research, both the seeds and the root are toxic and should be used with a caution.
The leaf decoction is applied to sore eyes, also serves as a diuretic and expectorant and treatment for rheumatism.
Rose Apple Tarts
Makes 24 tarts.
Crust:
- 1/2 cup butter
- 3 oz cream cheese
- 1 cup all-purpose flour
Blend and refrigerate for 1 hour
Filling:
- 2 qts rose apples
- 4 cups sugar
- 1 tsp ginger
- 1 tsp cinnamon
- 8 oz cream cheese
- water
Put fruits in pot with slightly less water than will cover fruits. Boil. Press fruit through colander and return to pot of fruit water. Add sugar. SImmer and reduce in volume by half. Add ginger and cinnamon. Cool to lukewarm. Add cream cheese.
Shape dough into 24 small balls. Press into mini cupcake pans and fill with filling. bake in 350F for 25 minutes.
Related Species of Myrtaceae
Eucalyptus deglupta
Eugenia aggregata
Eugenia brasiliensis
Eugenia luschnathiana
Eugenia reinwardtiana
Eugenia stipitata
Eugenia tomentosa
Eugenia uniflora
Feijoa sellowiana
Myrciaria cauliflora
Myrciaria vexator
Pimenta dioica
Pimenta racemosa
Psidium littorale
Psidium guajava
Syzygium aromaticum
Syzygium cumini
Syzygium malaccense
Syzygium paniculatum
Syzygium samarangense
Order the plant:
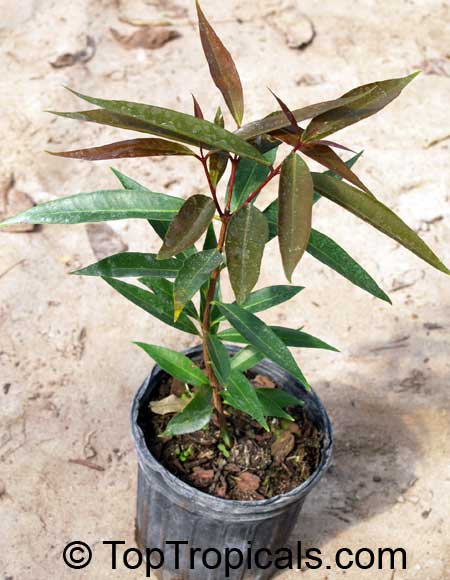
Rose Apple tree in 1 gal pot (see photo below)
Plants are 1-2 ft tall, 1.5-2 years old