Sweet Potatoes - healthy food for every kitchen
by Alex Butova, the Witch of Herbs and Cats
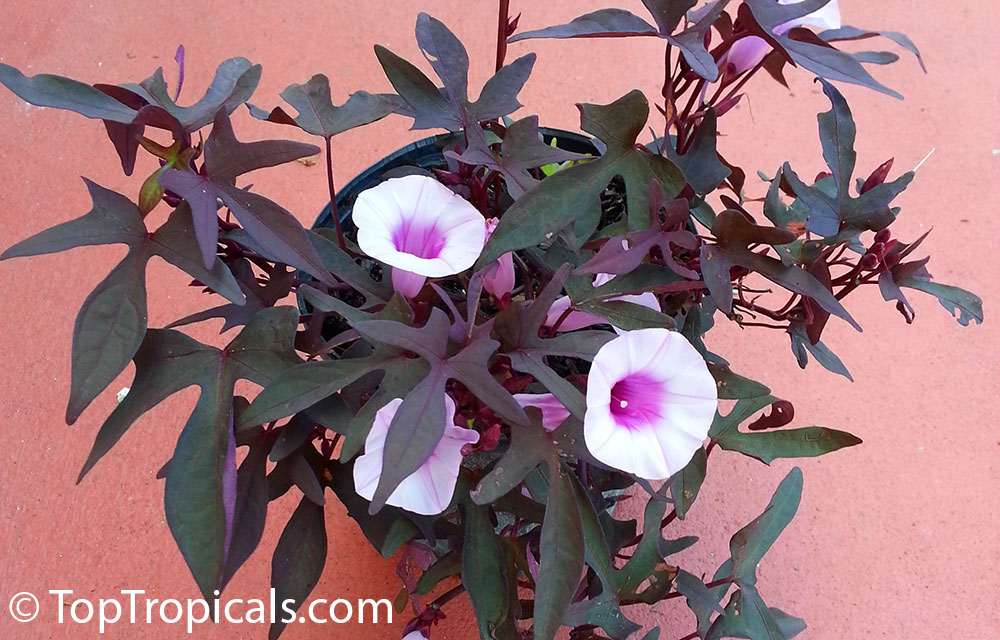

“Oh my, what is this luxurious vine? These large, bright flowers! Looks like the Morning Glory and... is not like anything! What is this, tell me please…” My friend smiled in answer. He was engaged in floriculture for many years, experimented with them, even brought out new varieties of some plants.
“You want to know what this is? This is my favorite breakfast, lunch and dinner. For breakfast - sweet, but healthy porridge, for lunch - a wonderful side dish, and at last this plant makes a wonderful dessert for a cup of tea or coffee after dinner!”
And looking at my surprised face, he said: “This is Ipomoeabatatas, or Sweet potatoes. Never heard of it?”
I didn't expect sweet potatoes to be represented by such a beautiful plant! So my old good friend introduced me to this supposedly ordinary, but spectacular and useful edible plant. Here is the story...
What is the Sweet Potato plant?
Ipomoeabatatas or Sweet Potato is a member of the Morning Glory family (Convolvulaceae), and only distantly related to the common potato (Solanum tuberosum) which belongs toNightshade family(Solanaceae) becouse both being in the orderSolanales. Nevertheless, they are completely different plants! The genusIpomoeathat contains the Sweet Potato also includes several garden flowers calledMorning Glories, though that term is not usually extended toIpomoea batatas.
Sweet potato is native to the tropical regions of the Central America or northwestern South America. Ipomoea batatas plants are known at this region from prehistoric times. Remains of sweet potato tubers, dating to about 8,080 BC, have been found in a cave in Peru. Sweet potato is now widely cultivated in tropical regions and temperate regions with hot summers.
Of the approximately 50generaand more than 1,000 species of Convolvulaceae, Ipomoea batatasis the only crop plant of major importance.

It is herbaceousis fast growing, perennialvine, or spreading ground cover, bearing alternate heart-shaped or palmately lobedleavesand medium-sizedsympetalousflowers. The stems are usually crawling on the ground and formadventitious rootsat thenodes.Depending on the variety, the total length of a stem can be between 5 and 13ft.
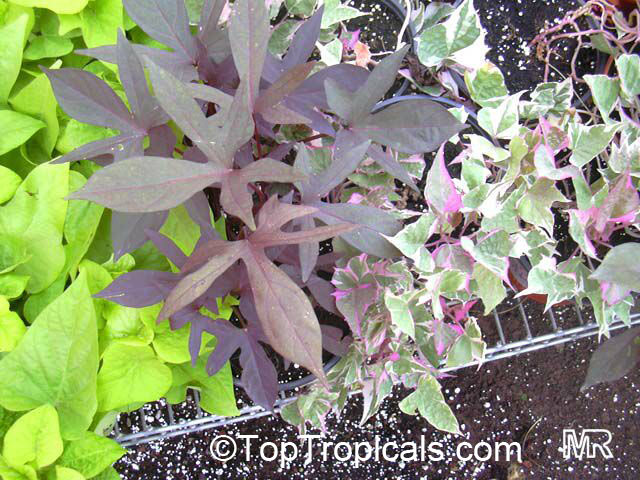
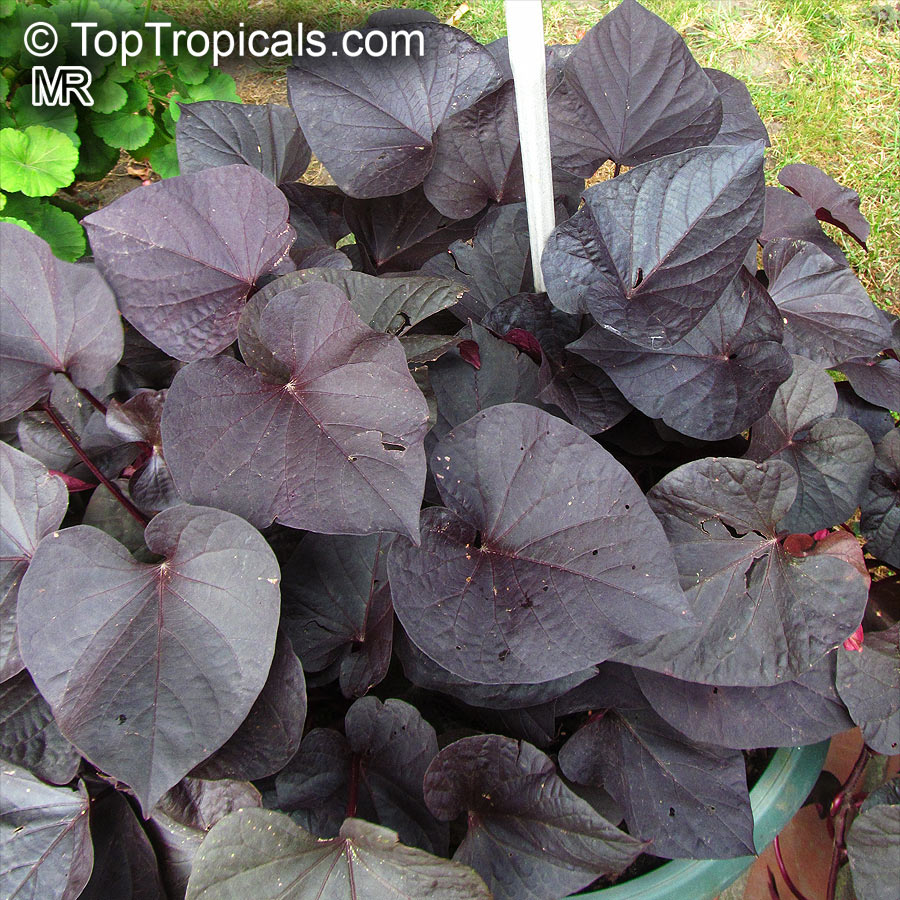
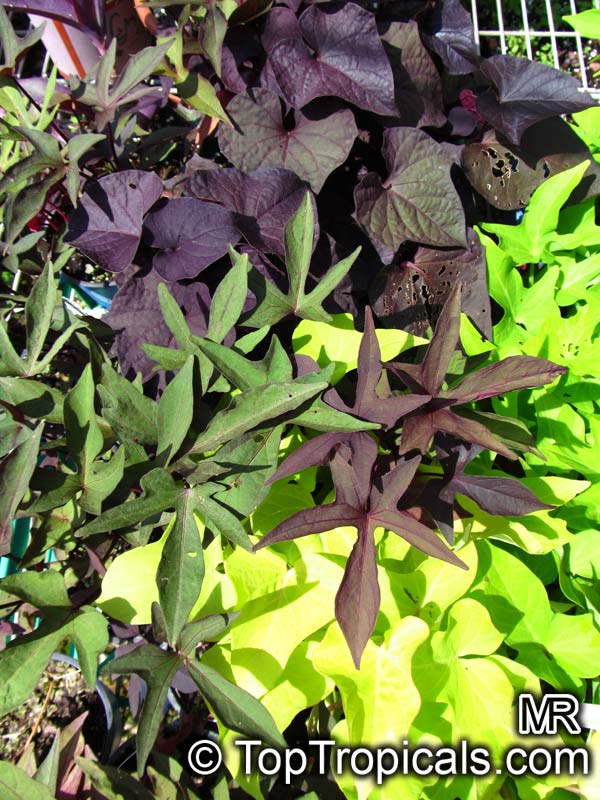
The leaves are very variable, 2 to 5in long, the shape is heart-, kidney-, egg-shaped, rounded or triangular and spear-shaped, the edge can be entire, toothed or often three to seven times lobed, cut or divided. Most of the leaf surfaces are bare, rarely hairy, and the tip is rounded to pointed. Many cultivars of different leaf colors and shapes exist in cultivation which gives the plant another exceptional value as ornamental.

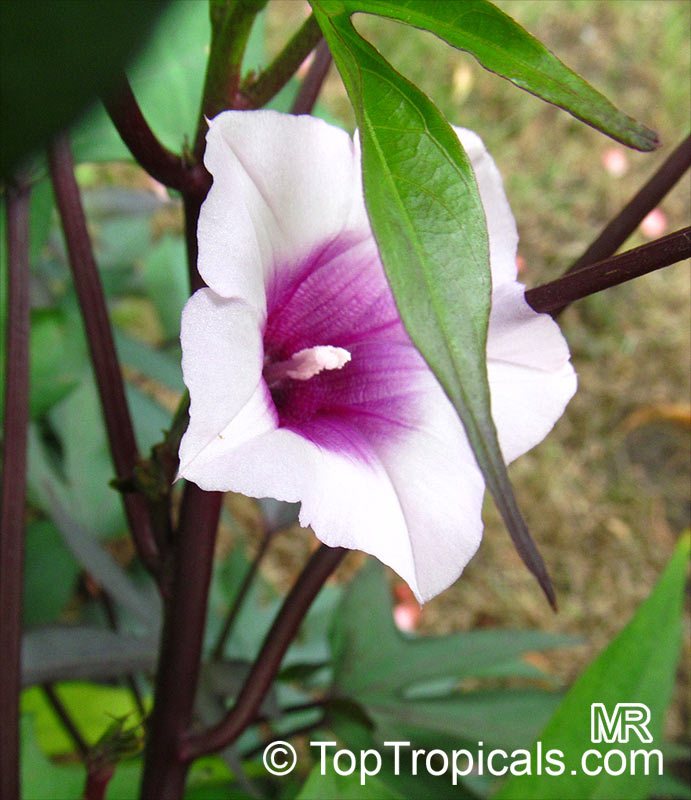
The plant bears gorgeous funnel-shaped flowers 2-3" long. Their folded crown, with a shorter hem, can be lavender to purple-lavender in color, often darker in color inside the tube, but white crowns can also appear. The plant has been flowered throughout the year. The flowers open before sunrise and stay open for a few hours. They close again in the morning and begin to wither.
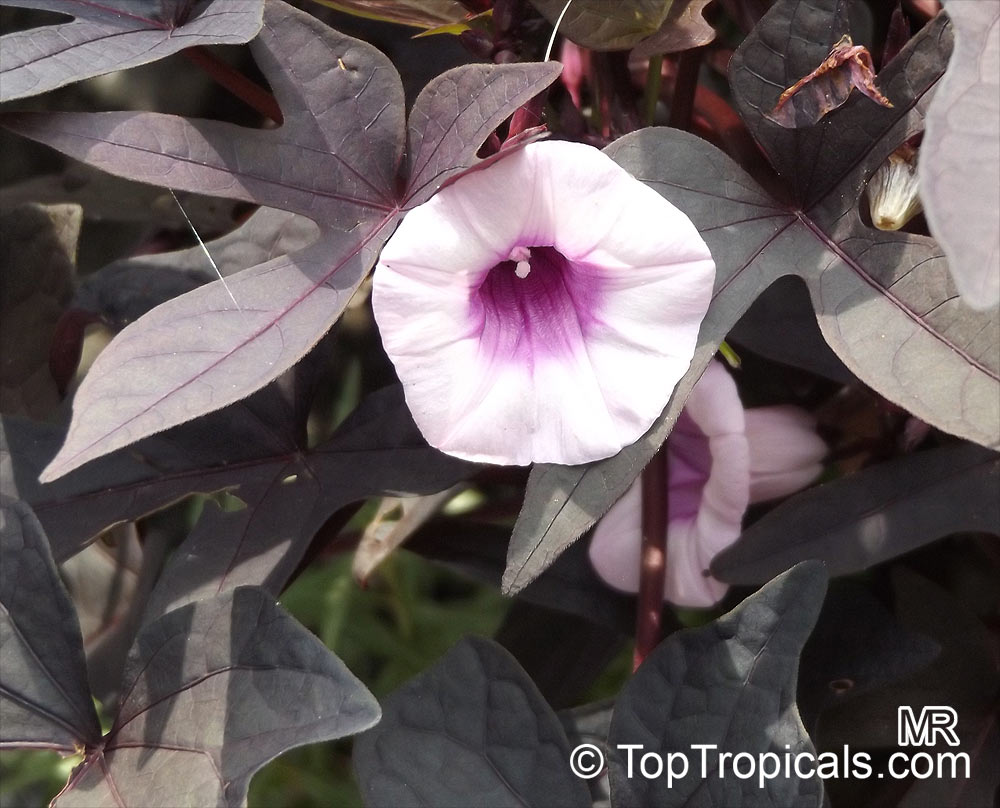

Sweet Potatoes are mostlycross-pollinatedby insects such asbumblebees, which carry pollen from other plants, though a substantial amount of self-fertilizing occurs as well. Seeds are only produced from cross-pollination.
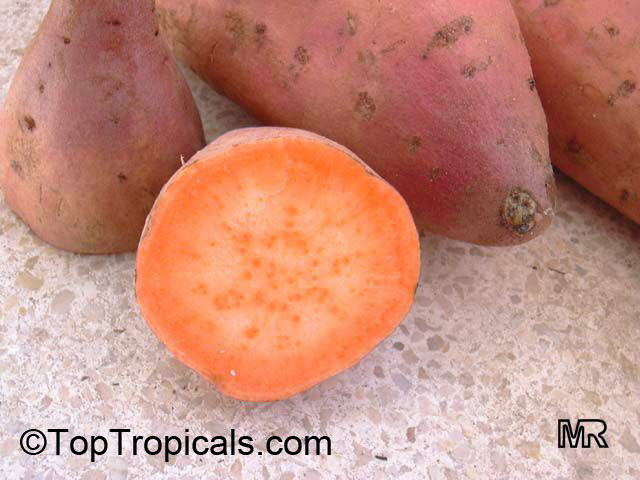
The edibletuberousroot is long and tapered, with a smooth skin whose color ranges between yellow, orange, red, brown, purple, and beige. Its flesh ranges from beige through white, red, pink, violet, yellow, orange, and purple! Sweet potatocultivarswith white or pale yellow flesh are less sweet and moist than those with red, pink or orange flesh...


Some cultivarsare grown asornamental plantsunder the name Tuberous Morning Glory for their attractive flowers and foliage. Many varieties with purple foliage are popular in hanging baskets. These plants are valued as dense, fast growing ground covers.

Sweet potato is considered to be the world's fifth most important root crop. It is mainly cultivated for its storage roots, which are consumed mainly as a vegetable in tropical countries. The tubers may be eaten in numerous ways, such as boiled, baked, fried, made into flour for biscuits, bread and pastries, dehydrated to make chips or creamed for use in desserts. The tubers are also boiled to make a sweet soup, fried to make French fries and stewed to make porridge.
The tender leaves and young shoots, which are rich in vitamins, minerals and proteins, are also eaten as green vegetables. In Singapore, as well as other parts of Southeast Asia, tender leaves are stir-fried with sambal belacan (spicy shrimp paste).
Ipomoeabatatas is very healthy food. Cooked sweet potato has 76% water, 21% carbohydrates, 2%protein, and contains negligiblefat. In a 100 g of baked sweet potato provides only 90calories, and rich contents ofvitamin A, vitamin C,vitamin B6, manganese andfibers. It is also moderate source ofB vitamins and potassium. Sweet potatoes with purple flesh are richer in anthocyanins.

Sweet potato is used as a source of alcohol and is fermented to make a Japanese spirit known asimo-jochu. Sweet potato is also used as animal-fodder.
A decoction of the leaves of Ipomoea batatas are known to be used in folk remedies for tumors of the mouth and throat. The plant is also used for other ailments, including asthma, fever and nausea.
Small portions of Ipomoea batatas crops are used for industrial purposes, including starch and alcohol production. Natural fibers fromIpomoea batatasare used in biodegradable plastic (polylactic acid bioplastic) used in the manufacture of Toyota cars.
Growing Sweet potatoes
Ipomoeabatatas does not toleratefrost. It grows best at an averagetemperatureof 75F, with abundant sunshine and warm nights.
Depending on the cultivar and conditions, tuberous roots mature in two to nine months. With care, early-maturing cultivars can be grown as anannualsummer crop intemperateareas.
They are mostly propagated by stem or root cuttings or by adventitious shoots called "slips" that grow out from the tuberous roots during storage. True seeds are used for breeding only.
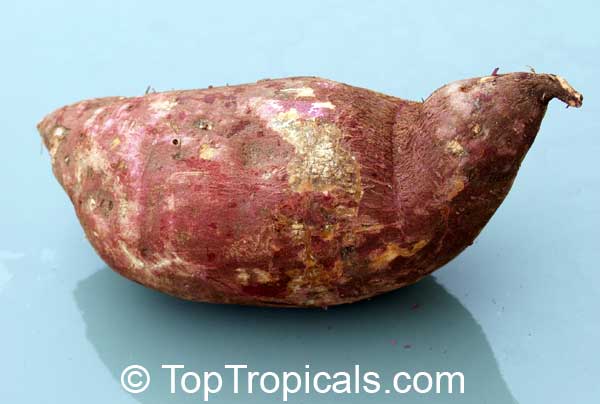

Sweet potato tubers or cuttings can be overwinter indoors. Plants can also be brought indoors and treated as houseplants. Store dormant tubers in a cool, dry place and replant in spring. Take cuttings several weeks before your average first frost date and place in water. Once roots have formed, cuttings can either be left in water until spring, or potted up.
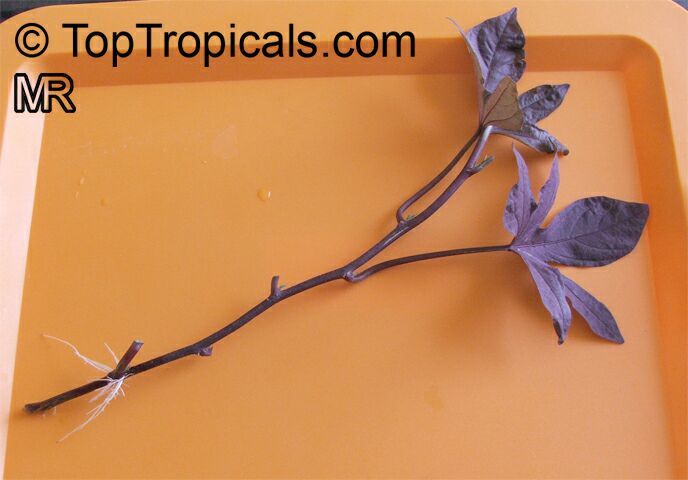

And then in Spring you can grow not only your own breakfast, lunch and dinner, but a floral beauty, from which you simply will not take your eye away!

See more articles by Alex Butova

