Garden Blog - Top Tropicals
Date:
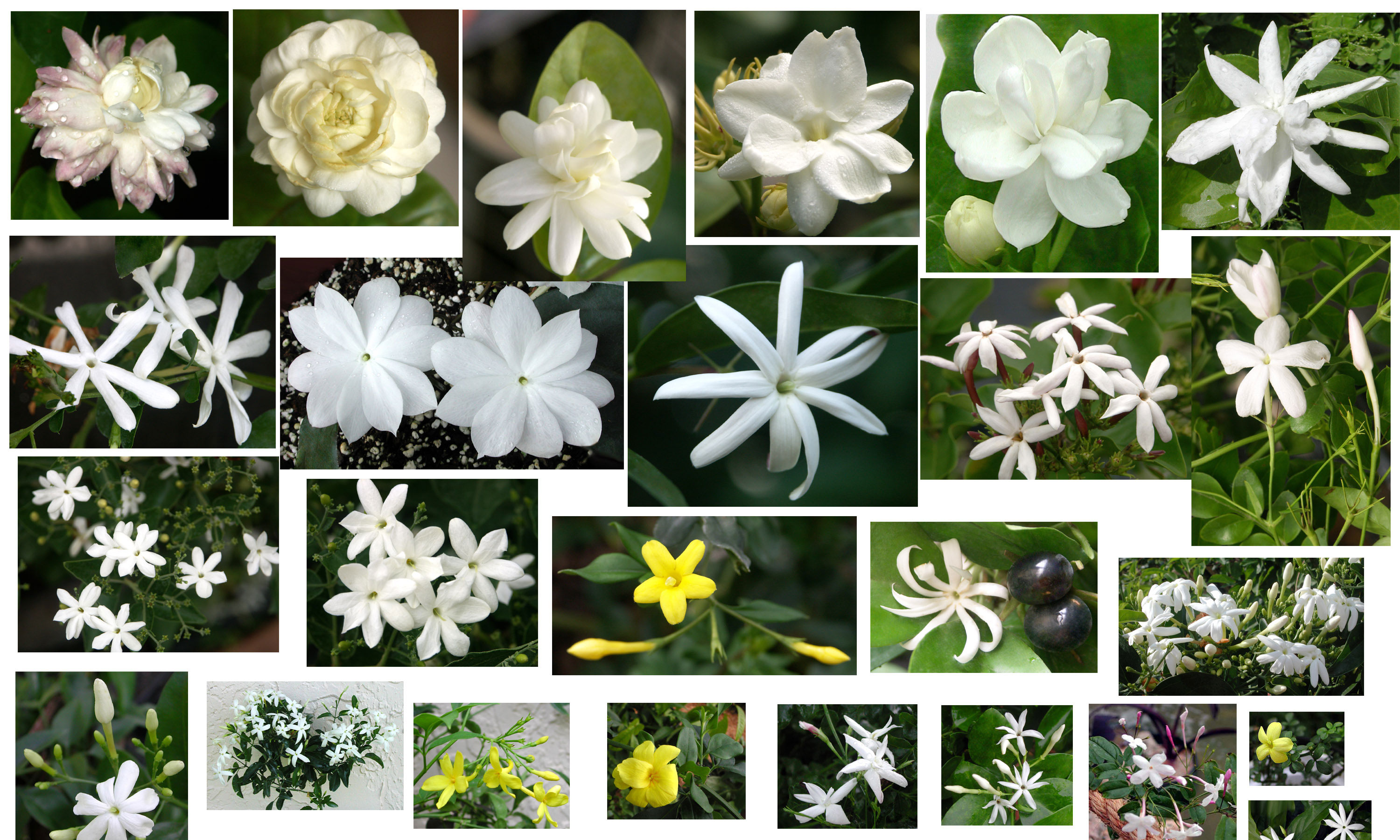
Selecting the right jasmine
Q: Would you please help me select the right jasmine? I want to find a jasmine that smells like lily of the valley or honeysuckle or roses, not the one that smells like gardenia. I'm in Missouri, zone 6, so I want a jasmine for my deck for the summer, so I want it to bloom this season.
A: There are 3 major types of tropical flower fragrances - Sweet, Fresh, and Fruity (including Lemony). Below are the most interesting fragrant tropical flowers, excluding Gardenias (which are sweet type). These are all same-year bloomers, so you can enjoy the fragrance this year assuming proper care and bloom booster feeding.
* - The fastest growers that can be treated as annuals. Others can be grown in a pot and brought inside for winter, and be enjoyed every year.
Sweet
*
Aloysia virgata - Almond Bush
*
Cestrum diurnum - White Chocolate Jasmine, Day Blooming Jasmine
*
Cestrum nocturnum - Night blooming jasmine
*
Heliotropium peruviana - Turnsole, Cherry Pie
Portlandia Cubanola domingensis - Cubanola (Warm white Chocolate)
Portlandia grandiflora - Glorious Flower of Cuba (Warm white Chocolate)
Fresh
Beaumontia grandiflora - Easter Lily Vine
*
Brugmansia Jean Pasco - Yellow Angels Trumpet
*
Brugmansia Variegated Orange Angel Trumpet
*
Brunfelsia americana - Lady of the night
*
Brunfelsia lactea - Lady of the night
*
Brunfelsia nitida - Lady of the night
Crinum Queen Emma - Spider lily
*
Eucharis grandiflora - Amazon Lily
*
Hedychium coronarium - Butterfly Ginger
Hiptage benghalensis - Helicopter Flower
Hoya odorata - Fragrant Hoya
Ixora hybrid Sea Green
Ixora odorata - Fragrant Ixora
*
Jasminum azoricum - River Jasmine
*
Jasminum Molle - Indian Jui
Jasminum nitidum - Star Jasmine
*
Jasminum officinale Flore Pleno - French Perfume Jasmine
*
Jasminum polyanthum - Pink Winter Jasmine
*
Jasminum sambac Belle of India
*
Jasminum sambac Grand Duke
*
Jasminum sambac Maid of Orleans
*
Polianthes tuberosa - Tuberose
*Sclerochiton harveyanus - Blue Lips, Mazabuka (Lavender-violet-like)
Fruity
Aglaia odorata - Chinese Perfume Plant (Lemony)
Artabotrys siamensis - Climbing Ylang-Ylang (Lemony)
Cananga fruticosa - Dwarf Ylang-Ylang
Carissa grandiflora - Natal Plum
Cerbera x manghas hybrid - Enchanted Incense
*
Jasminum dichotomum - Rose Bud Jasmine
*
Lonicera japonica - Japanese Honeysuckle
Magnolia figo - Banana Magnolia (Banana-like)
Magnolia x Alba grafted (Bubble-gum-like)
*
Mirabilis jalapa - Four oclock plant
Oxyceros horridus, Randia siamensis
*
Quisqualis - Rangoon Creeper
*
Radermachera Kunming - Dwarf Tree Jasmine
*
Stephanotis floribunda - Bridal Bouquet
Strophanthus gratus - Climbing Oleander
Telosoma cordata - Pakalana vine (Lemony)
Fertilizers for profuse flowering:
Pink N Good Daily Plant Food - Flower Booster
Tropical Allure - Smart-Release Booster
SUNSHINE-Superfood micro-elements
Date:
True love of Night Blooming Jasmine
By Onika Amell, tropical plant specialist
Q: I live in New Cumberland, West Virginia. I love the smell of Night-Blooming jasmine. Is it possible to grow it in the northern panhandle of West Virginia? Do I have to plant it every year or do I keep it in a pot and take it inside during the winter months?
A: Technically, Night Blooming Jasmine is not a true jasmine
(those plants belong to Oleaceae, or Olive family). Night Blooming Jasmine
belongs to the Solanaceae family, also known as the Nightshade or "Potato" family
of plants. Yes, this sweet fragrant flower called Jasmine for its perfume is
related to potatoes and tomatoes!
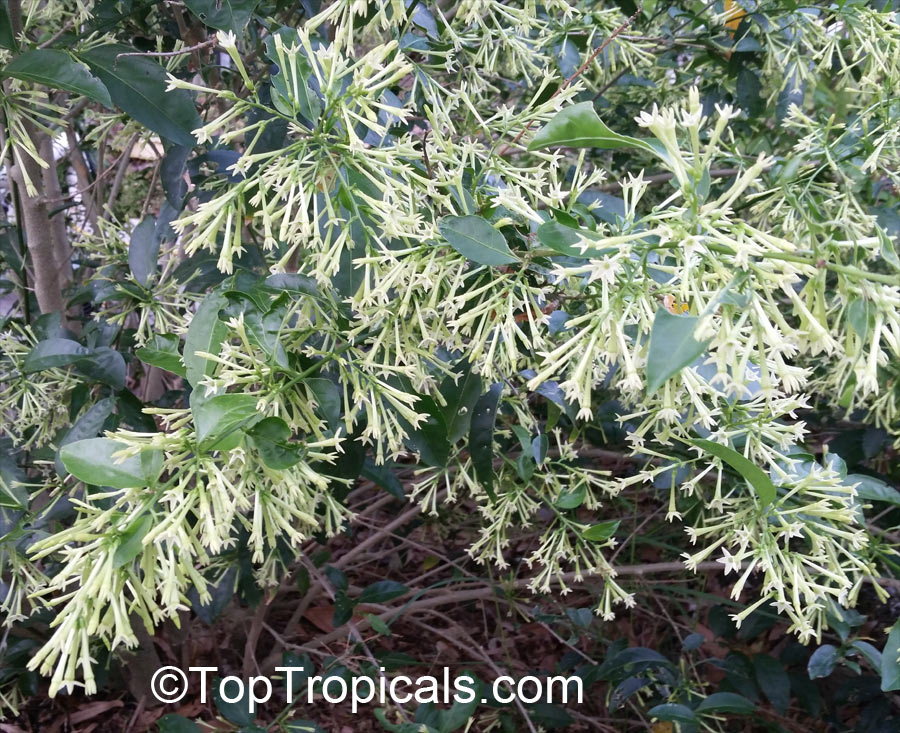
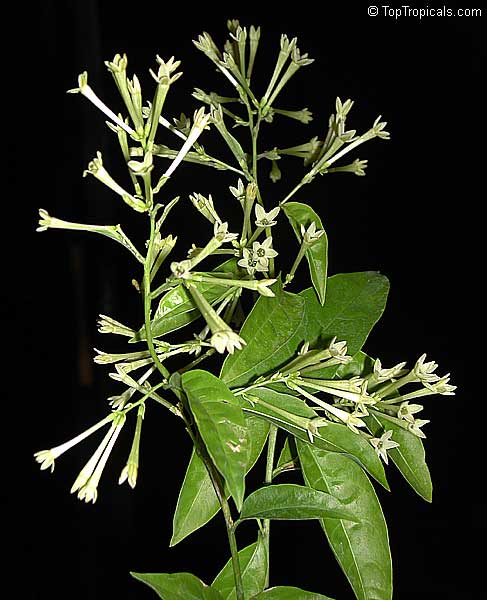
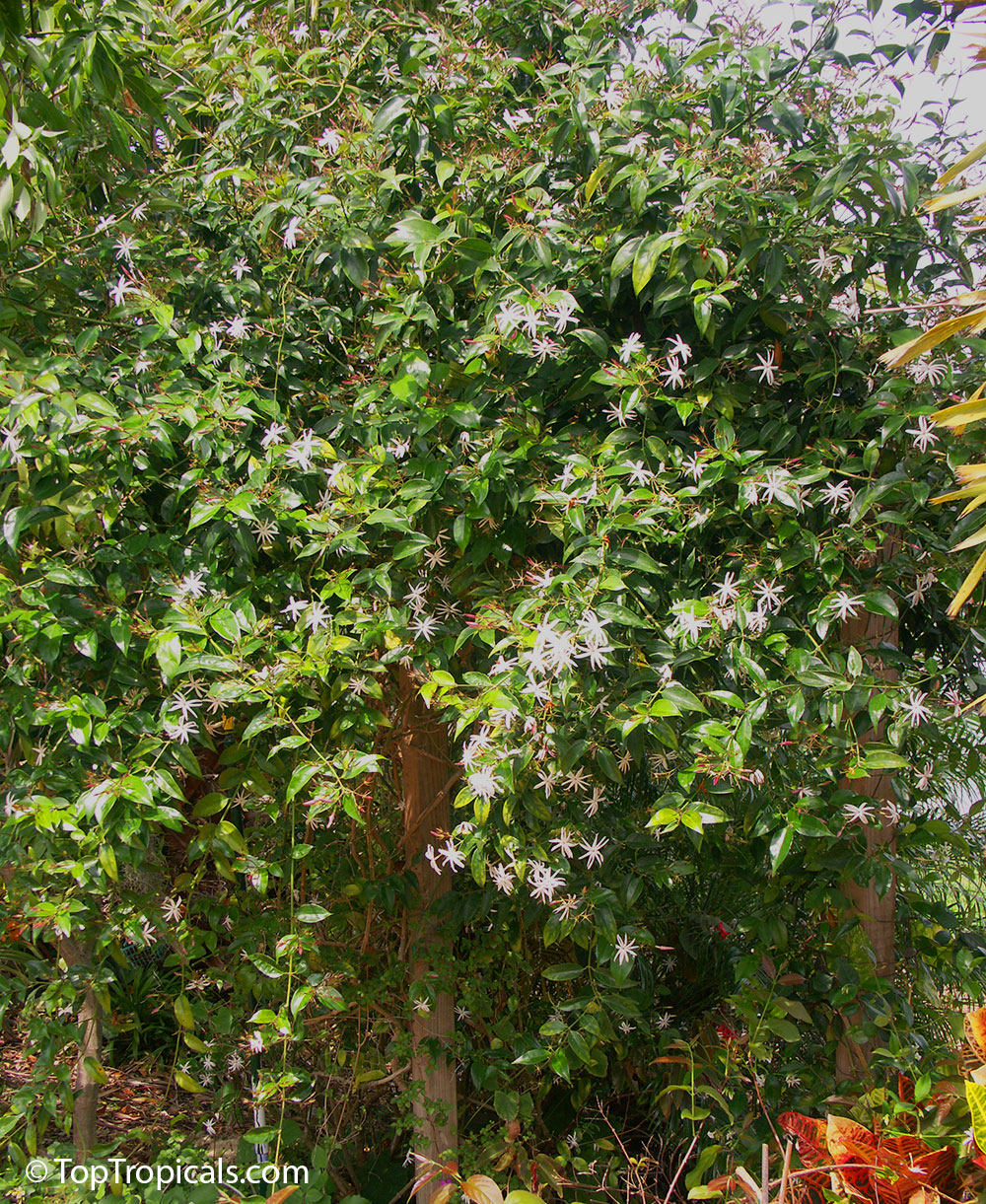
Night Blooming Jasmine - Cestrum nocturnum - is loved by many gardeners for its beautiful
fragrance at night. It is one of the most fragrant tropical evergreen shrubs
available. Cascading clusters of tiny, tubular pale yellow to white flowers open at
night and release a heavenly fragrance throughout the garden, especially on
warm summer evenings. The fragrance is much lighter during the day.
Night Blooming Jasmine is grown year-round in zones 9-11. It is at its
happiest in a sunny to a partially sunny spot in your garden in well-drained soil
but can be grown in cooler climates as a container or greenhouse plant.
You would absolutely be able to enjoy this plant during the warm months
in West Virginia, but it will most certainly not survive outside during the
winter. You will have to bring it inside. Take it outside again only once you
are confident there is no more possibility of frost. When grown indoors, be
sure to give it the sunniest, South facing window in your home. When grown in
a container, you will need to re-pot it every two to three years so it
doesn't become root-bound.
For those who are lucky to live in frost-free areas, in ideal growing
conditions outside, it can easily reach 8 feet with a spread of 5 feet. It has
a lovely informal look that can soften a more manicured garden. Add organic
matter to the planting hole when you plant to enrich the soil around the root
ball. Water well in the summer, but allow them to dry out a bit between
watering in the winter. Plant this Jasmine near pools, porches, doors, windows,
and walkways where its lovely fragrance can be enjoyed. The shrub is also an
excellent plant for privacy hedges and screens. When grown as a hedge, plant 3
feet apart.
Trim lightly after a bloom cycle to shape and then do a hard pruning in
fall or spring to control the size of this plant. Fertilize 3 times a year -
in spring, summer, and autumn - with a good quality granular fertilizer.
Recommended fertilizers:
Pink N Good Daily Plant Food - Flower Booster
Tropical Allure - Smart-Release Booster
Interesting facts:
Night-blooming jasmine is an excellent mosquito repellent. The powerful
scent of the flowers attracts moths and bats that feed on mosquitoes and
other small insects.
The flowers of the Night Blooming jasmine are widely used in India and
other countries of South Asia for perfumery, medicinal applications and in
religious ceremonies.
Limited time special offer:
Instant $5 off Night Blooming Jasmine
Date:
How to get a Jasmine to bloom.
Caring for jasmines as container plants during Winter
Locate the jasmine plant where it will receive bright filtered light at least six hours every day.
Put a few pebbles in a shallow plate or tray and pour fresh water over the pebbles. Set the pot on the pebbles, but don't let the water level touch the bottom of the pot. This increases the humidity in the air around the jasmine. Keep the plant away from wood stoves, heat vents and radiators.
Water the jasmine when the top 1/2 inch of the soil feels dry. Don't let the soil get soggy, and never let the pot sit in water. Water the plant sparingly during the winter.
Feed jasmine twice a month between Spring and early Fall, using a granulated slow-release, or water-soluble houseplant fertilizer mixed at half strength. Don't fertilize during the winter months.
Prune the jasmine as needed to maintain the desired shape. Never prune in winter, as the plant will be preparing to bud.
Encourage the jasmine to bloom by putting it in a cool room at night for four to five weeks during Fall to Early Winter. The plant should get plenty of sunlight during the day, but during the night, move it to a pitch-dark room where the temperature is between 40 and 50 degrees F. After four to five weeks, leave the plant in its regular, daytime location. The plant should start blooming in mid-Winter to early Spring.
See all jasmine plants...
Date:
Secrets of flowering of Jasmine Sambac
Q: Q: My Jasmine sambac Maid of Orleans is growing very fast and produced lots of branches and dark green leaves, when will I see flowers? I only saw 2 or 3 flowers since since Spring. I is planted by East wall of the house. Should I use some special fertilizer perhaps?
A: Jasmine sambac is a tropical bush or vine that enjoys hot summers. Since it
tolerates wide range of light conditions, it can be grown both in shade or sun; this is why it is highly recommended for indoor
culture where light level is limited. Remember though that profuse blooming directly depends on the light level. Your Eastern
exposure location may not be providing enough light for the flowering. Dark green leaves are also a sign of a filtered light
sitution. Extra fertilizing may not help to induce flowering if the light is low, although it is always beneficial for a plant
(it may just start producing even more leaves and branches). The ideal conditions for Sambac's flowering are - full sun all
day long, high temperatures (upper 80's-90's, even over 100F is fine), and very good drainage. Some gardeners call Jasmine
sambac "almost a succulent", referring to its low watering needs. To be exact, this plant requires regular watering, but will
produce lots of flowers only providing perfect drainage. You may never see flowers if the plant has wet feet or water-logging
occurs. If your summers are rainy (like in Florida), make sure your jasmine is planted with at least 4-5" elevation and not in a
low/wet spot.
See Top Tropicals Video about jasmine Sambac:
- varieties, history and use.
Date:
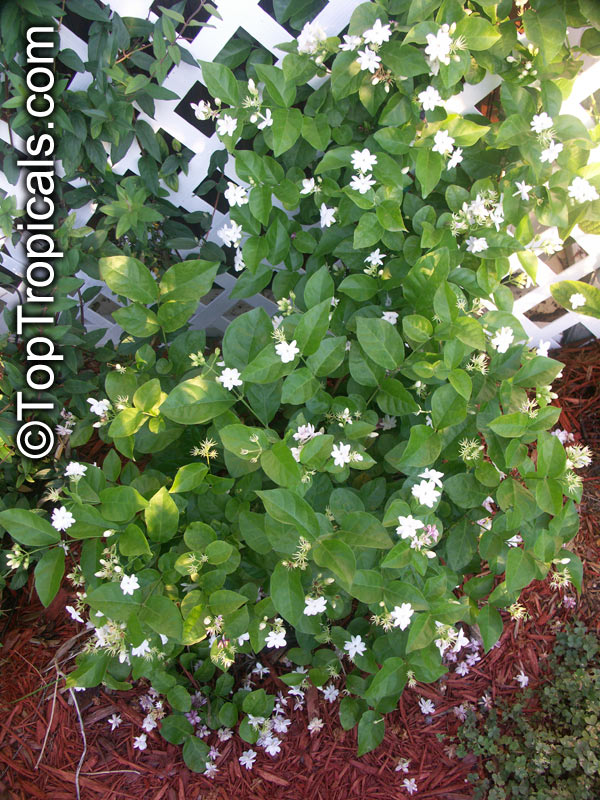
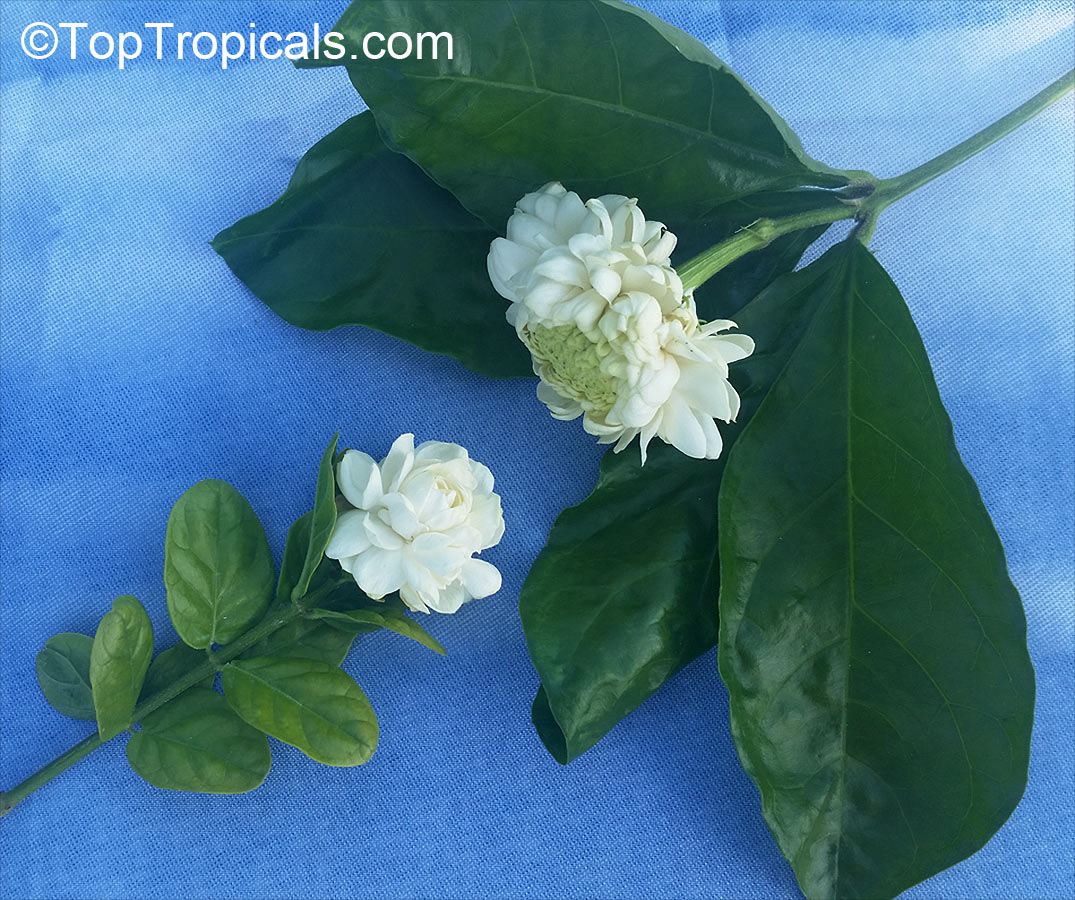
Jasmine for a fence
In the photo: Jasmine Maid of Orleans
Q:We are looking for a jasmine variety without thorns that we can grow on a wire fence...
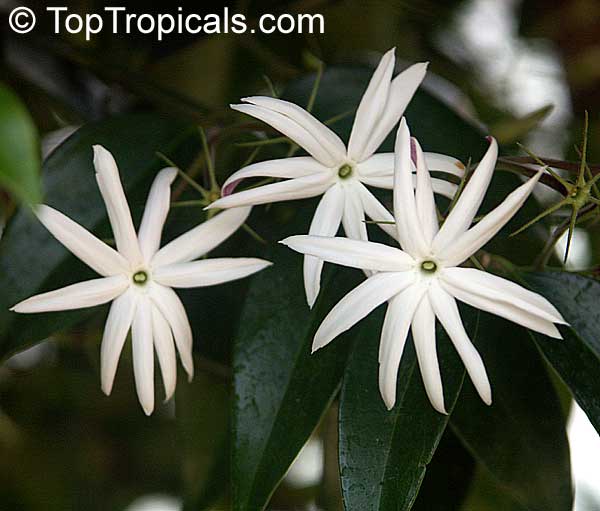
A: All true jasmines (Jasminum spp.) are thornless. So you are safe to get anyone you like. The most vigorous, fast growing jasmines that grow into a vine, are:
Jasminum dichotomum
Jasminum pubescens
Jasminum nitidum
Jasminum officinale
Jasminum sambac Maid of Orleans - the
most fragrant!
In the photos: Jasminum nitidum (Star Jasmine)
Date:
How to get Jasmines to flower
Q: On the picture, these are a few of the jasmine plants that I have from Top Tropicals. I have bought so many plants from you over the years, not just jasmine. I have several varieties of jasmine. They were all doing very well. However this year I didn't get a single flower. There are a lot of buds... But before the buds open they become brown and withered. I bought fertilizer from you. Fertilized the plants once a month like I always do. I water the plants once a week. I repotted the plants hoping that would take care of this problem. Some of the jasmine plants I pruned... the plants came back vigorous growth with a lot of buds... BUT it is the same problem! Please help.
A: One of the possible reasons why they have flower issues is - maybe they don't have enough sunlight. They need to be in full sun all day long for profuse blooming and proper flower forming. However since the buds are forming, there may be just enough light. In this case, dropping buds may be a sign of overwatering.
Important steps - how to make Jasmine Sambac flower:
1. Soil. Use only well-drained soil
2. Water. Keep plants on a dry side and never over water. If the top of the soil is still moist, do not water.
3. Sun. Keep in full sun all day long. The more sun, the more flowers.
4. Bloom booster. Use Flower booster fertilizers:
Pink N Good Daily Plant Food - Flower Booster
Fragrant Plant Special booster, this 90-day Smart-Release container
plant food:
Plumeria Top Dress - Smart-Release Booster
Do not use fertilizers with high Nitrogen (1st number in NPK formula)
- those will promote more leaves instead of flowers.
5. Micro-elements. Use Apply micro-elements, they will help the
plant to develop healthy and long-lasting flowers:
SUNSHINE SuperFood - plant booster
Here is more information on growing Jasmine
Date:
Best picks of the Season
Special SALE deals - from our horticulturist
These plants are large, developed and beautiful NOW!
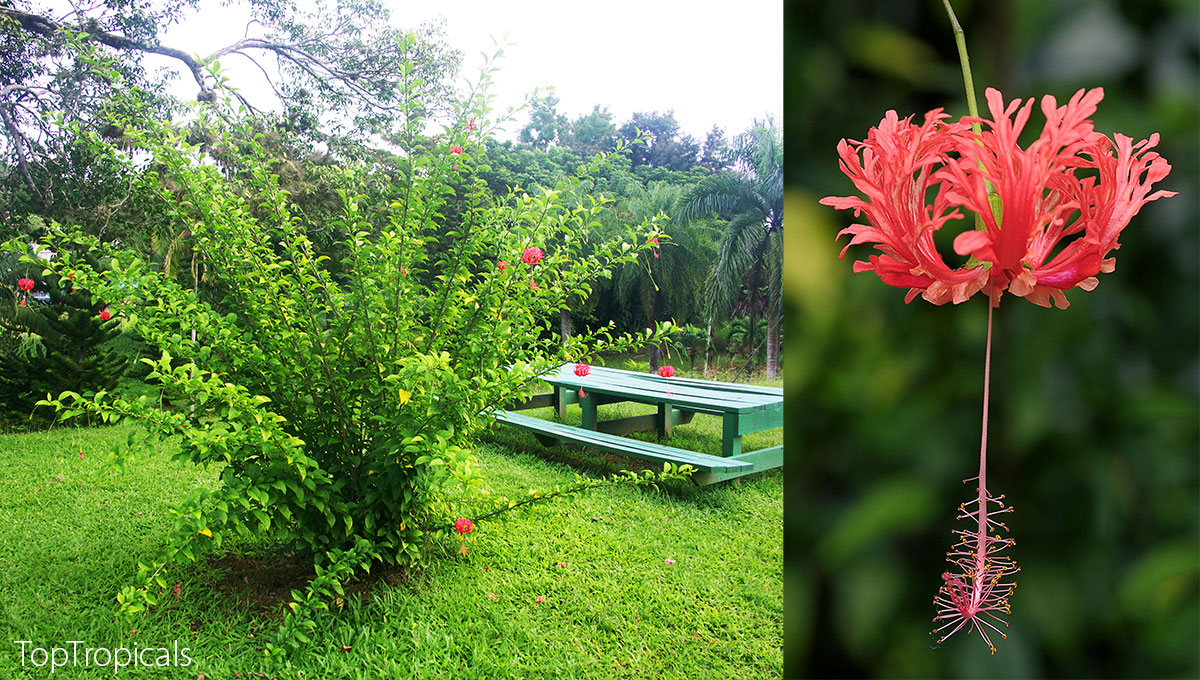
Hibiscus schizopetalus - Coral Hibiscus. Spectacular weeping tree hibiscus, rare and hard to find. Grows rapidly and blooms freely. Flowers look like parachutes and can be recognized by the fringed and lacy petals which are bent backward. It has slender and gracefully curved stems. Can be trained into a showy standard.
Cestrum nocturnum - Night blooming jasmine. Garden favorite - the sweetest fragrance at night is intoxicating. One of the most famous and desirable fragrant plants. Flowers are pale yellow to white, open at night and stay extremely fragrant until sunrise. These flowers are widely used in India and other countries of South Asia for perfumery, medicinal applications and in religious ceremonies. Best location will be near driveway, window or entrance, where the magic fragrance can be appreciated.
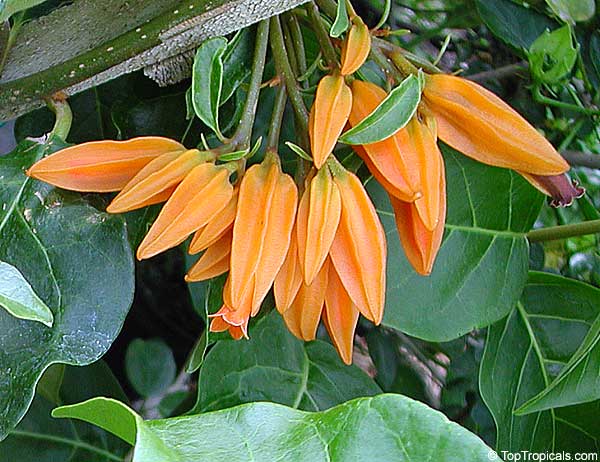
Juanulloa aurantiaca - Gold Finger plant, Mexican Spoon Flower - this one is soooo pretty! Unusual looking vine or shrub with yellow-orange fleshy flowers, everblooming and a VERY fast growing. Rare, collectible plant.
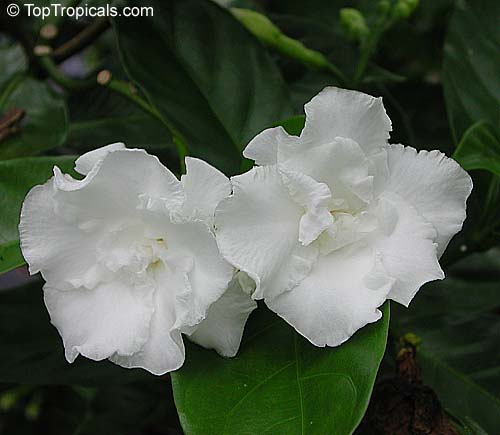
Tabernaemontana Flore Pleno - Crape Jasmine, Carnation of India, Florida Gardenia - this fast growing bush with waxy leaves and beautiful fragrant flowers is a must in tropical garden. Easy to grow and free flowering, dense bush.
Microsorum musifolium - Alligator Fern, Crocodile Fern from Australasia. Perfect for shade! An epiphytic fern with cool alligator-skin looking leaves. The strikingly shaped, light green fronds of the fern form a lovely backdrop to its stunning stiff, leathery, dark green alligator-skin foliage. Perfect as a houseplant, or planted under a tree. Grows to 2-3 ft in height and likes a sheltered, semi-shaded location, no direct sunlight.
Date:
NEW INTRODUCTION:
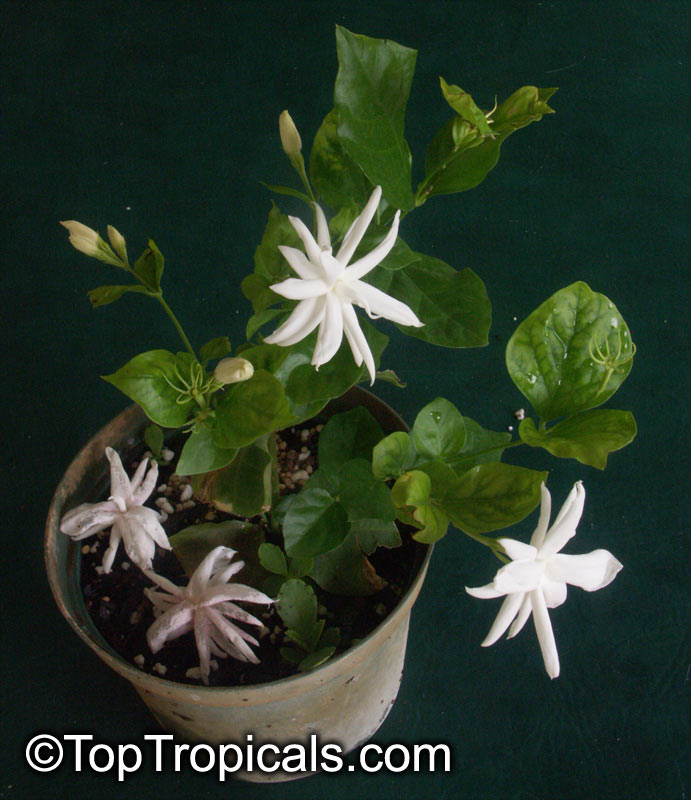
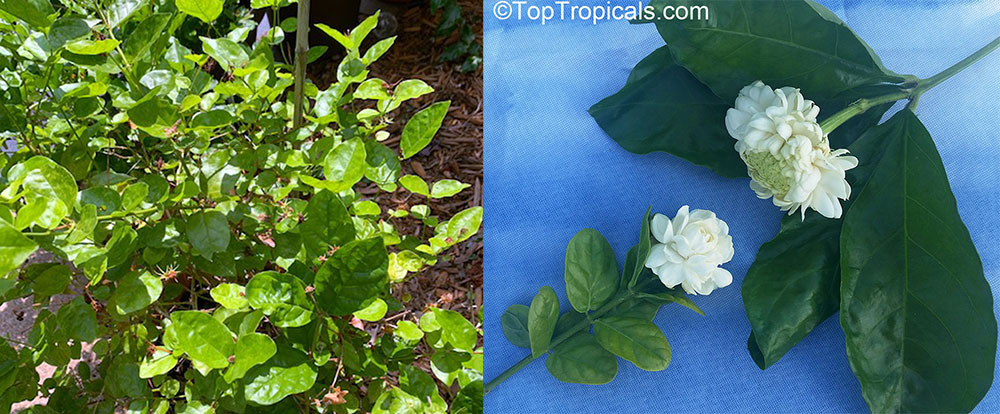
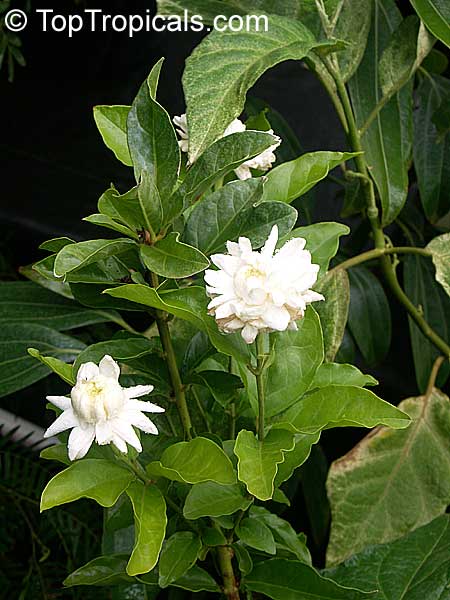
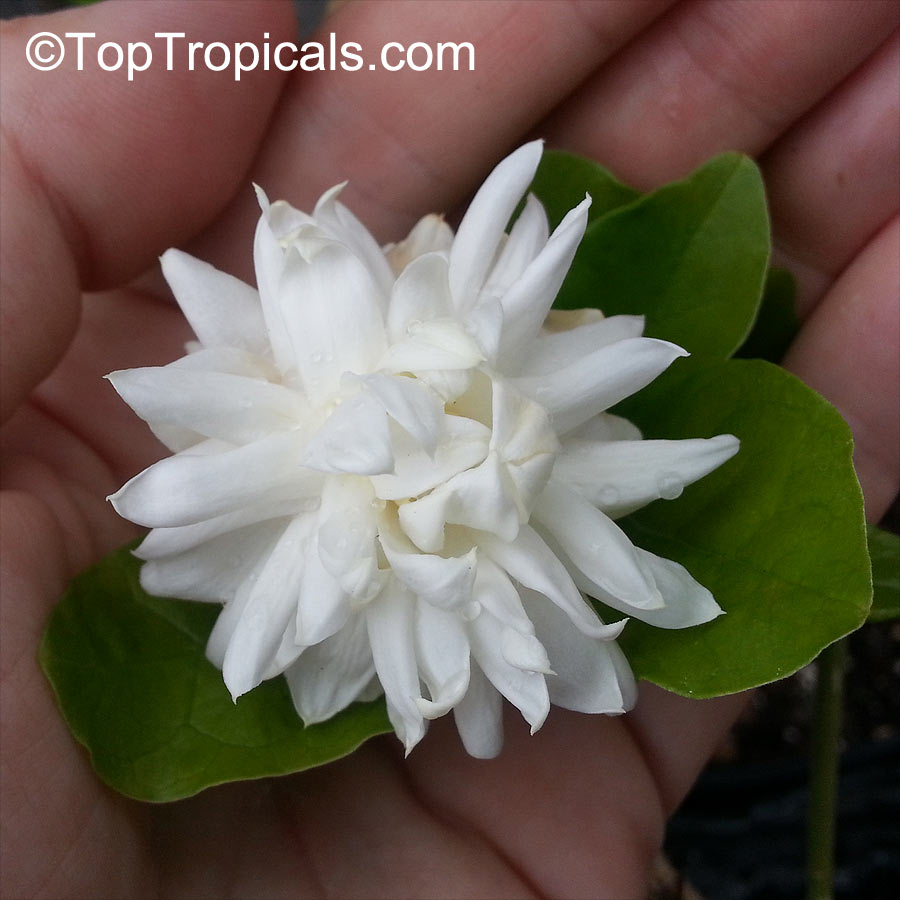
Little Duke - new variety of Jasmine Sambac
We are exited to introduce to the world of tropical plant lovers a new
hybrid of Jasmine sambac Grand Duke Supreme - Little Duke!
This new variety combines benefits of 1-1.5" large, triple flowers with a
compact, bushy growth habit. What an amazing gift for every jasmine lover!
Unlike regular Grand Duke that tends to be leggy, this variety branches out much
more and stays short with minimal pruning. Leaves are similar to Grand Duke
Supreme - elongated and come in swirls of 3's and 4's. It is a fast grower,
reaching mature size in no time, but the plant stays compact, producing
multiple flowers on every branch.
Little Duke, or Baby Duke, is a profuse bloomer, providing lots of sun,
warmth, and moderate water.
It is a perfect houseplant with the strongest jasmine fragrance in the
world. A must have for every jasmine collector!
The plants we currently have in stock are very large and developed, with multiple stems, some are full of buds and ready to flower for you. They are in 1 gal pots, ready to be stepped up soon. But hurry up! We have limited stock that will be sold FAST! Don't wait and get this gem today for your fragrant plant collection, before they all sold out! The next batch won't be coming until a few months later and the plants will be much smaller...
Date:
Healthy Plants: Q&A from Mr Booster
Jasmine Grand Duke flowering
Q: Hey can you help me figure out why my jasmine grand duke supreme is not flowering? Ive had it for almost a year (in NY) and only had 1 flower bloom and that immediately turned brown and died. Since then no flowers have come. The leaves are green and healthy and its growing like crazy but not flowers. Please help me figure this out.
A: For profuse flowering, Jasmine sambac needs 2 things: bright light and special plant food.
We have plenty of both here in Florida. If your grow this plant indoors in
colder climate, get it to flowering can be a bit tricky.
Your plant grows well overall with lots of vegetative growth, this is a
good sign, it means it's healthy, and not being overwatered which is one of the
most common problems with Sambacs. You're doing a great job! This jasmine
just needs more sun and fertilizer.
Make sure to keep it in the brightest spot of your home. The more hours of
light, the better. When night temperatures stay above 65F, it is beneficial
to bring the plant outside on a balcony, patio, or in a garden in full sun as
a potted specimen (move to bright light gradually).
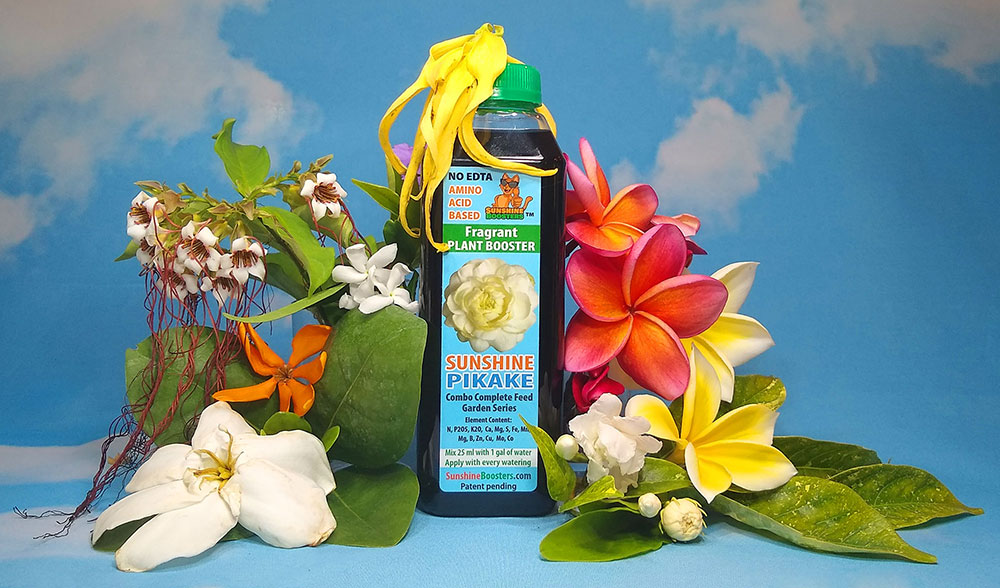
You should give this Jasmine plenty of food with every watering. We
recommend SUNSHINE Pikake - Fragrant Flower Booster. This is a natural fertilizer
that can be applied to plants year round without risk of burning the roots
or nutrient lock up in the soil. It provides all necessary elements for the
flowering cycle - just add a bit into watering can, every time you water.
Why everybody wants this plant? Intoxicating sweet fragrance is the answer! Do you have one?
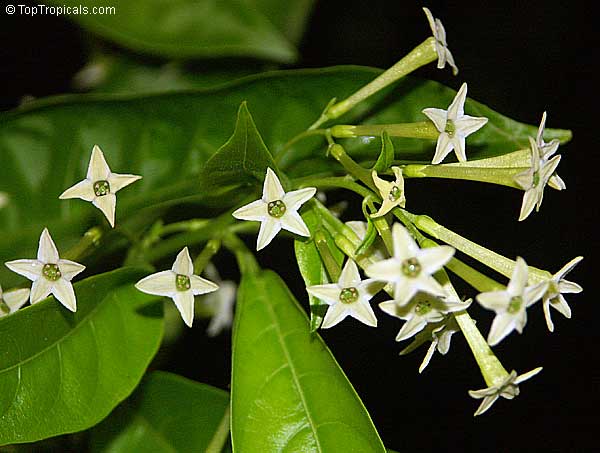

Cestrum nocturnum - Night blooming jasmine
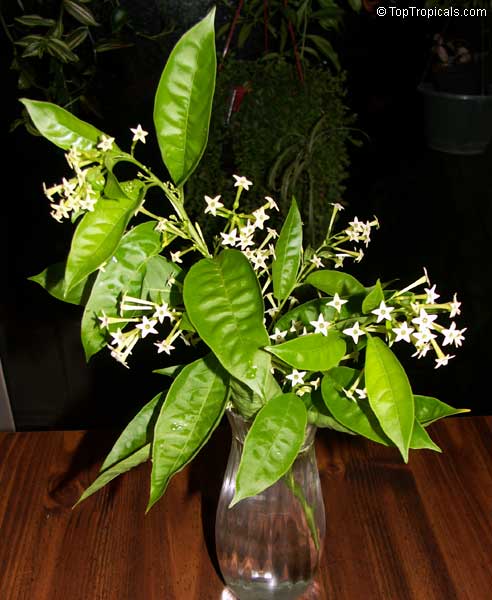

Cestrum nocturnum - Night blooming jasmine
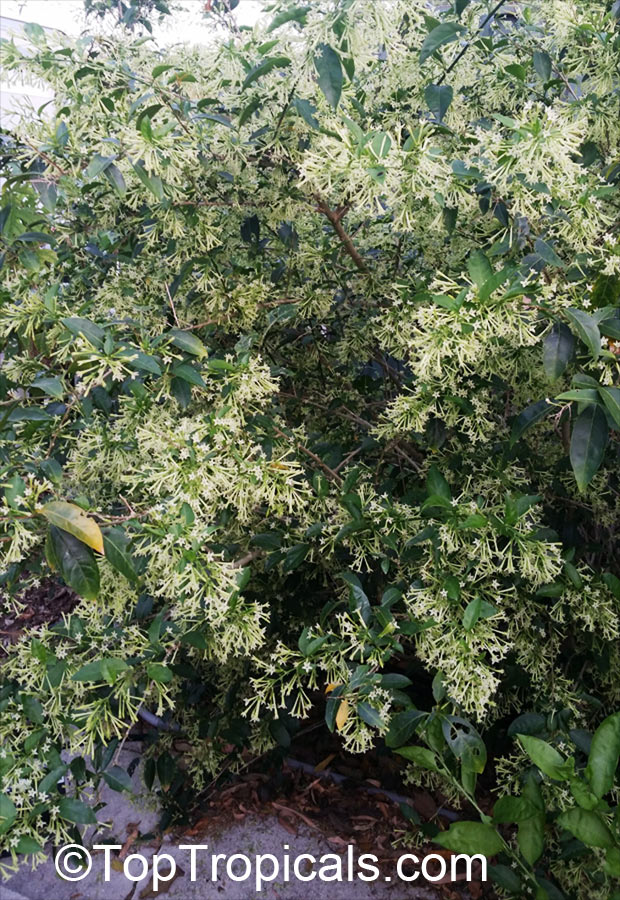

Cestrum nocturnum - Night blooming jasmine
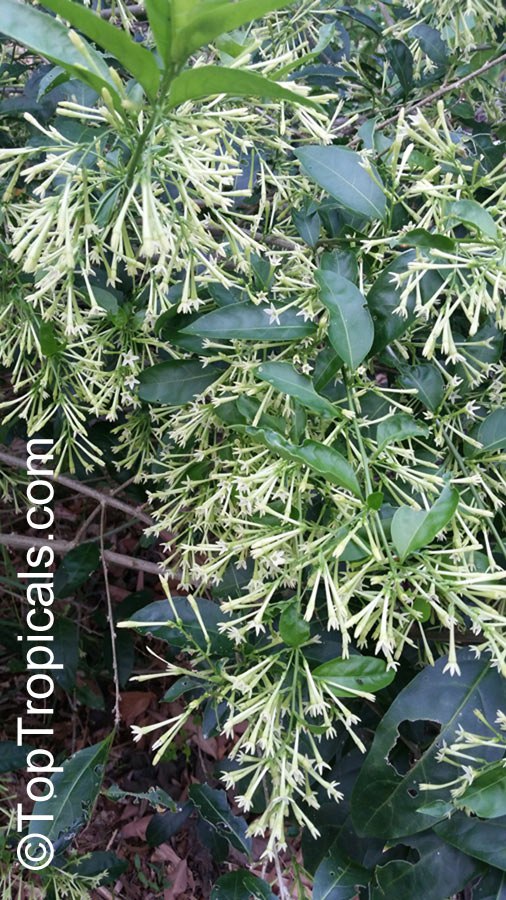

Cestrum nocturnum - Night blooming jasmine
⭐️ This fast growing, dense shrub is a garden favorite, one of the most famous and desirable fragrant plants.
🌃 The sweetest fragrance at night is intoxicating.
🌄 Flowers are pale yellow to white, open at night and stay extremely fragrant until sunrise.
🙏 These flowers are widely used in India and other countries of South Asia for perfumery, medicinal applications and in religious ceremonies.
🏡 Best location will be near driveway, window or entrance, where the magic fragrance can be appreciated.
🛒 Order online
#Perfume_Plants #Hedges_with_benefits
🏵 TopTropicals