Syzygium - Plant Encyclopedia Results
| Number of plants found: 19 | Next | 
|
Go to page: | 1 | 2 |
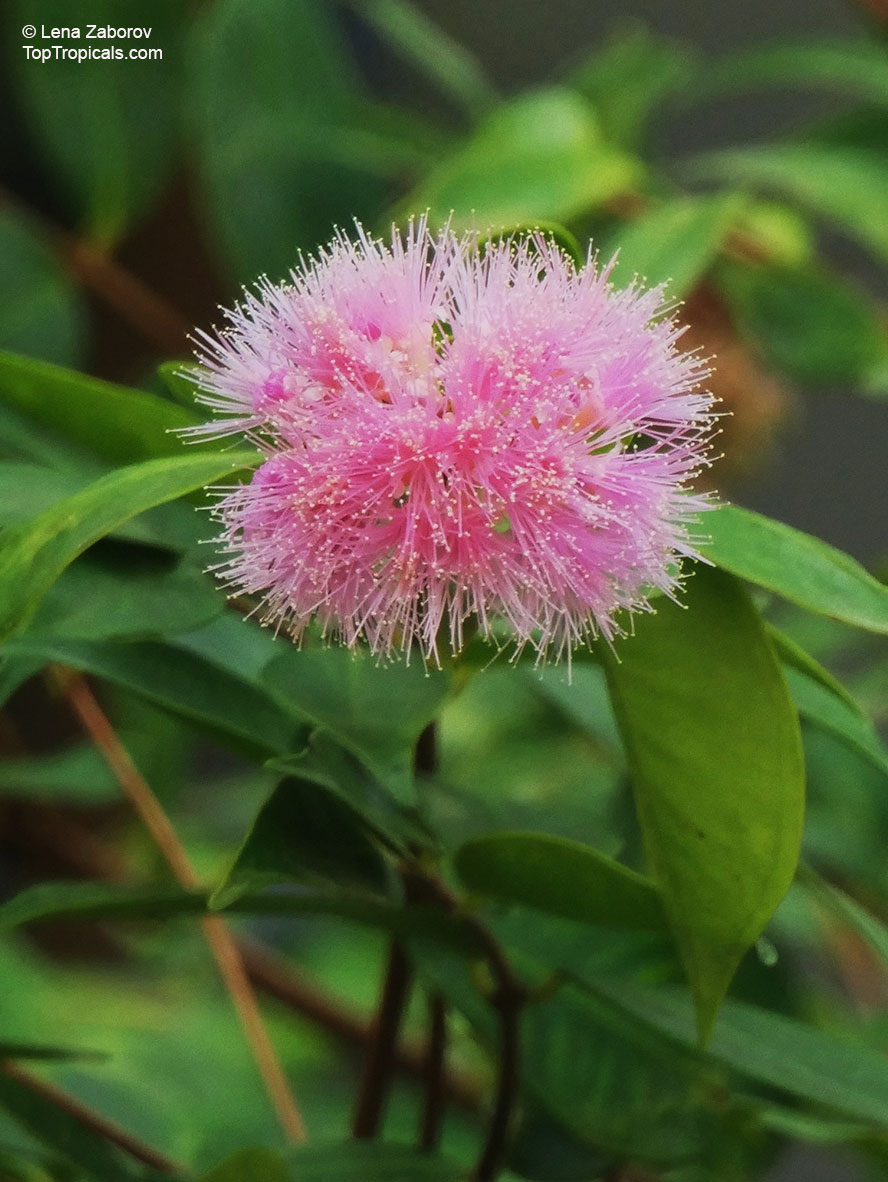
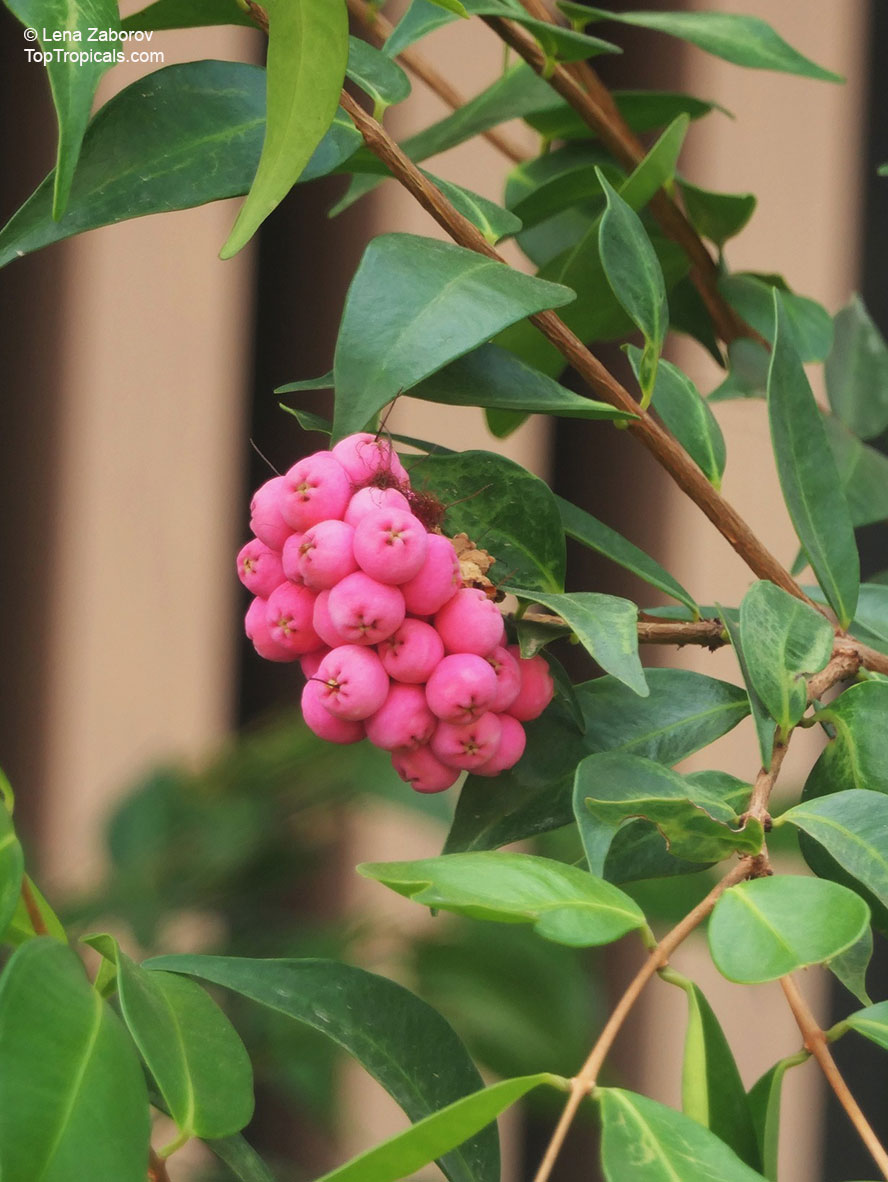
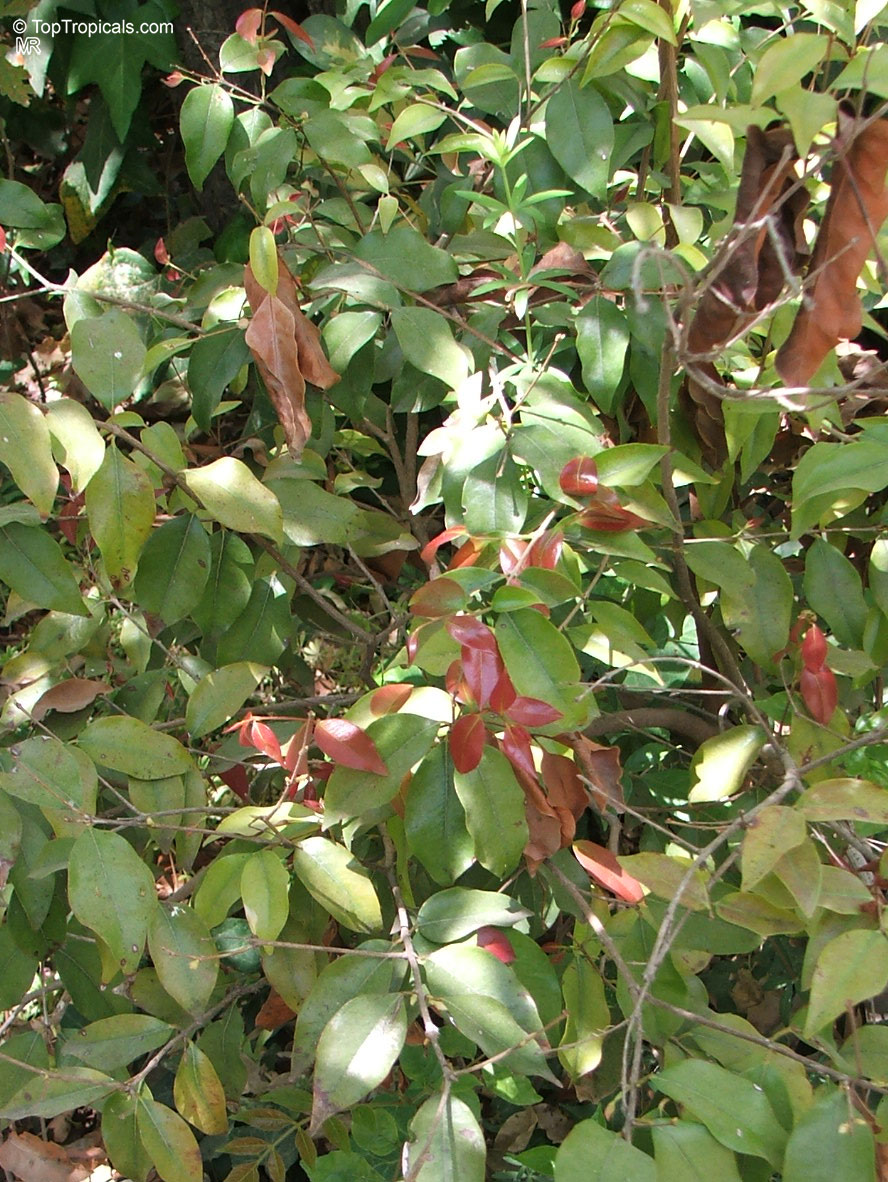
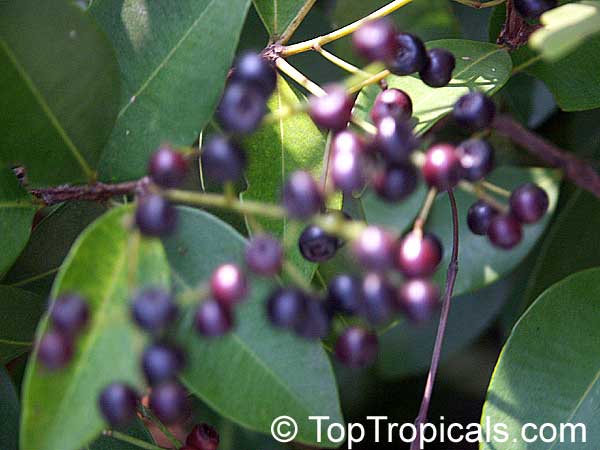
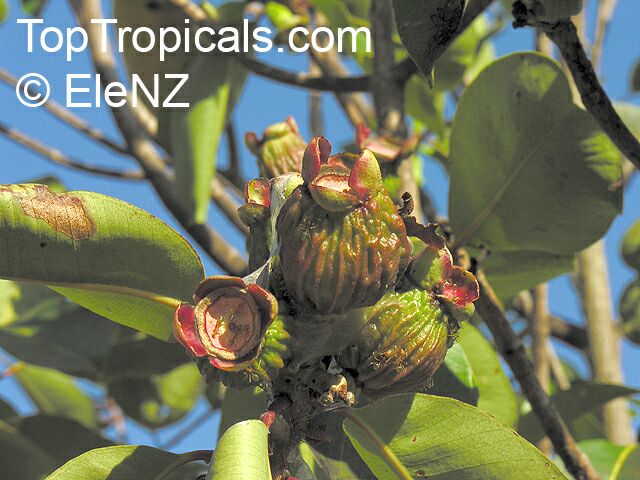
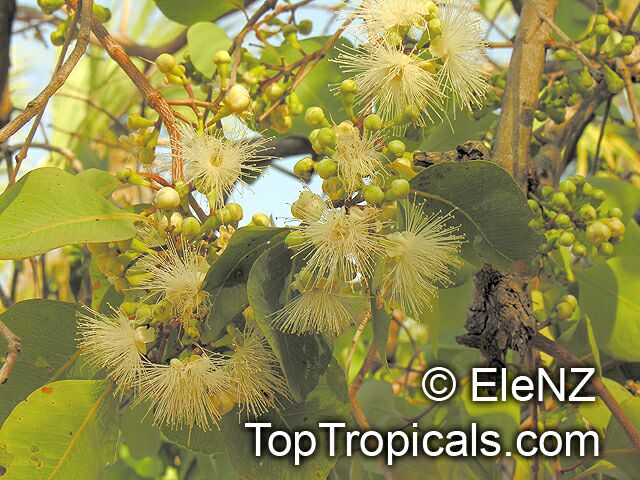
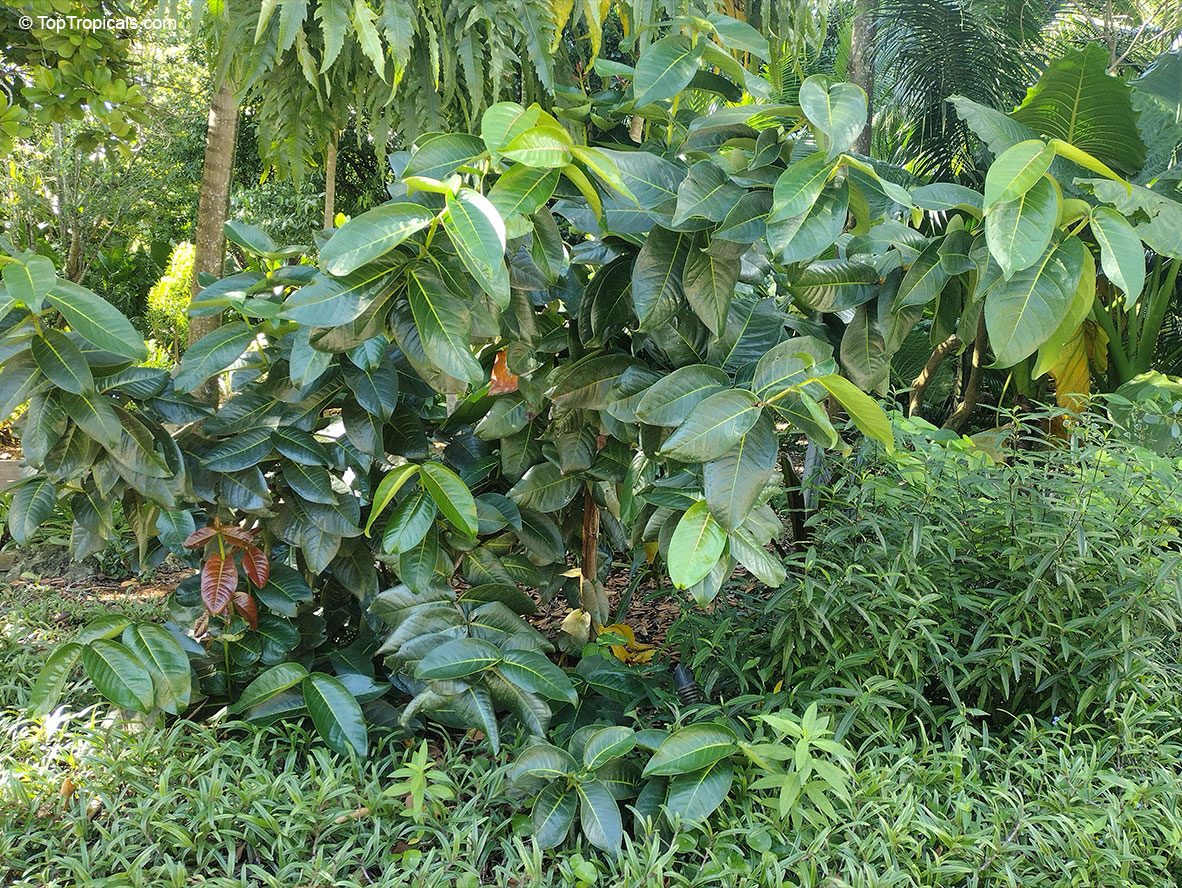
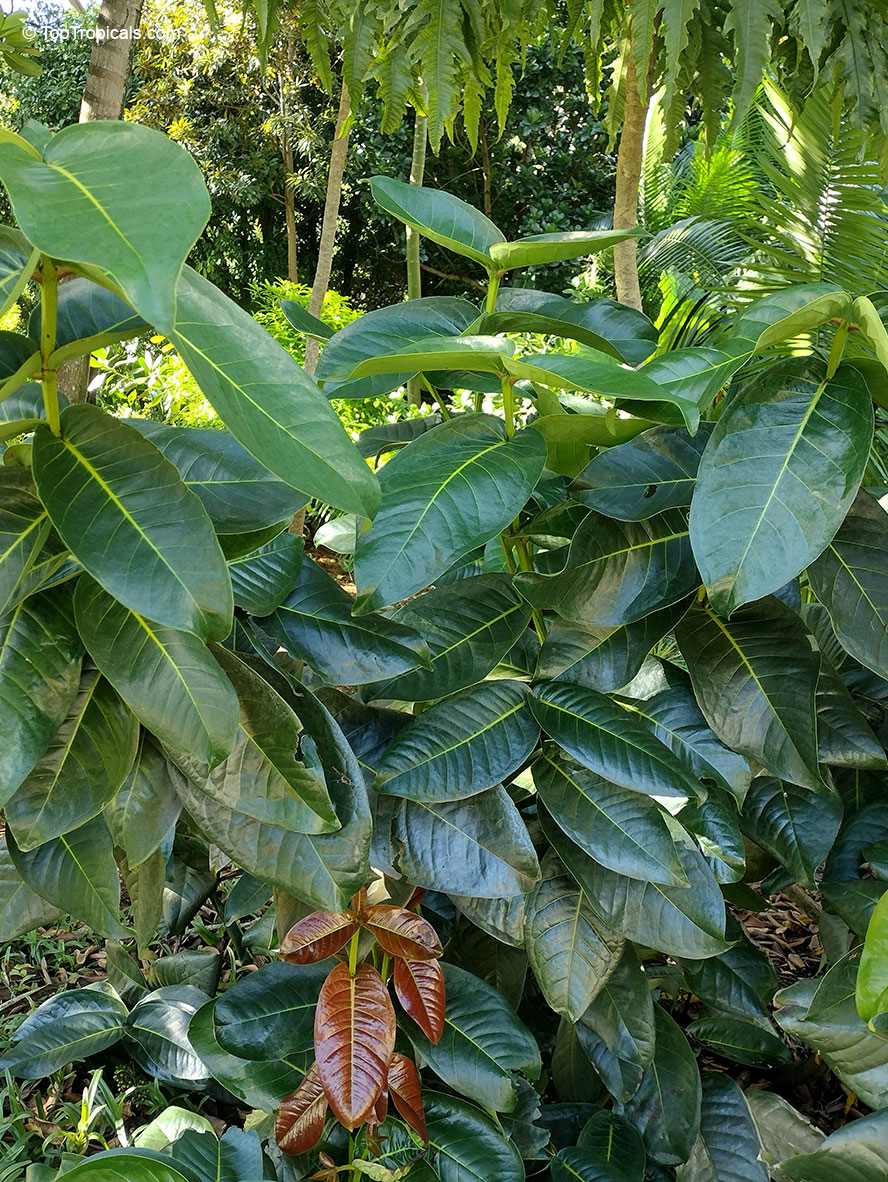
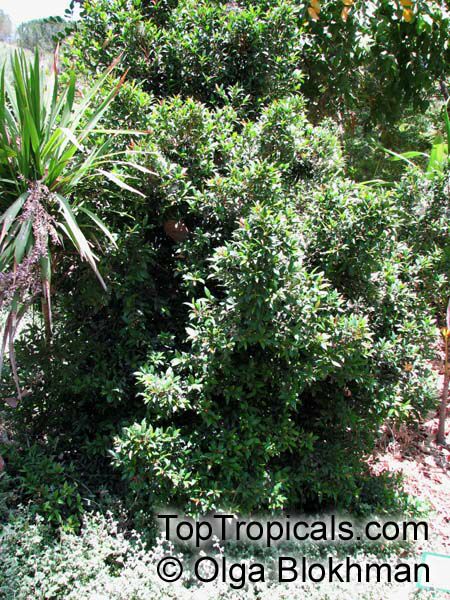
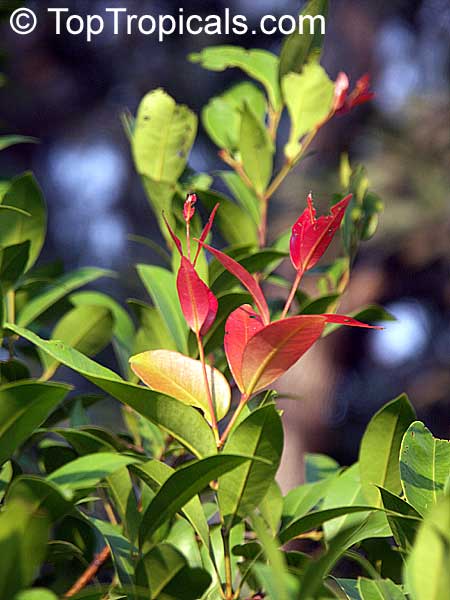
Botanical name: Syzygium thalassicum
Common name: Syzygium
Family: Myrtaceae
Origin: Solomon Islands





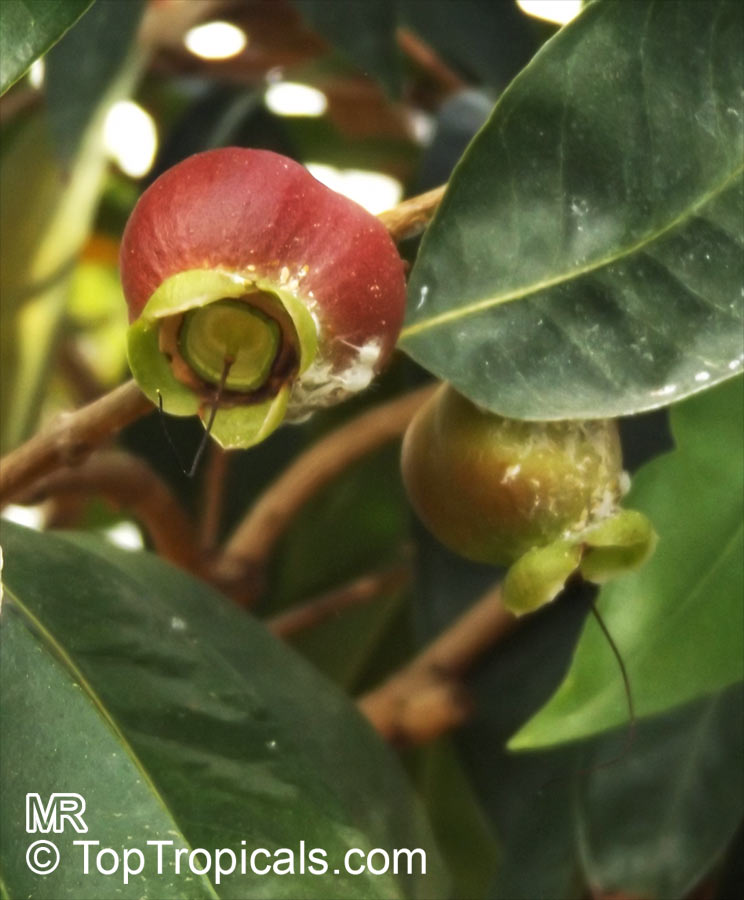
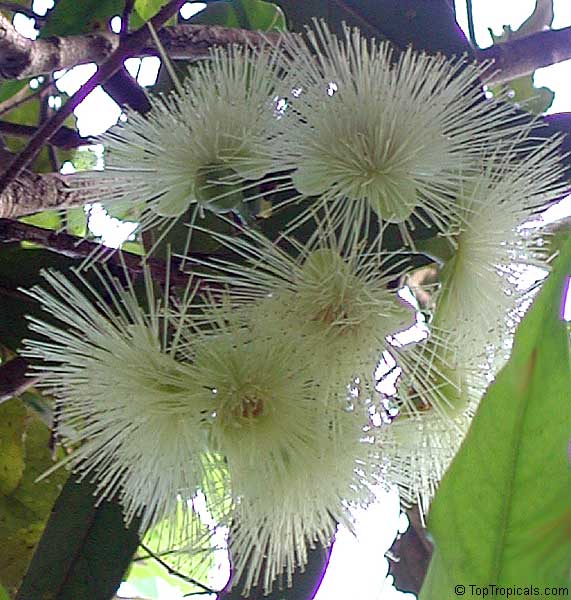
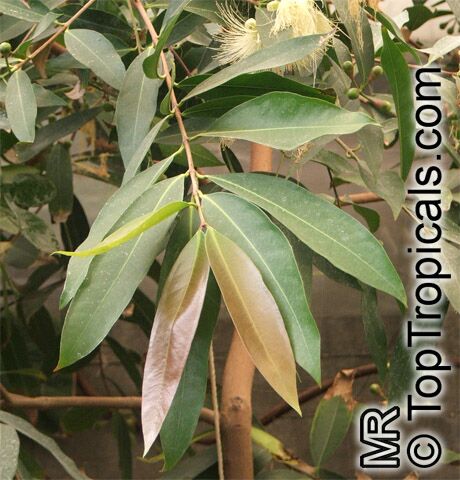
Syzygium thalassicum is a large-leafed shrub to small tree, growing in the wet tropical biome of the Solomon Islands. The leaves are wide, dark green and glossy when mature, but a striking red when emerging. It blooms beautiful white "powder puff" flowers and produces red fruits. The fruit are edible, yet not as tasty as other Syzygium species.
Botanical names: Syzygium antisepticum, Syzygium gratum, Eugenia glaucicalyx, Eugenia grata, Syzygium glaucicalyx
Common names: Kalaum, Malaruhat
Family: Myrtaceae
Origin: Southeast Asia








This species is similar to Syzygium zeylanicum however it differs in size (bigger tree), leaves are dark glossy green on topside with longer petioles and the white fruits are slightly smaller than those of Syzygium zeylanicum.
Botanical name: Syzygium australe
Common name: Scrub Cherry
Family: Myrtaceae
Origin: Australia







The species formerly known as Eugenia australis is now regarded as two separate species, Syzygium australe and Syzygium paniculatum.
Botanical names: Syzygium campanulatum, Syzygium myrtifolium, Eugenia oleina
Common name: Wild Cinnamon
Family: Myrtaceae
Origin: Southeast Asia






Syzygium campanulatum or Wild Cinnamon is a small tree native to Southeast Asia, growing about 10-20 feet in height. It's a perfect choice for those looking for an attractive, fragrant ornamental tree. It is a sun-loving tree, requiring full sun exposure, and regular water.
The tree produces an abundance of white, off-white flowers, often tinged with red and crimson, or vinous. These fragrant flowers are a sight to behold, emitting an unmistakable cinnamon scent.
Wild Cinnamon is typically grown in hardiness zones 9-11, making it a great choice if you live in one of these zones. It grows well in soil that is both well-drained and slightly acidic. The tree prefers a mildly acidic soil pH of 6-6.5, but it is quite tolerant of a wide range of soil pH.
When planted in a pot, Wild Cinnamon can survive in colder climates. It needs regular watering, at least 2-3 times a week, to ensure that the soil does not dry out completely. Also, make sure to keep the soil cold, as the tree prefers temperatures between 55-65°F. You can also protect the tree in cold months by using mulch and insulating fabrics to guard it against frost.
The Wild Cinnamon tree is an excellent choice as an ornamental tree, providing fragrant flowers and leafy smell of cinnamon. With proper care and maintenance, this small tree is sure to make a great addition to any garden.
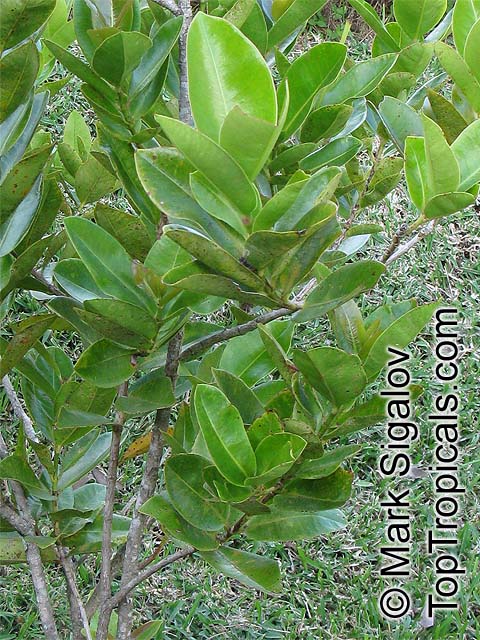
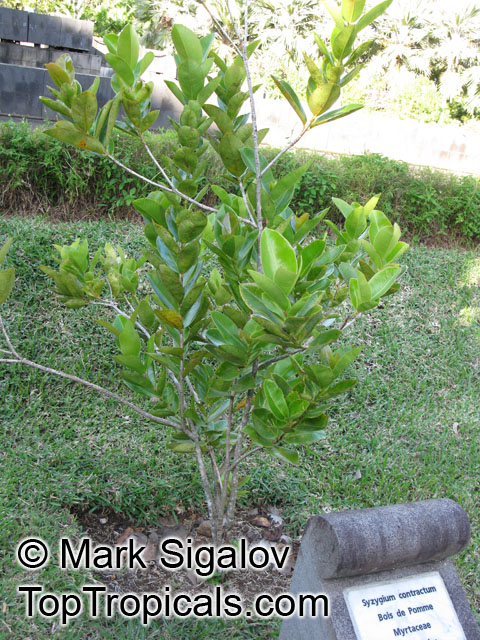
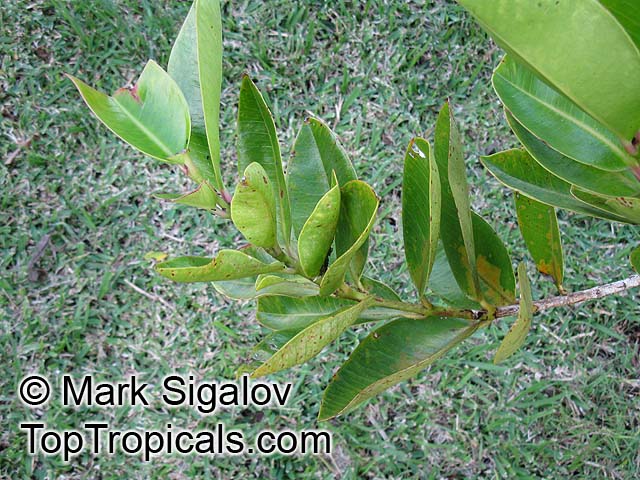
Botanical name: Syzygium contractum
Common names: Bois de Pomme, Bois Boeuf
Family: Myrtaceae
Origin: Mauritius







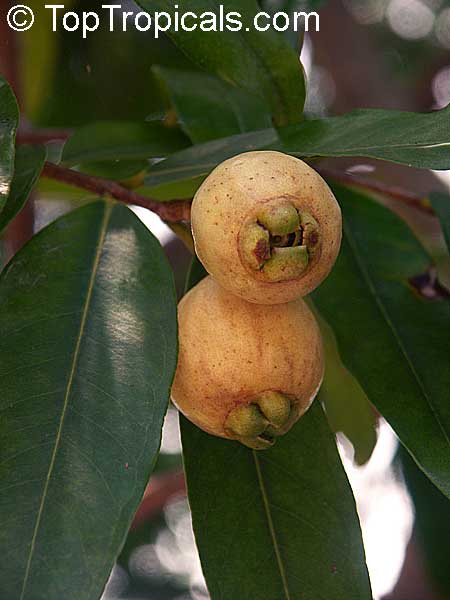
Syzygium contractum is a large shrub that can reach 5-10 feet tall and is native to Mauritius. It needs full sun to semi shade, and needs a moderate amount of water for optimal growth and health. It makes a great ornamental addition to most landscapes with its bright pink flowers appearing in the late spring and early summer. The bright edible berries which follow are purple in colour and reach 2cm in diameter.
When growing this plant, in colder parts of the country, it is best to keep Syzygium contractum in a pot. It needs to be moved inside or sheltered from the weather during the coldest months of winter. It prefers a well-draining soil, although it can tolerate more moisture if needed. It is recommended to water regularly and evenly in order to keep the soil moist.
Syzygium contractum is not only a beautiful addition to any landscape, but it can also provide many edible benefits. The edible fruit of the shrub contains high amounts of vitamin C and is used to make jams and jellies. It is also considered to be a superfood due to its high amount of antioxidants, minerals and vitamins. It can even be used to make wine. Syzygium contractum can bear up to three fruits per branch and one plant can easily produce over ten fruits in a season.
Overall, Syzygium contractum is a great ornamental plant to add to any garden. Its bright pink flowers, followed by edible fruits make it a great addition for any garden. It is easy to care for, just needing full sun to semi shade and regular water. Its edible benefits such as its high levels of vitamin c, minerals and antioxidants make it a great superfood, and it can easily produce up to ten fruits a season.
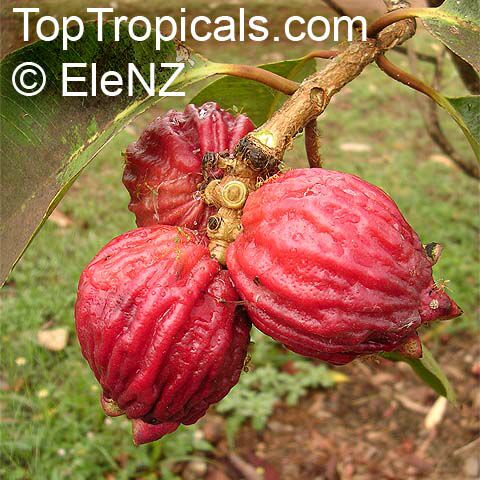
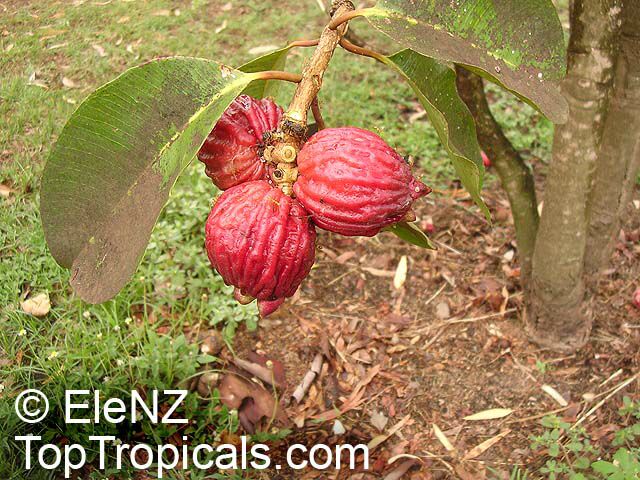
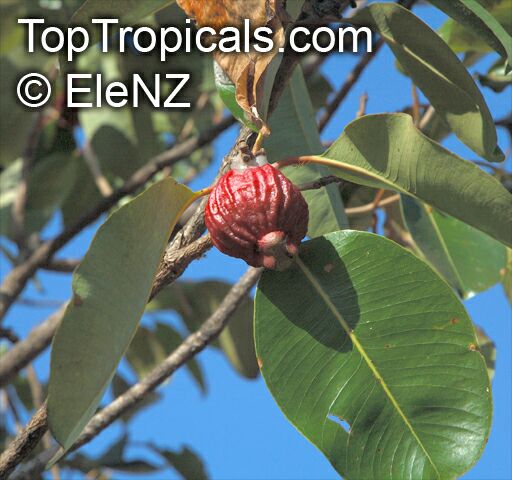
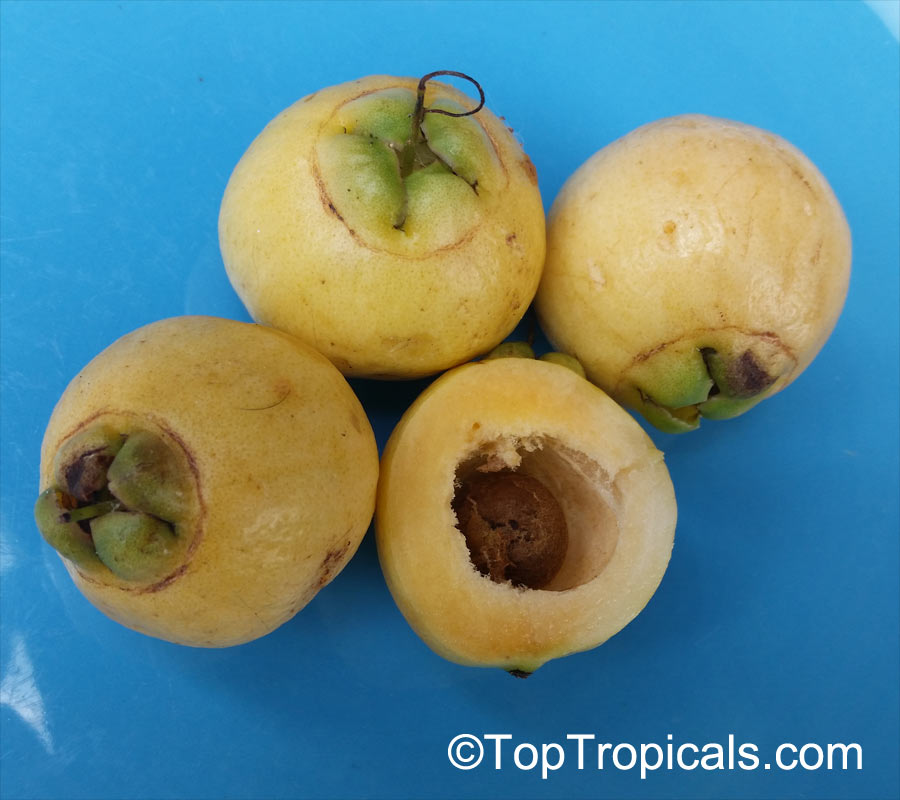
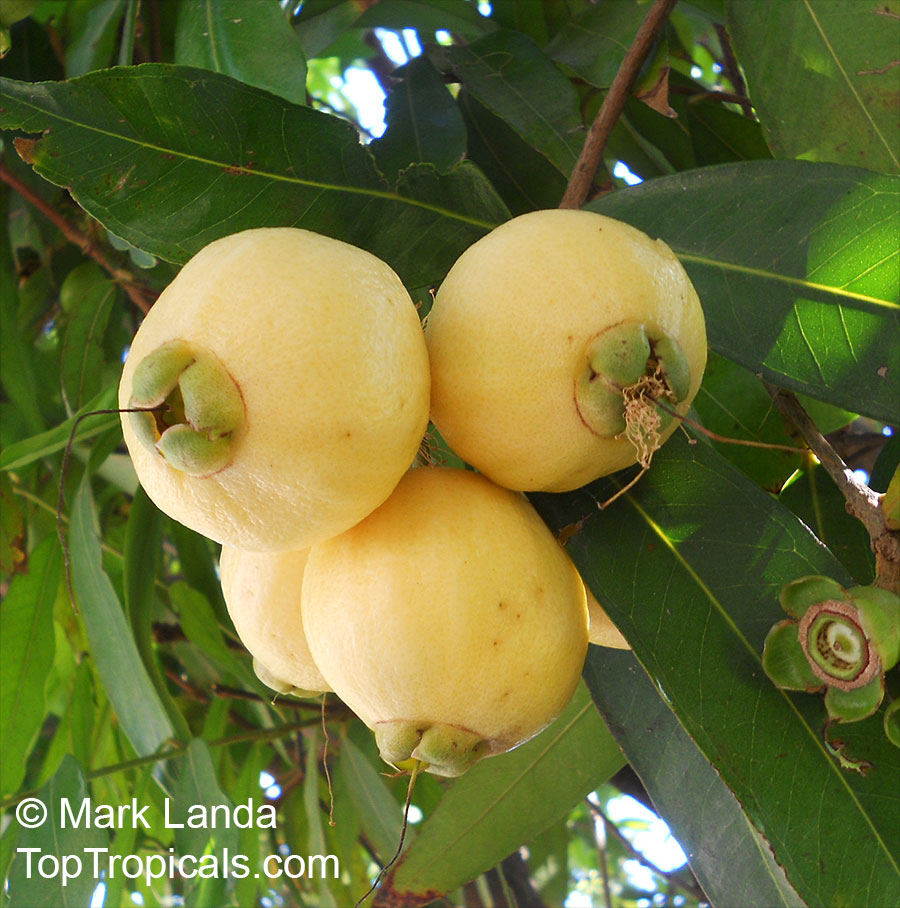
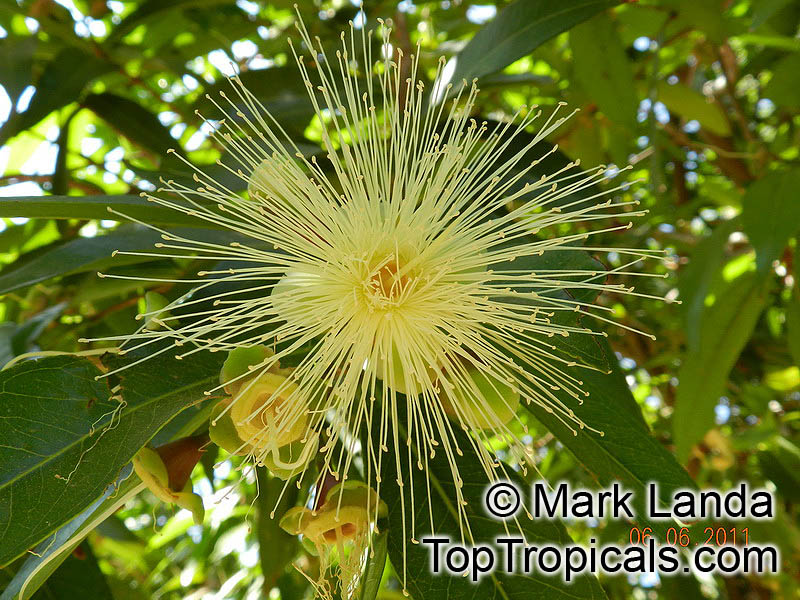
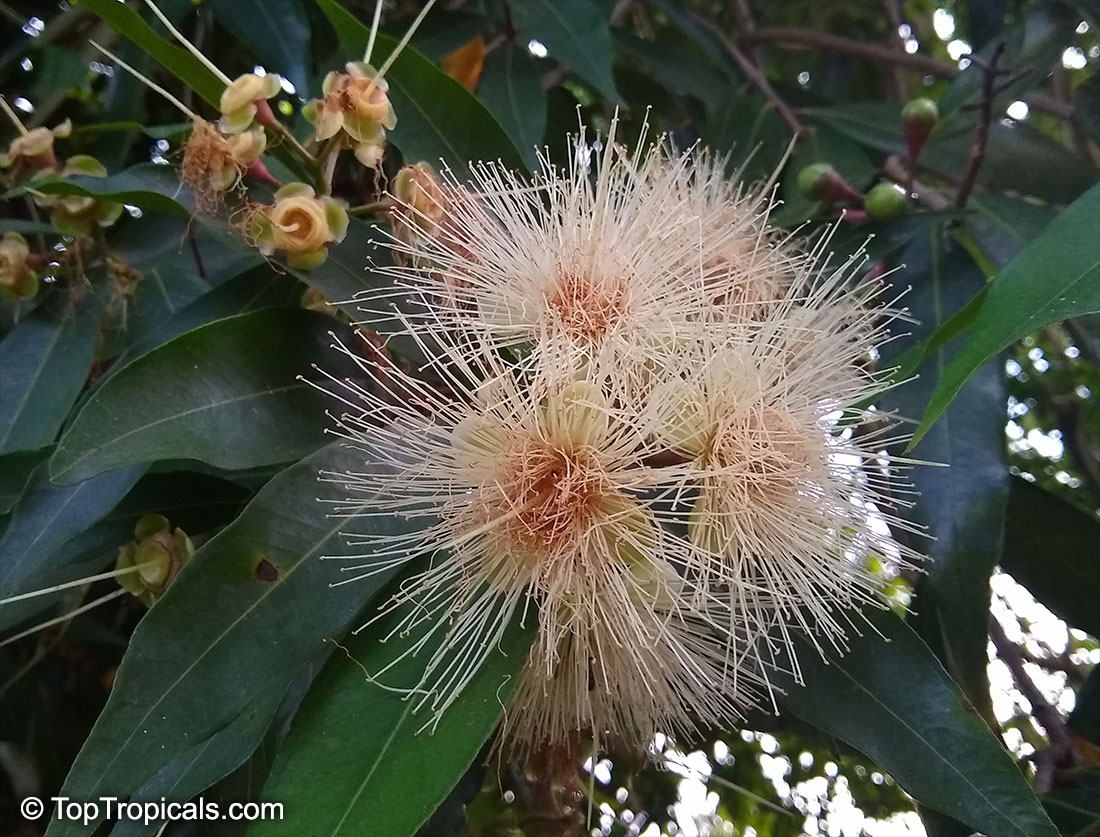
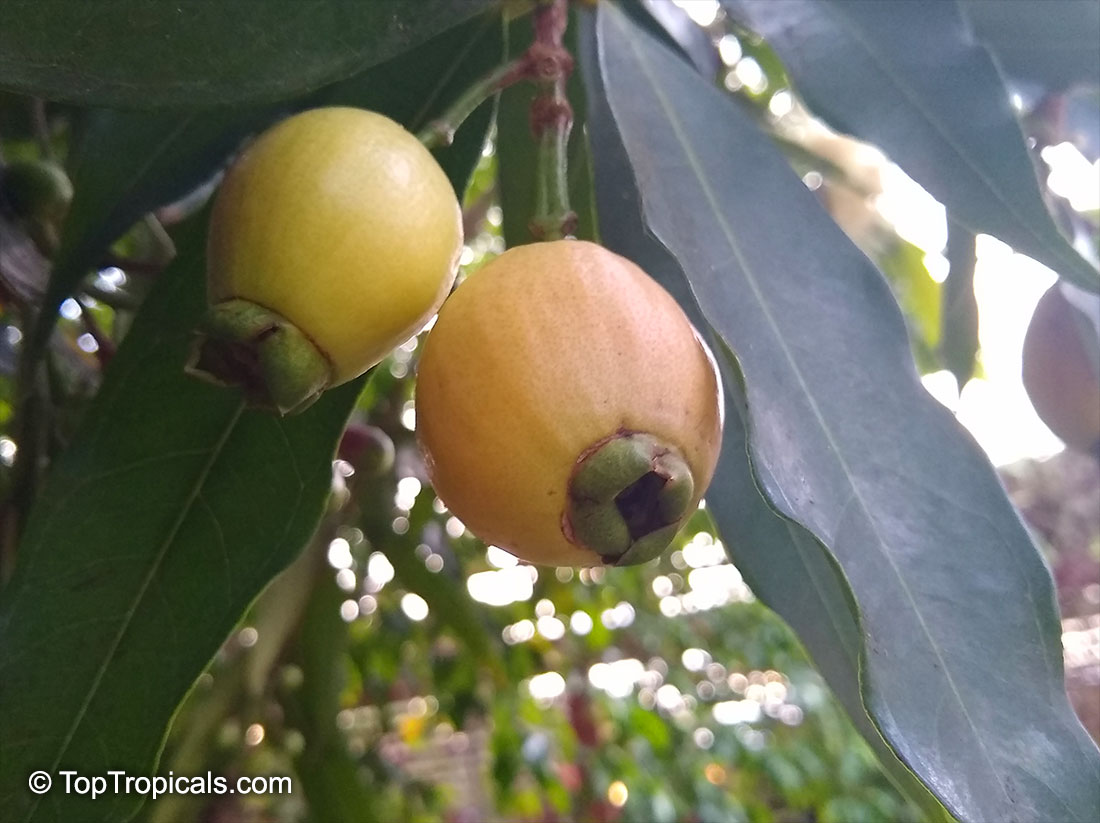
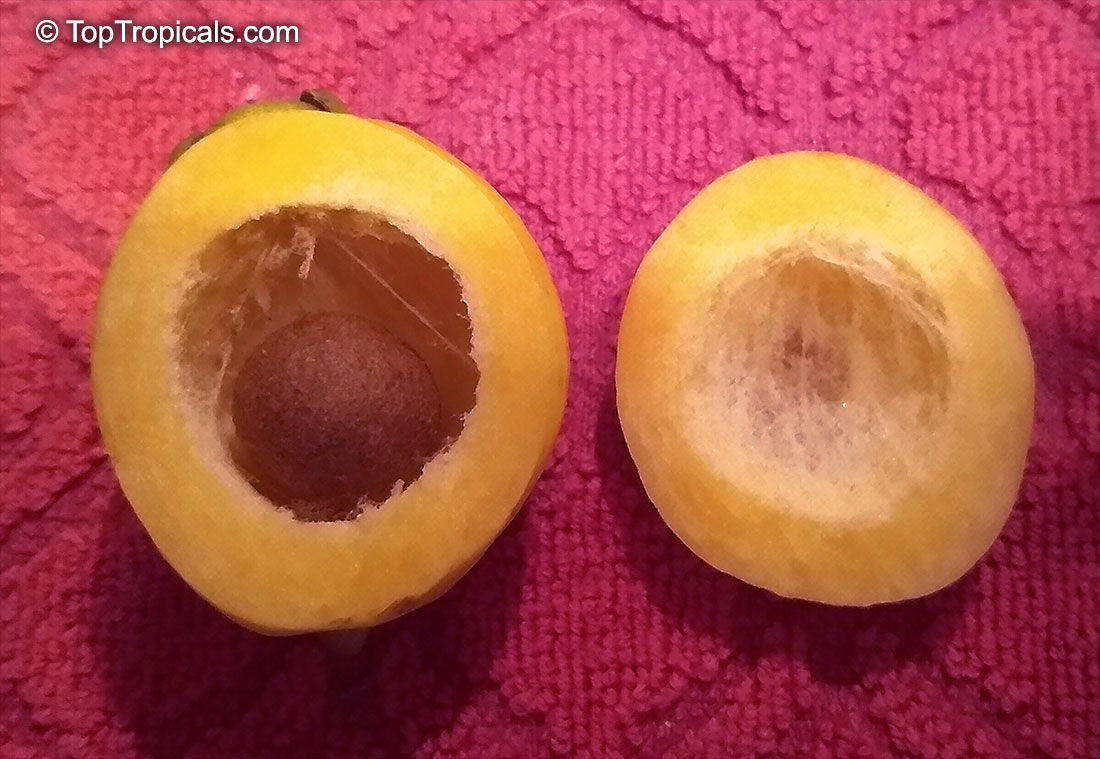
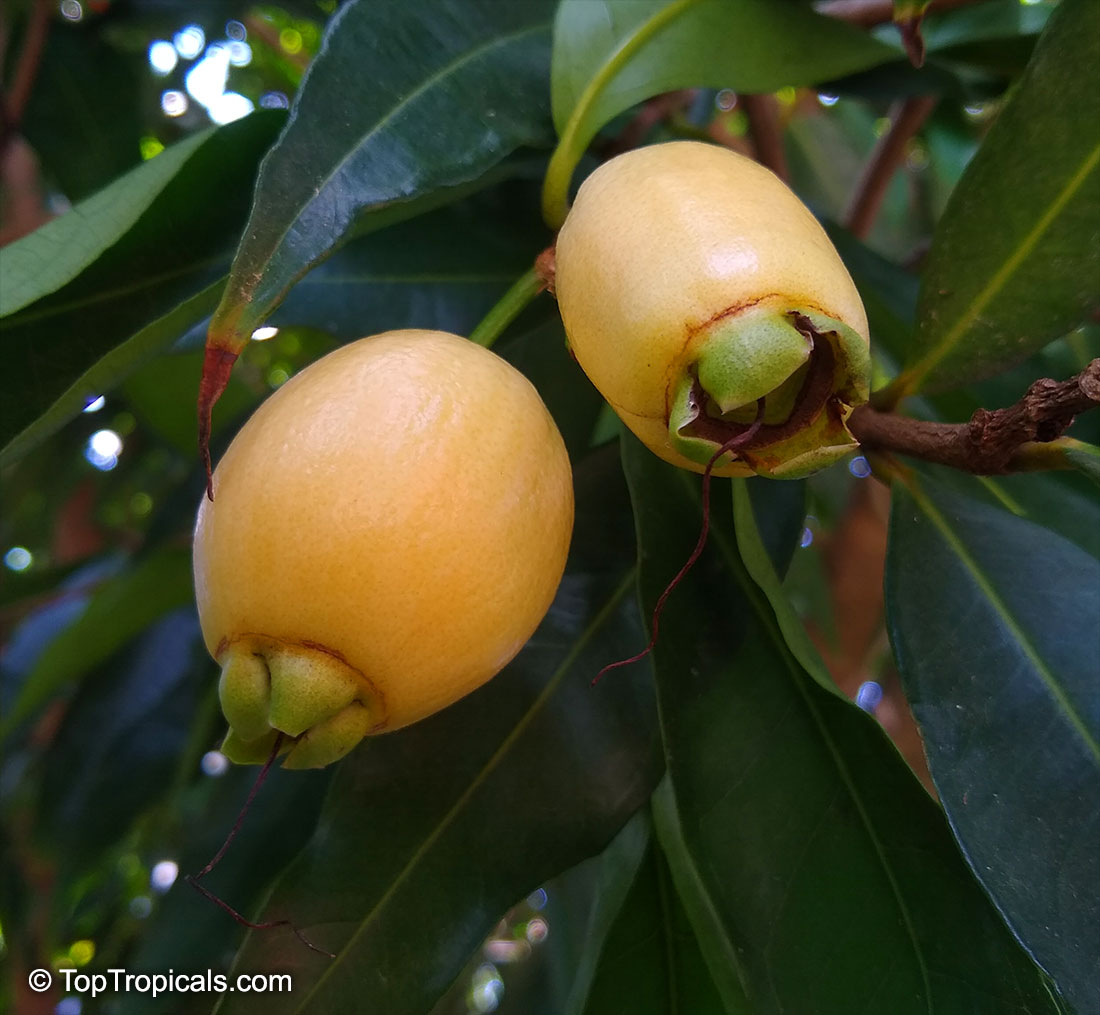
Botanical names: Syzygium jambos, Eugenia jambos, Jambosa jambos
Common names: Rose apple, Malabar Plum, Pomme rosa
Family: Myrtaceae
Origin: East Indies and Malaya










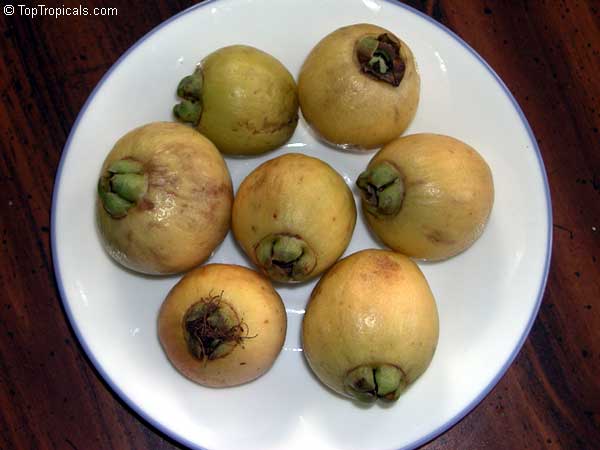
Rose Apple is a popular fruit native to Southeast Asia. The beautiful blossoms contain hundreds of showy stamens. The crisp and juicy fruits are very distinctly rose scented and highly prized for jellies and confections. The plant is easy to grow, moderately cold hardy and tolerates poor soils. Makes an attractive, wide-spreading shade tree as well as compact and bushy container fruiting plant.
See our video about Rose Apple.
Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE C-Cibus - Crop Nutrition Booster
SUNSHINE-Honey - sugar booster
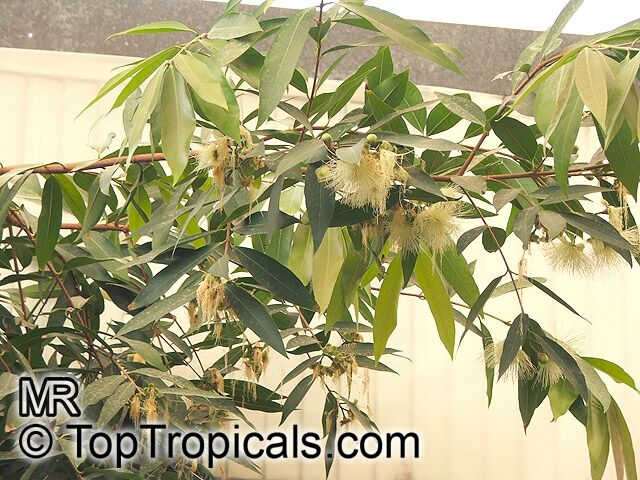
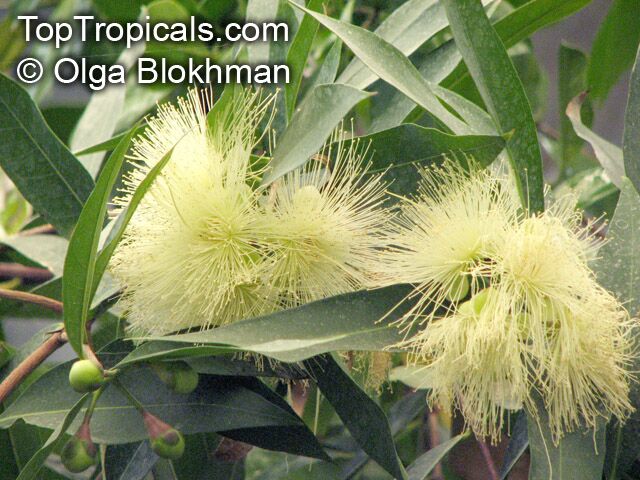
Botanical name: Syzygium luehmannii
Common name: Small Leaved Lilly Pilly
Family: Myrtaceae
Origin: Australia









Syzygium luehmannii, also known as Small Leaved Lilly Pilly, is a native plant to Australia. This small tree grows between 10-20 ft in height and can be used for bonsai. It prefers full sun to semi-shade and requires regular water, although it can tolerate moderate water. White to off-white flowers attract butterflies and hummingbirds from further distances. Grown in USDA Zone 9-11, this tree can be grown in both pot and soil in cold regions.
The fruit of the Syzygium luehmannii is edible and have a sweet-tart flavor. The fruit is full of antioxidants and can be used to make jams and preserves. As a healthy snack, the fruit can be eaten straight or used in salads or other recipes. Depending on the size, a single Syzygium luehmannii tree can produce between 10-20 pounds of fruit per year.
When growing the Syzygium luehmannii, it is important to protect it from the midday sun and provide regular water. It is also important to prune regularly, especially in the spring months, to maintain a desired shape. To enhance the fruits production, adding organic matter such as manure or compost to the soil will help the plant flower and produce fruit.
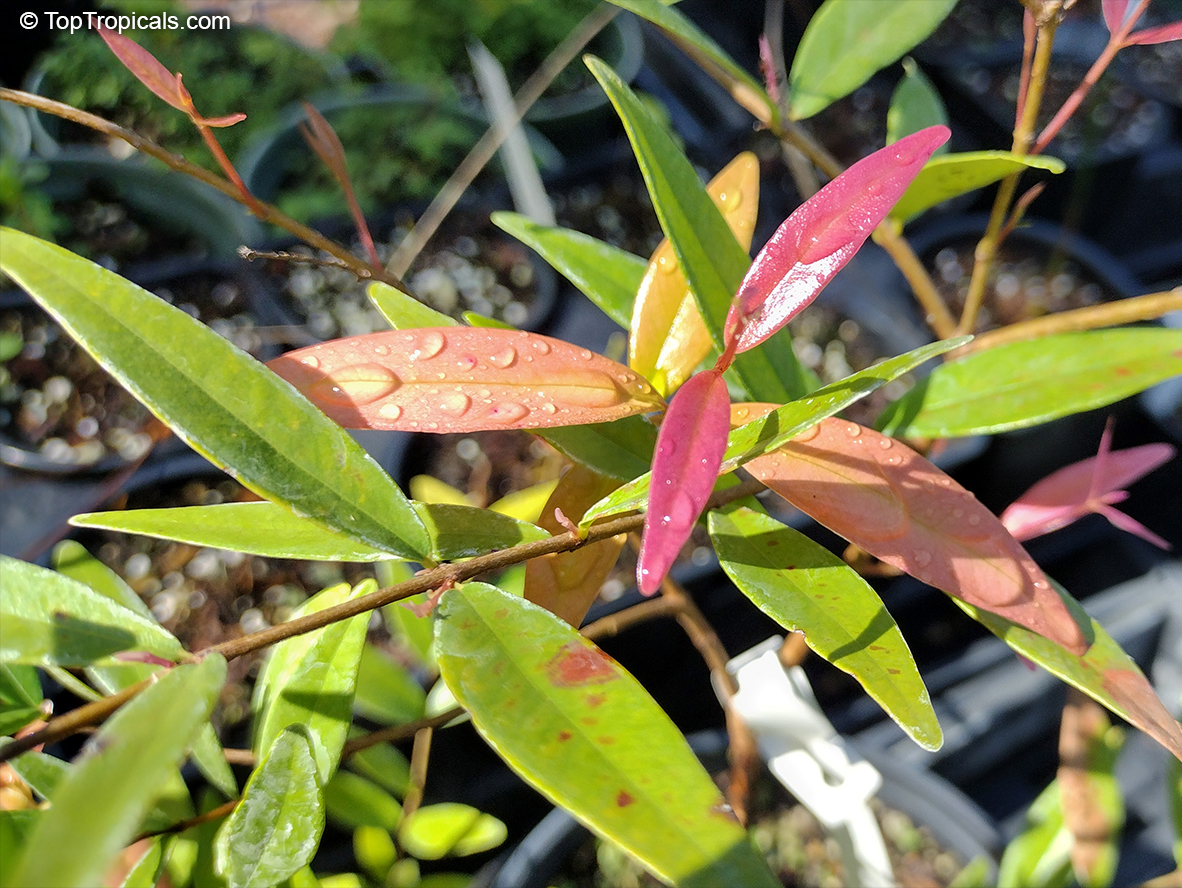
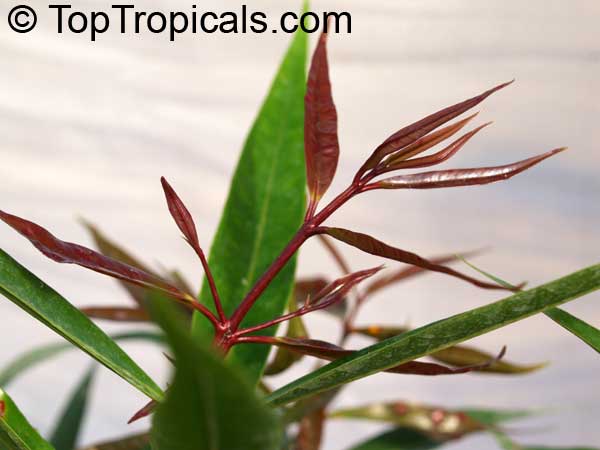
Botanical names: Syzygium myrtifolium, Eugenia oleina, Eugenia myrtifolia, Syzygium campanulatum
Common names: Wild Cinnamon, Australian Brush-Cherry, Kelat Oil, Kelat Paya, Red Lip
Family: Myrtaceae
Origin: Southeast Asia








The young leaves of Syzygium myrtifolium are often either yellow or orange. There is a cultivar with dark red young leaves and bright pink to maroon flowers.
They are often used as a hedging plant or ornamental tree, also sculptured into topiaries or even made into bonsai.
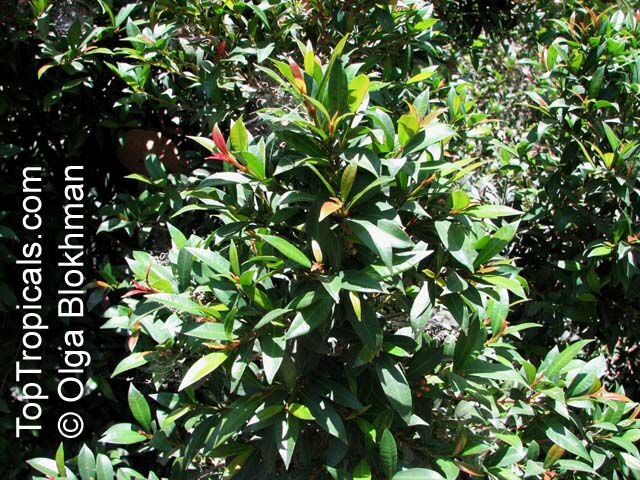
Botanical name: Syzygium oleosum
Common name: Blue Lilly Pilly
Family: Myrtaceae
Origin: Australia









The Blue Lilly Pilly is a native to Australia and is found abundantly in northern parts of the continent. The Syzygium oleosum, more popularly known as the Blue Lilly Pilly, is a type of shrub that can grow as either a large bush or a more sizable small tree, reaching up to a maximum height of 20-40 feet. This species is fairly hardy and generally only requires a subtropical climate to grow its best. However, it is wise to provide protection from long or hard freezes. These plants enjoy profuse amounts of water, but they will still manage to grow in drier climates if they are in areas that receive a combination of light sun and shade.
The Blue Lilly Pilly produces many beautiful off-white, creamy-colored flowers that give off a pleasant, fragrant aroma. This aroma has also been found to act as a natural attractant to both butterflies and hummingbirds. In addition to its natural beauty, the Blue Lilly Pilly can produce an edible fruit. This fruit is small, dark green, and turns black when ripe. The fruit is generally enjoyed raw or cooked and can also be used to make jams, jellies, preserves, and various drinks.
The Blue Lilly Pilly has many healthy benefits. It contains many useful chemicals and nutrients, including zinc, iron, magnesium, and vitamin C. Also, it is known to be rich in anti-microbial characteristics, helping to keep the immune system functioning efficiently. In terms of how much fruit the plant can produce, it will depend on the climate, care, and nurturing. A well-kept Blue Lilly Pilly can produce up to 30 fruits per season.
Those looking to grow their own Blue Lilly Pilly will best succeed in USDA Zones 9-11. In particular, those located in colder climates may benefit from growing their plant in a pot. Seeing as the Blue Lilly Pilly is native to Australia, it may take a bit of extra care and nurturing, but with some patience, it is possible to grow these beauties successfully in a pot or a sunny spot in the yard.
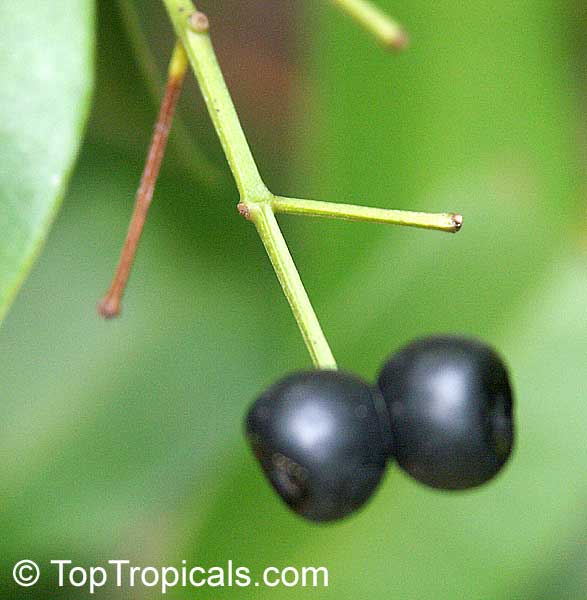
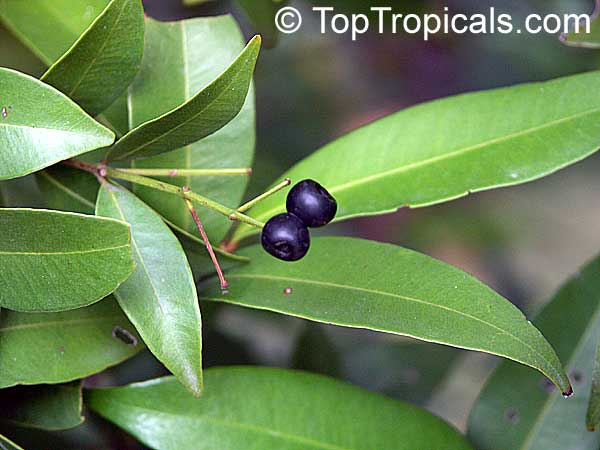
Botanical names: Syzygium suborbiculare, Eugenia suborbicularis
Common names: Red Bush Apple, Lady Apple
Family: Myrtaceae
Origin: Australia









Syzygium suborbiculare (Red Bush Apple) is a large shrub or small tree that typically grows 5-10 ft tall, but can reach up to 20 ft in full sun with moderate water. It is native to Australia, and well-known for its ethnomedical properties. It produces white or off-white flowers that attract butterflies and hummingbirds.
The fruits of Syzygium suborbiculare are a characteristic dark blood red color, with a firm and crunchy flesh that easily breaks away from the single large seed. The fruit is sour and tangy, and is both edible and highly coveted among bush travelers. Aborigines have been known to use the fruit for medicinal purposes, such as treating chest congestion and earache. On average, each tree produces between 5-15 fruits each year, but when provided with the right conditions, a mature tree can potentially produce up to 40 or more. Nutritionally, the fruits are high in vitamin C, beta-carotene, fructose, and various other minerals and antioxidants. They have been found to help boost the immune system, reduce inflammation, and improve digestion.
Given its drought, salt spray, and fire resistance, Syzygium suborbiculare makes a great addition to any garden, especially in areas with dry tropics. It provides a good amount of shade, stunning white flowers, and delicious red fruit with many health benefits.
| Next |  |
Use link to repeat this search:
https://toptropicals.com/cgi-bin/garden_catalog/cat.cgi?find=Syzygium&search_op=and&keyword_op=and&language=e&number=10
&no_change_lang=1&user=tt&sale=1&first=0
































 SUNSHINE C-Cibus (NPK 2-2-4) - Crop Booster for every watering.
SUNSHINE C-Cibus (NPK 2-2-4) - Crop Booster for every watering.  SUNSHINE C-Cibus (NPK 2-2-4) - Crop Booster for every watering.
SUNSHINE C-Cibus (NPK 2-2-4) - Crop Booster for every watering. 














