Zingiber officinale (Spice Ginger)
Botanical name: Zingiber officinale
Common names: Spice Ginger, Edible Ginger, Common Ginger, Cooking Ginger, Canton Ginger, Halia
Family: Zingiberaceae
Origin: tropical Asia











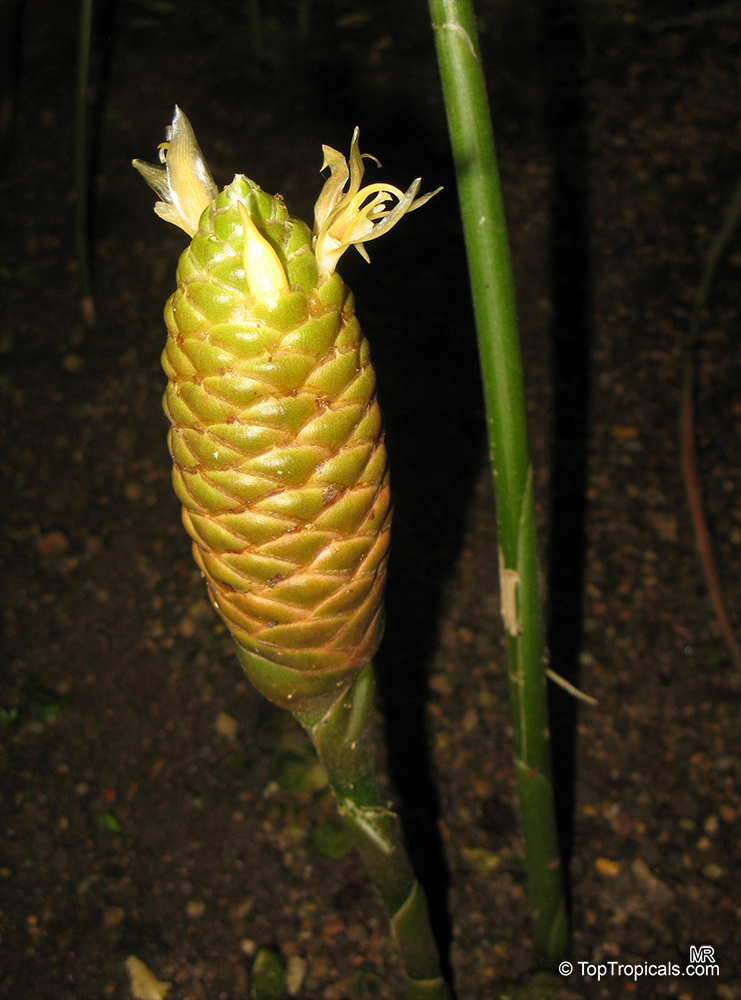
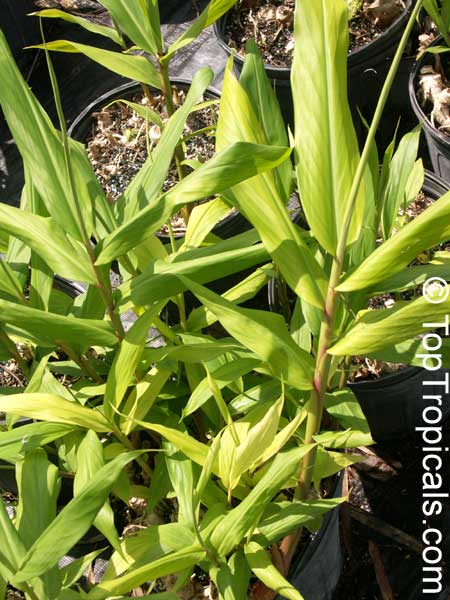
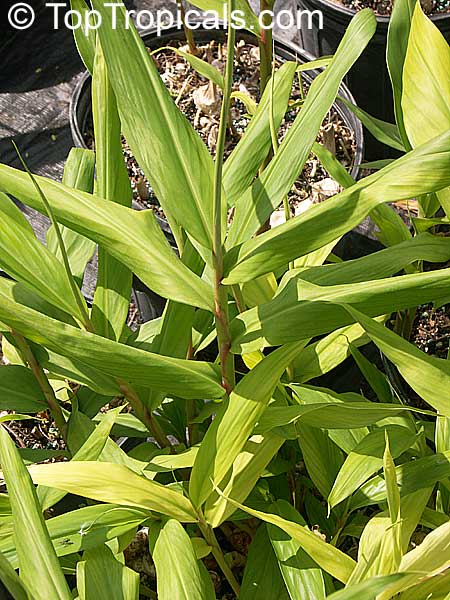
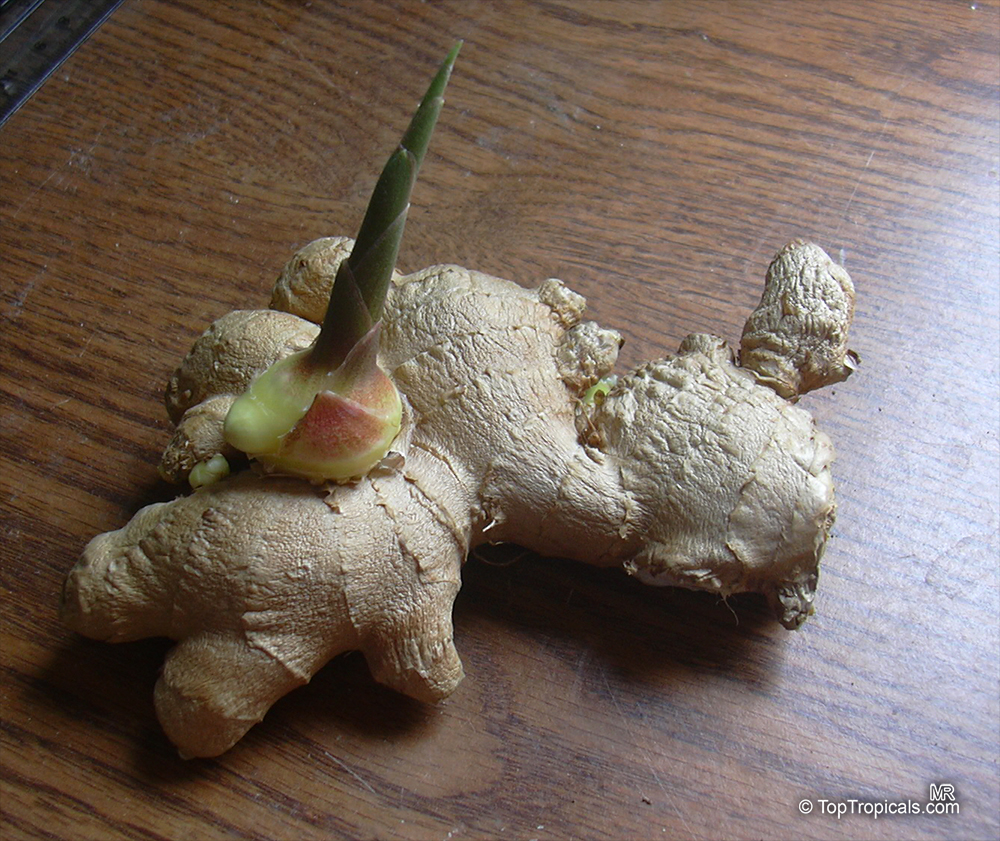
This ginger has tall, erect stems with narrow leaves, this basal bloomer produces green cones that turn red when mature. It is a herbaceous perennial with upright stems and narrow medium green leaves arranged in two ranks on each stem. Ginger grows from an aromatic tuberlike rhizome (underground stem) which is warty and branched. The inflorescence grows on a separate stem from the foliage stem, and forms a dense spike. The bracts are green with translucent margins and the small flowers are yellow green with purple lips and cream colored blotches. Most of edible gingers in cultivation are sterile cultivars grown for the edible rhizome, and the flower is rarely seen. Ginger is often grown in a container and brought indoors in winter when water and light are reduced and the plant is allowed to "rest." Common cooking gingers are rarely found in garden centers as potted plants because they do not have much ornamental value. Plant this ginger in the garden to produce your own fresh ginger.
Similar plants: Zingiber officinale (Spice Ginger)
- Alpinia gigantifolia (Red Ginger Lily)
- Zingiber cochinchinense (Chinese Ginger)
- Zingiber collinsii (Ginger Silver Streaks)
- Zingiber gramineum (Grassy Ginger)
- Zingiber malaysianum (Black Ginger)
- Zingiber neglectum (Jewel Pagoda)
- Zingiber newmanii (Red Frogs Ginger)
- Zingiber parishii (Lemon Lights)
- Zingiber pellitum (Ginger)
- Zingiber peninsulare (Red Thai Ginger)