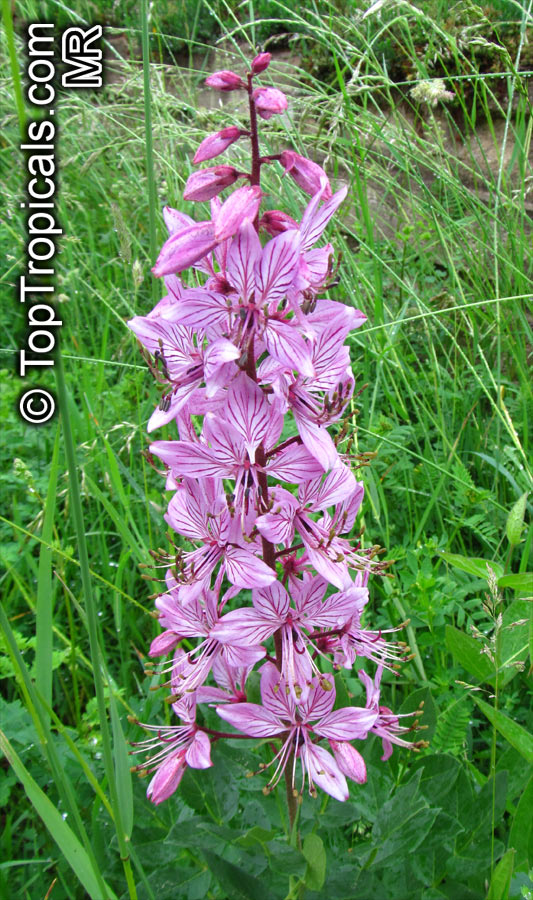
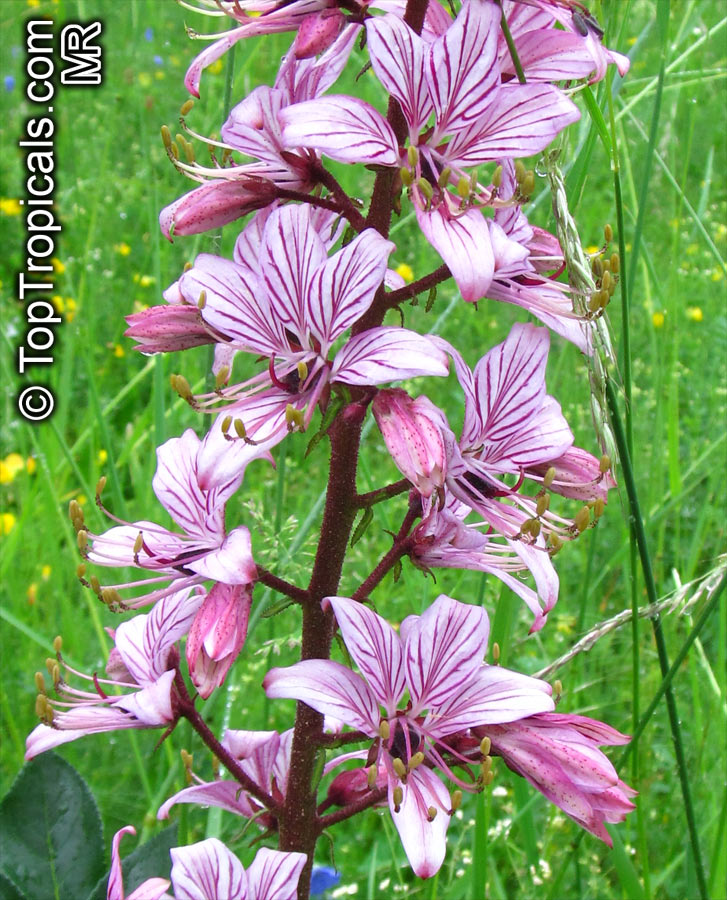
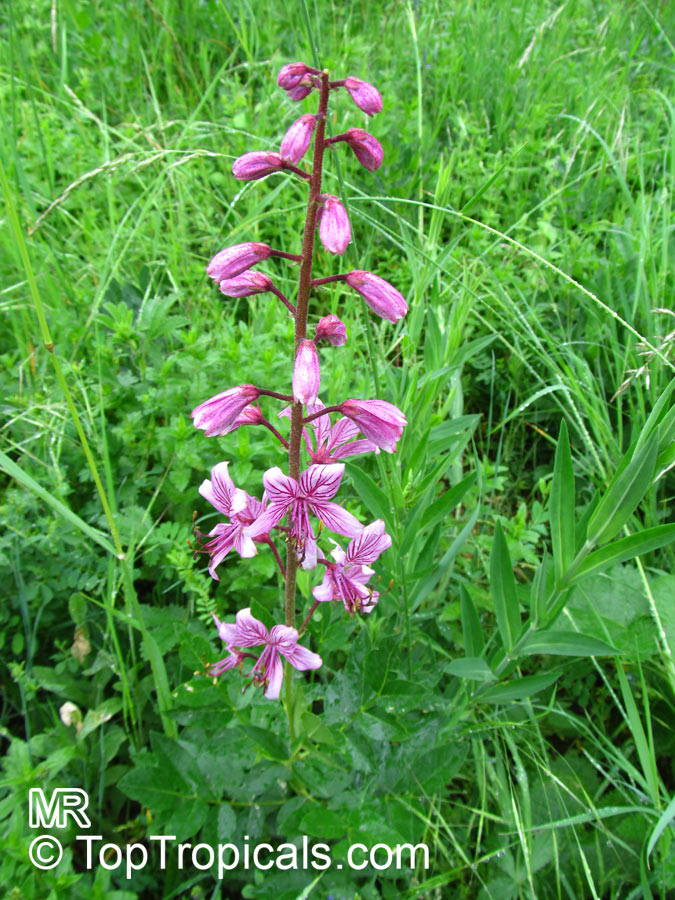
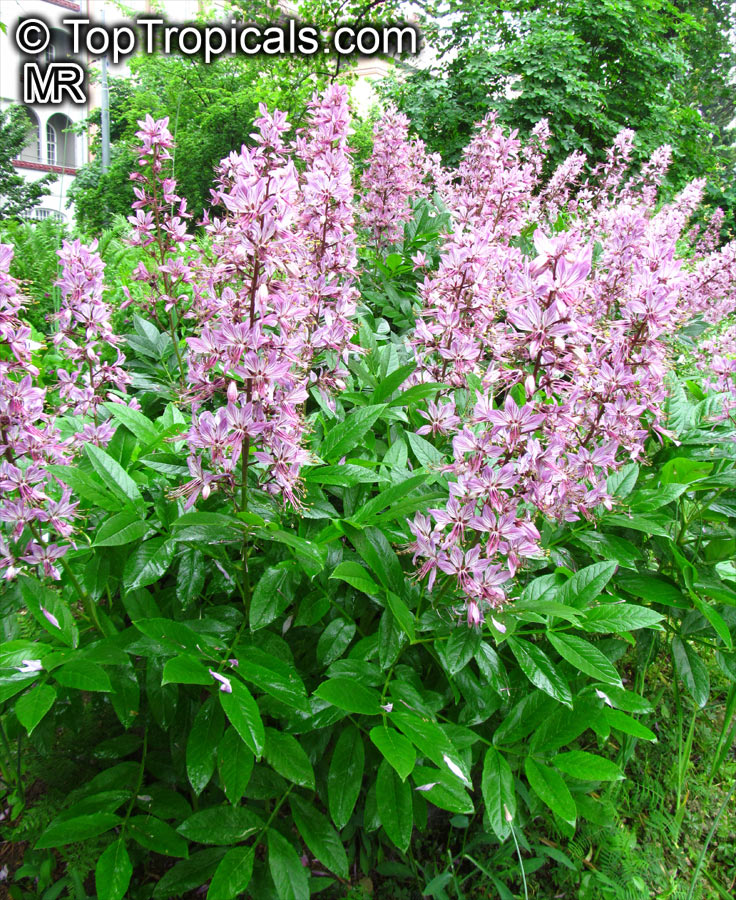
Dictamnus albus (Burning Bush)
Botanical names: Dictamnus albus, Dictamnus fraxinella
Common names: Burning Bush, Gas Plant, Dittany
Family: Rutaceae
Origin: Southwest Europe, South and Central Asia









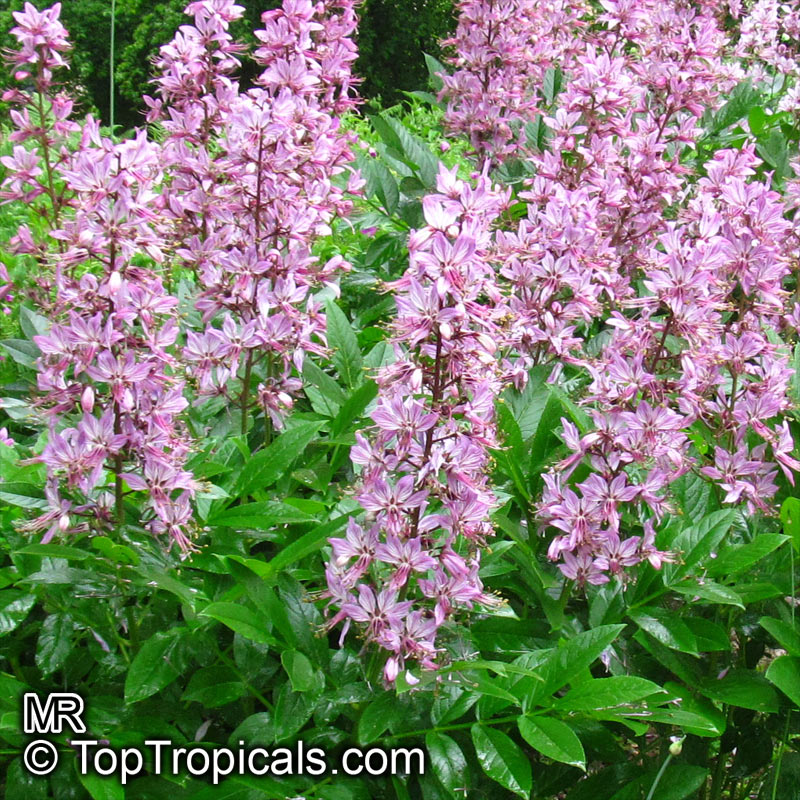
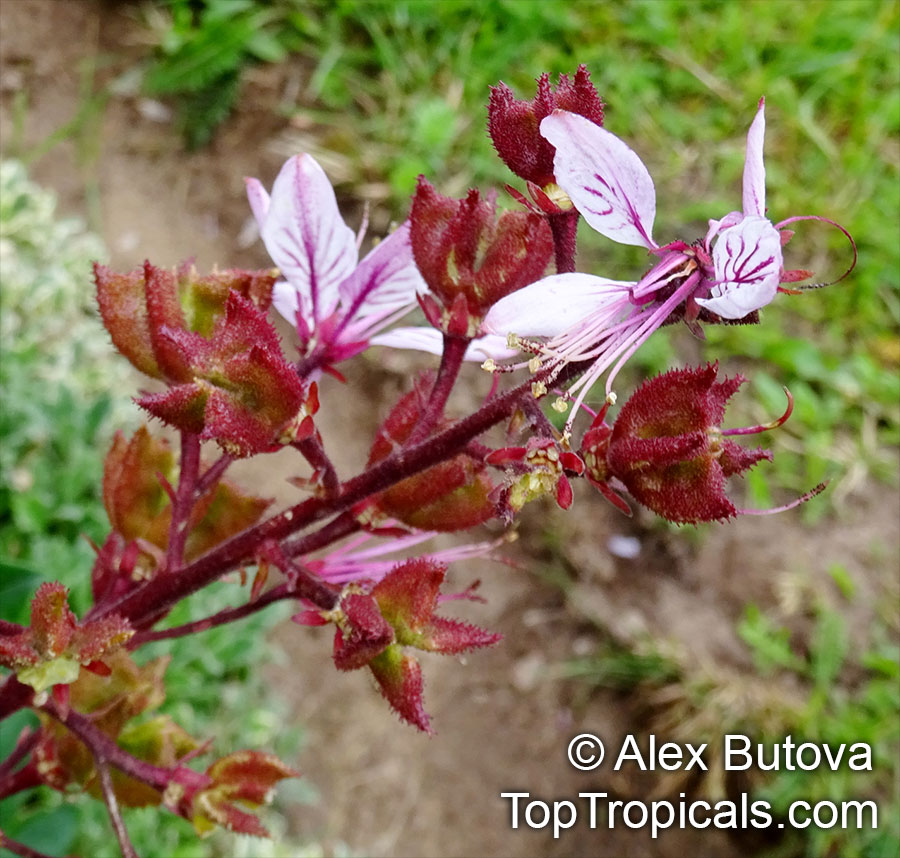
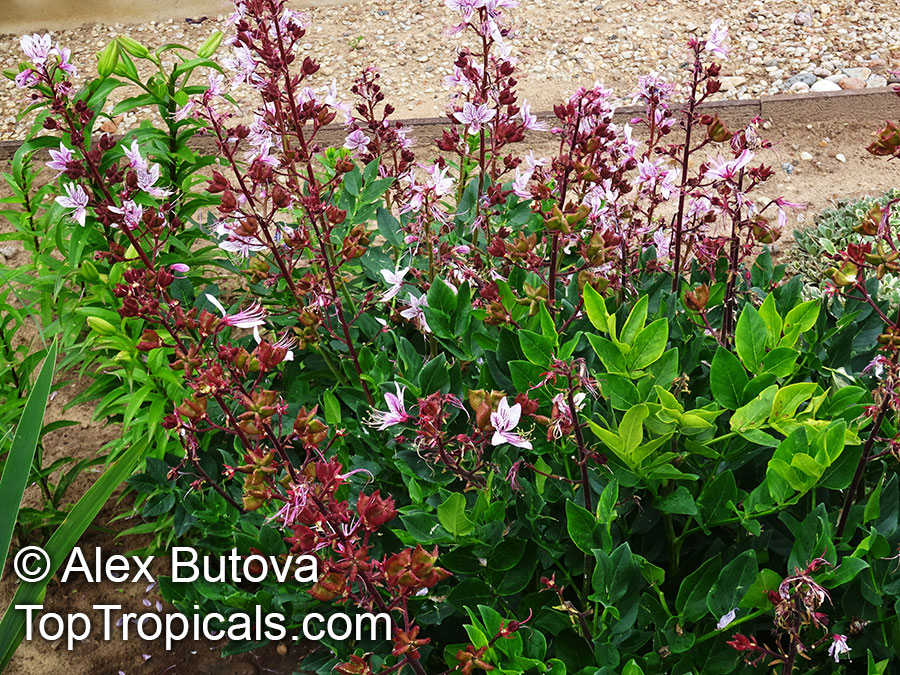
The Burning Bush, also known as Dictamnus albus, is a perennial herb that is native to certain regions of Asia and Europe. It is called Burning Bush due to its ability to produce a flammable oil from its leaves and seed pods, which can ignite when exposed to flame. Despite this, the plant is not damaged by the fire.
In terms of cultivation, Burning Bushes are hardy in USDA zones 3-7 and prefer full sun, although they can tolerate some light shade in the hottest months. They can be grown in most well-draining garden soils, but benefit from the addition of lime at planting time. It's important to choose the planting location carefully, as these plants do not tolerate transplanting well. Once established, they are drought-tolerant. A mature plant can reach a height of 2-3 ft tall and produces small white, pink, or red flowers that are about 1 inch in diameter.
In addition to its horticultural uses, Burning Bush has a long history of use in Chinese herbal medicine, where a lemon-scented tea is made from the dried leaves. It is worth noting that the oil produced by the plant can irritate some people's skin, potentially causing chemical burns and blisters. However, if the exposed skin is washed before it is exposed to too much direct sunlight, irritation can be avoided.










