Spice or herb plant - Plant Encyclopedia Results
Top Tropicals Plant Encyclopedia
| Number of plants found: 169 | Next | 
|
Go to page: | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Last |
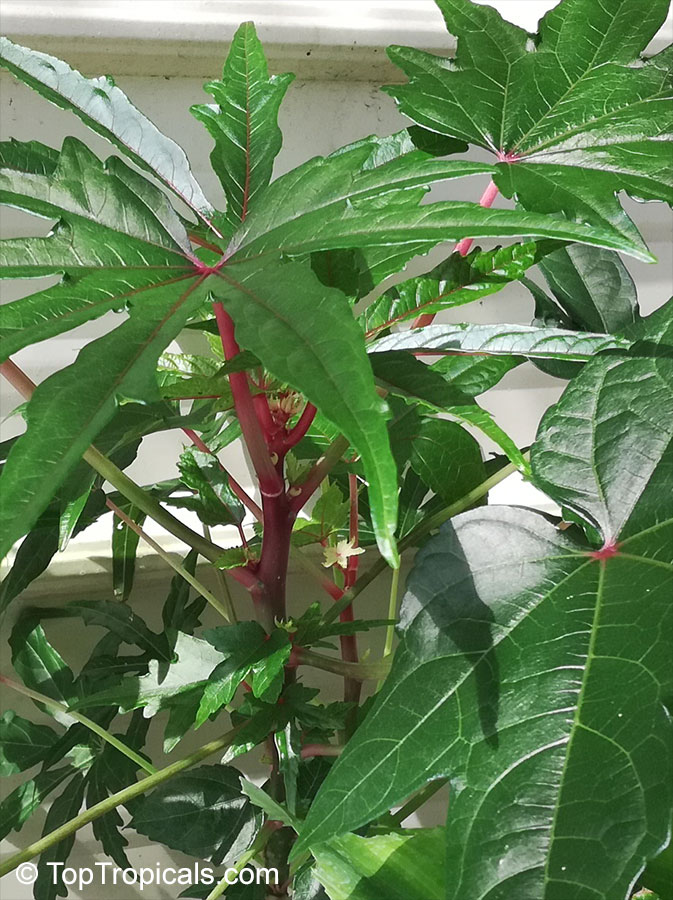
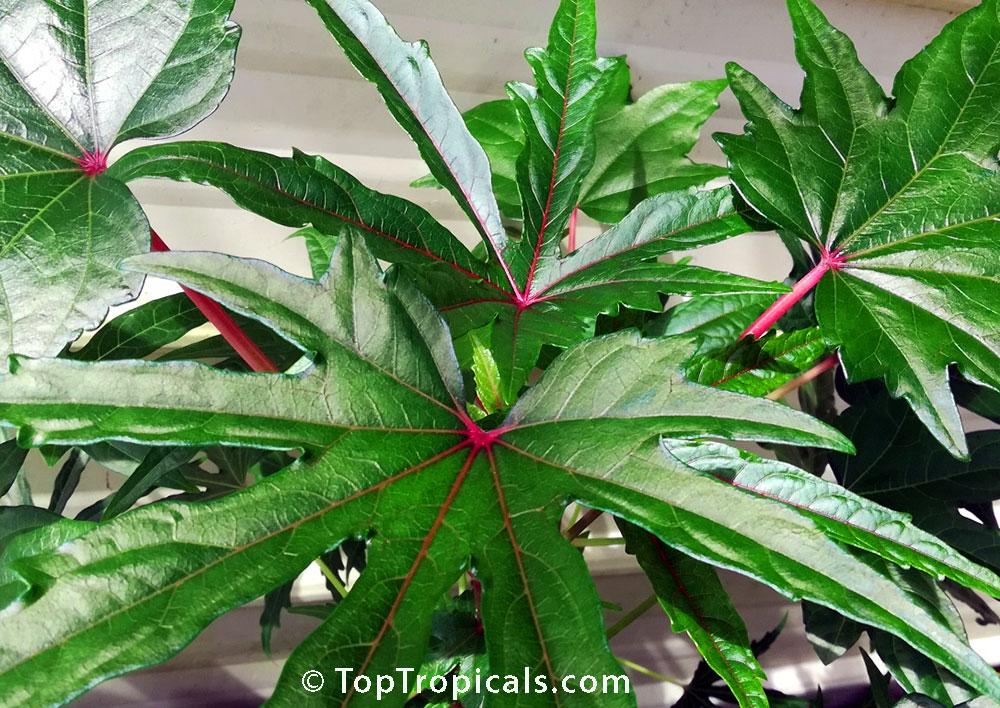
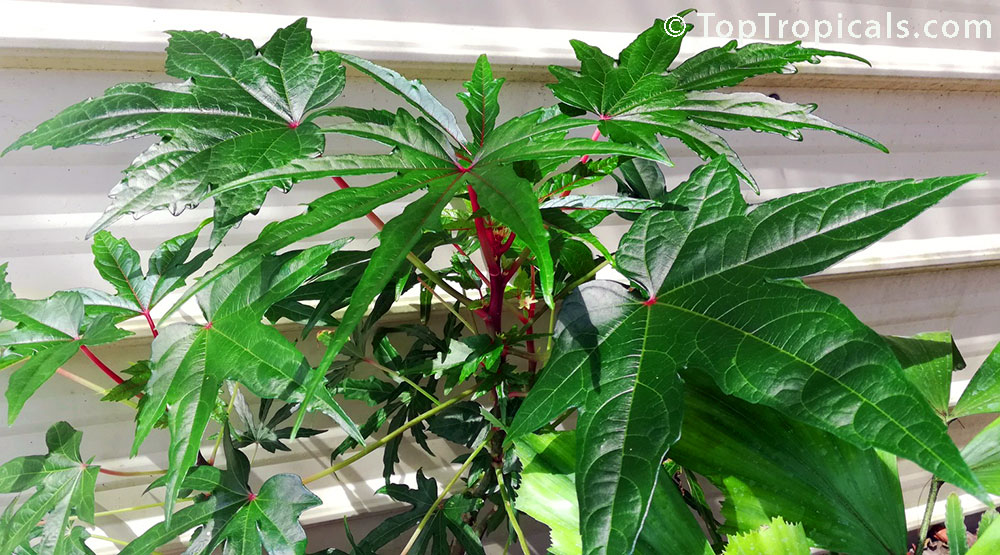
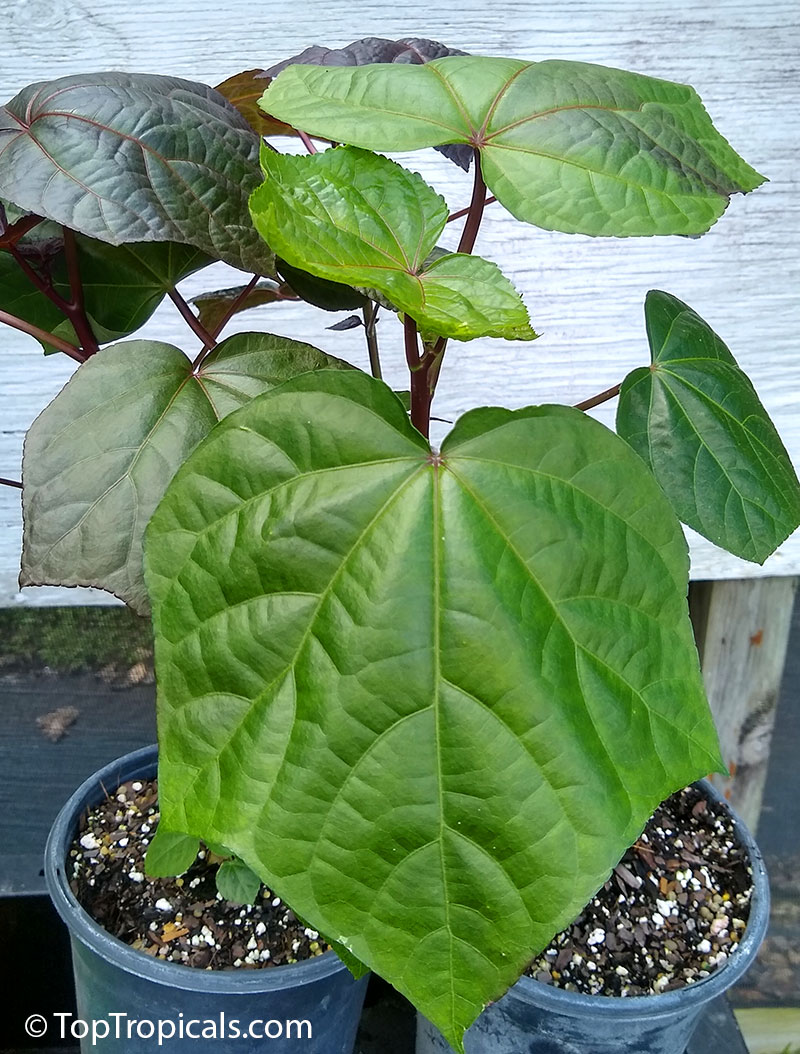
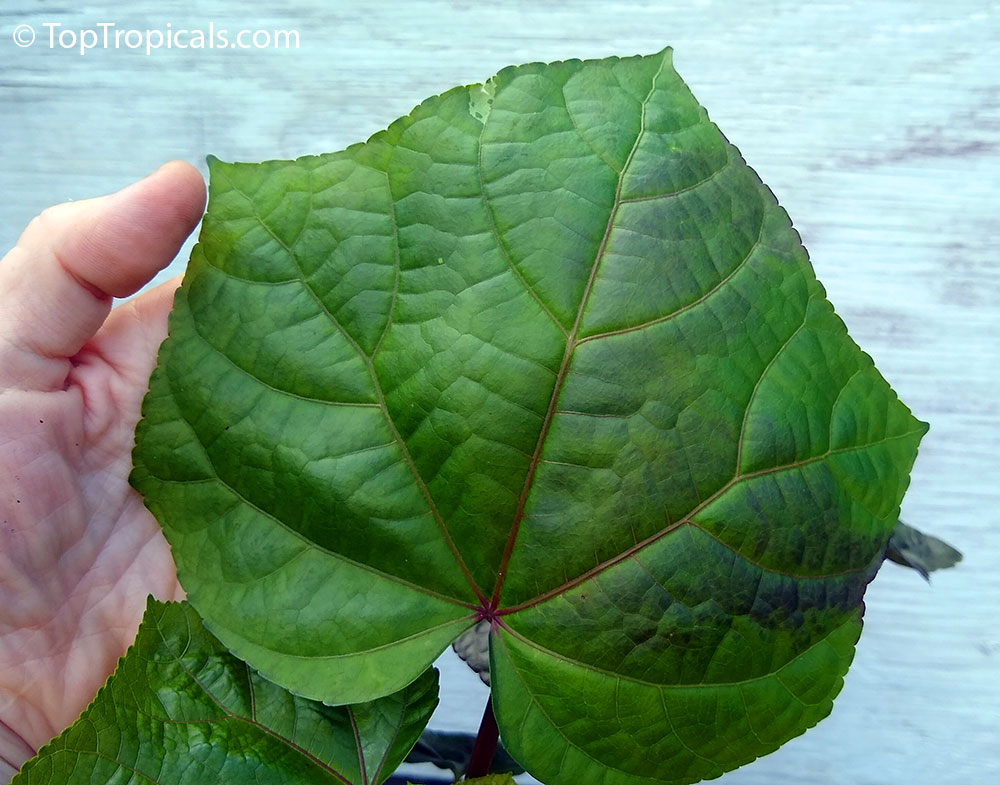
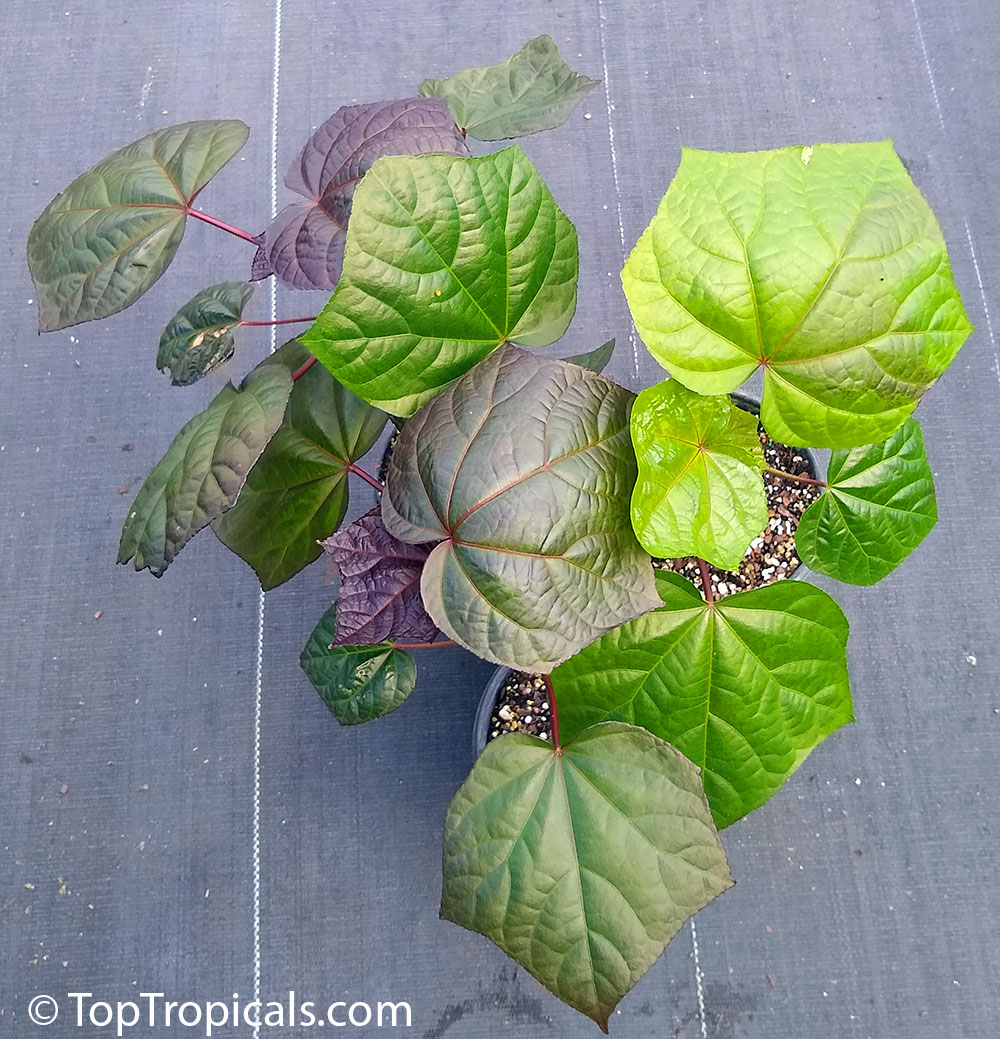
Botanical name: Abelmoschus manihot
Common names: South Sea Salad Tree, Bele tree, Sunset Muskmallow, Sunset Hibiscus, Hibiscus Manihot
Family: Malvaceae
Origin: Southeast Asia
Hardiness: 20°F









Its palmate leaves are highly dissected with five to nine deep lobes. The largest, widest leaves form at the base of the plant, where there may be some small side branches. The blooms (4-5" in diameter) are pale yellow with a dark maroon to purple center eye, and emerge from the terminal end of a central flowering stalk.It is easily propagated from cuttings, easy to cultivate, relatively disease-resistant and even is considered to be of medicinal value. It is widely planted either along borders of gardens or as an intercrop throughout many traditional gardens in the tropics. A nice flowering addition to the vegetable garden.
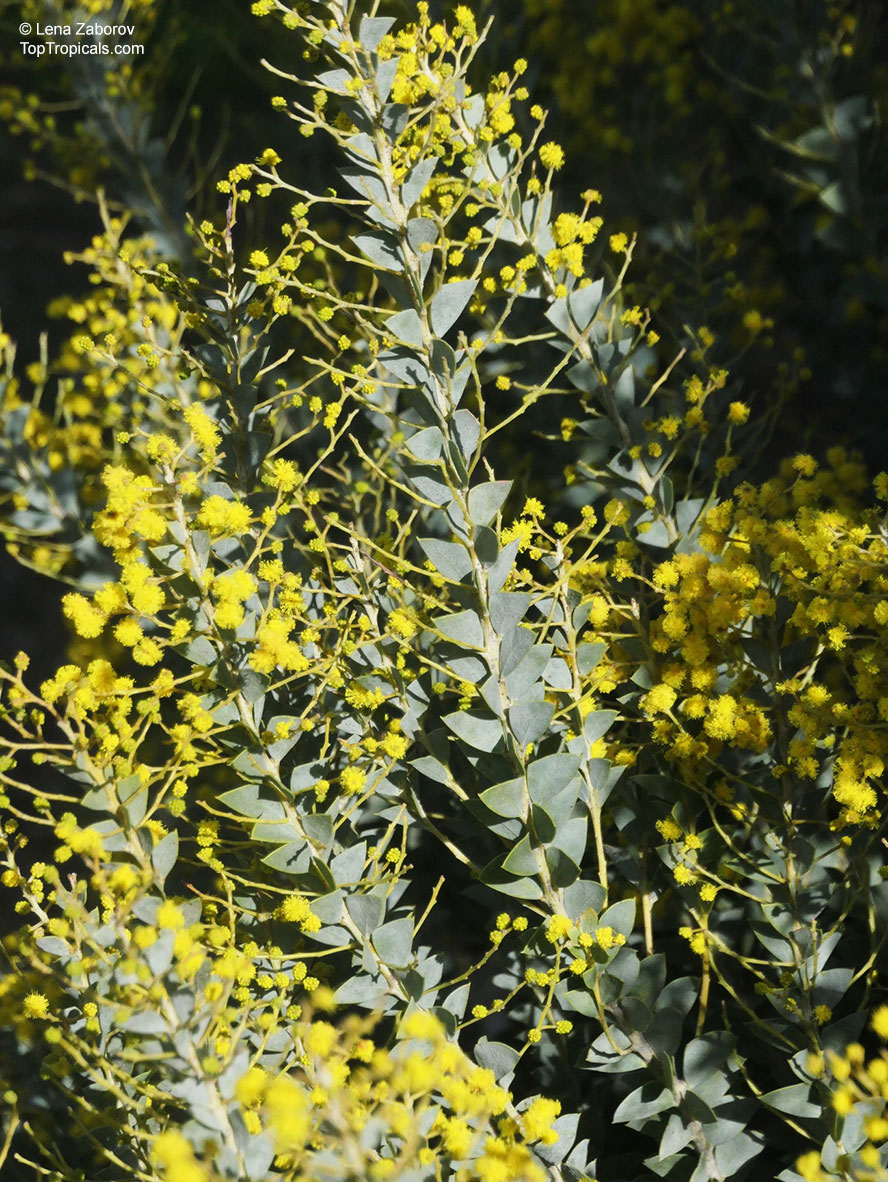
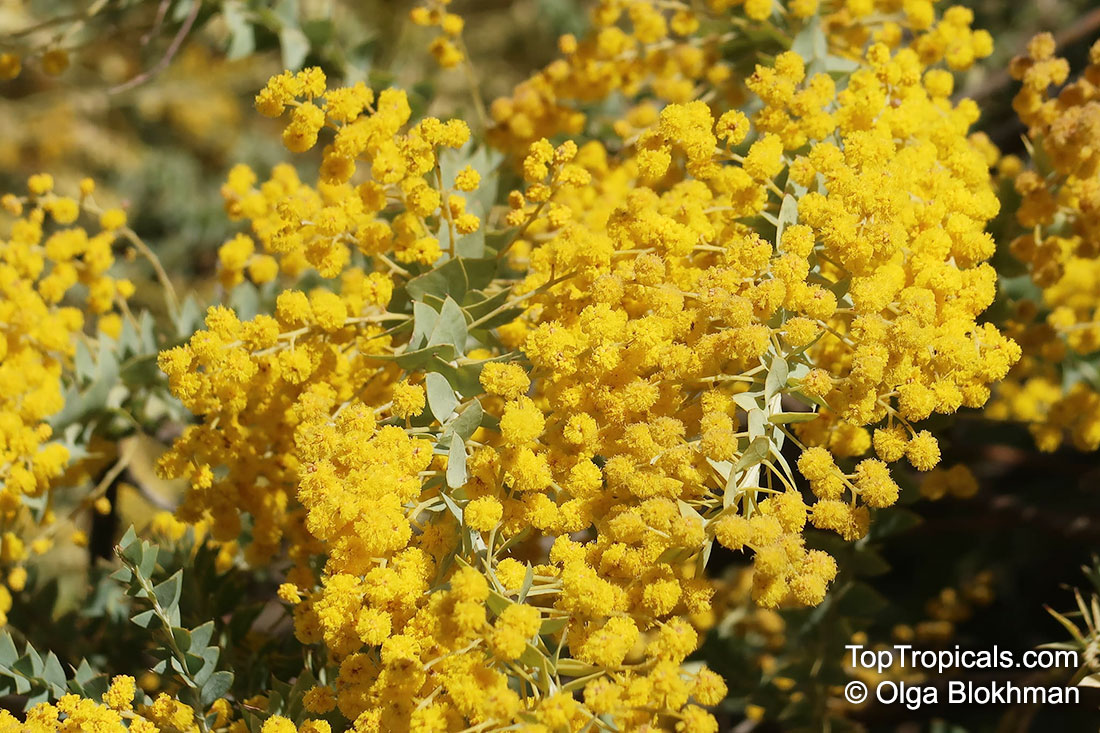
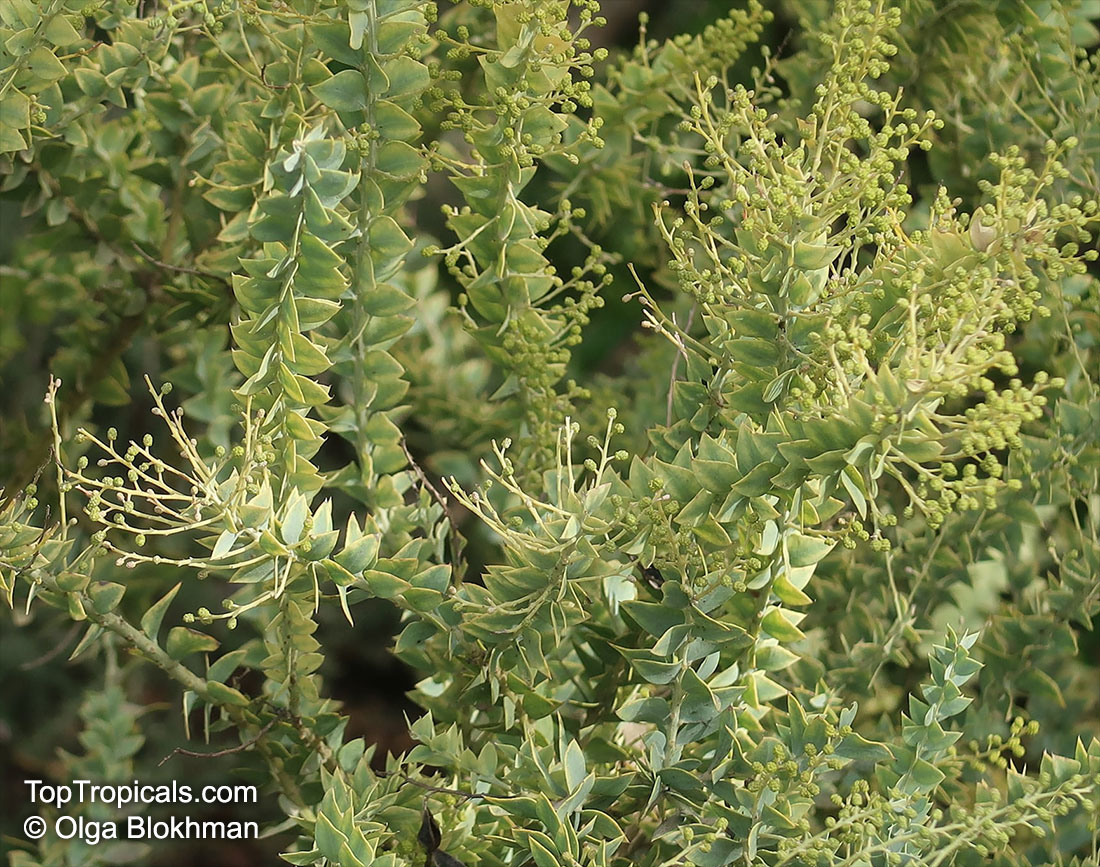
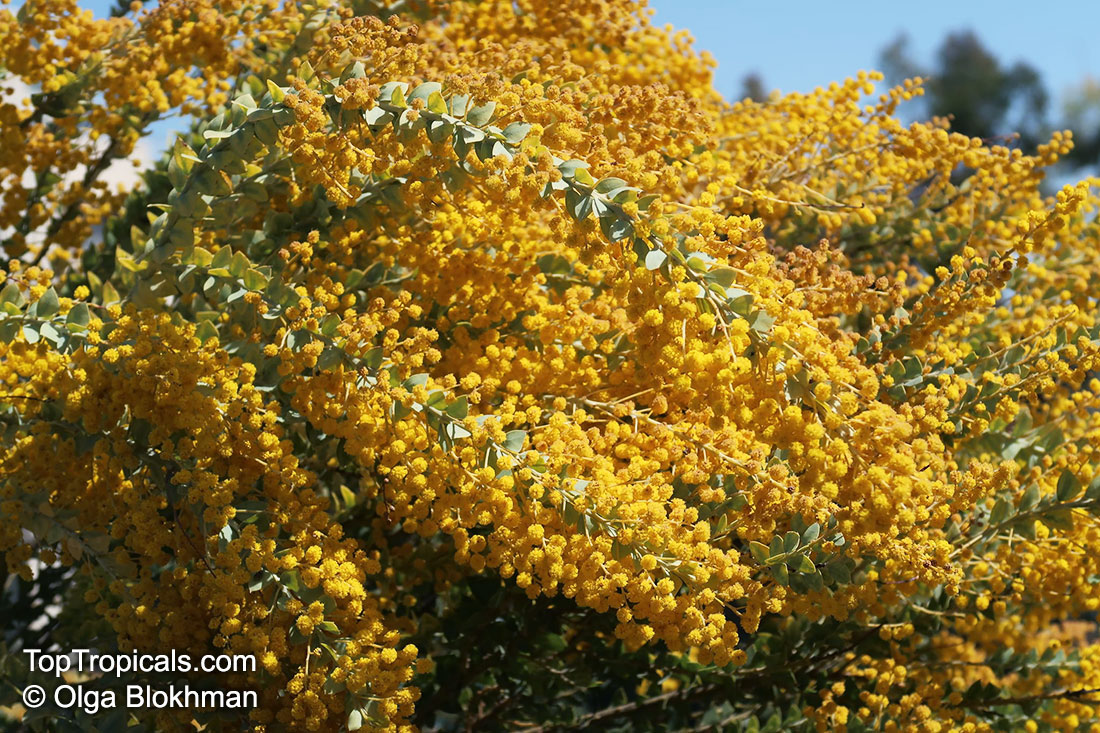
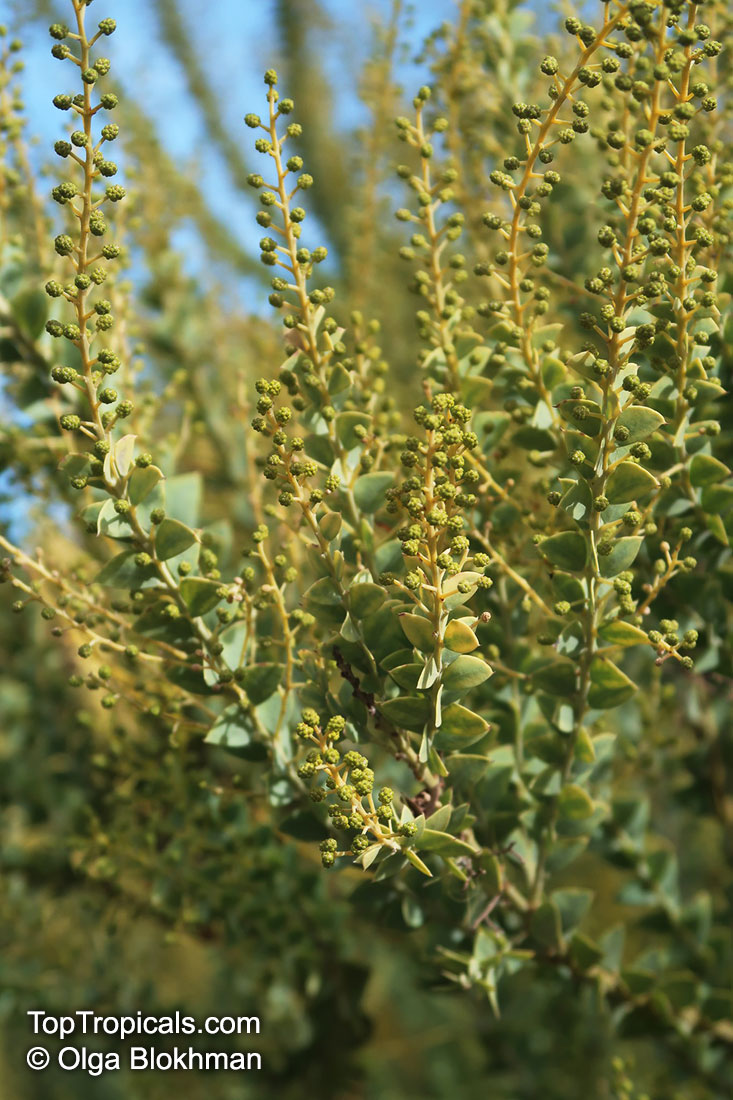
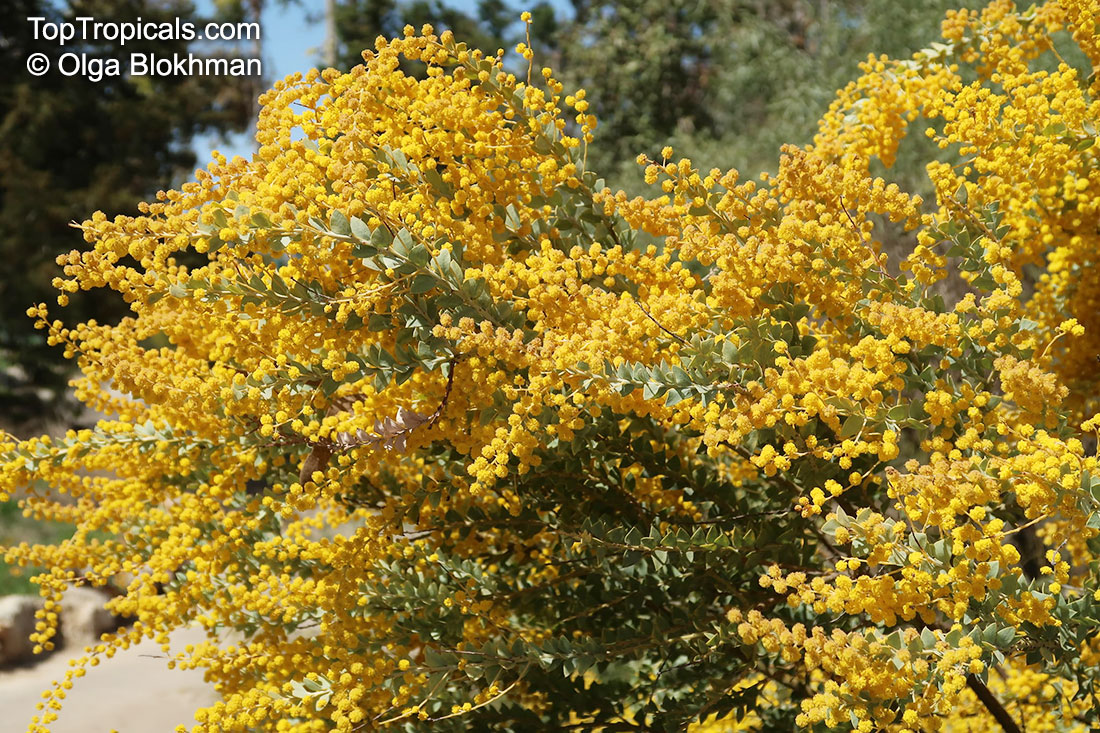
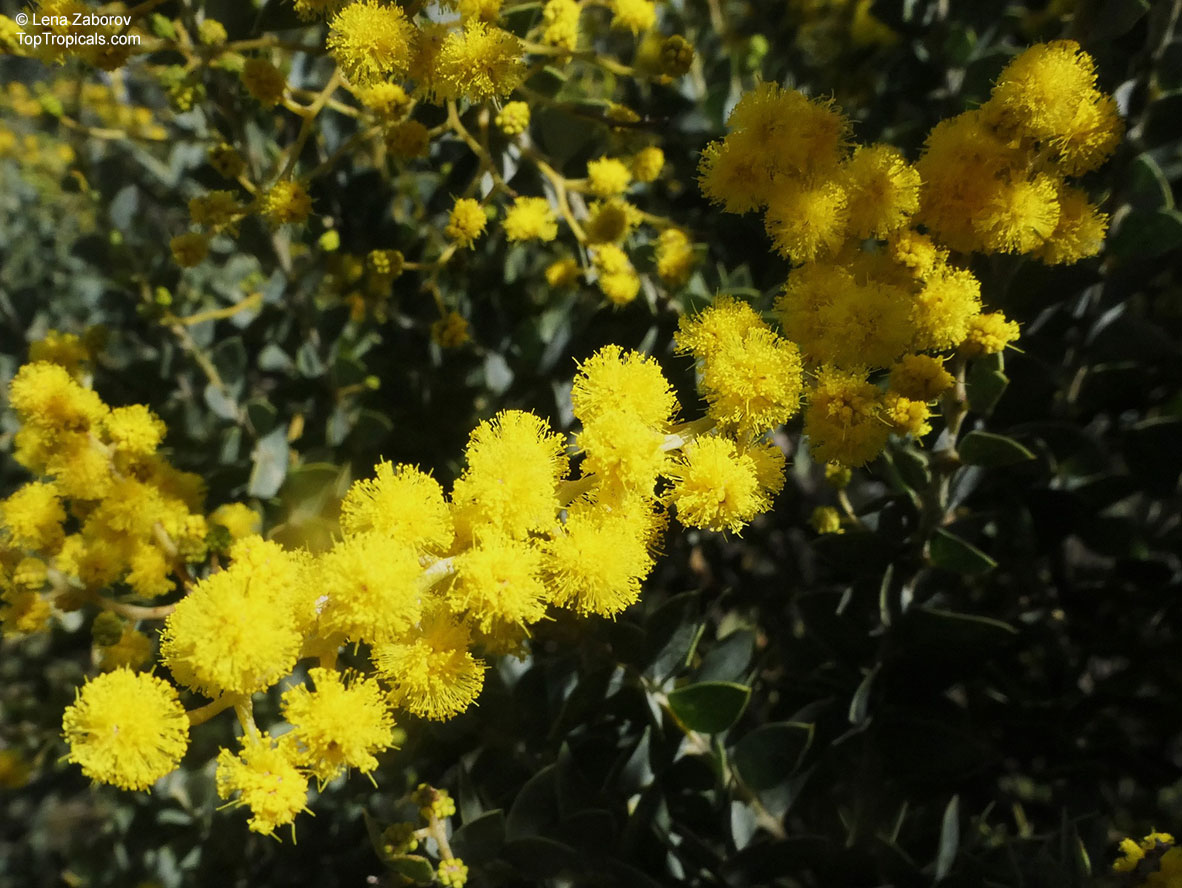
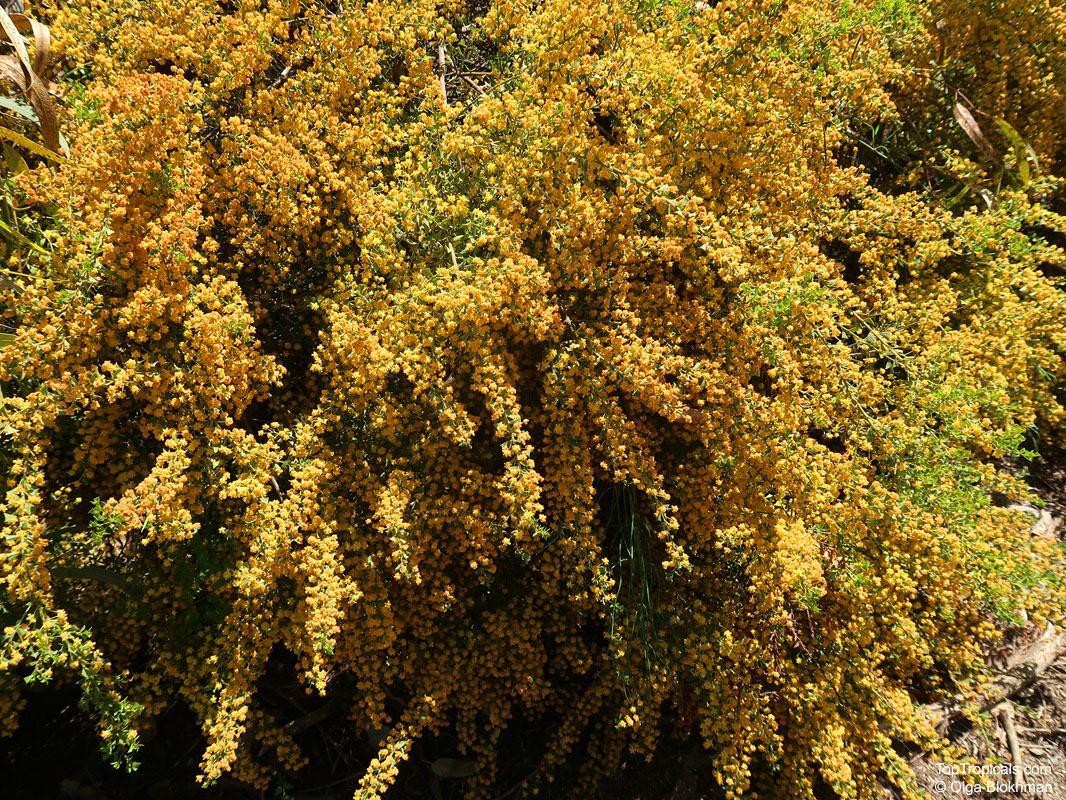
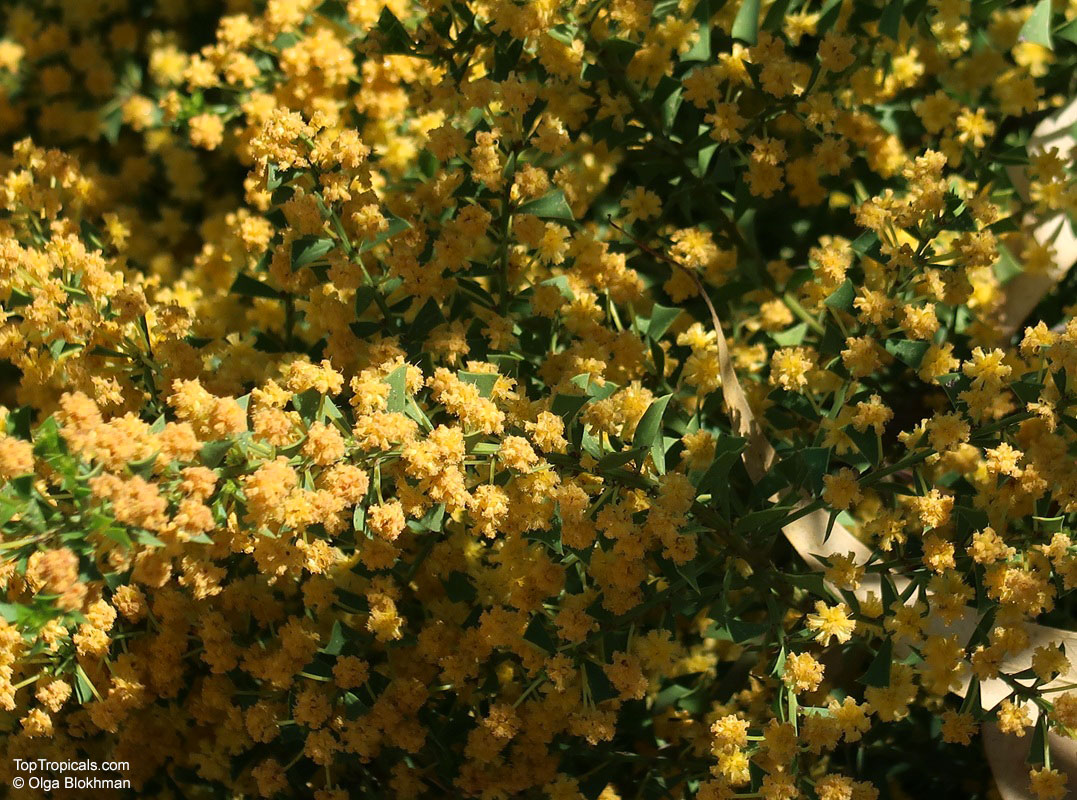
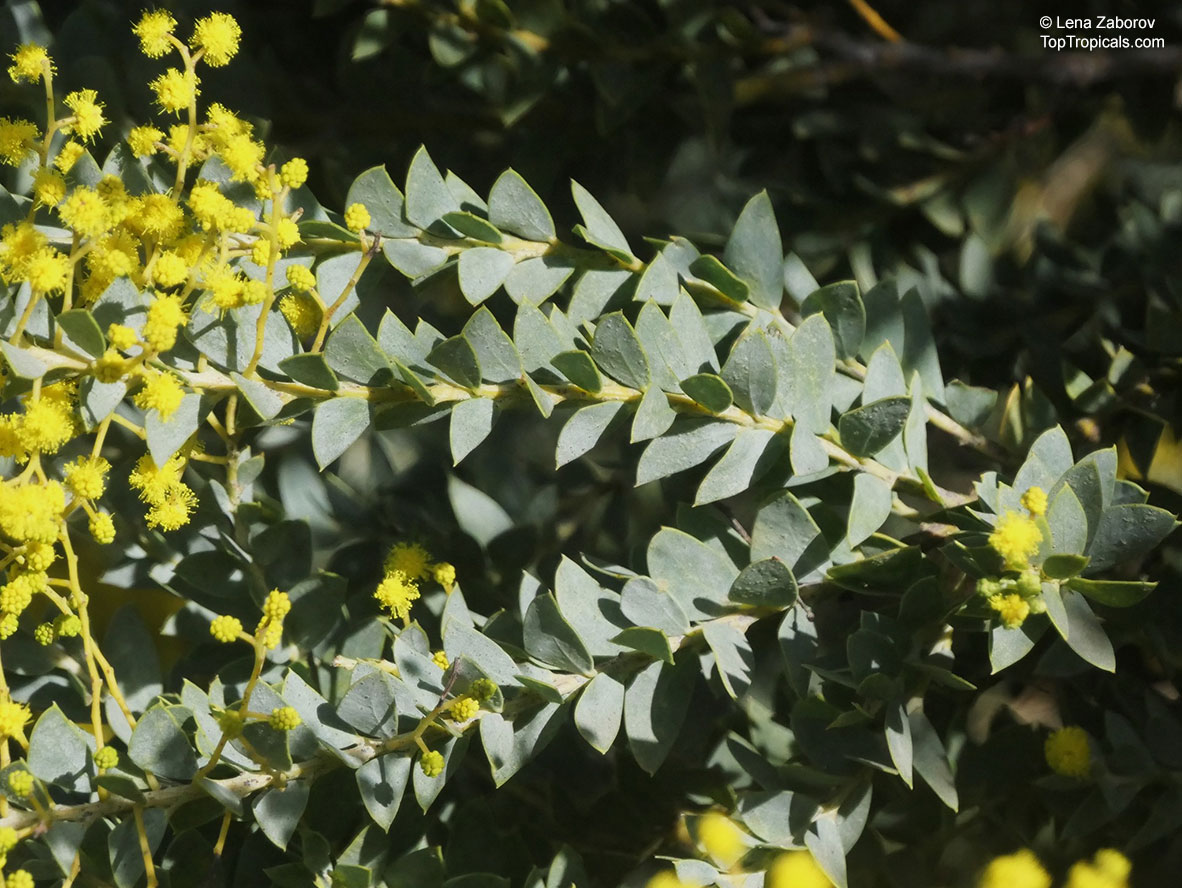
Botanical name: Acacia cultriformis
Common names: Knife-leaf Wattle, Dogtooth Wattle, Half-moon Wattle, Golden-glow Wattle
Family: Fabaceae
Subfamily: Mimosoideae
Origin: Australia
Hardiness: 25°F







Acacia cultriformis is a woody shrub with an upright or spreading habit that grows to 4 m (13 ft) in height.
Its bright flowers and attractive leaves make Acacia cultriformis one of the most popular wattles in cultivation. Drought tolerant, it can be used to combat soil erosion.
The flowers are edible and they are an ingredient used in some fritters. Yellow dye is extracted from the flowers and green dye is extracted from the seed pods
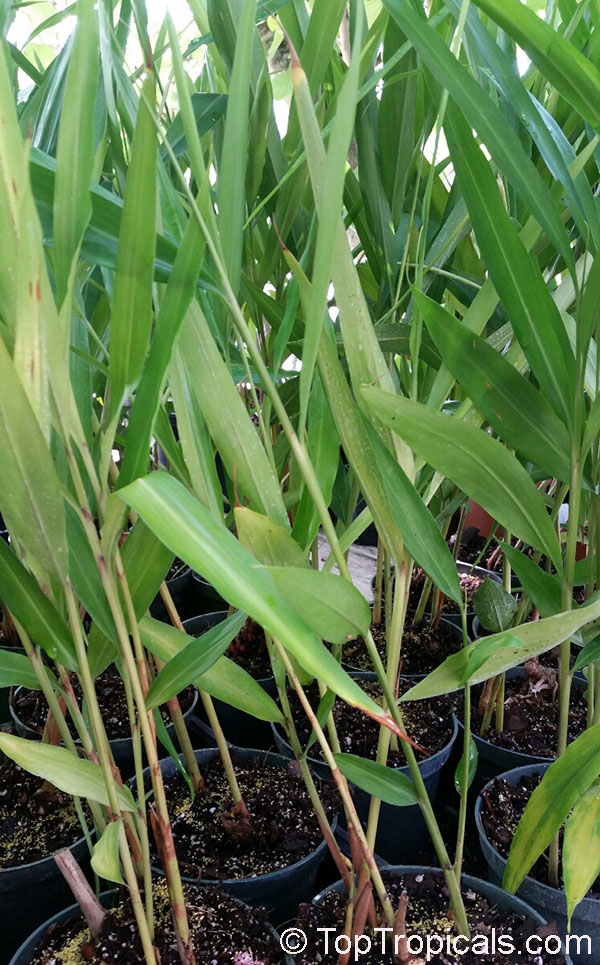
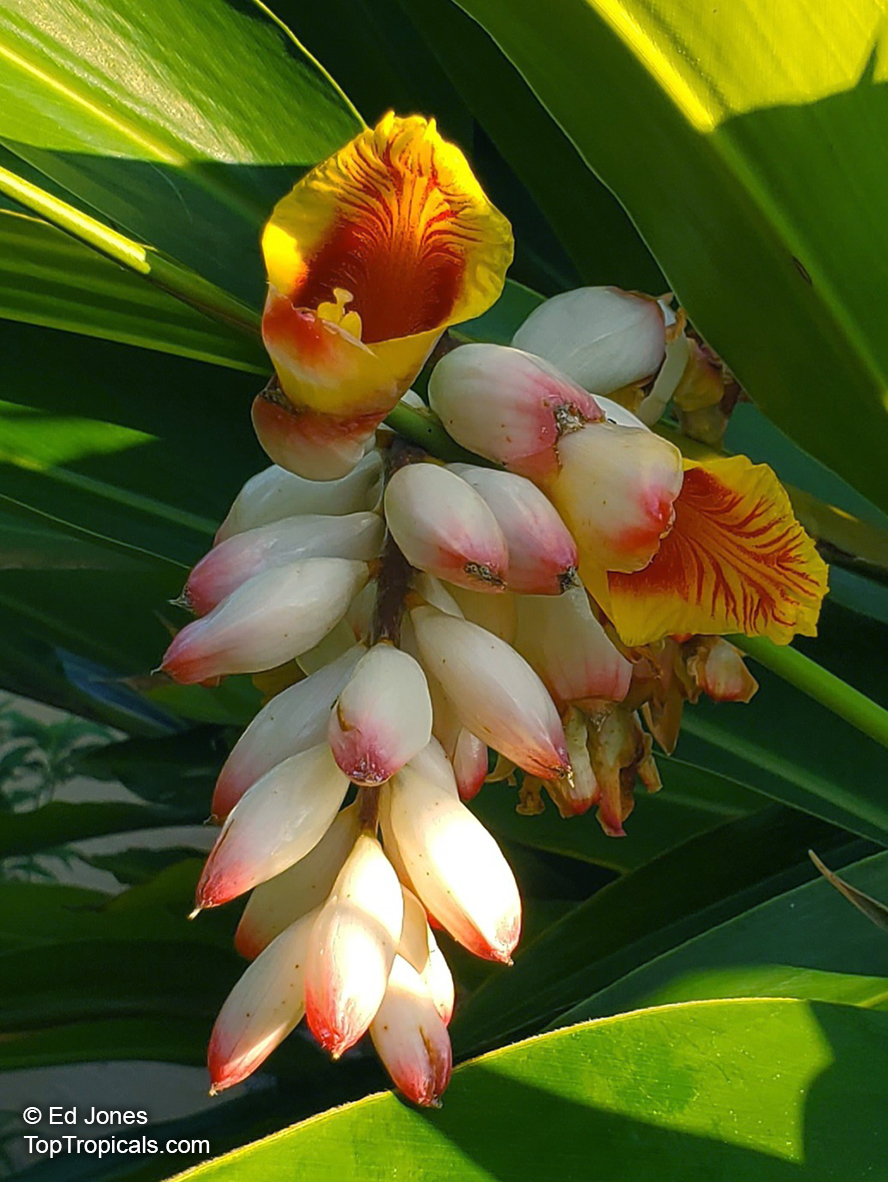
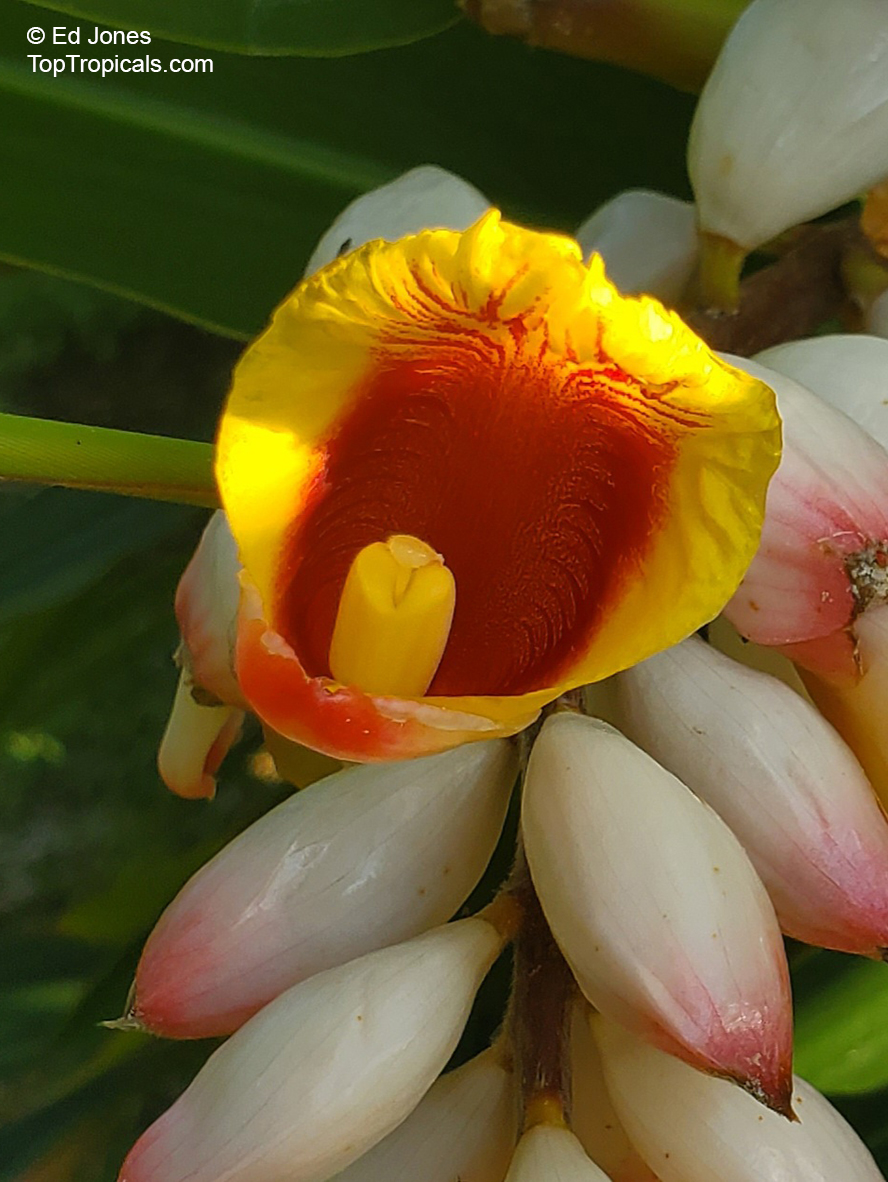
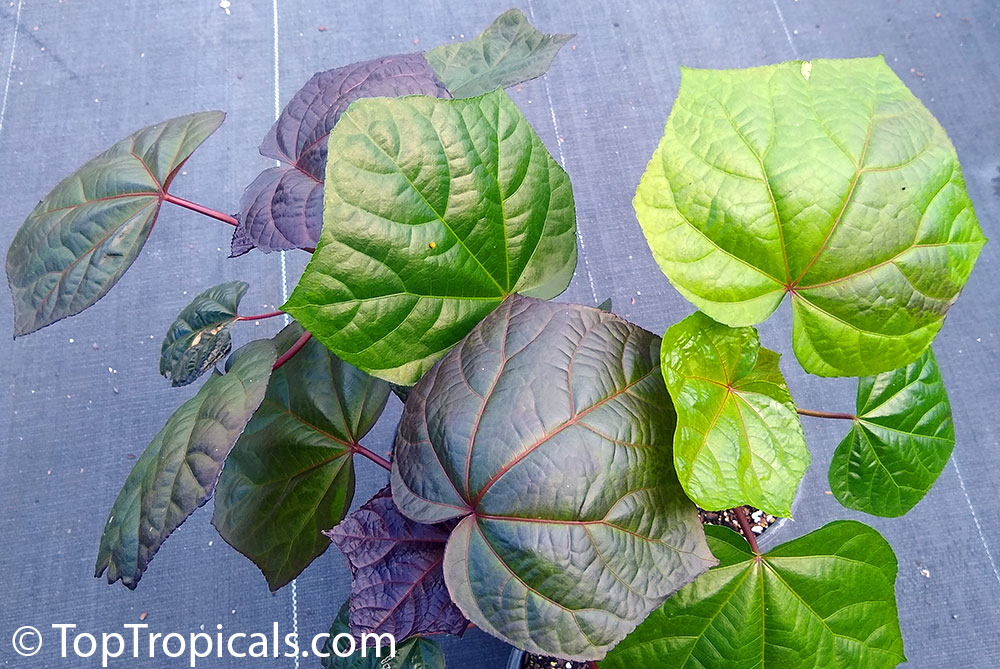
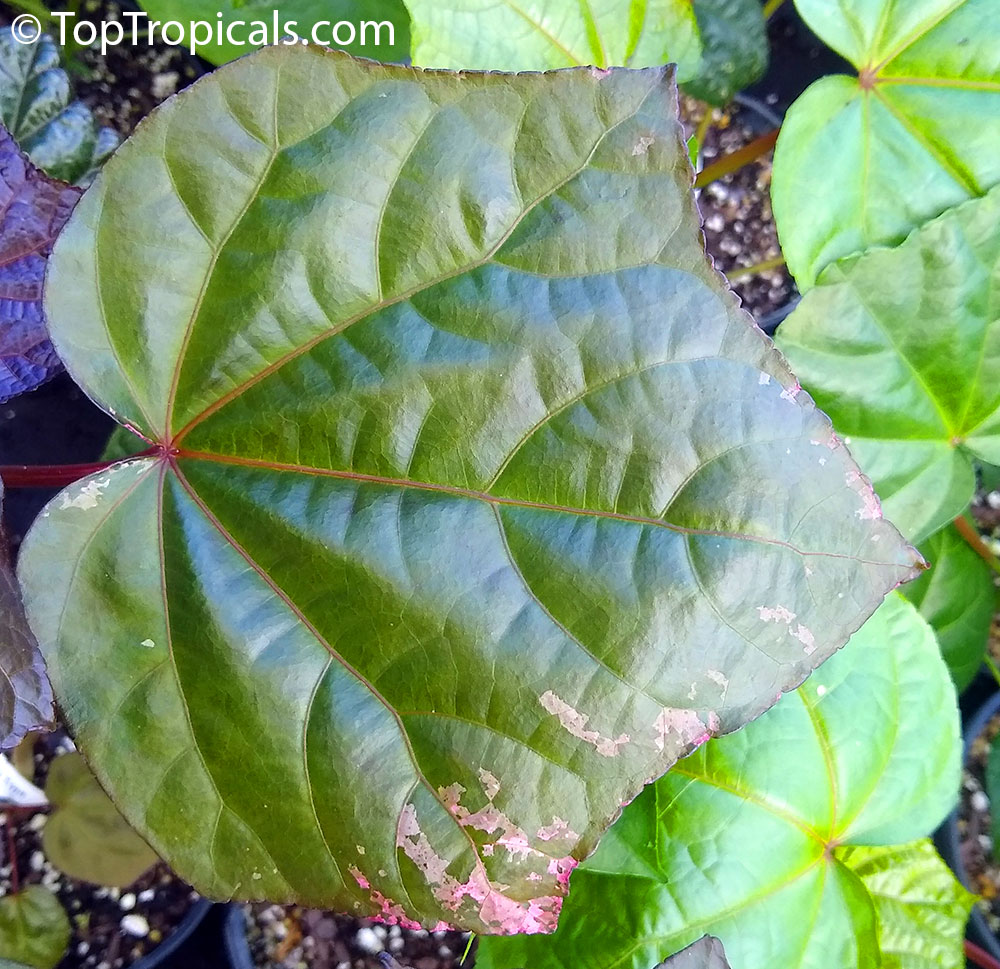
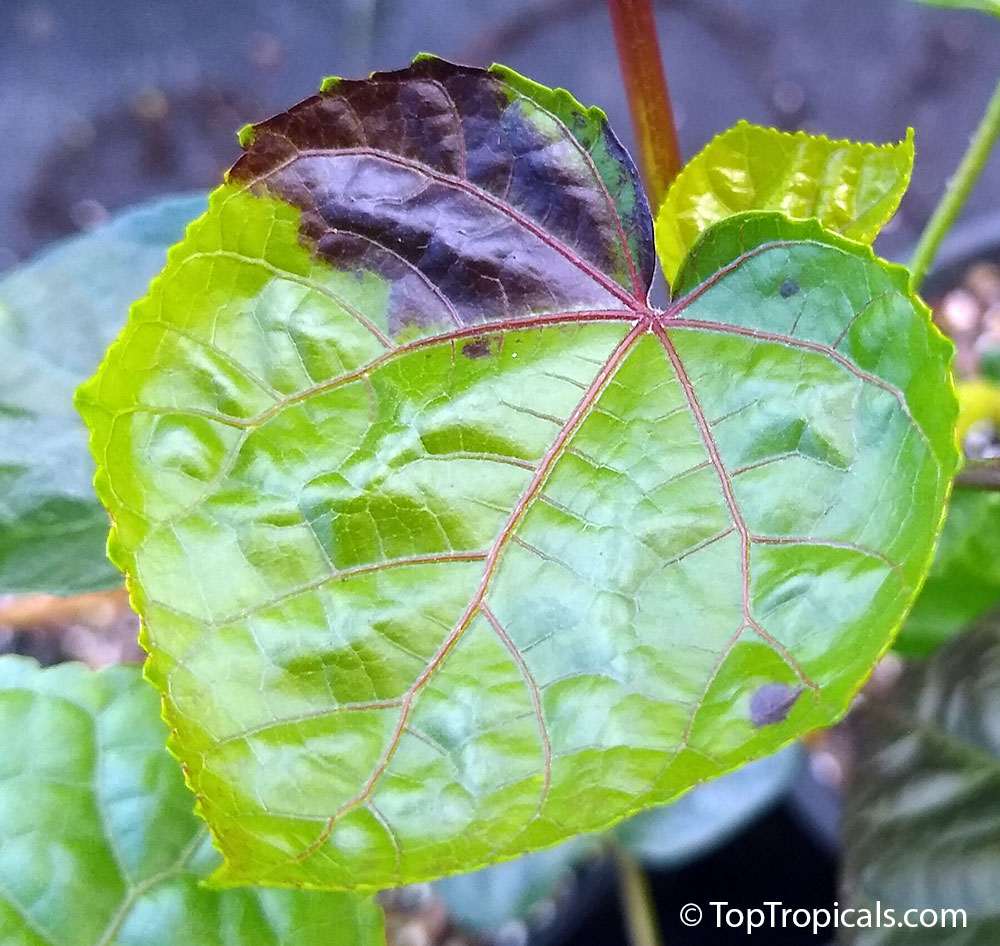
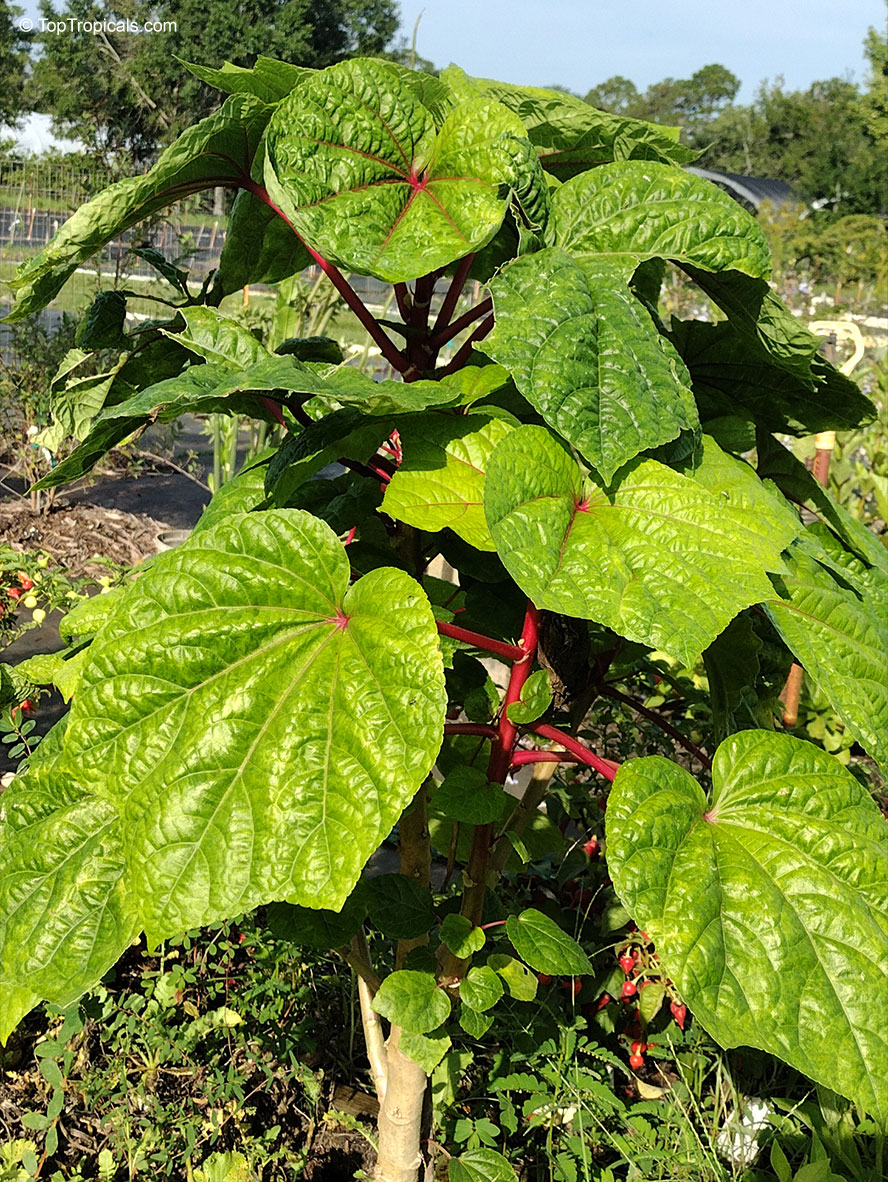
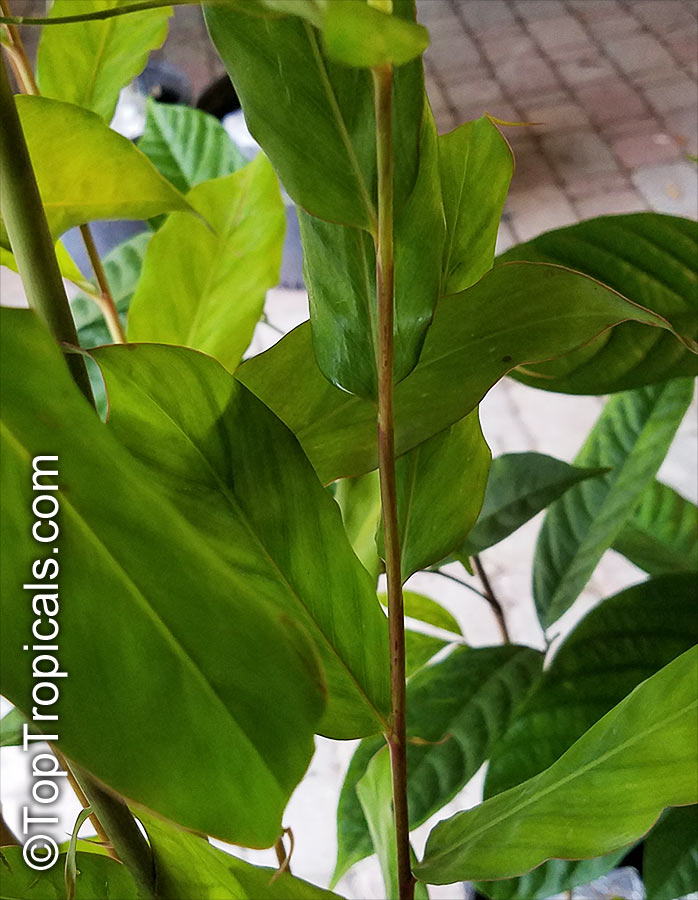
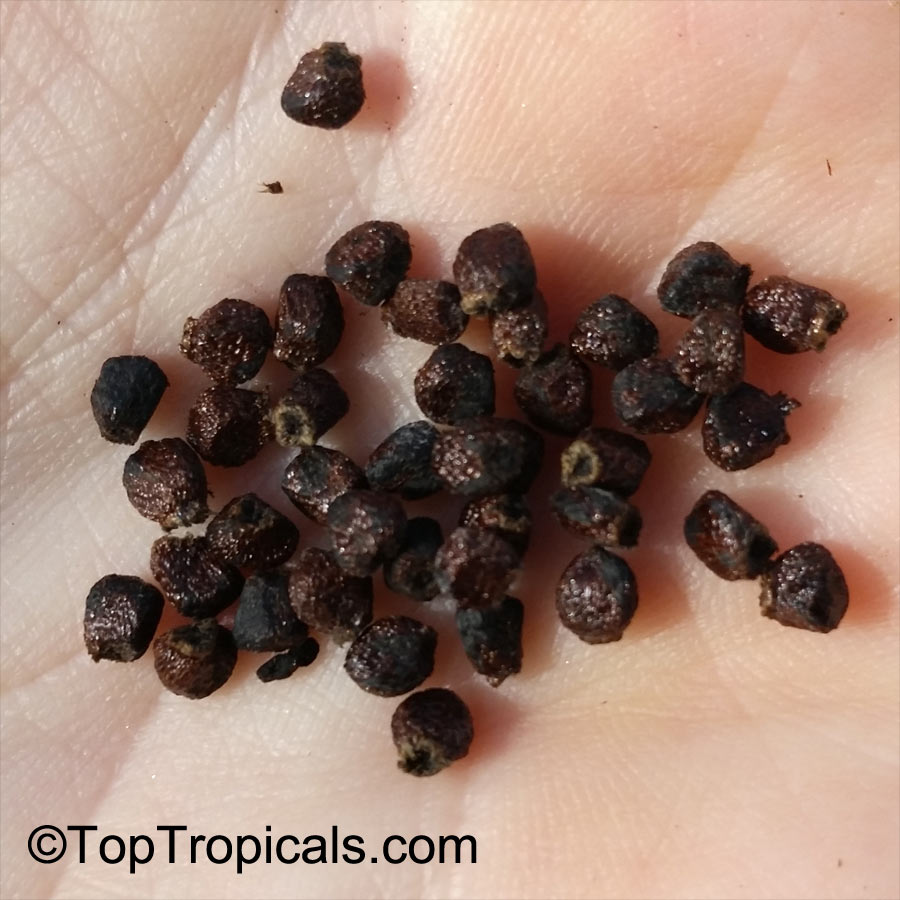
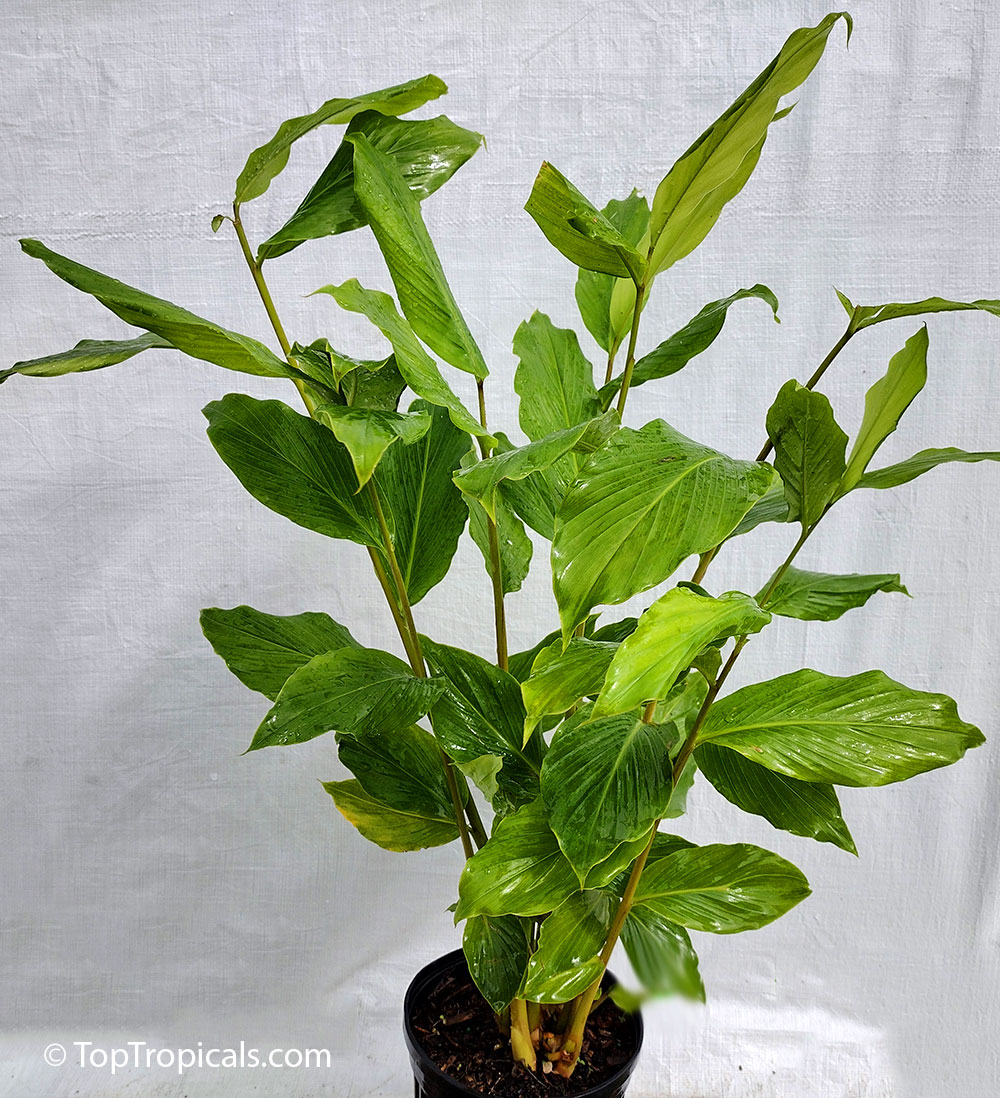
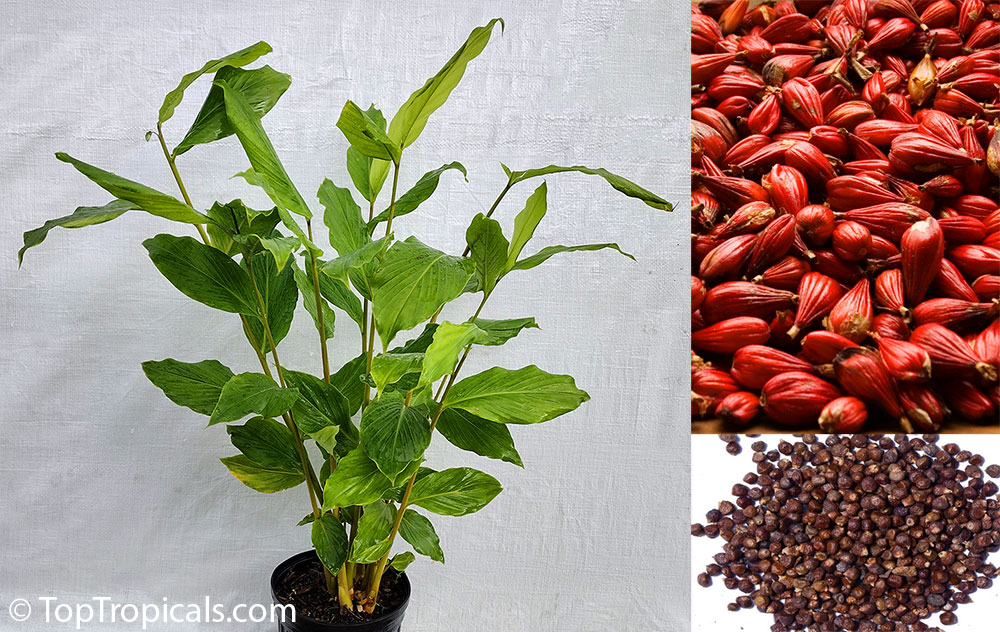
Botanical name: Aframomum sp.
Common names: Aframomum, Melegueta pepper, Guinea grain, Guinea pepper, Alligator Pepper, Grains of Paradise
Family: Zingiberaceae
Origin: Tropical Africa







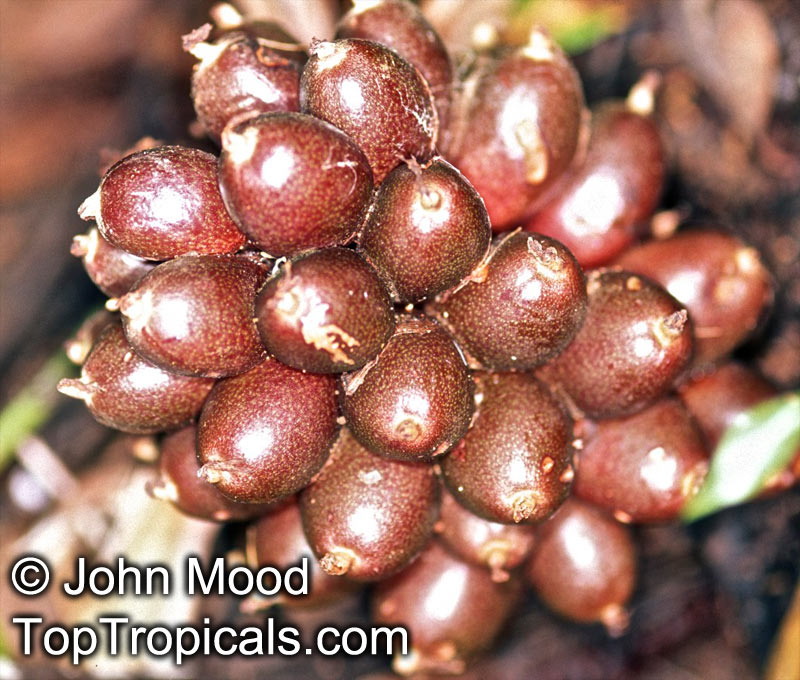
The genus Aframomum is well known in African forests because the bright red, fleshy fruit of several species contain a sweet juicy pulp and is eaten widely by primates and other mammals.
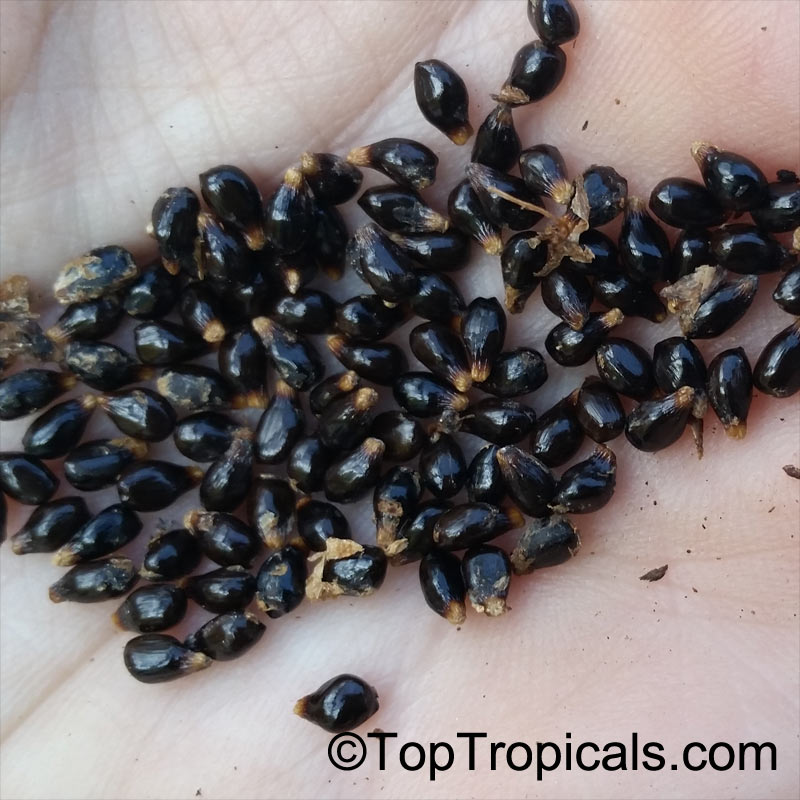
Aframomum melegueta is a herbaceous perennial plant native to swampy habitats along the West African coast. Its trumpet-shaped, purple flowers develop into 5- to 7-cm long pods containing numerous small, reddish-brown seeds.
Seeds of this rare Ginger are similar in flavor to cardamom and used as a pungent spice. This Ginger has many bioactives, great for digestive and intestinal health. The plant has many other medicinal values: anti-diabetic and anti-obese mechanisms, aphrodisiac and testosterone boosting properties. Aframomum melegueta may be promising for a spice to add to a diet in hopes of body recomposition. Studies show this spice increases sexual behavior.
Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Robusta - Rapid Growth Booster
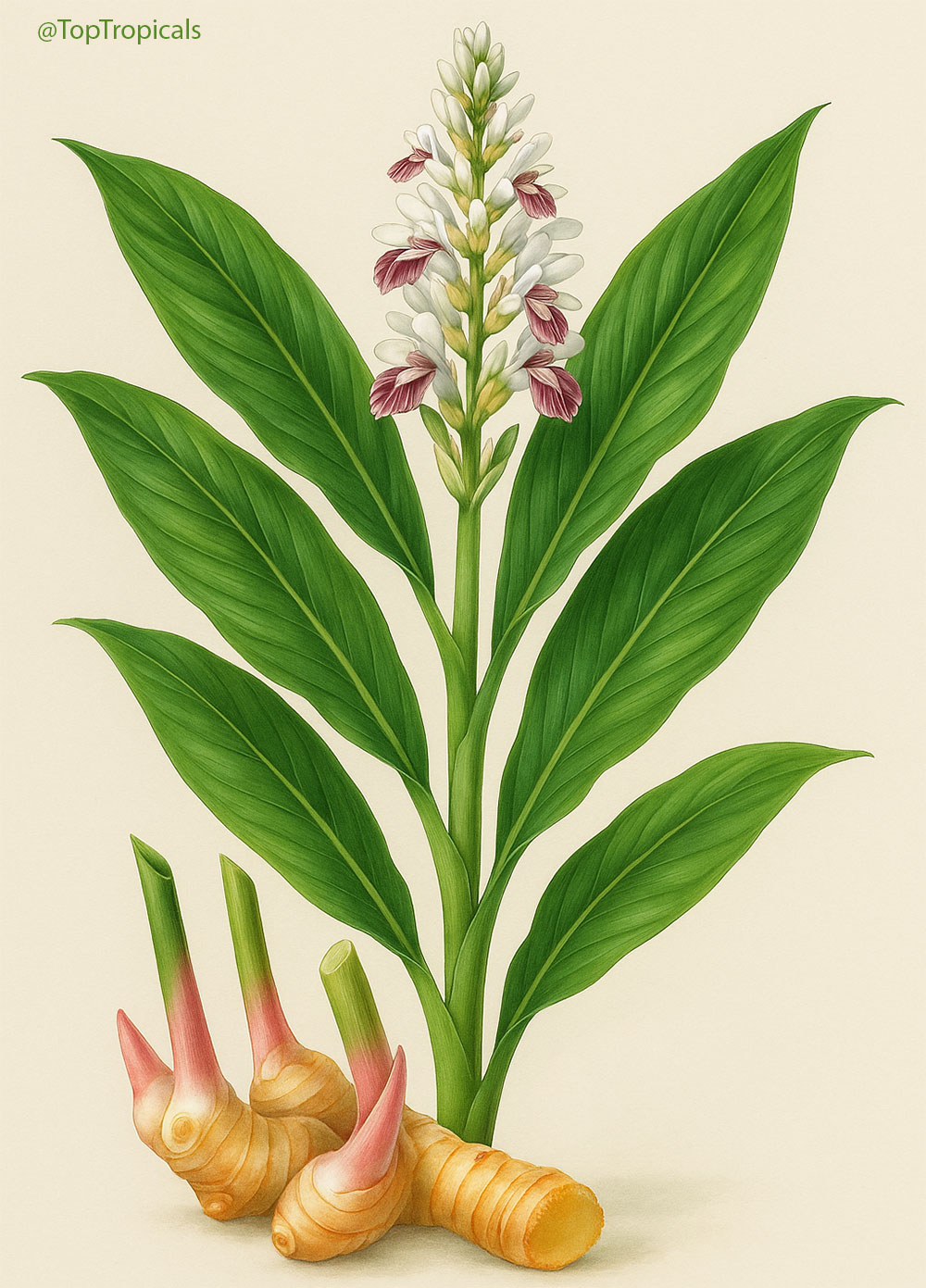
Botanical names: Alpinia galanga, Languas galanga
Common names: Galanga Root, Galangal, Thai Ginger, Laos
Family: Zingiberaceae
Origin: SE Asia









Galanga is an herb used in cooking, especially in Indonesian and Thai cuisines. It is one of four plants known as galangal, and is differentiated from the others with the common name greater galangal (or simply Thai galangal). The galangals are also called blue ginger or Thai ginger.
A. galanga is called laos in Indonesian and is the most common form of galangal used in cooking. It is also known as lengkuas and galanga root.
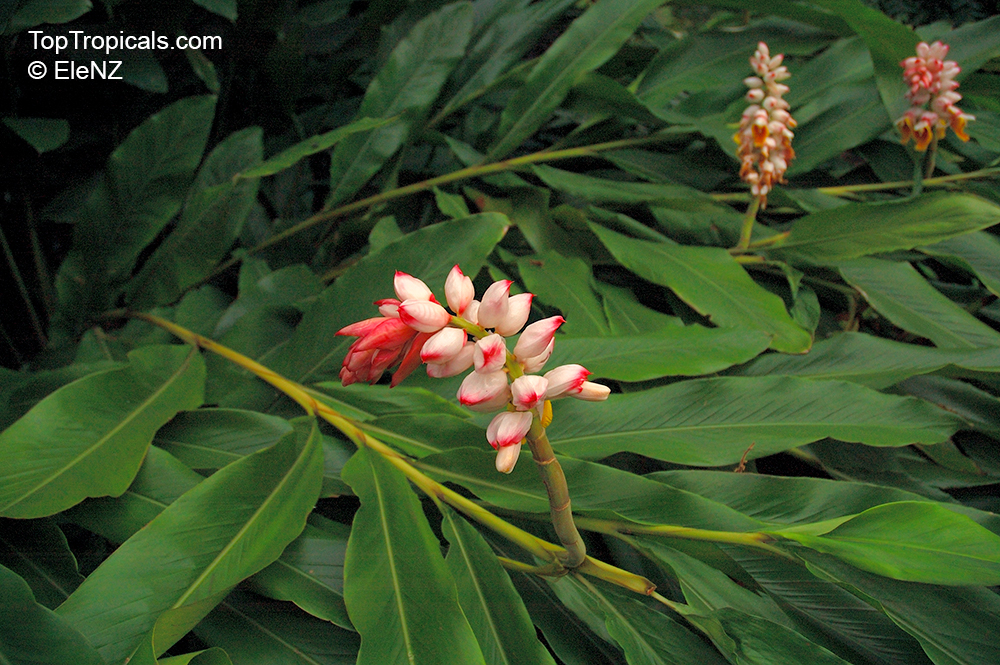
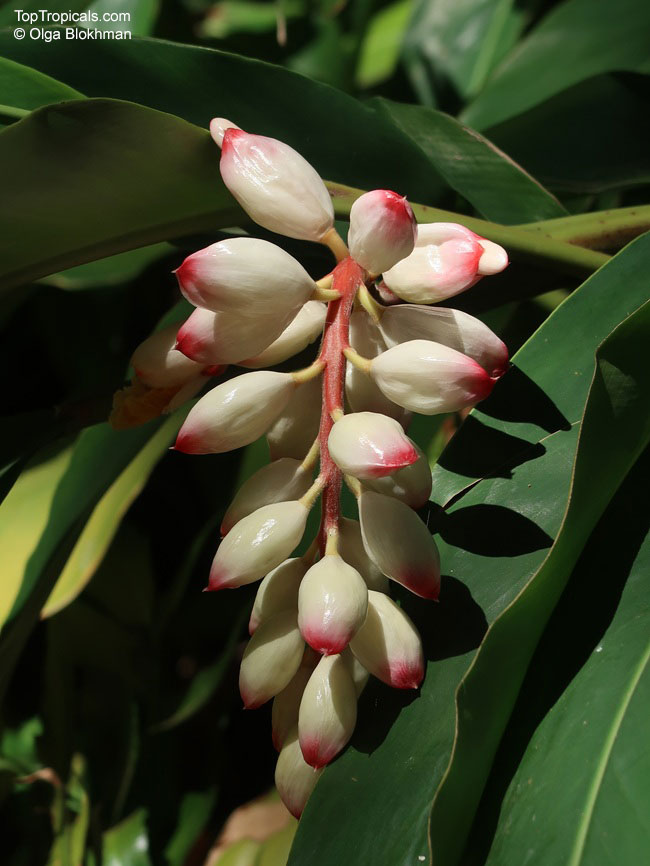
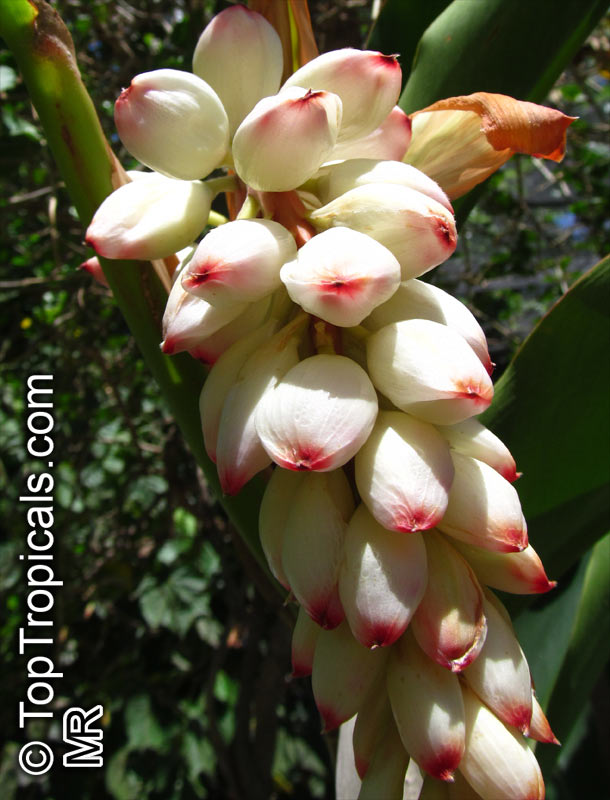
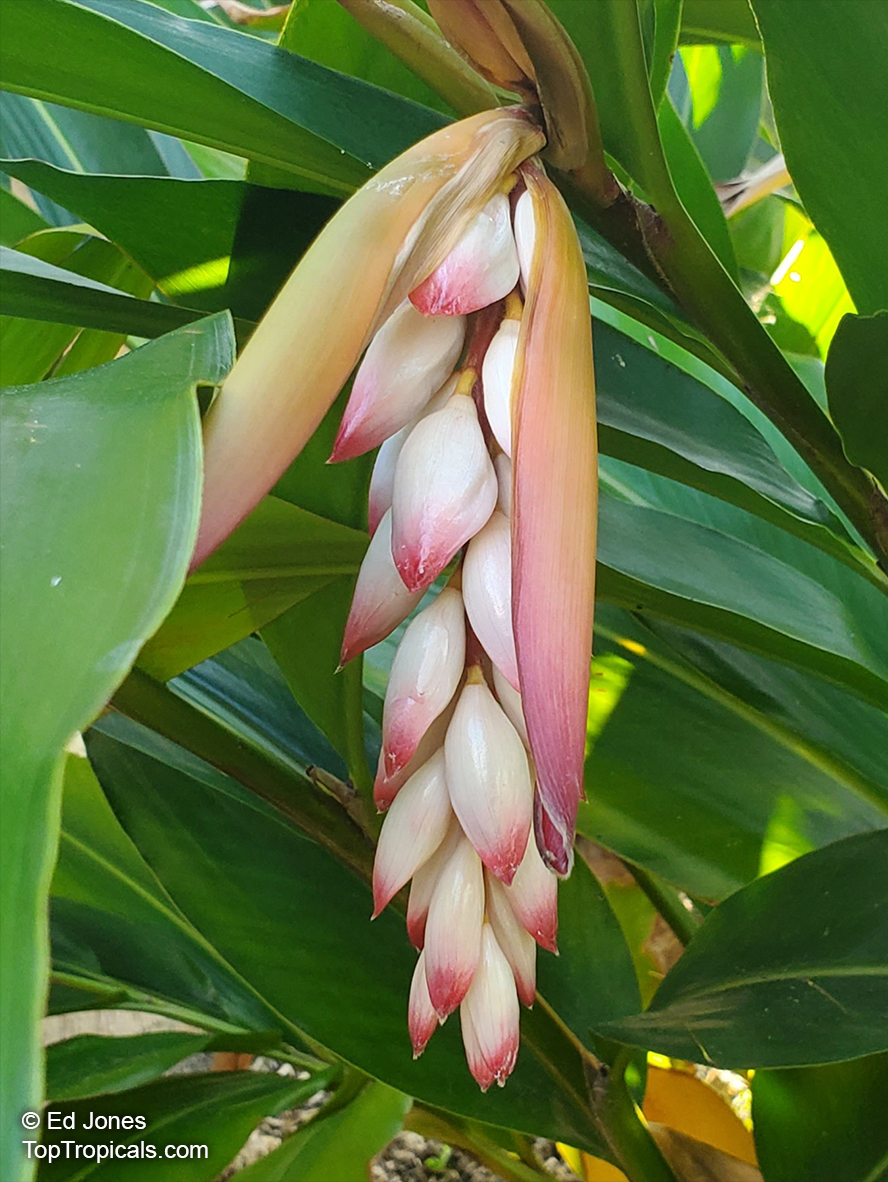
Botanical names: Alpinia nutans, Alpinia speciosa
Common names: Shell ginger, Pink porcelain lily, Narrow-Leaf Cinnamon Ginger, Shellflower, Dwarf cardamom, False cardamom
Family: Zingiberaceae
Origin: China and Japan
Hardiness: 20°F











The plant is quite versatile and makes for an excellent garden plant in USDA growing zones 7-9. It can either be grown as a large shrub of 5-10 feet in height or as a small shrub of 2-5 feet. Alpinia nutans requires full sun or partial shade, but prefers humid conditions and regular watering. Its stunning hot pink flowers, borne atop long flowering stems, bloom beginning in June and continue until the Fall.
It is a fairly salt tolerant plant, making it suitable for seaside areas. In cold climates, the mature plant is hardy at least to the low 30s Fahrenheit for a short time, although for best results it should be grown in a pot and stored in an area that does not freeze in the winter, such as a greenhouse or garage. Watering should be reduced in cold conditions and kept to a minimum until warm weather resumes. During the spring, the rhizome should be restrained or it will overthrow its container. Plants should be repotted in the spring if they outgrow their original container. Fertilize annually with compost or an appropriate plant food to encourage growth, and do regular pest and disease checks.
Alpinia nutans is similar to Alpinia malaccensis and Alpinia zerumbet. Alpinia nutans var. longiramosa is a synonym of Alpinia zerumbet.
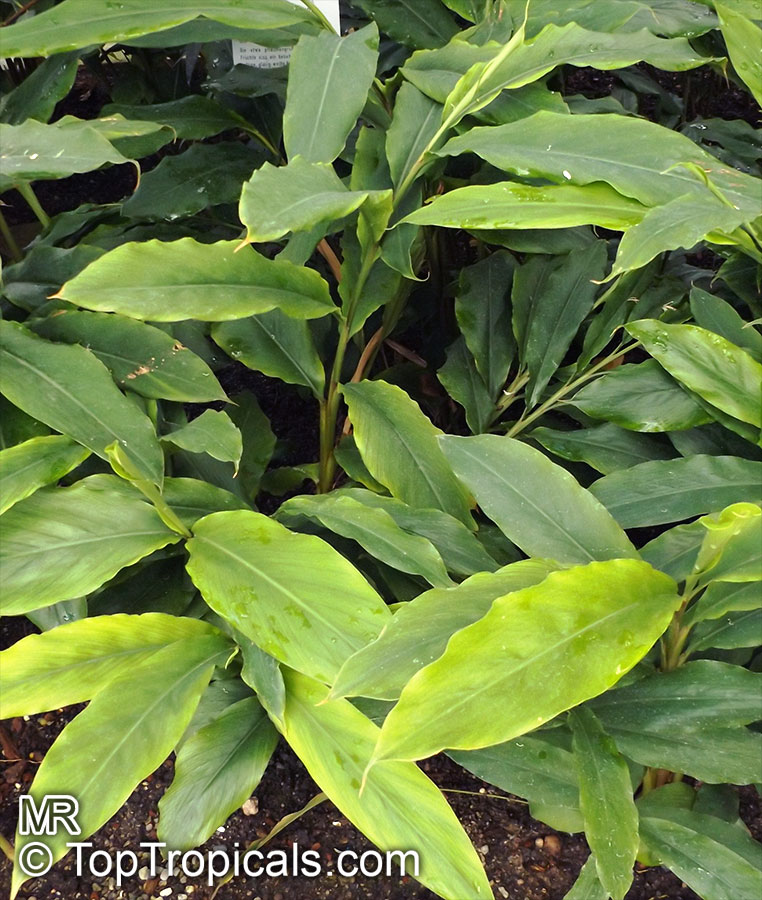
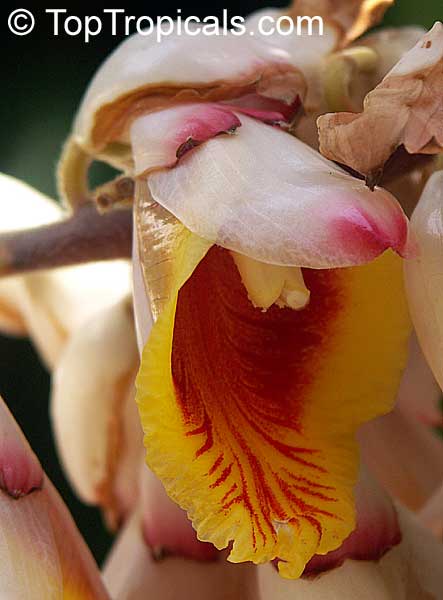
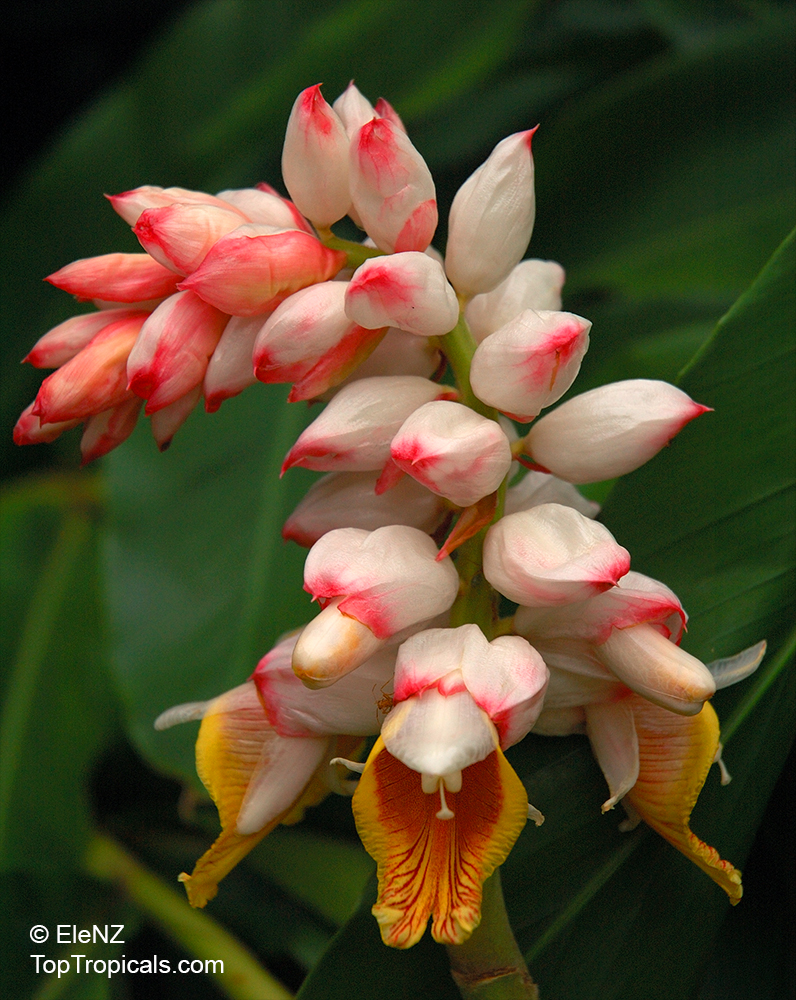
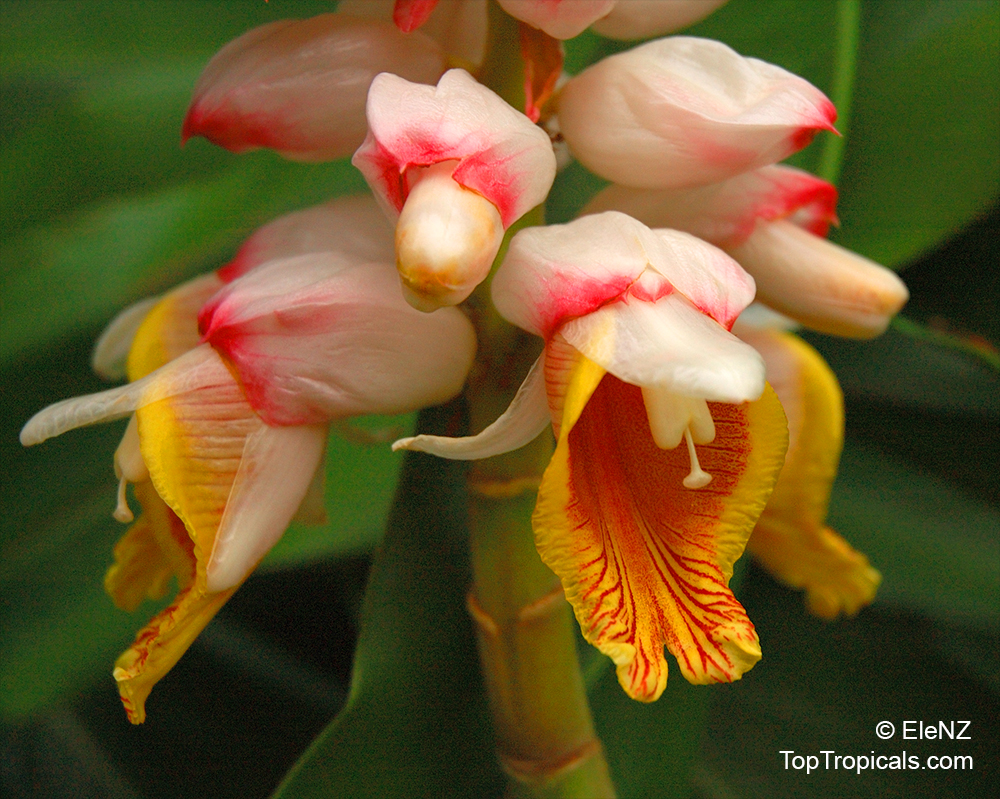
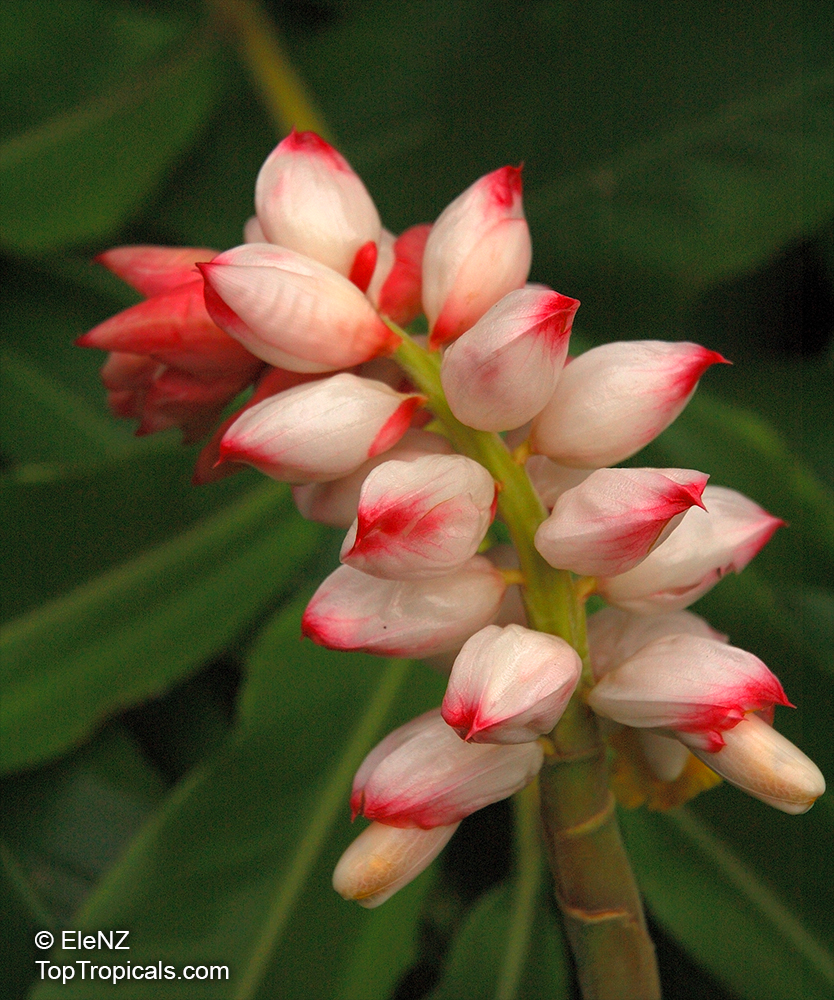
Botanical name: Alpinia officinarum
Common name: Lesser Galangal
Family: Zingiberaceae
Origin: China










Galanga Root, Lesser Galangal, Thai gingeris more than just a fast growing ornamental ginger and flavorful root - it's also a powerful healing plant with centuries of use in both kitchens and traditional medicine. It supports digestion, reduces inflammation, boosts circulation, and helps fight infections with its natural antimicrobial properties. Rich in antioxidants, galangal may also support brain health and relieve respiratory issues. A must-have plant for both cooking and wellness.
It has long narrow leaves and reddish-white flowers. Galanga is an herb used in cooking, especially in Indonesian and Thai cuisines. The rhizomes, known as galangal, are valued for their spicy flavor and aromatic scent. These are used throughout Asia in curries and perfumes, and were previously used widely in Europe.
Alpinia officinarum (Lesser Galangal) is typically measuring 5-10 feet in height. It prefers semi-shade and regular watering, but will tolerate moderate water during dry spells. The flowers are a cluster of pink, white, or off-white blossoms, giving a beautiful display.
It is not just an ornamental plant. In China, it is also valued for its ethnomedical properties, used as a spice or a herb. Grown across USDA zone 9-11, it can easily be grown in pots in cold regions.
For proper care and growth, this plant requires a slightly acidic and well-drained soil. Provide light shade if grown outdoors, and ensure the pot is well-drained for optimal water retention. Water the plant regularly, but avoid excessive wetting of the soil. It will thrive under the right conditions and can last for years.
Fertilize Alpinia officinarum with a balanced formula throughout the growing season.
Alpinia officinarum is a beautiful, versatile plant. With proper care and maintenance, it will thrive and bring a splash of color and fragrance to any garden.
The rhizomes, known as galangal, are valued for their spicy flavor and aromatic scent. These are used throughout the world in curries and perfumes.
Botanical names: Alpinia zerumbet, Alpinia nutans var. longiramosa
Common name: Shell Ginger
Family: Zingiberaceae
Origin: East Asia
Hardiness: 20°F










Alpinia zerumbet is called a "shell ginger" or "shell flower" most commonly, because its individual pink flowers, especially when in bud, resemble sea shells.
Alpinia zerumbet is similar to Alpinia malaccensis and Alpinia nutans
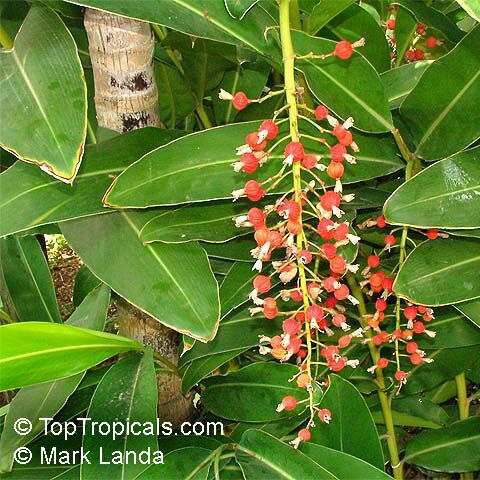
Botanical name: Amomum dealbatum
Common name: Amomum
Family: Zingiberaceae
Origin: Southeastern Asia








This relative of ginger is an aromatic medicine, which was often used as an antidote to poisoning.
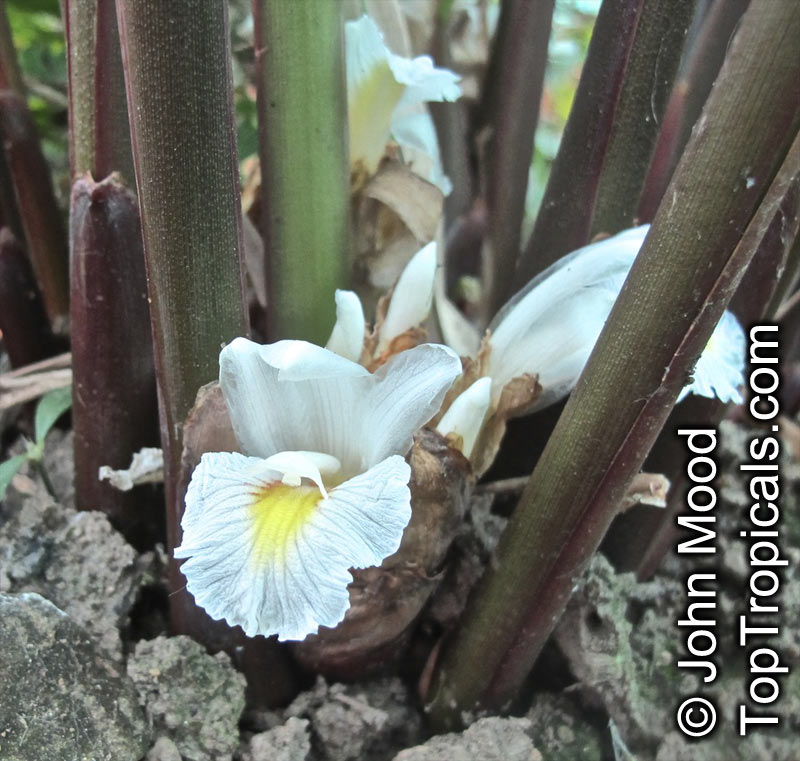
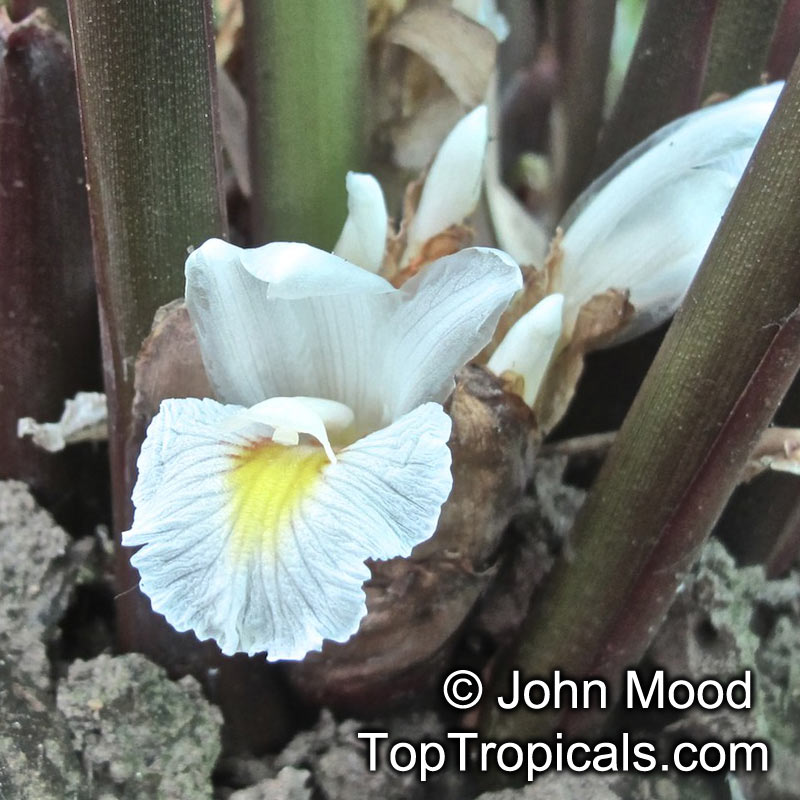
Botanical name: Anemopsis californica
Common names: Yerba Mansa, Lizard Tail
Family: Saururaceae
Origin: Southwestern North America




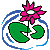




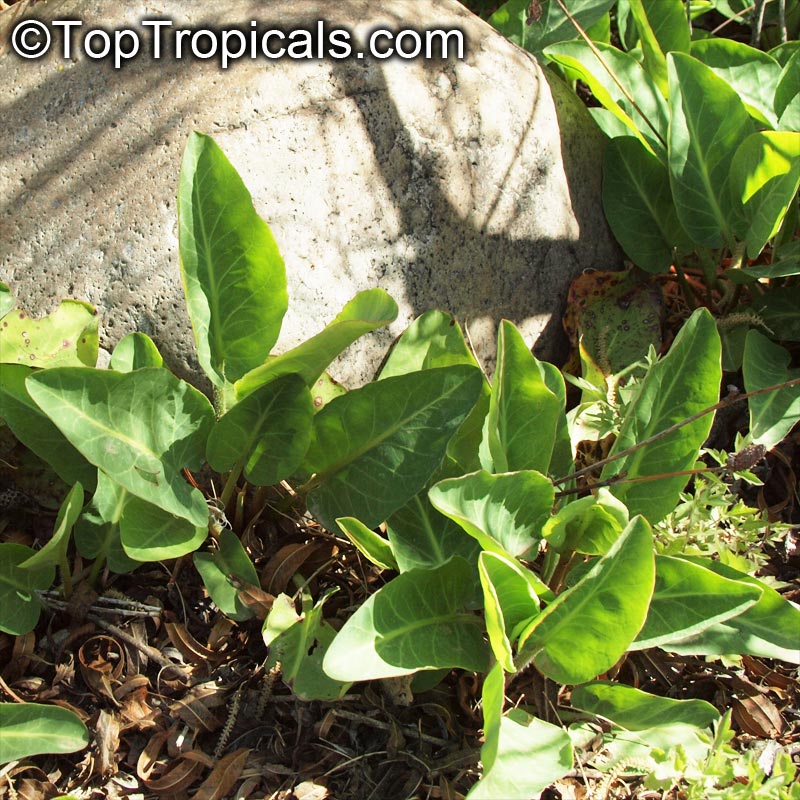
Anemopsis californica is a small shrub, typically only reaching 2-5 feet in height and width. The plant prefers to grow in full sun or semi-shade, with rich and well-draining soils. Under the right conditions, Anemopsis californica is an excellent bog or aquatic plant, and can tolerate periodic flooding during winter months. Anemopsis californica loves regular water, and will not tolerate drought, so make sure to keep the soil evenly moist. Due to the large leaves of the species, they do well in warmer climates, and anemopsis grows best in USDA Zones 9-11.
Anemopsis californica has cup-like structures of white, off-white flowers that hang down and produce a spicy, delicate fragrance throughout the warmer months. Anemopsis californica has some unique ethnomedical properties and is used to treat a variety of ailments in both mainstream and folk medicine, ranging from digestive issues to mouth infections. The plant is also popularly used as a spice or herb, and its sweet aroma adds both flavor and fragrance to food.
When planting Anemopsis californica in cold regions, it is best to grow in a pot in a sunny area and move indoors to protect against frost. Keep the soil moist and the plant in the container until warm weather returns, then move it back out into the garden and gradually allow it to adjust to its new environment. If planted outdoors in colder climates, be sure to provide ample insulation with layers of mulch and other protective materials, and cover with a tarp or blanket during particularly cold weather.
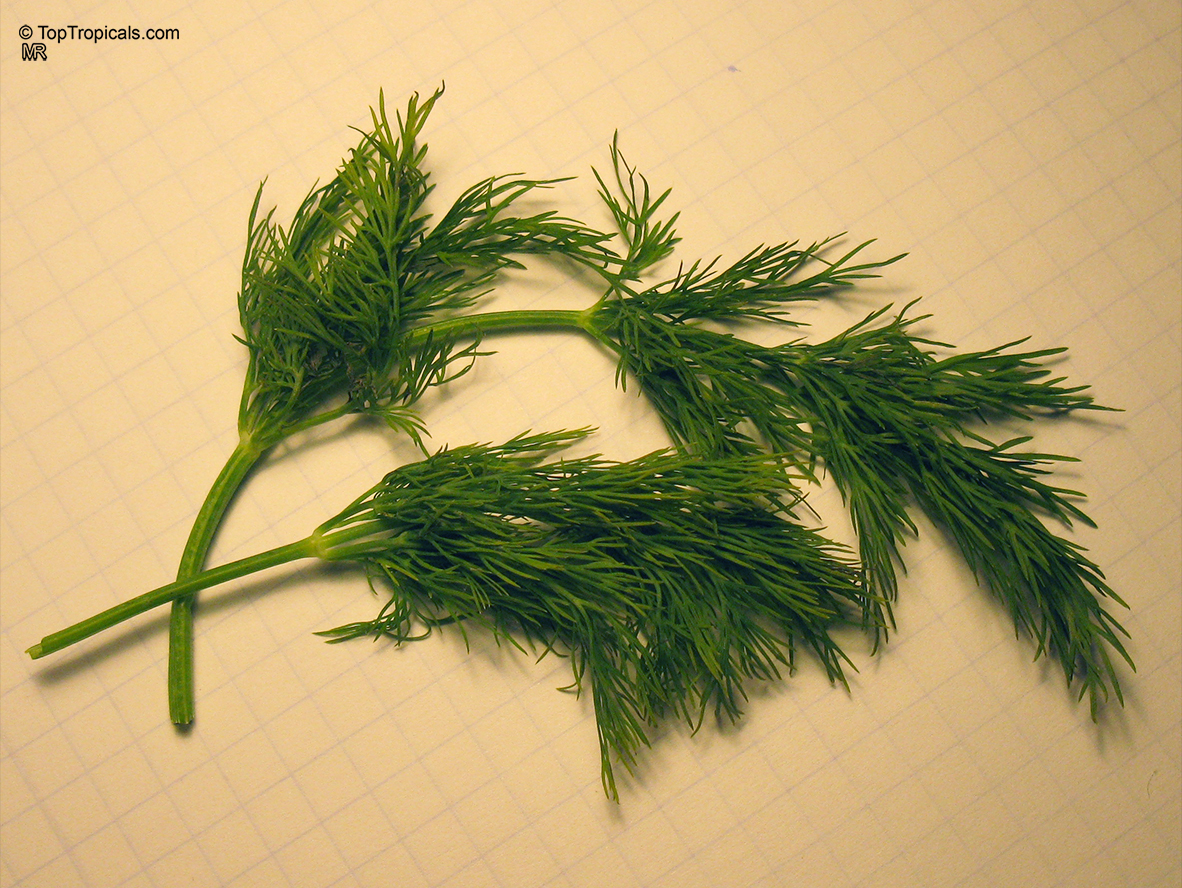
Botanical name: Anethum graveolens
Common name: Dill
Family: Apiaceae / Umbelliferae
Origin: Eastern Europe









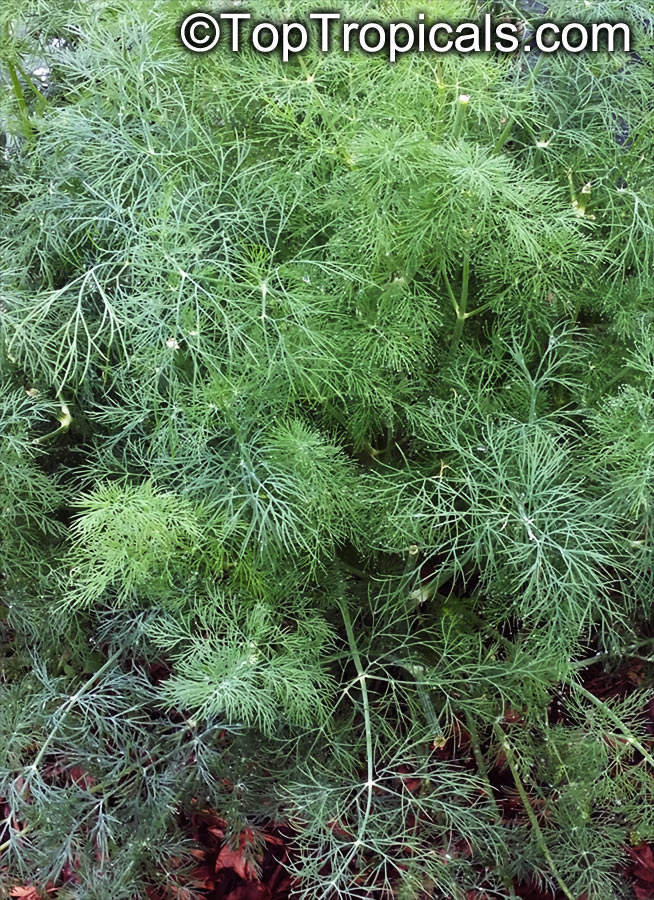
Dill is a short-lived perennial herb. It is the sole species of the genus Anethum, though classified by some botanists in a related genus as Peucedanum graveolens. The name dill comes from Old English dile, thought to have originated from a Norse or Anglo-Saxon word dylle meaning to soothe or lull, the plant having the carminative property of relieving gas. In Sanskrit, this herb is termed as Shatapushpa. In Semitic languages it is known by the name of Shubit. The Talmud requires that tithes shall be paid on the seeds, leaves, and stem of dill. The Bible states that the Pharisees were in the habit of paying dill as tithe. Jesus rebuked them for tithing dill but omitting justice, mercy and faithfulness. To the Greeks the presence of dill was an indication of prosperity. In the 8th century, Charlemagne used it at banquets to relieve hiccups and in the Middle Ages it was used in a love potion and was believed to keep witches away.
Fresh and dried dill leaves (sometimes called "dill weed" to distinguish it from dill seed) are used as herbs.
Like caraway, its fernlike leaves are aromatic, and are used to flavor many foods, such as gravlax (cured salmon), borscht and other soups, and pickles (where sometimes the dill flower is used). Dill is said to be best when used fresh, as it loses its flavor rapidly if dried; however, freeze-dried dill leaves preserve their flavor relatively well for a few months.
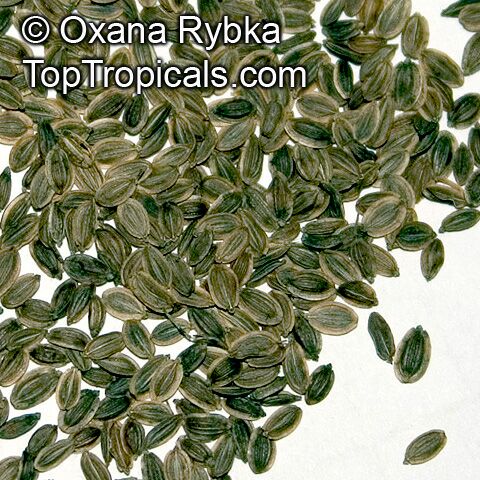
Dill seed is used as a spice, with a flavor somewhat similar to caraway, but also resembling that of fresh or dried dill weed. Dill seeds were traditionally used to soothe the stomach after meals. And, dill oil can be extracted from the leaves, stems and seeds of the plant.
Used in: Teas; seasoning for butter, cakes, bread, vinegars, soups, fish, pickles, salads, etc.; flowers in crafts.
Successful cultivation requires warm to hot summers with high sunshine levels; even partial shade will reduce the yield substantially. It also prefers rich, well drained soil. The seeds are viable for 3-10 years.
| Next |  |
Use link to repeat this search:
https://toptropicals.com/cgi-bin/garden_catalog/cat.cgi?search_op=and&keyword_op=and&language=e&number=10&no_change_lang=1
&v1=spc&user=tt&sale=1&first=0




























 SUNSHINE Robusta (NPK 2-1-3) - Vegetative Vigor Booster for every watering. Formulated especially for vegetative stage of plant development. Can be used for a quick build-up of vegetative growth, for establishing and recovering damaged plants that lost many leaves. This is an eco-friendly nutrition booster that can be used for edibles and organic gardens. Can be used for daily feeding with every watering. Scientifically-balanced stable formula is organic Amino-acid based and has NO EDTA chelators to eliminate nutrients lockup; it does not affect crop taste. Organic Amino acids greatly enhance stability of all Sunshine boosters and provide excellent absorption of trace elements. Pollinating insects friendly.
SUNSHINE Robusta (NPK 2-1-3) - Vegetative Vigor Booster for every watering. Formulated especially for vegetative stage of plant development. Can be used for a quick build-up of vegetative growth, for establishing and recovering damaged plants that lost many leaves. This is an eco-friendly nutrition booster that can be used for edibles and organic gardens. Can be used for daily feeding with every watering. Scientifically-balanced stable formula is organic Amino-acid based and has NO EDTA chelators to eliminate nutrients lockup; it does not affect crop taste. Organic Amino acids greatly enhance stability of all Sunshine boosters and provide excellent absorption of trace elements. Pollinating insects friendly. SUNSHINE Robusta (NPK 2-1-3) - Vegetative Vigor Booster for every watering. Formulated especially for vegetative stage of plant development. Can be used for a quick build-up of vegetative growth, for establishing and recovering damaged plants that lost many leaves. This is an eco-friendly nutrition booster that can be used for edibles and organic gardens. Can be used for daily feeding with every watering. Scientifically-balanced stable formula is organic Amino-acid based and has NO EDTA chelators to eliminate nutrients lockup; it does not affect crop taste. Organic Amino acids greatly enhance stability of all Sunshine boosters and provide excellent absorption of trace elements. Pollinating insects friendly.
SUNSHINE Robusta (NPK 2-1-3) - Vegetative Vigor Booster for every watering. Formulated especially for vegetative stage of plant development. Can be used for a quick build-up of vegetative growth, for establishing and recovering damaged plants that lost many leaves. This is an eco-friendly nutrition booster that can be used for edibles and organic gardens. Can be used for daily feeding with every watering. Scientifically-balanced stable formula is organic Amino-acid based and has NO EDTA chelators to eliminate nutrients lockup; it does not affect crop taste. Organic Amino acids greatly enhance stability of all Sunshine boosters and provide excellent absorption of trace elements. Pollinating insects friendly.




















