Amaryllidaceae - Botanical Family
| Number of plants found: 46 | Next | 
|
Go to page: | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
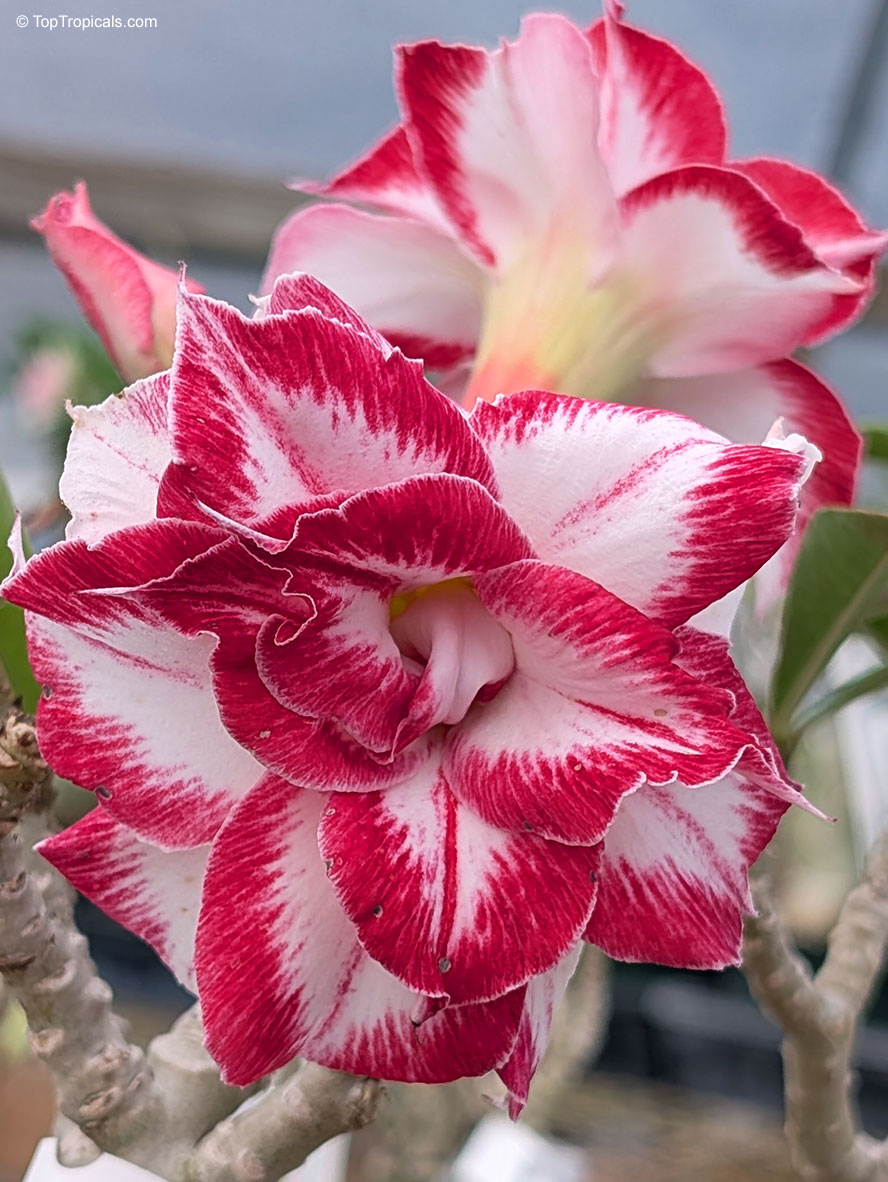
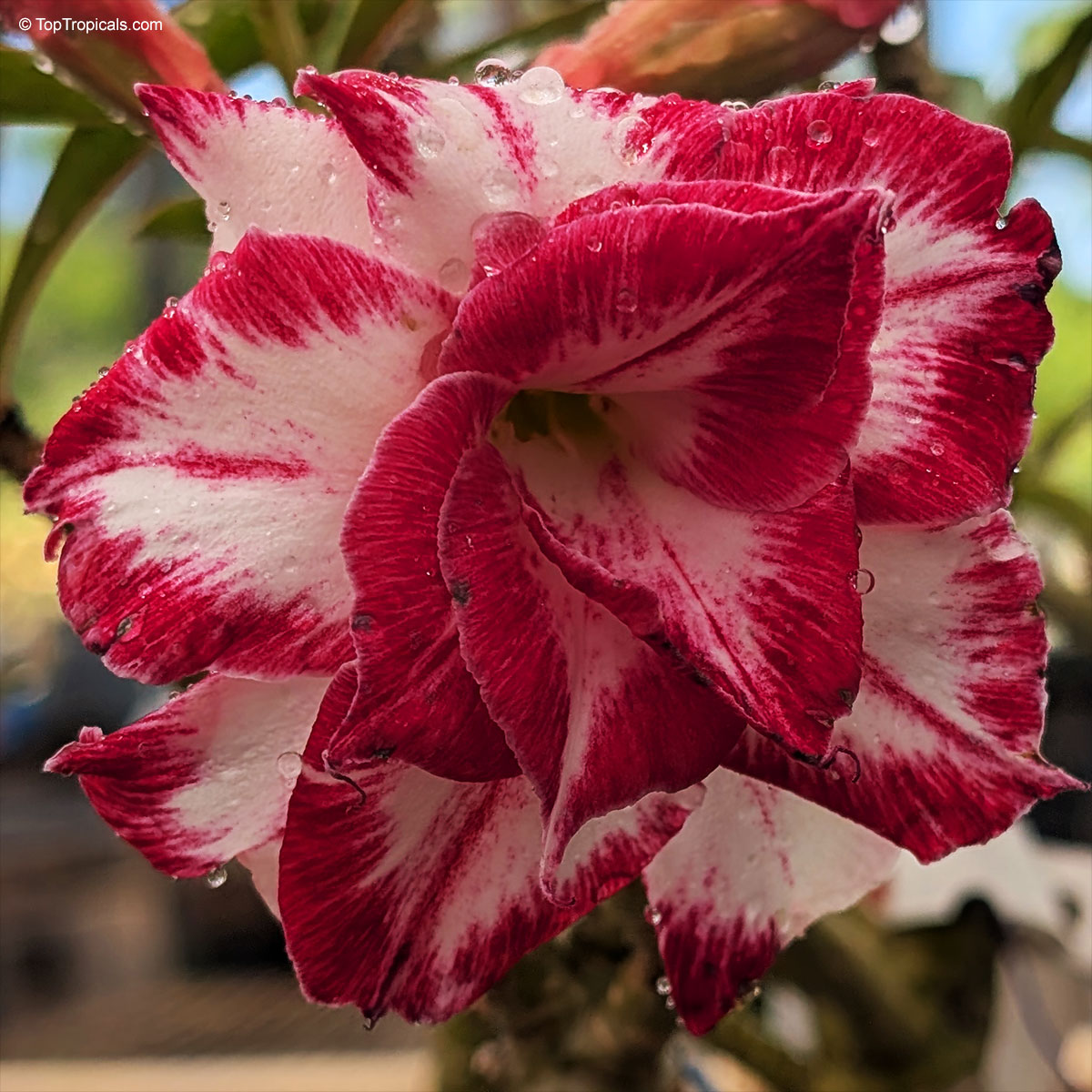
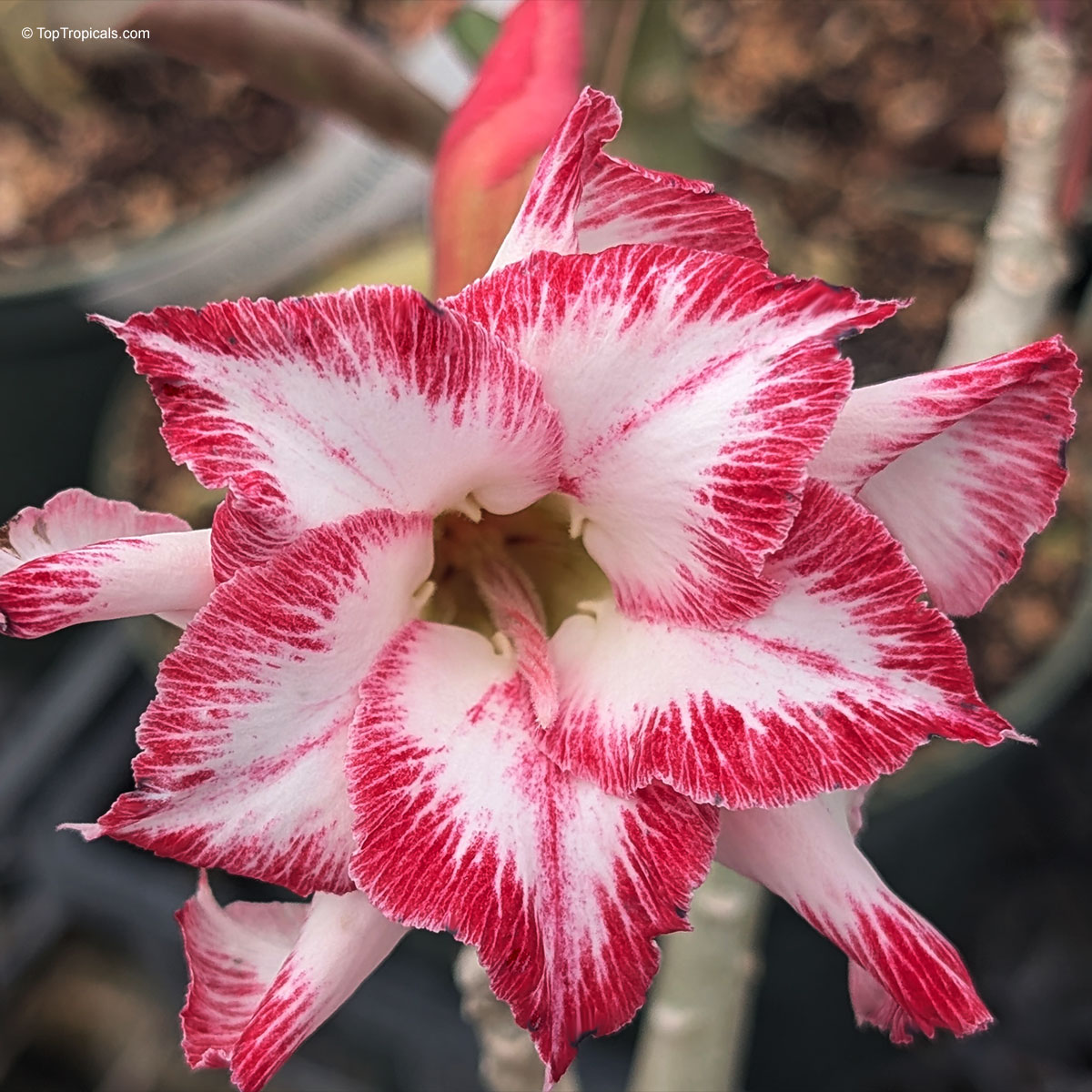
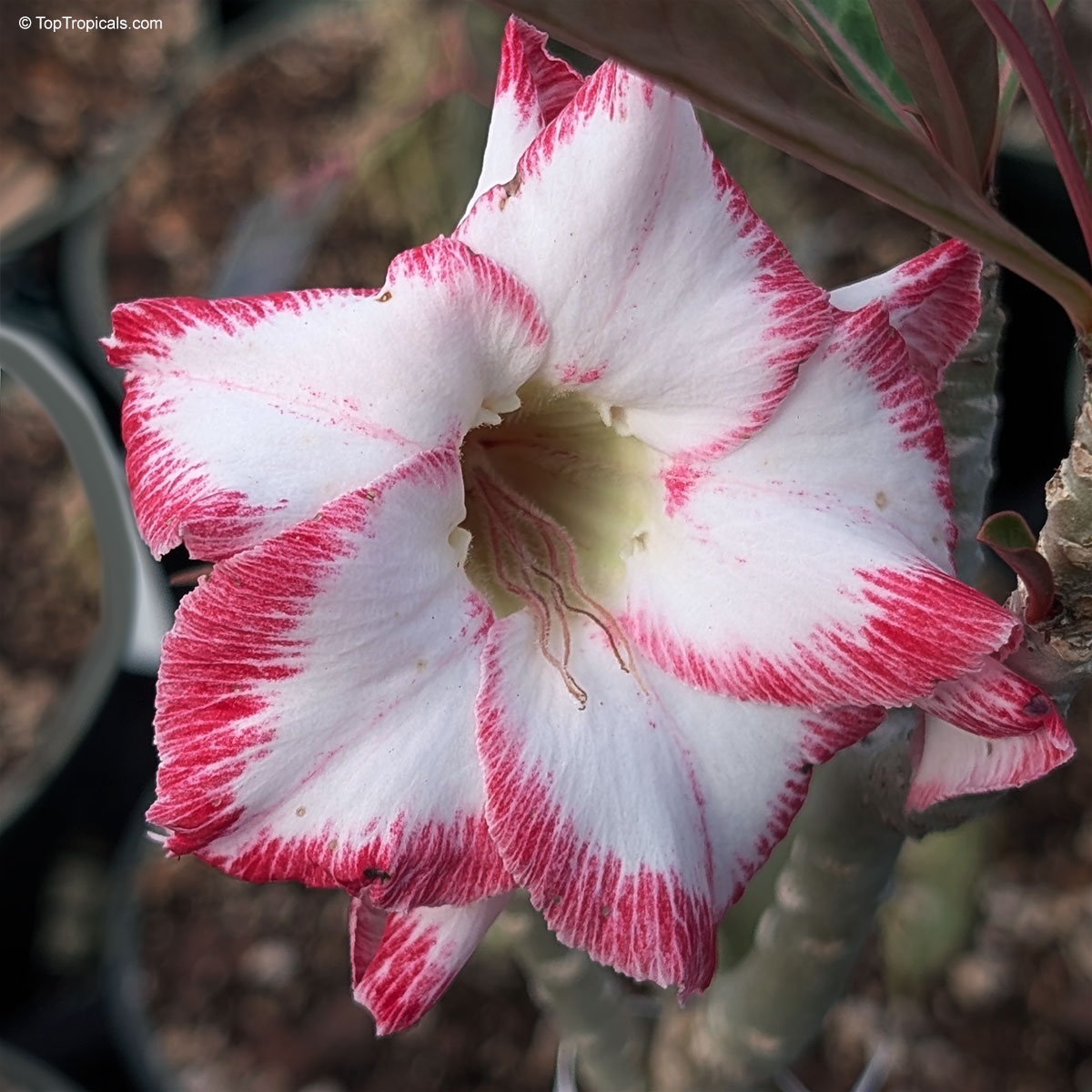
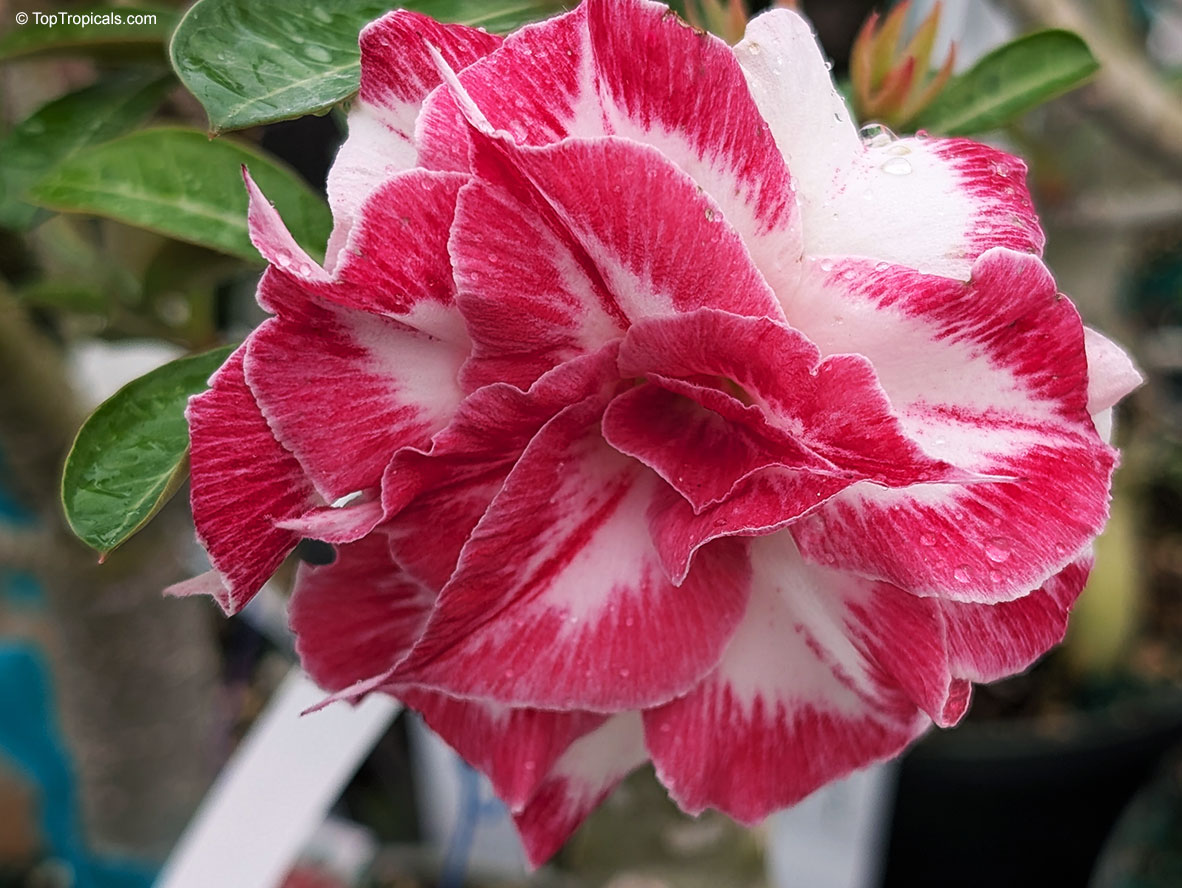
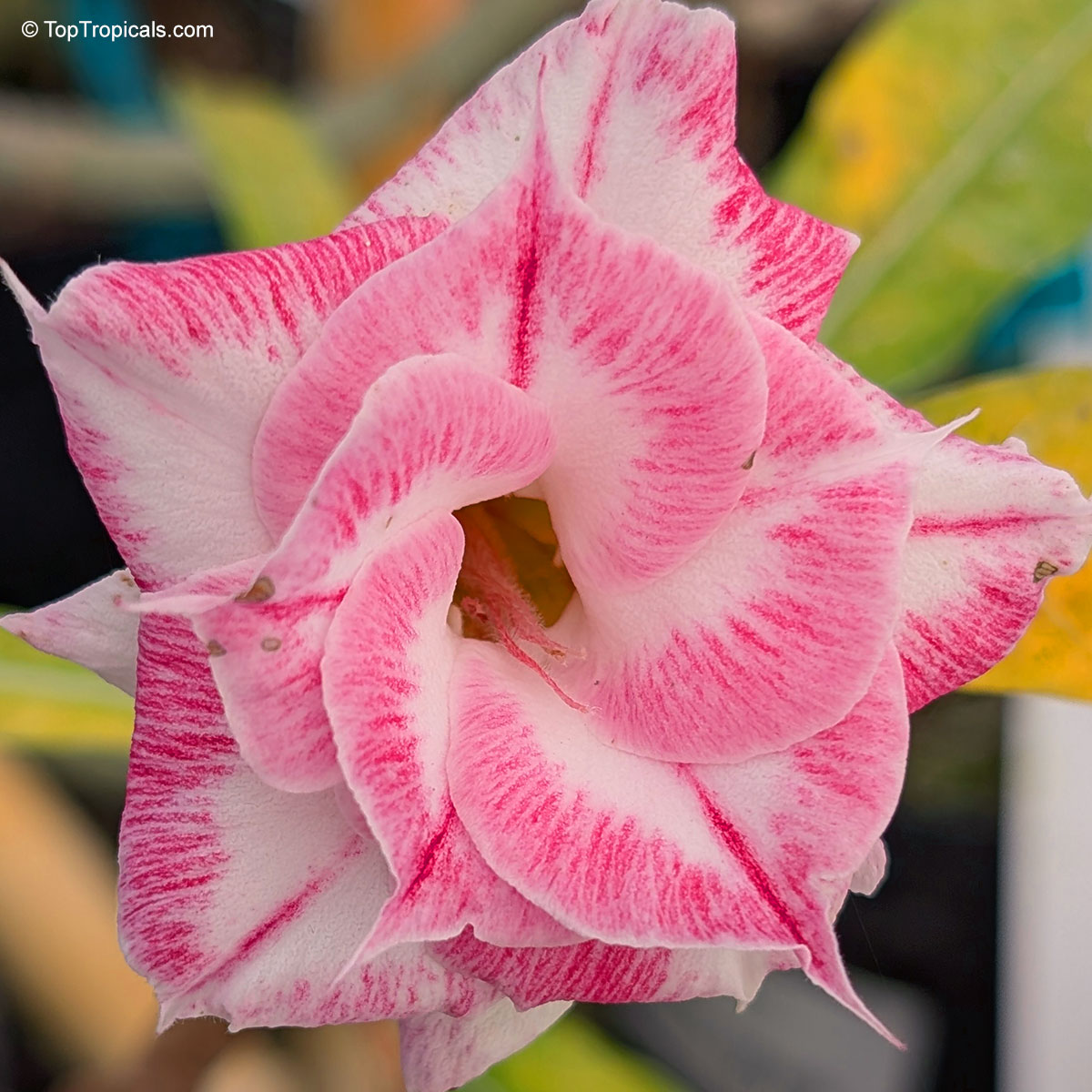
Botanical name: Adenium sp.
Common name: 'Black Amaryllis' Desert Rose
Cultivar: Black Amaryllis
Family: Apocynaceae
Origin: Arabia and East Africa









These bizarre hybrids appeared on the market a few years ago. At first, pictures looked confusing and unreal. When our first Black adeniums went into bloom, we were disappointed with red buds popped up on the plants... However after the dark red flowers opened, they started to darken as they aged, and some varieties turned so dark in color that it was close to black or brown. Some varieties have only black contour around red flower. So, black flower is actually a very old flower! So be, patient and let it age as an old good vine. See picture of darkening process.
Adeniums have many spectacular hybrids. The basic culture is very similar to orchids. A small pot with excellent drainage is a must. Adeniums do not like both over-watering or drying-out. There is a little secret of how to create a weird shape of the base: lift the plant a bit every time you re-pot the plant, so that the upper part of roots will be a little exposed. The plant will form more roots that will go down. To make your plant develop a large swollen base/trunk, you'll need a good quality fertilizer. Fertilizer requirement for swelling up trunks is also used to increase flowering. It shouldn't be too high in nitrogen, the middle number should be the highest. Never apply fertilizer directly on roots and do not liquid feed when a plant is thirsty: always water first slightly to avoid root burn and leaf drop. Do not wet leaves. Adeniums need lots of light for heavy flowering. Most hybrids and species start blooming in the spring when the conditions are warm and days get longer, and continue blooming through the fall and winter in warmer climates. Adeniums like a neutral to hard water. Acidic water tends to sour the soil too fast and may cause root rot. Water plants preferably in the early morning, and allow them to drink up throughout the day. Watering can be done daily to every few days. Never allow your plants to sit in a saucer of water, but don't let them to dry out too often - this causes adeniums to go into early dormancy.
Adenium 'Black Amaryllis' striking double flower with deep crimson edges blending into creamy white, resembling a painted amaryllis. A true showstopper for warm, sunny spots. 'Black Amaryllis' Desert Rose often opens with pale pink to nearly white flowers that deepen gradually as the bloom matures. The final intensity of the dark pink to burgundy pattern depends on growing conditions, with cooler temperatures tending to enhance darker tones, stronger light producing richer coloration, and plant nutrition and moisture also influencing pigment development. Natural genetic variation within this hybrid line can further explain why some flowers remain relatively light while others become much darker.
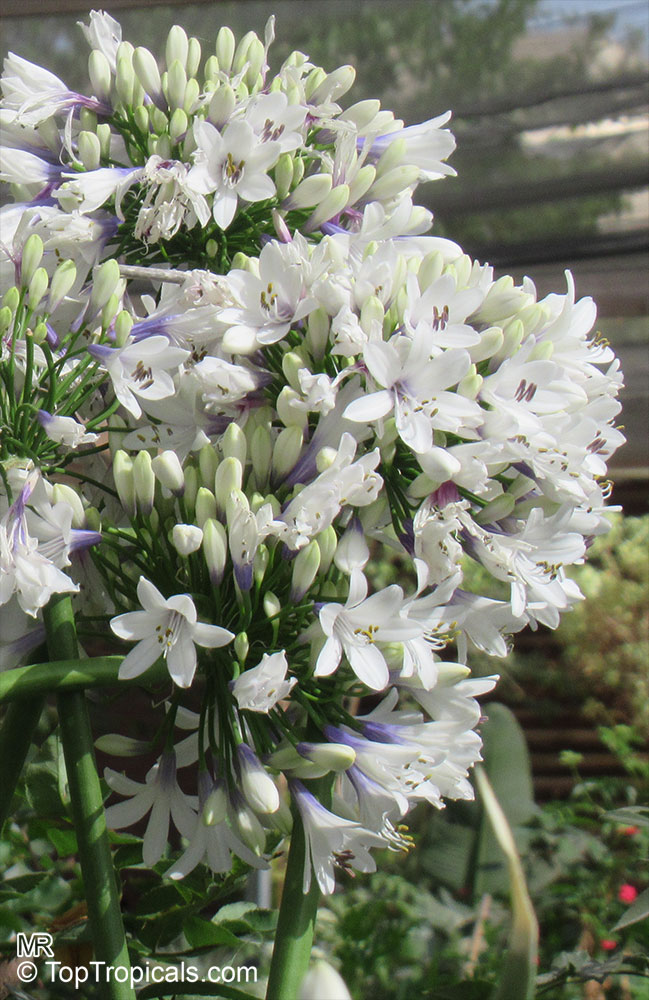
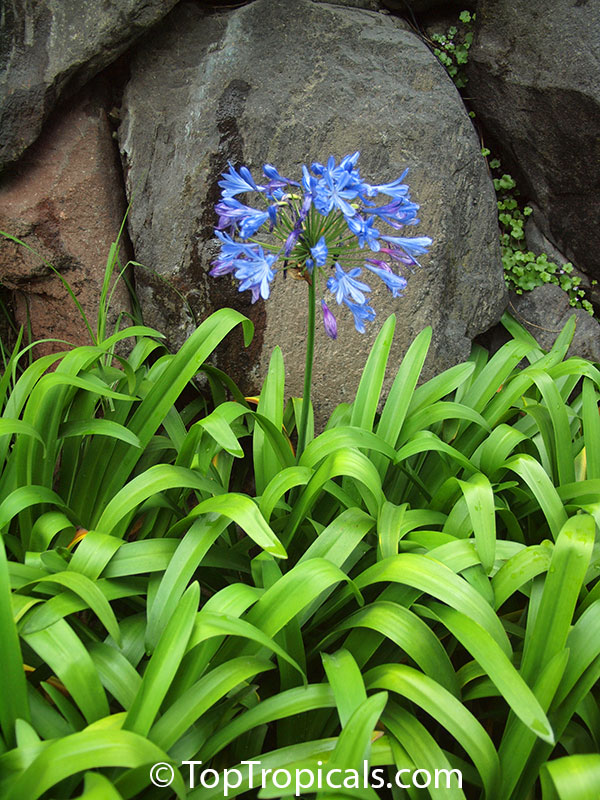
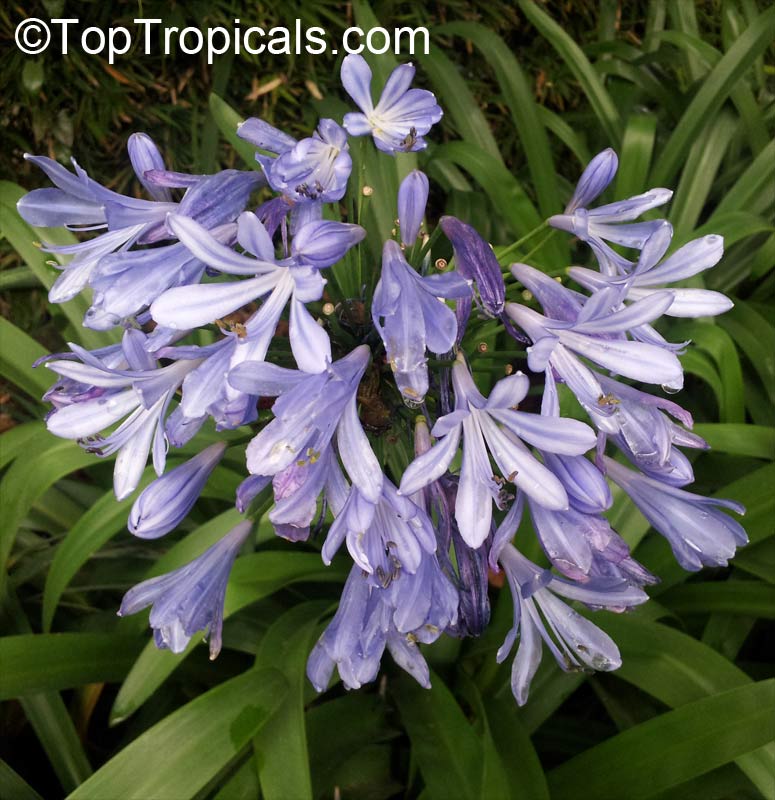
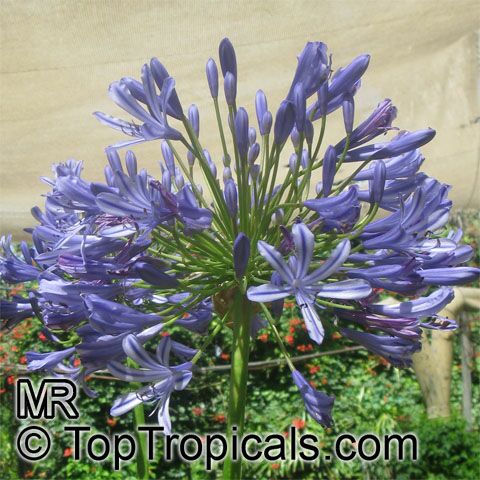
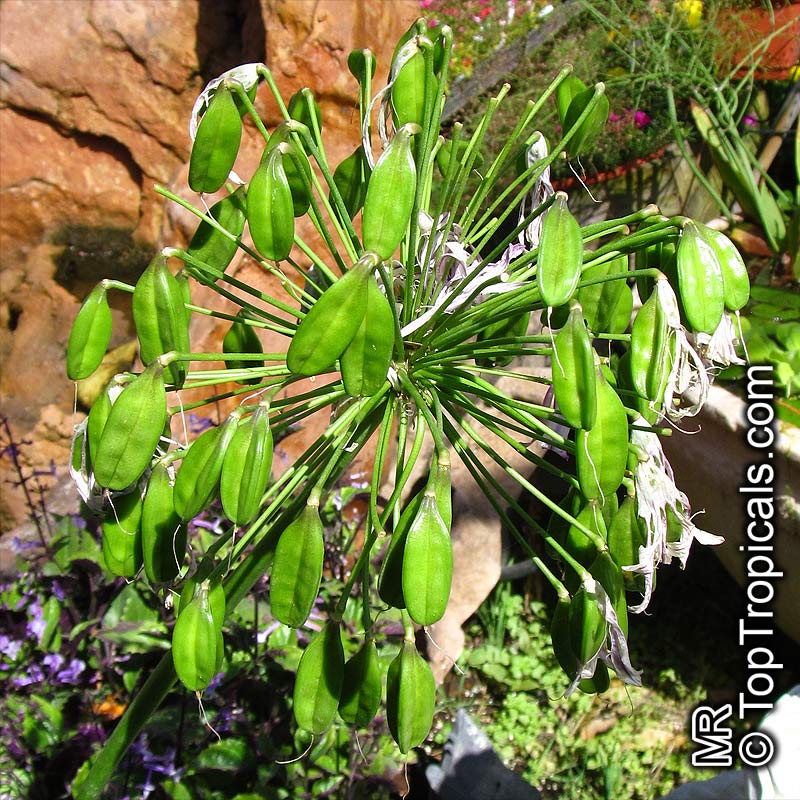
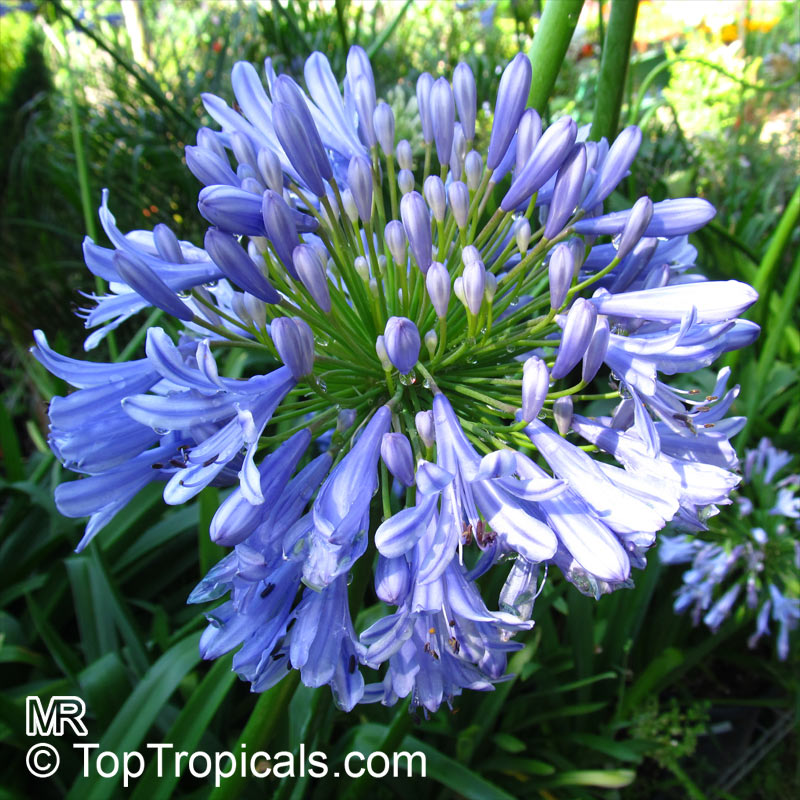
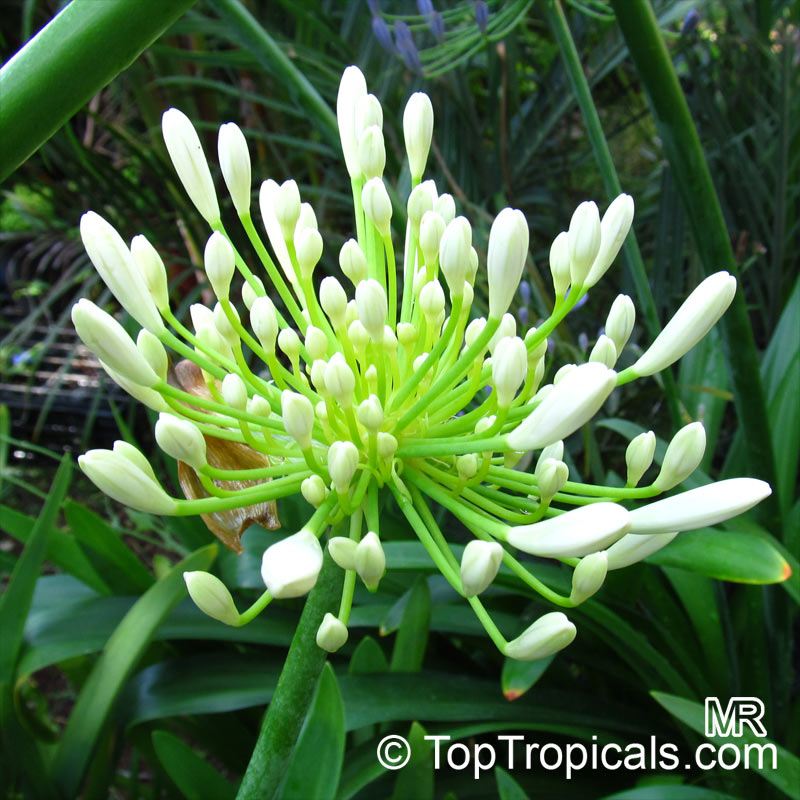
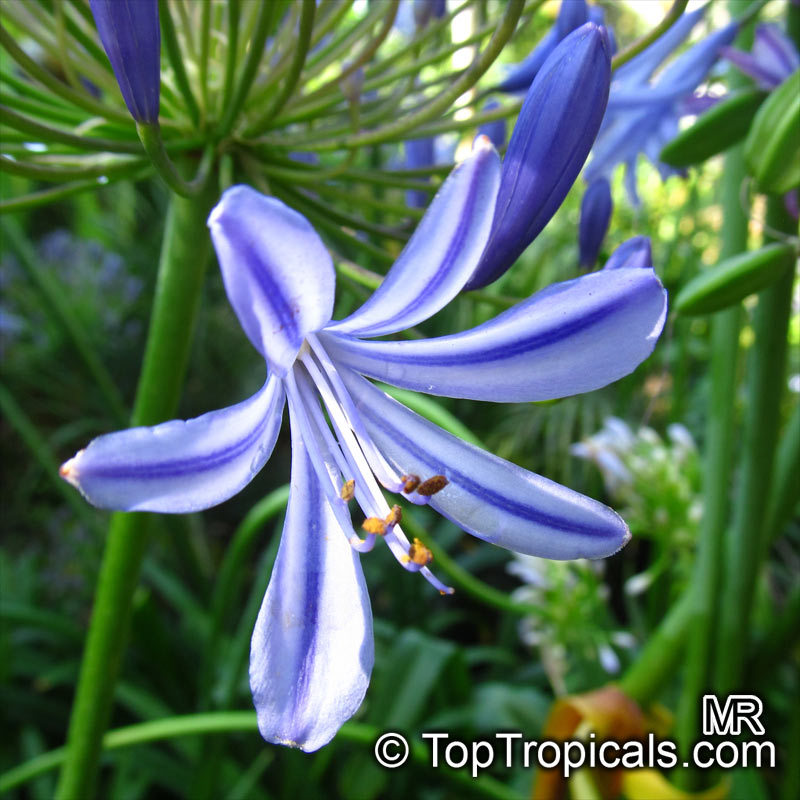
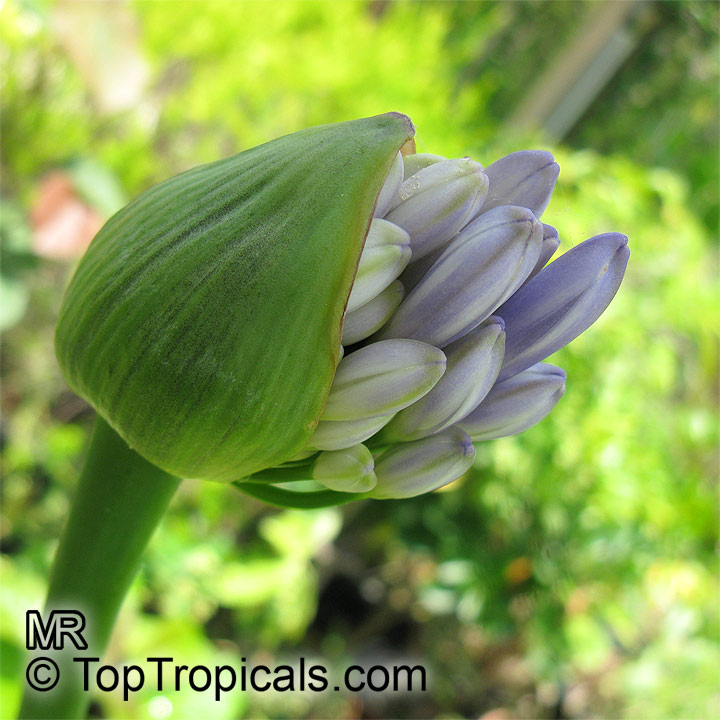
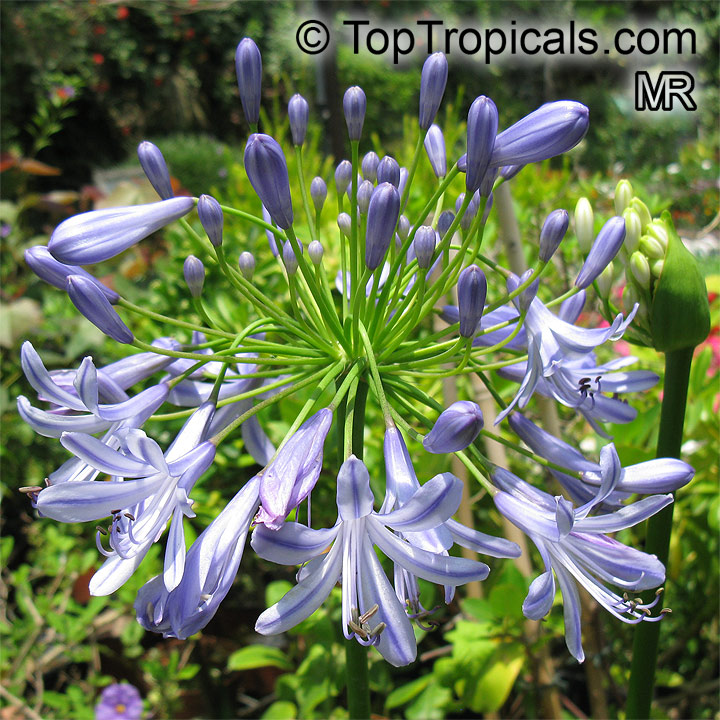
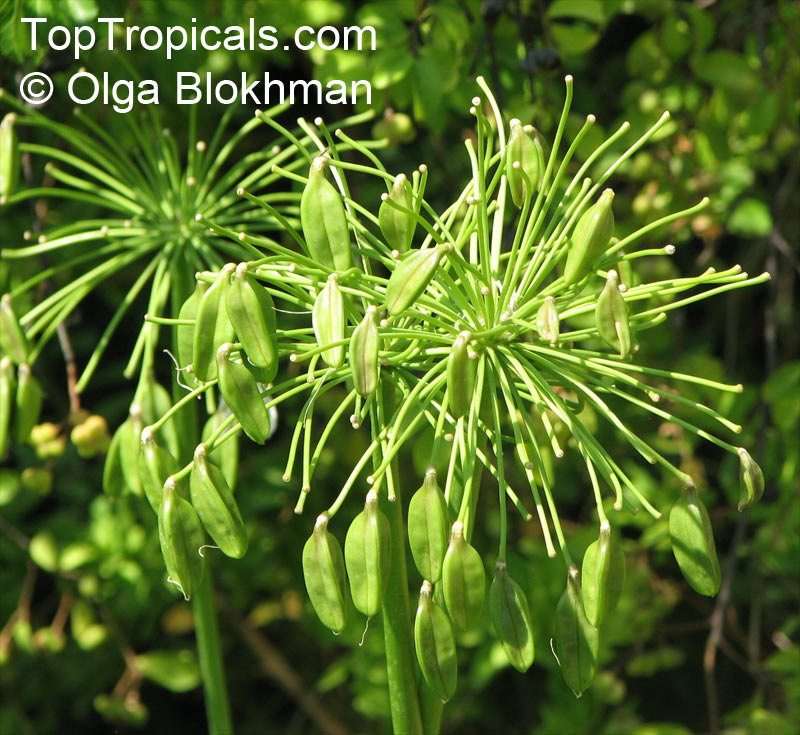
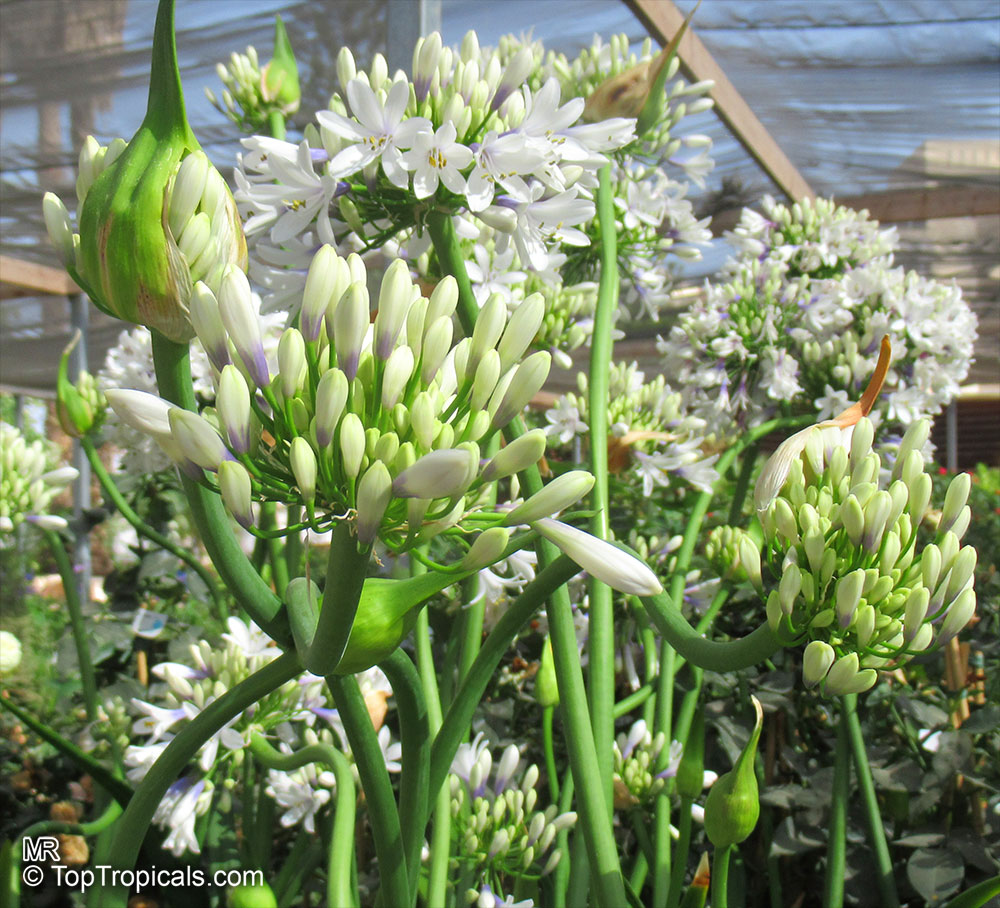
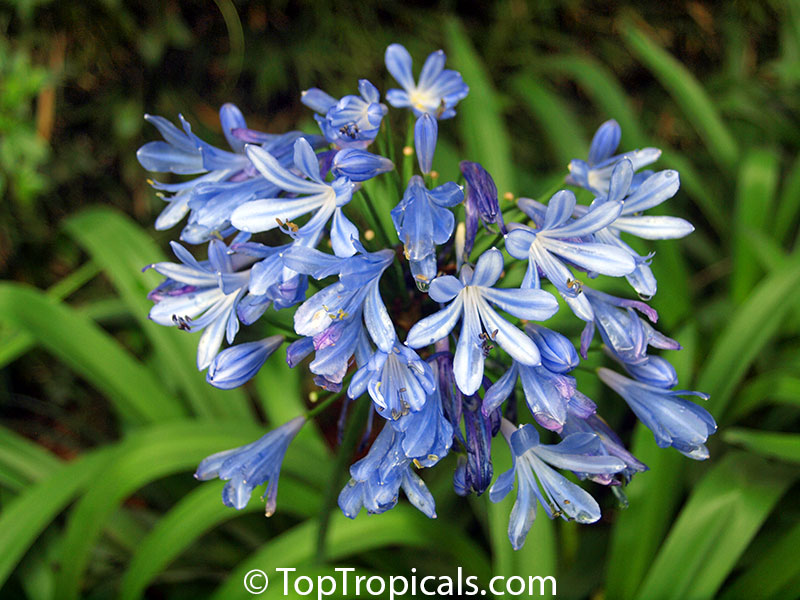
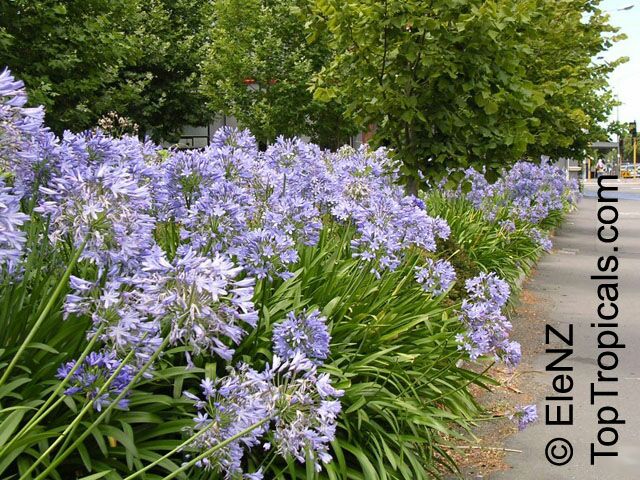
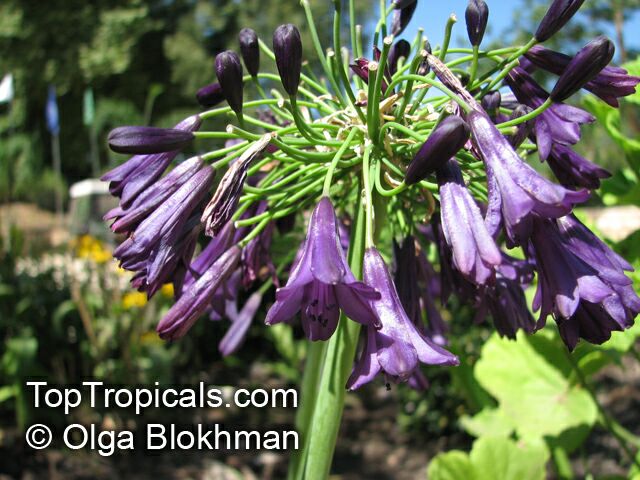
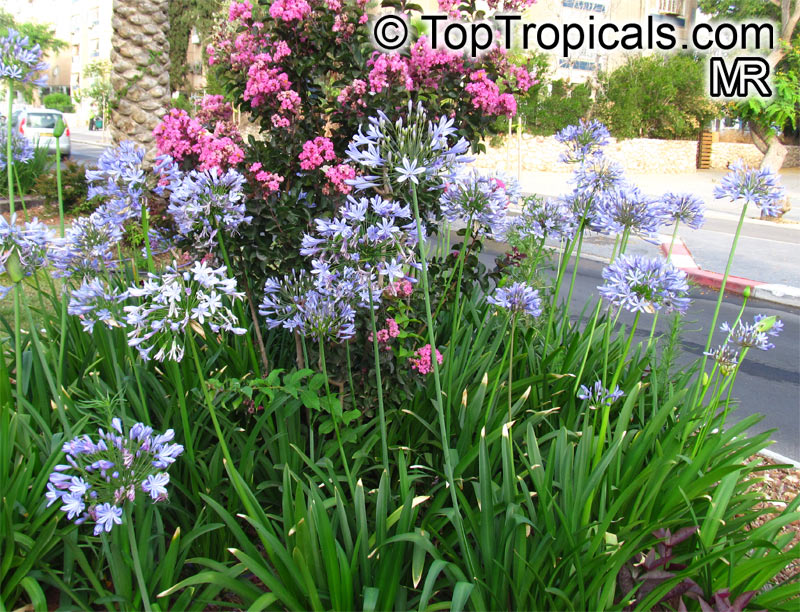
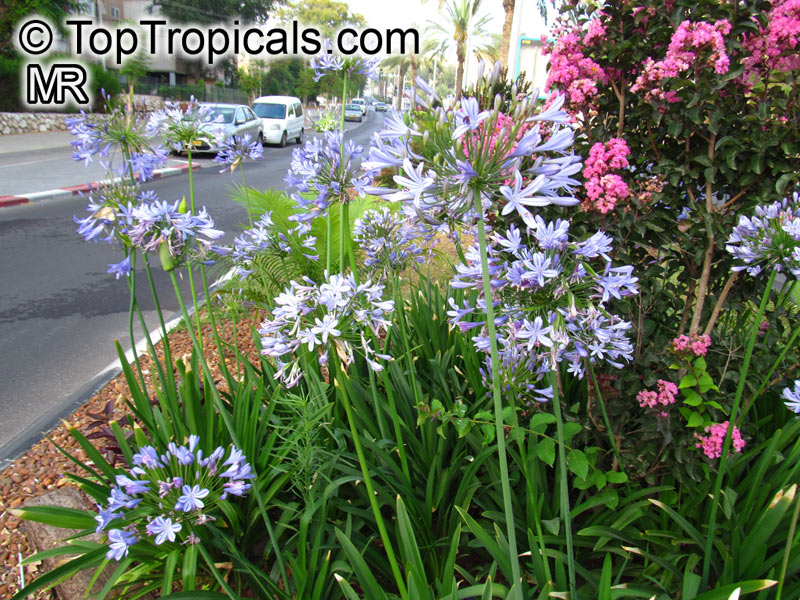
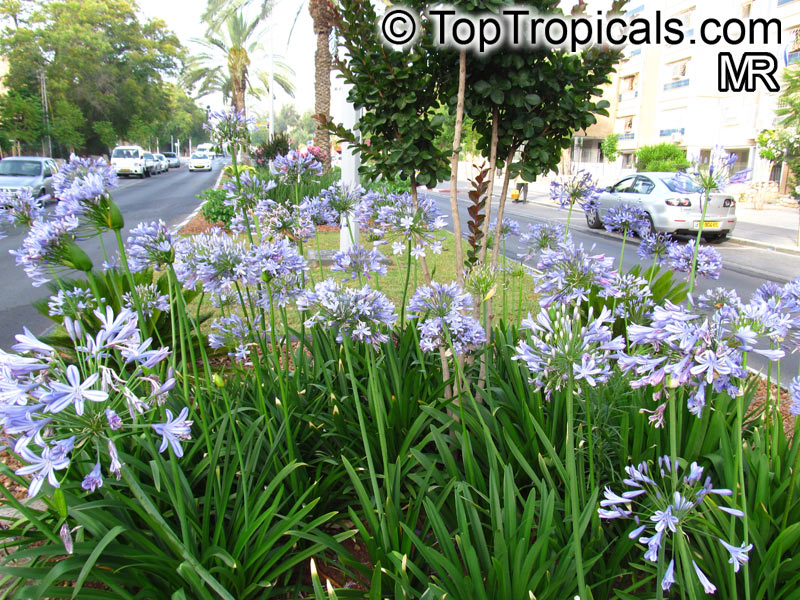
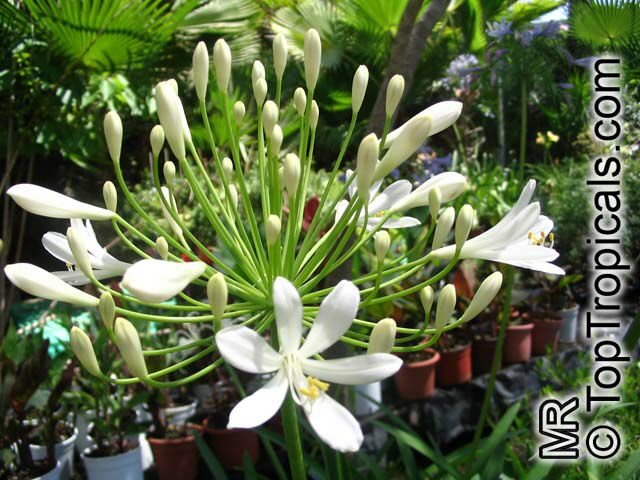
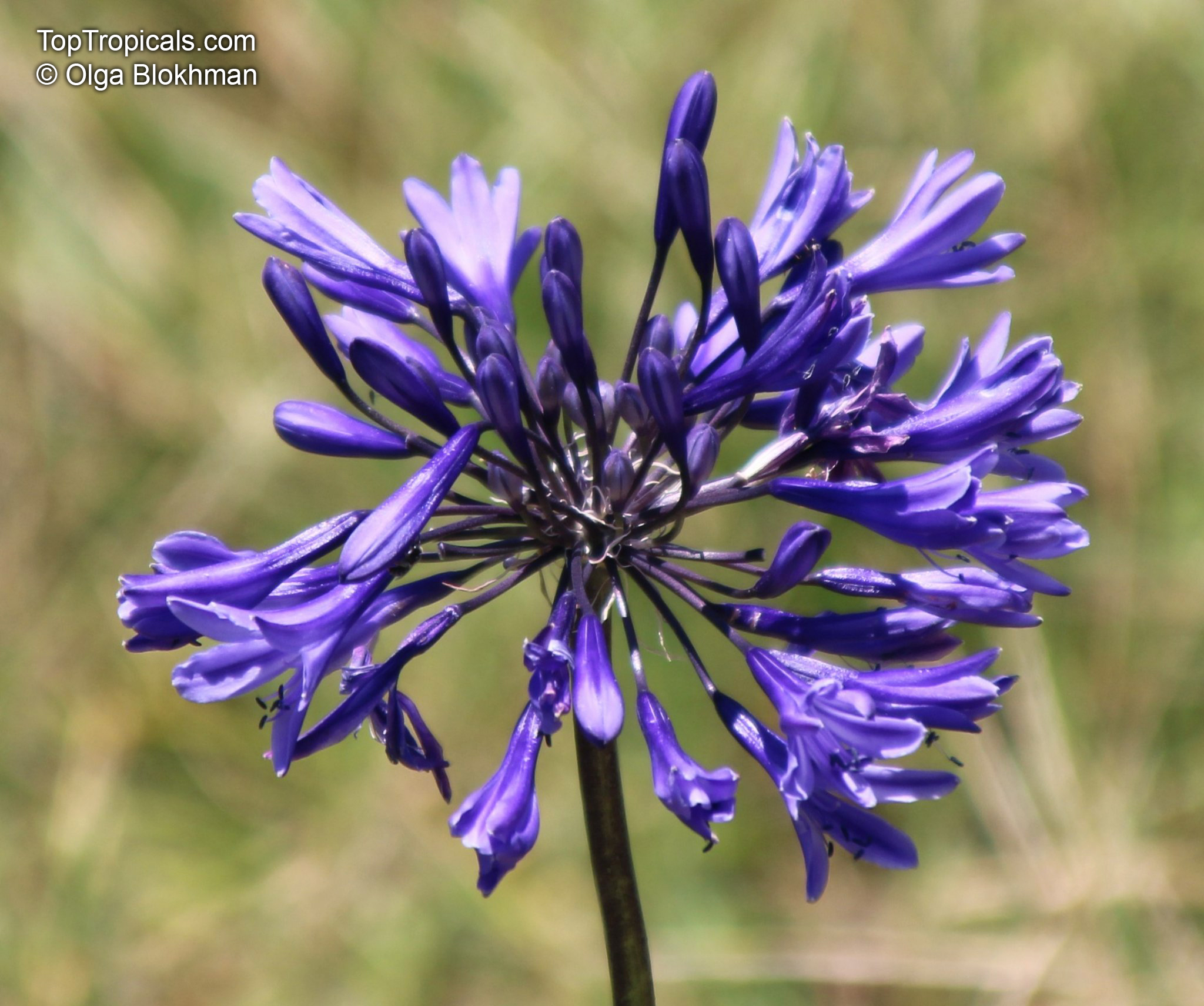
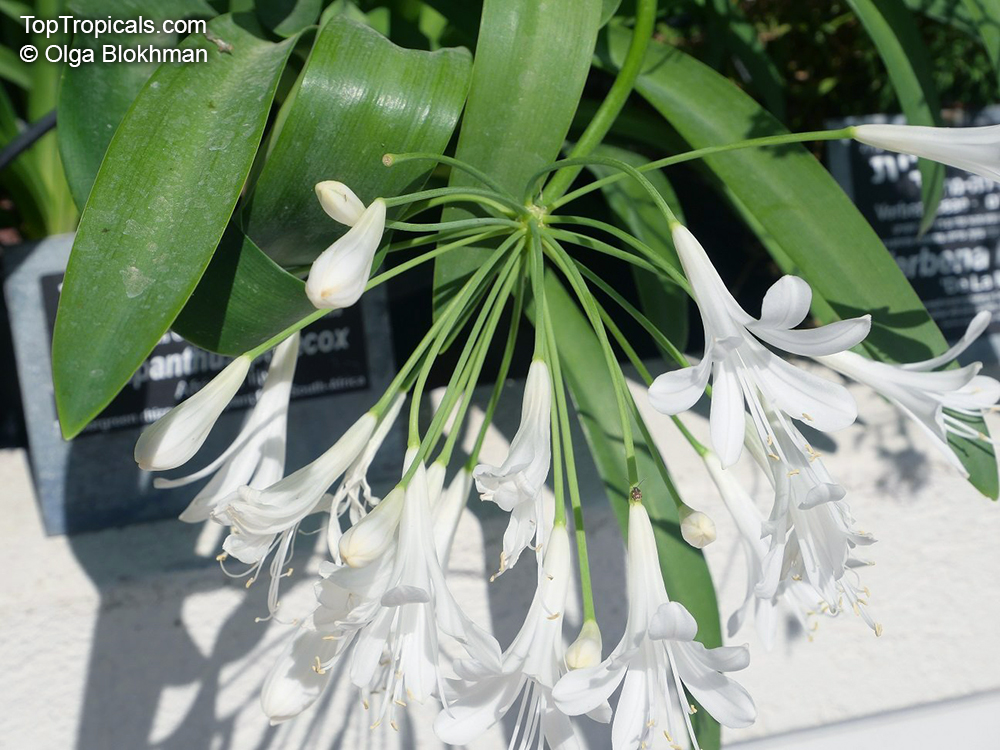
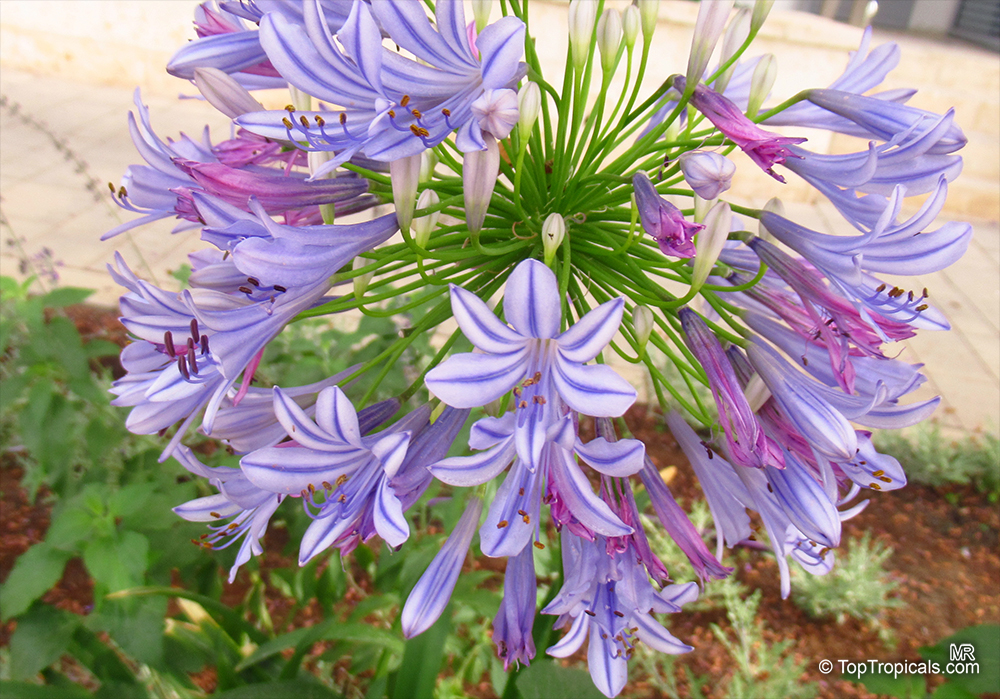
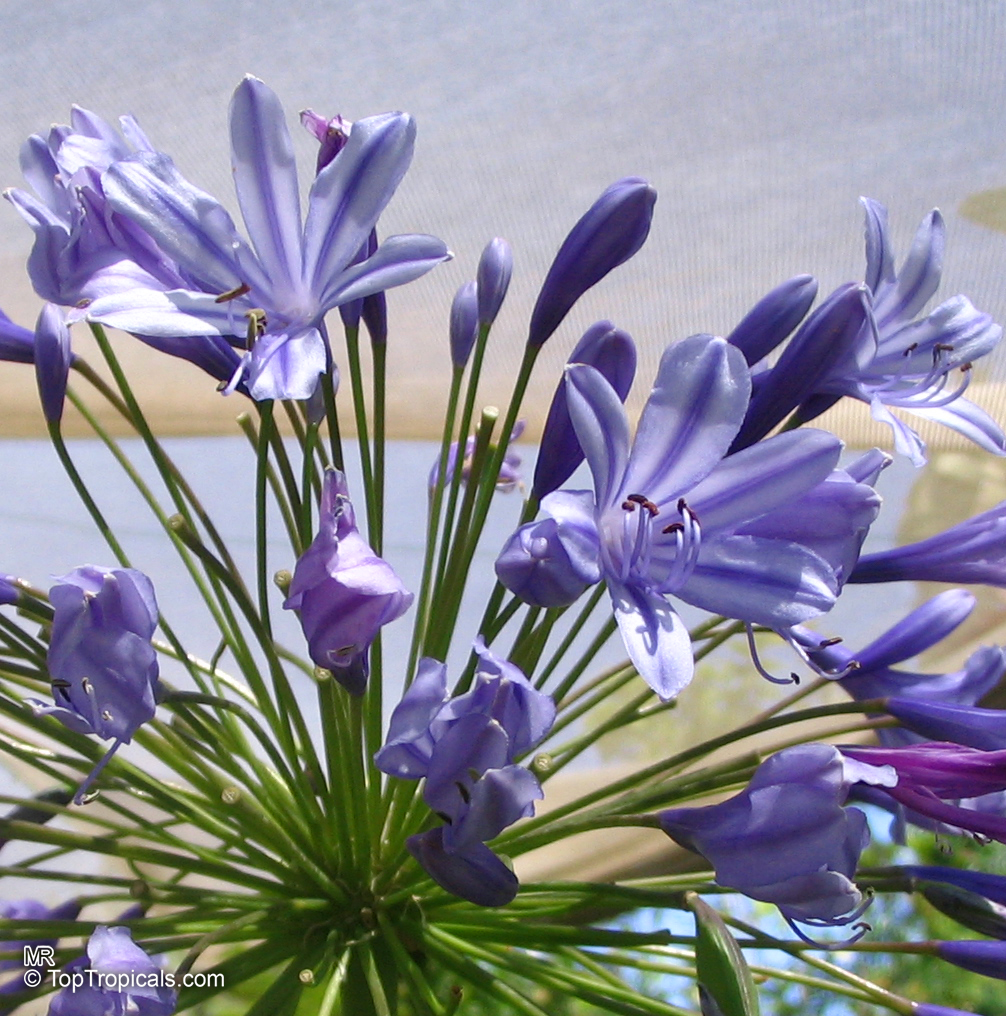
Botanical name: Agapanthus sp.
Common name: African Lily
Family: Amaryllidaceae (Formerly:Alliaceae / Liliaceae /Amaryllidaceae)
Subfamily: Agapanthoideae
Origin: South Africa







Sky blue funnel-shaped flowers occur in many-flowered cymes on long, erect stems. Agapanthus is originating from Southern Africa. Both deciduous and evergreen, some have thick, strappy leaves and others grass-like foliage. They range from fully hardy to half hardy, with the evergreen varieties generally the most tender.
Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Megaflor - Bloom Nutrition Booster
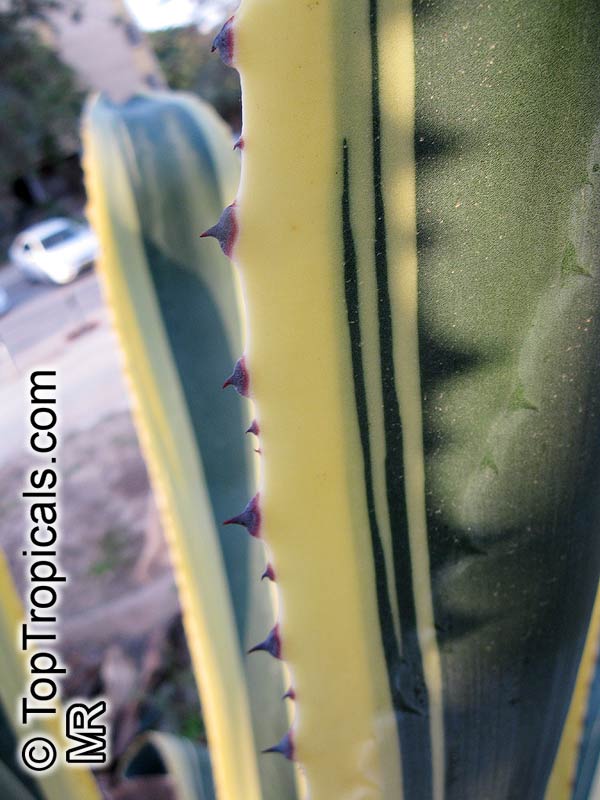
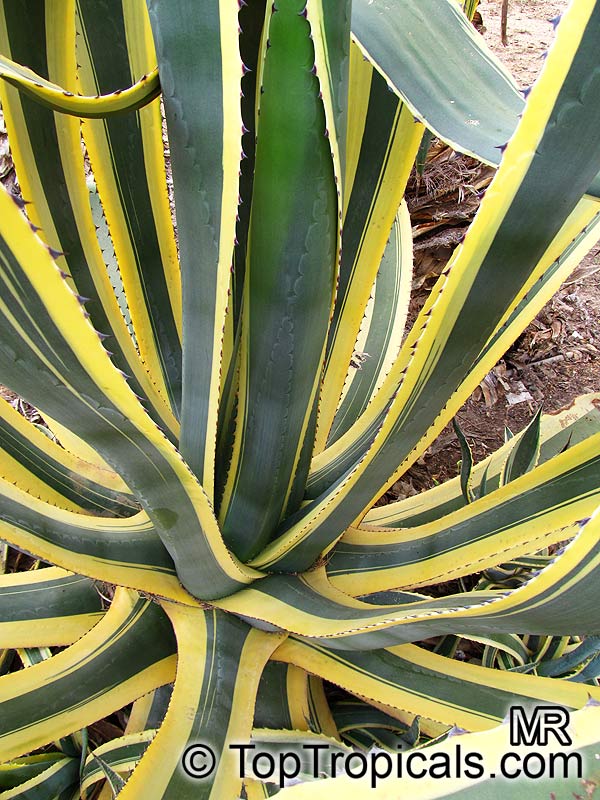
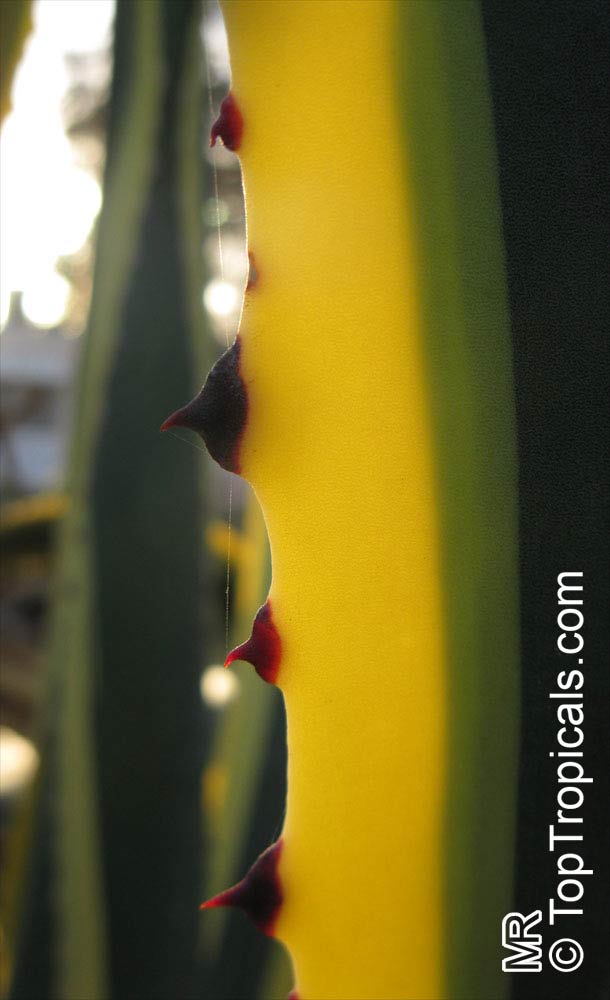
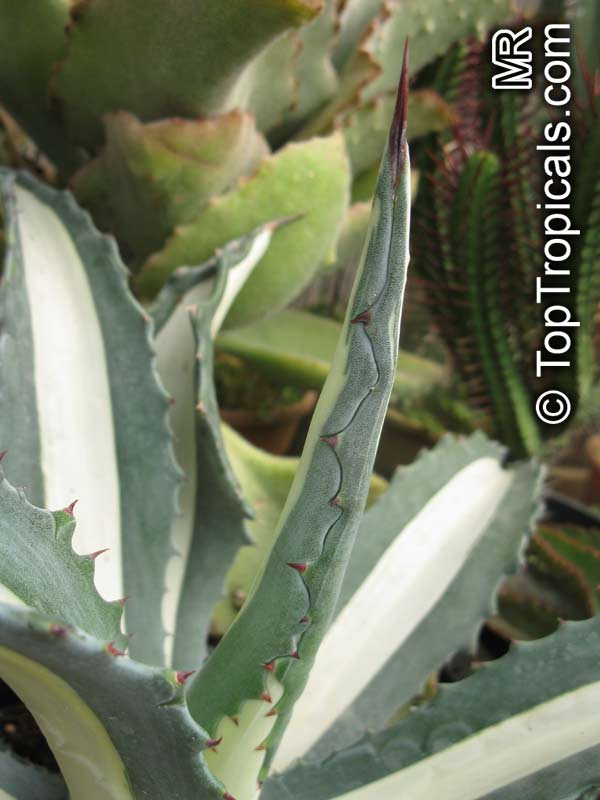
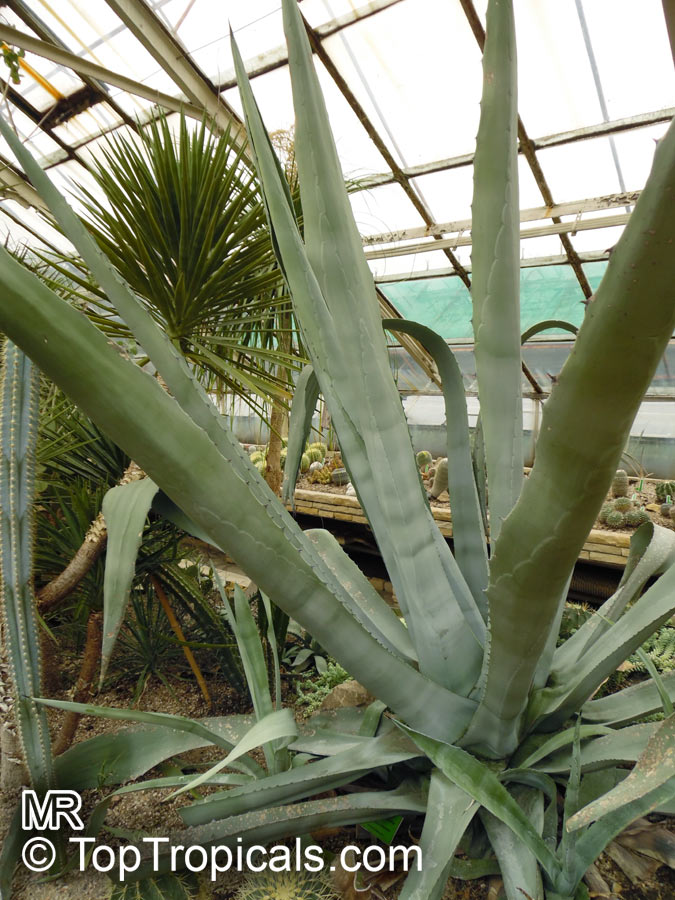
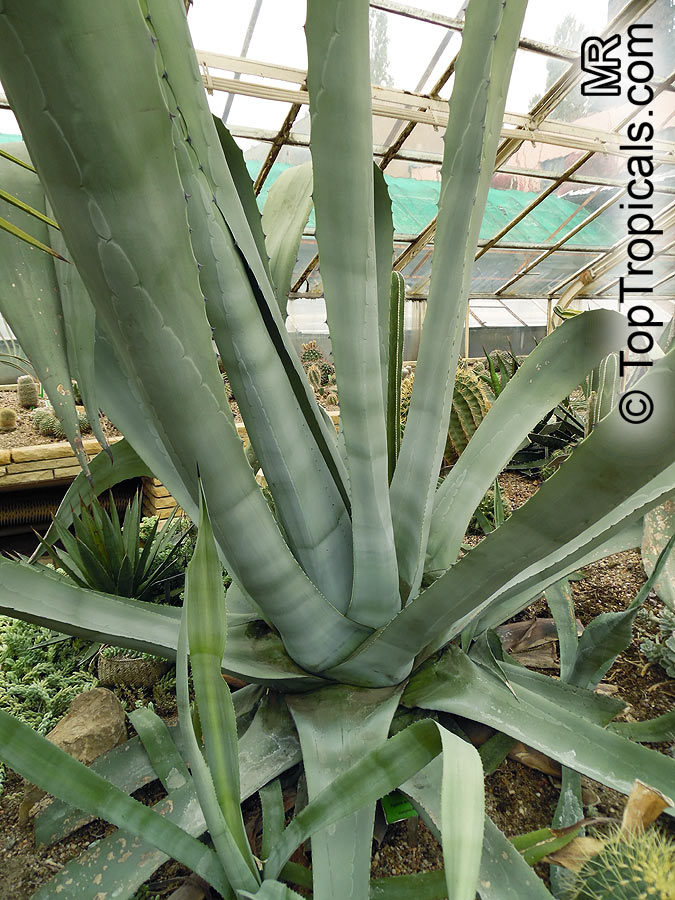
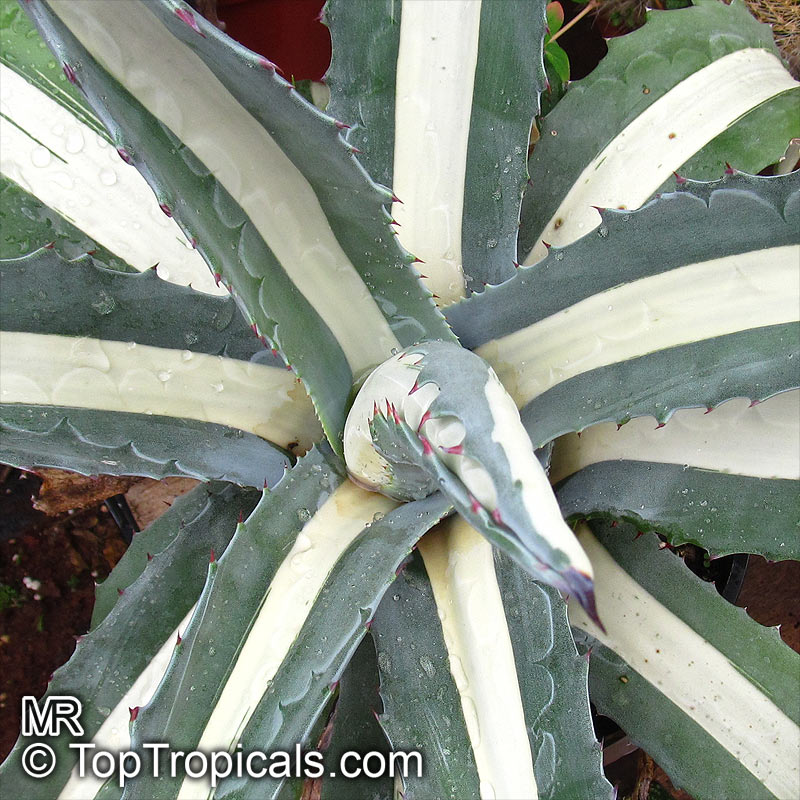
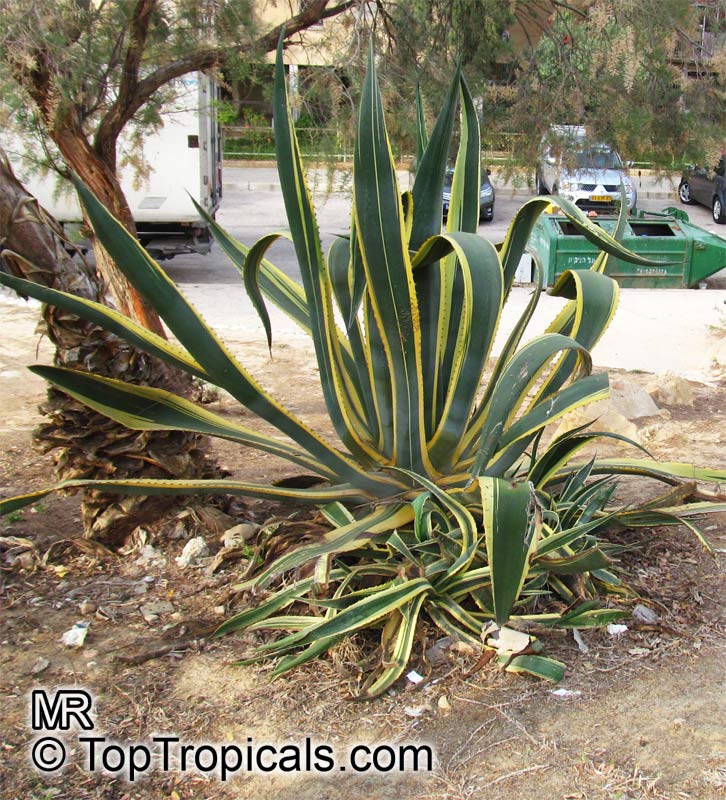
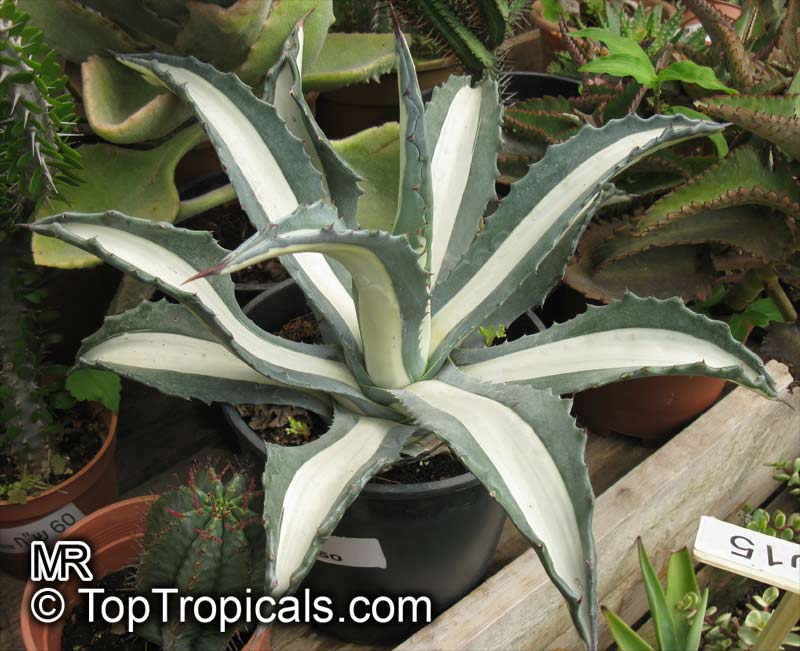
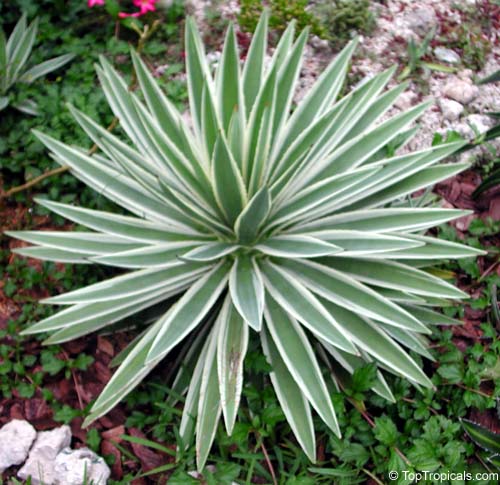
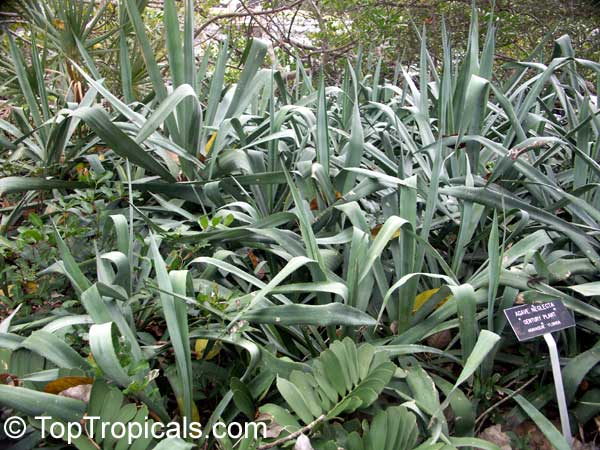
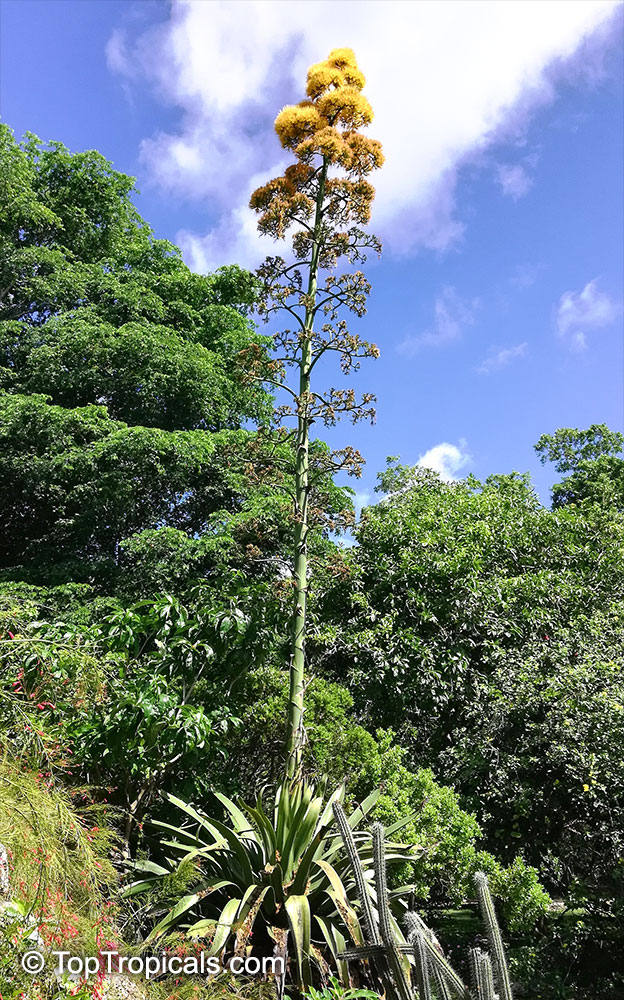
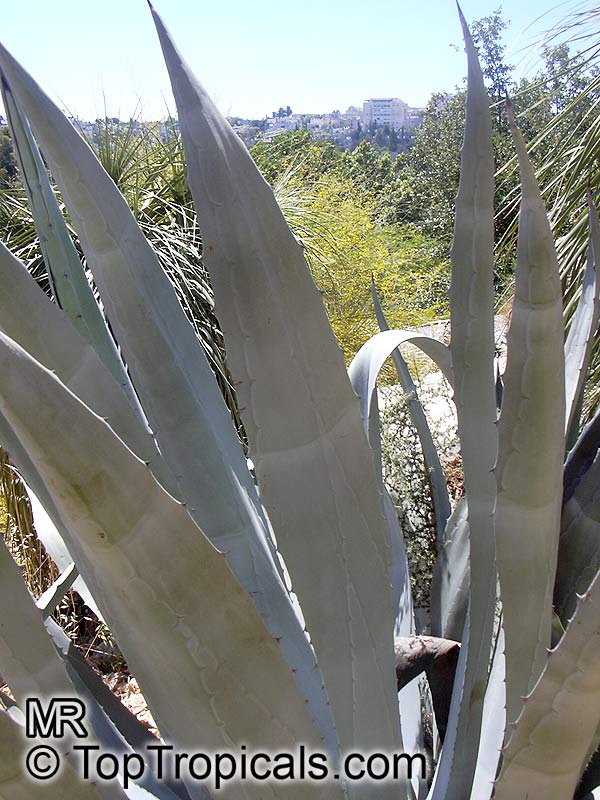
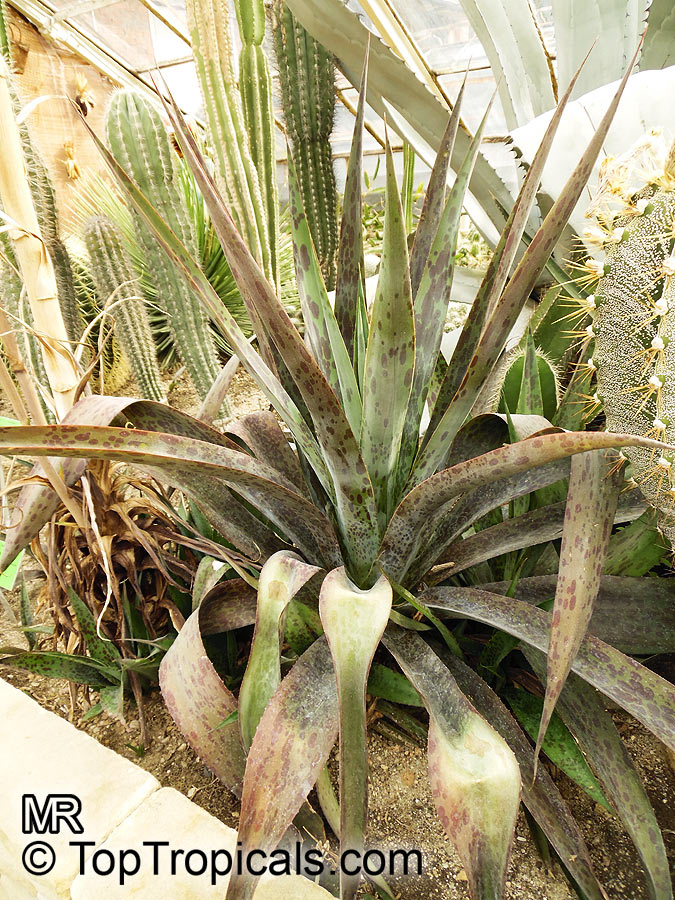
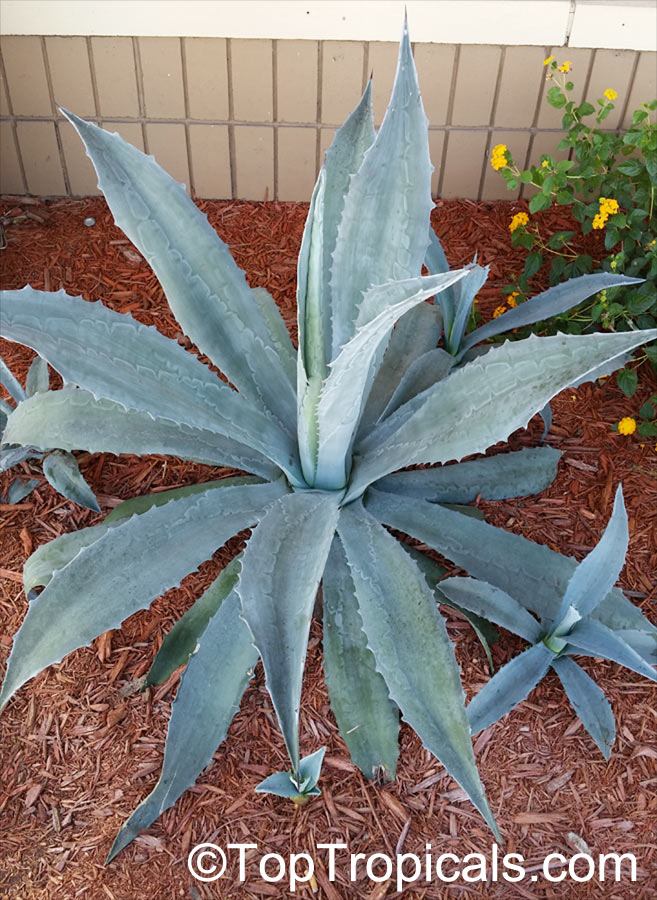
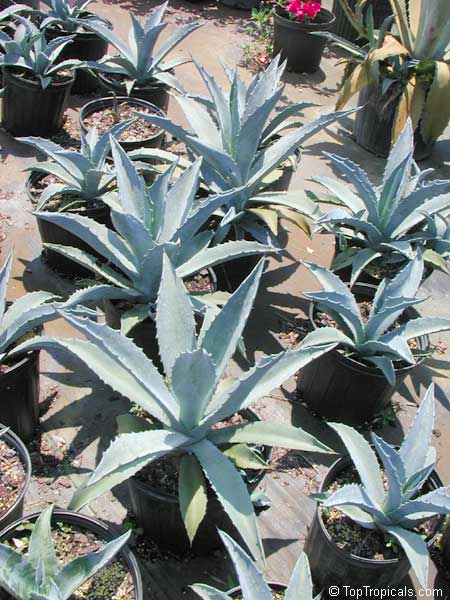
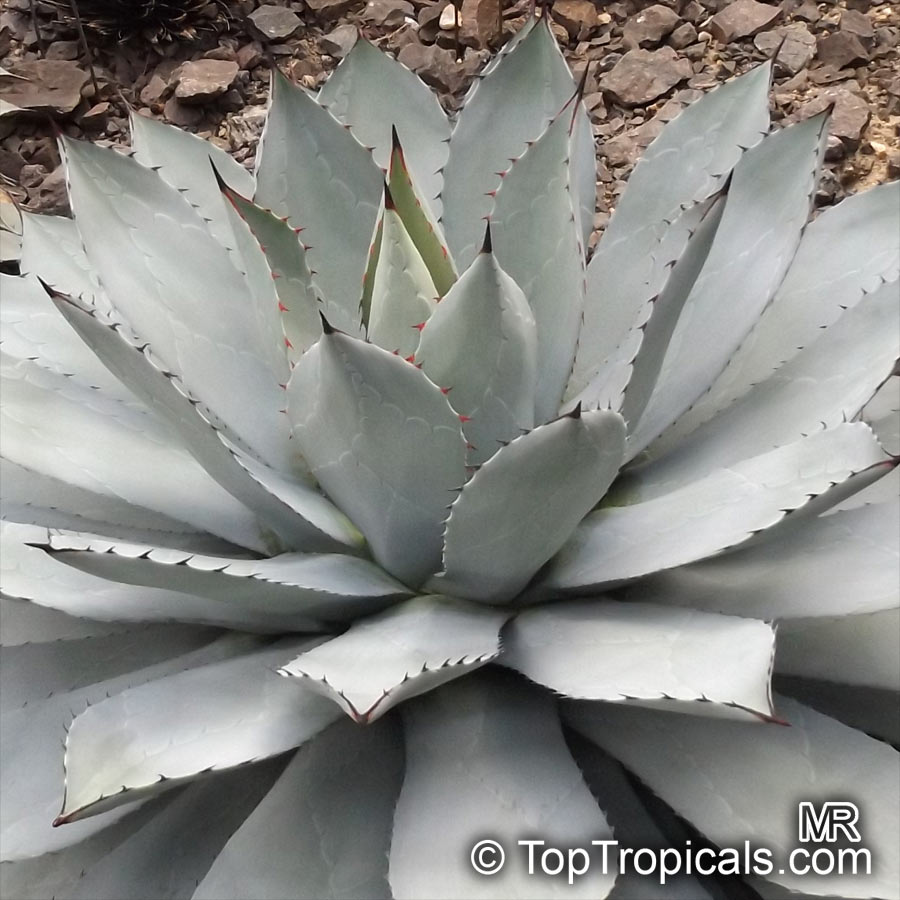
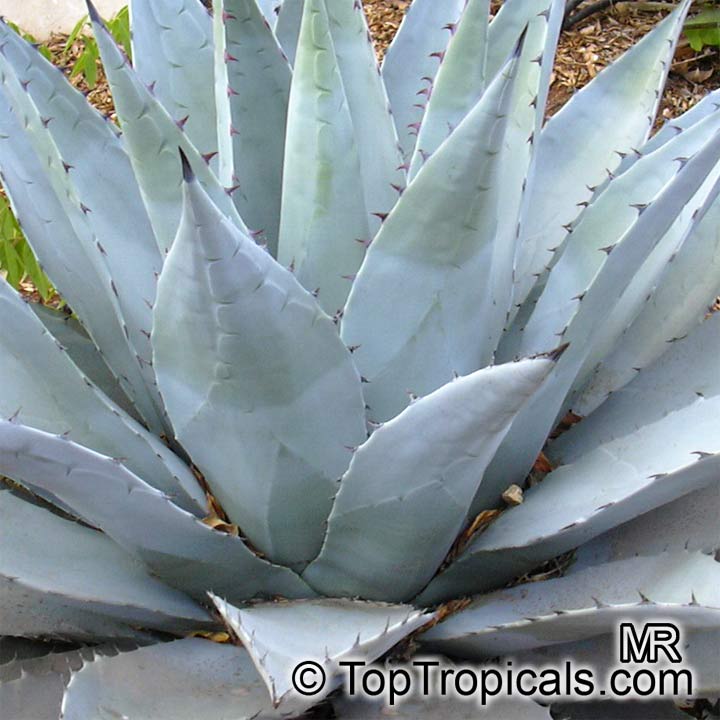
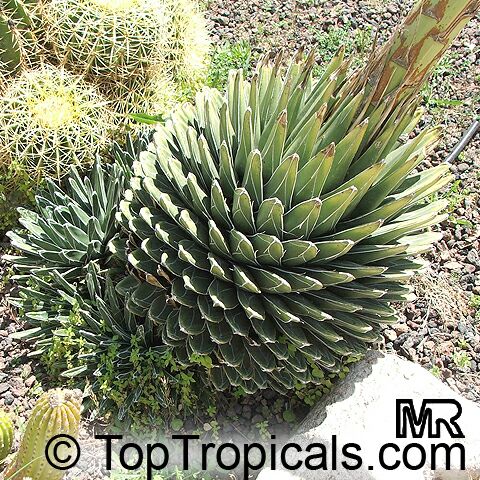
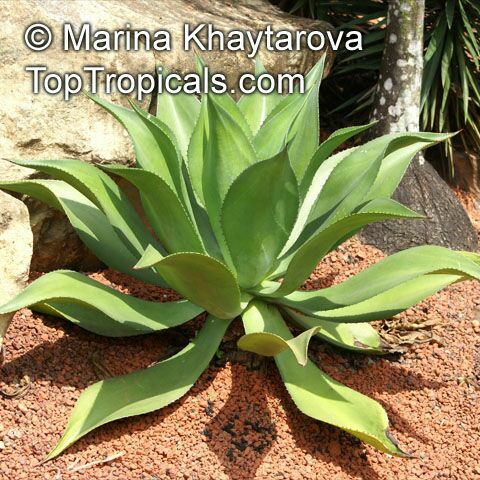
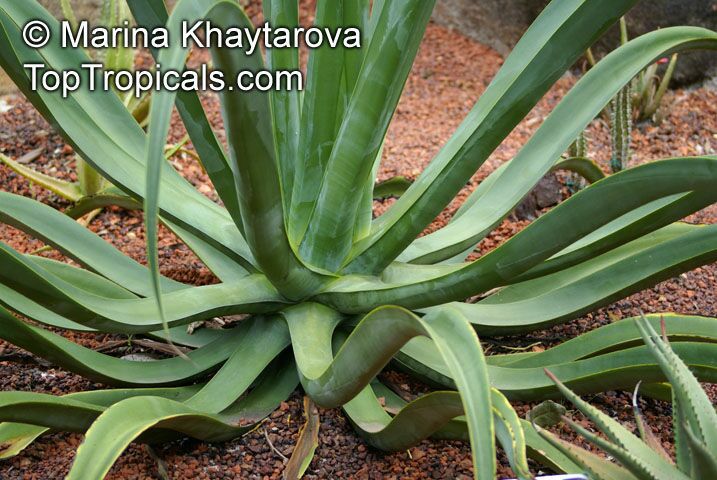
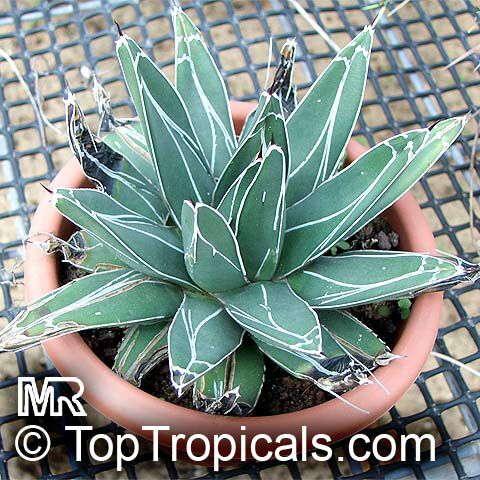
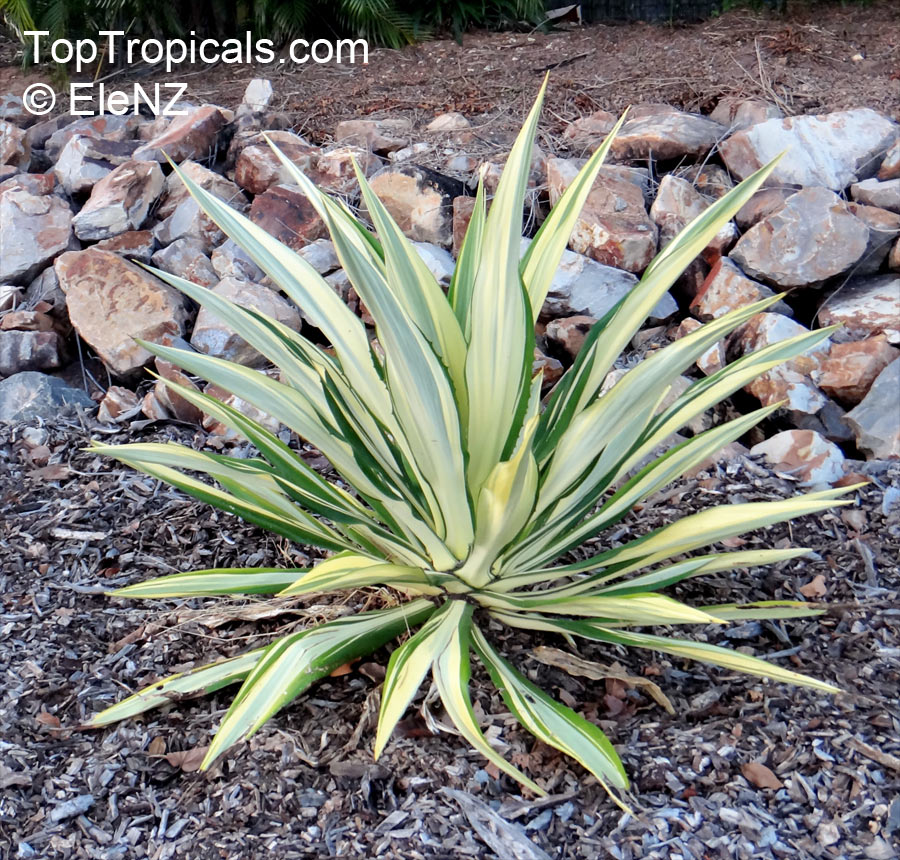
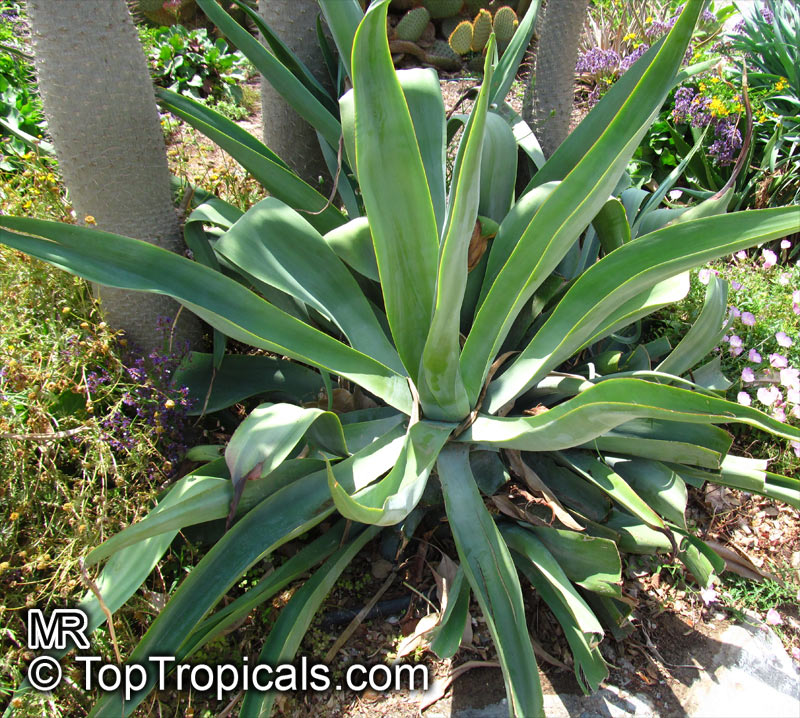
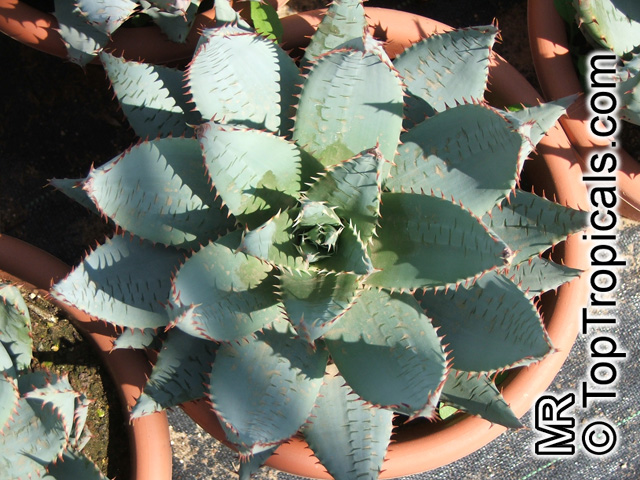
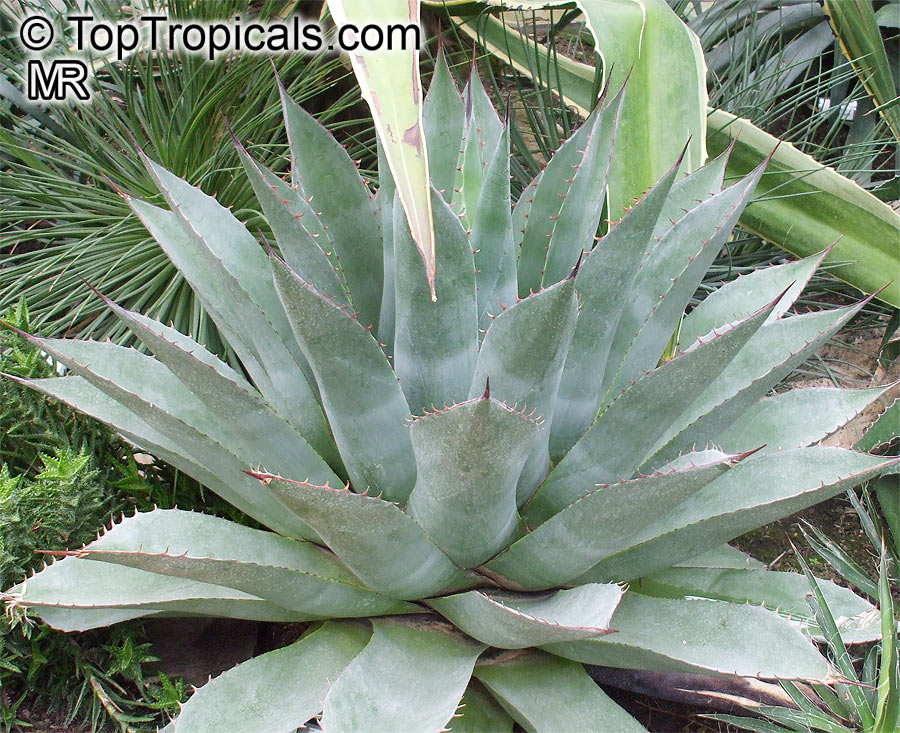
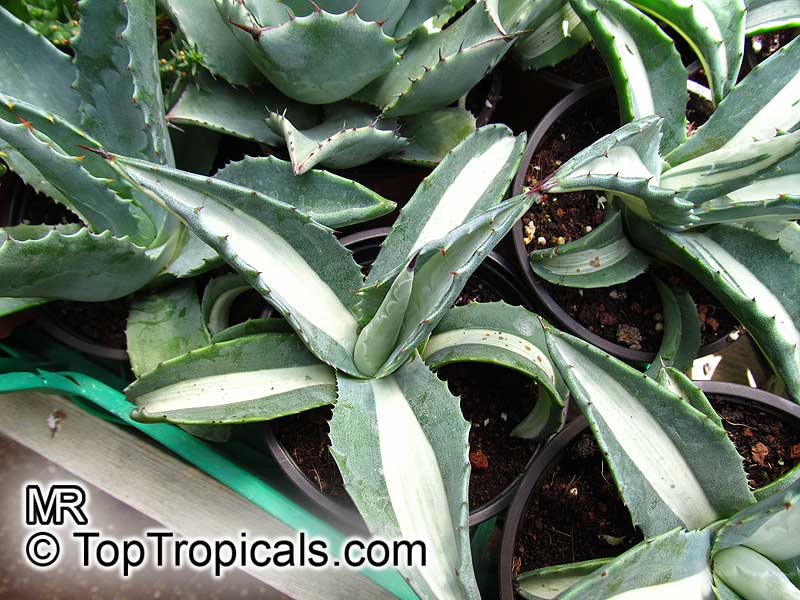
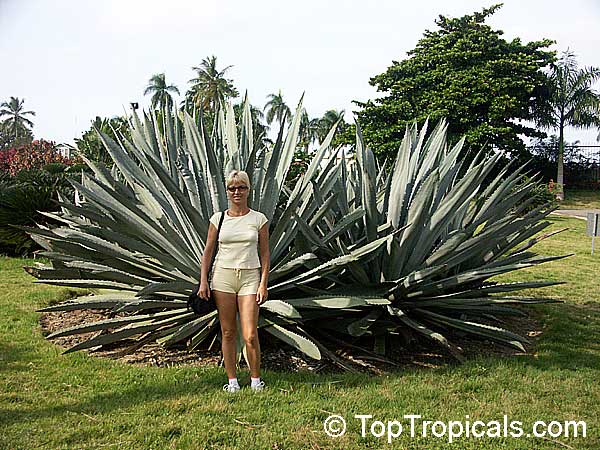
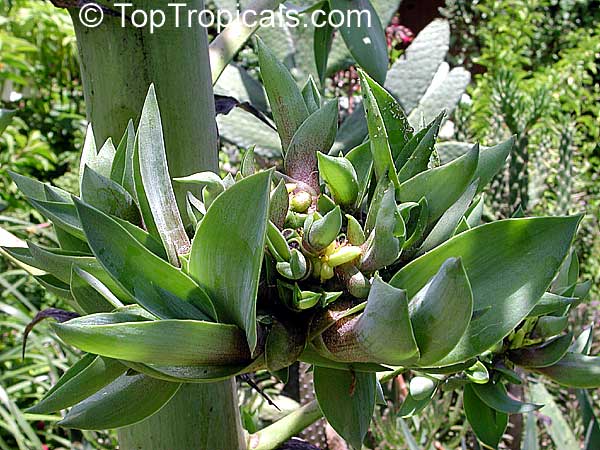
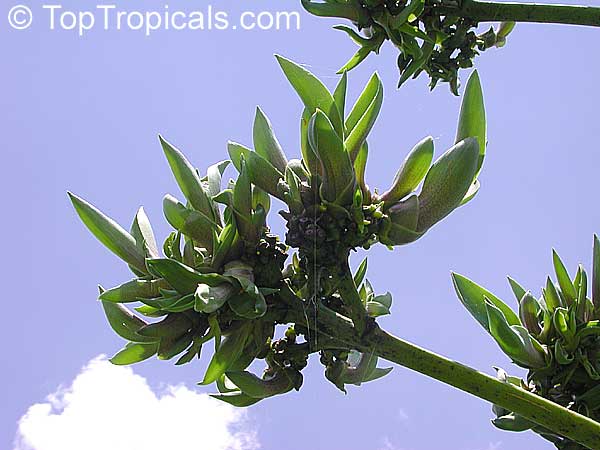
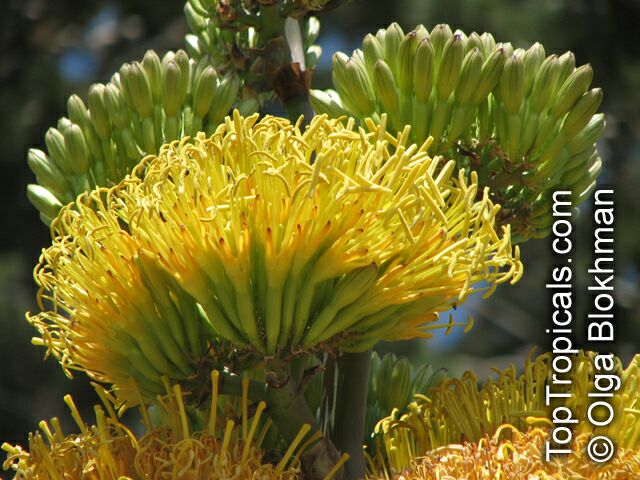
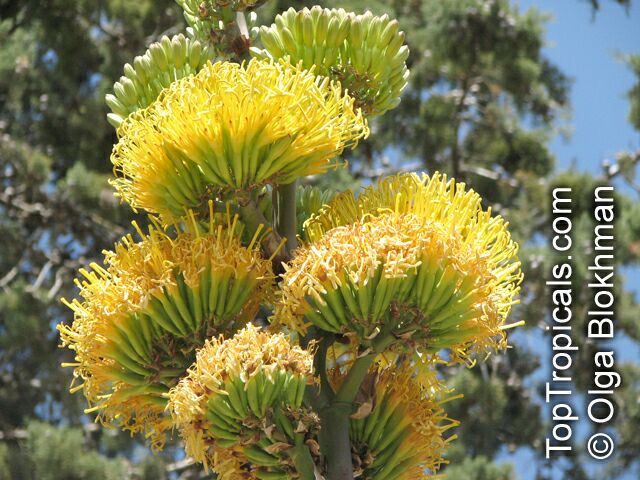
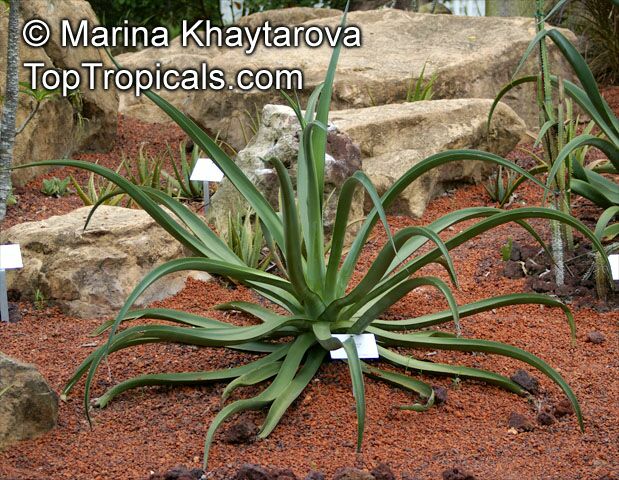
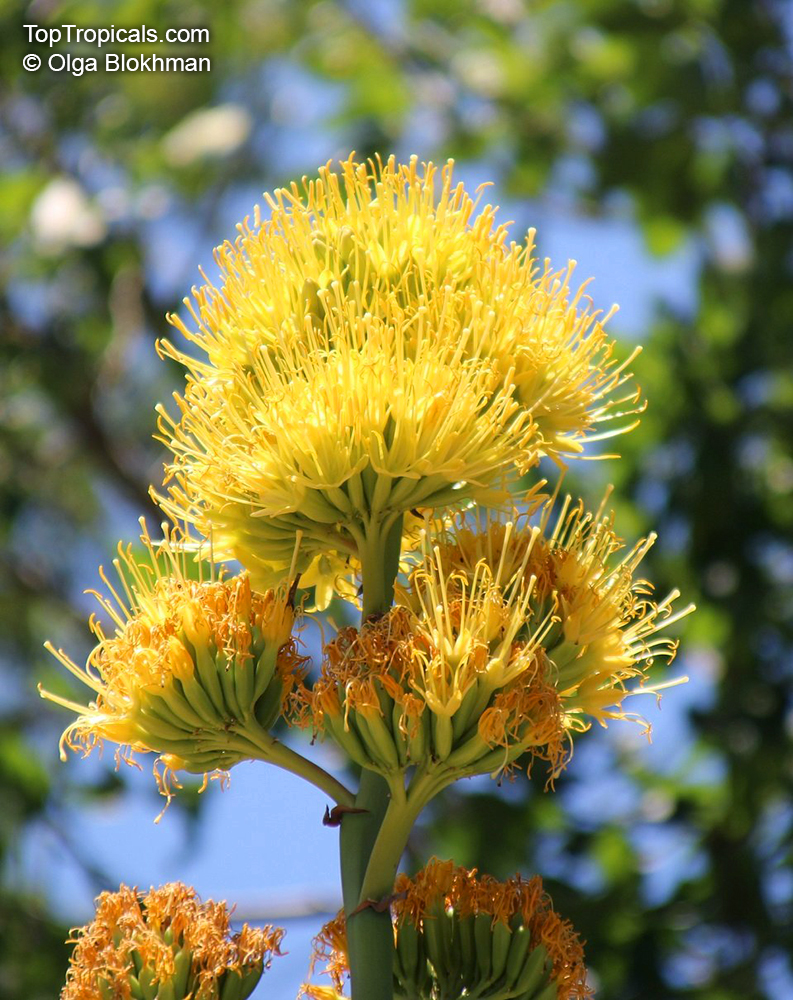
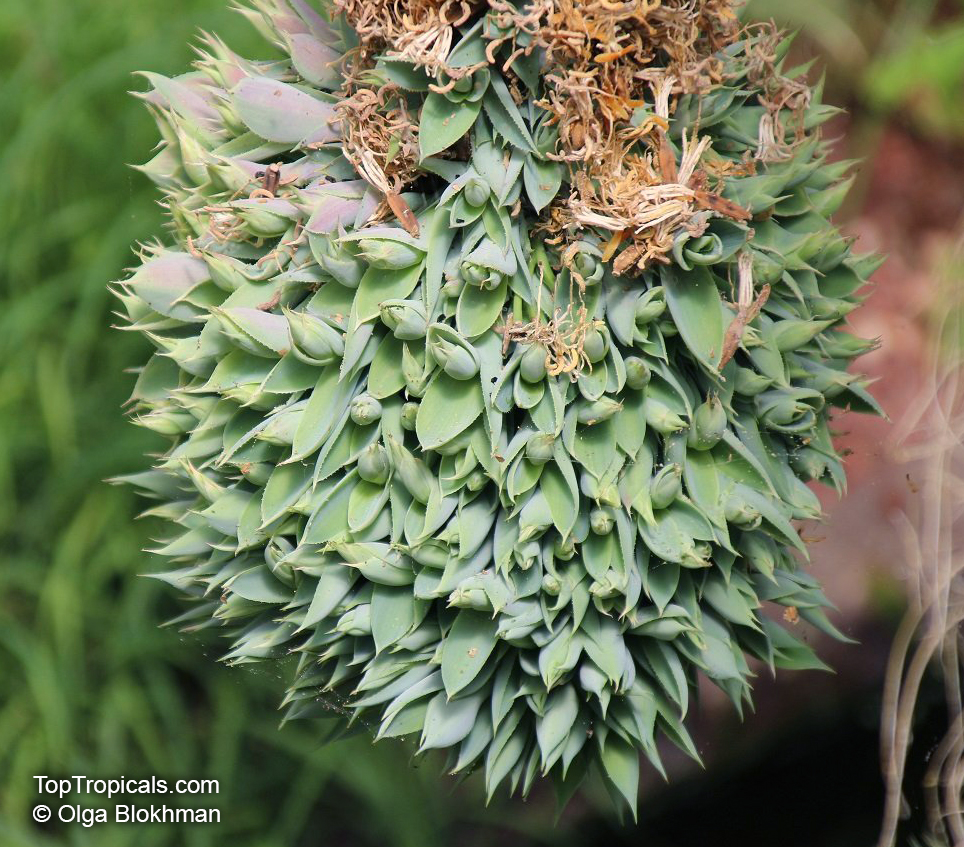
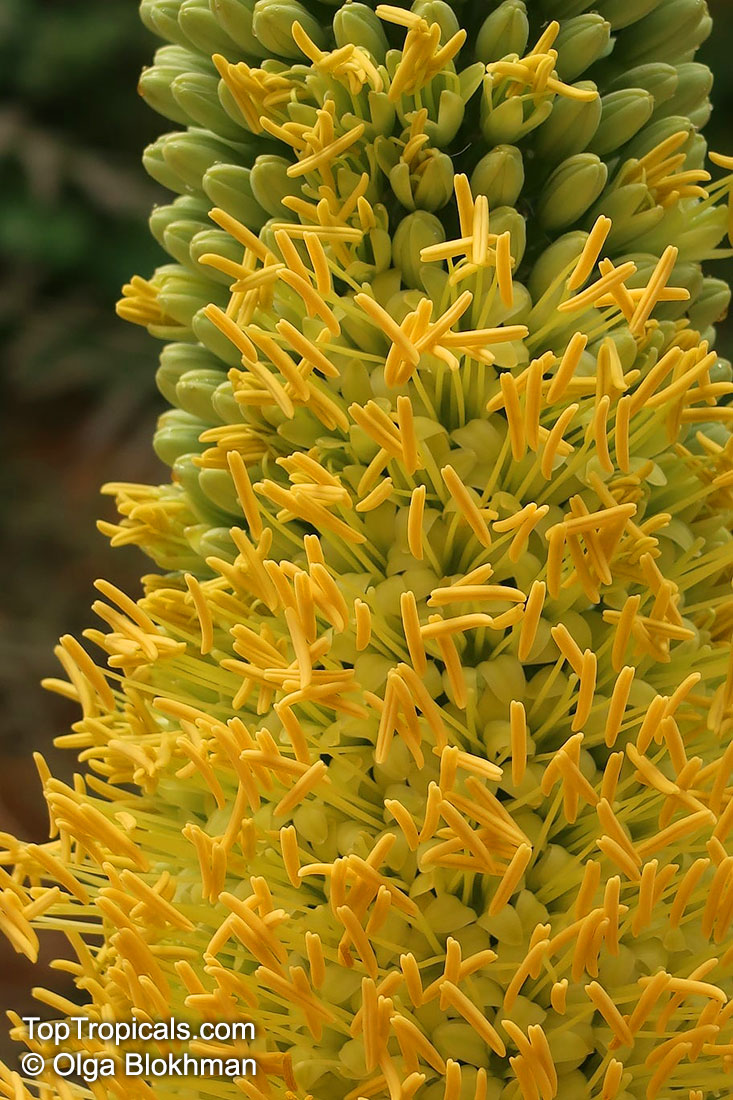
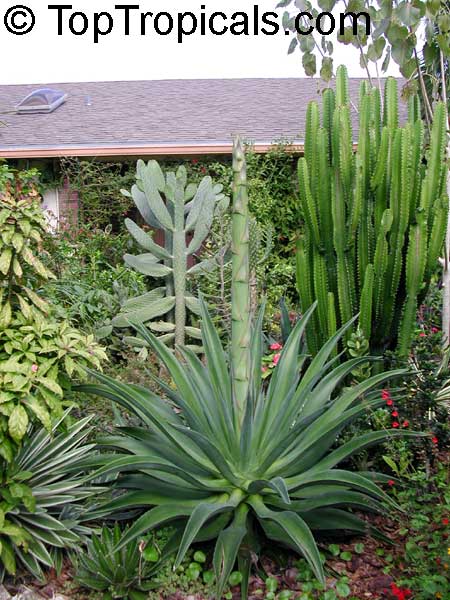
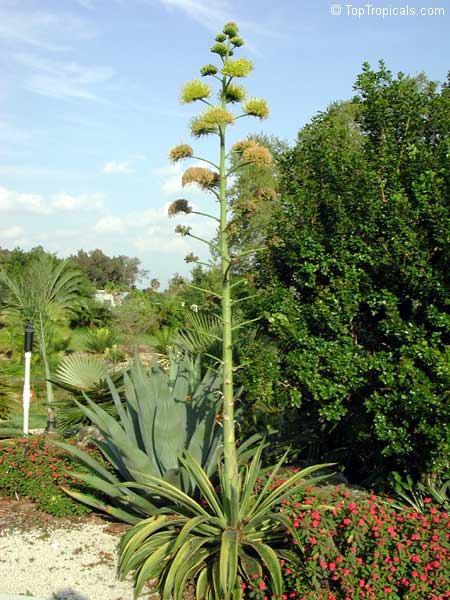
Botanical name: Agave americana
Common name: Century plant
Family: Asparagaceae (Formerly:Agavaceae / Amaryllidaceae)
Subfamily: Agavoideae
Origin: Mexican highlands





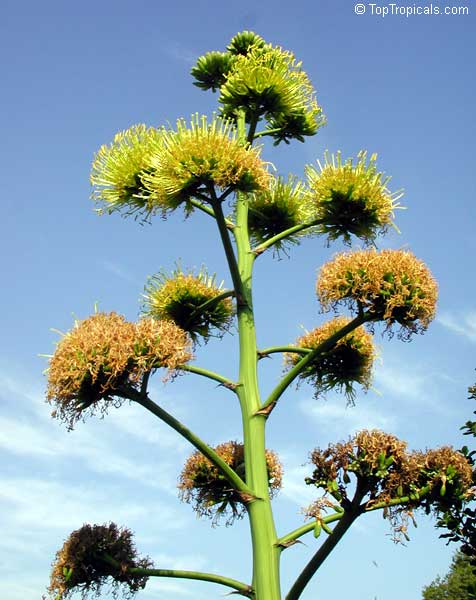
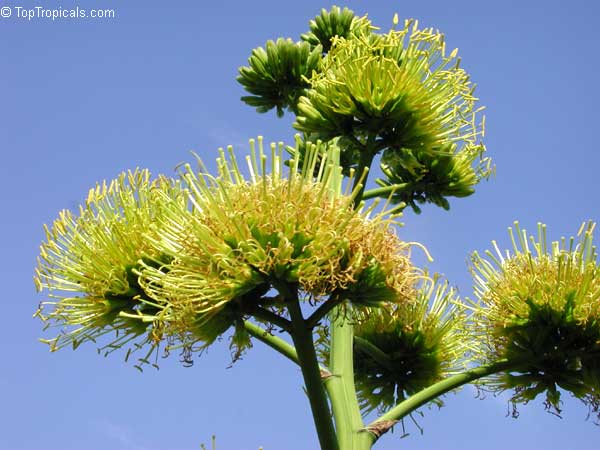
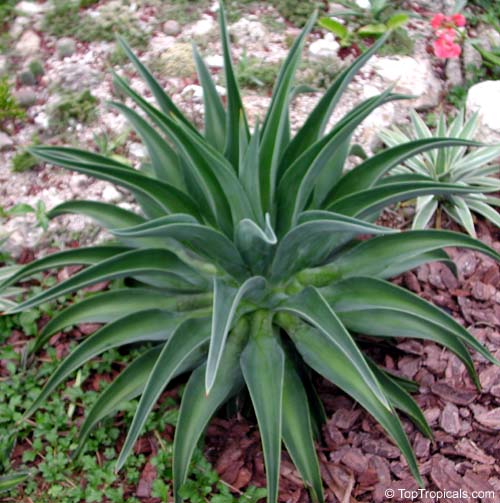
Agave americana, commonly known as the century plant, is a striking succulent renowned for its dramatic, spiky leaves and towering flower stalk that can reach heights of up to 30 feet. Native to Mexico, this hardy plant is celebrated for its adaptability to arid environments and its ability to produce a spectacular bloom just once in its lifetime, typically after several decades. Its versatility extends beyond ornamental use, as it has been traditionally utilized for its fibers, sweet sap, and medicinal properties.
The genus of more than 200 species of rosette-forming, mostly monocarpic, or sometimes perennial succulents from the desert and mountainous regions of the Americas. The most popular Agave is the Century Plant, so-called because of the mistaken belief that it flowers only once every 100 years. There are two colorful varietis - Agava americana marginata (green leaves edged with yellow) and Agava americana mediopicta (cream leaves edged with green). These plants produce leaves 3 or 4 feet long, and their size makes them unsuitable for an ordinary room. In winter watering this plant can be done once every 1-2 months, there is no need to mist the leaves.
Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Robusta - Rapid Growth Booster
Local pickup only. This item is not available for shipping. Local delivery may be available in Ft. Myers or Sebring, Florida. Contact us for an estimate. Non-pickup orders are subject to restocking fees.
Last one
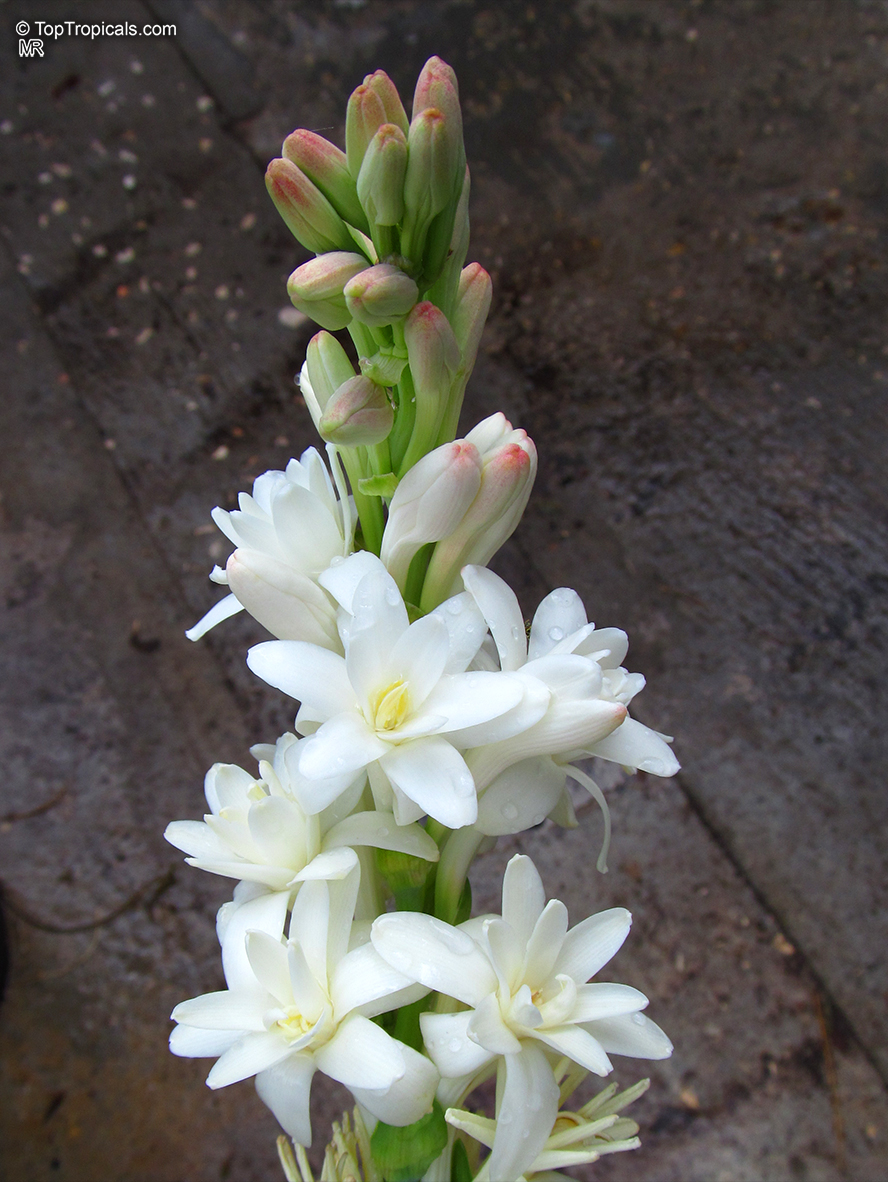
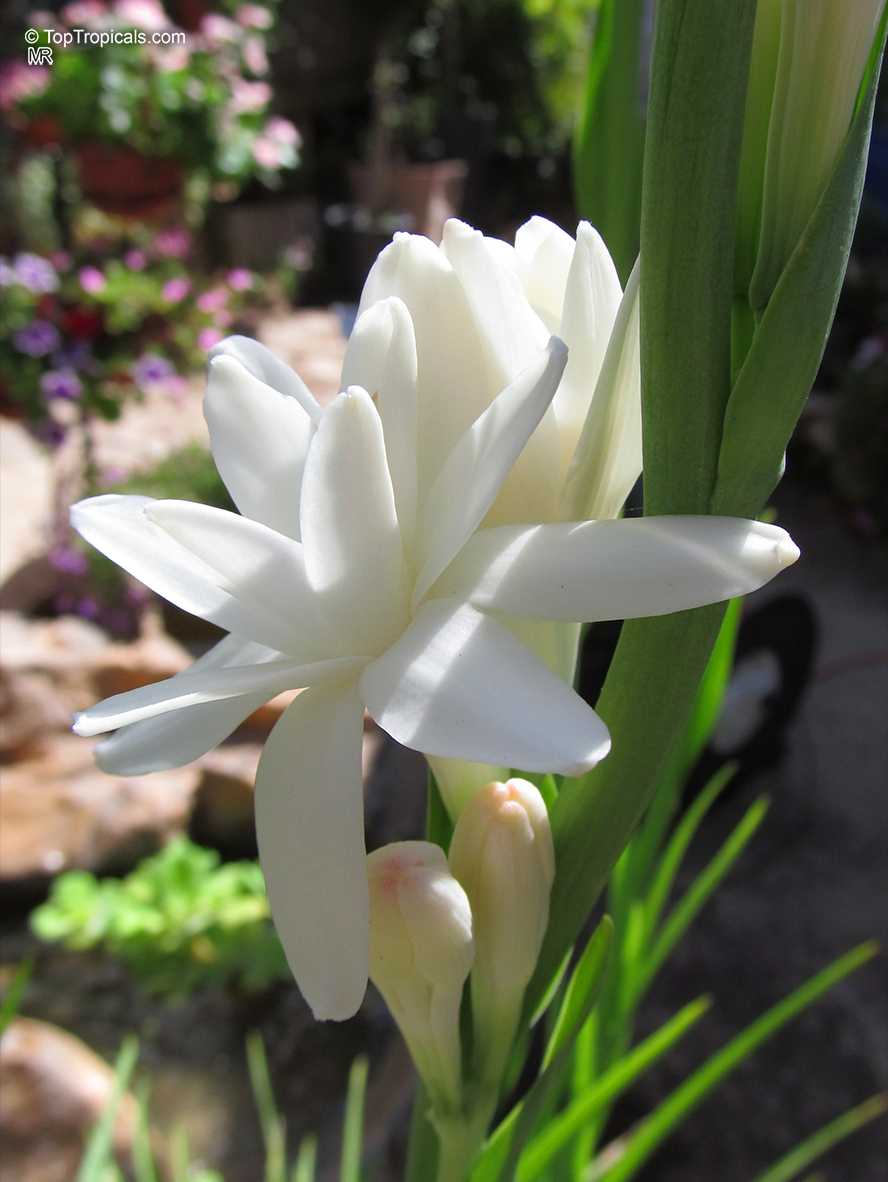
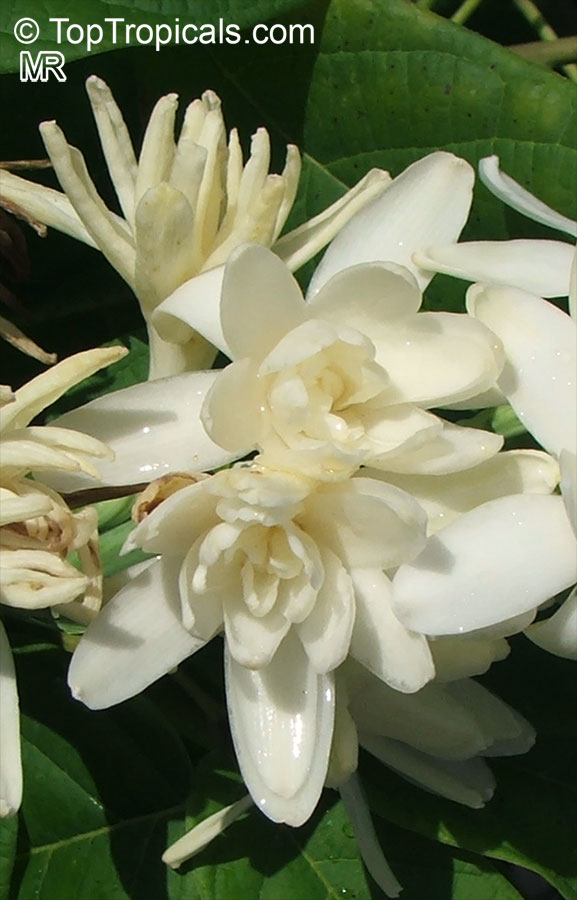
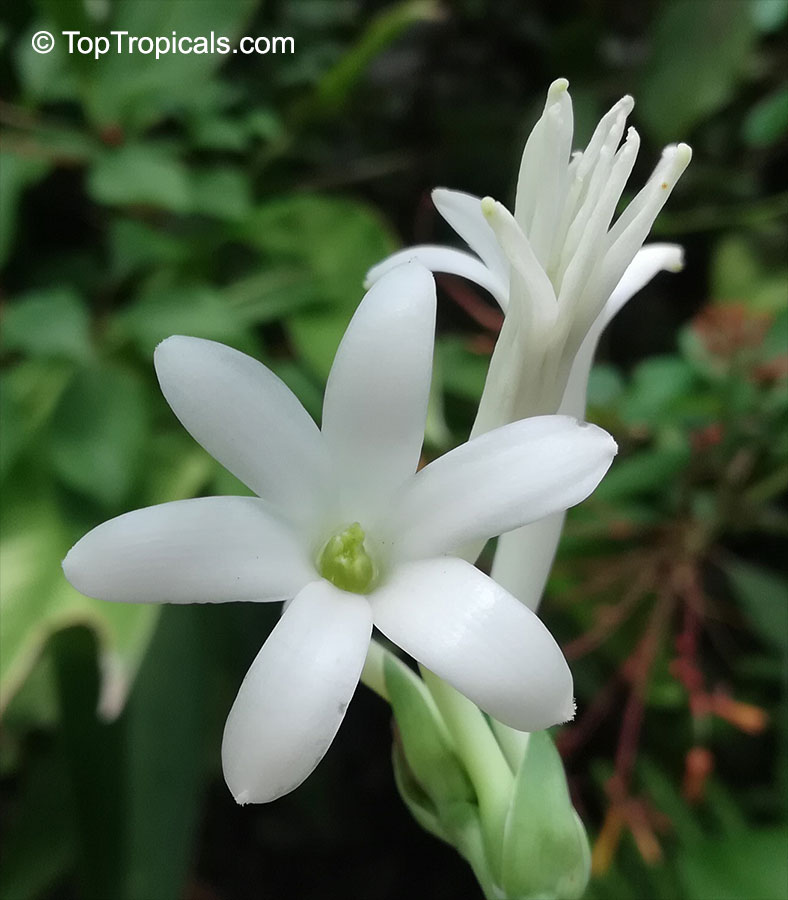
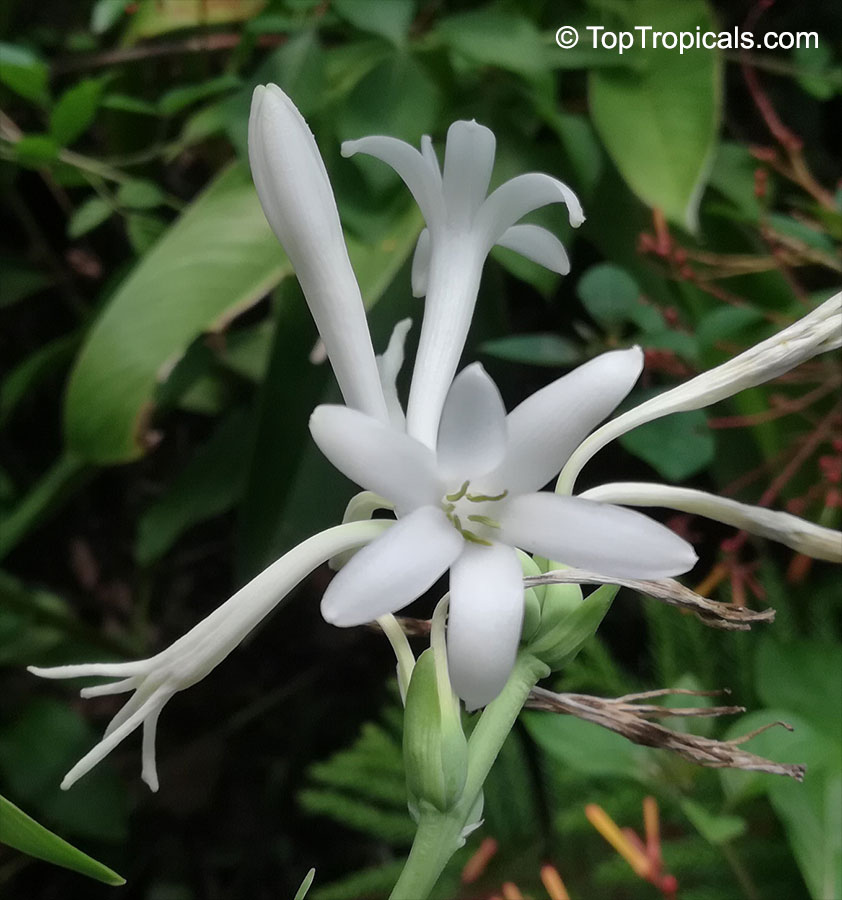
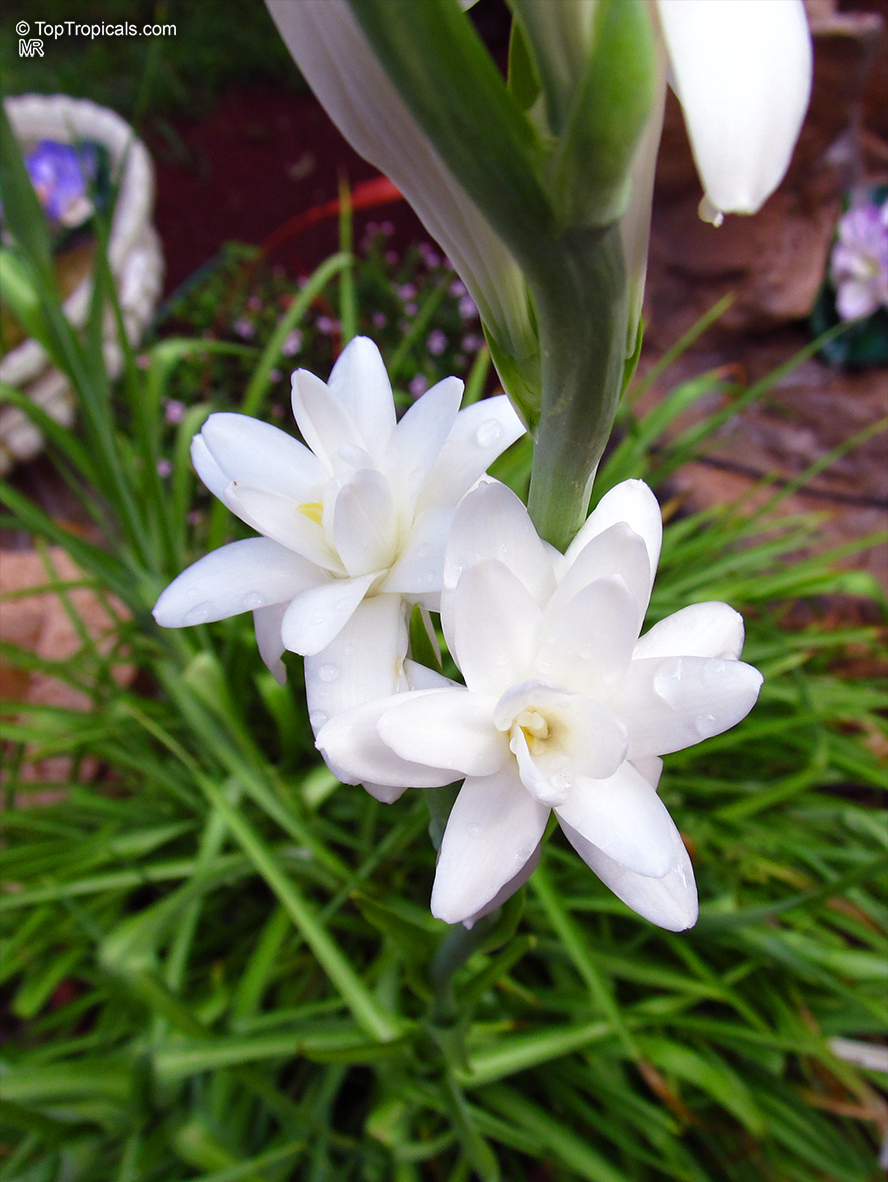
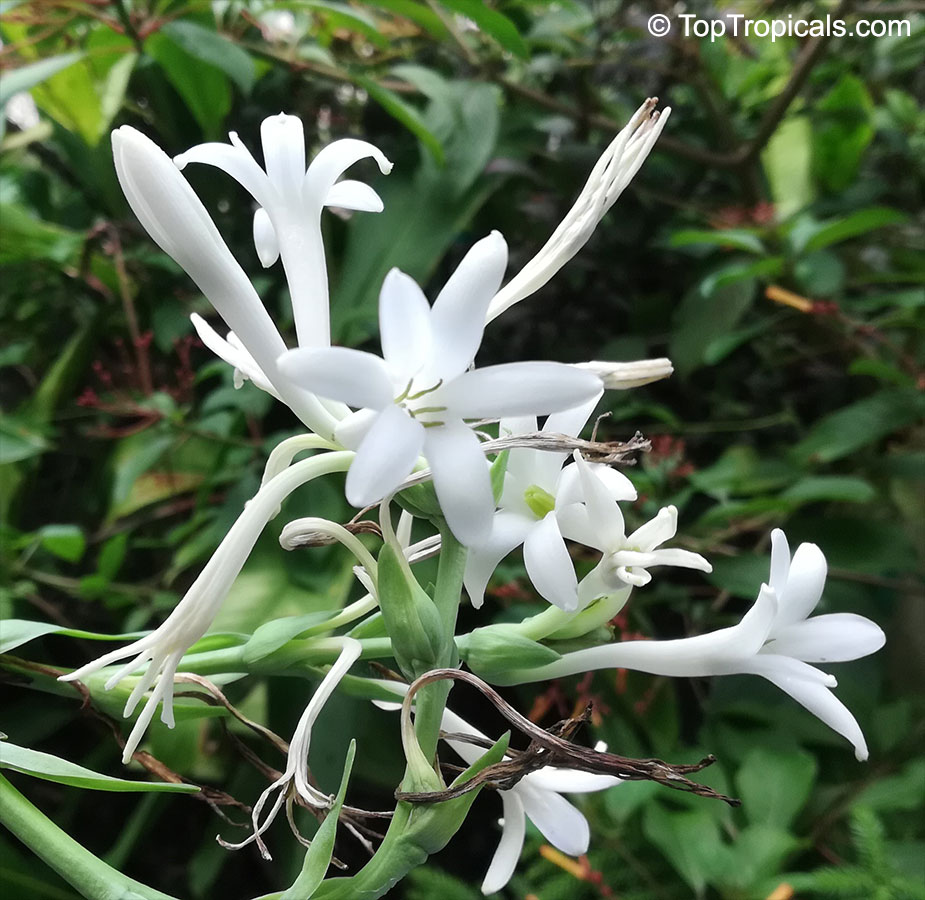
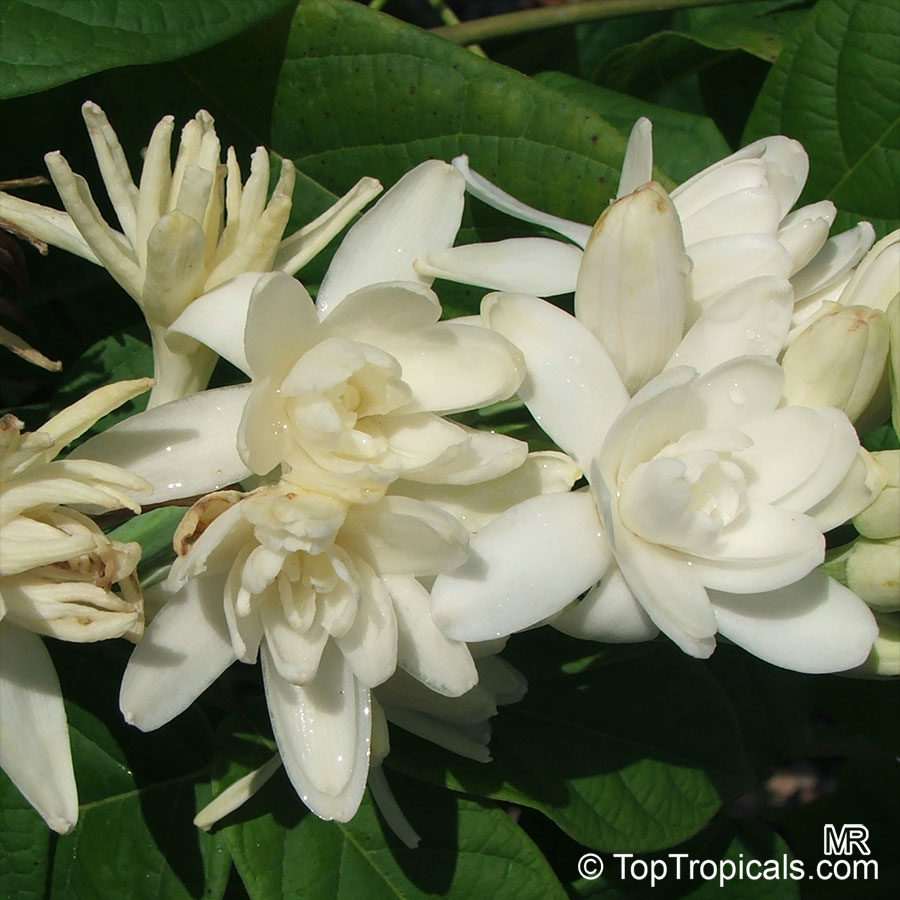
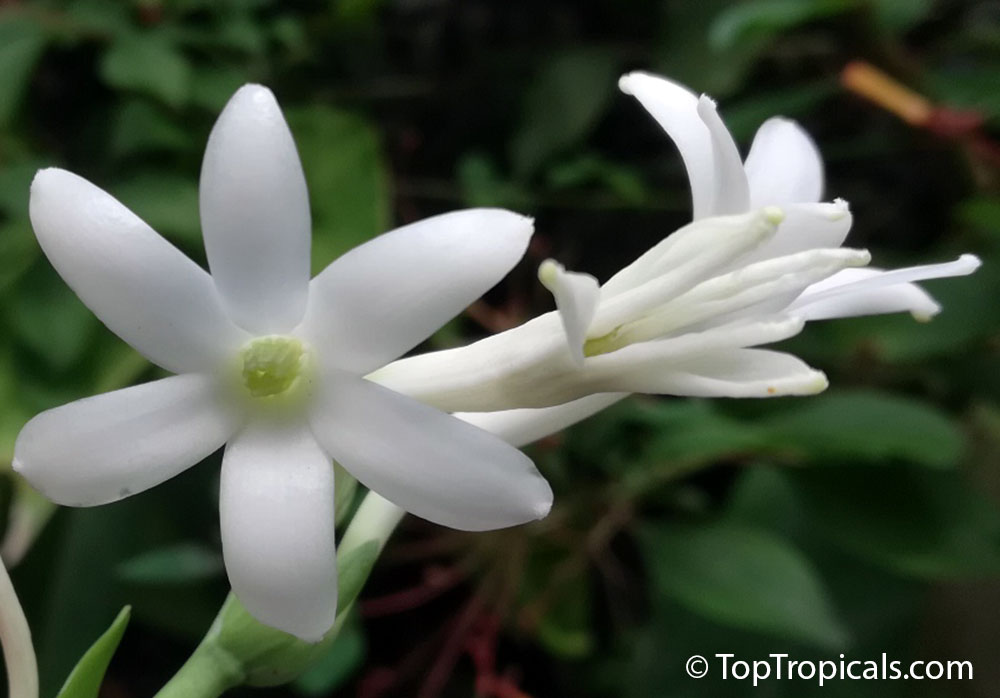
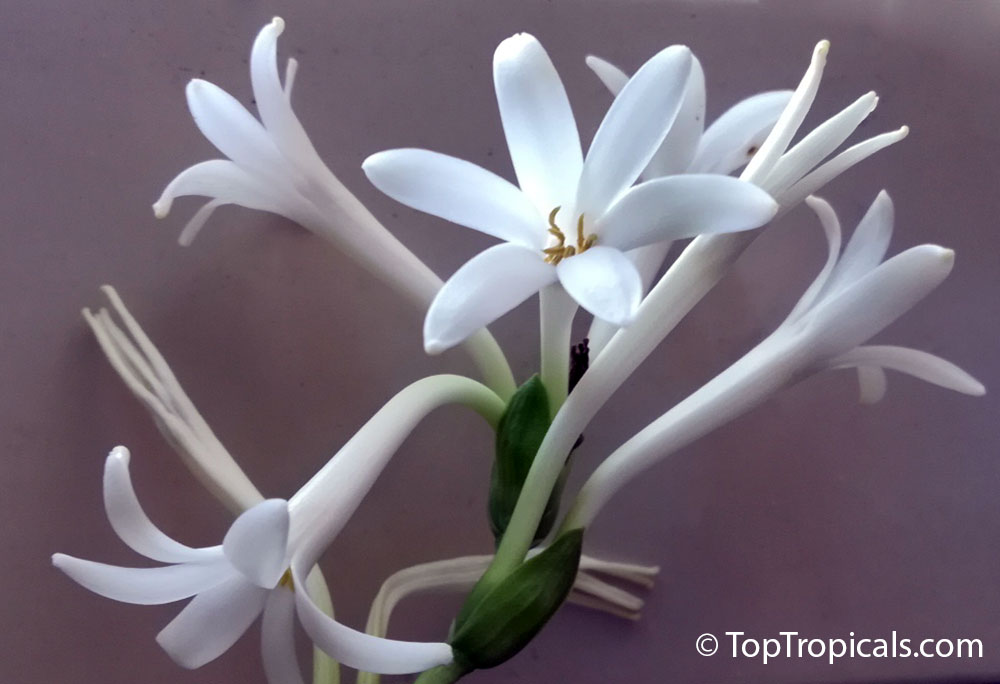
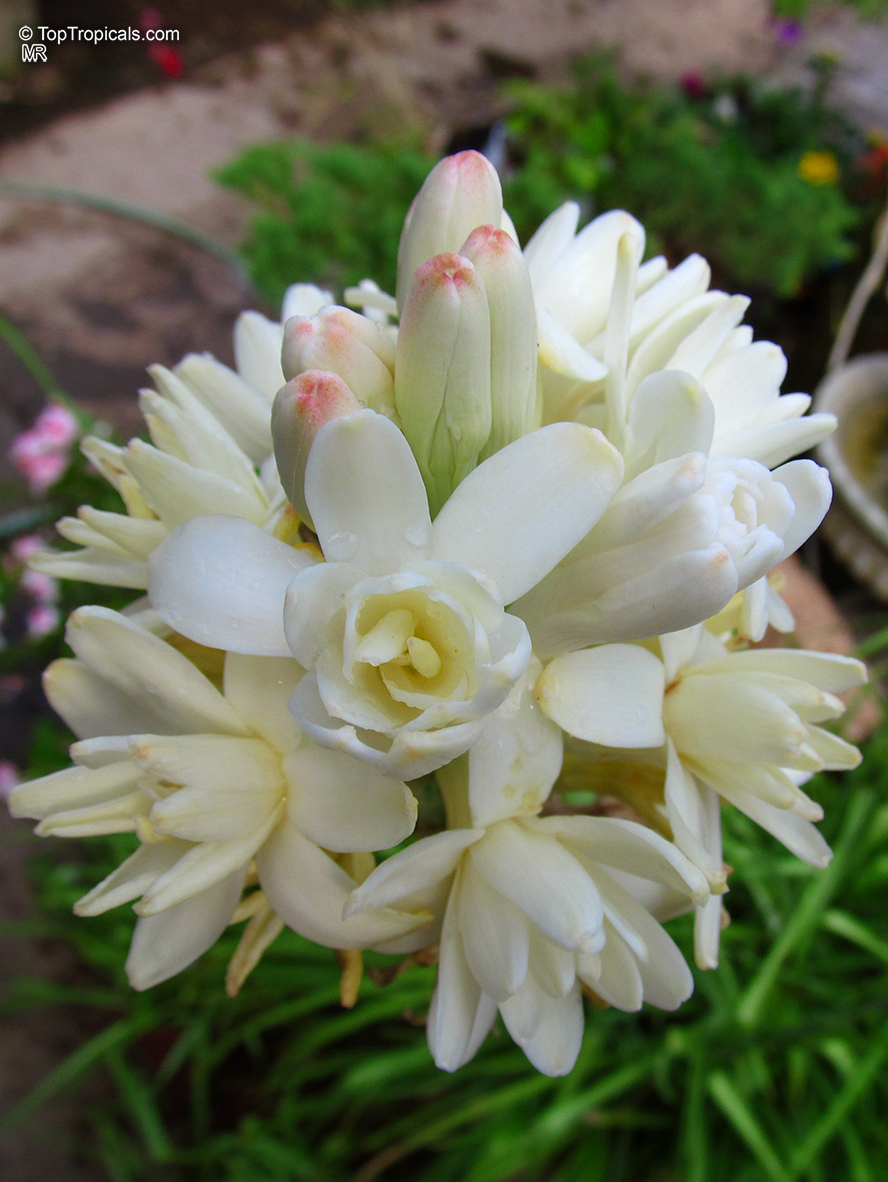
Botanical names: Agave amica, Polianthes tuberosa
Common name: Tuberose
Family: Asparagaceae (Formerly:Agavaceae / Amaryllidaceae)
Subfamily: Agavoideae
Origin: Mexico









The Tuberose grows in elongated spikes up to 45 cm (18 in) long that produce clusters of fragrant waxy white flowers that bloom from the bottom towards the top of the spike. It has long, bright green leaves clustered at the base of the plant and smaller, clasping leaves along the stem.
Tuberose may grow wild in Mexico and surrounding countries, but the cultivation of tuberose is usually in Morocco, the Comores Islands, France, Hawaii, South Africa, India, and China.
Long-lasting as a cut flower in water (with lots of changes.)Most flowers begin to lose their scent when they are picked. Not so with tuberose, like jasmine, the heady floral scent continues to produce itself. In Ayurvedic medicine, attars are held in high esteem not only for their exquisite fragrance, but their healing properties. Tuberose is known to improve one's capacity for emotional depth.
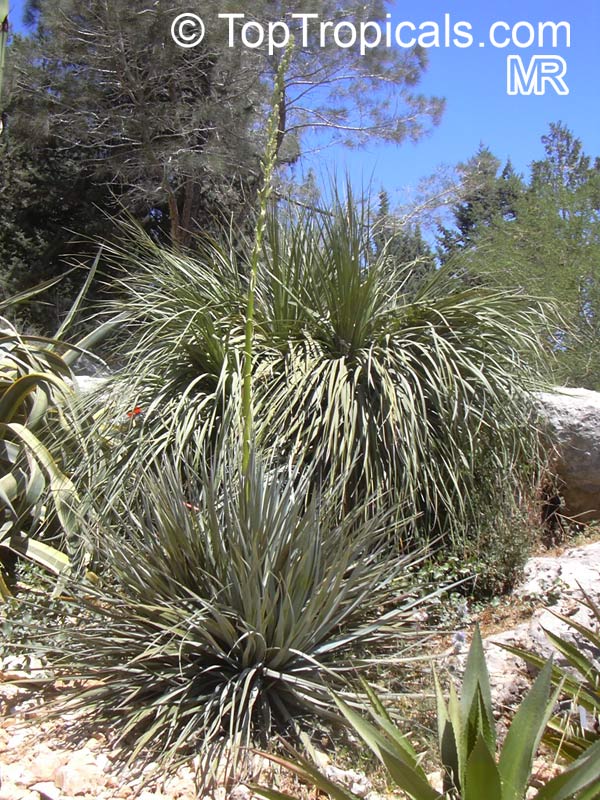
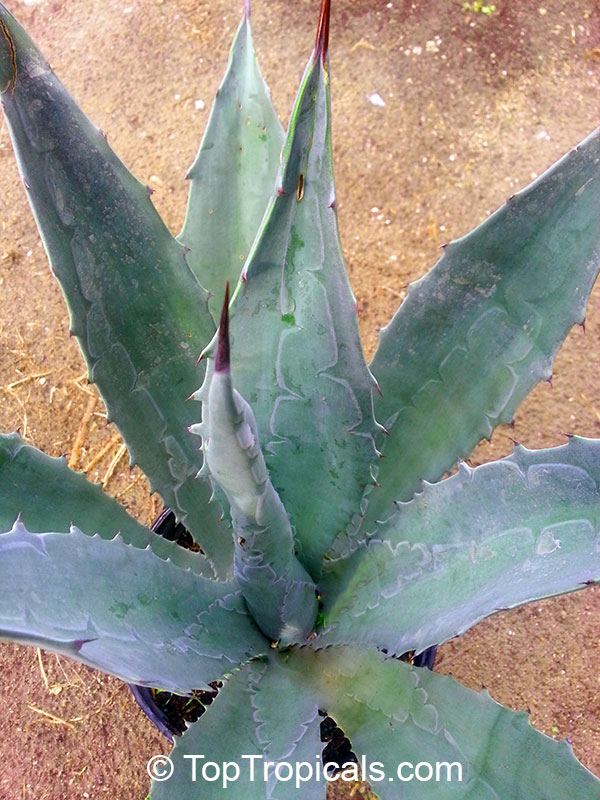
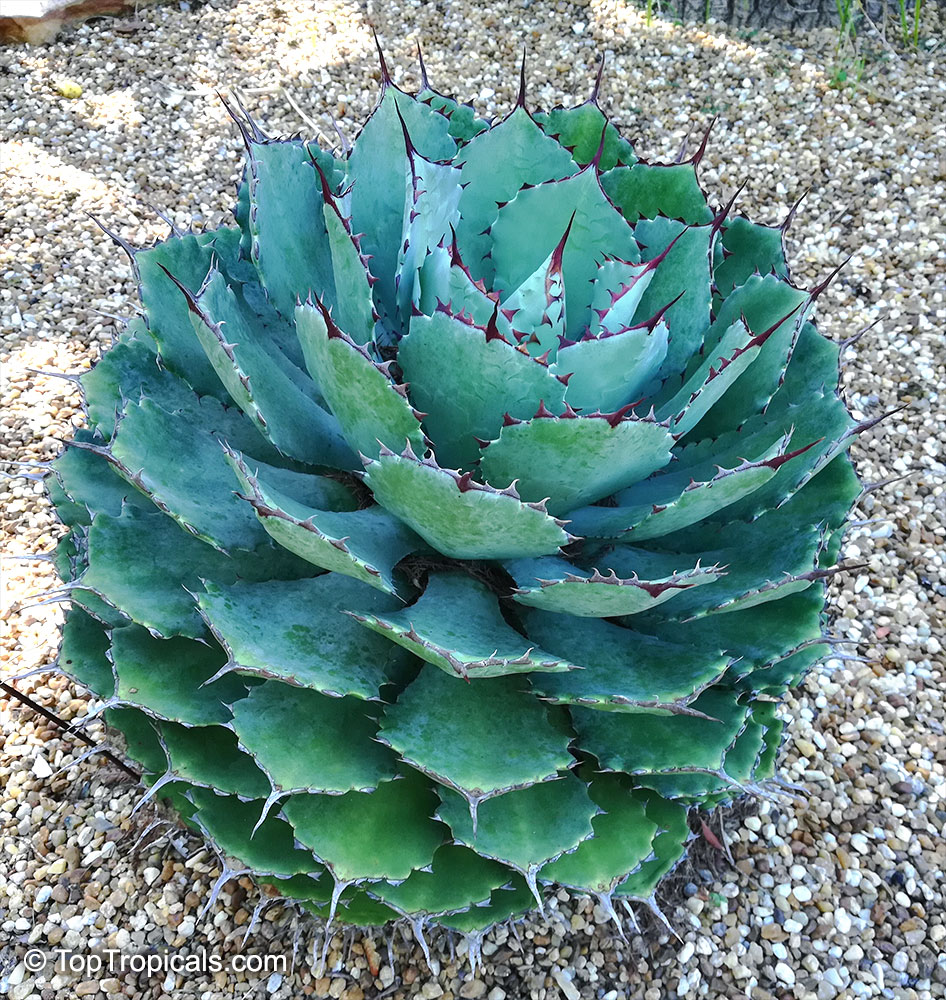
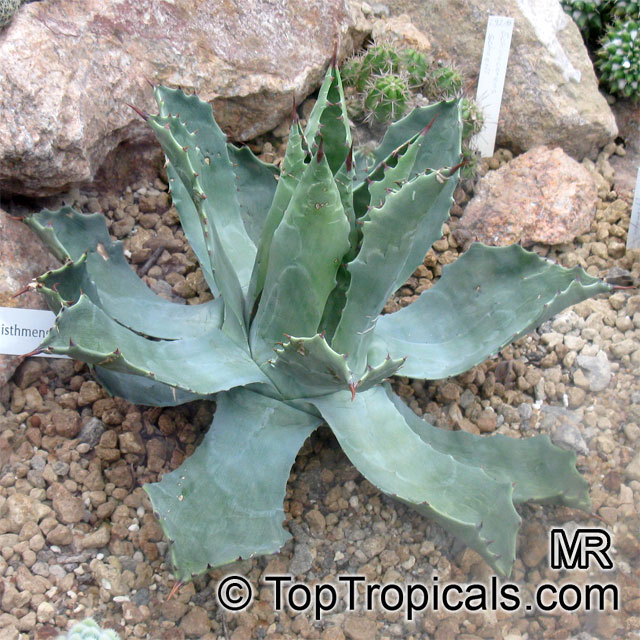
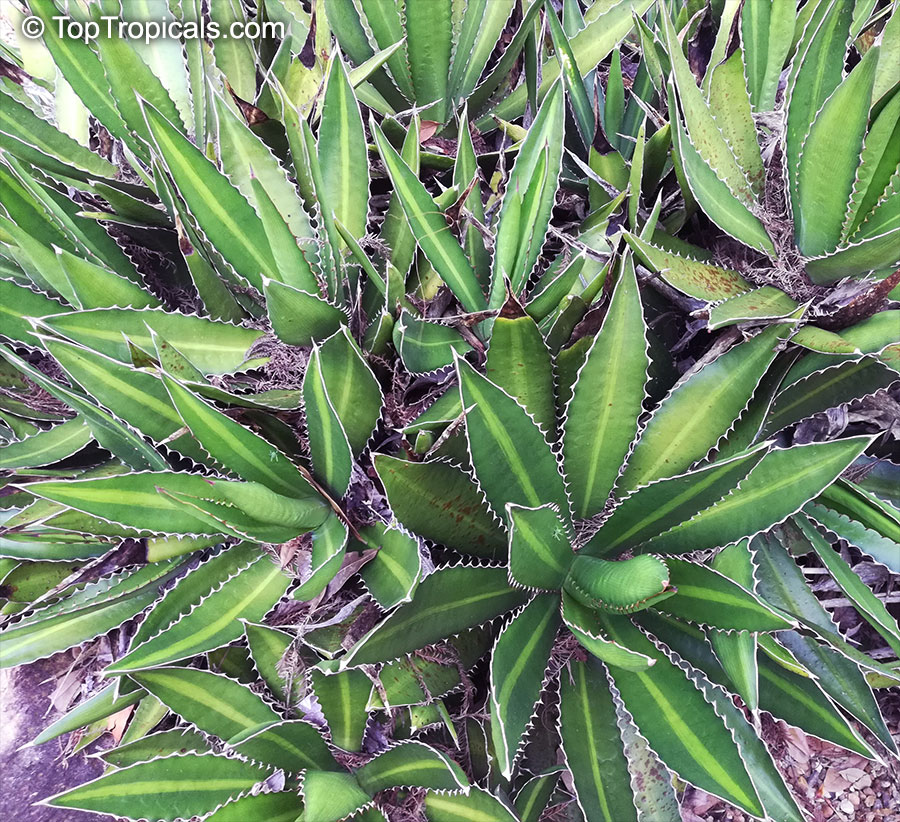
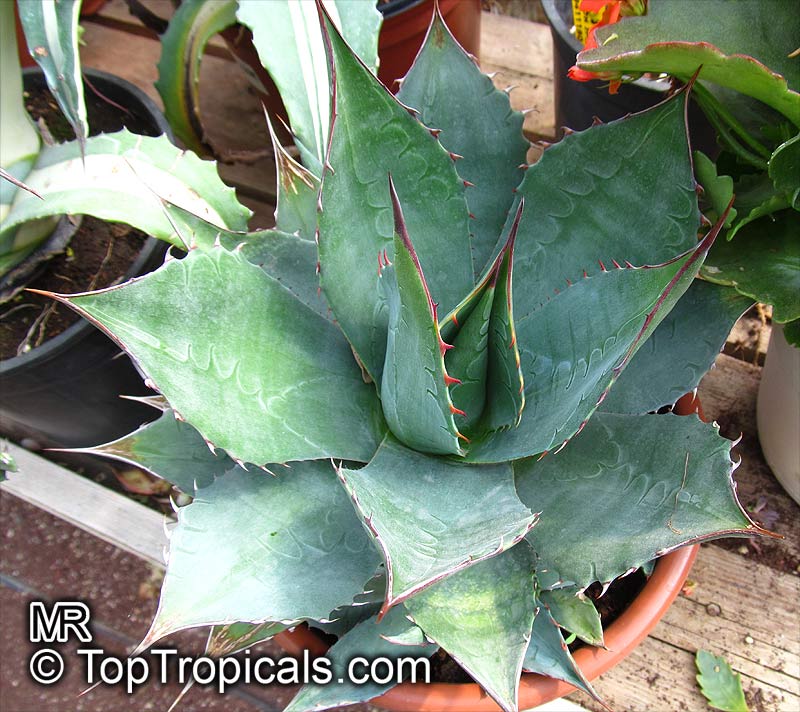
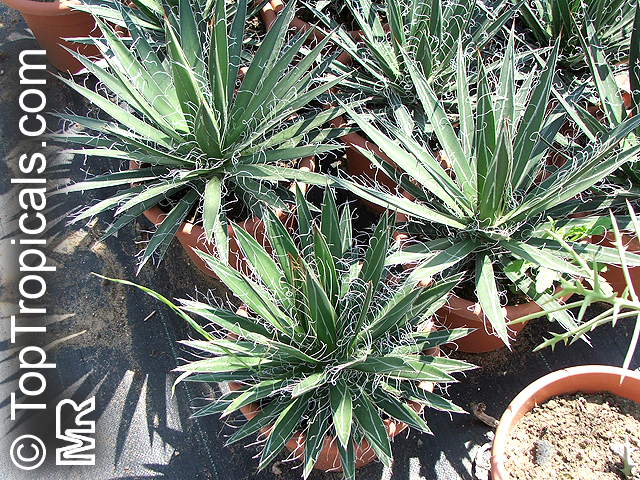
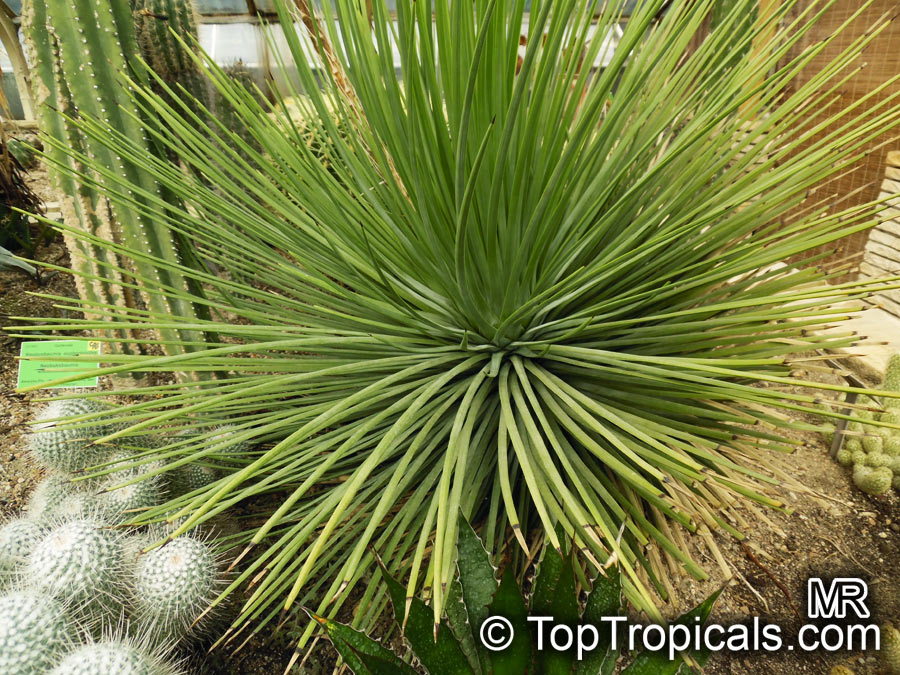
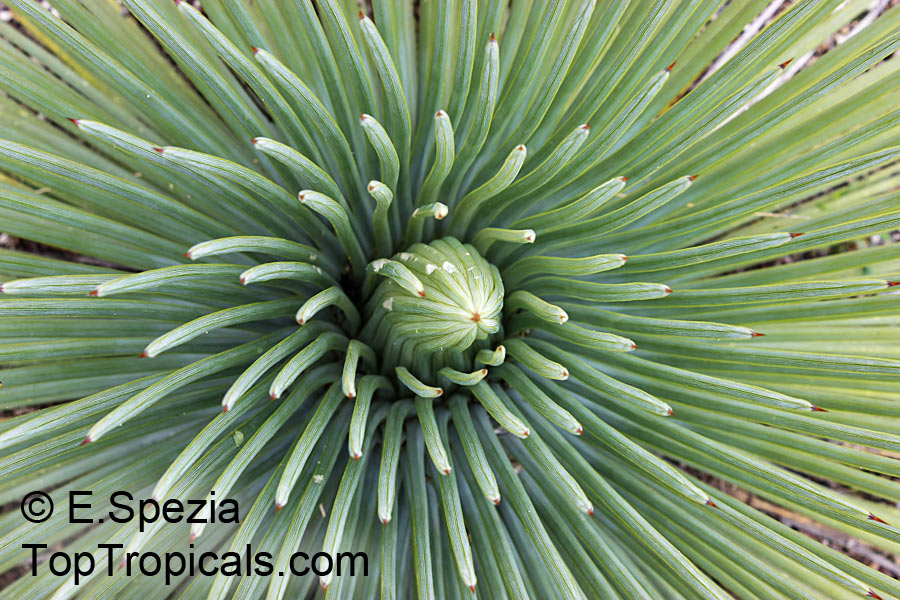
Botanical name: Agave angustifolia
Common name: Agave Maguey Lechugilla
Cultivar: Marginata
Family: Asparagaceae (Formerly:Agavaceae / Amaryllidaceae)
Subfamily: Agavoideae
Origin: Mexico





Agave angustifolia Marginata, more commonly known as the Agave Maguey Lechugilla, is a small shrub native to Mexico. This spiny or thorny succulent is popular for its ornamental foliage and grows between 2-5 feet in full sun, and in dry conditions. This is a hardy succulent, suitable for use in xeriscaping and is grown in USDA zone 9-11.
Agave Maguey Lechugilla, like most succulents, will produce best results in well-draining soil. Watering should be done sparingly and with care, as too much water can lead to the plant's death. When water is necessary, it should be done deep and slow. During the winter months, when growth is at a minimum, water should be reduced even more.
In cold regions, where freezing temperatures are expected, the best way to grow Agave Maguey Lechugilla is in a pot. Containers should also ensure adequate drainage, and during the hot summer months should be moved to a sunny spot outdoors and brought inside during winter.
Overall, the Agave Maguey Lechugilla is an attractive and hardy plant. When growing conditions are provided and cared for, the plant will grow to a maximum of 5 feet. Foliage is normally very ornamental, and is sure to be a winning addition to any xeriscape or cacti garden.
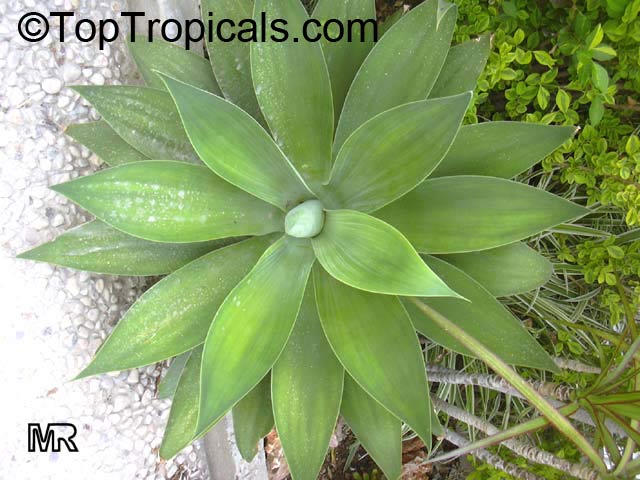
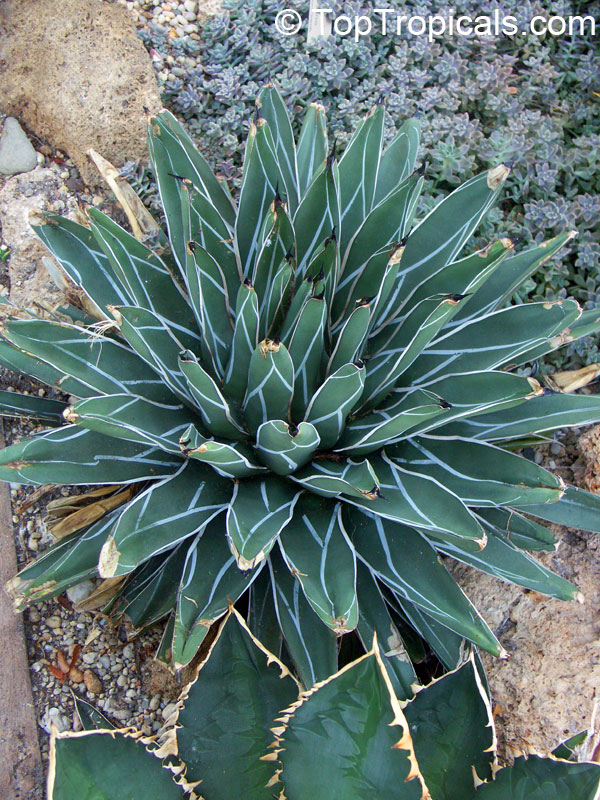
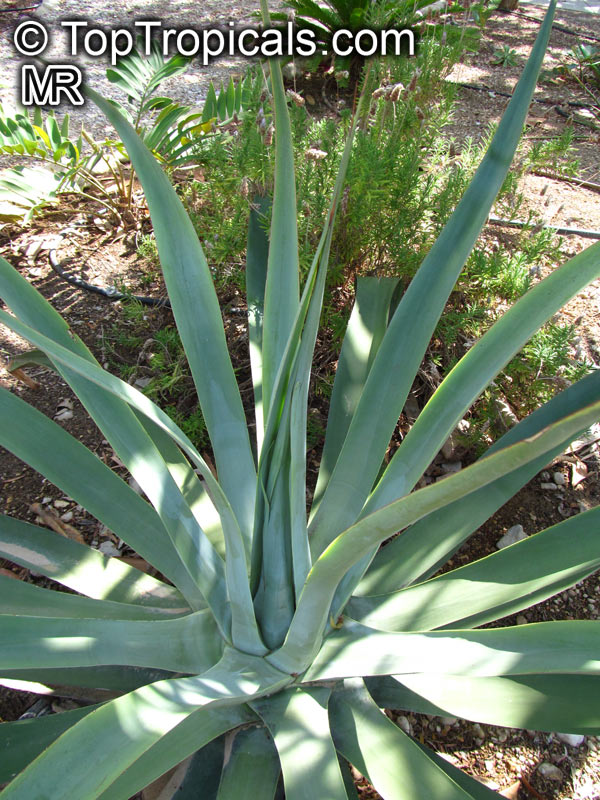
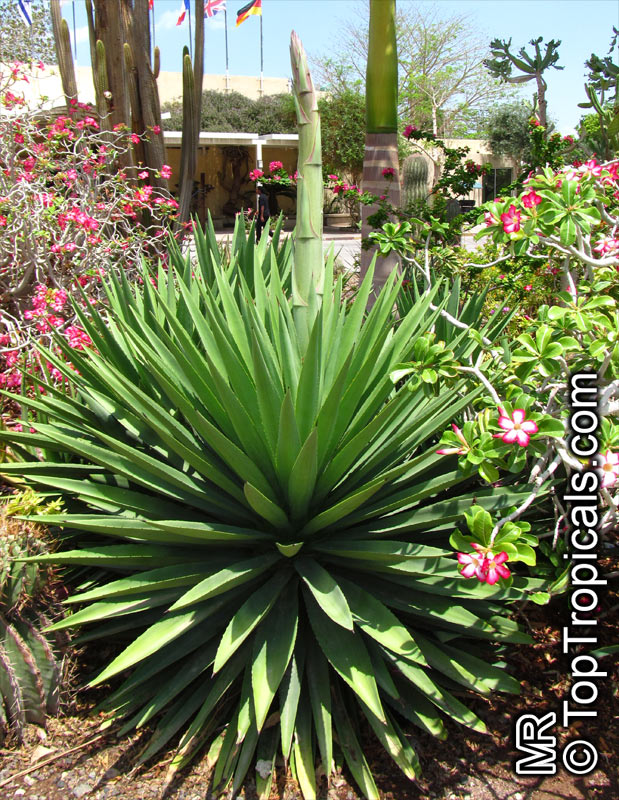
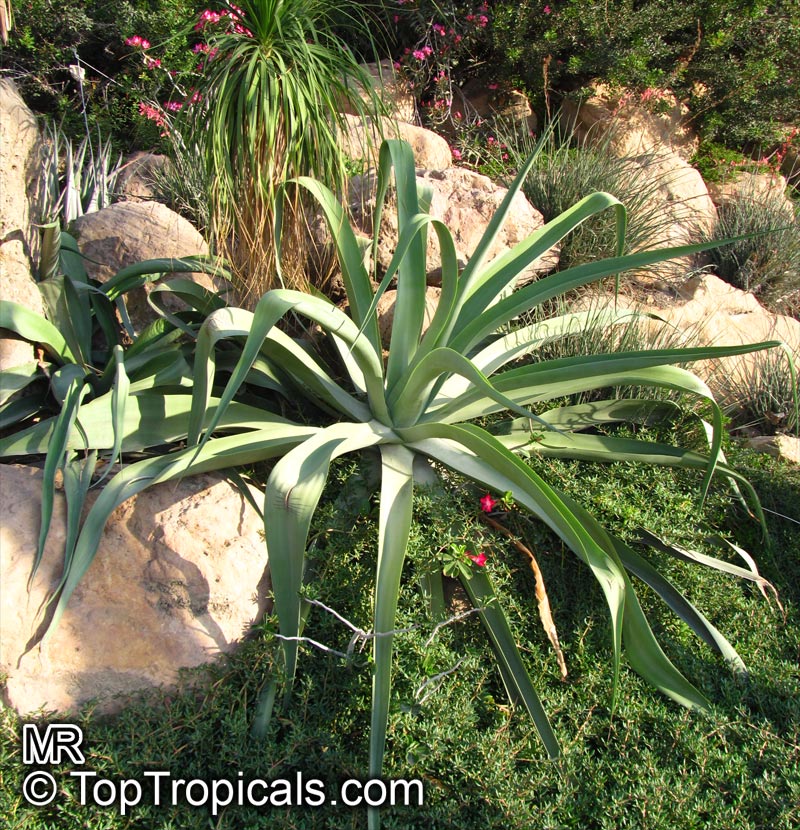
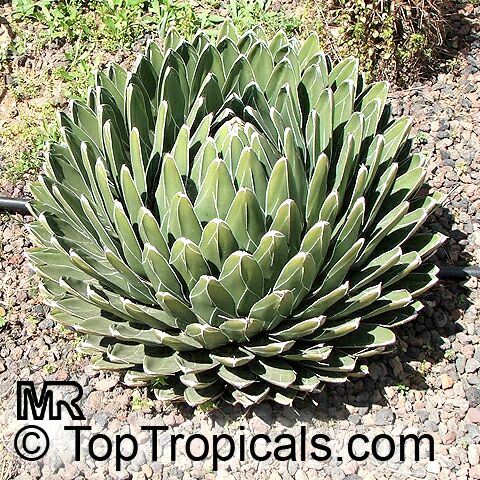
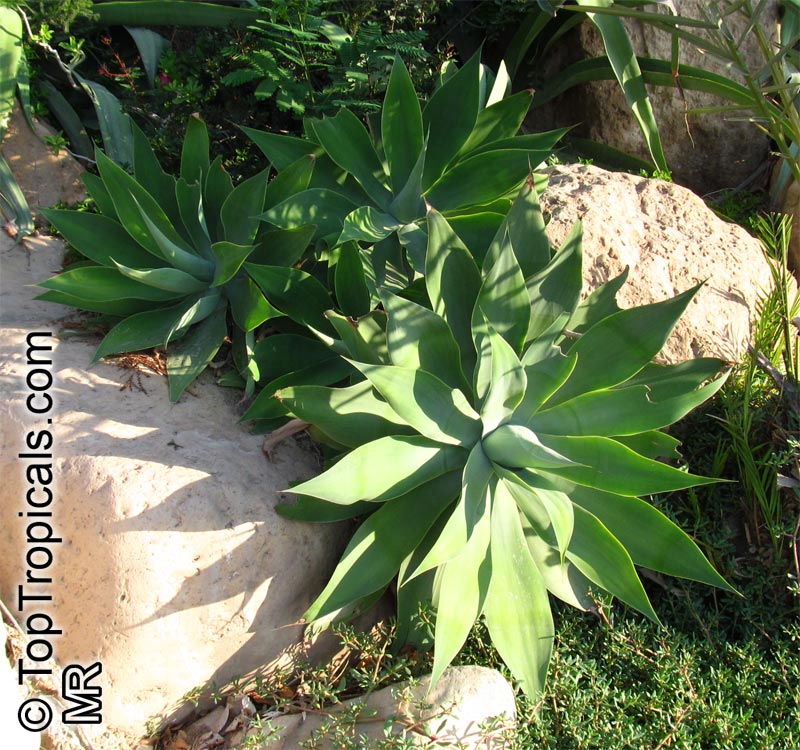
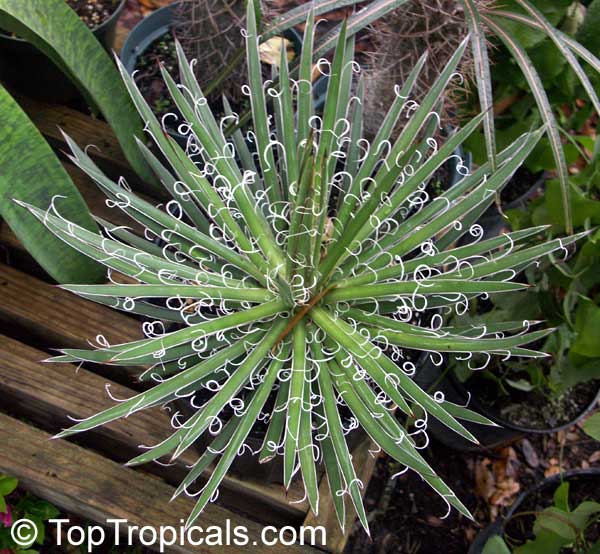
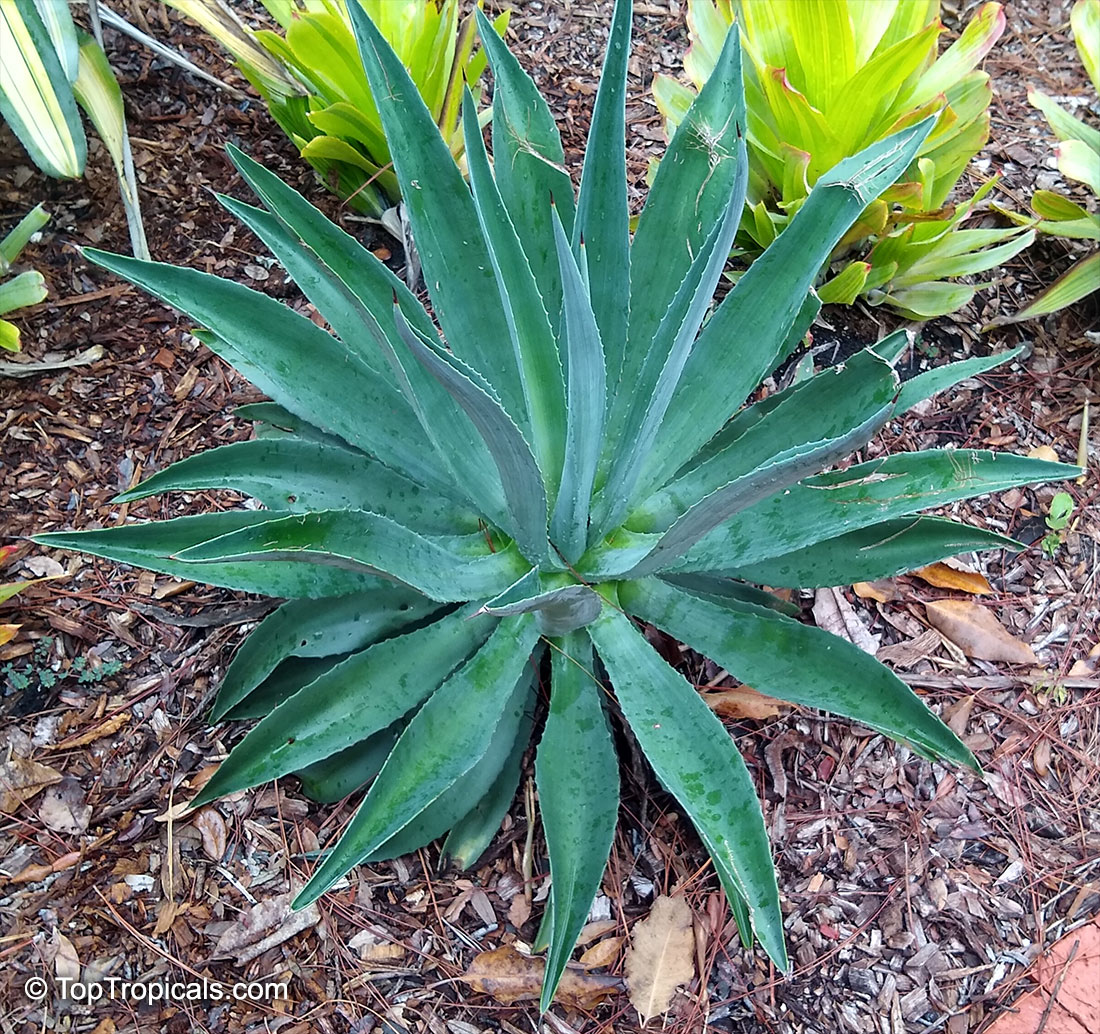
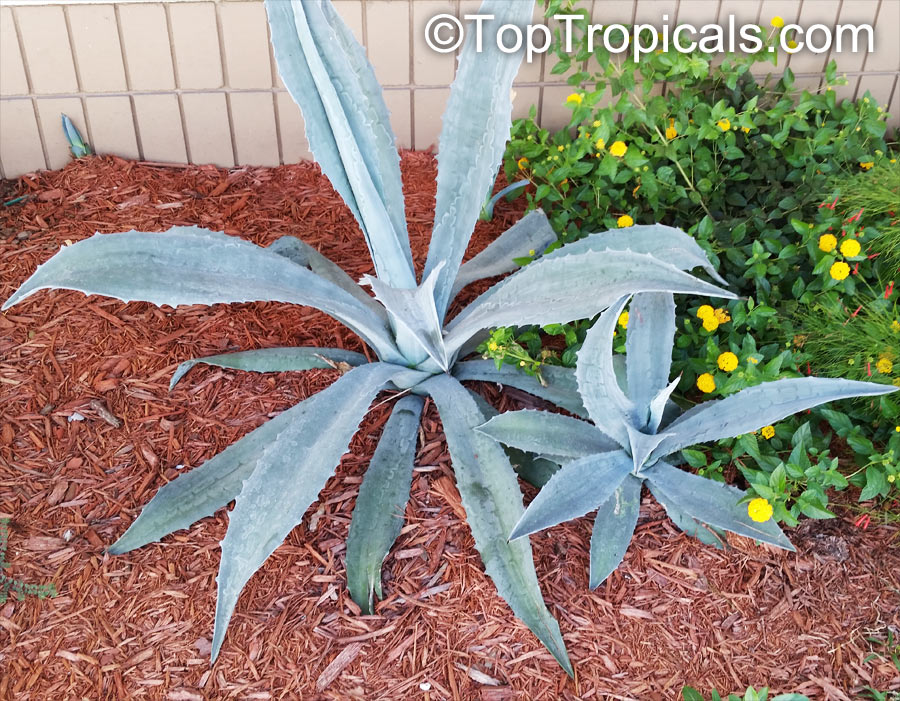
Botanical name: Agave attenuata
Common names: Fox Tail Agave, Swan's Neck Agave
Family: Asparagaceae (Formerly:Agavaceae / Amaryllidaceae)
Subfamily: Agavoideae
Origin: Mexico






Native to the tropical climates of Mexico, Agave attenuata (Fox Tail Agave) is a small shrub that grows between 2 - 5 feet. It prefers full sun to light shade, and requires moderate wateringthough it doesn't tolerate overly wet conditions. It prefers to grow in dry, well-draining soils. The plant is renowned for its light grey-green wavy-edged leaves with a hint of ivory powder. Fox Tail Agave's short, flowering stems emerge from the heart of the plant in summer or fall and produce yellow or orange clusters of fragrant flowers. The spiny or thorny leaves help to deter browsing animals and offer a unique addition to gardens and landscapes.
Agave attenuata is an excellent home garden choice because it is low-maintenance, drought tolerant and can survive in a range of conditions. In addition, it can be grown in USDA Hardiness Zones 9-11 with minimal care. However, if you are located in a colder region and plan to grow this plant in a pot, you should move it indoors during the winter months to protect it from the frost. As long as you ensure your Fox Tail Agave has plenty of sun and water it should thrive in your garden or home.
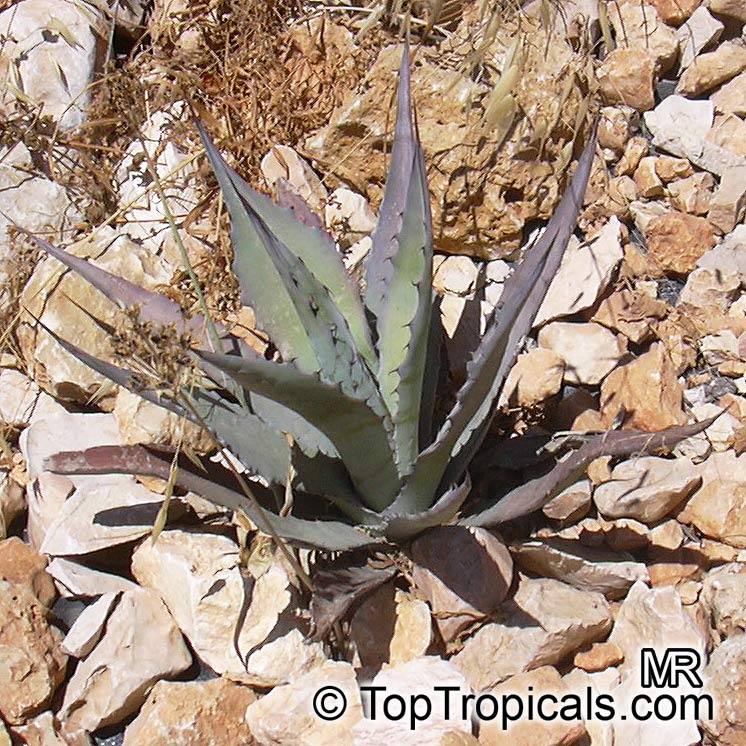
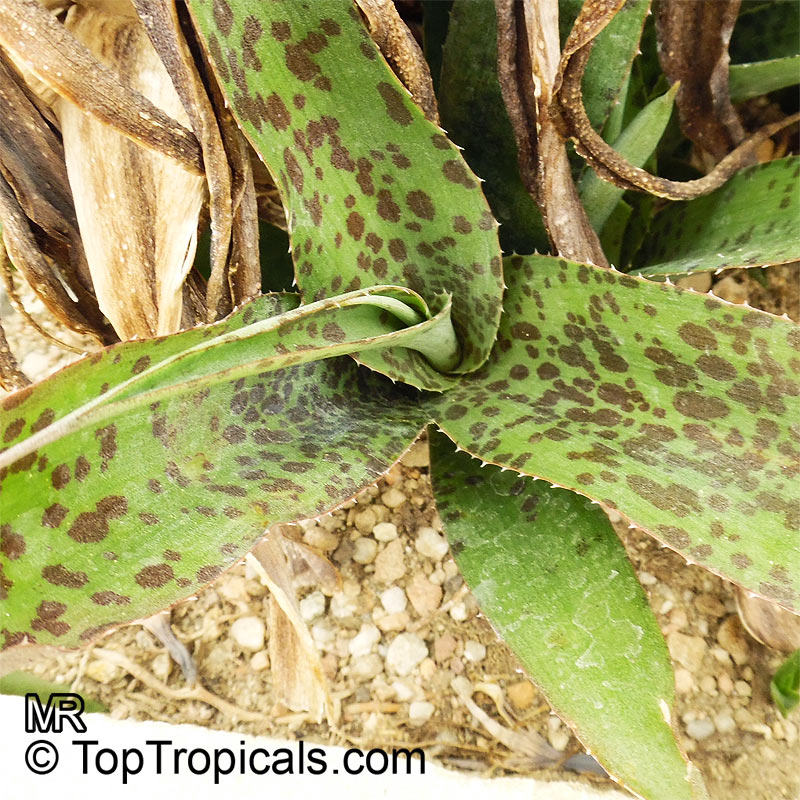
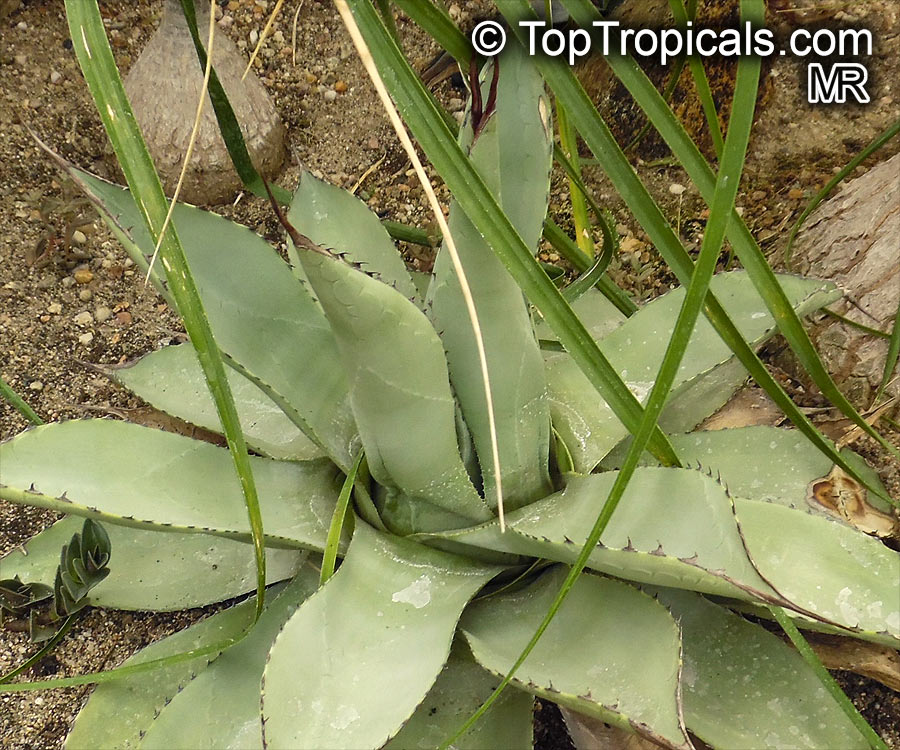
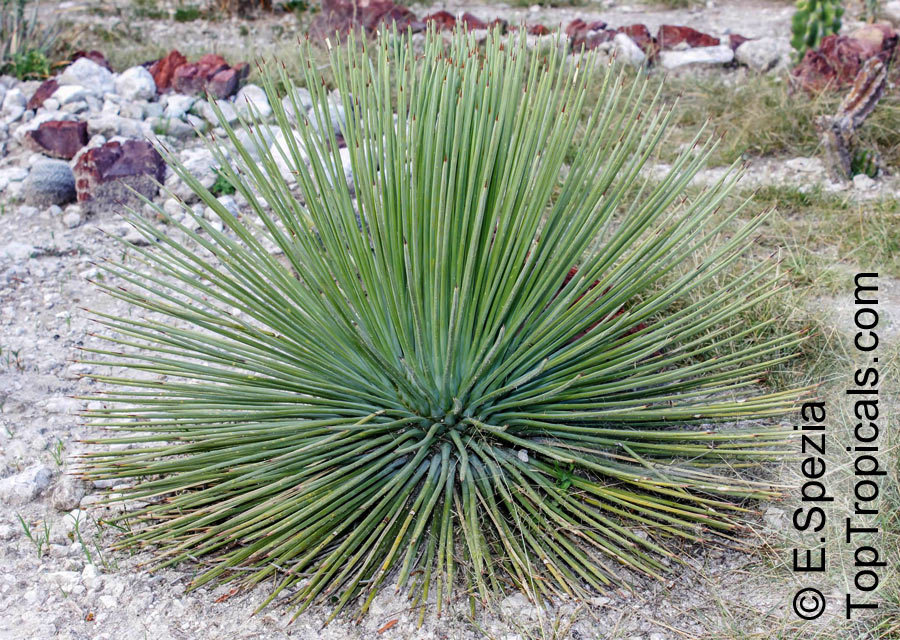
Botanical name: Agave neglecta
Common name: Small agave
Family: Asparagaceae (Formerly:Agavaceae / Amaryllidaceae)
Origin: Florida





Agave neglecta has been regarded as endemic to Florida, but is now treated as the same species as the Mexican Agave weberi and only naturalized in Florida through human agency.
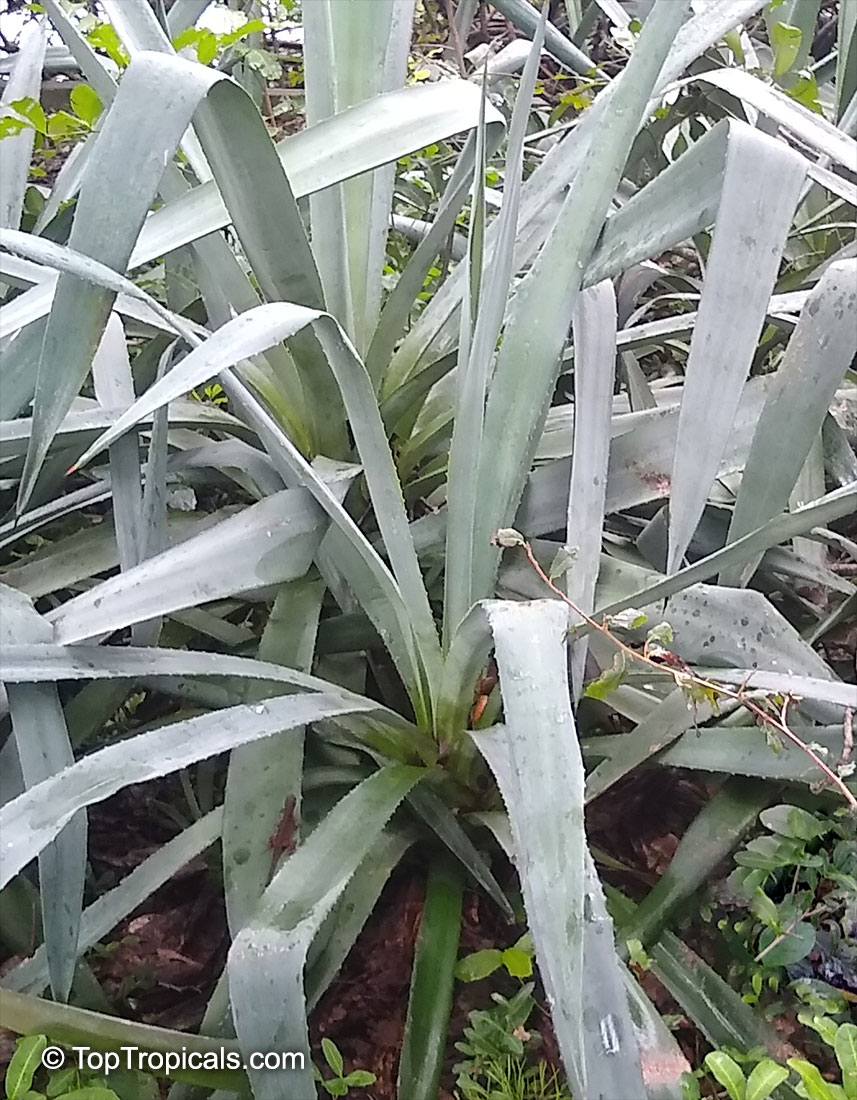
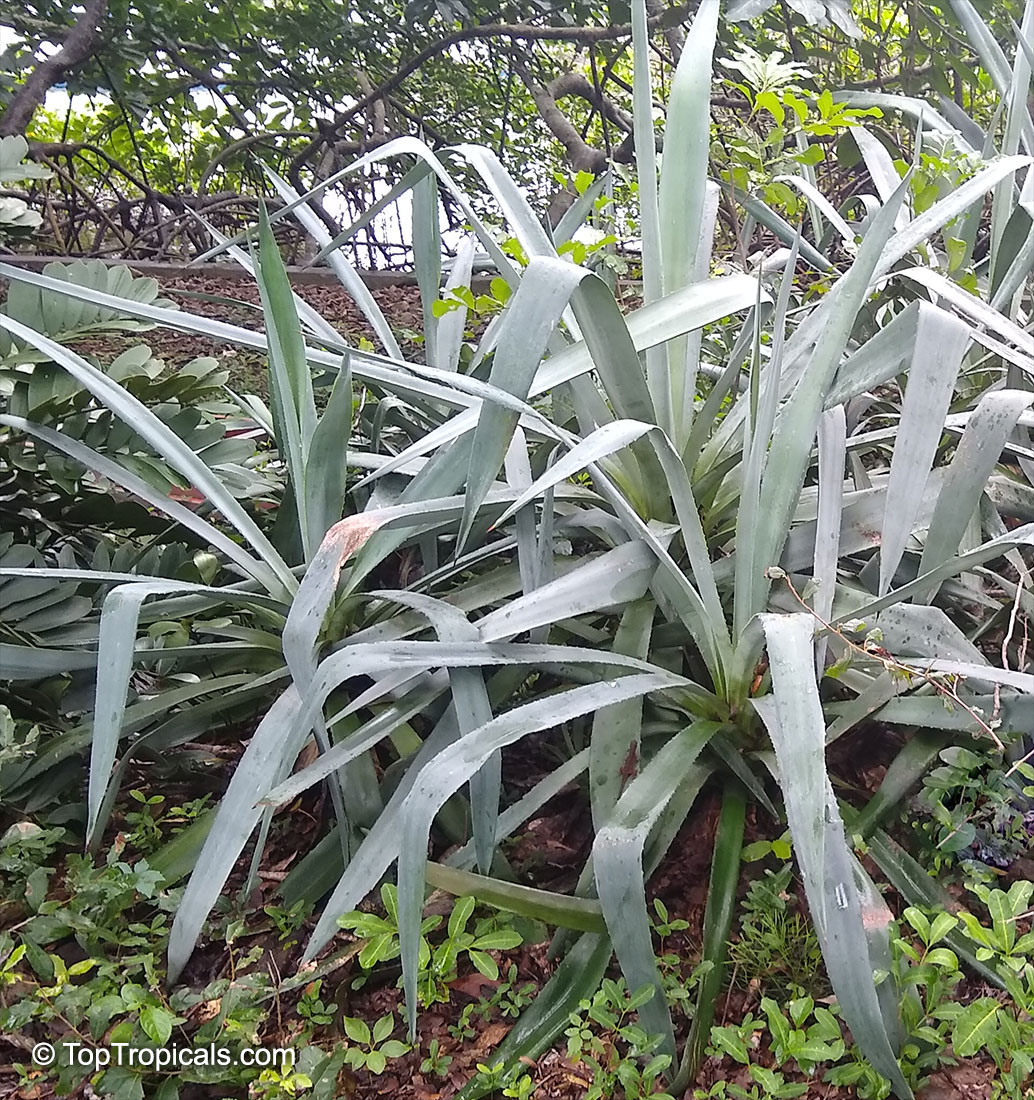
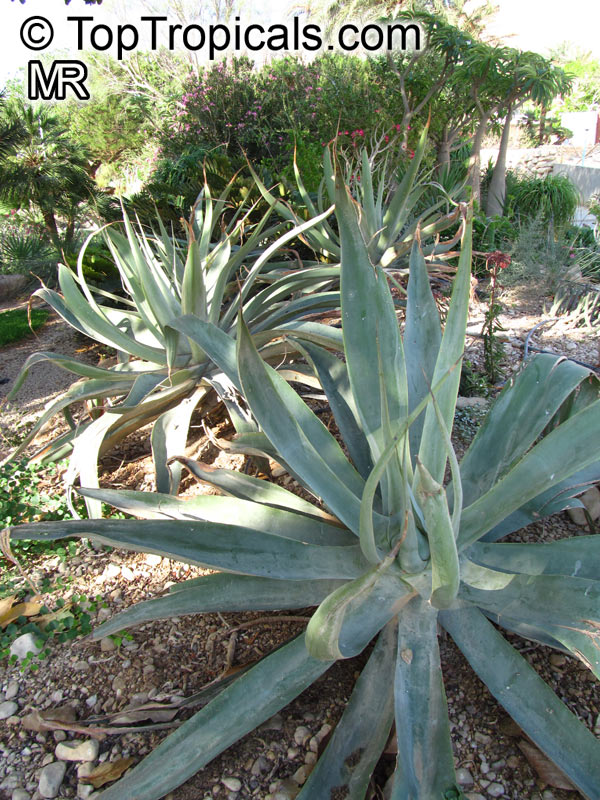
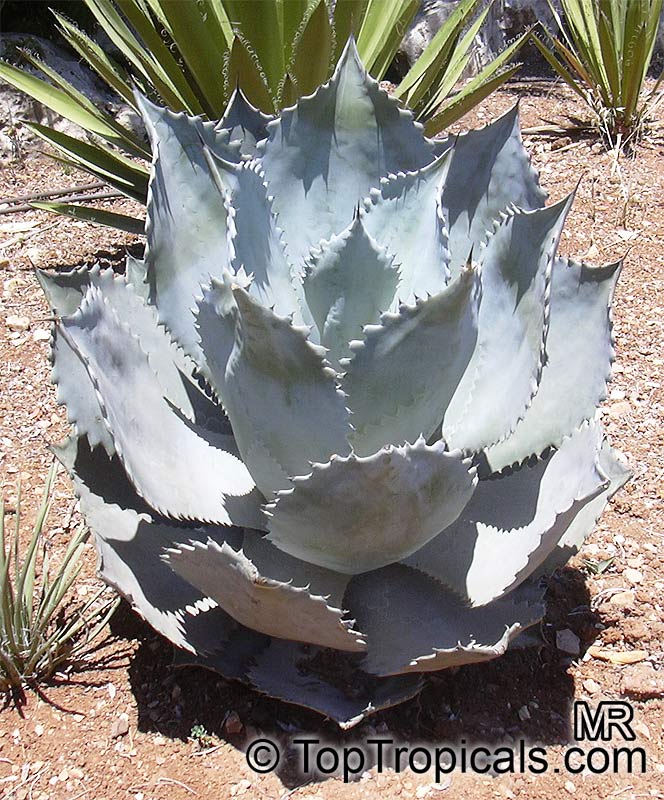
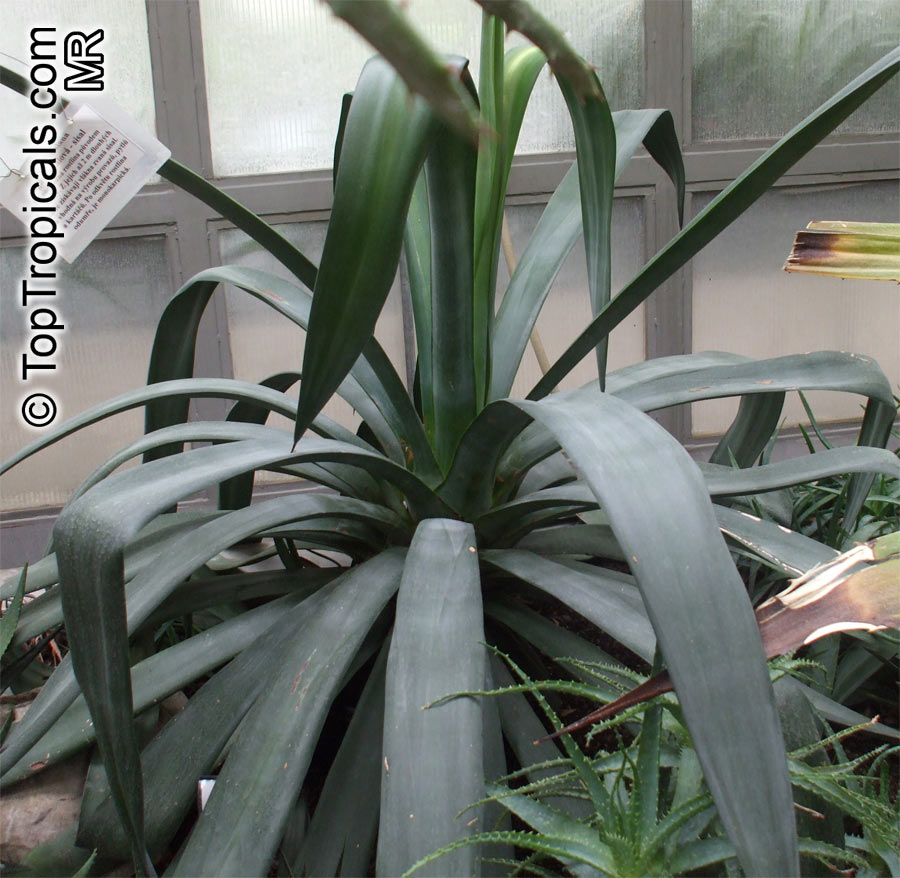
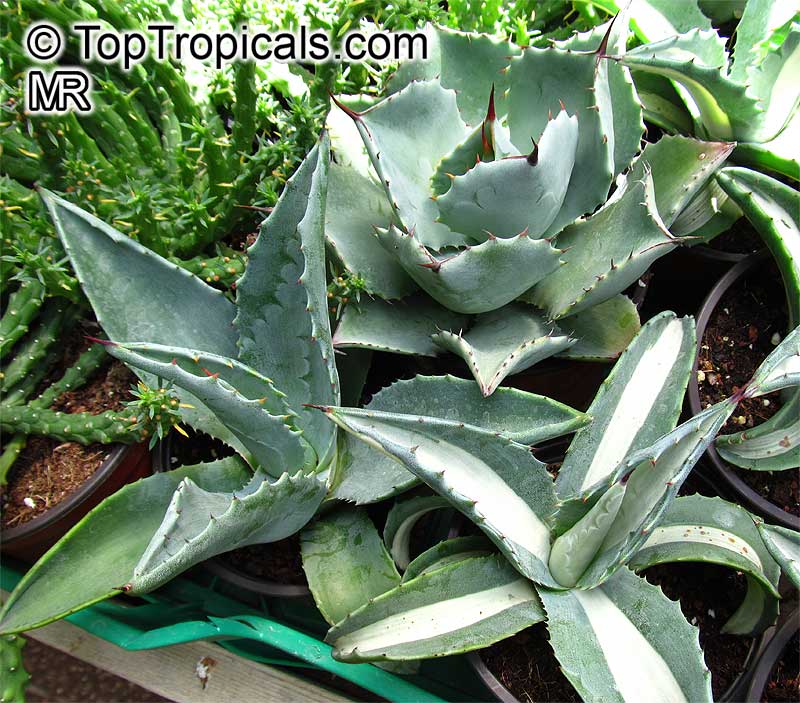
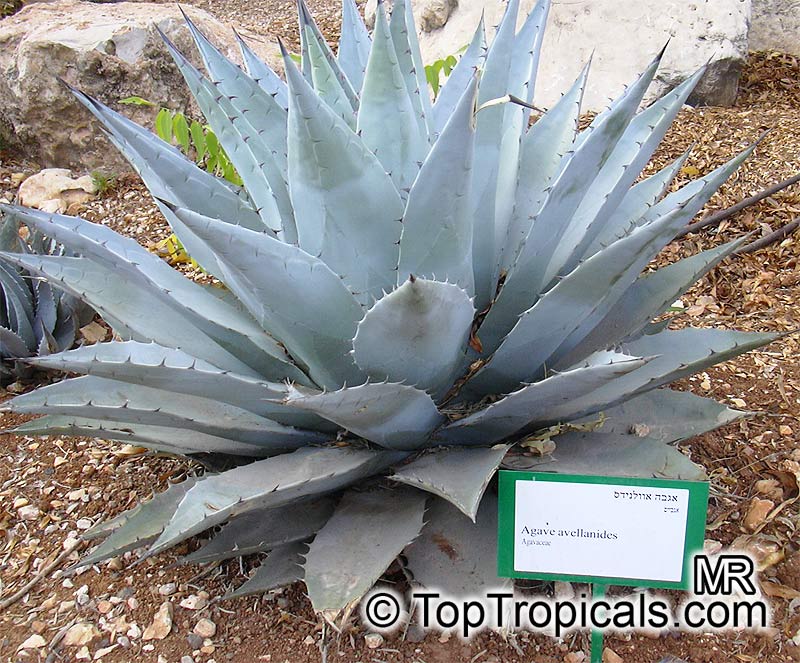
Botanical name: Agave sp.
Common name: Agave
Family: Asparagaceae (Formerly:Agavaceae / Amaryllidaceae)
Subfamily: Agavoideae
Origin: Mexico
Hardiness: 20°F







Agaves are rosette plants that live for many several years before flowering. Each rosette will flower only once, then die. The English common name, Century Plant, is based on the mistaken belief that the plants grow for 100 years before blooming. In fact, some of the smaller species flower when only 3 to 4 years old. The larger species may live for 40 to 50 years before flowering. They may be planted outdoors in mild climates, especially those that are desert and semi-desert; otherwise, they may be grown in a greenhouse and when small as houseplants. In regions with harsh winters, Agaves may be planted outdoors in the summer and brought in during the winter. The sizes of the Agaves vary from 6 inches to 15 feet wide between the species.
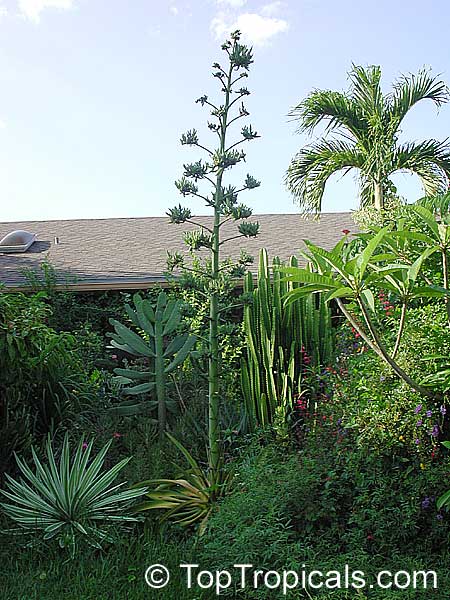
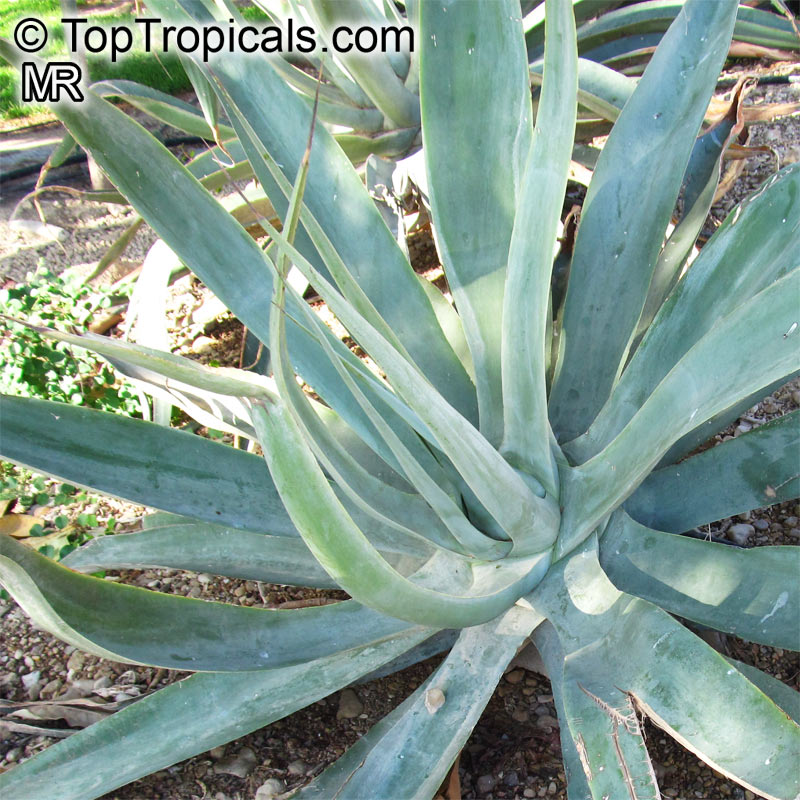
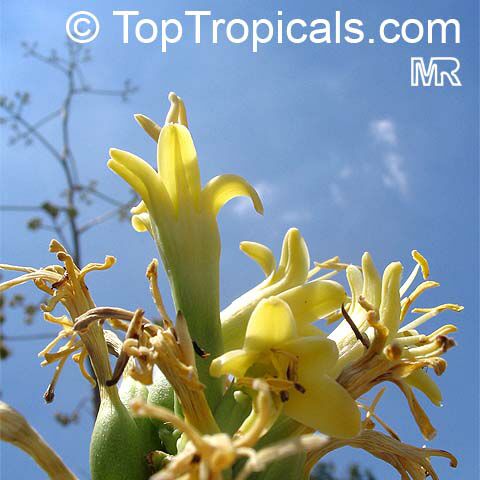
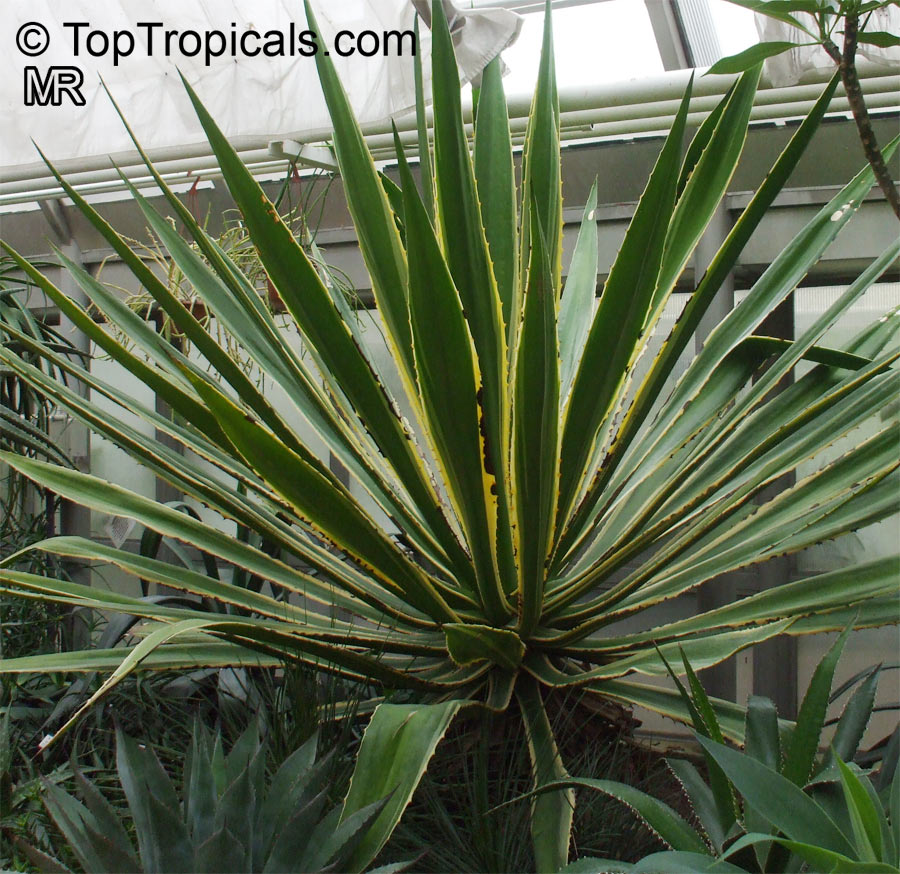
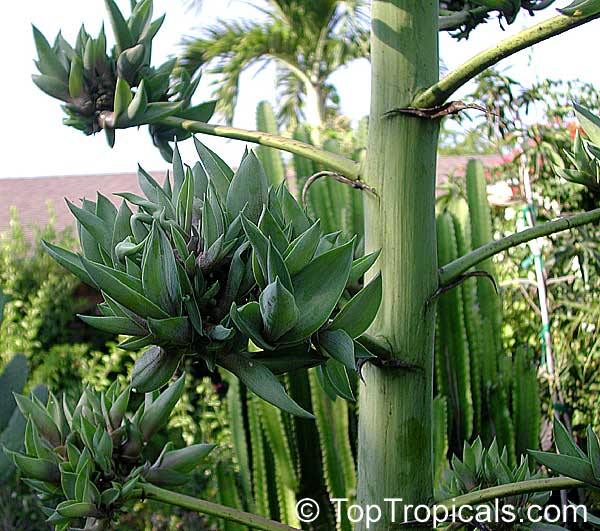
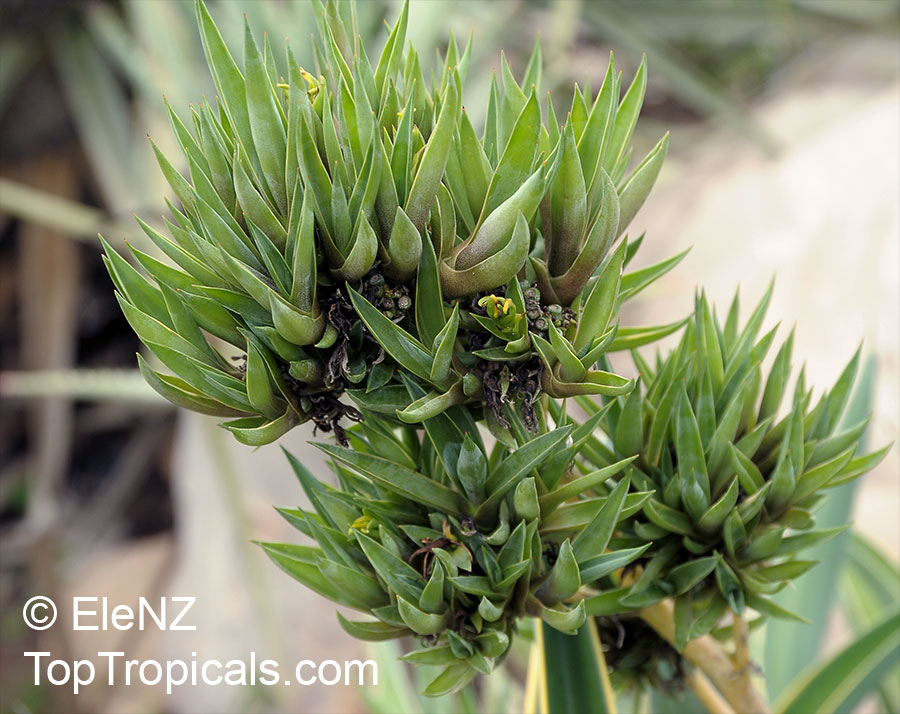
Botanical name: Agave tequilana
Common names: Tequila Agave, Century Plant
Family: Asparagaceae (Formerly:Agavaceae / Amaryllidaceae)
Subfamily: Agavoideae
Origin: Mexico






Tequila Agave, Century Plant. Agave tequilana, commonly called blue agave (agave azul) or tequila agave, is an agave plant that is an important economic product of Jalisco, Mexico, due to its role as the base ingredient of tequila, a popular distilled beverage. The high production of sugars, mostly fructose, in the core of the plant is the main characteristic that makes it suitable for the preparation of alcoholic beverages. Great addition to cactus - rock gardens - ethno-botanical collections. Drought-tolerant; suitable for xeriscaping. Grows fairly fast in summer if provided with extra water.
Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Robusta - Rapid Growth Booster
Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Robusta - Rapid Growth Booster
Local pickup only. This item is not available for shipping. Local delivery may be available in Ft. Myers or Sebring, Florida. Contact us for an estimate. Non-pickup orders are subject to restocking fees.
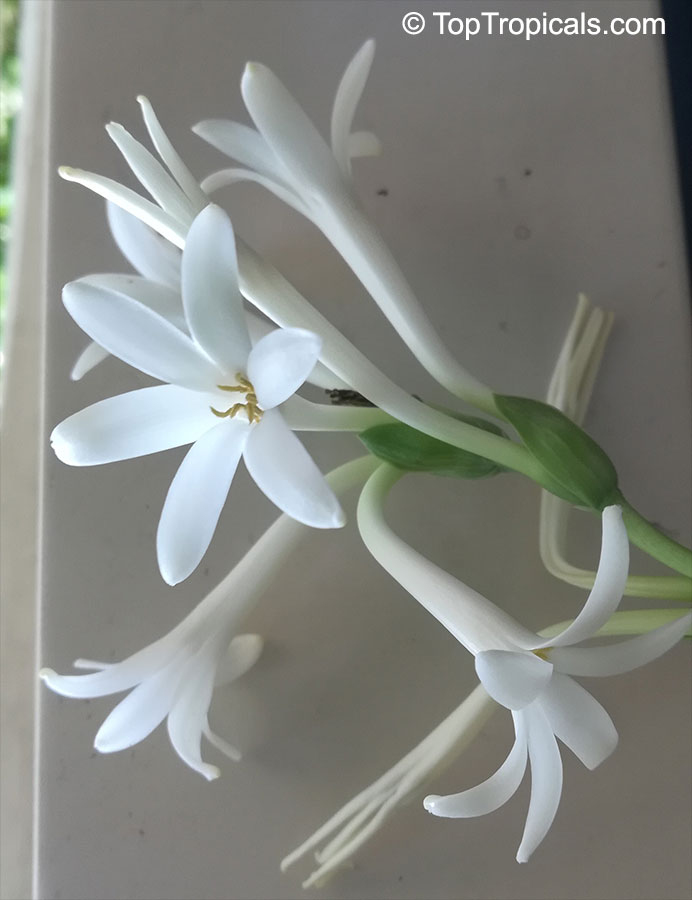
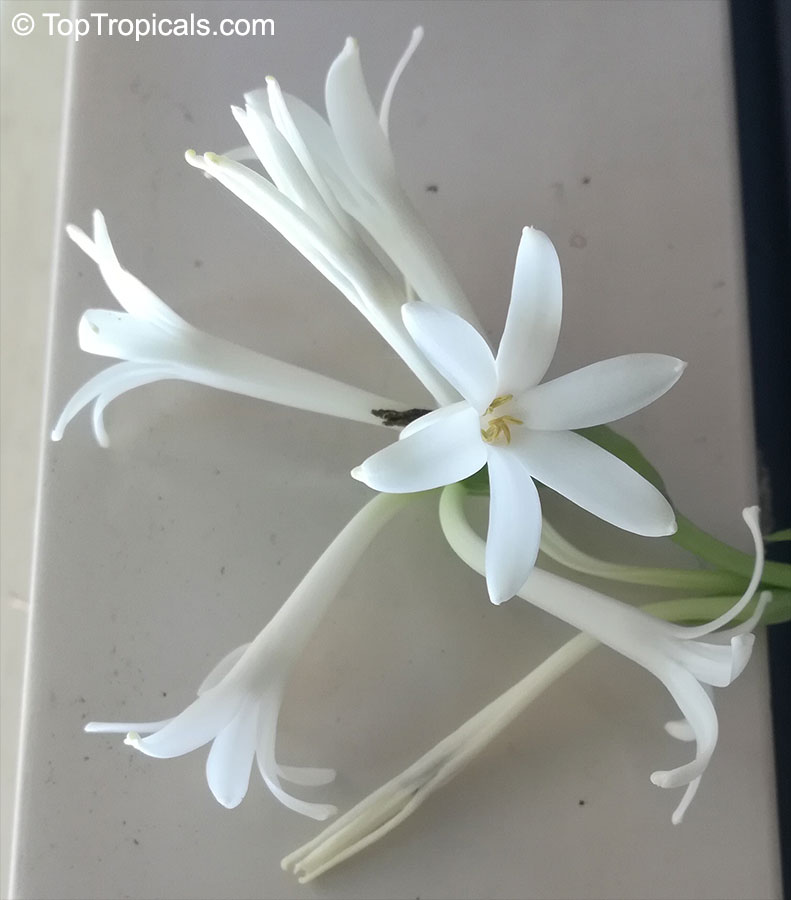
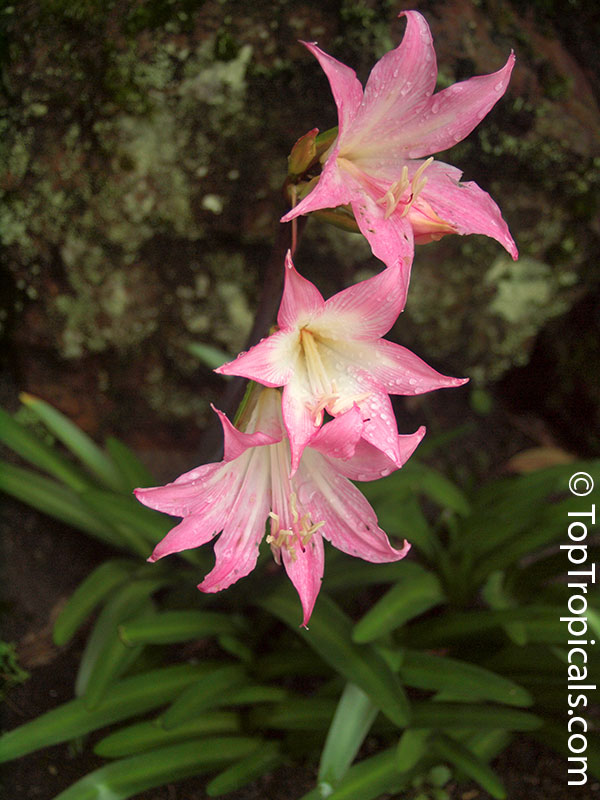
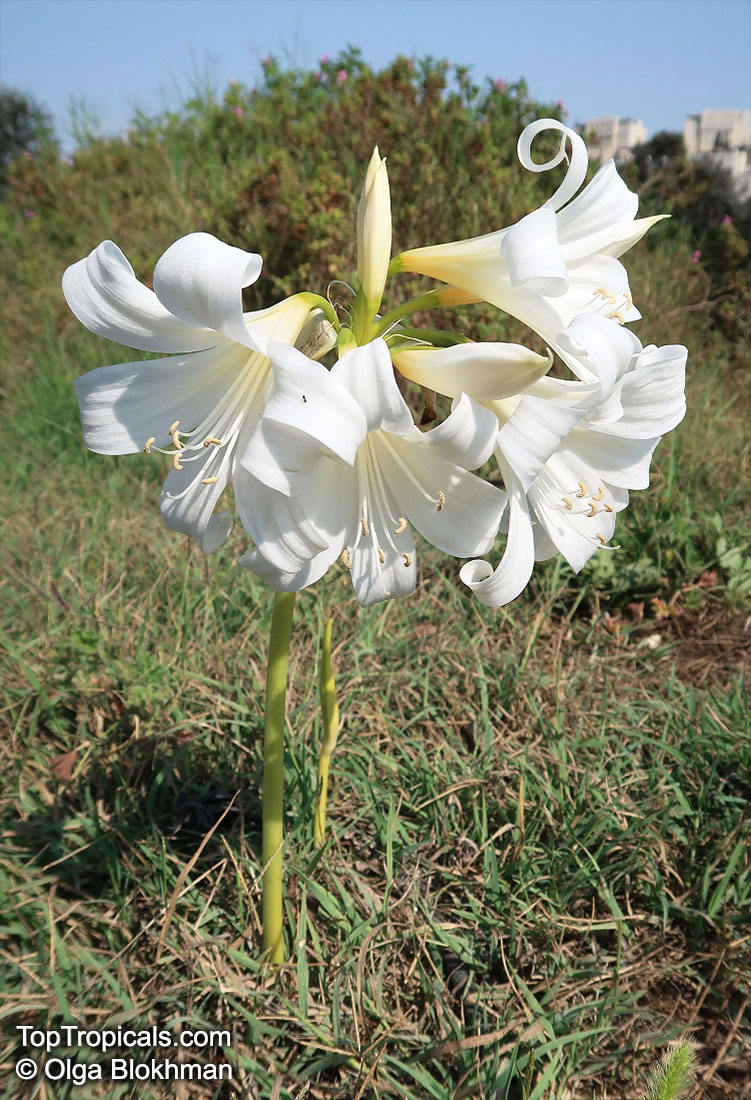
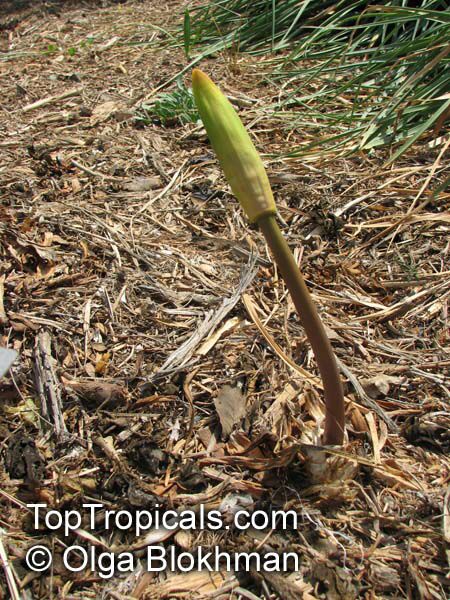
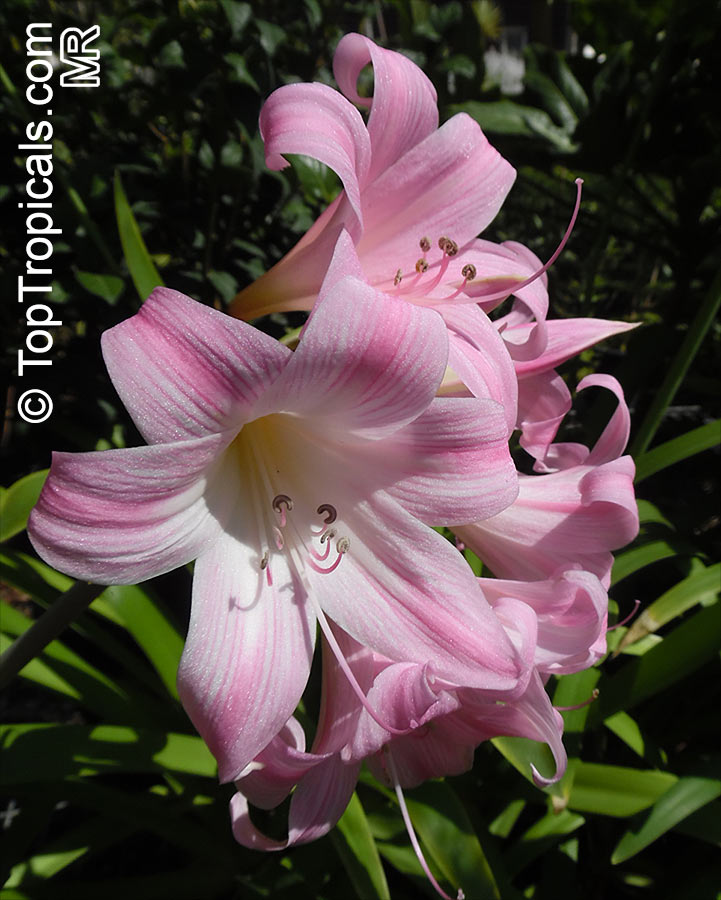
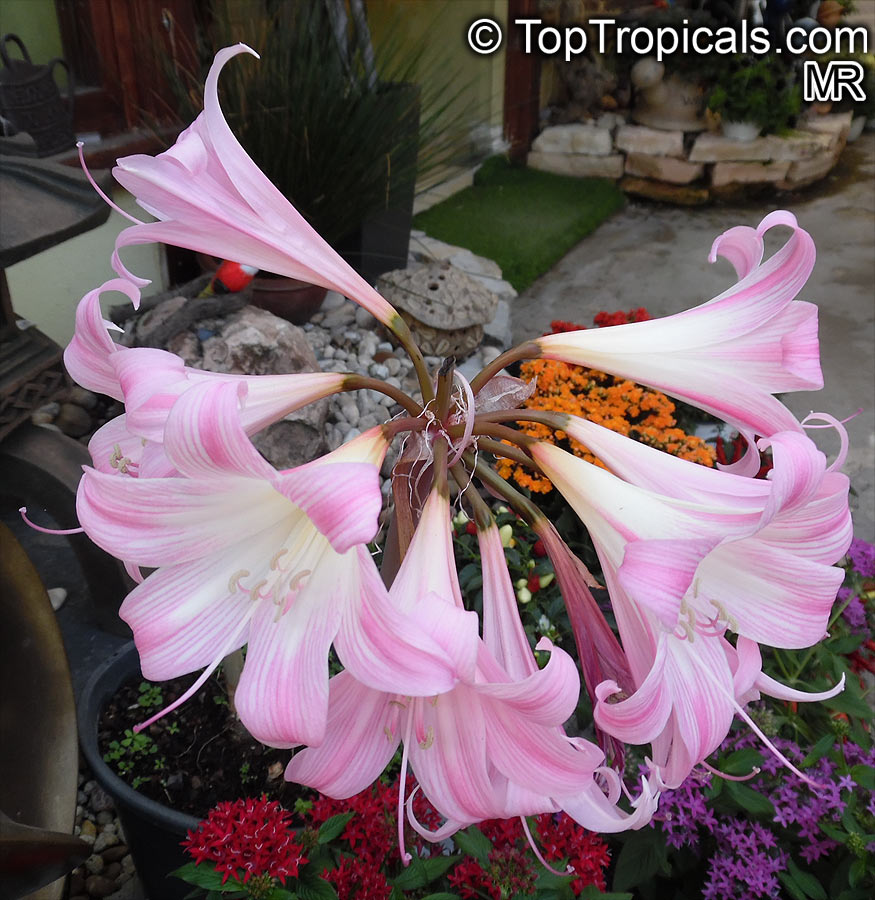
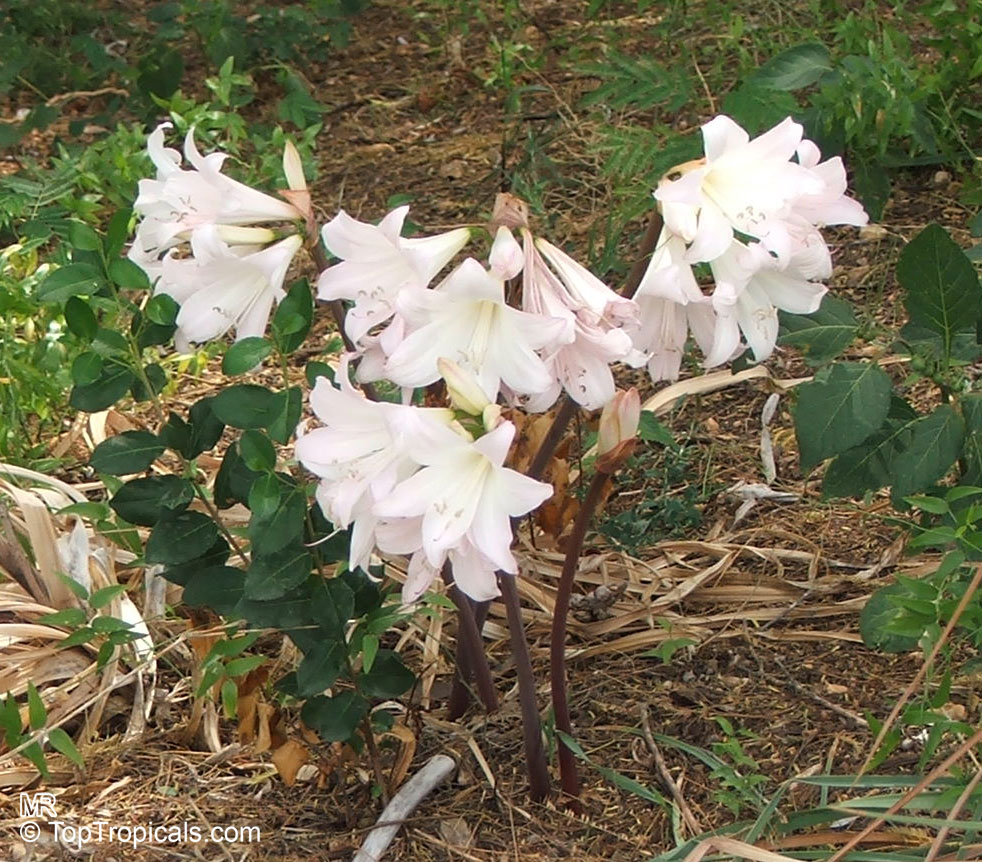
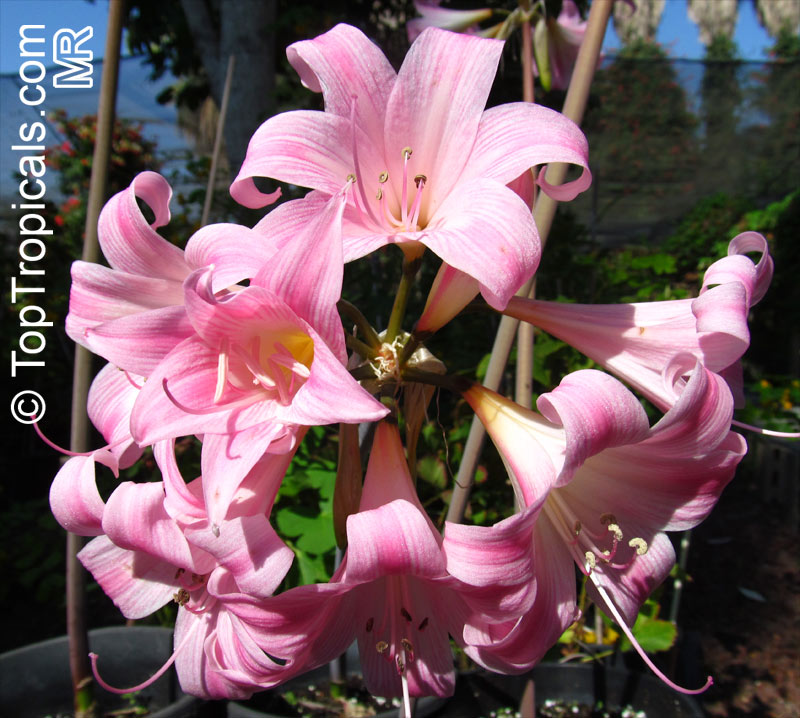
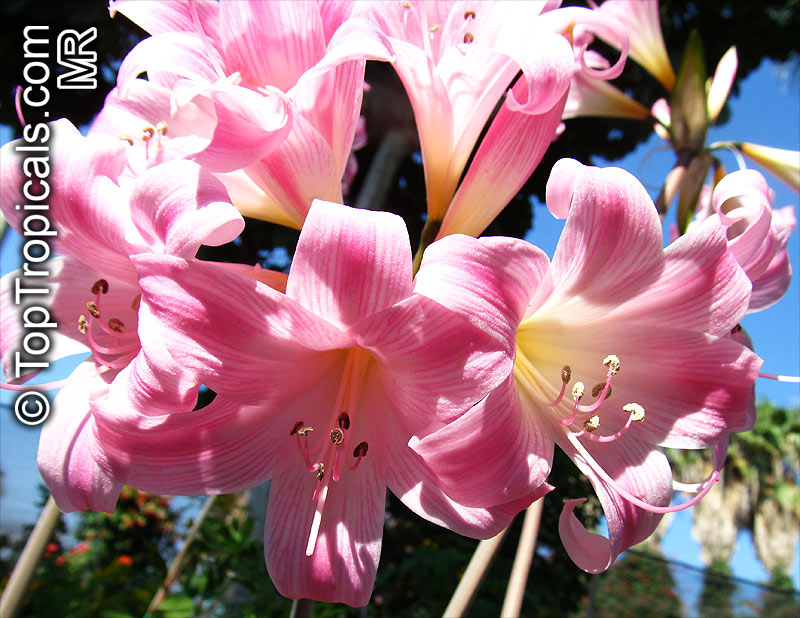
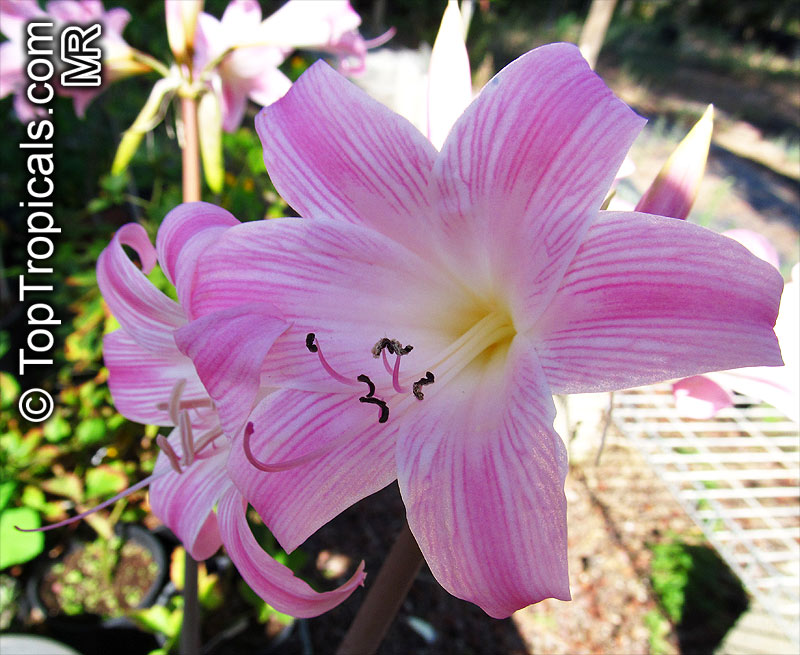
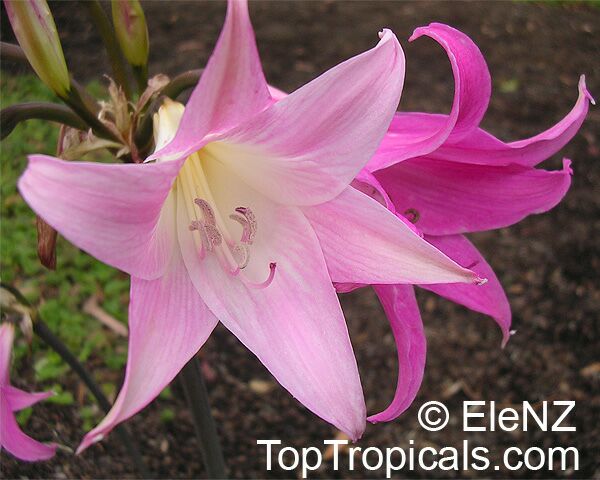
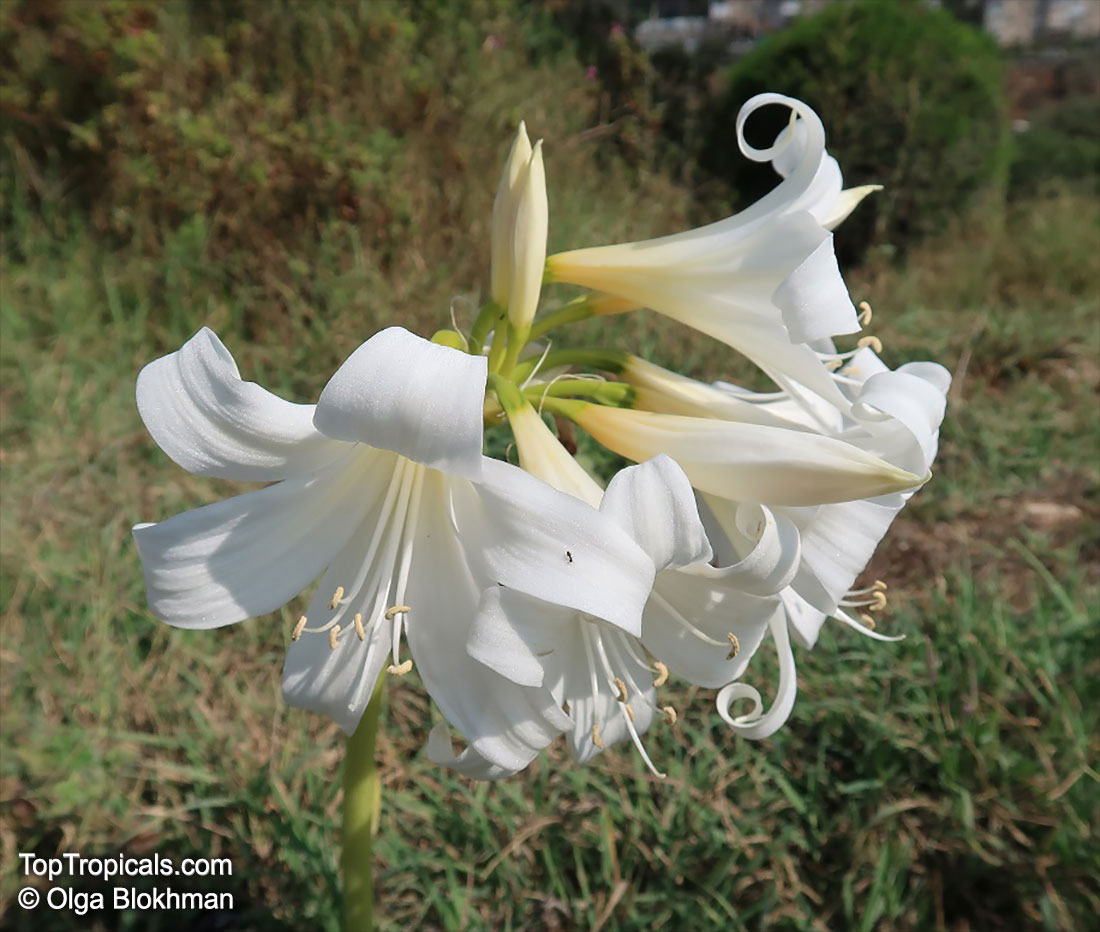
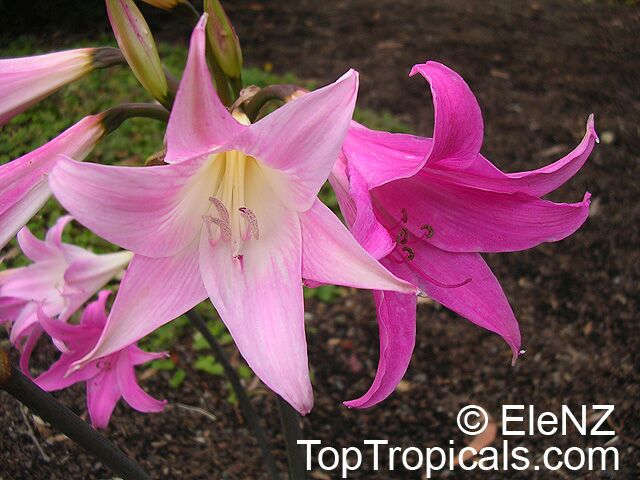
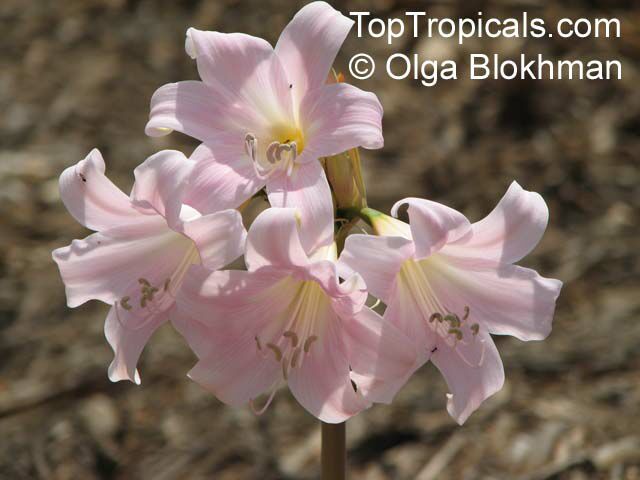
Botanical names: Amaryllis belladonna, Callicore rosea
Common names: Belladonna Lily, March Lily, Naked Lady
Family: Amaryllidaceae (Formerly:Amaryllidaceae / Liliaceae)
Subfamily: Amaryllidoideae
Origin: South Africa









The large clusters of scented, trumpet-shaped pink or white flowers are carried on a long purplish-red and green stem appearing 50cm above the soil. Up to twelve flowers are produced from the flowering stem. These flowers are 10cm long and apically flare open about 8cm. The inflorescence tends to face the direction that receives the most sun.
The strap-like leaves are deciduous and are produced after flowering.
| Next |  |
Use link to repeat this search:
https://toptropicals.com/cgi-bin/garden_catalog/cat.cgi?search_op=and&keyword_op=and&language=e&family=Amaryllidaceae
&number=10&no_change_lang=1&user=tt&sale=1&first=0

























































































































































