Mimosa - Plant Encyclopedia Results
| Number of plants found: 20 | Next | 
|
Go to page: | 1 | 2 |
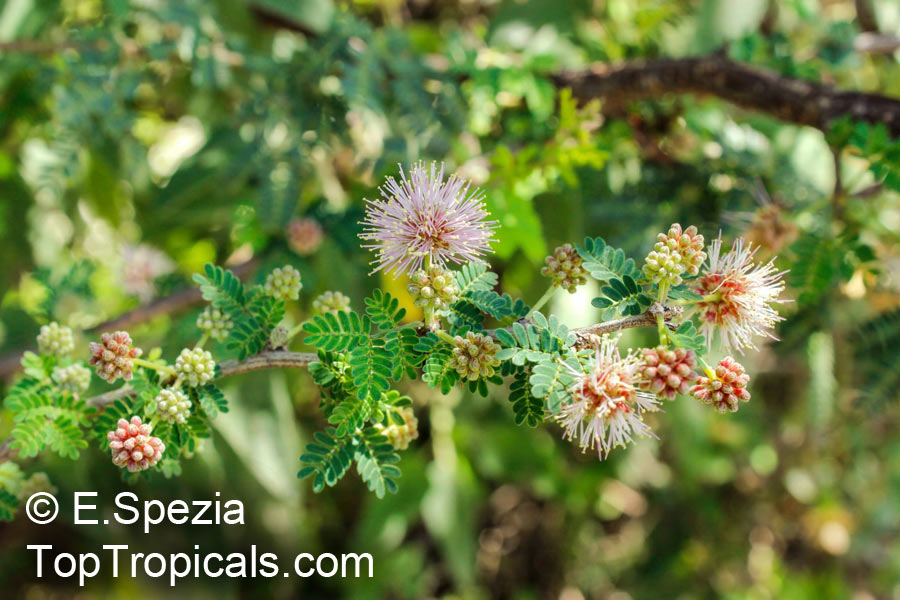
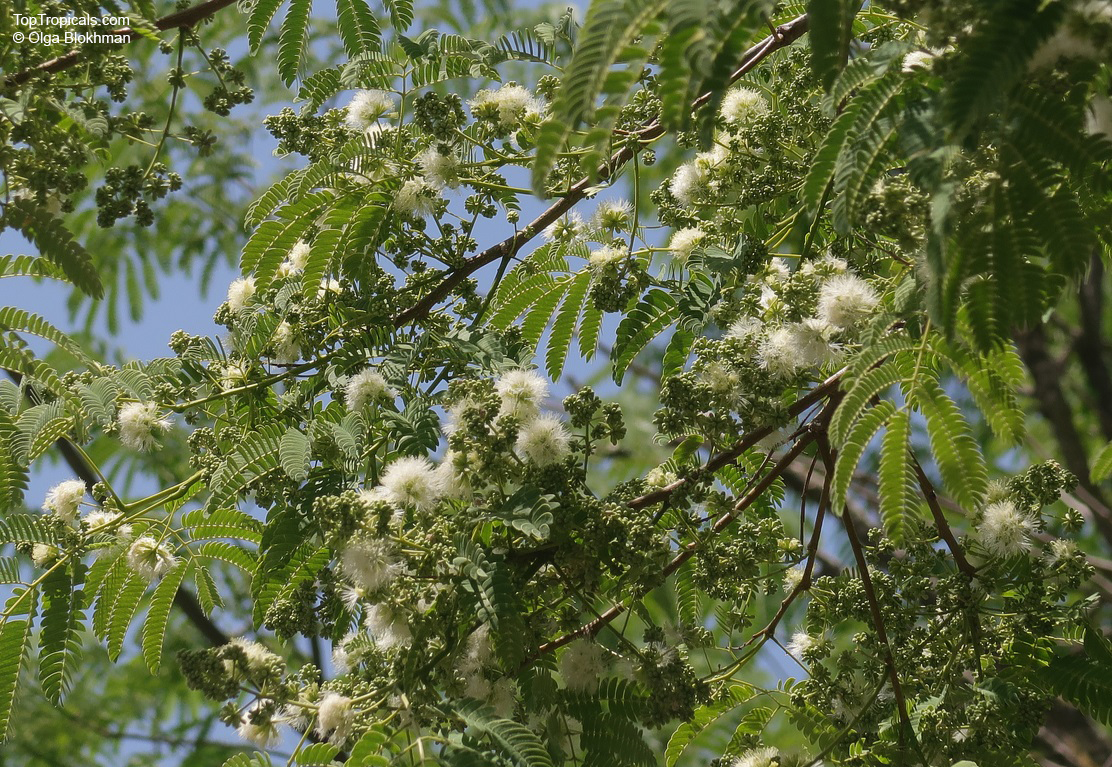
Botanical name: Mimosa borealis
Common names: Fragrant Mimosa, Pink Mimosa
Family: Fabaceae
Subfamily: Mimosoideae
Origin: Mexico









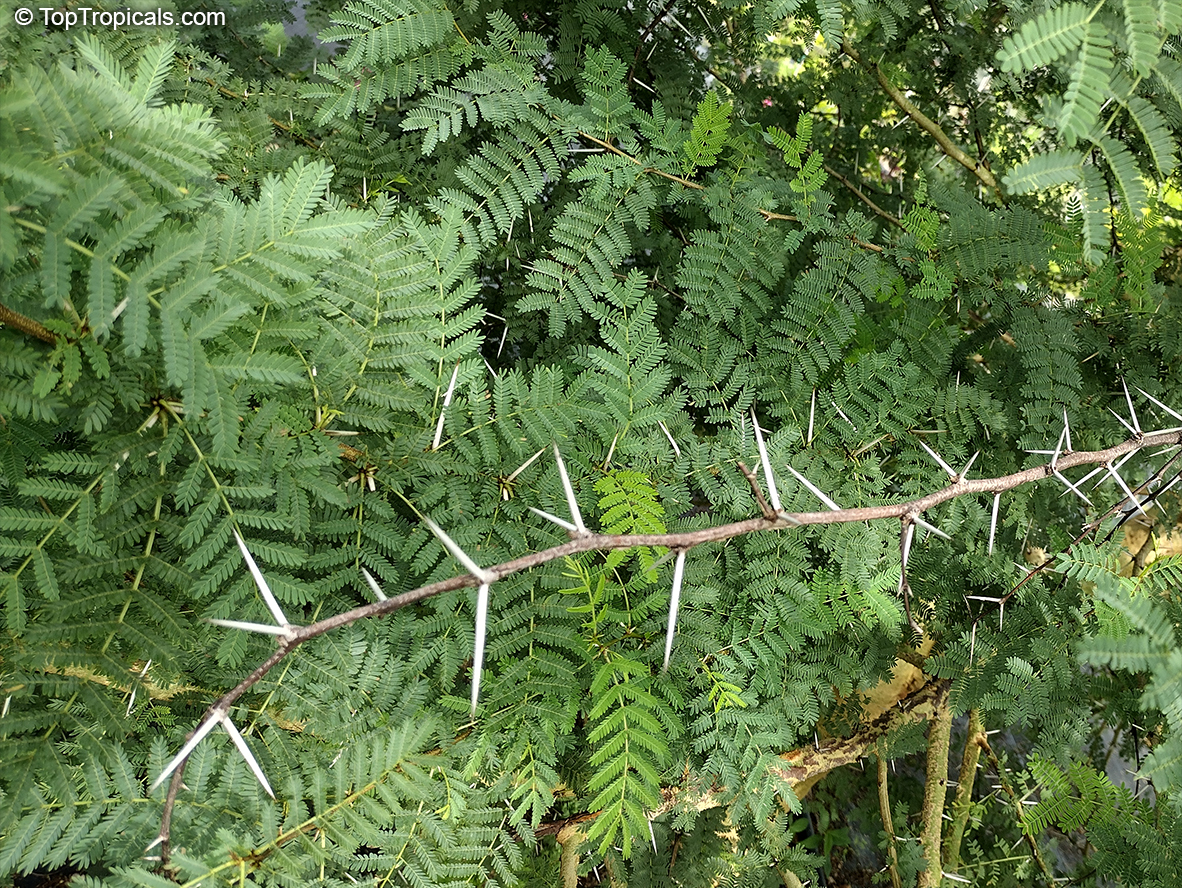
Fragrant Mimosa is a deciduous, small shrub, 3 by 3 feet, with somewhat zigzag, rigid branches with small, delicate pinnately compound leaves. The soft pink puffballs are a contrast to the sneaky, strongly recurved thorns up and down the branches.
An excellent plant for a xeriscape garden, Fragrant Mimosa can be planted in a garden with a desert theme, in rocky, sunny areas or as a backdrop. It will also tolerate partial shade. It makes a great background shrub.
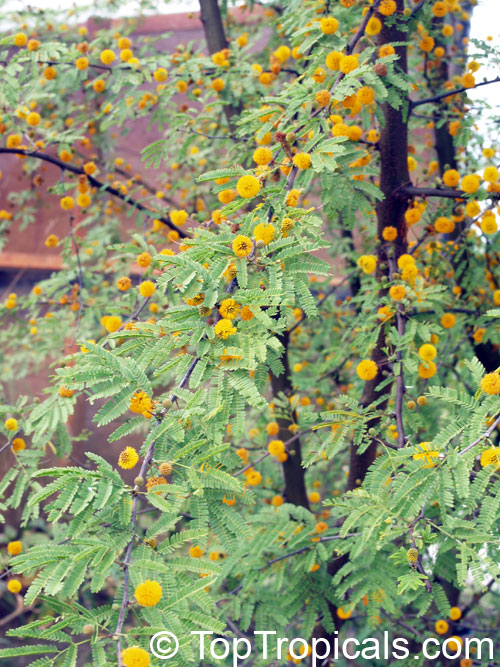
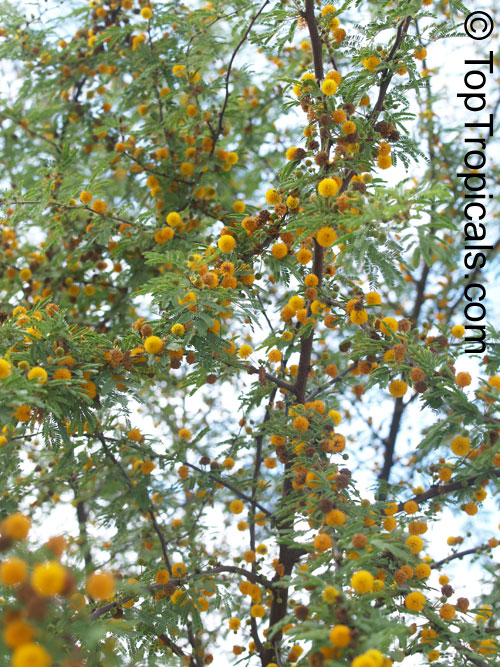
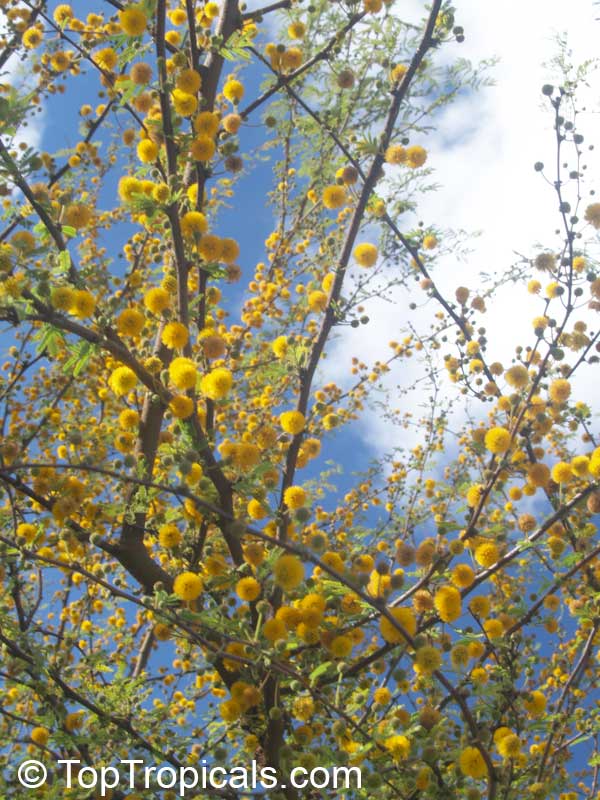
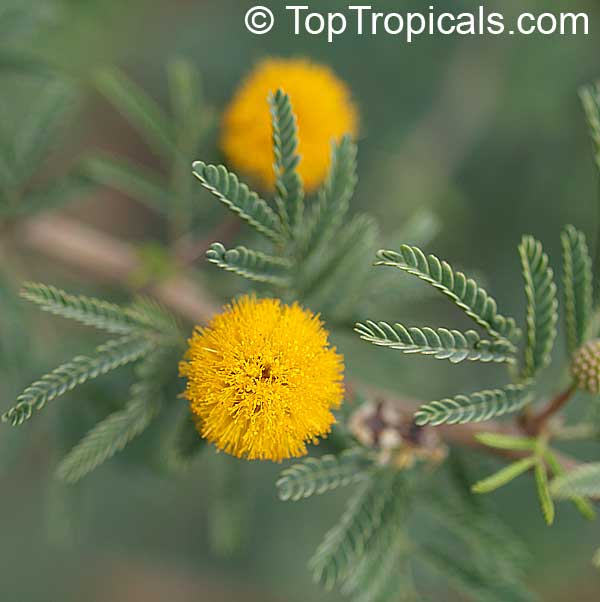
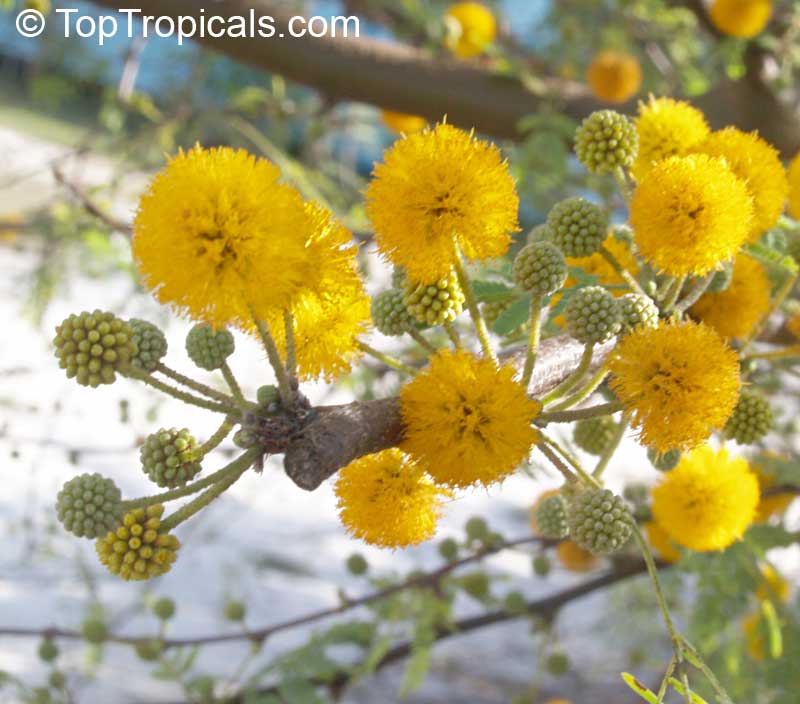
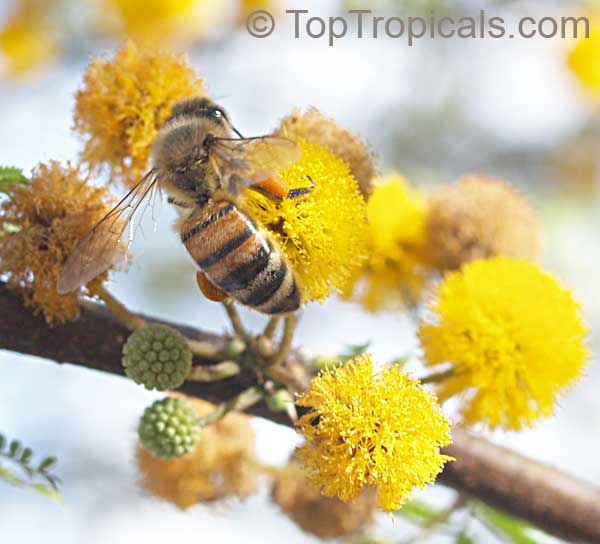
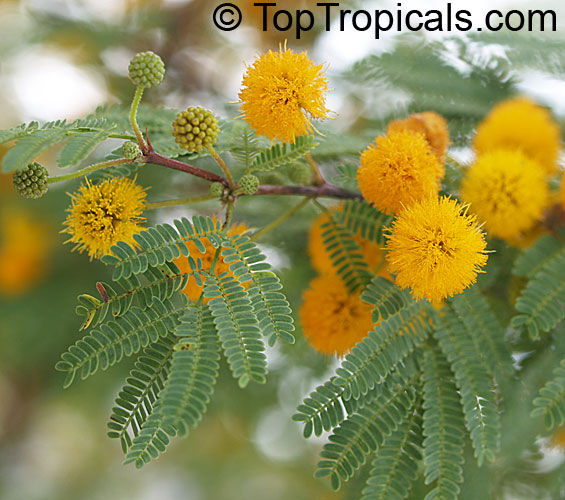
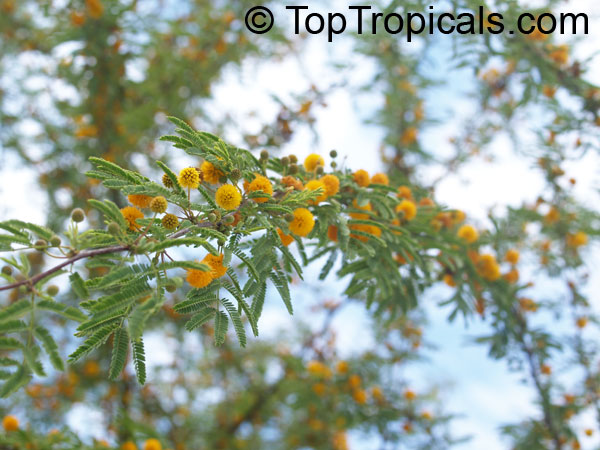
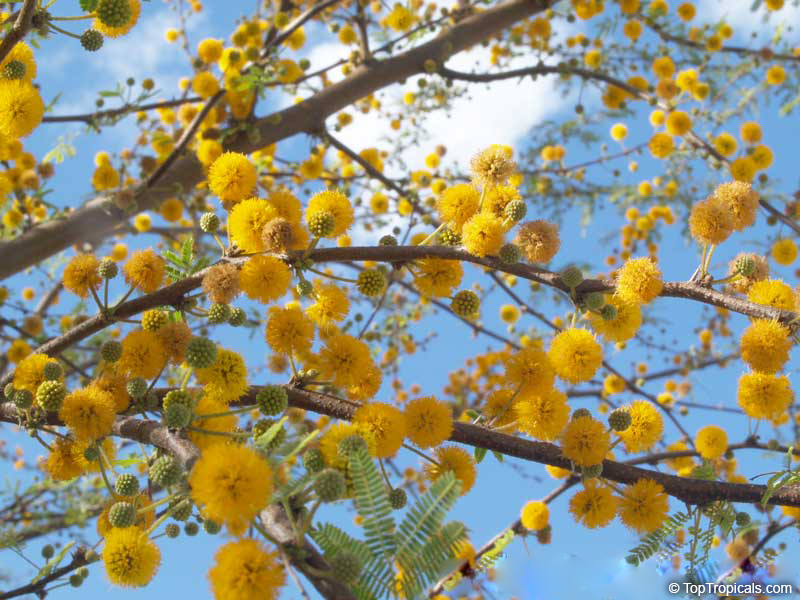
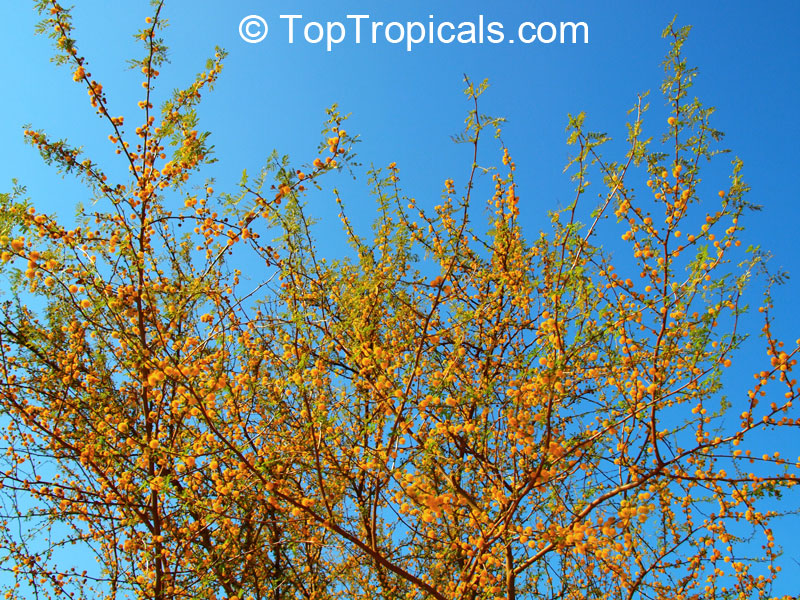
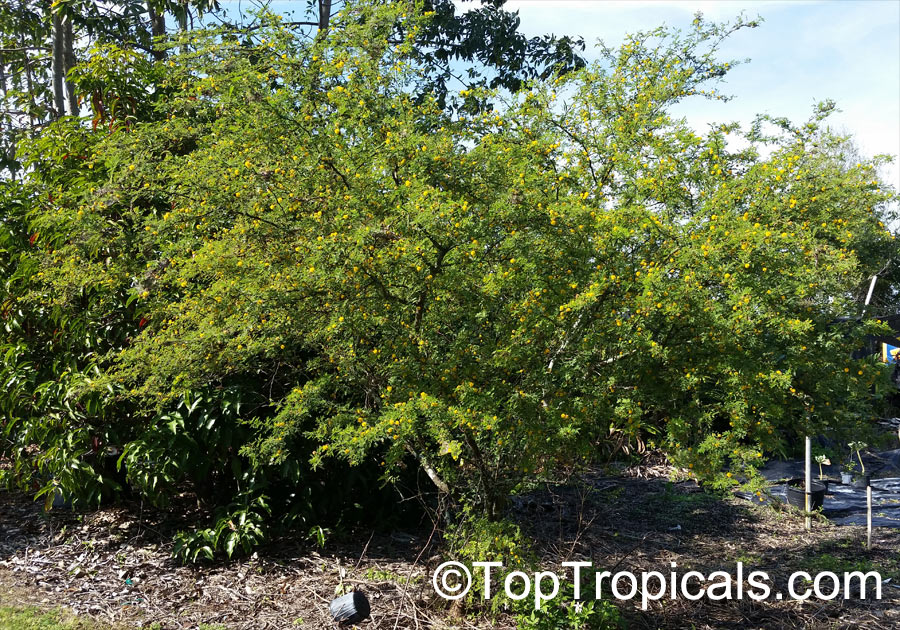
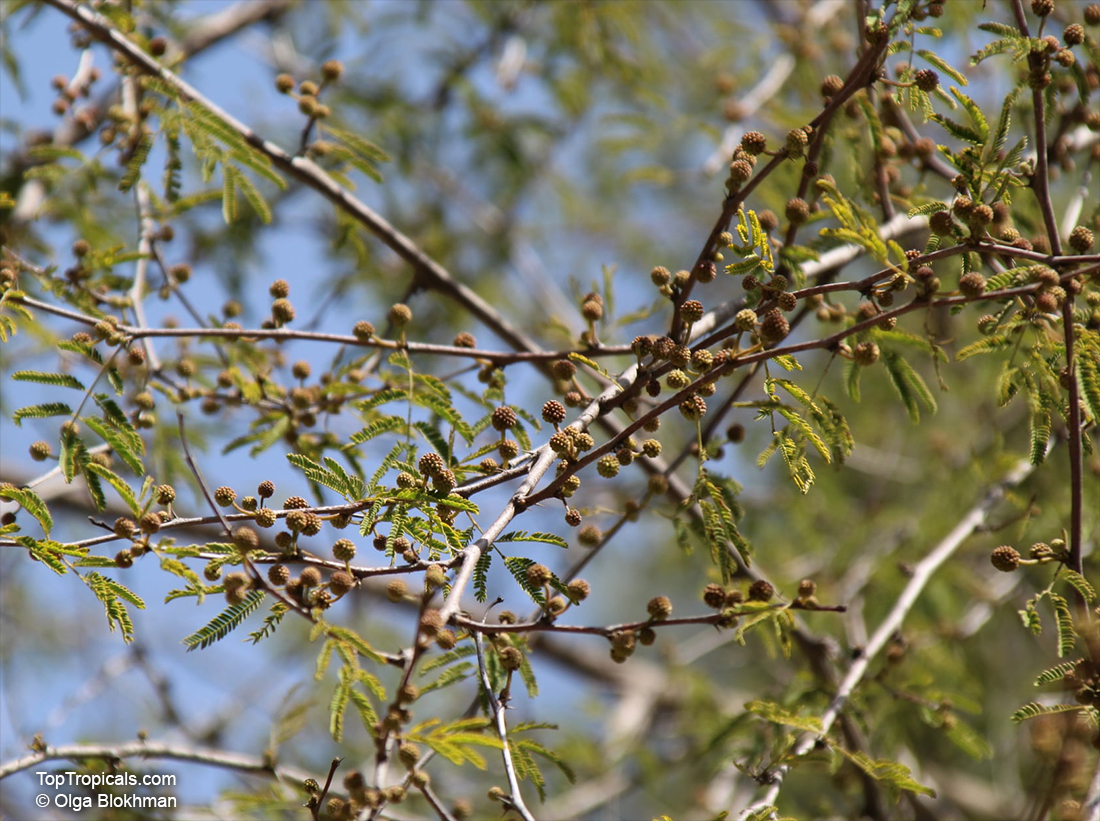
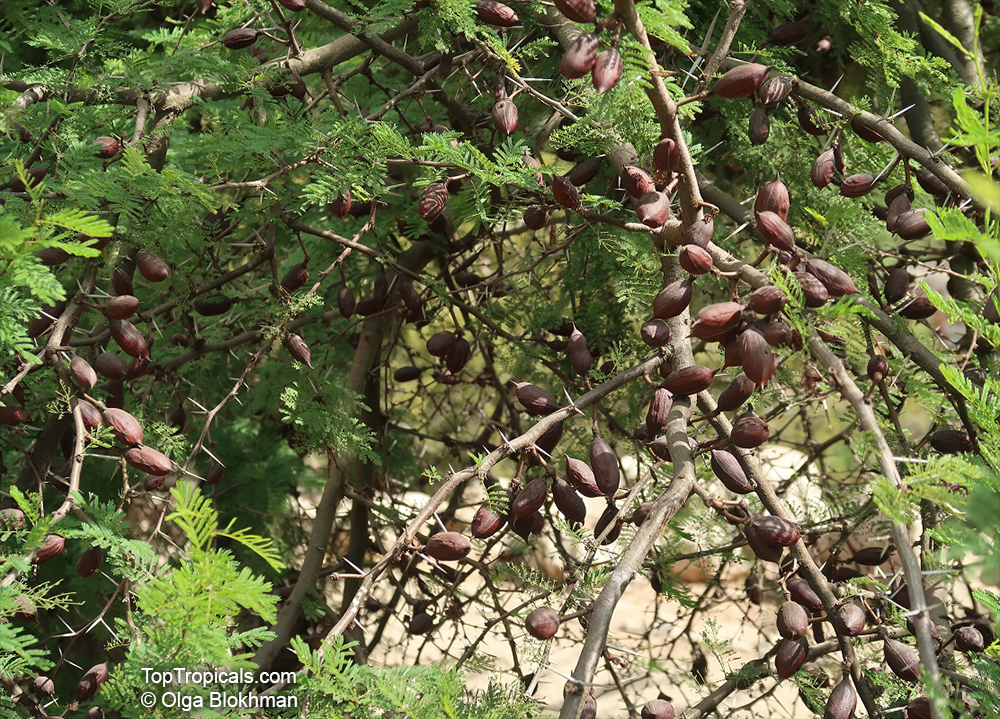
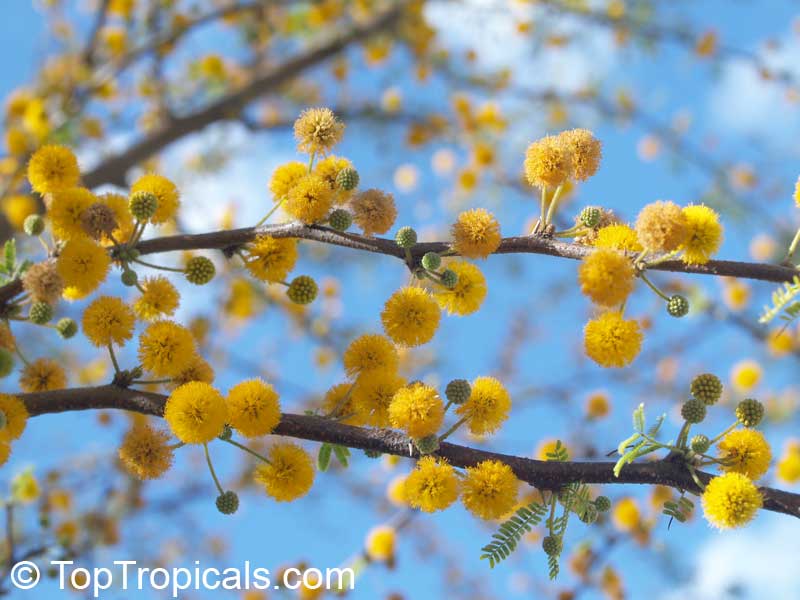
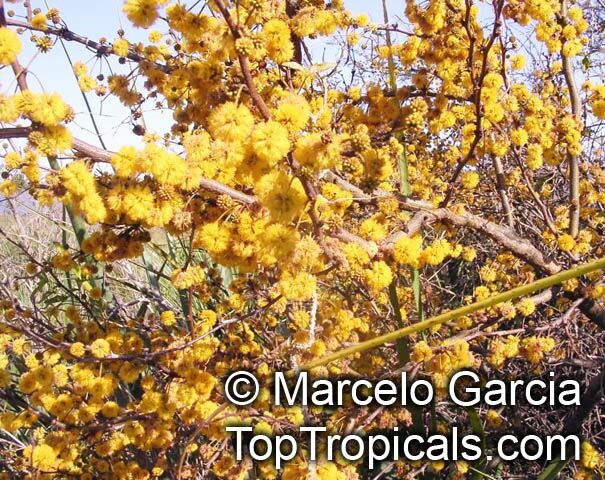
Botanical names: Vachellia farnesiana, Acacia farnesiana, Mimosa farnesiana
Common names: Yellow Mimosa, Sweet Wattle
Family: Fabaceae
Subfamily: Mimosoideae
Origin: Tropical America










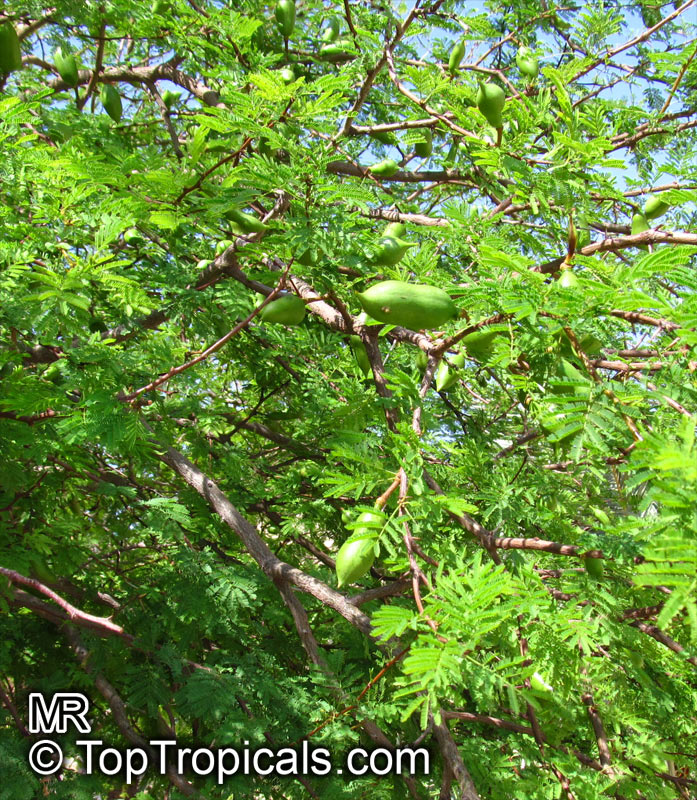
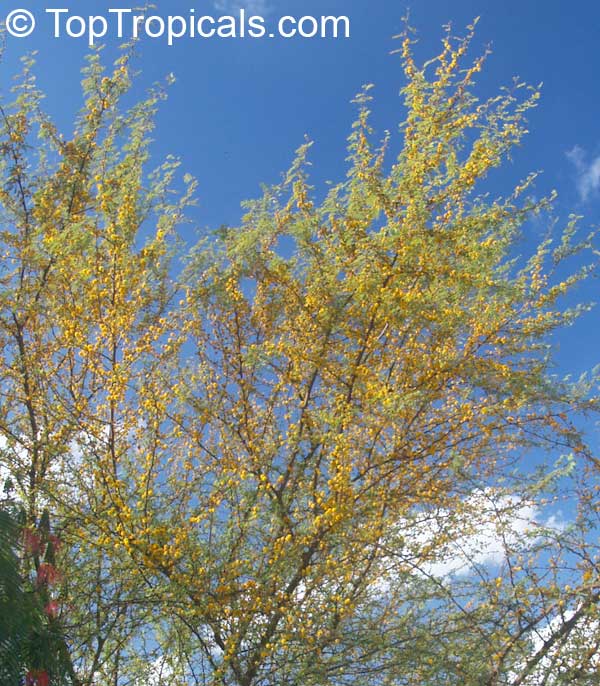
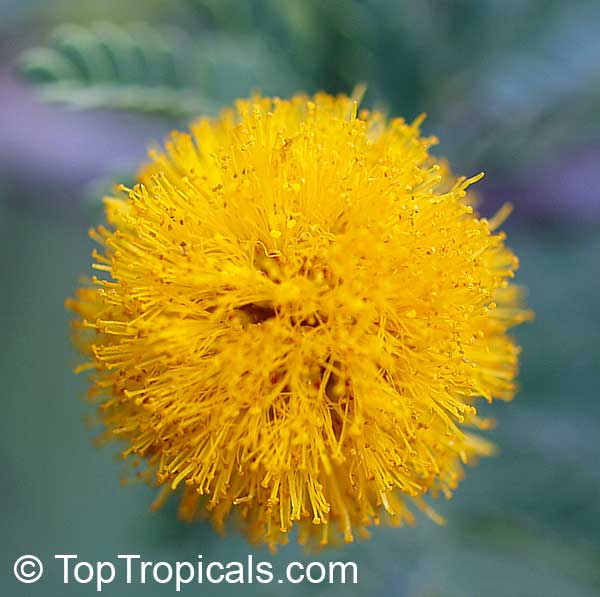
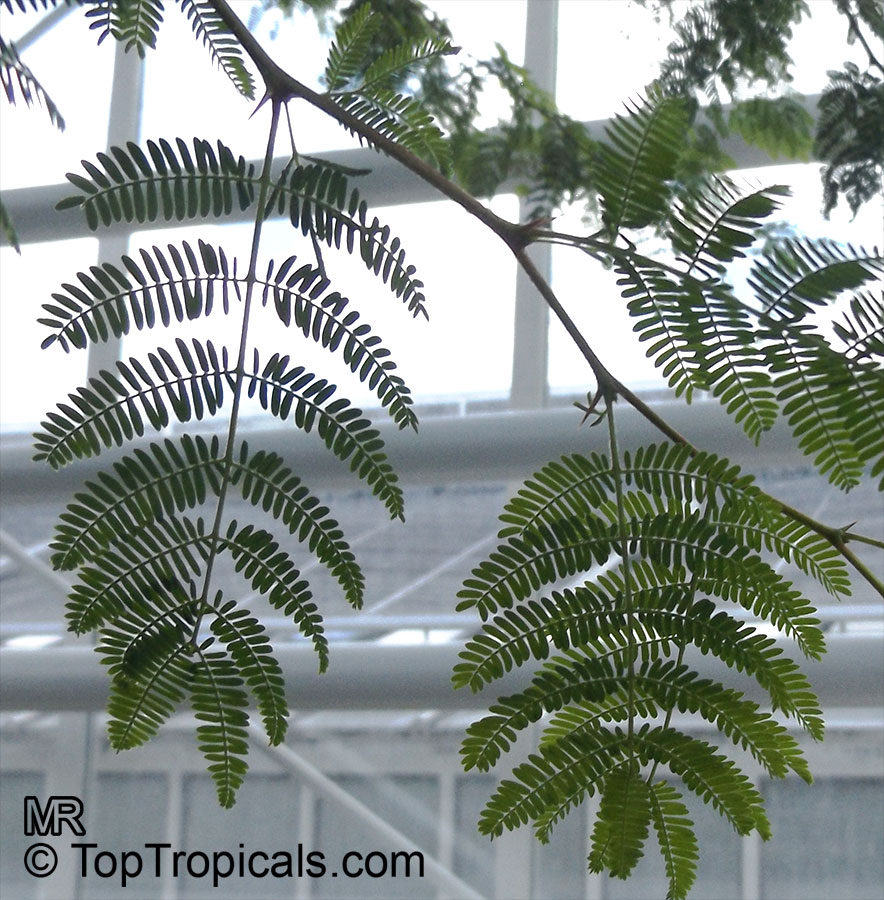
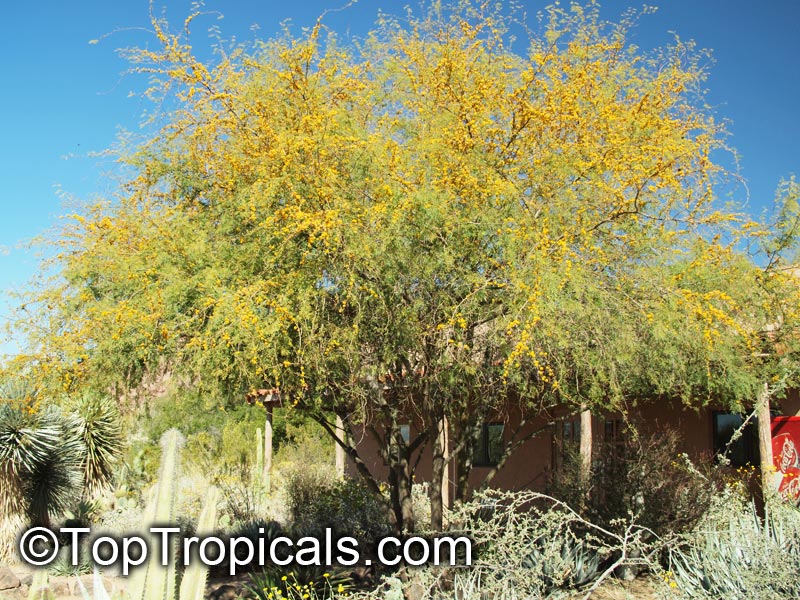
Vachellia farnesiana, also known as the Yellow Mimosa, is a beautiful large shrub or small tree native to Tropical America. It reaches a height of 5-10 ft when grown as a shrub, and 10-20 when grown as a small tree. Vachellia farnesiana grows best in full sun to semi-shade areas with moderate water. This plant is a favorite of butterflies and hummingbirds due to its vibrant, yellow and orange flowers that are also sweetly fragrant. The puffs of yellow flowers give Vachellia farnesiana a beautiful look, while they also make it an ideal accent or specimen plant.
This plant can be grown in a pot in cold regions if kept like houseplants, as it is hardy in USDA Zone 8-11. It is a surprisingly tough plant and can withstand even quite cold temperatures for short periods of time, being mature plant cold hardy at least to 30s F. It is also pretty salt tolerant, making it a great option for seaside locations.
When growing Vachellia farnesiana, the soil should be well-drained and should be fertilized regularly. This bushy shrub can reach a height of 5-10 ft when grown as a shrub, and 10-20 ft when grown as a small tree. Pruning regularly and training it while young would be beneficial as it will help produce more flowers. When grown as a shrub, it should be pruned heavily at around 3-4 ft to promote branching and flowering.
To ensure a healthy plant, water it regularly and do not let it dry out too much. Mulching is also important to protect the plant from extreme temperatures and to prevent water evaporation from the soil. It is also essential to watch out for pests and weeds, and to be mindful of the quantity of water and fertilizer that is used to prevent any burn or damage to the roots.
Ordering seeds info
RECOMMENDED SUPPLIES:
Seed Germination Mix #3, professional grade
SUNSHINE-Epi - Seeds and cuttings booster
SUNSHINE Bombino - Young Plant Booster
Botanical name: Mimosa albida
Common name: Mimosa
Family: Fabaceae
Subfamily: Mimosoideae
Origin: Tropical America







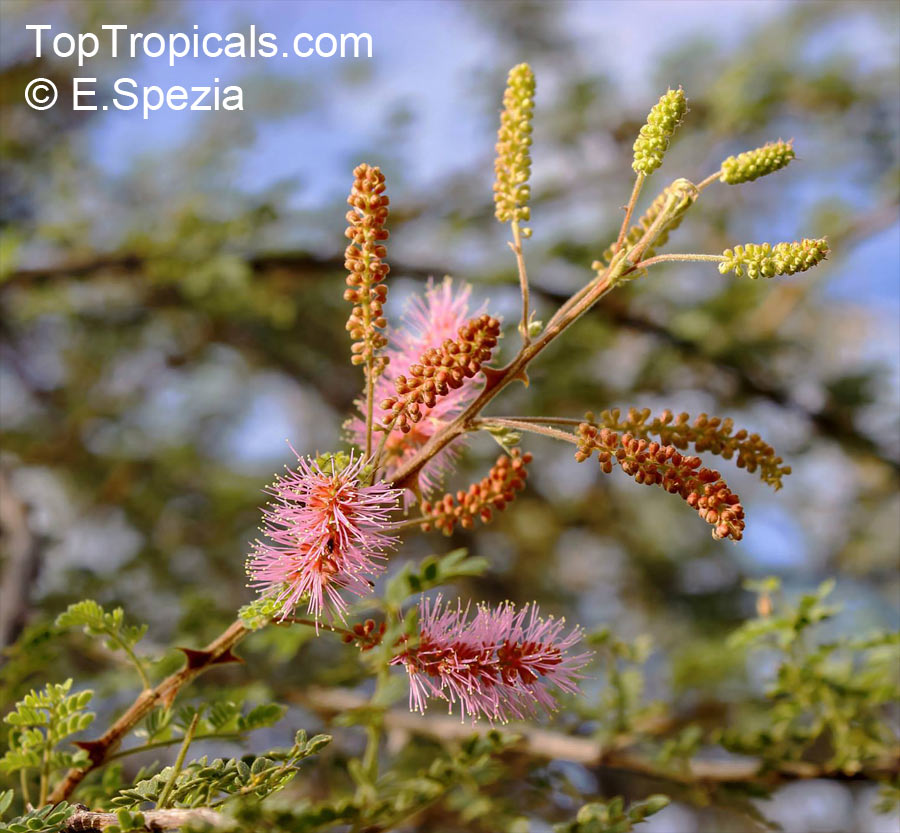
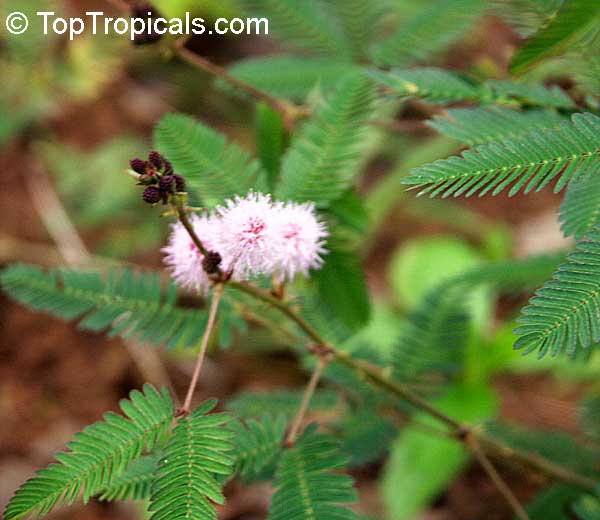
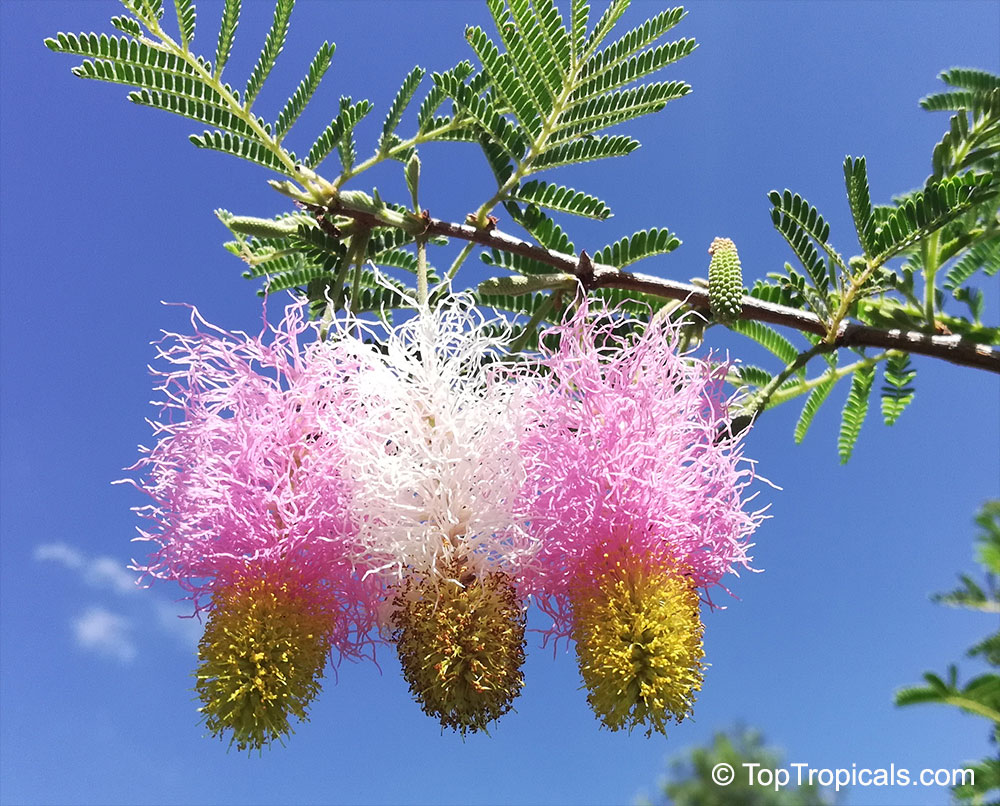
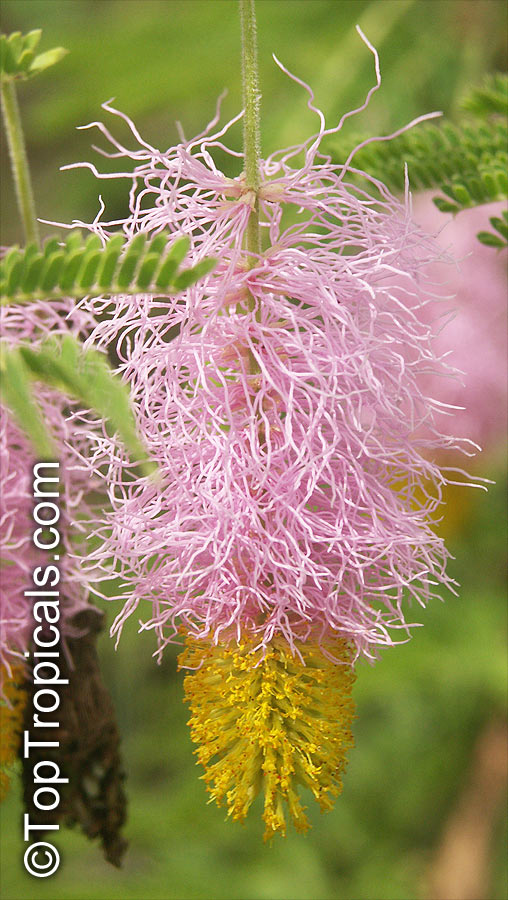
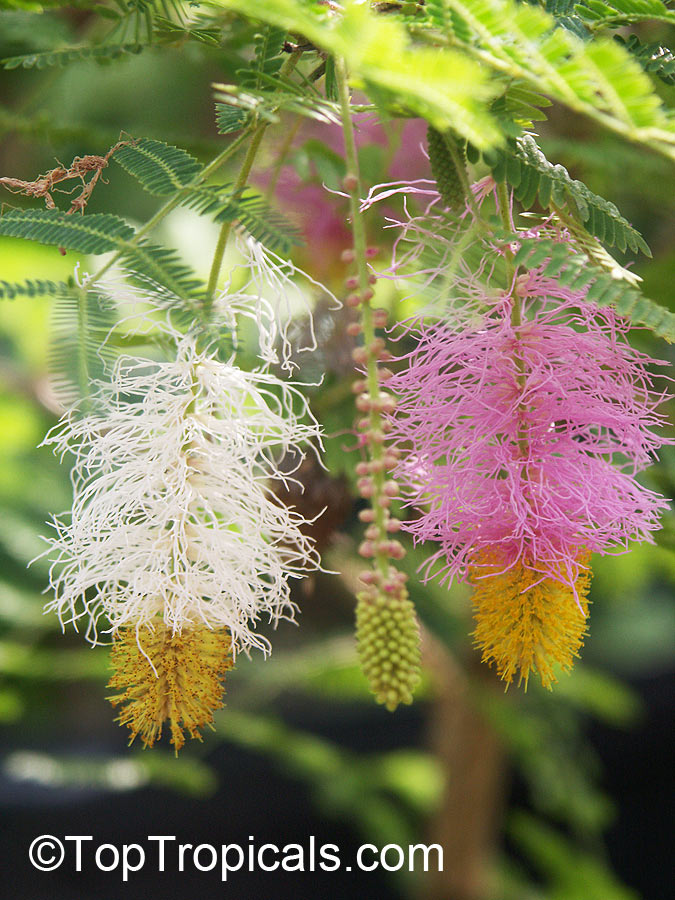
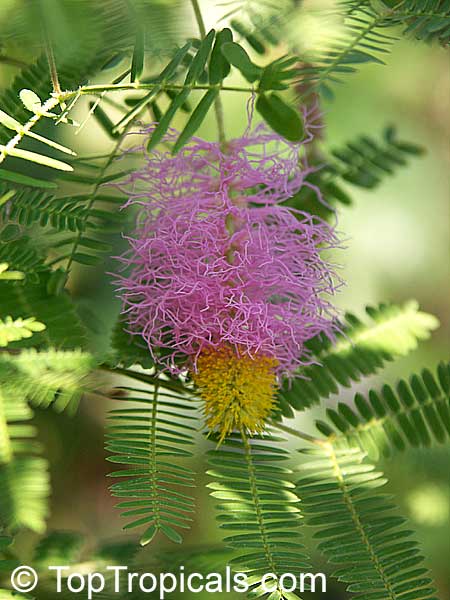
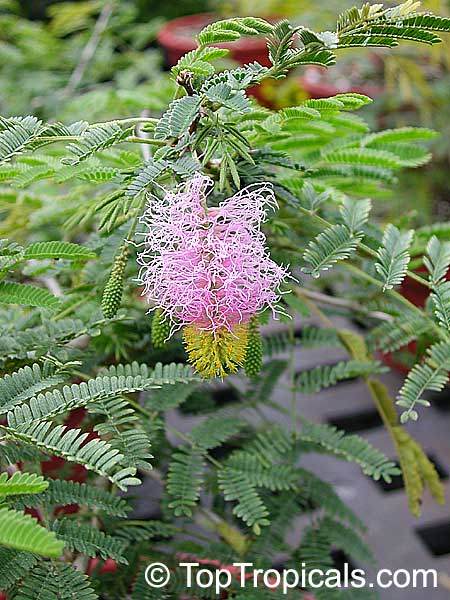
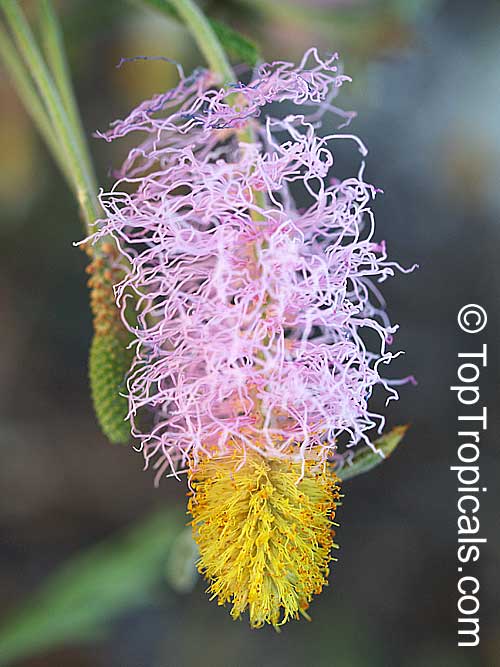
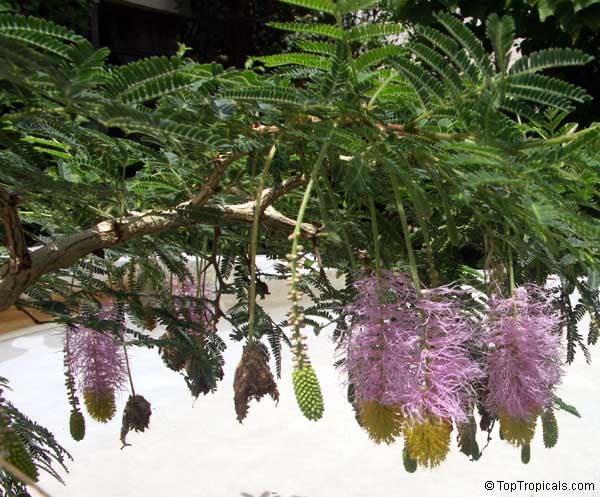
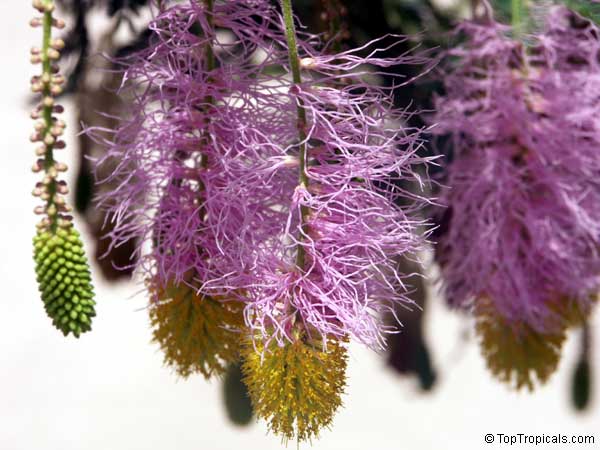
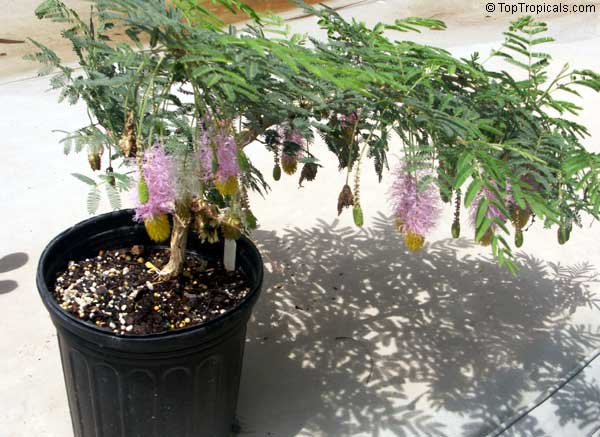
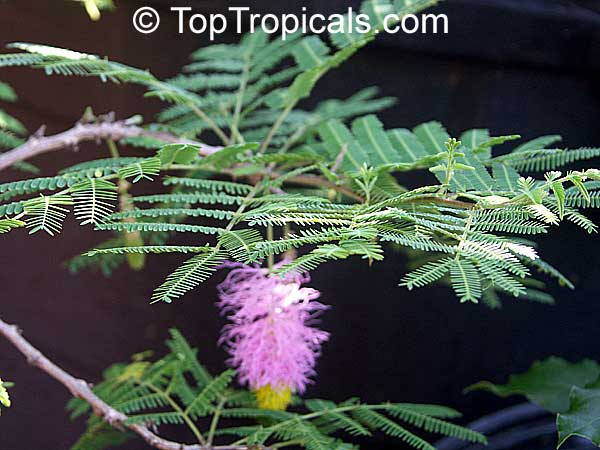
Botanical name: Mimosa dysocarpa
Common names: Velvet Pod Mimosa, Gatuno, Velvetpod Catclaw
Family: Fabaceae
Subfamily: Mimosoideae
Origin: Mexico








Numerous short, widely divergent, irregular but densely prickly branches bear pubescent (downy) bipinnate leaves and extremely showy, fragrant, pinkish-purple cylindrical flower spikes.
This plant is extremely drought tolerant and can take reflected heat.
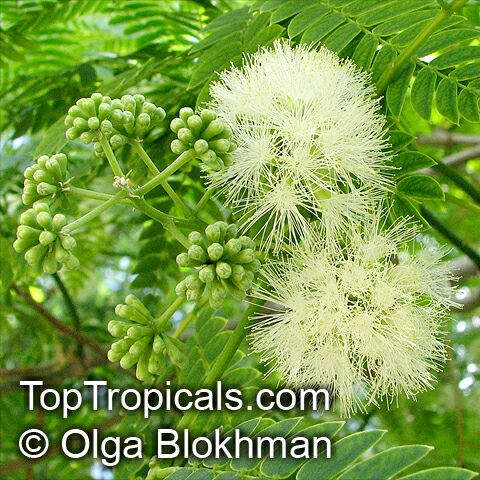
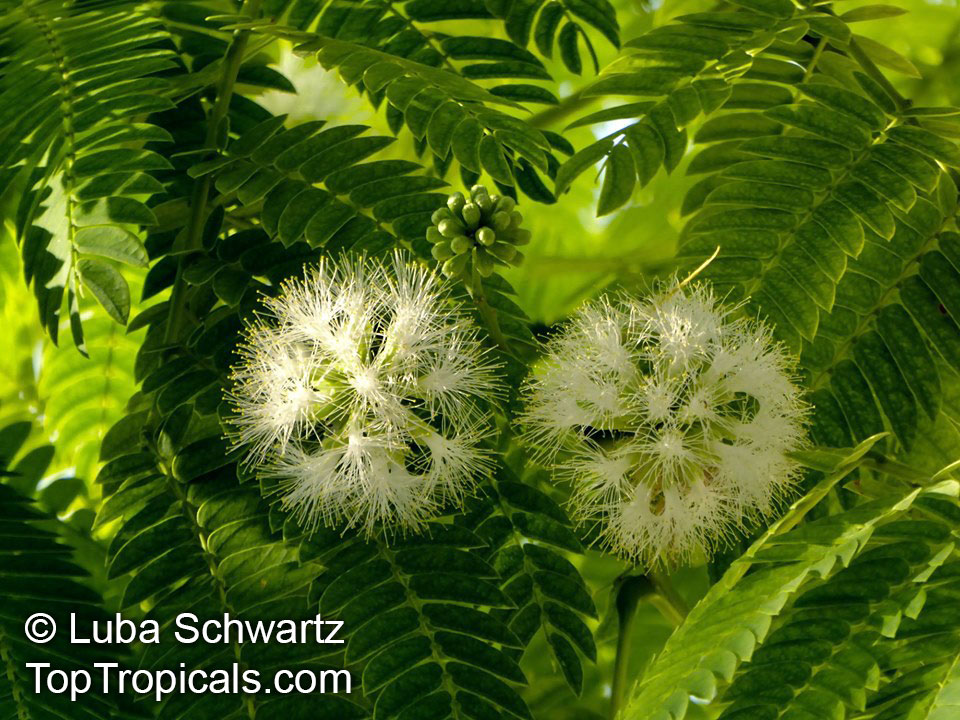
Botanical names: Albizia lebbeck, Mimosa lebbeck
Common names: Womans tongue, Siris-tree, Rain tree, East Indian walnut, Kokko, Soros-tree, Raom tree
Family: Fabaceae
Subfamily: Mimosoideae
Origin: India, Burma and the Andaman Island
Hardiness: 30°F







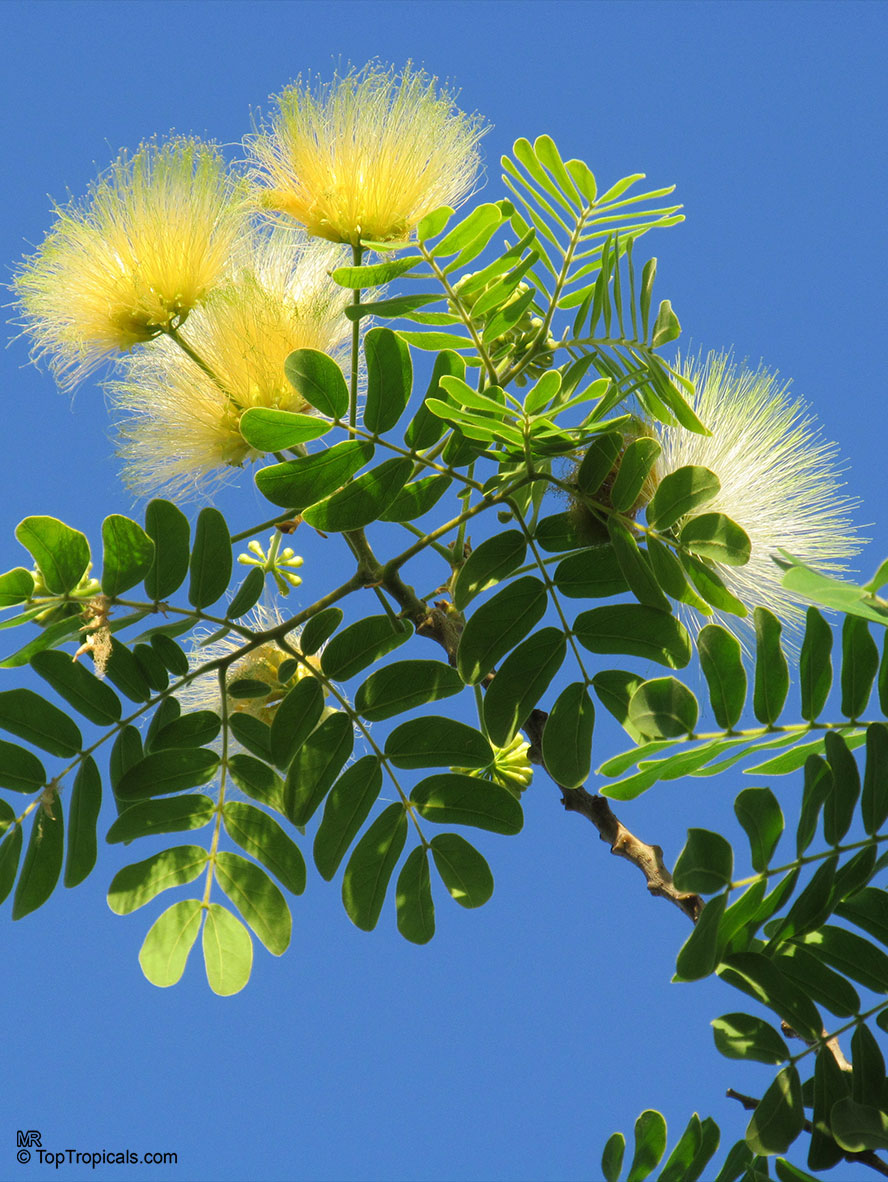
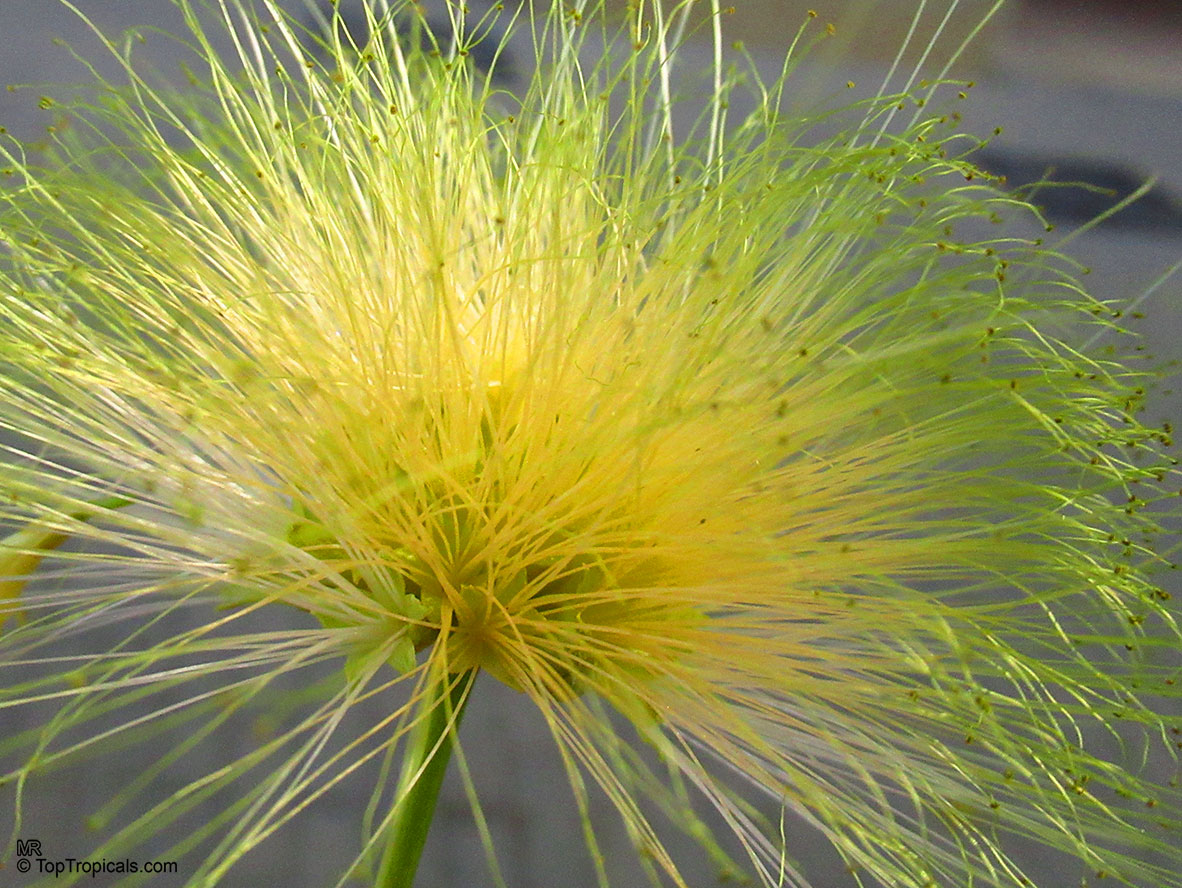
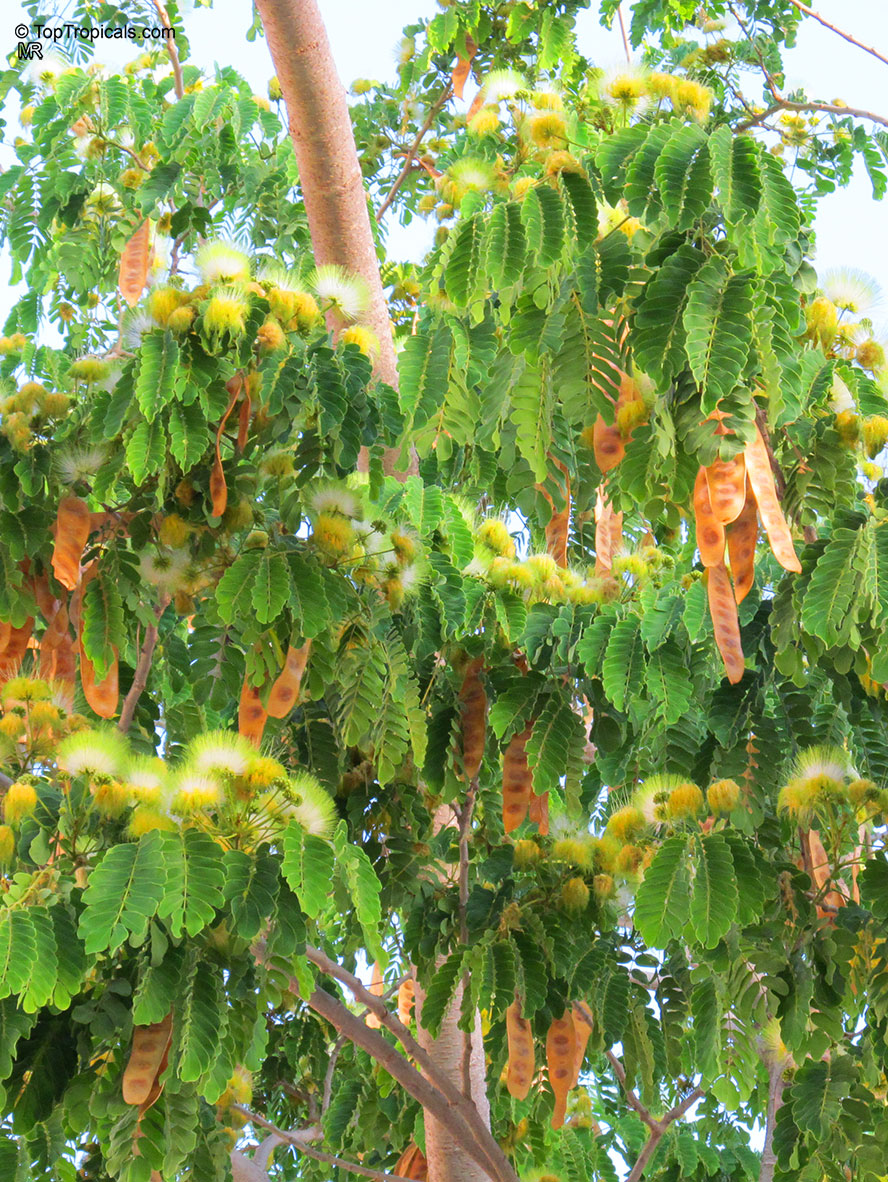
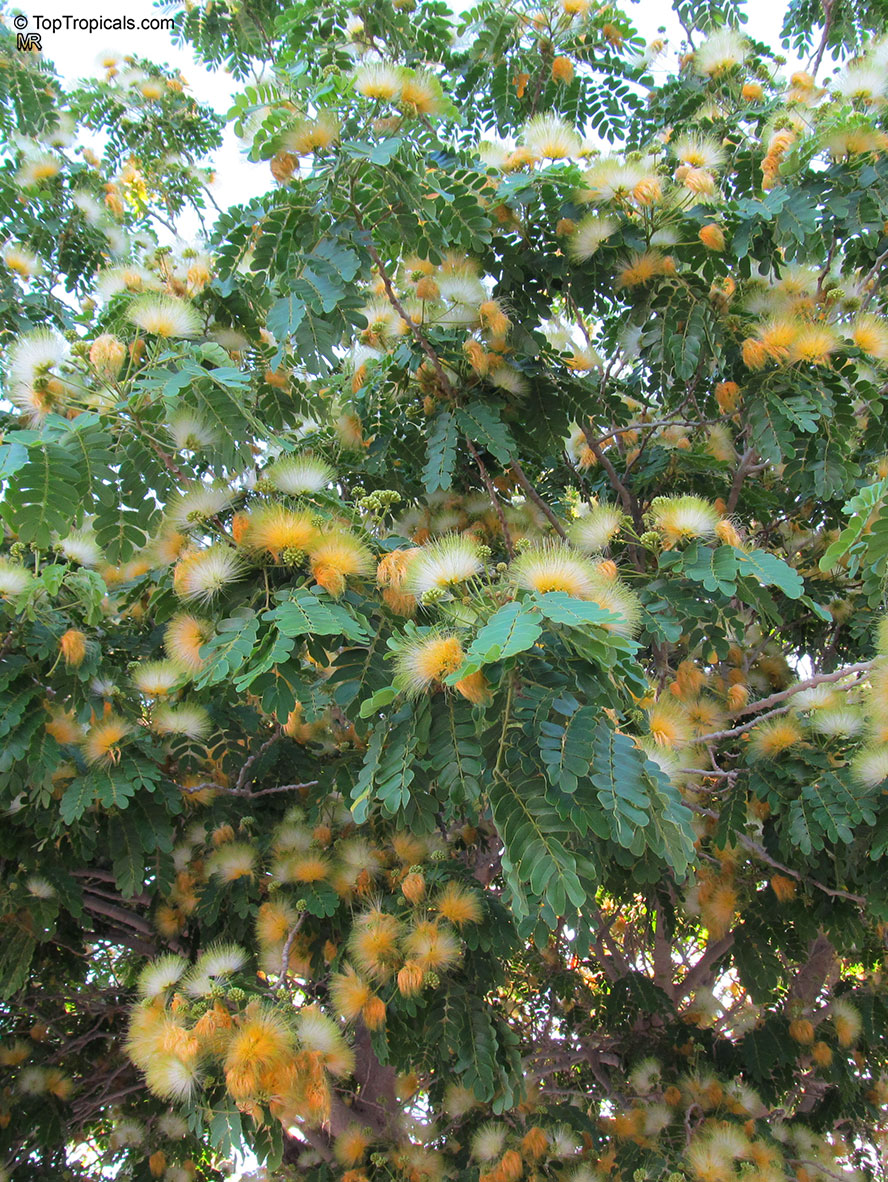
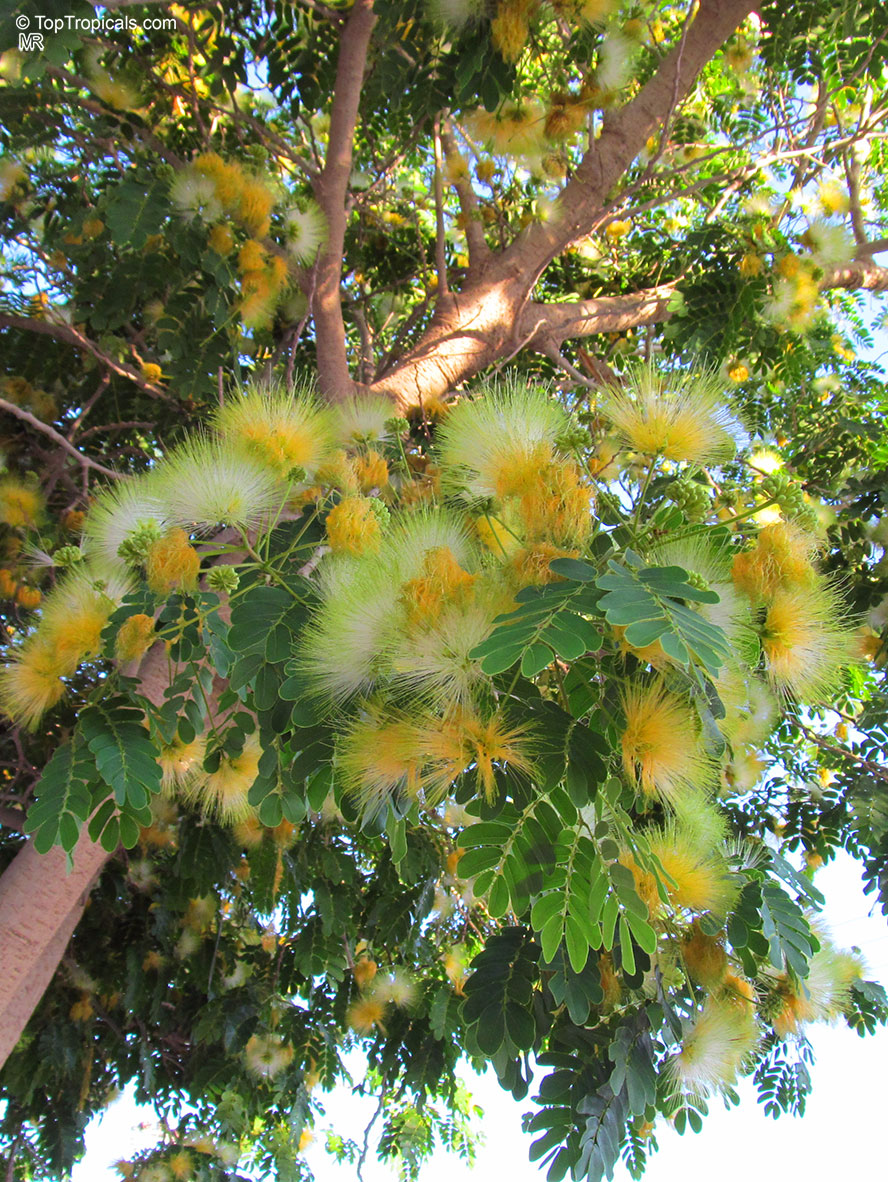
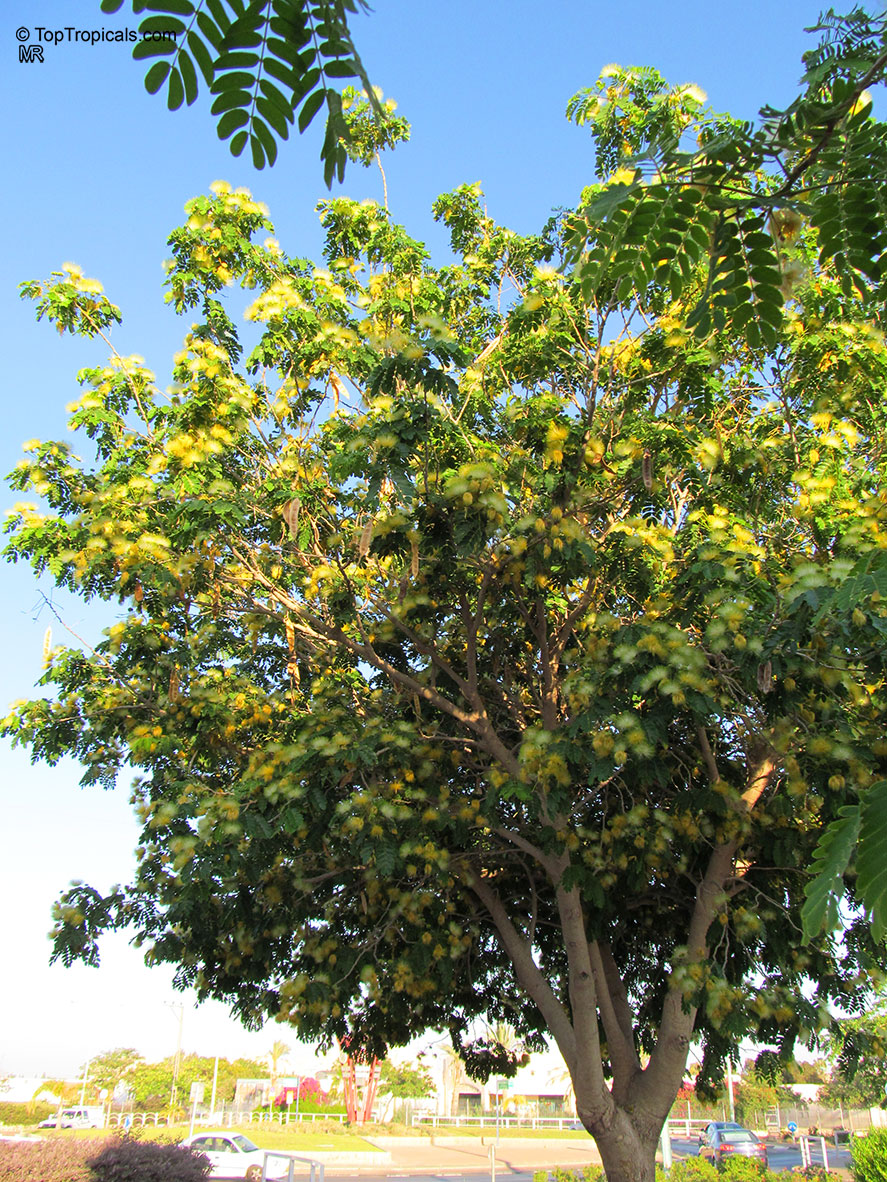
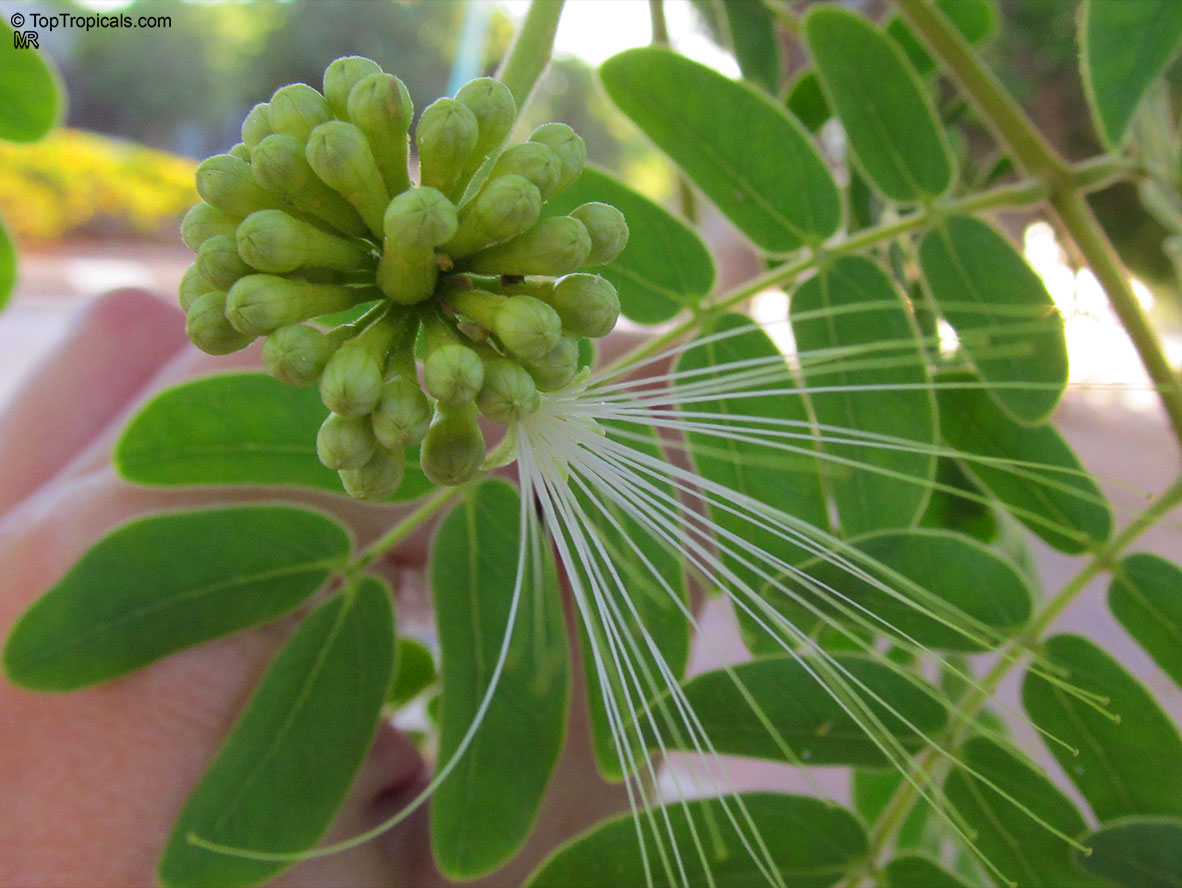
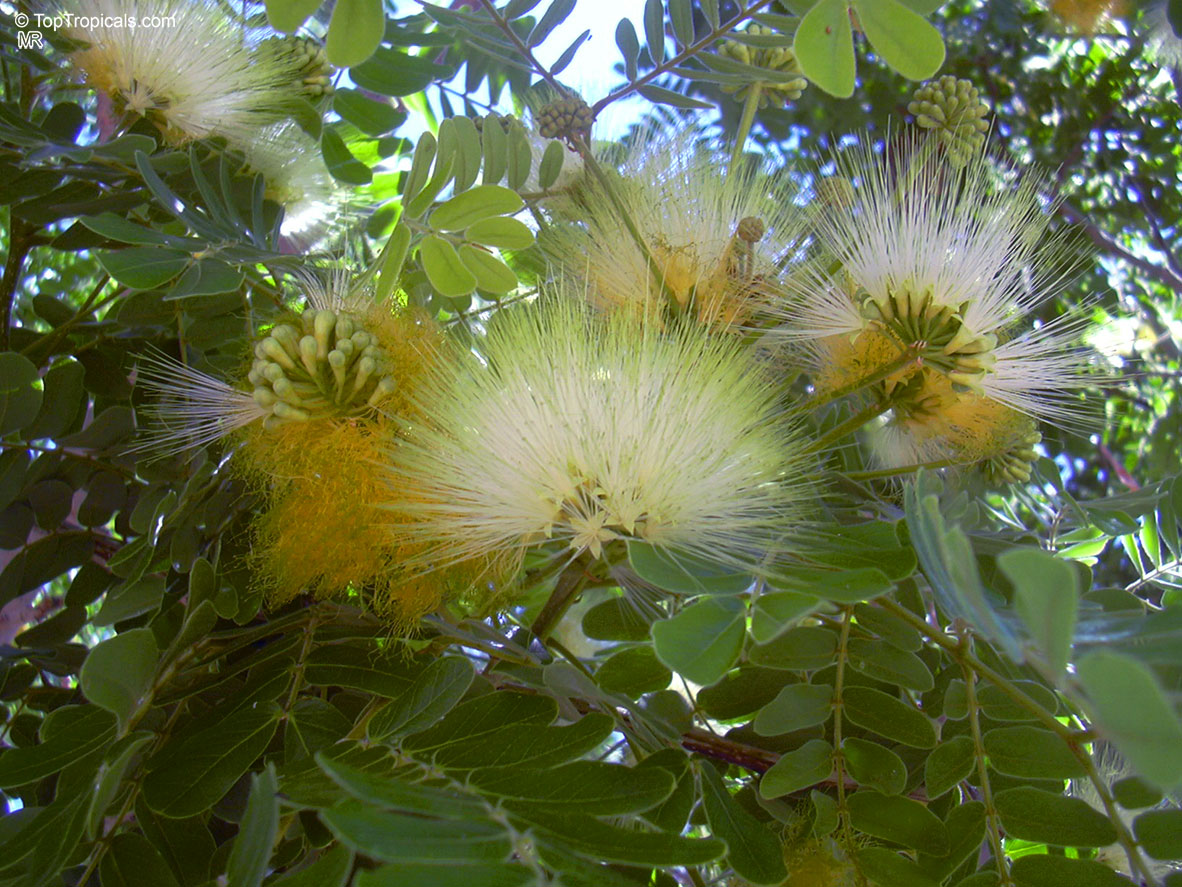
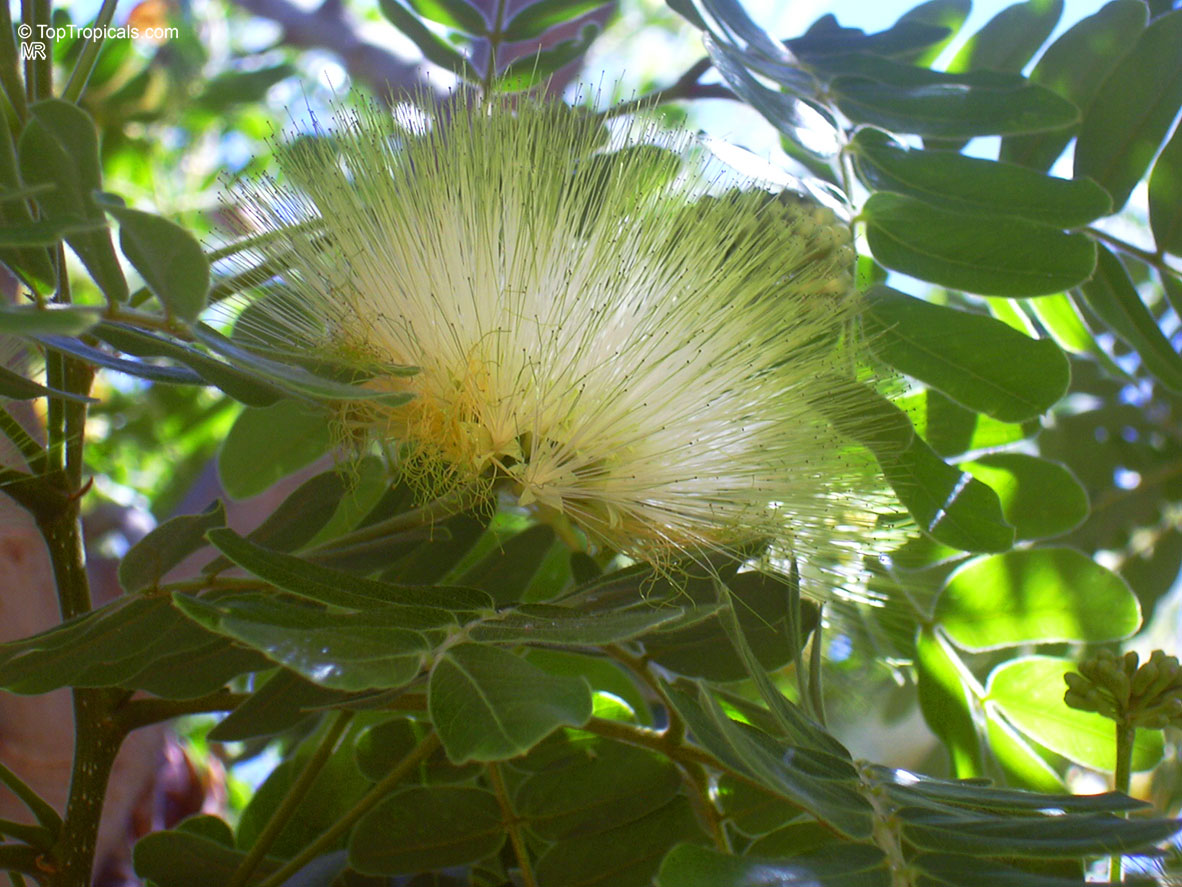
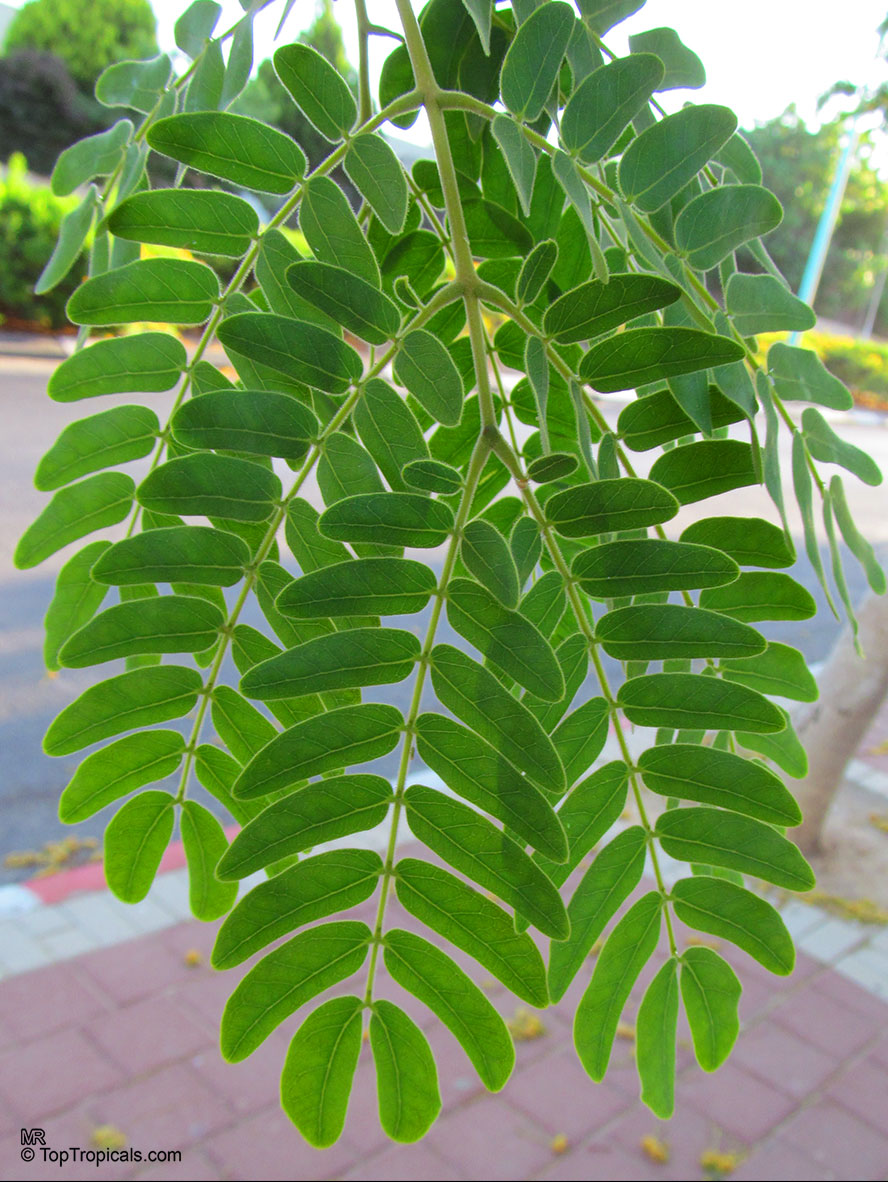
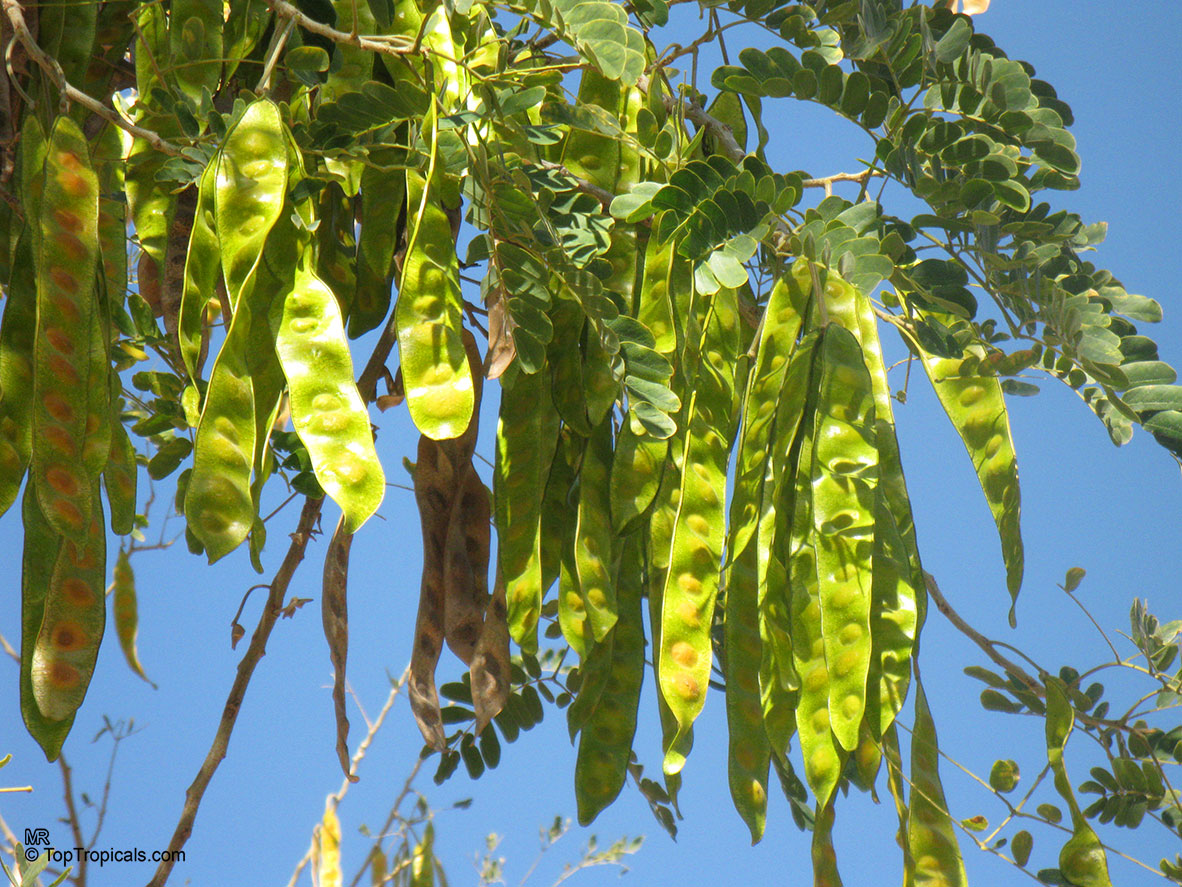
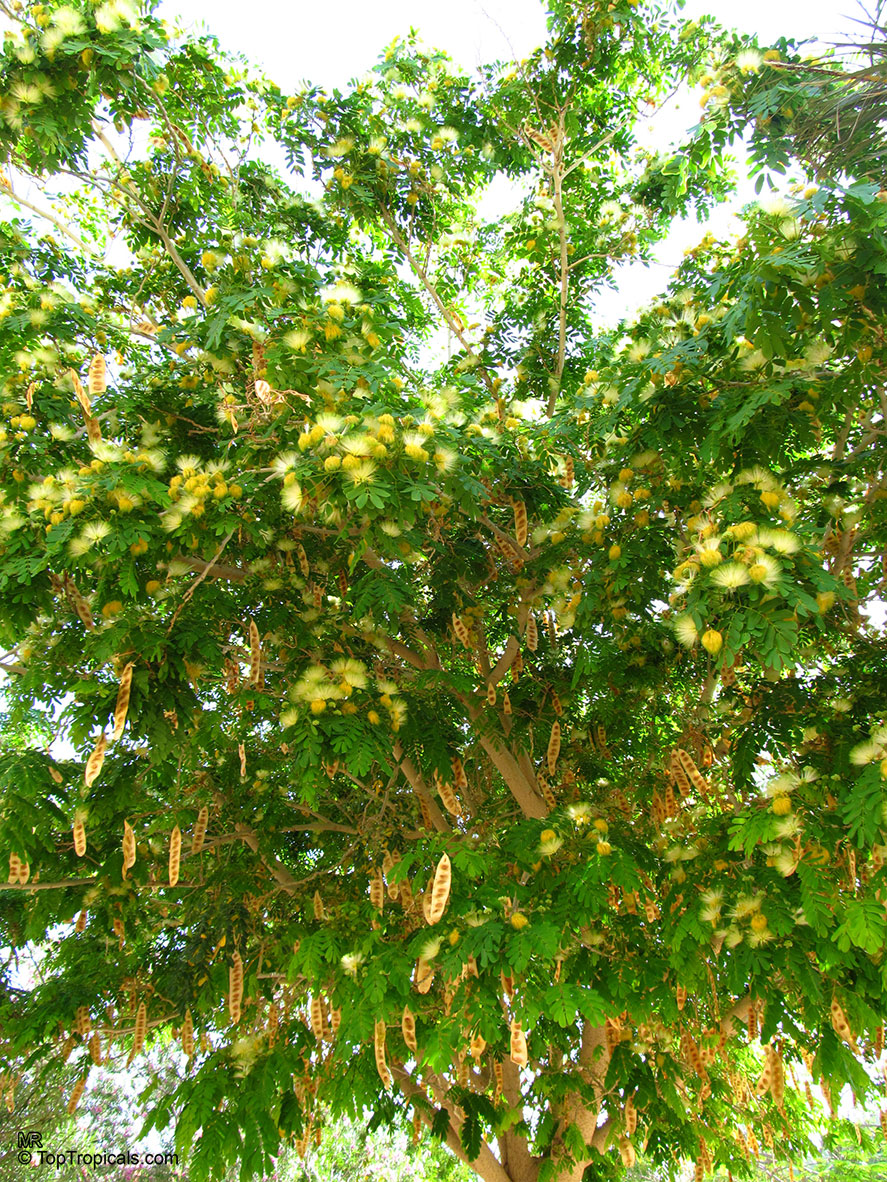
Albizia lebbeck, Mimosa lebbeck is a fast-growing tree, that is susceptible to wind damage. A moderate to large, deciduous tree can grow up to 100 feet high in rain forests. The tree develops a straight trunk when it is grown in dense forests, but is spreading and low branching in the open. Unless trimmed frequently, the trees will annually produce an abundance of seed from papery pods about 8" long and 1" wide (author). Common names such as "woman's tongue" and "rattle pod" derive from the noise of pods shaking in the wind. The foliage is pale green when young and gray-green at maturity. Flowers are cream colored, hemispheric pom-poms. Seeds germinate well without scarification.
The tree is used as a folk remedy for many ailments. Another common use is as an avenue tree, and sometimes it is used to shade coffee and tea. Saponins and tannins in the bark can be used for making soap and in tanning, respectively. Bee keepers like the species for the light-colored honey its nectar provides, and the tree hosts the lac insect.
Botanical name: Mimosa pigra
Common name: Giant Sensitive Tree
Family: Fabaceae
Subfamily: Mimosoideae
Origin: Tropical America








Mimosa pigra is a leguminous shrub, which can reach up to 6m in height.
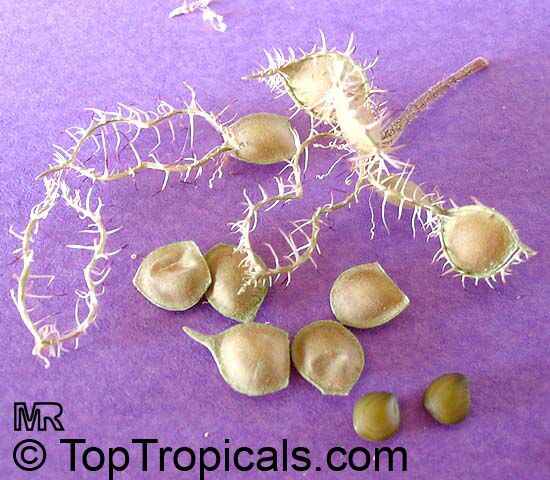
Mimosa pigra is closely related to Mimosa pudica. It can be distinguished from Mimosa pudica by its large size, large pods (6 to 8 cm long as opposed to 2.5 cm long) and leaves, which have 6 to 16 pairs of pinnae as opposed to 1 to 2 pairs on Mimosa pudica leaves
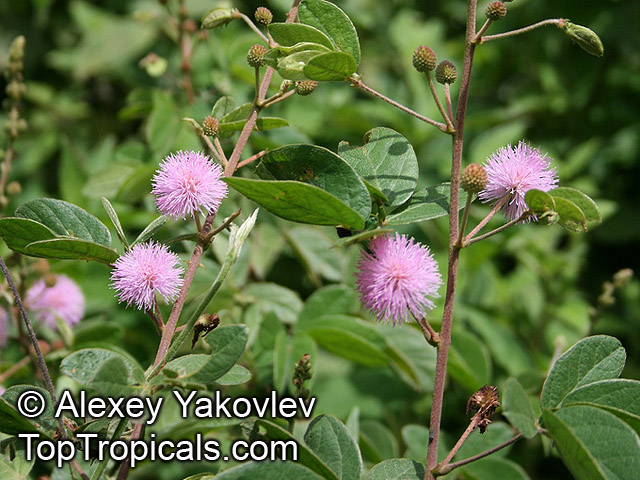
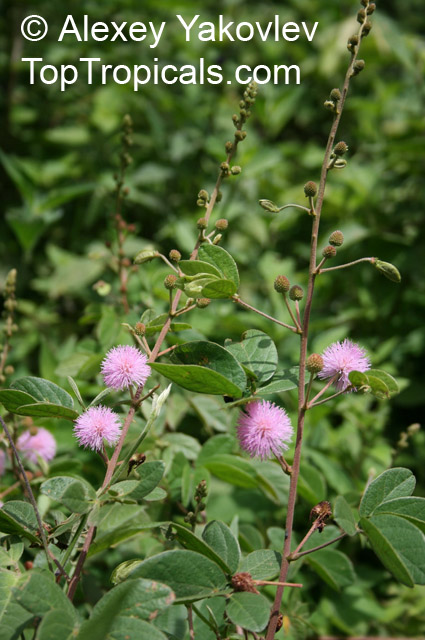
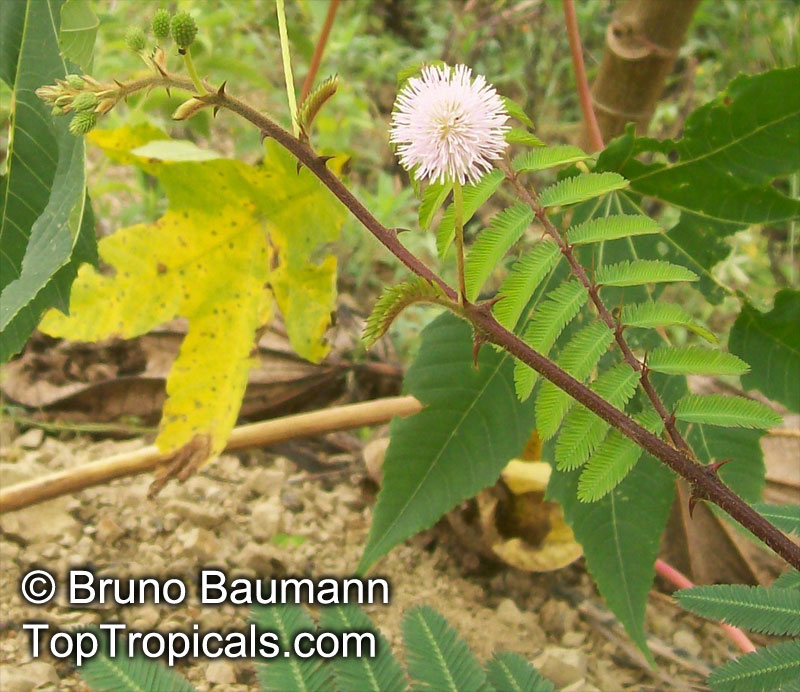
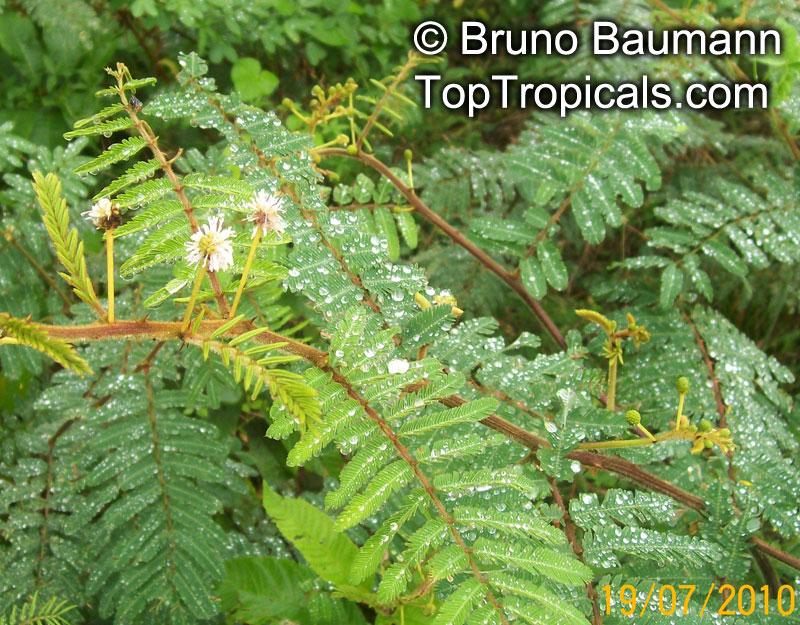
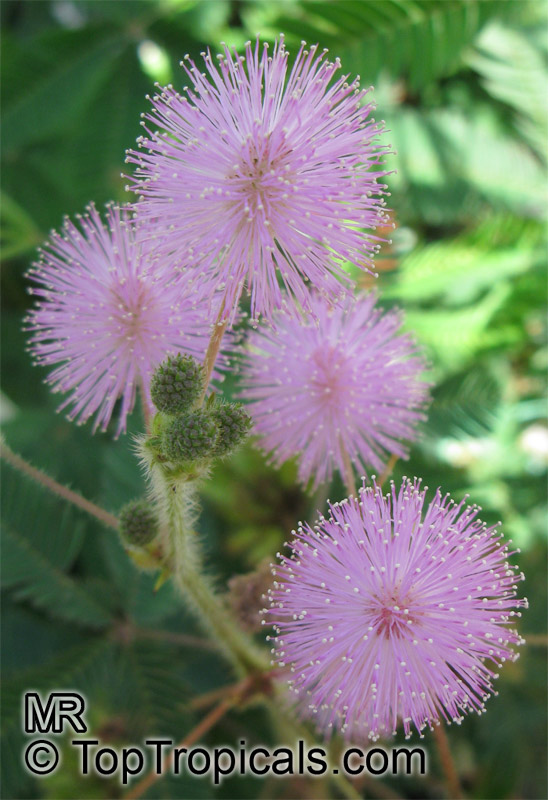
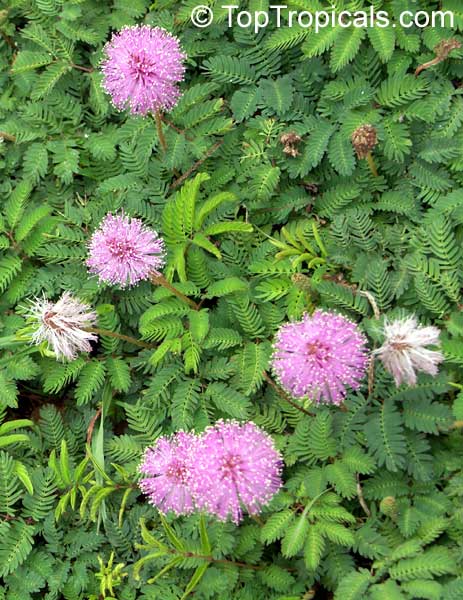
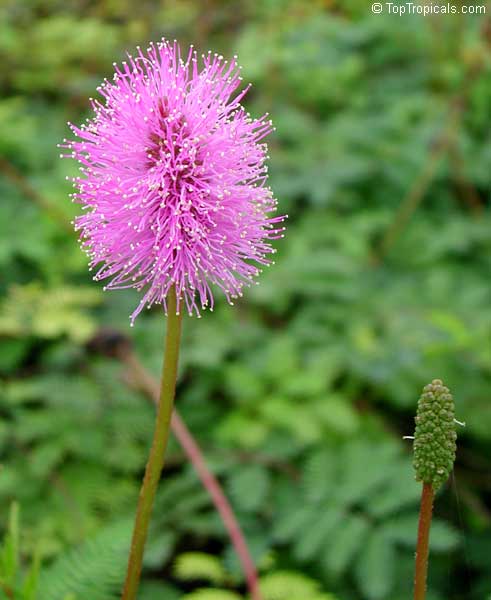
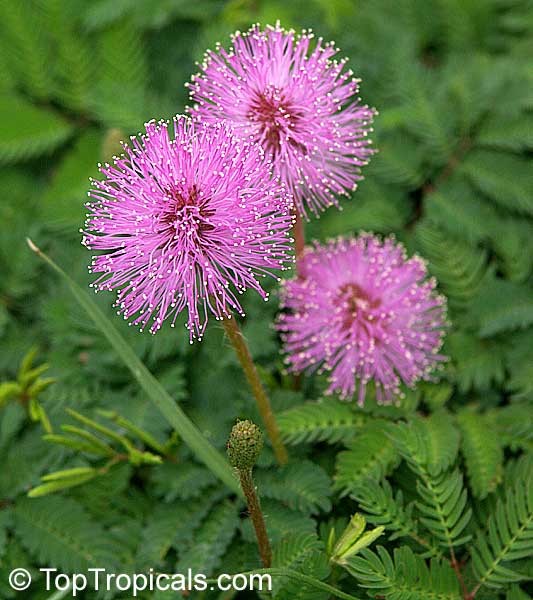
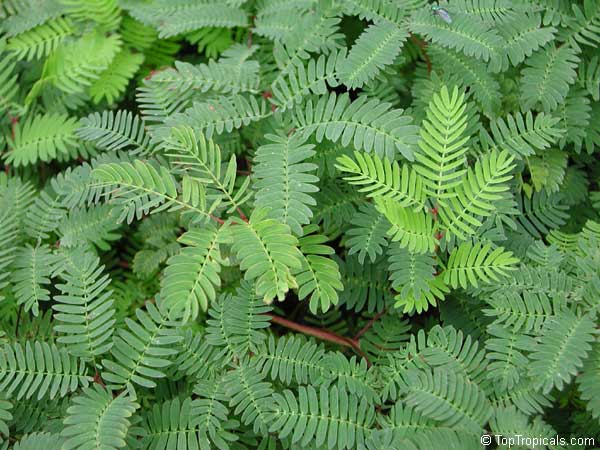
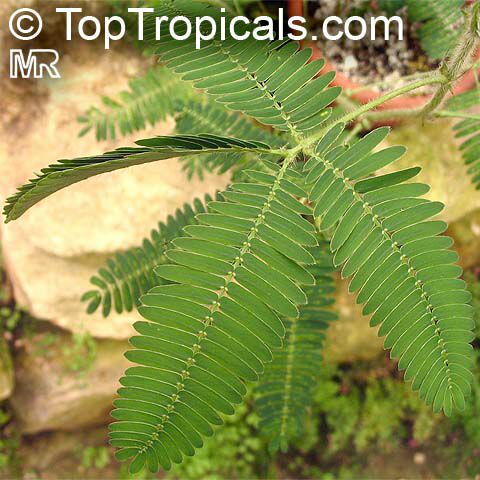
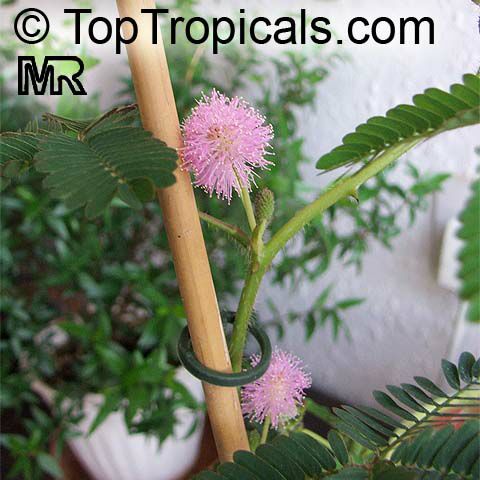
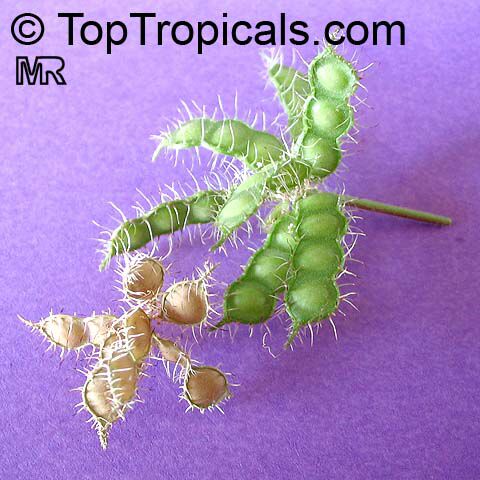
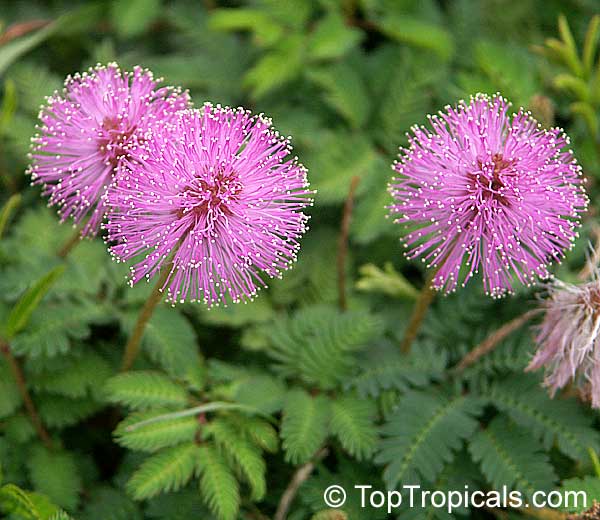
Botanical names: Mimosa pudica, Mimosa strigillosa
Common name: Sensitive Plant
Family: Fabaceae
Subfamily: Mimosoideae
Origin: Tropical America





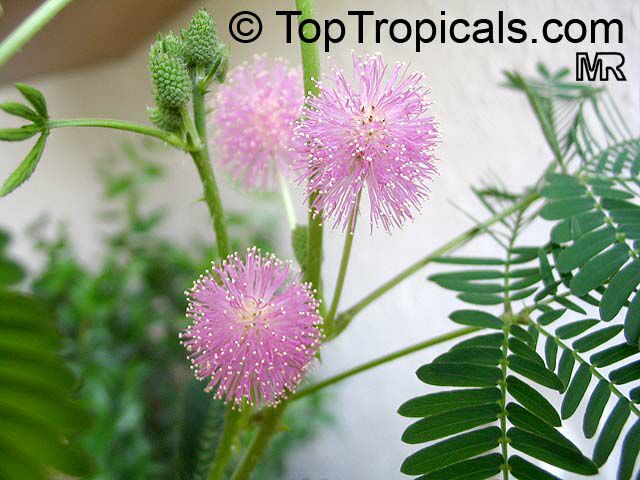
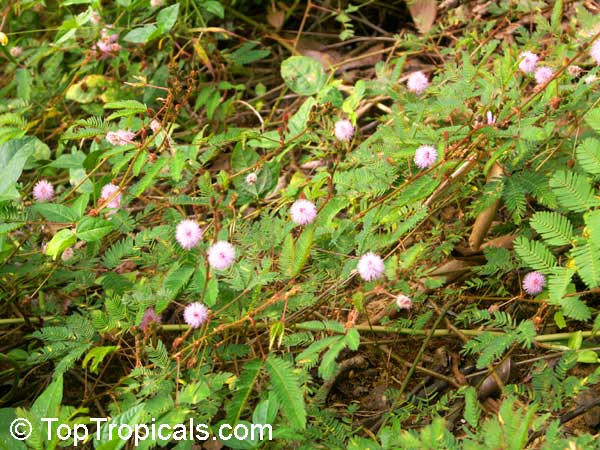
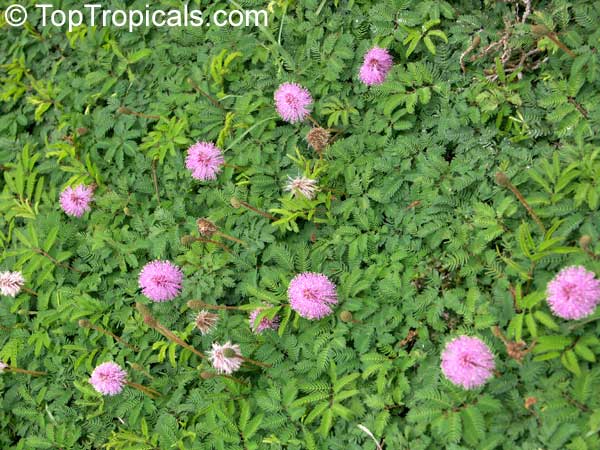
It is a fun plant to grow. The leaves fold up when touched. If touched with a bit more force, the petioles will also bend at their pulvinis and the leaves droop. These movements are called seismonastic movements (reaction to physical shock). At night, the leaves will also fold and bend in movements known as nyctonastic movements (reaction to absence of light). The plant flowers in mid to late summer. The flowers are globe shaped, about 1" across. Mimosa pudica needs full sun to partial shade, with a rich moist soil. We use a soil mix consisting of 2 parts peat moss to 2 parts loam to 1 part sand or perlite. The soil should be kept evenly moist but not saturated. During the growing season, the plant are fertilized on a weekly basis with a balanced fertilizer diluted to 1/2 the strength recommended on the label. During the winter months, fertilize on a monthly basis. Winter temperatures should not fall below 65F; if they do get chilled, then the plant suffers with yellowing of leaves and stems. Propagation: Mimosa pudica is propagated from seed. Seed will germinate in 14 to 21 days at 70F.
Close related species - Mimosa strigillosa that is also used as a ground cover.
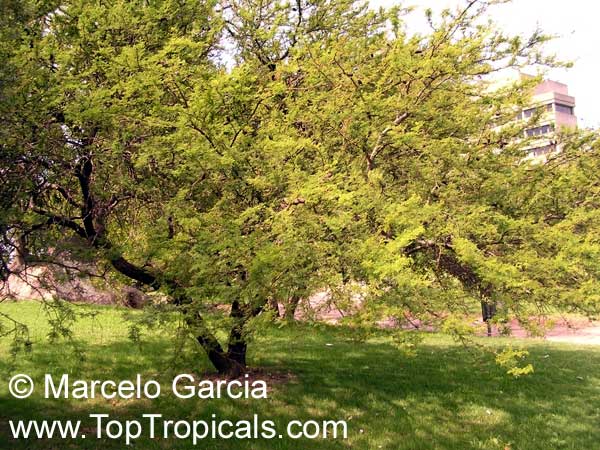
Botanical names: Acacia cavenia, Mimosa caven
Common names: Espino Cavan, Roman Cassie
Family: Fabaceae
Subfamily: Mimosoideae
Origin: Chile and Argentina





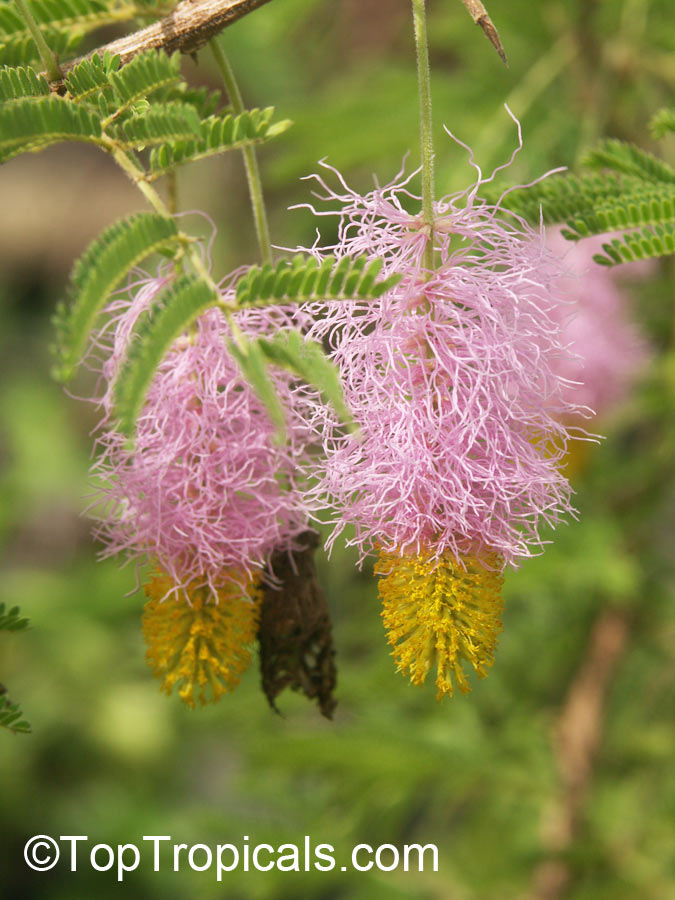
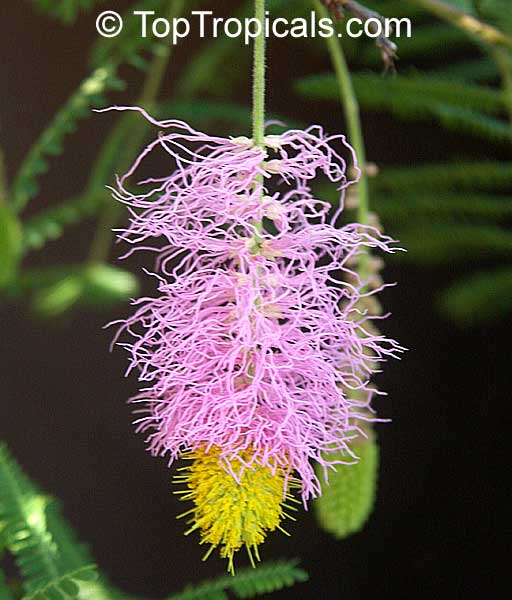
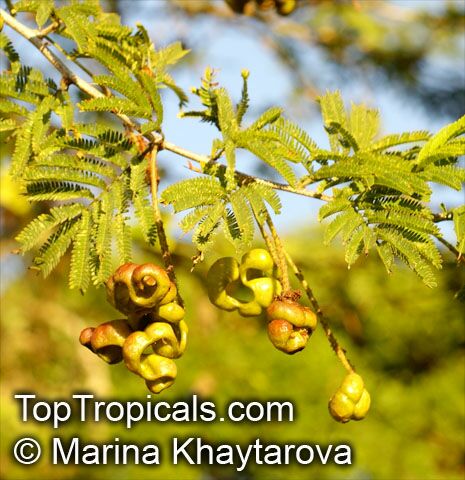
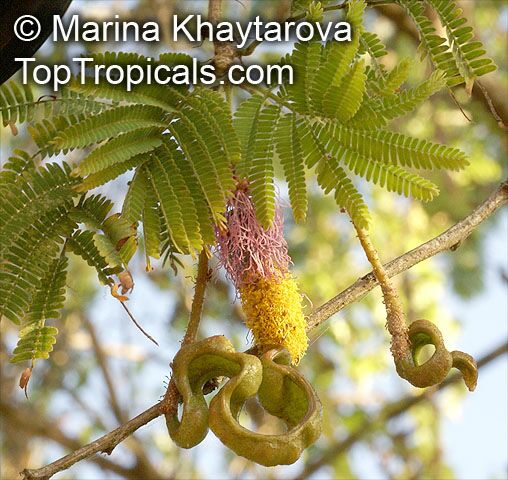
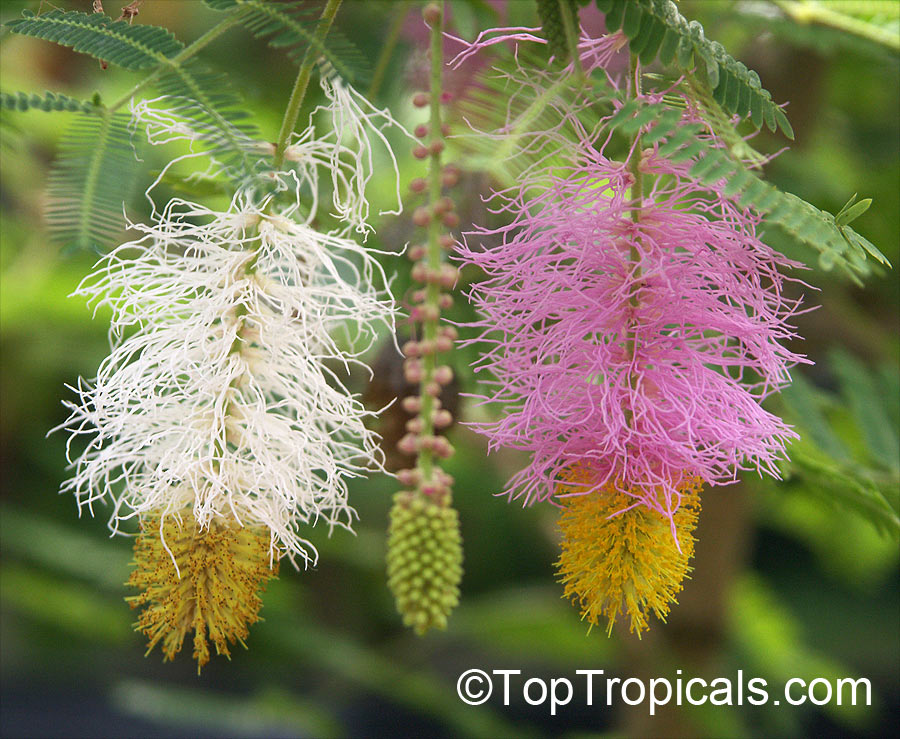
Botanical names: Dichrostachys cinerea, Cailliea glomerata, Dichrostachys glomerata, Dichrostachys nutans, Mimosa cinerea
Common names: West African Sickle Bush, Marabou Thorn, Aroma, Kalahari Christmas tree, Chinese lantern tree, Marabou-thorn, Princess Earrings
Family: Fabaceae
Subfamily: Mimosoideae
Origin: Africa to India, Southern Thailand and Malesia, Northern Territories of Australia










Interesting powderpuff-like pink flowers make this plant unforgettable. Shrub up to 9ft high with grey bark and solitary thorns often bearing one or two leaves. Leaves bipinnate and finely pubescent, 1" to 3" long. Pendulous flower heads that are pink in the upper part and yellow in the lower part. Dark-brown pods, borne in clusters, twisted, each 1" to 3" long and 1" broad. Good plant for bonsai.
Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE Megaflor - Bloom Nutrition Booster
Ordering seeds info
RECOMMENDED SUPPLIES:
Seed Germination Mix #3, professional grade
SUNSHINE-Epi - Seeds and cuttings booster
SUNSHINE Bombino - Young Plant Booster
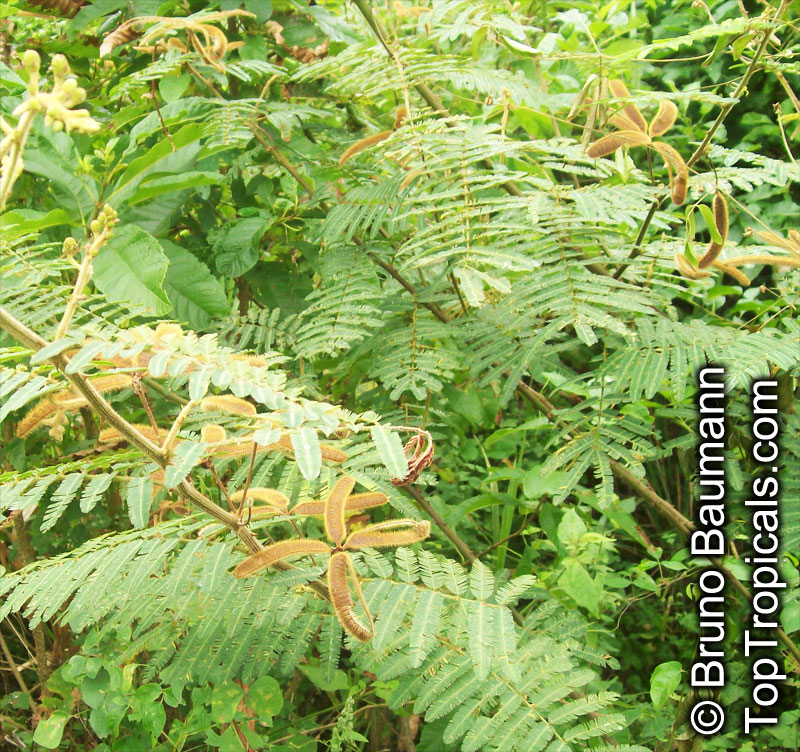
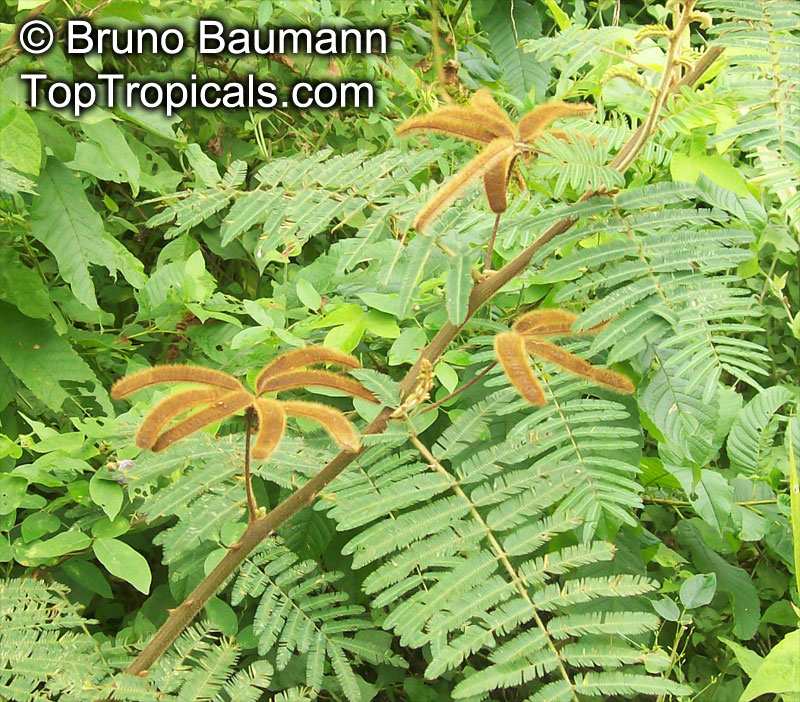
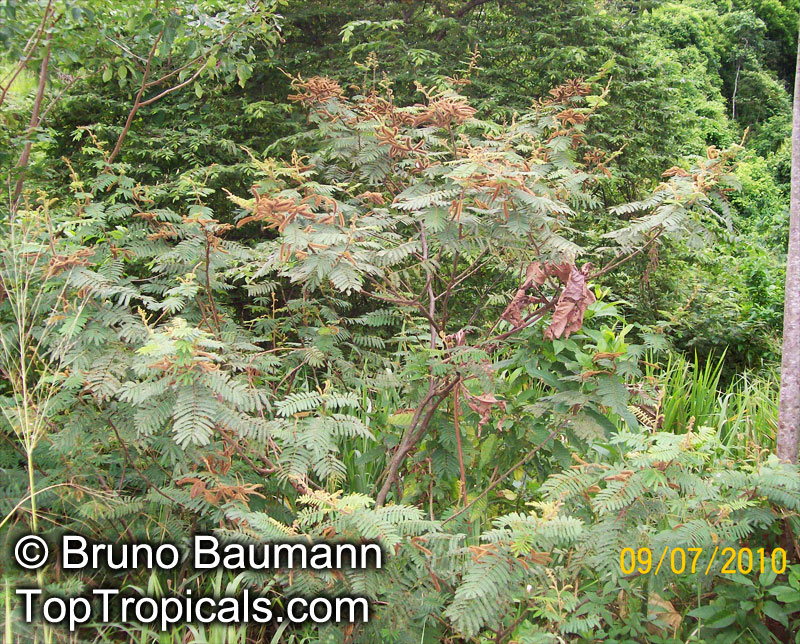
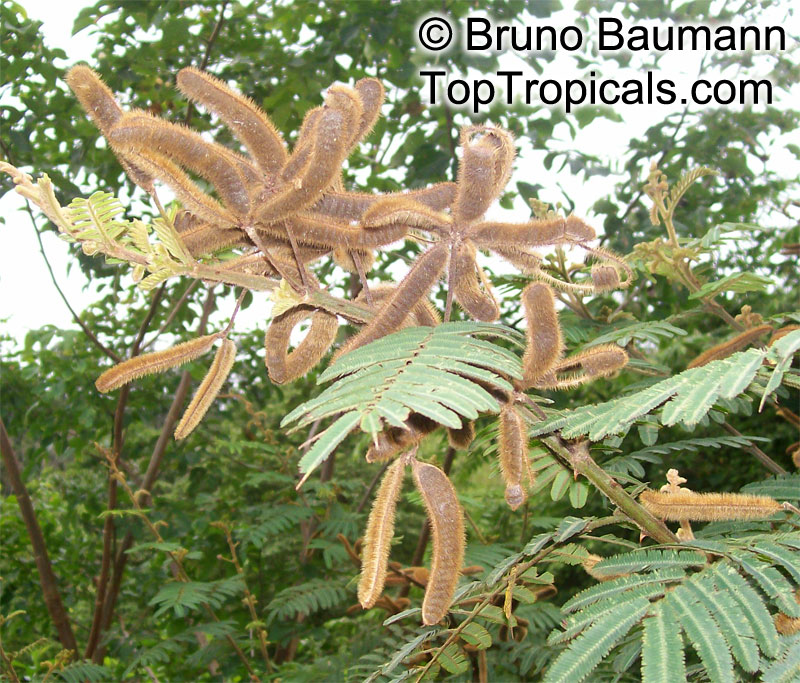
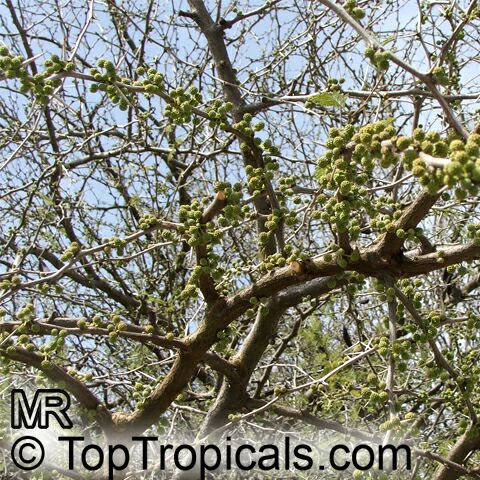
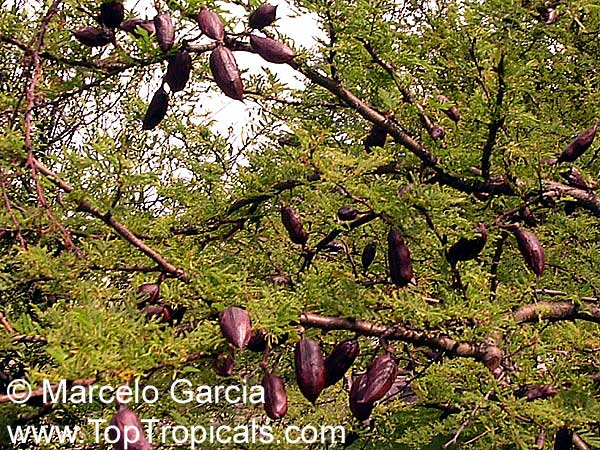
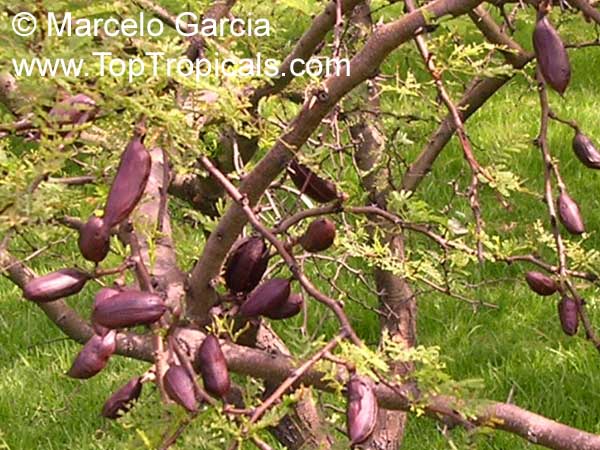
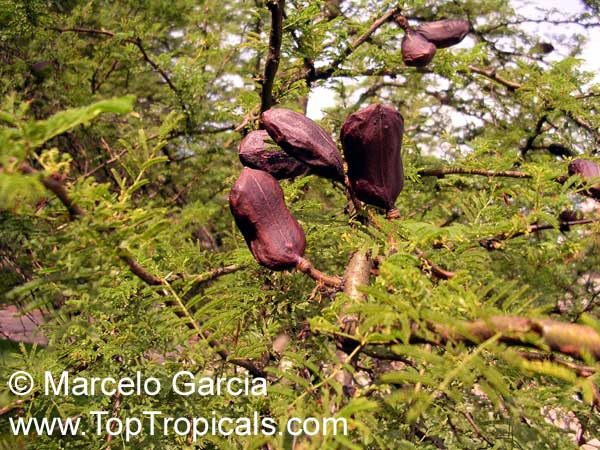
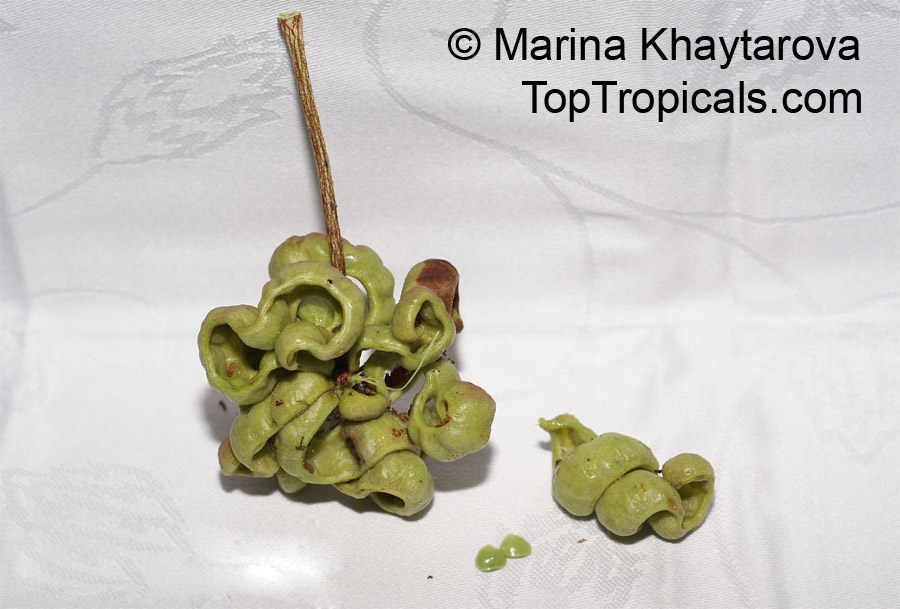
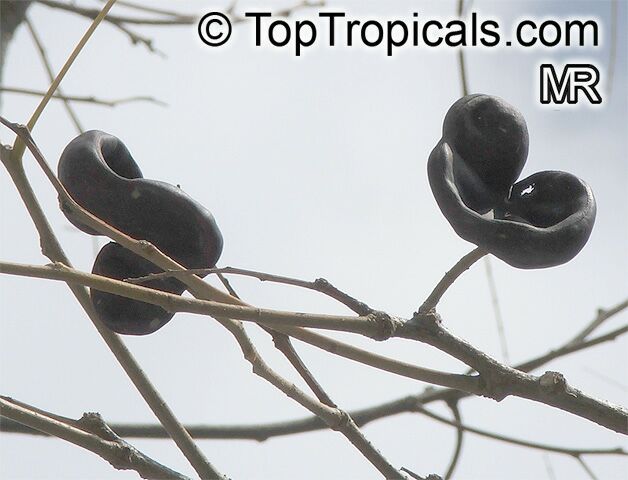
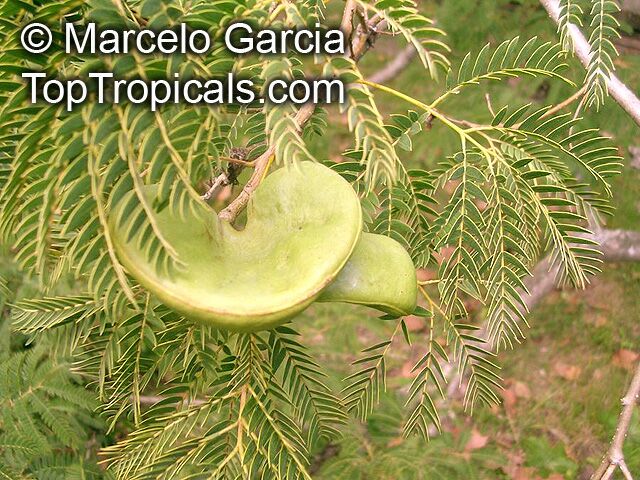
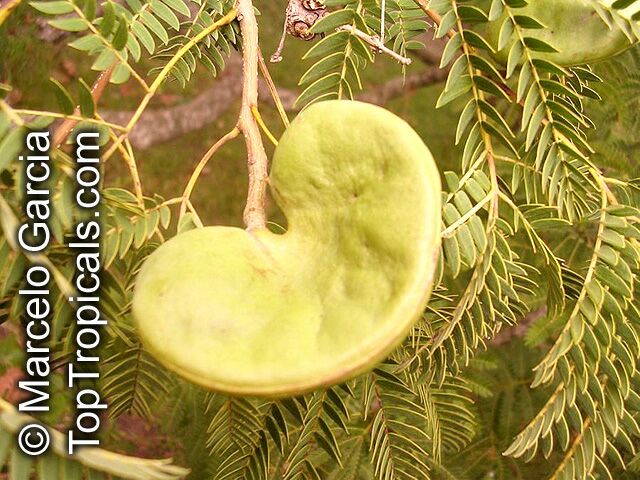
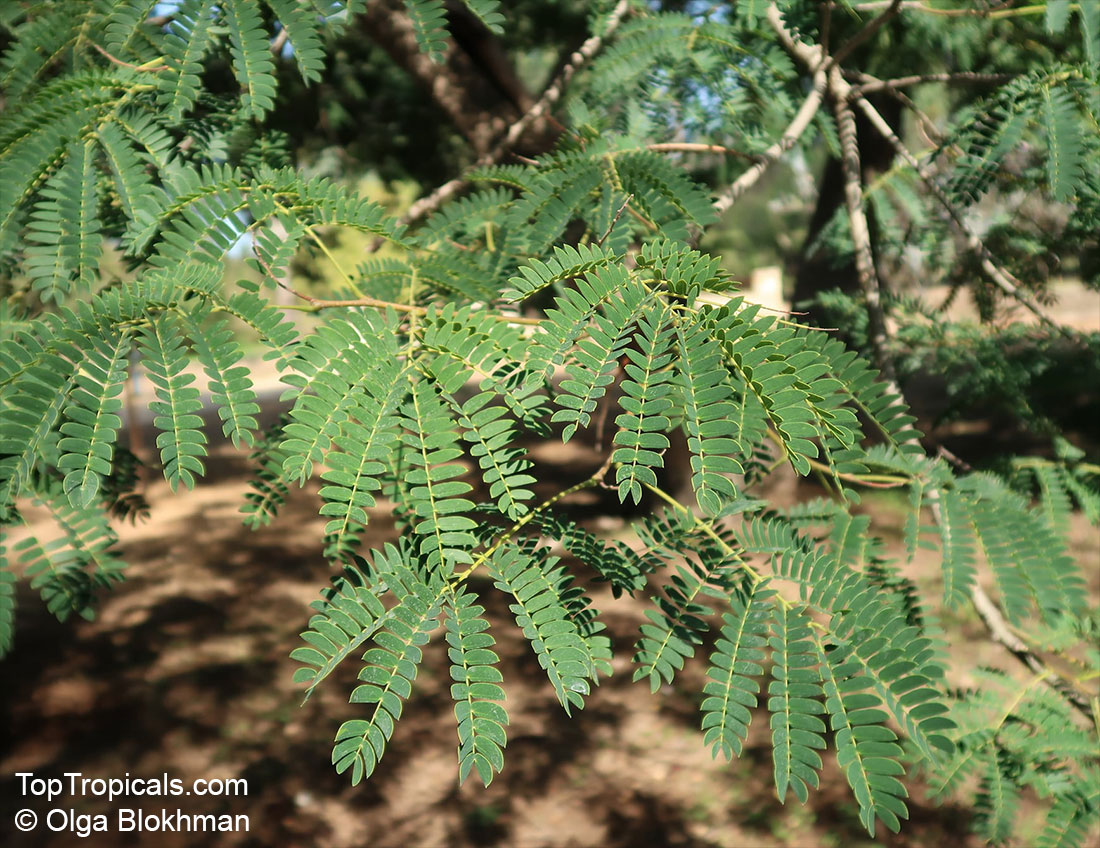
Botanical names: Enterolobium contortisiliquum, Mimosa contortisiliqua
Common names: Earpod Tree, Orelha-de-macaco
Family: Fabaceae
Subfamily: Mimosoideae
Origin: South America





Enterolobium contortisiliquum, also known as Earpod Tree, is a deciduous plant native to South America. It is a big tree, growing taller than 20 ft with a broad crown, and can be found in USDA zones 9-11. It is a comparatively low maintenance tree, preferring full sun and an occasional watering. In the right conditions, it can be grown without irrigation.
The tree produces off-white to white flowers in the spring and early summer, which are followed by large and distinctive seedpods. These pods can be up to 6 in long and look like elephant ears. The leaves are bipinnate and can reach lengths of up to 12 in.
The Enterolobium contortisiliquum is a spectacular and unique addition to any garden or landscape. Its fruit and foliage provide texture to the landscape and its large size, beautiful flowers and ornamental seedpods guarantee a head-turning display.
Planting Enterolobium contortisiliquum is easy and, once established, requires minimal care. Plant it in well-draining soil and, if you live in a dry region, it can be beneficial to form a basin around the base of the trunk which will capture run-off water. In especially cold regions, potting up this tree can help it survive a harsher winter. When you do, opt for a large pot and use a mixture of potting soil, mulch and compost for a rich, well-draining mix. You should also use rainwater in the pot, as this will be better for your tree than tap water.
Overall, the Enterolobium contortisiliquum is an attractive and low-maintenance addition to any outdoor space. With its impressive size and ornamental look, it can add depth and character to any garden.
| Next |  |
Use link to repeat this search:
https://toptropicals.com/cgi-bin/garden_catalog/cat.cgi?find=Mimosa&search_op=and&keyword_op=and&language=e&number=10
&no_change_lang=1&user=tt&sale=1&first=0






























































































