Brachychiton - Plant Encyclopedia Results
| Number of plants found: 9 |
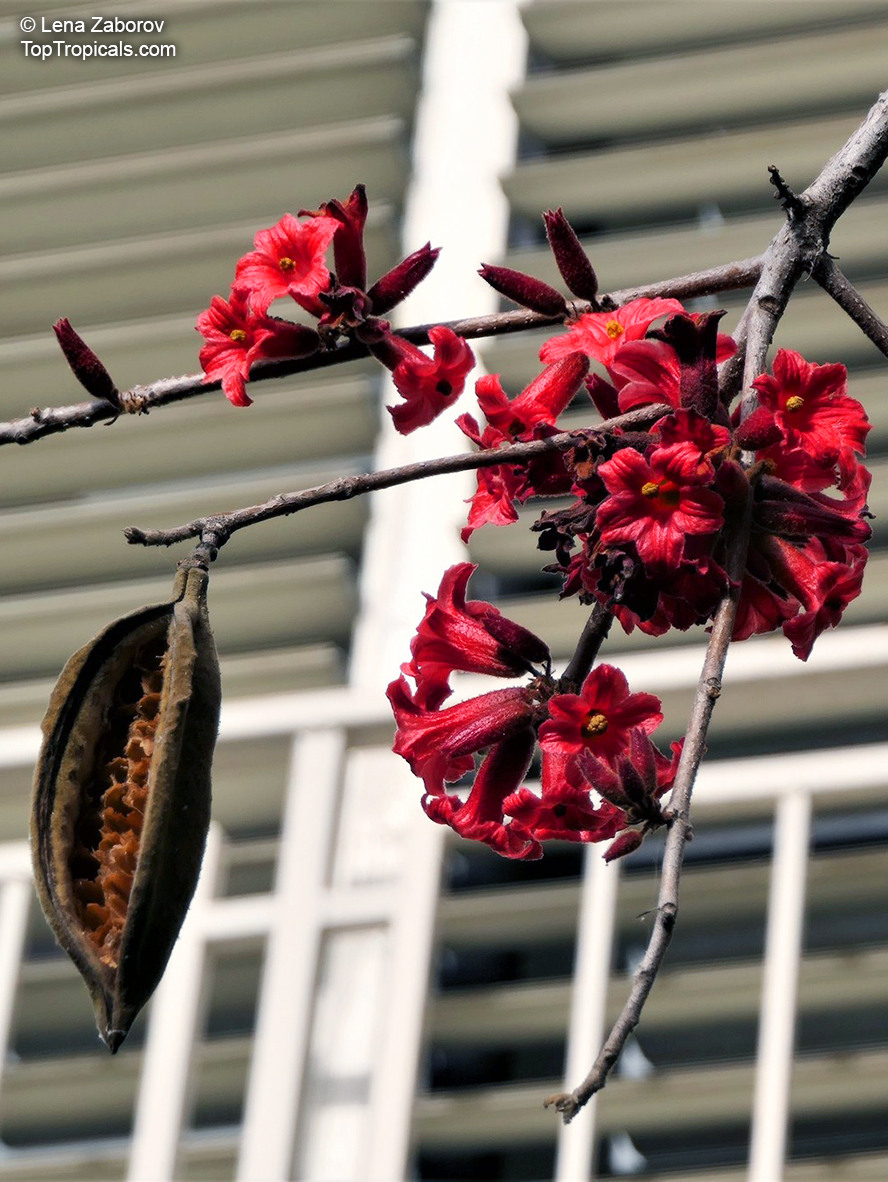
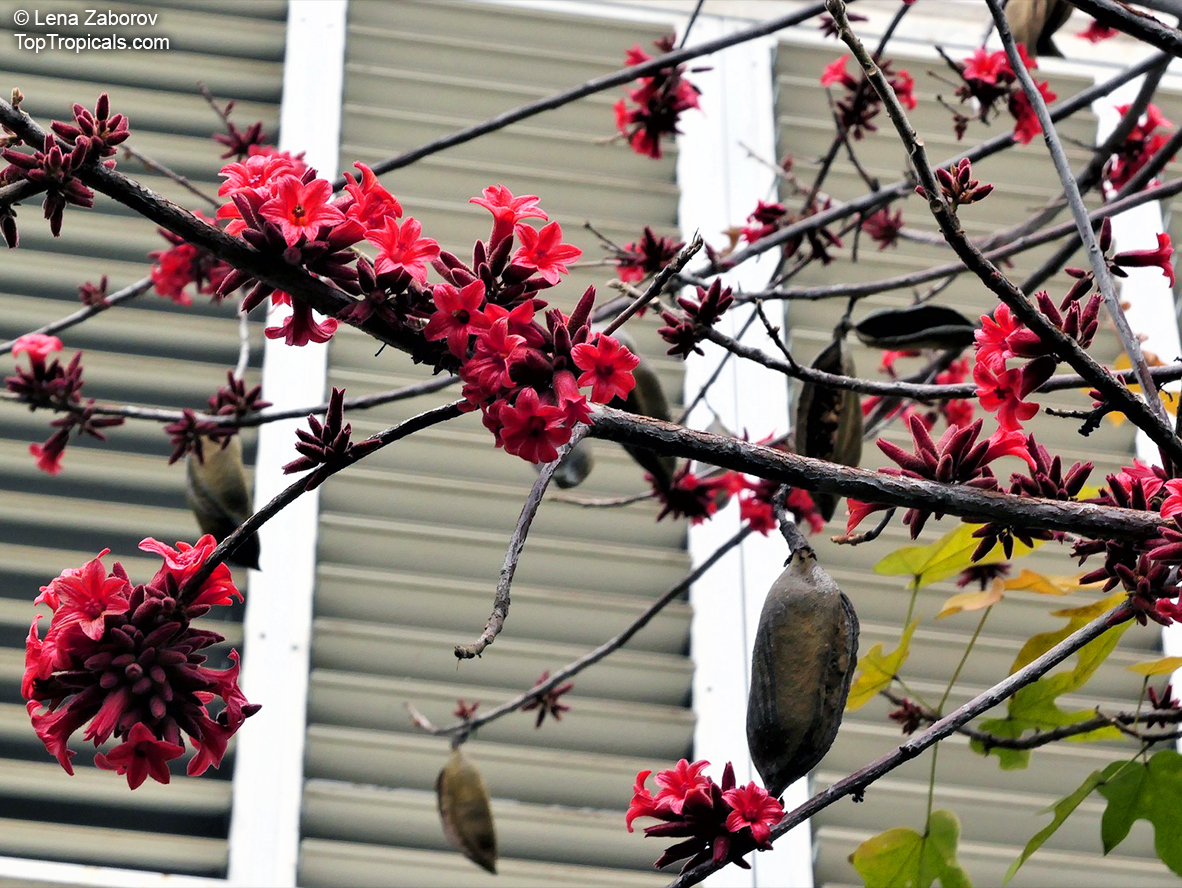
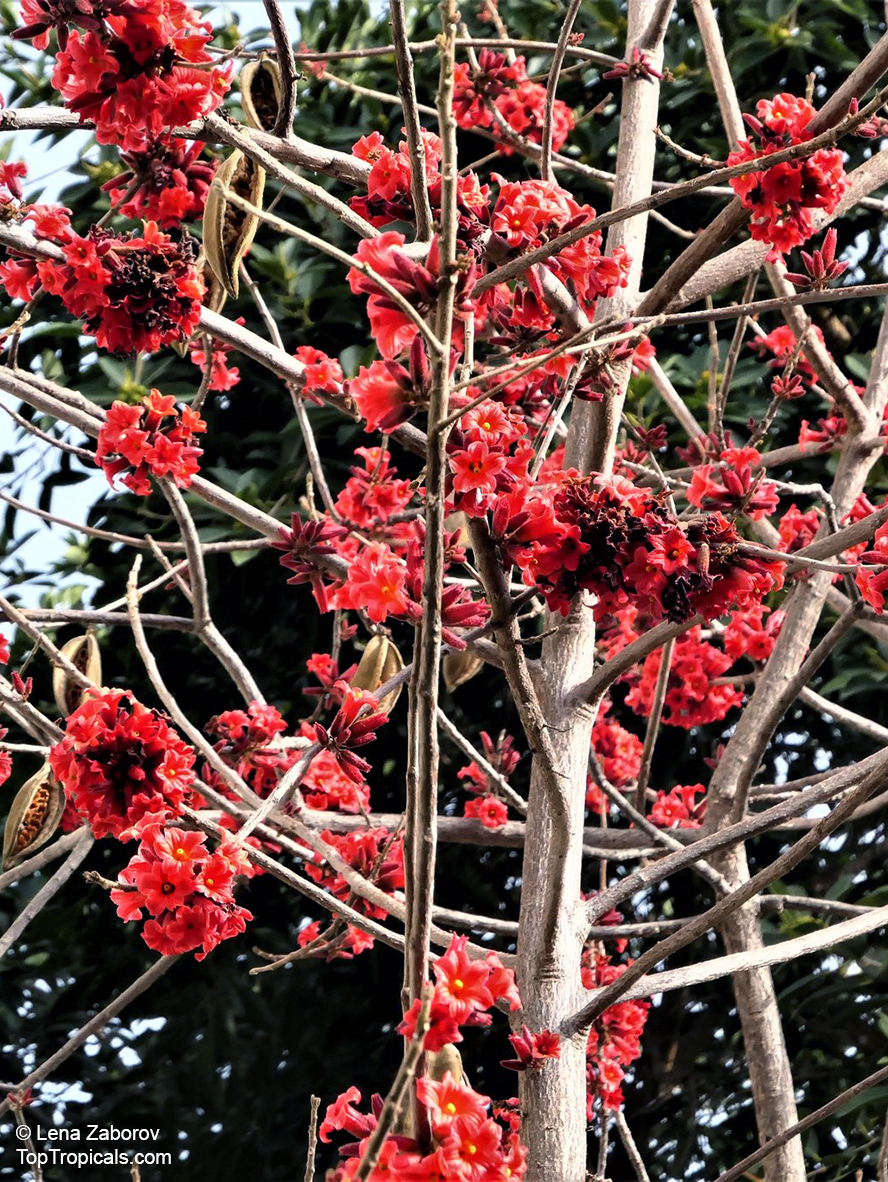
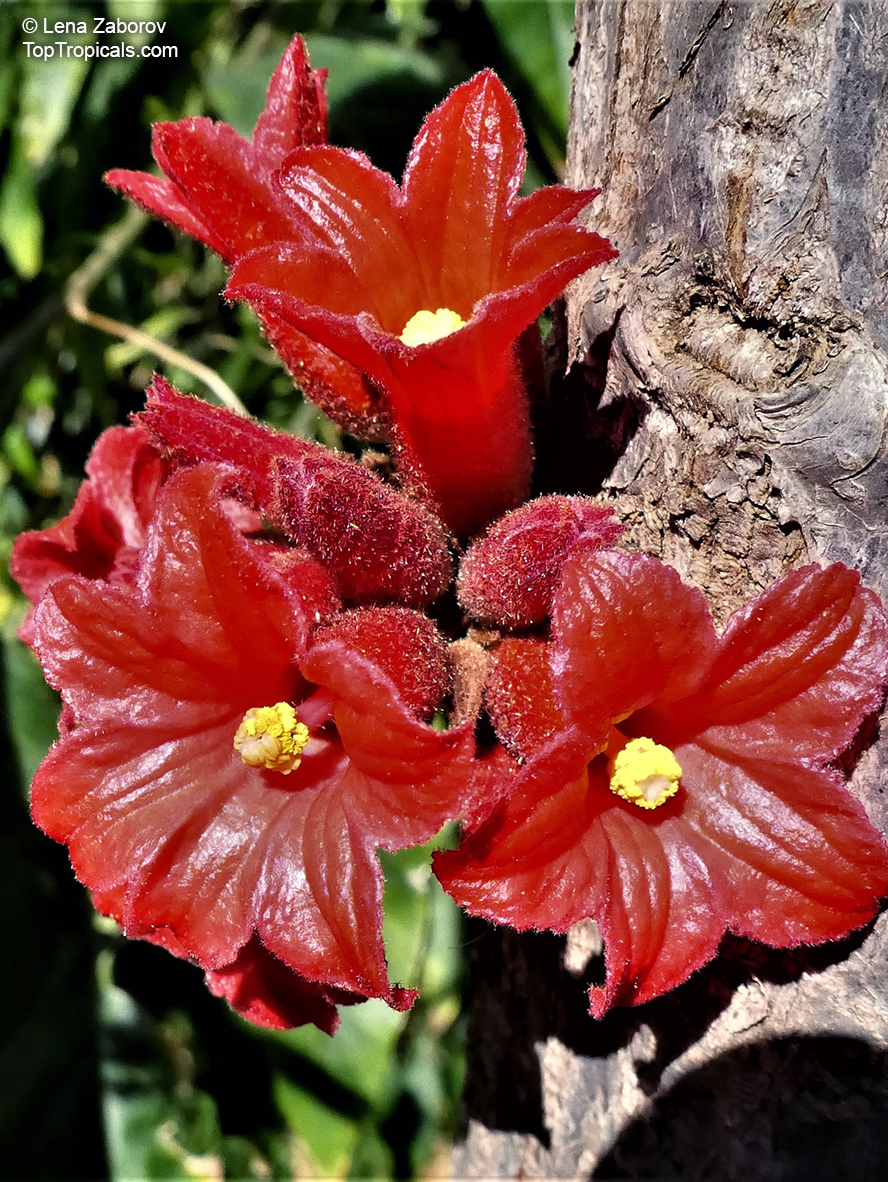
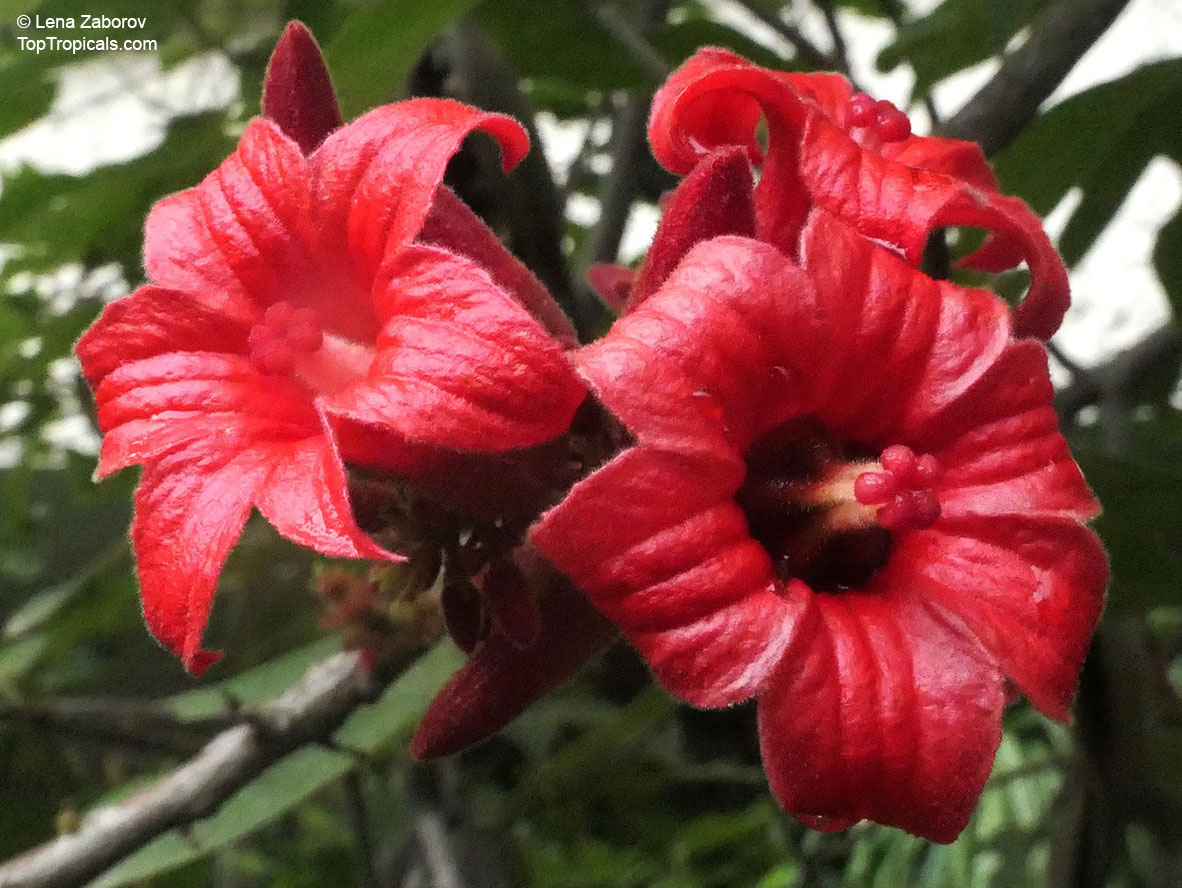
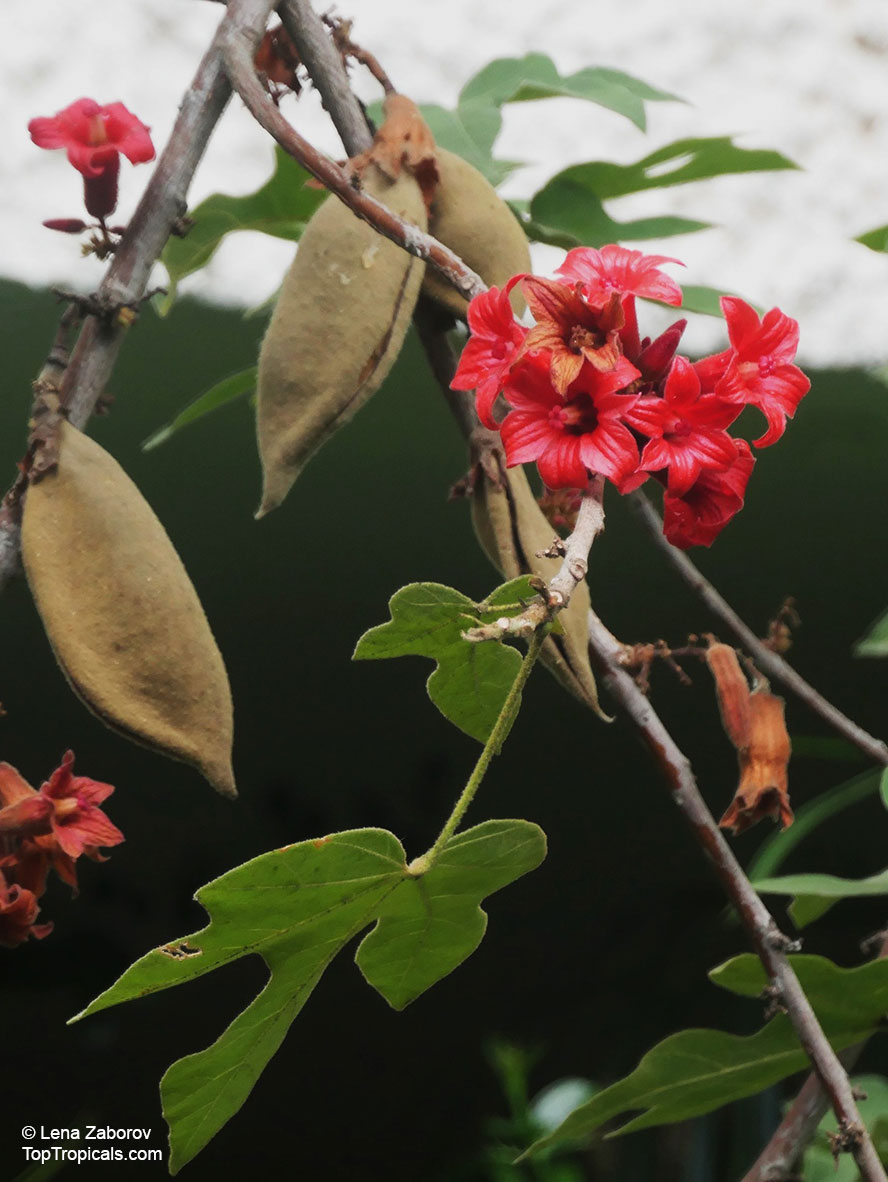
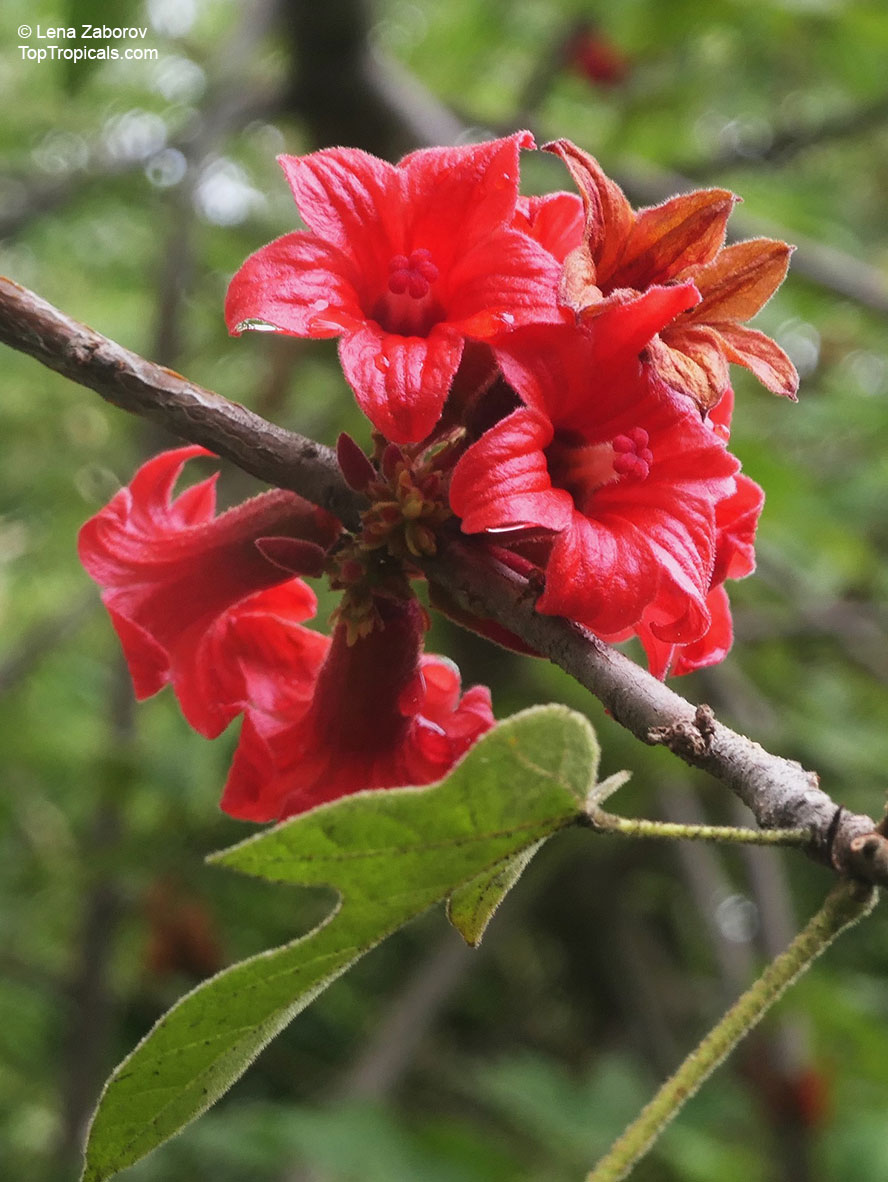
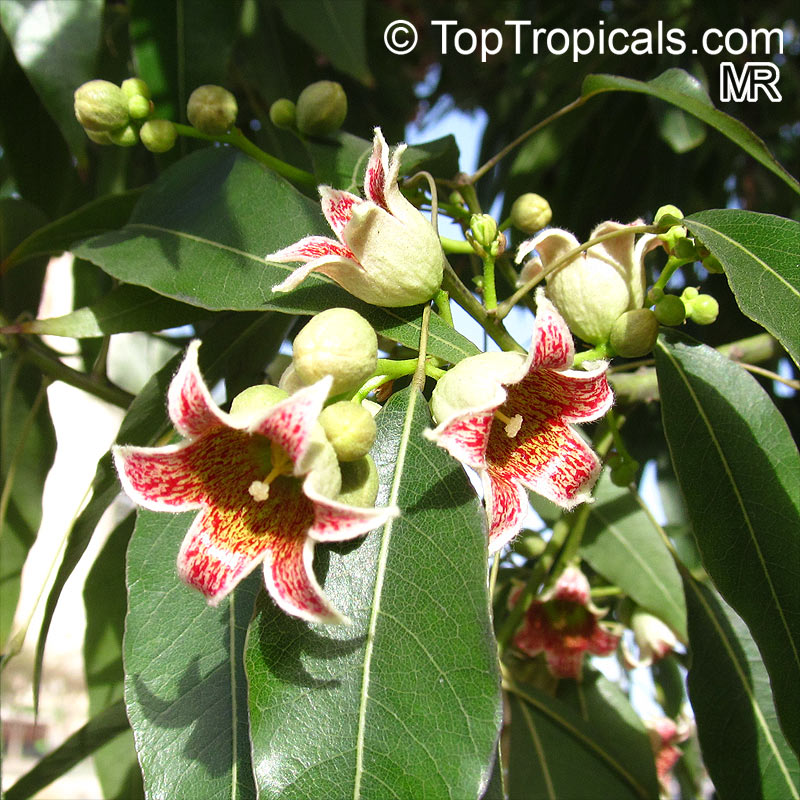
Botanical names: Brachychiton bidwillii, Brachychiton paradoxus var. bidwillii
Common name: Little Kurrajong
Family: Malvaceae
Subfamily: Sterculioideae
Origin: Australia
Hardiness: 30°F







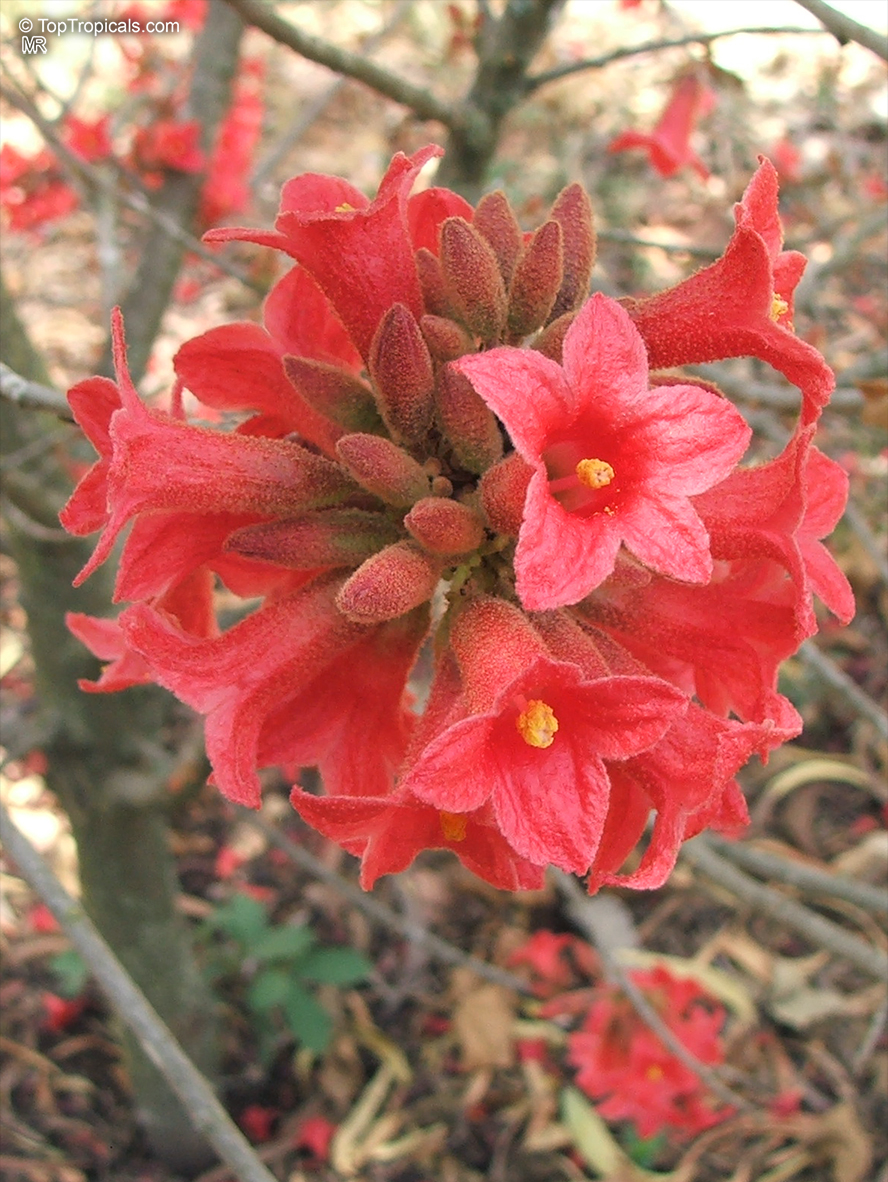
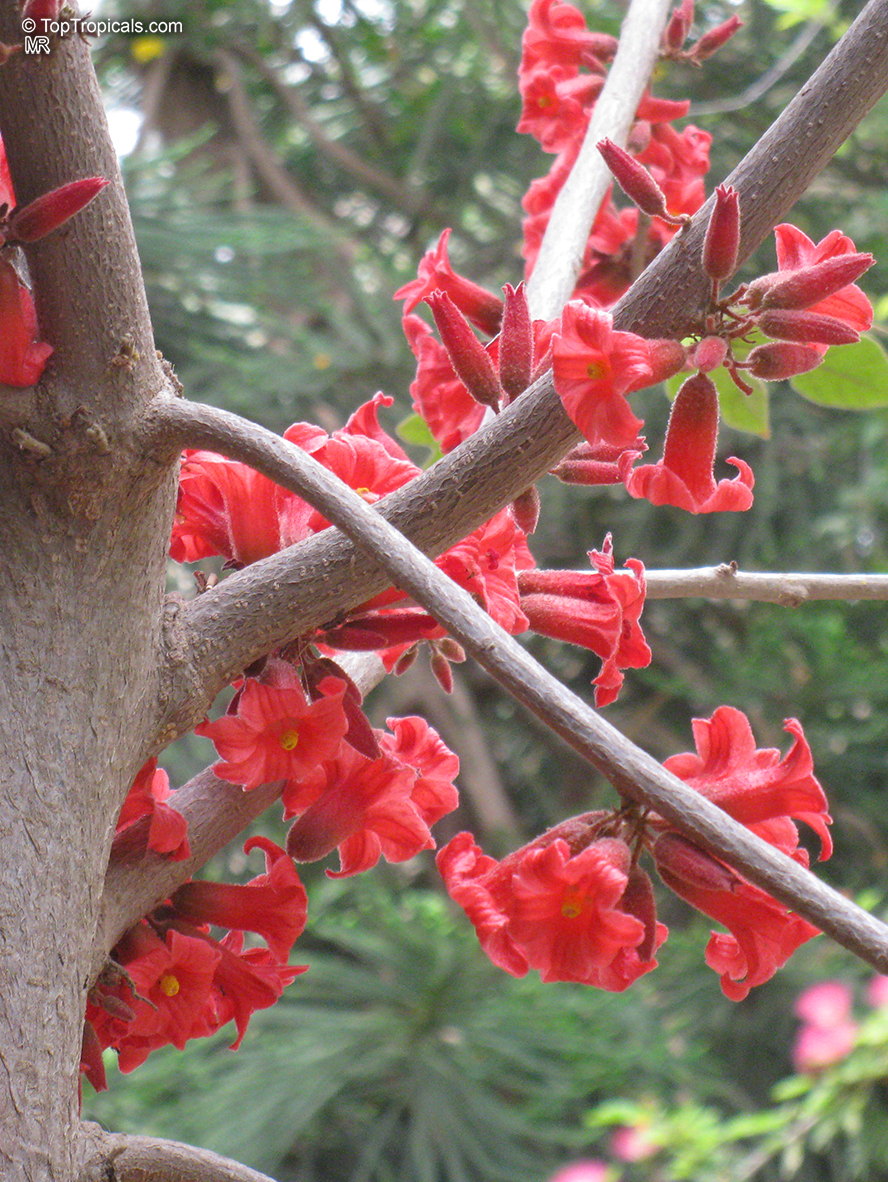
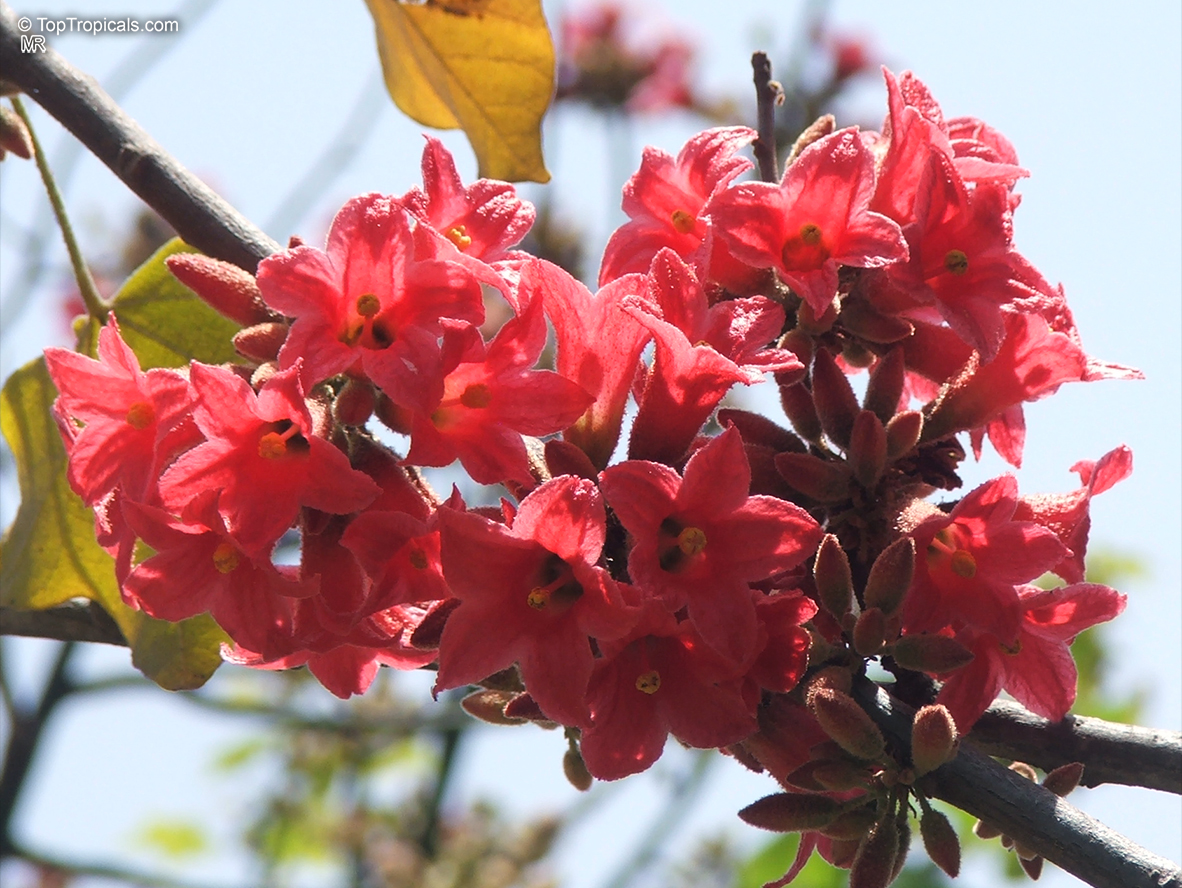
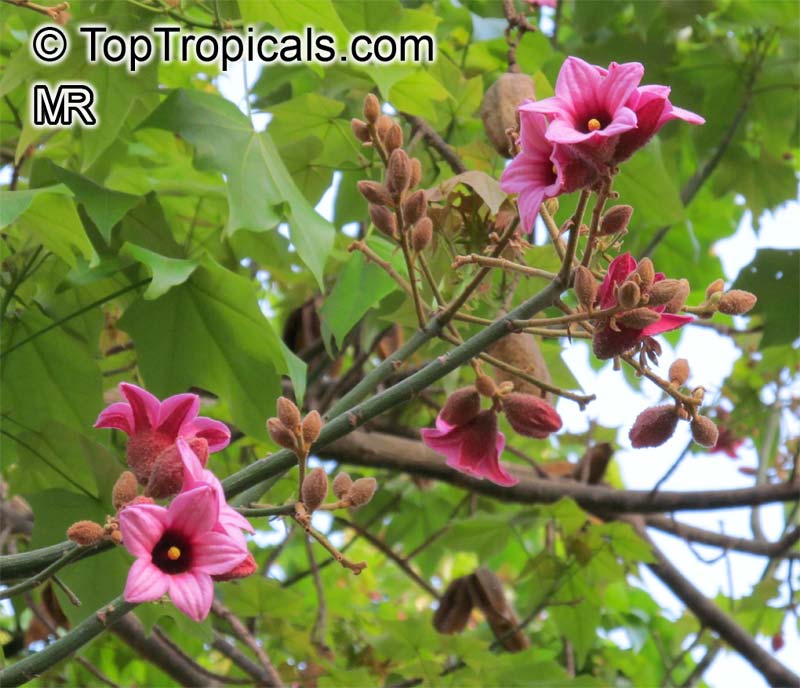
In regions with colder climates, Grown in USDA Zone 9-11, it is possible to grow Brachychiton bidwillii in a pot. The roots of this plant are very vulnerable to cold temperatures and should be protected during winter. When potted, select a pot big enough to hold the plant, soil and roots comfortably and use a potting mix that is comprised of two parts soil, two parts sand and one part compost. Brachychiton bidwillii should be positioned in full sun and watered moderately, allowing the soil to dry between watering. The plant should be allowed to enter a dormant period during the winter months, during which time the watering should be reduced. Prune Brachychiton bidwillii as needed to shape its size and form, but be aware that pruning too heavily may reduce the flowering potential of the plant.
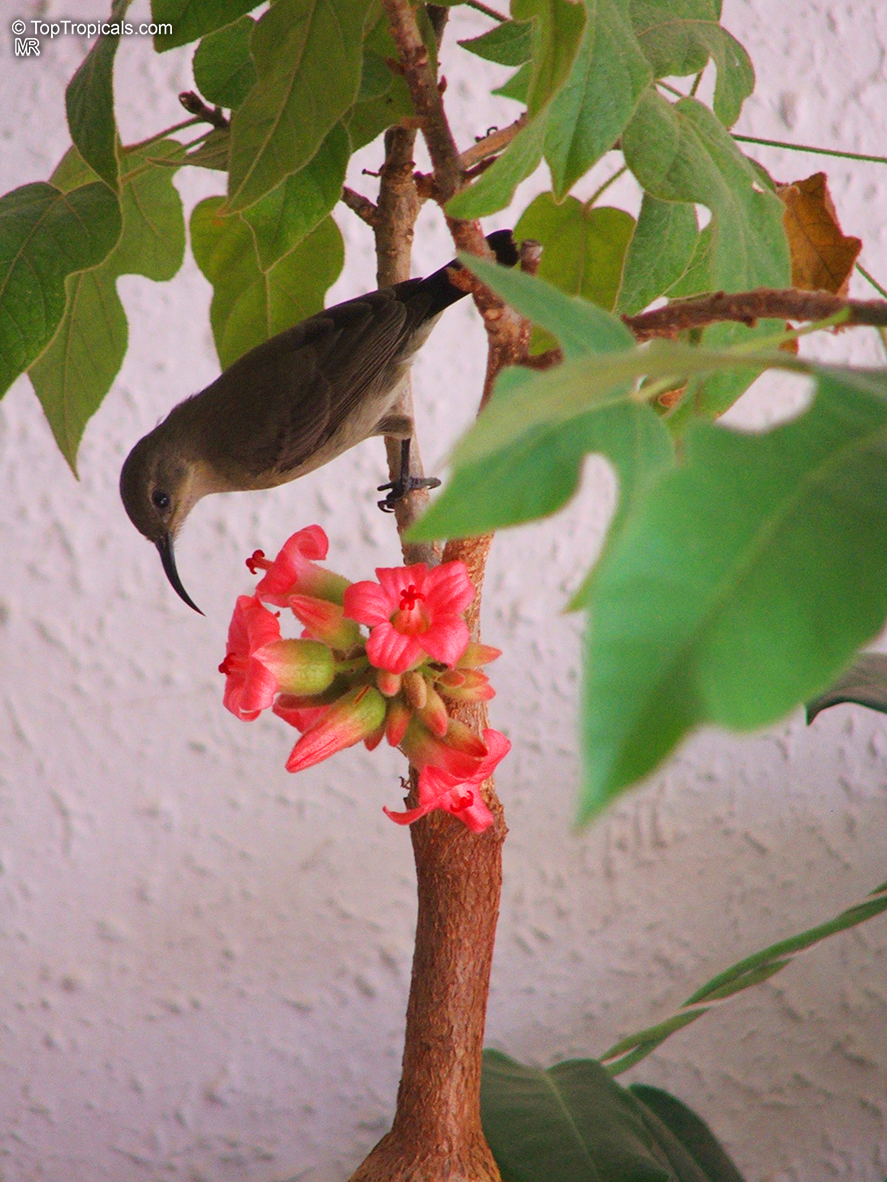
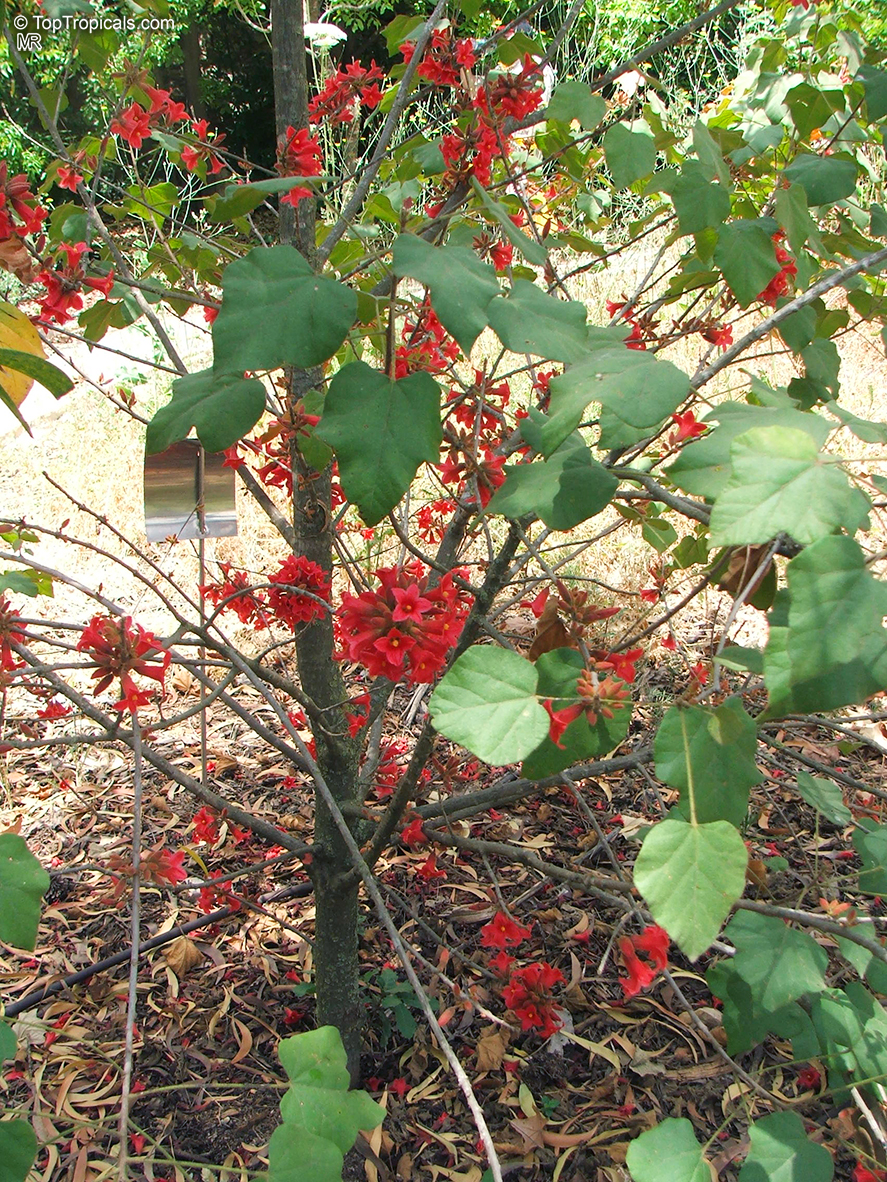
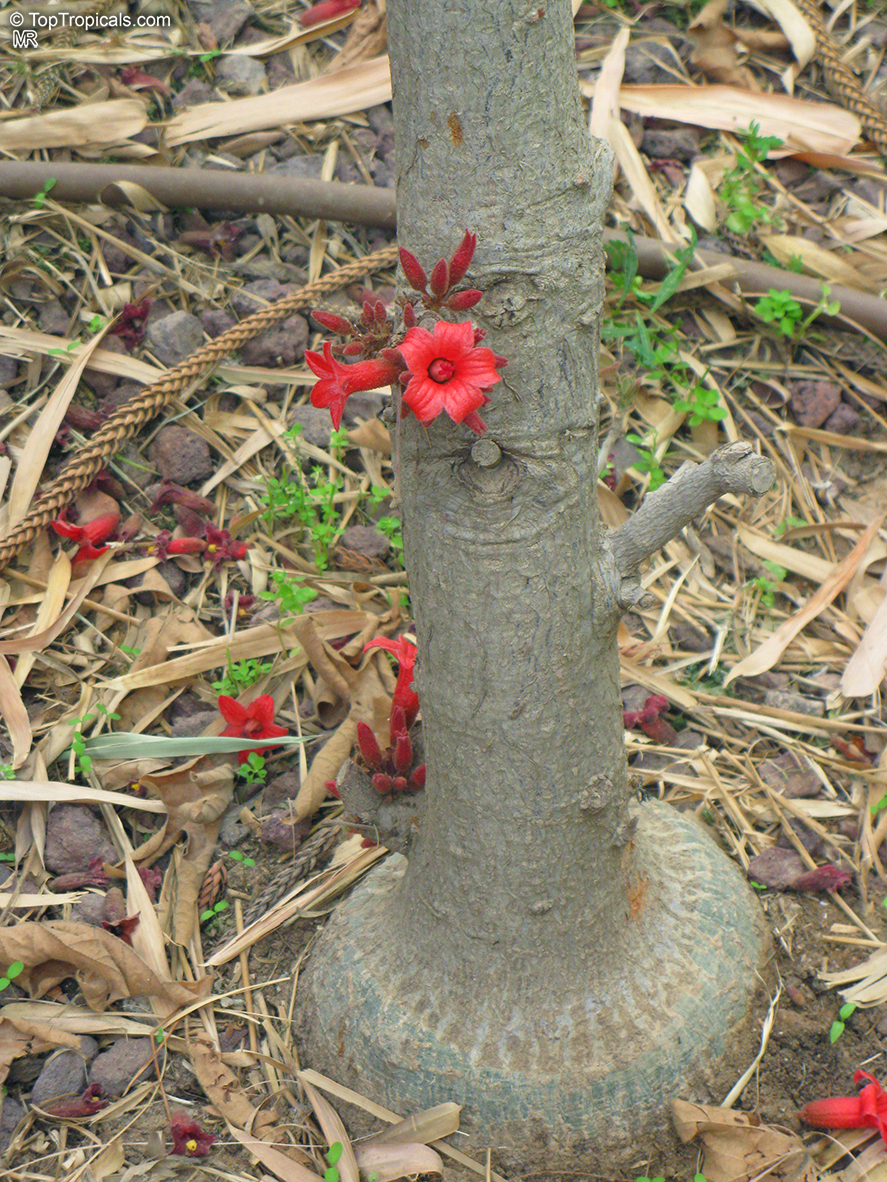
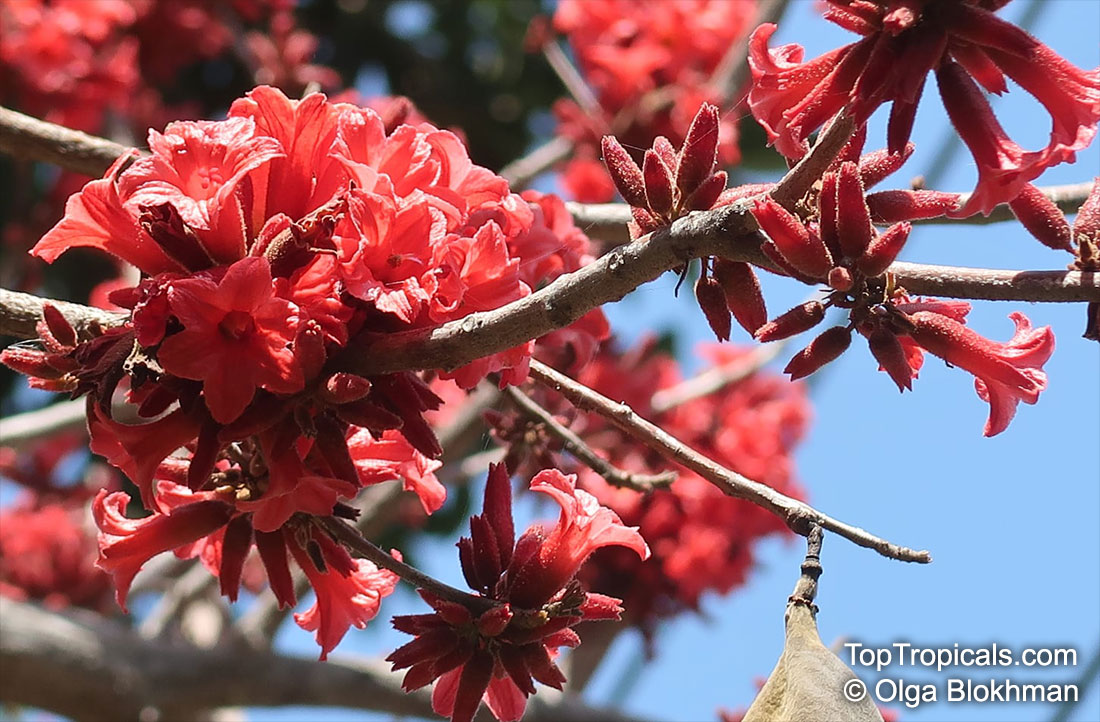
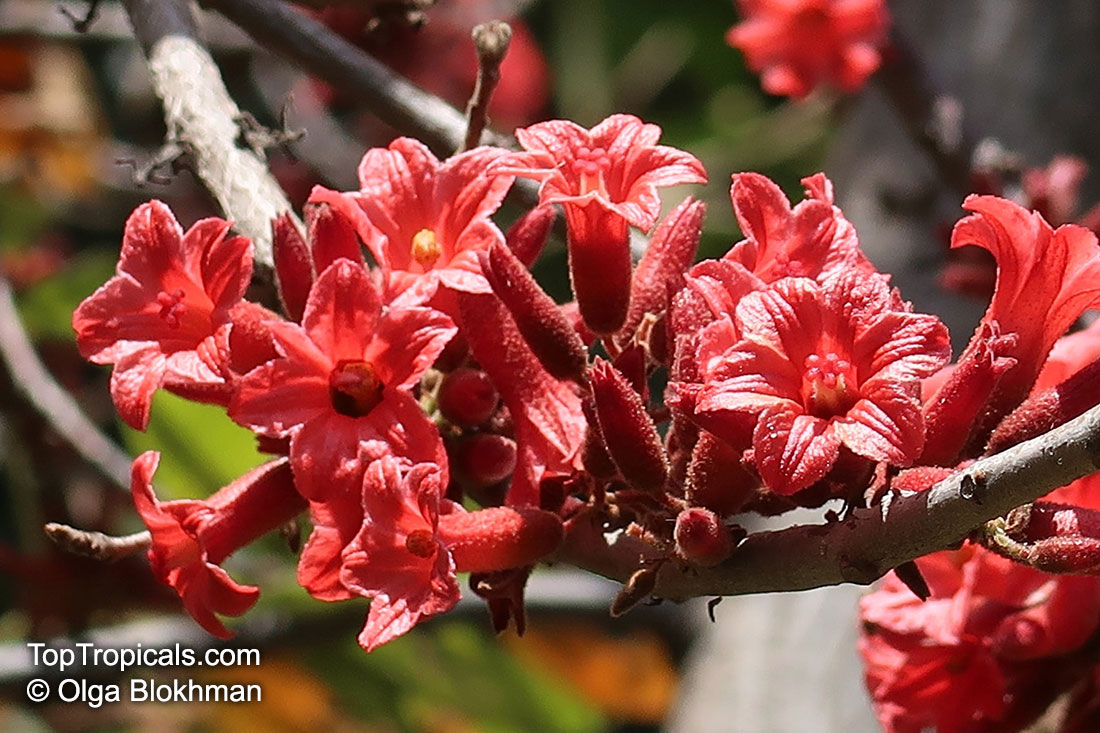
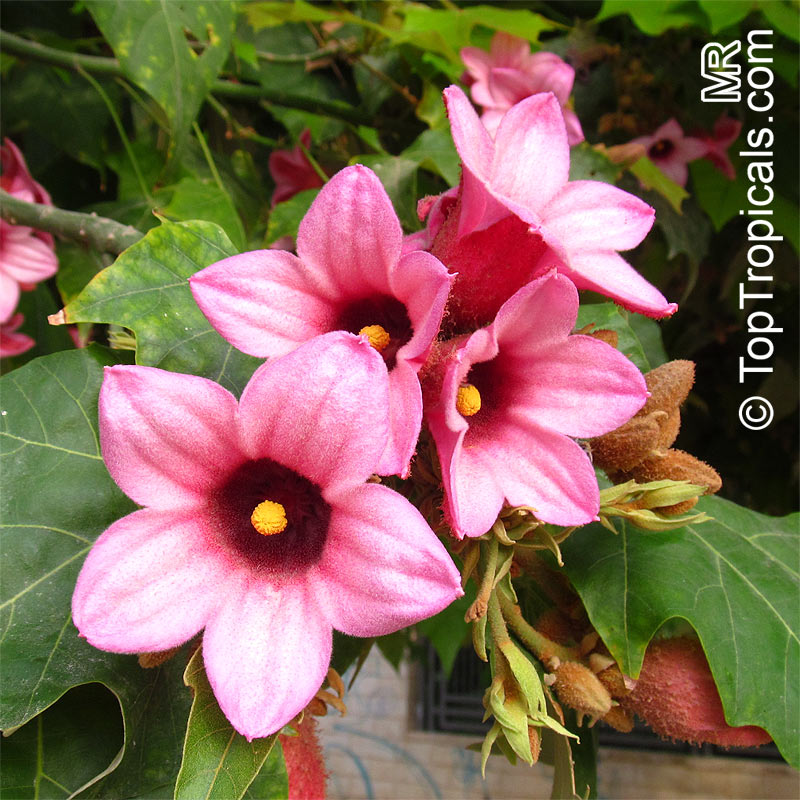
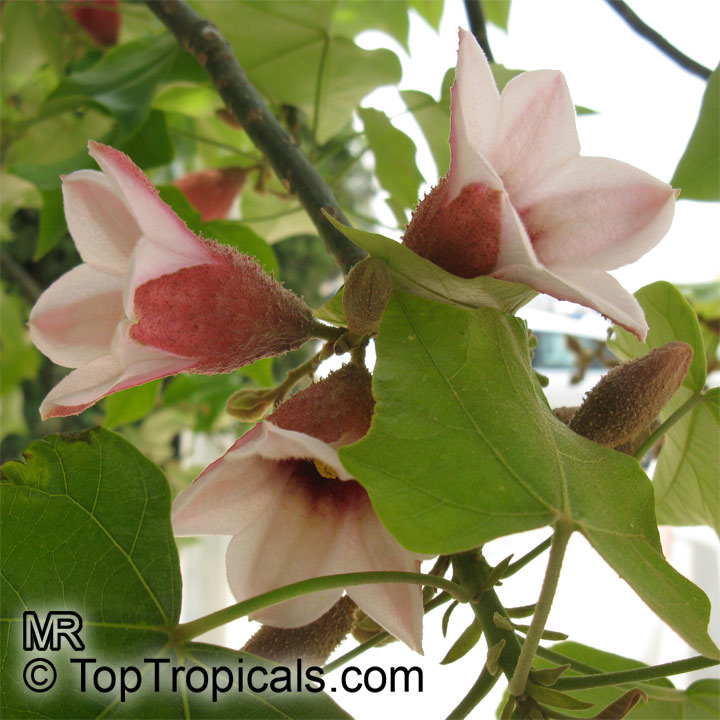
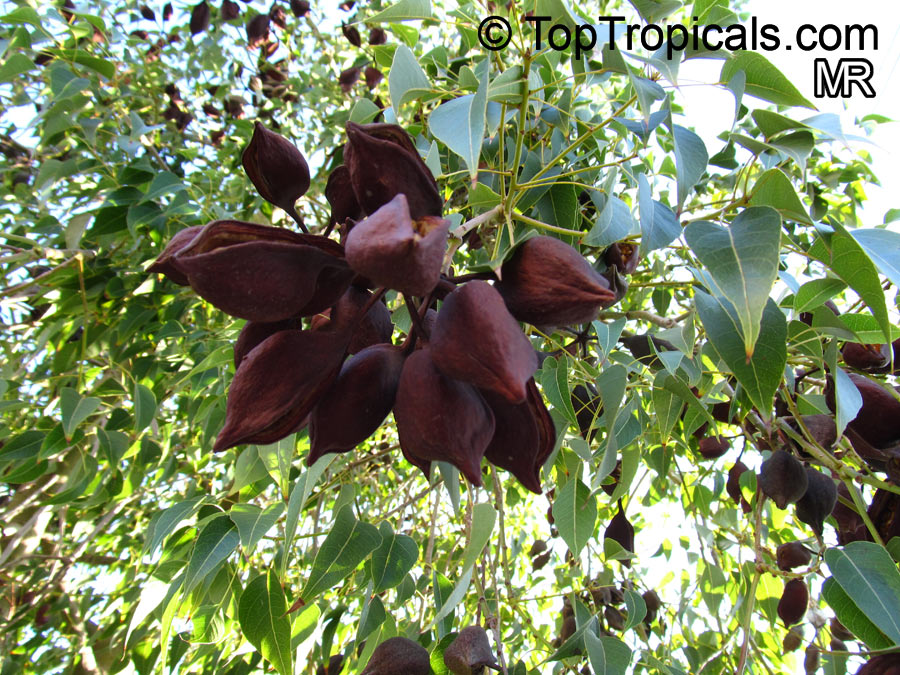
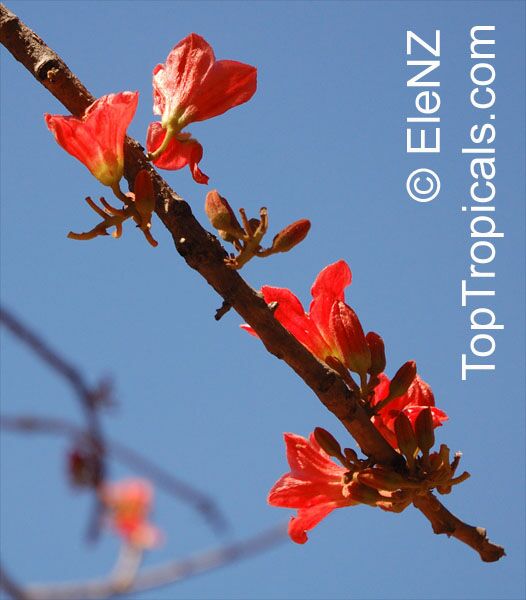
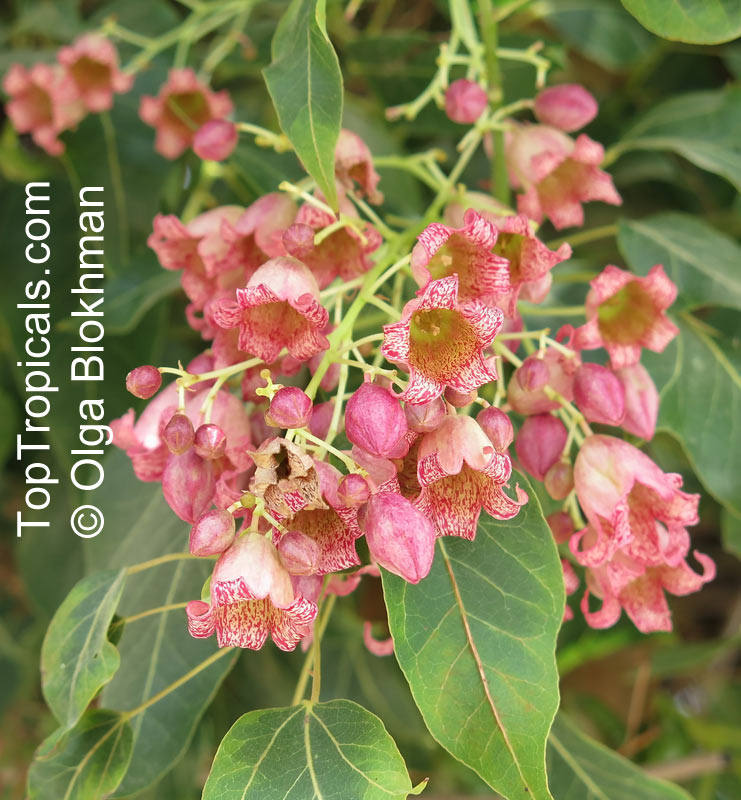
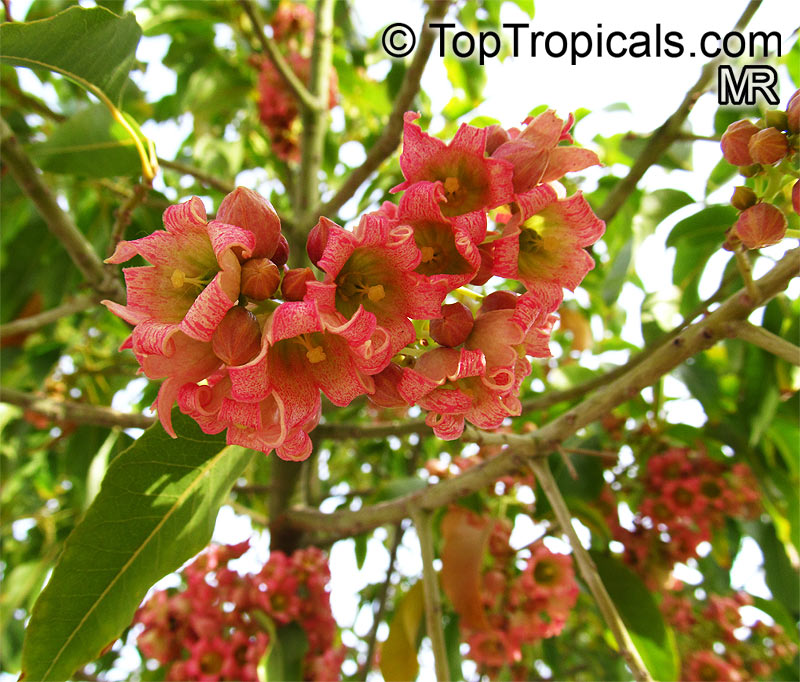
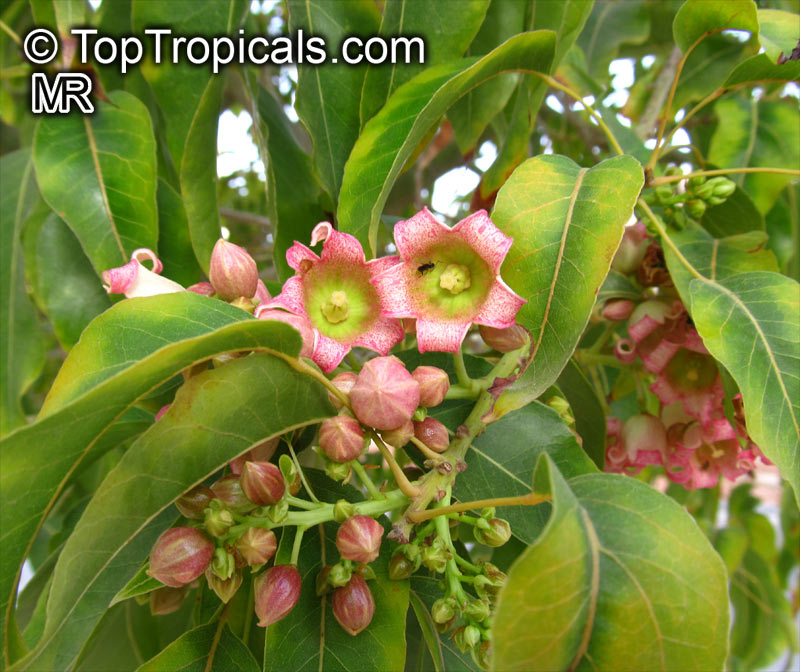
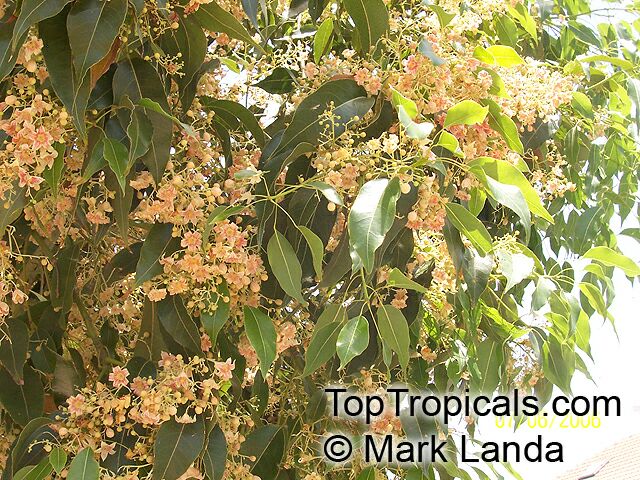
Brachychiton bidwillii is a native of Australia and has small, green leaves. It's an evergreen species which can reach a height of 10-20 ft. It has reddish to crimson and vinous coloured flowers which are attractive to butterflies and hummingbirds during their blooming period. The kind of flower displayed depends on the form of the plant. It can be used for Bonsai. Its trunk is covered in a brown, corky bark that is used by some aboriginals for canoes and other items. The caudex (trunk) of the plant is swollen and can store large amounts of water in its fleshy stems. This is a benefit to the plant in drought conditions.
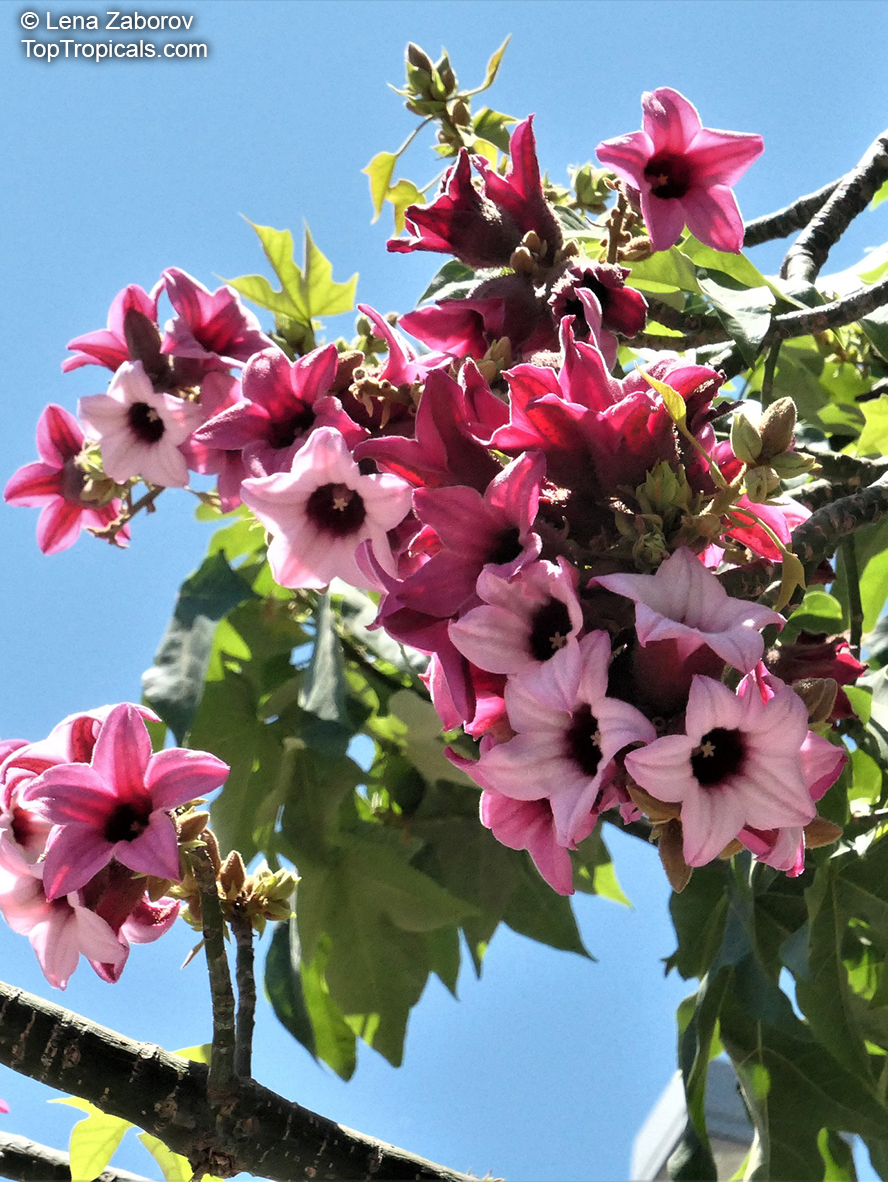
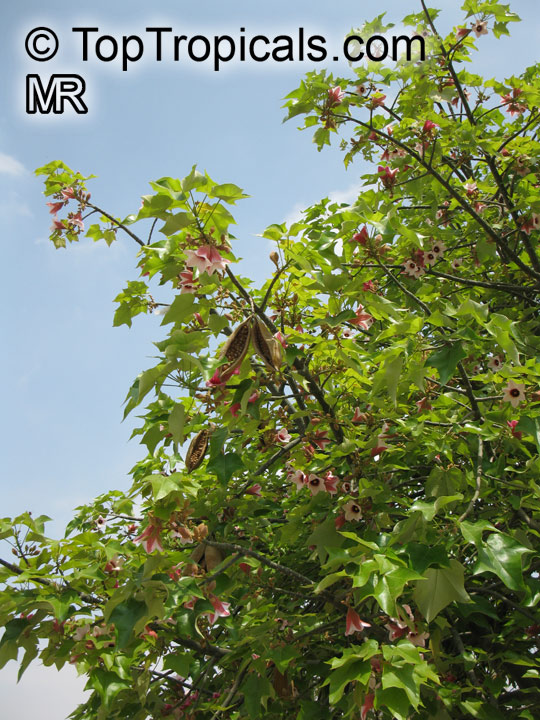
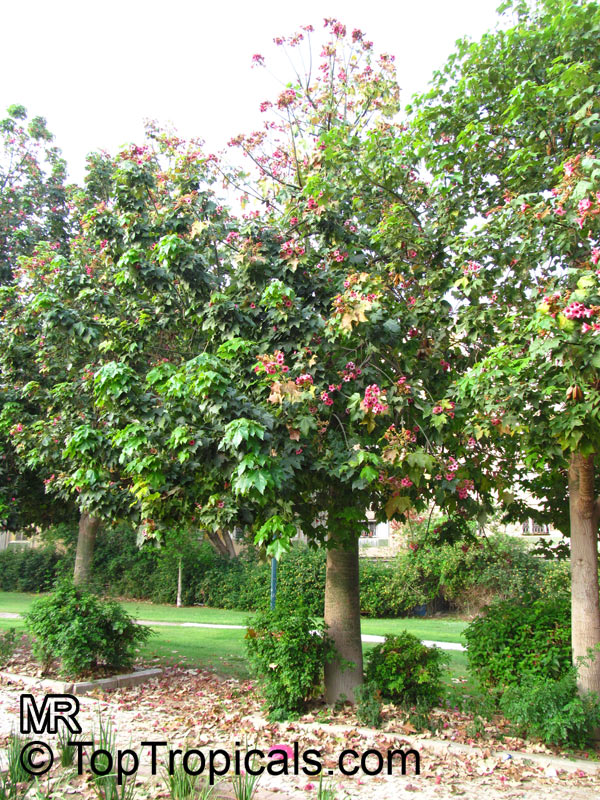
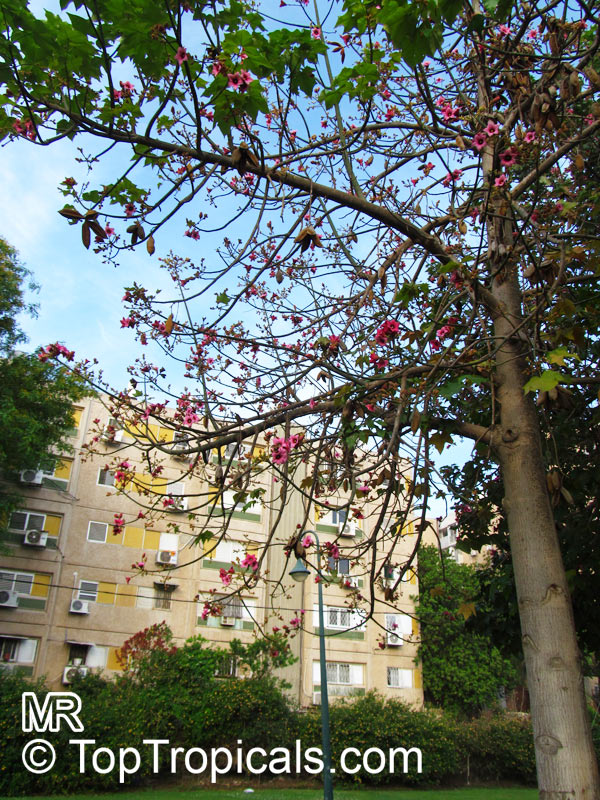
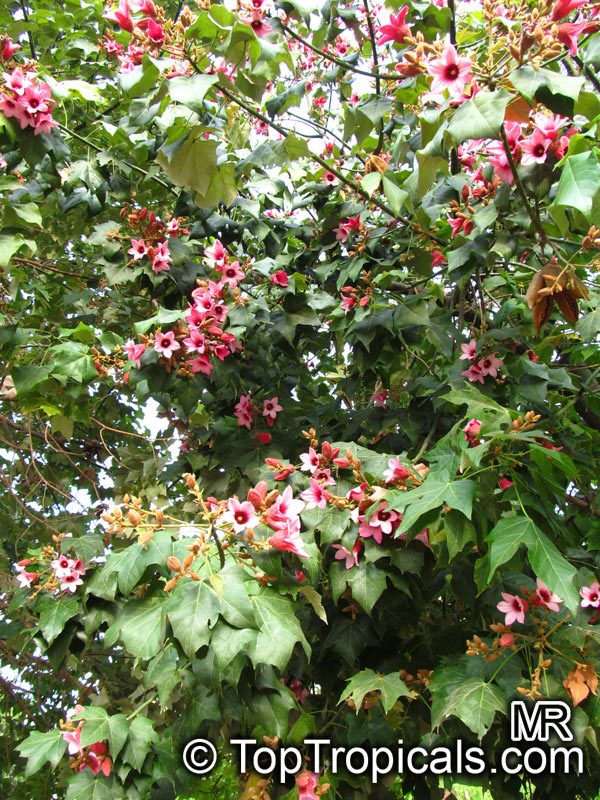
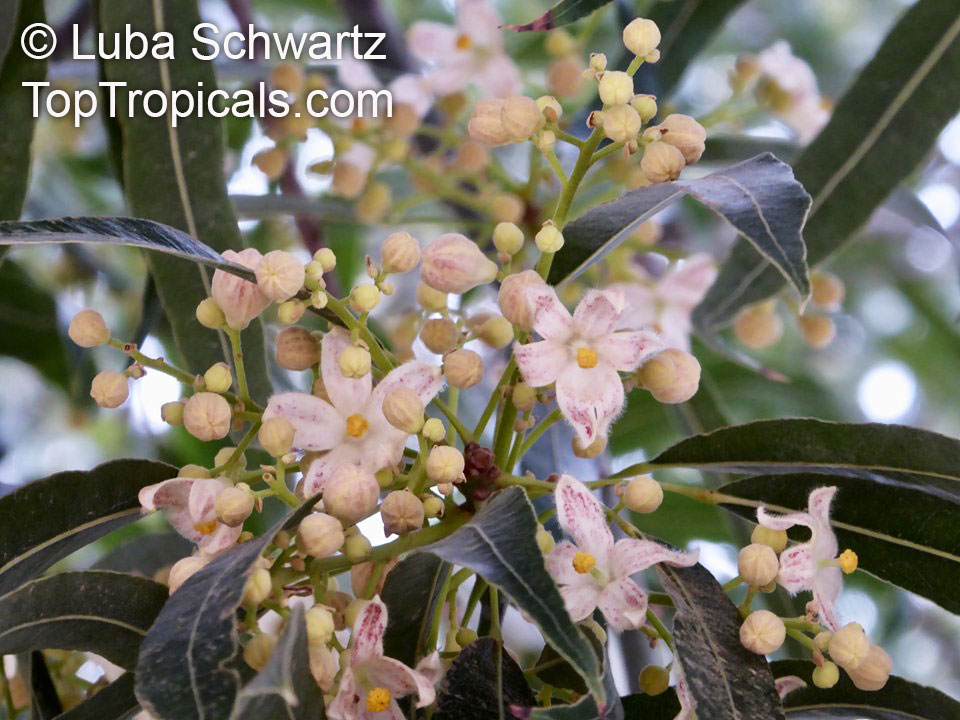
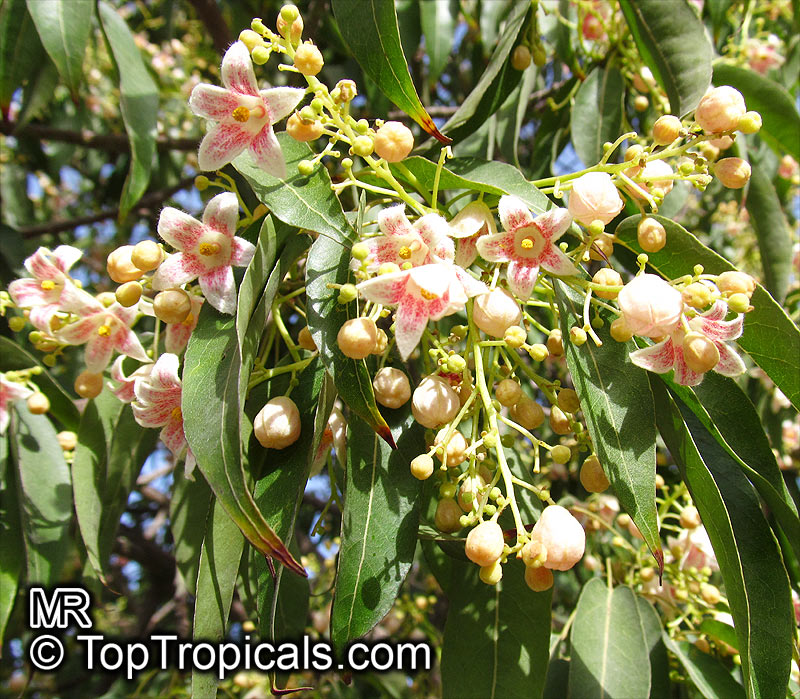
Botanical names: Brachychiton discolor, Brachychiton paradoxus var. discolor
Common names: Lacebark Kurrajong, Pink Flame Tree
Family: Malvaceae
Subfamily: Sterculioideae
Origin: South-Eastern Queensland





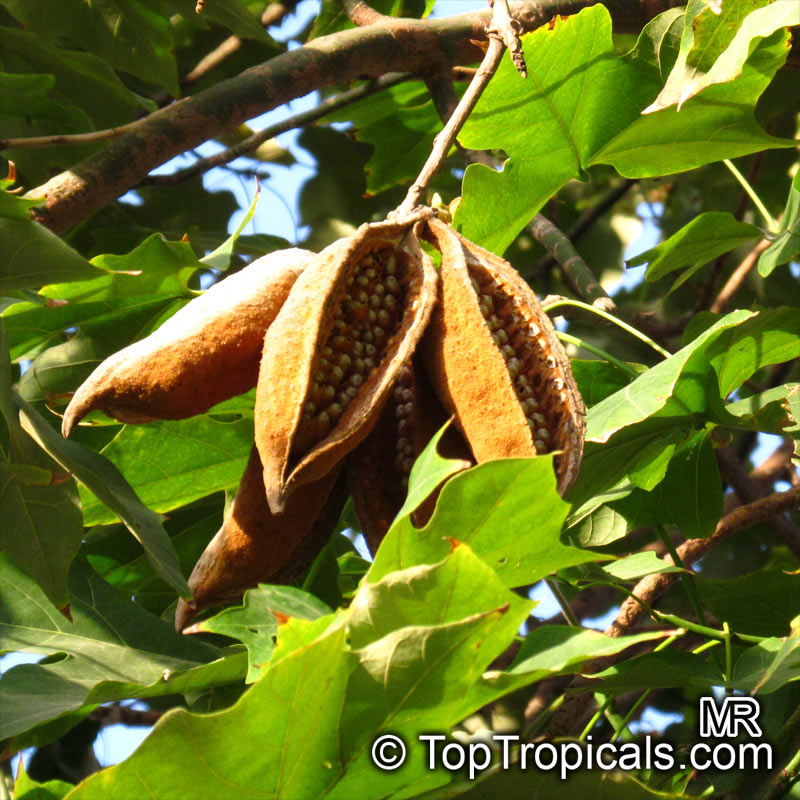
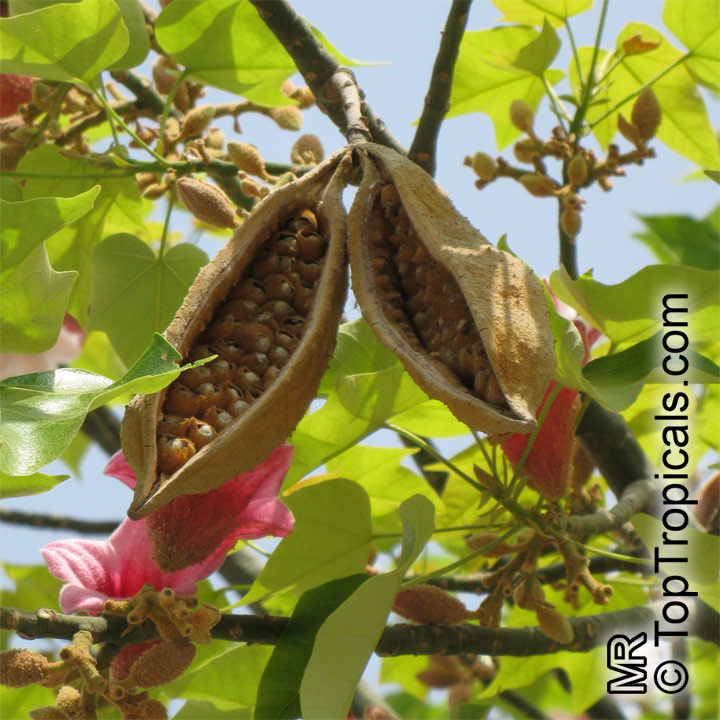
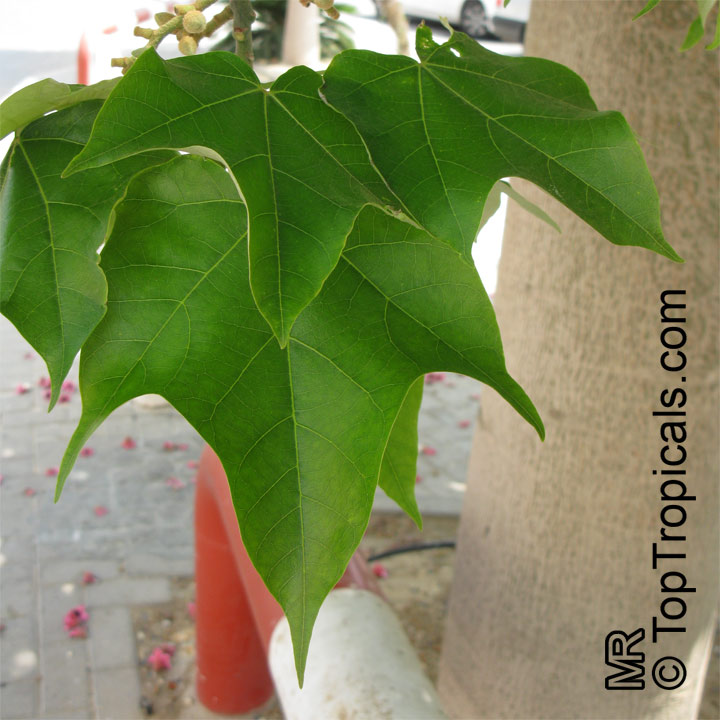
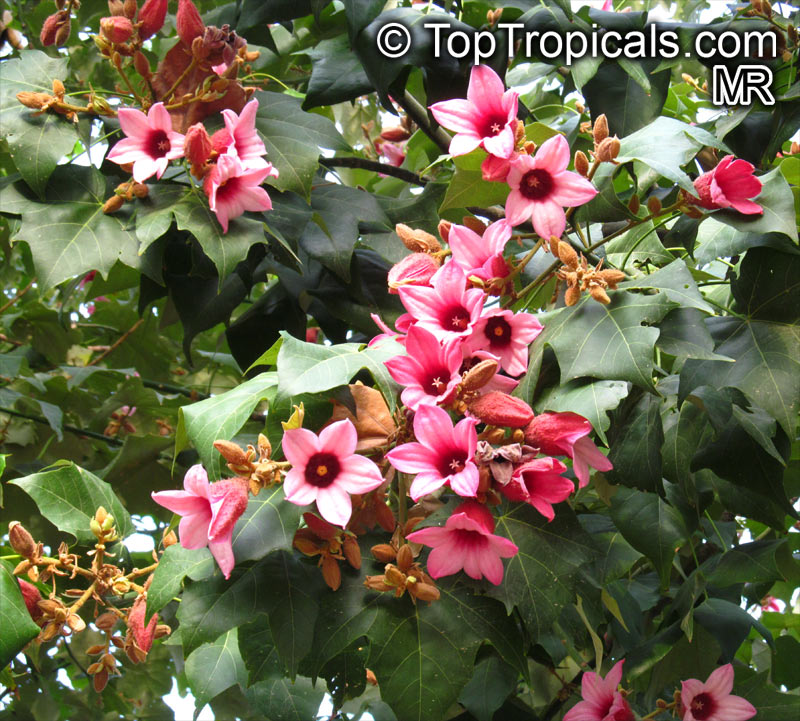
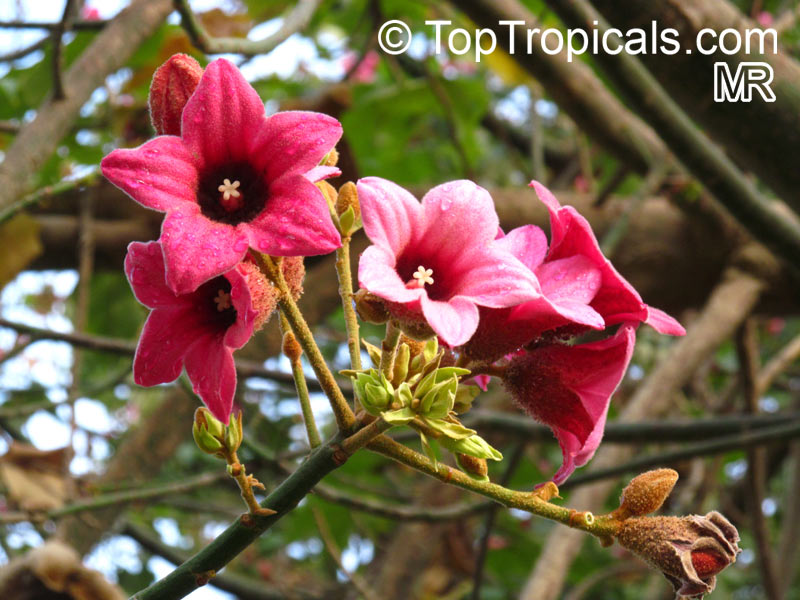
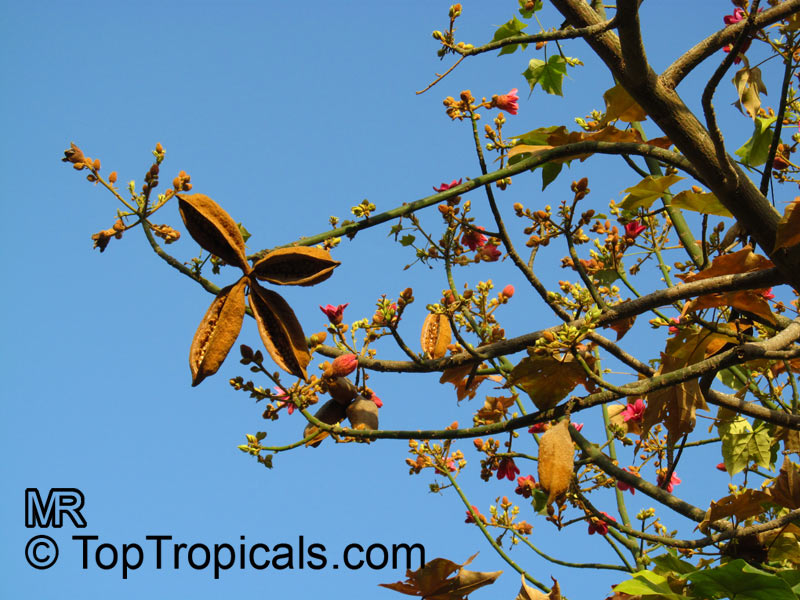
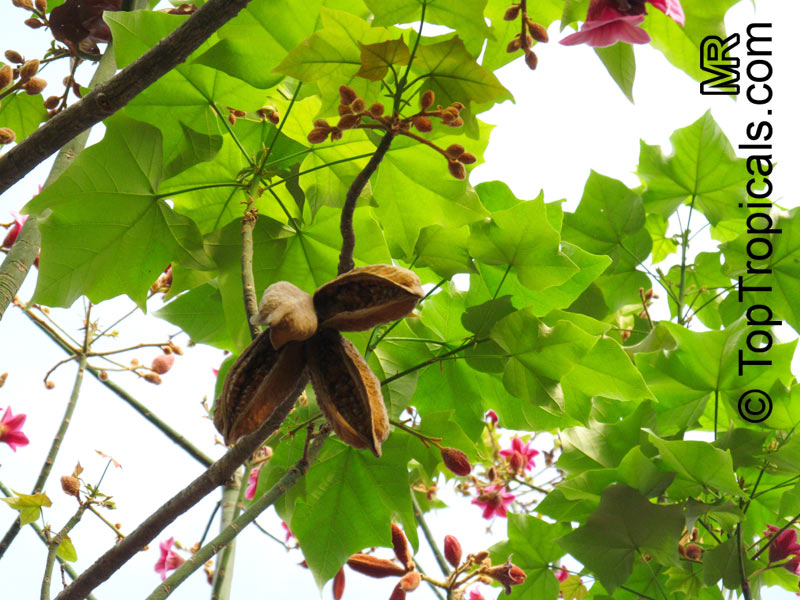
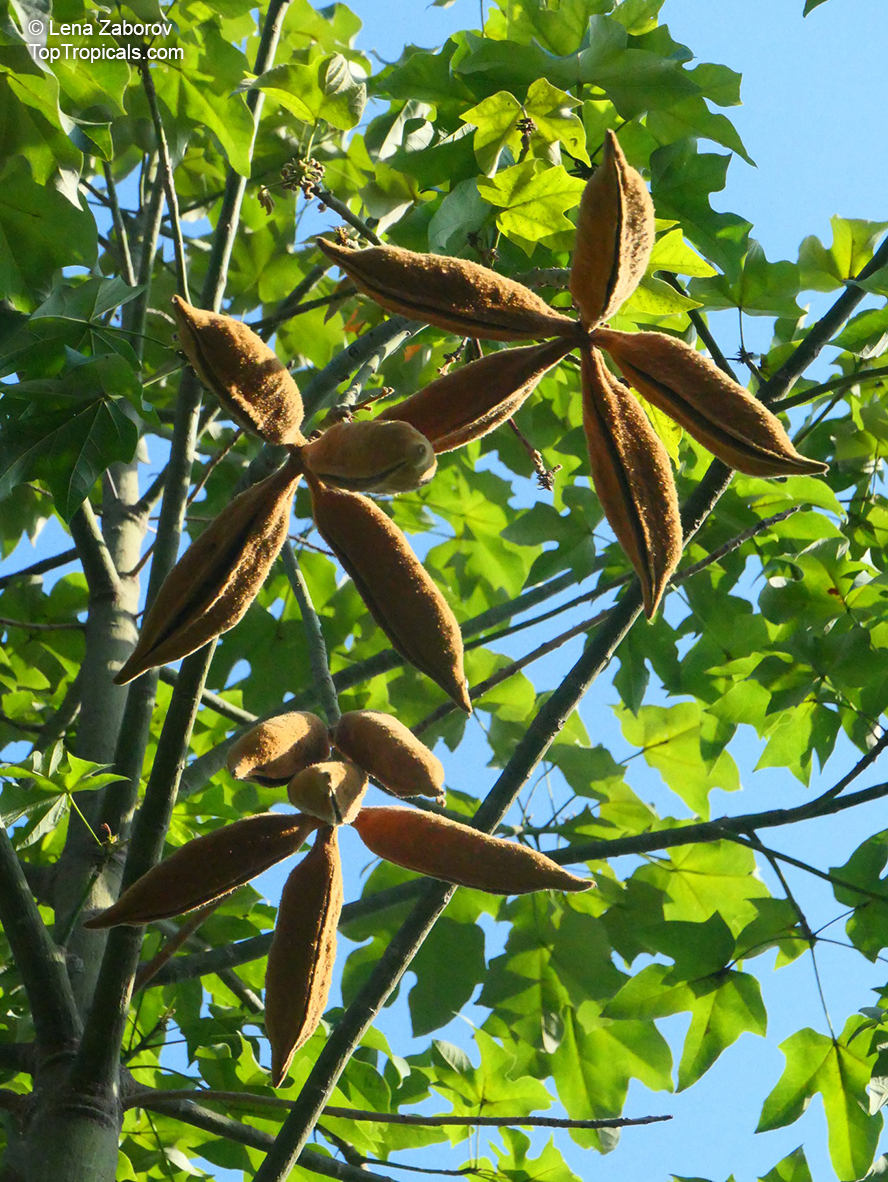
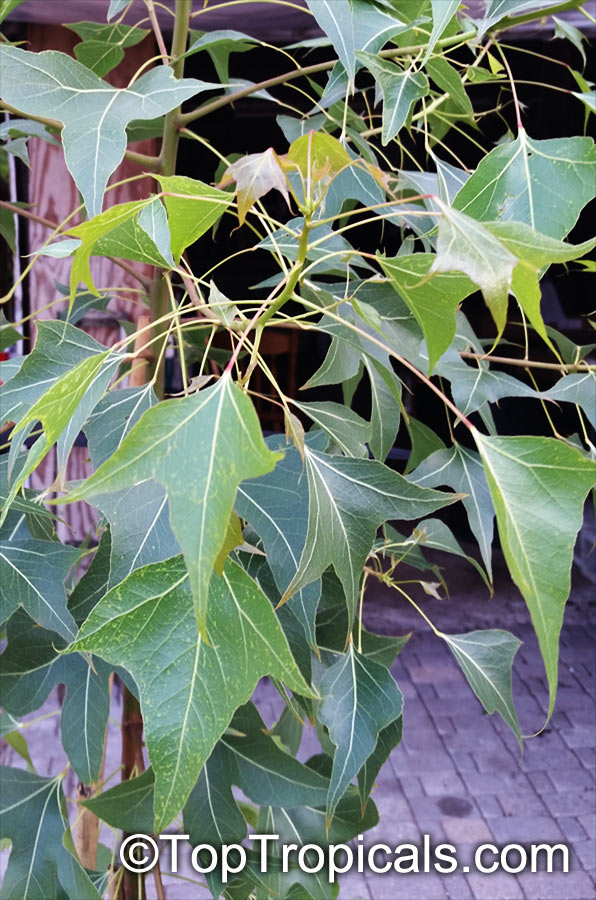
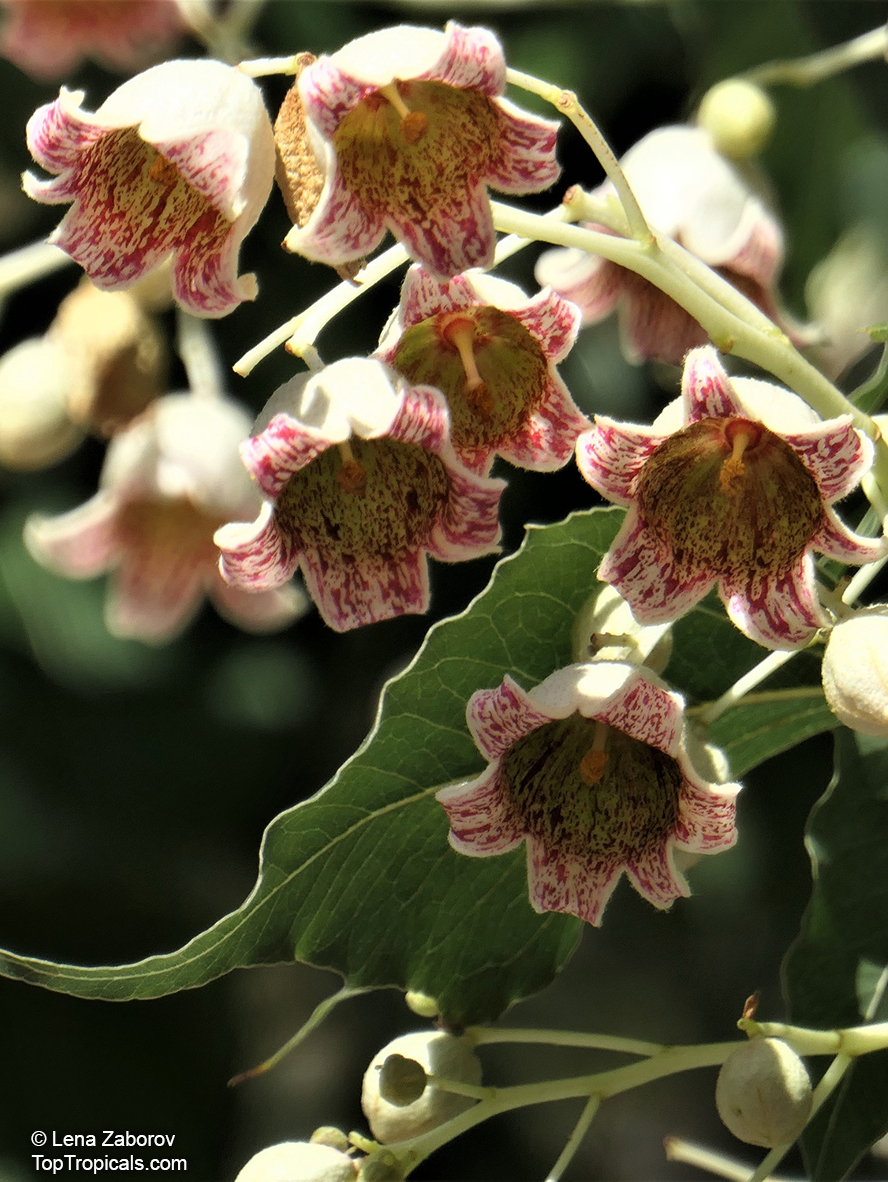
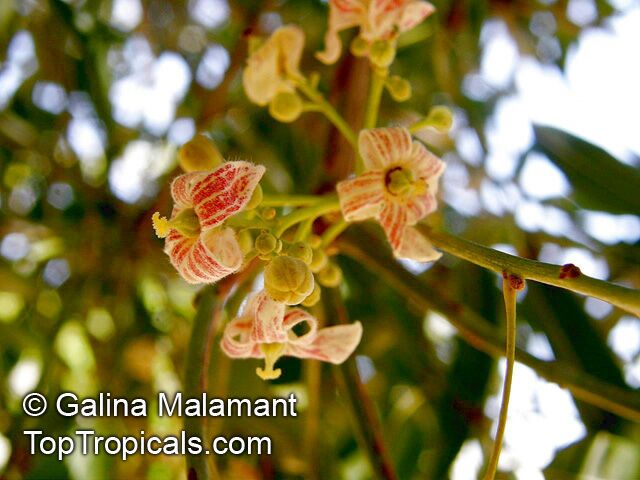
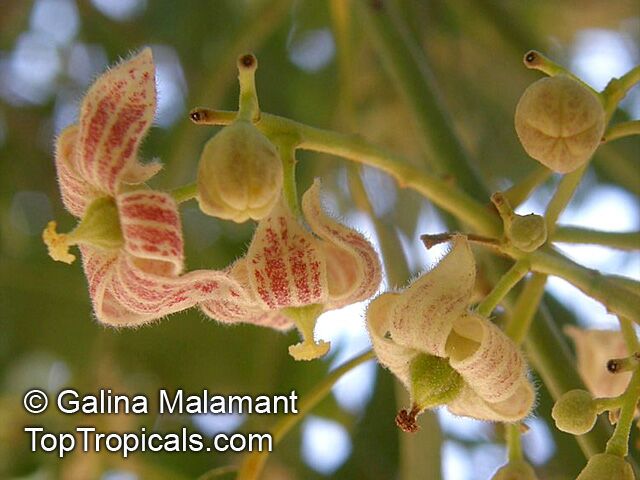
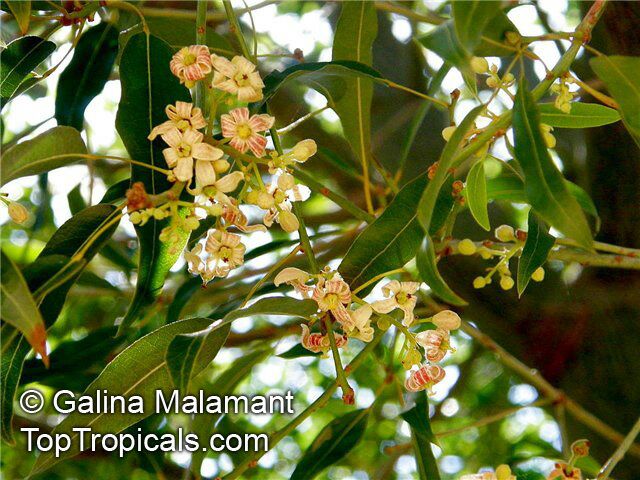
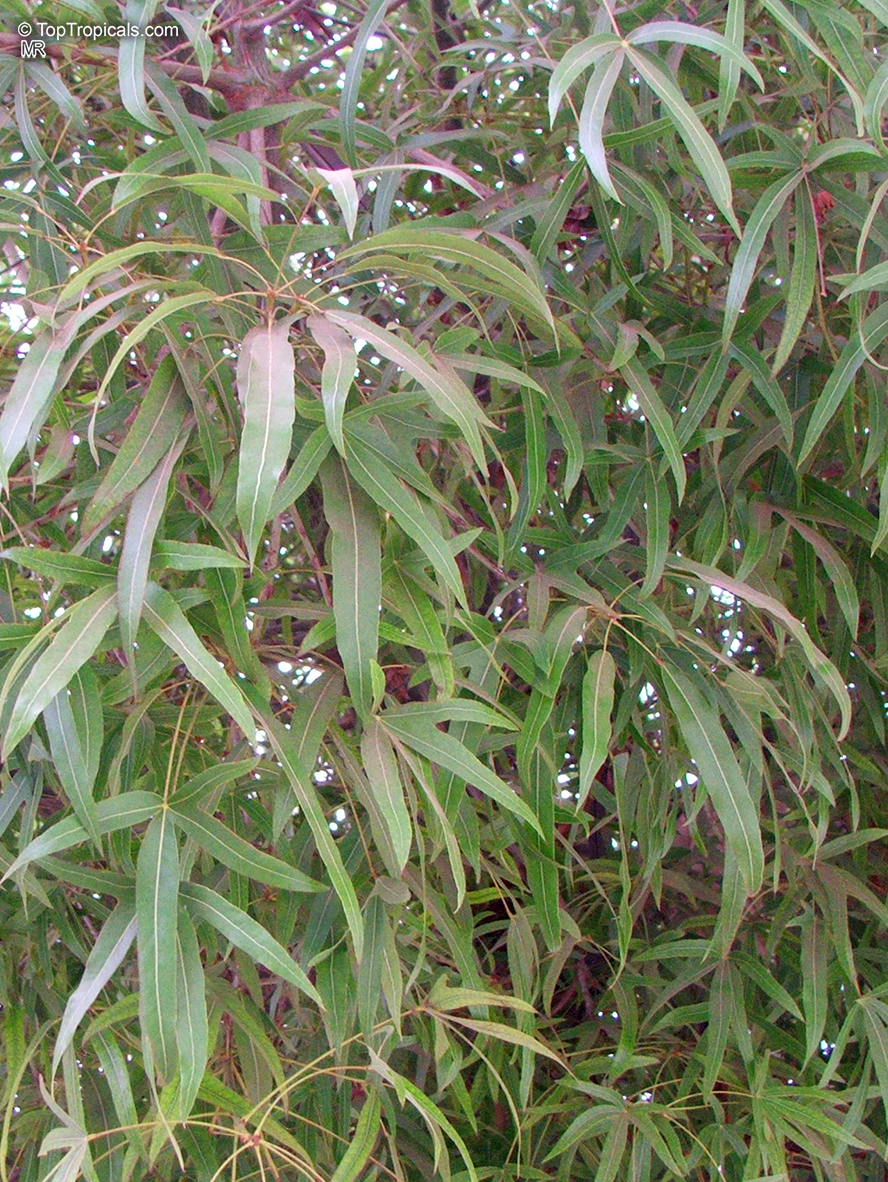
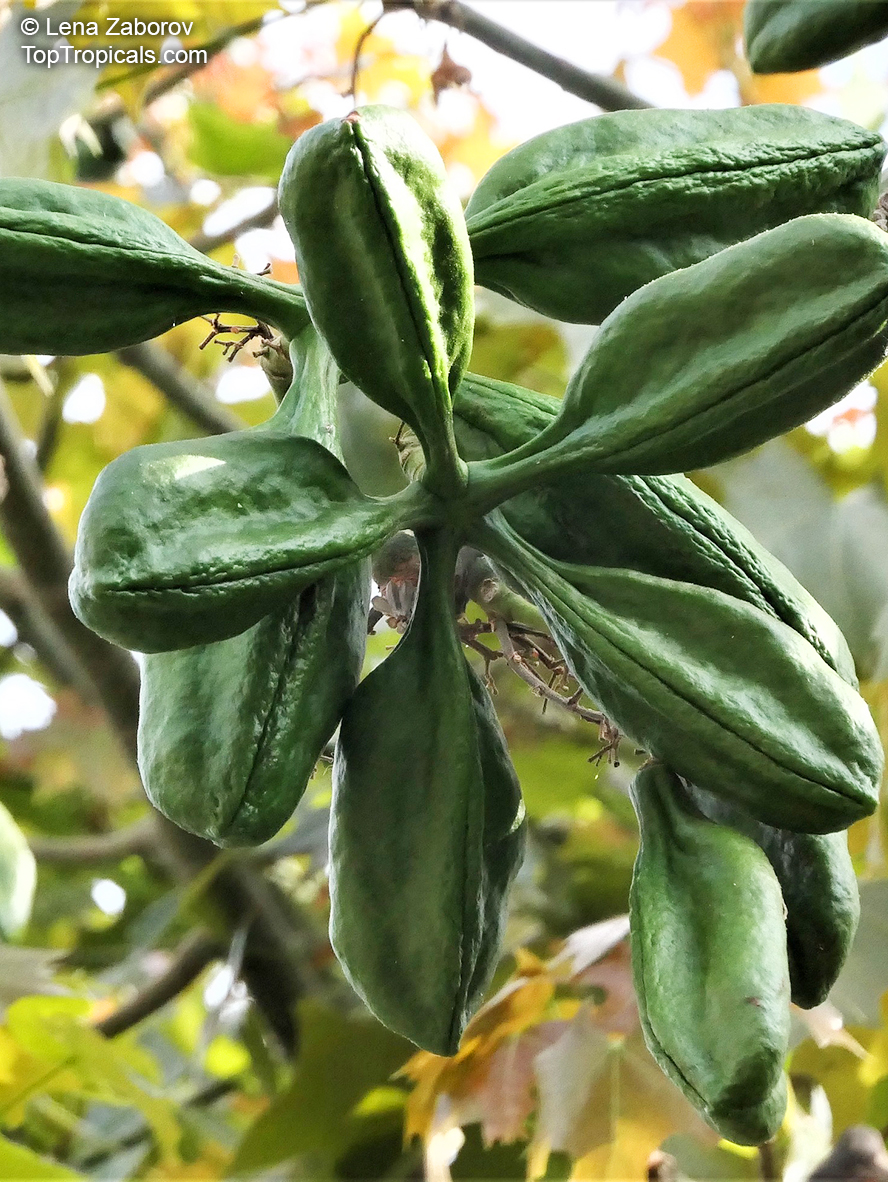
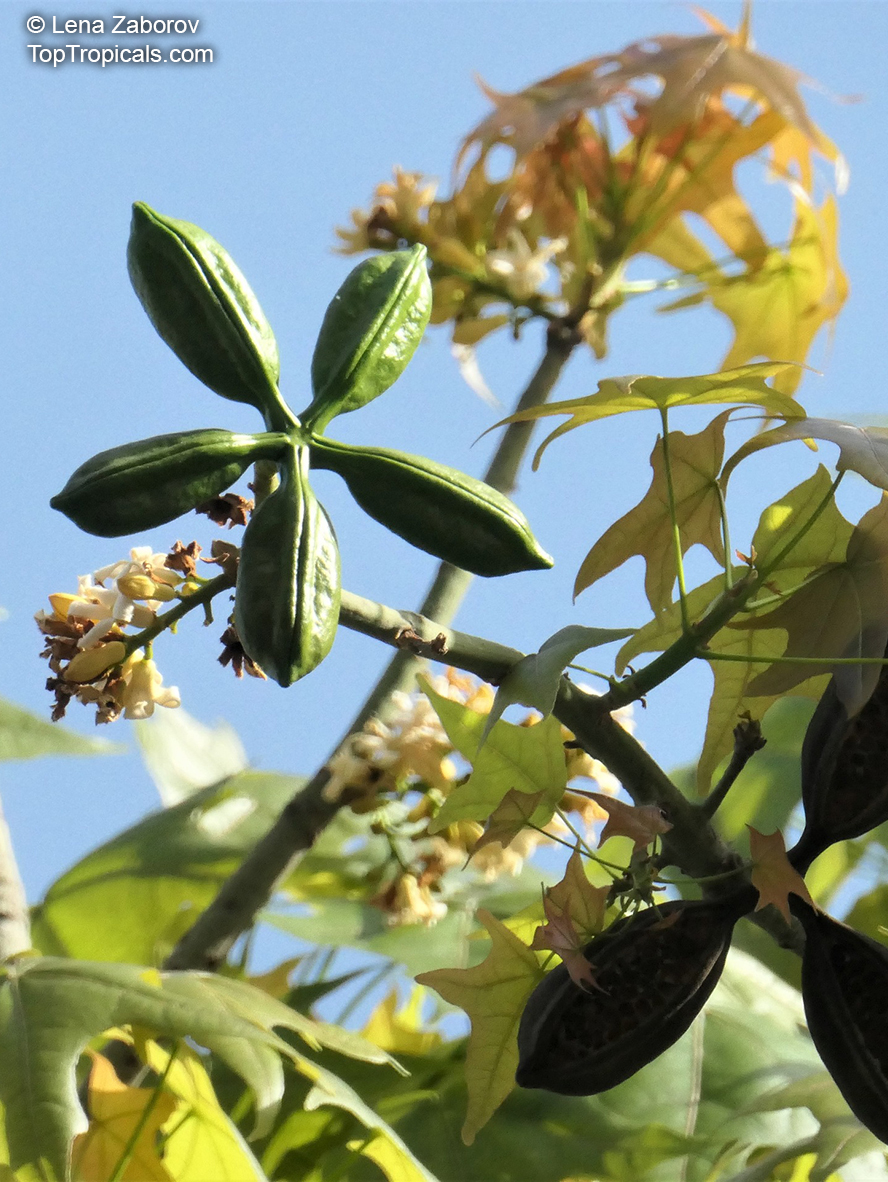
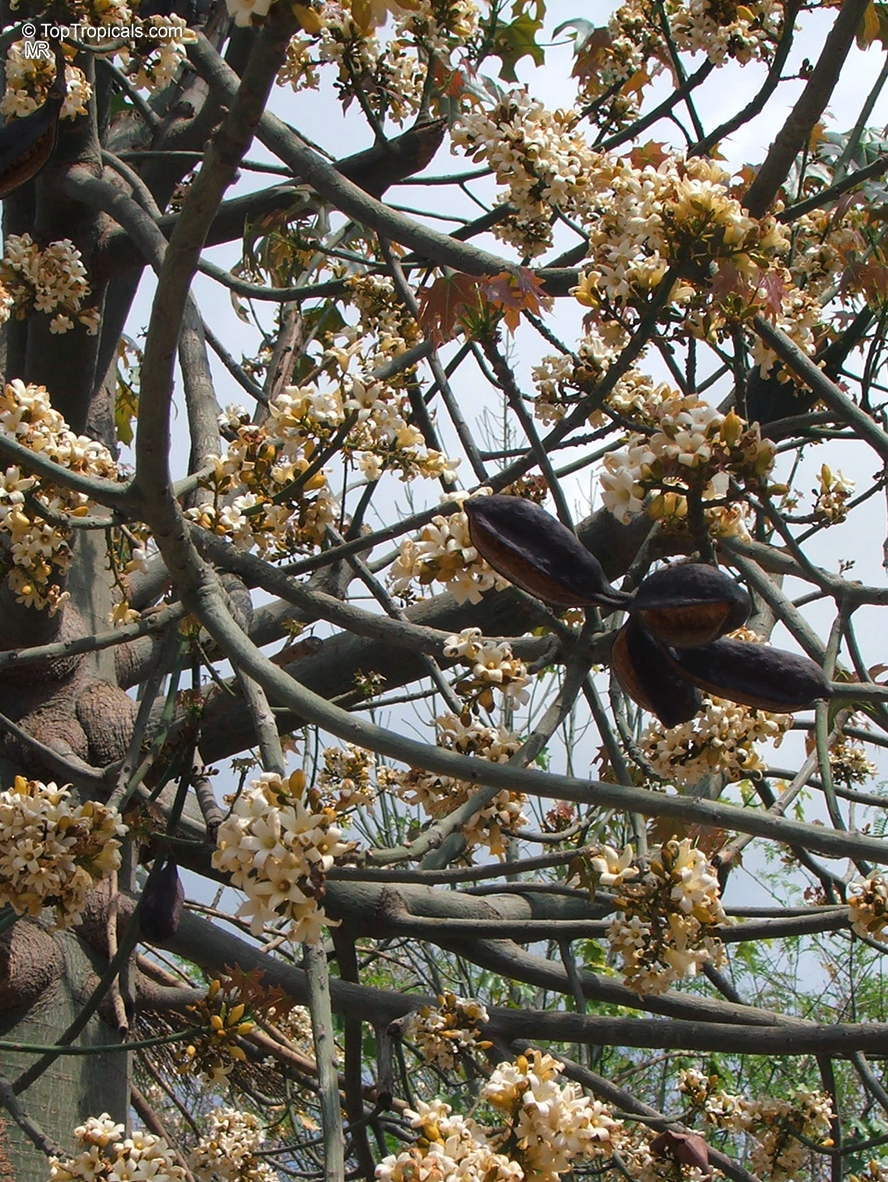
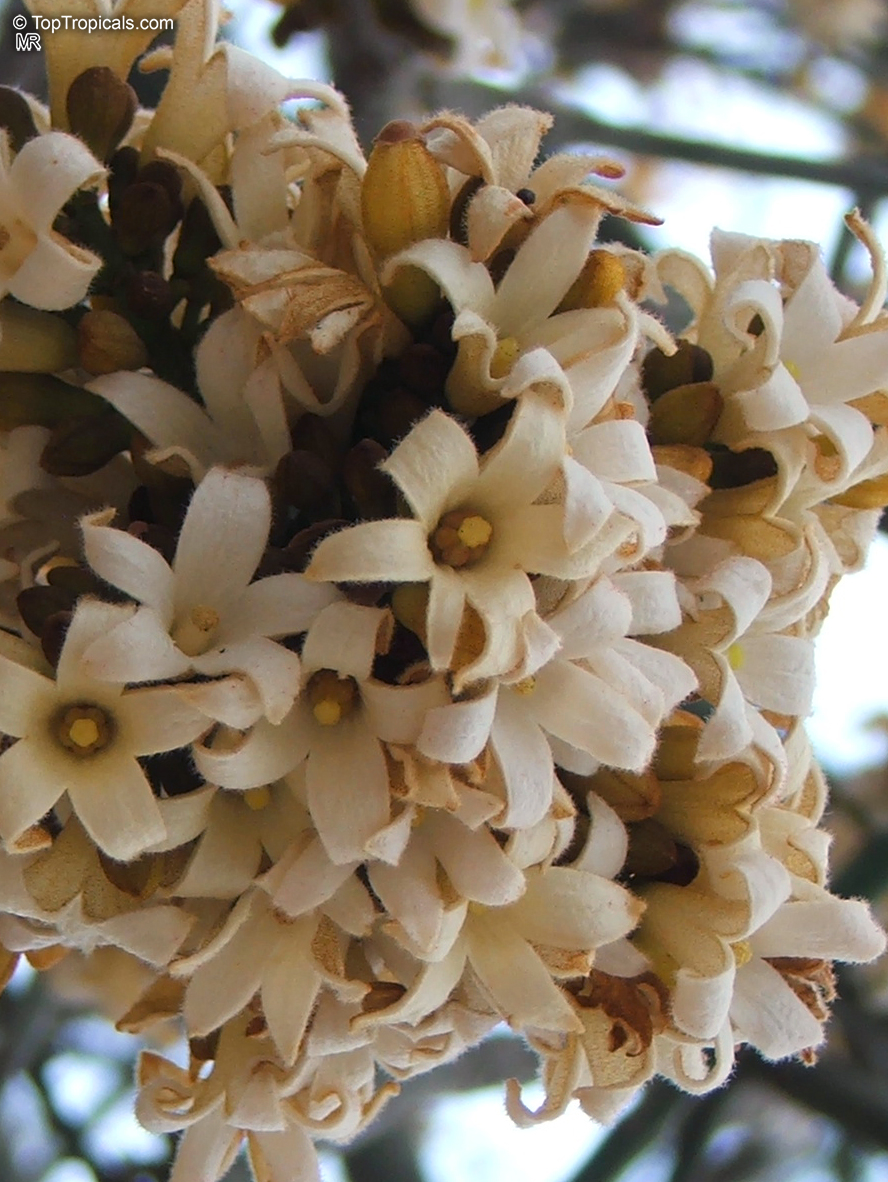
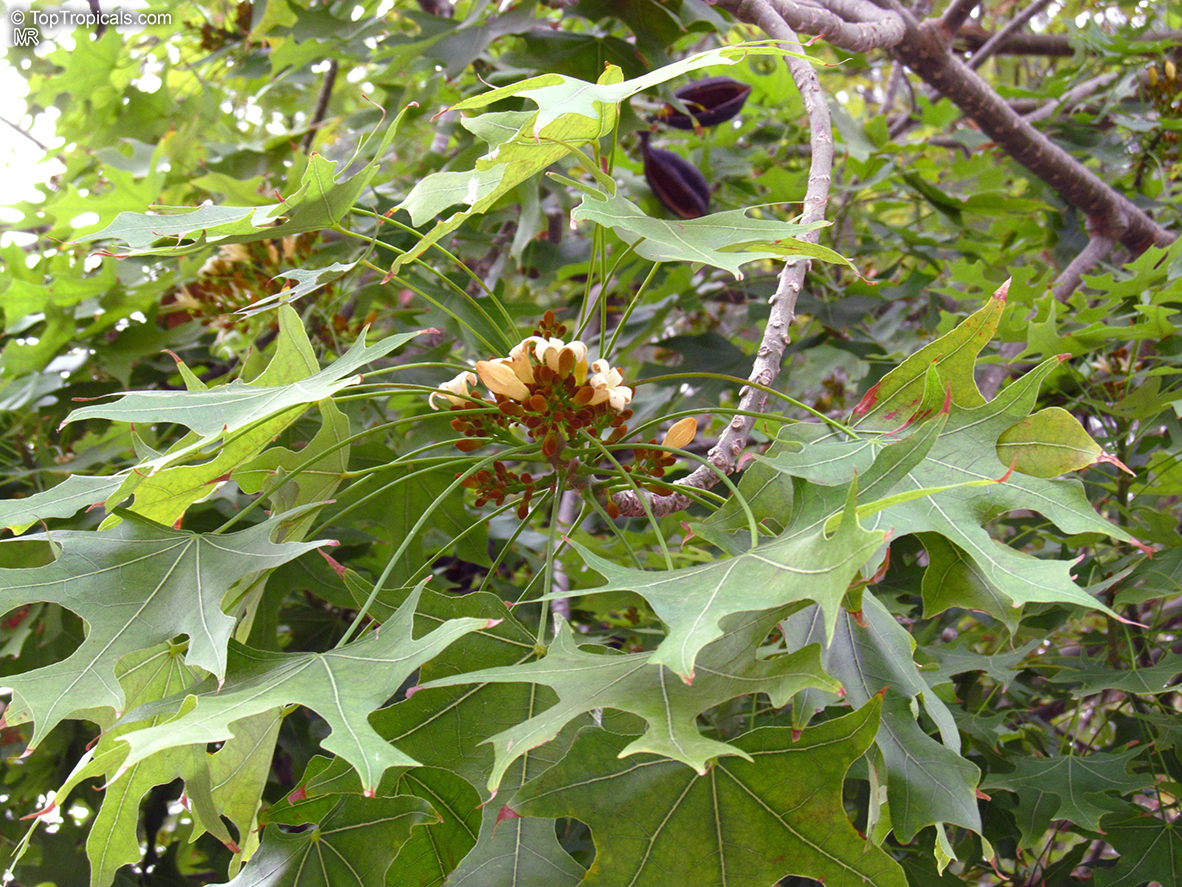
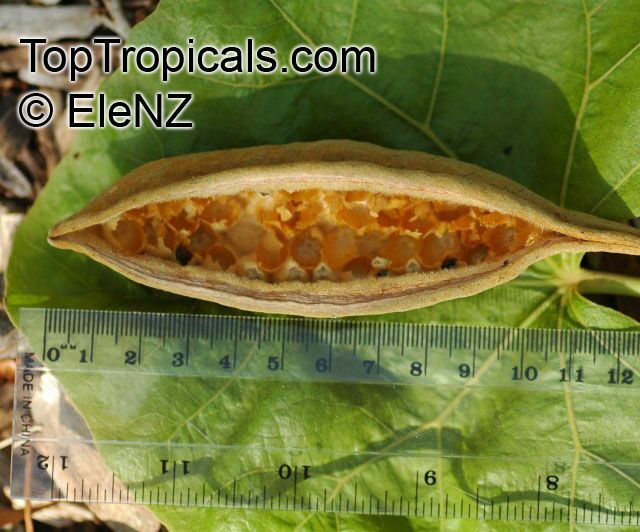
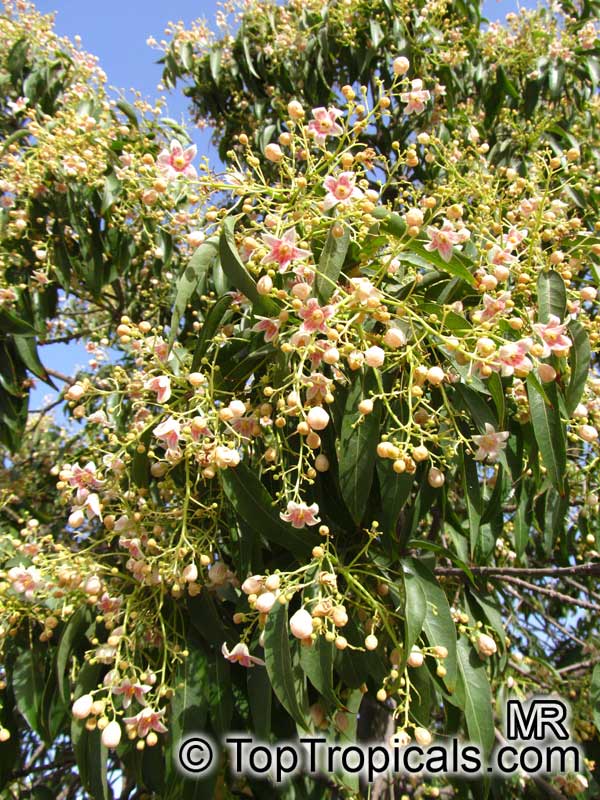
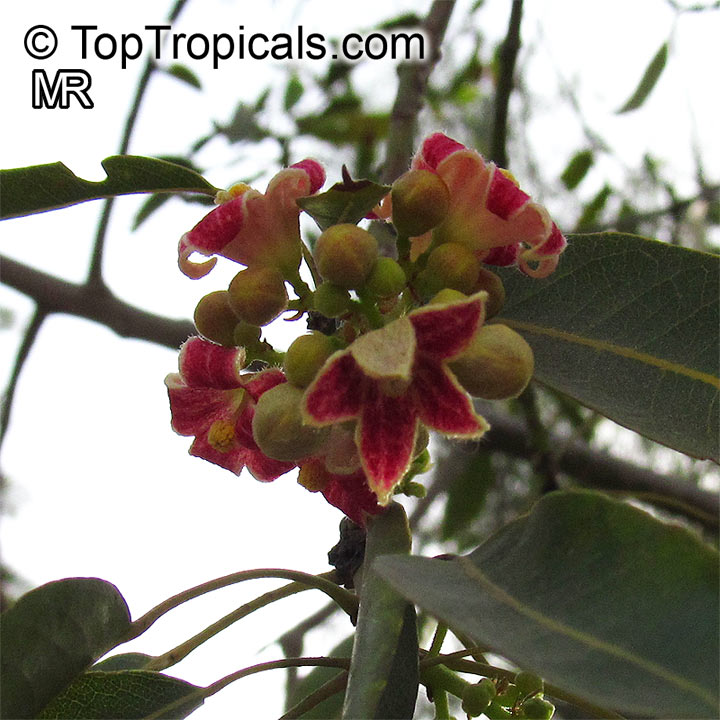
Brachychiton is a genus of 30 or more species, most of which occur in tropical parts of Australia in dry areas or in rainforest. They are large shrubs or trees. One of the most commonly cultivated is the Illawarra flame tree (Brachychiton acerifolius) which is popular due to its spectacular crimson flowers. The Kurrajong (B.populneus) is one of the most widely distributed and is also a common tree in cultivation. Leaves are about 4" to 6" long and deeply lobed. The large, bell-shaped flowers are usually deep pink and occur in clusters at the ends of the branches. The flowers are very spectacular and are followed by seed capsules which contain many large seeds. B. Discolor is reasonably common in cultivation and is hardy in a range of climates although it may be slow growing. It tolerates a range of soils.
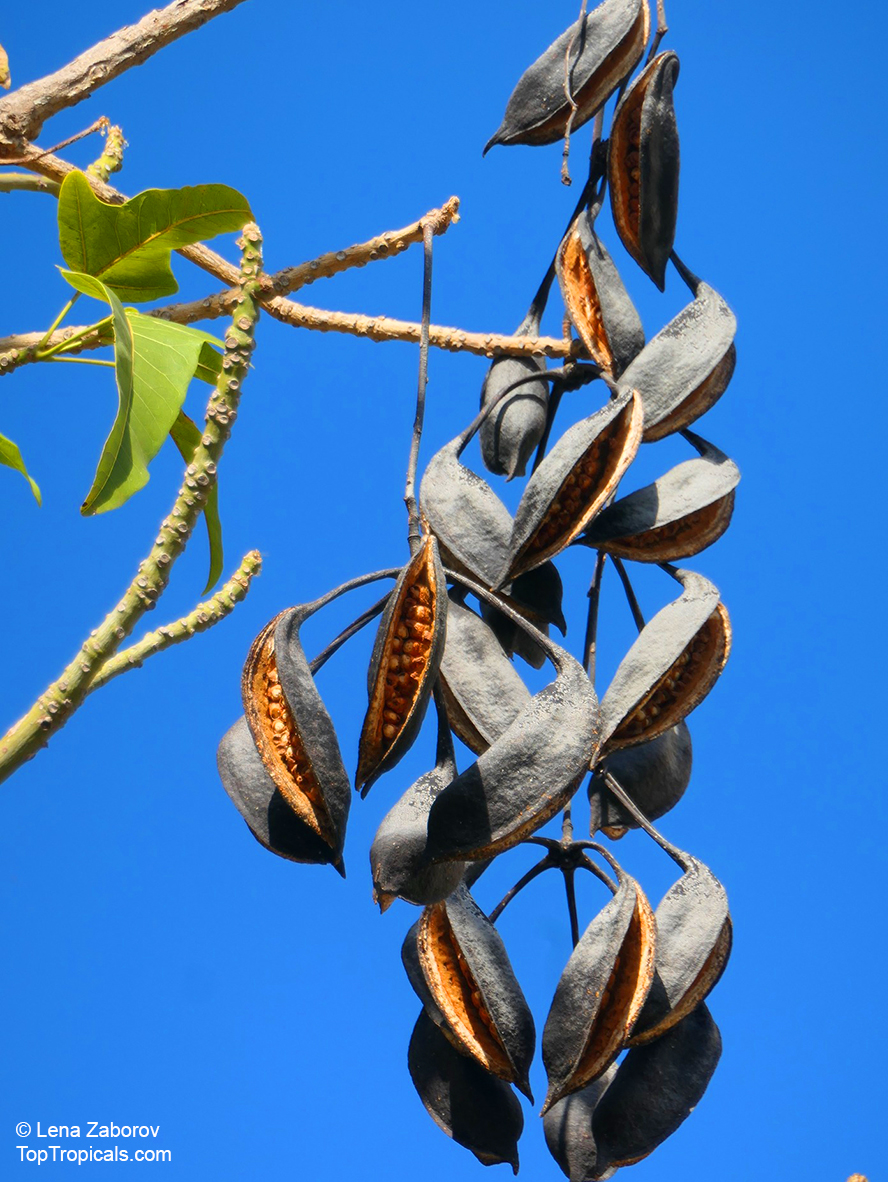
Propagation from seed is relatively easy without any pretreatment. The seeds are surrounded in the capsule by irritant hairs and are best collected using gloves. Brachychiton - from Greek, brachys, short and chiton, a tunic, a reference to the coating on the seed. Discolor -two different colors.
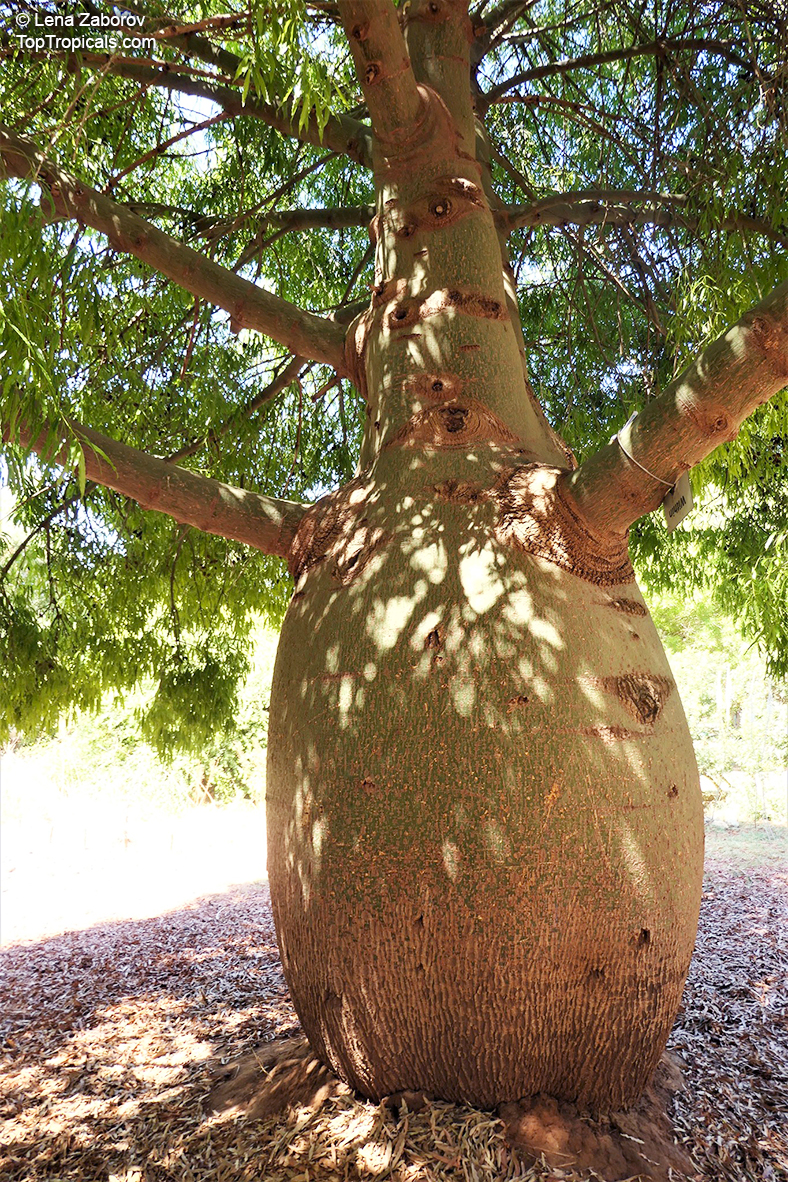
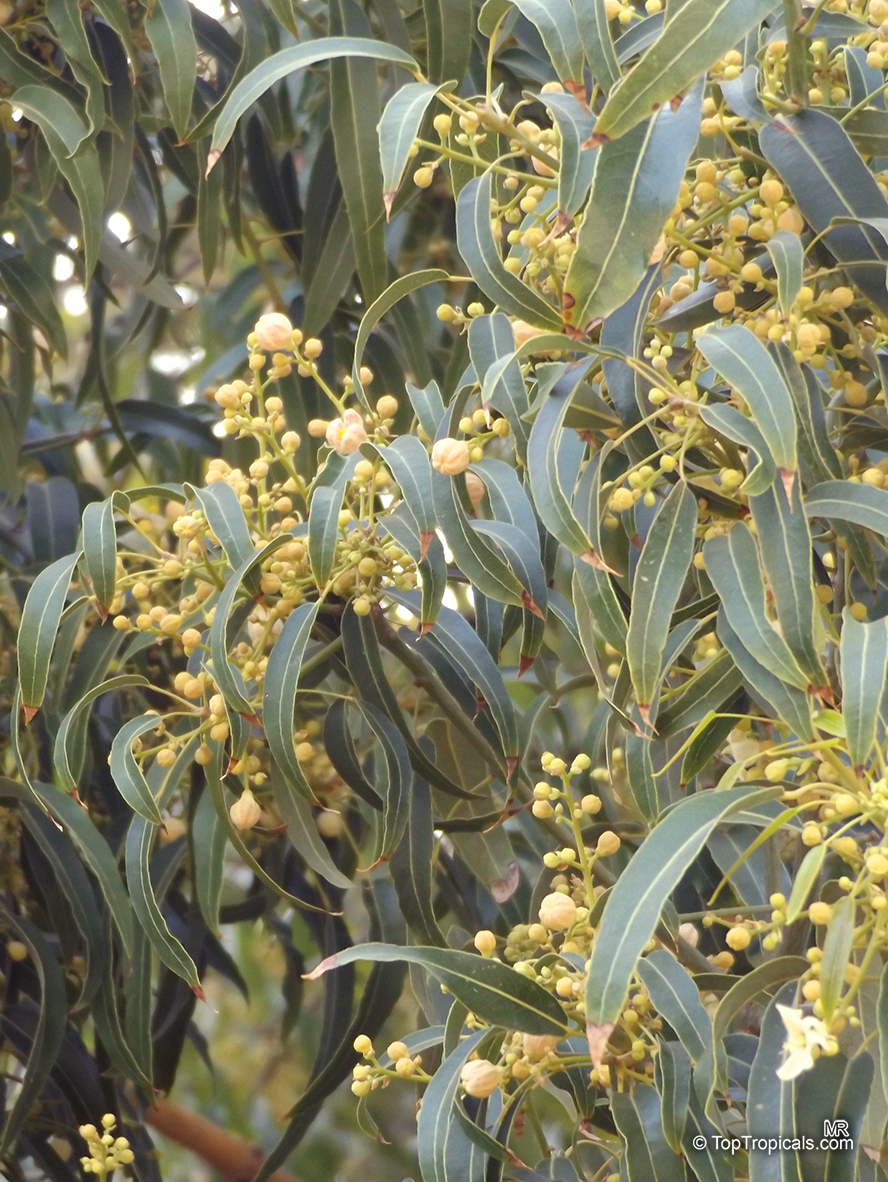
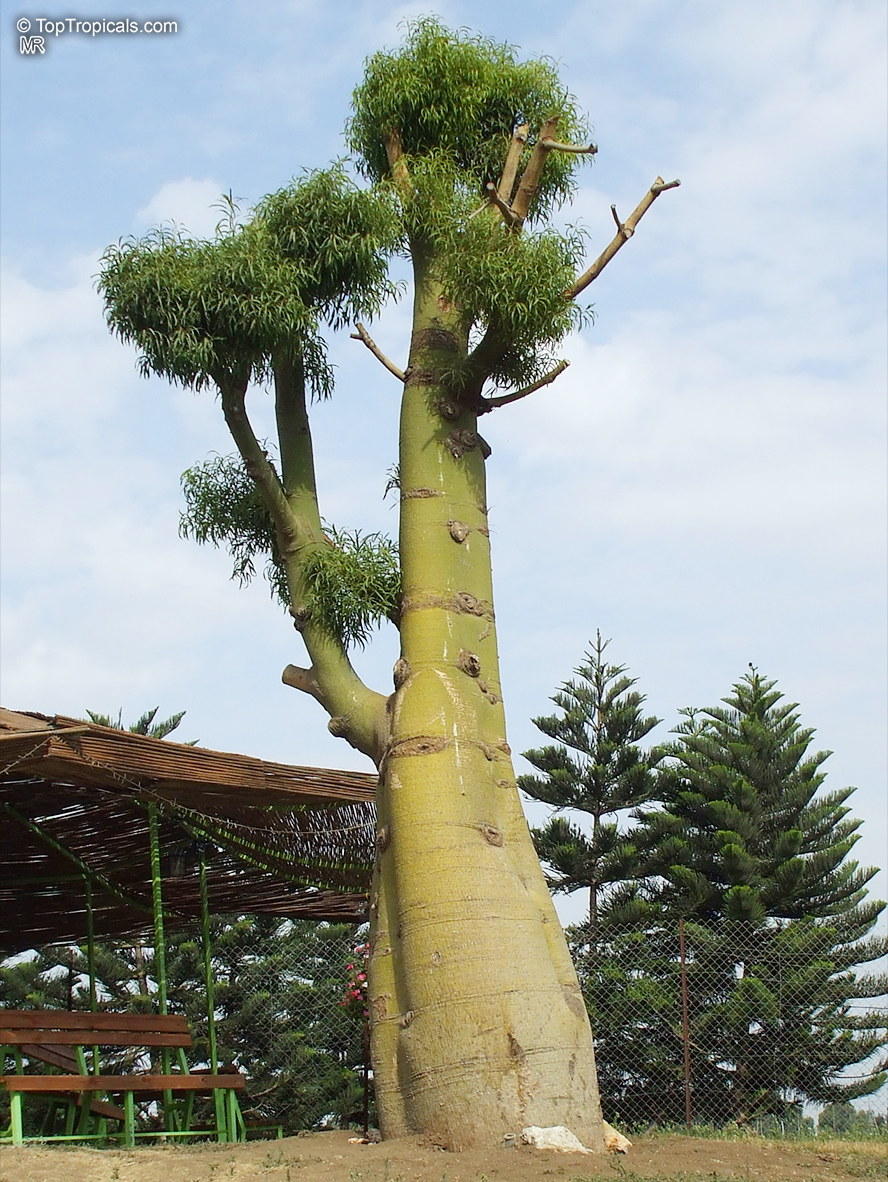
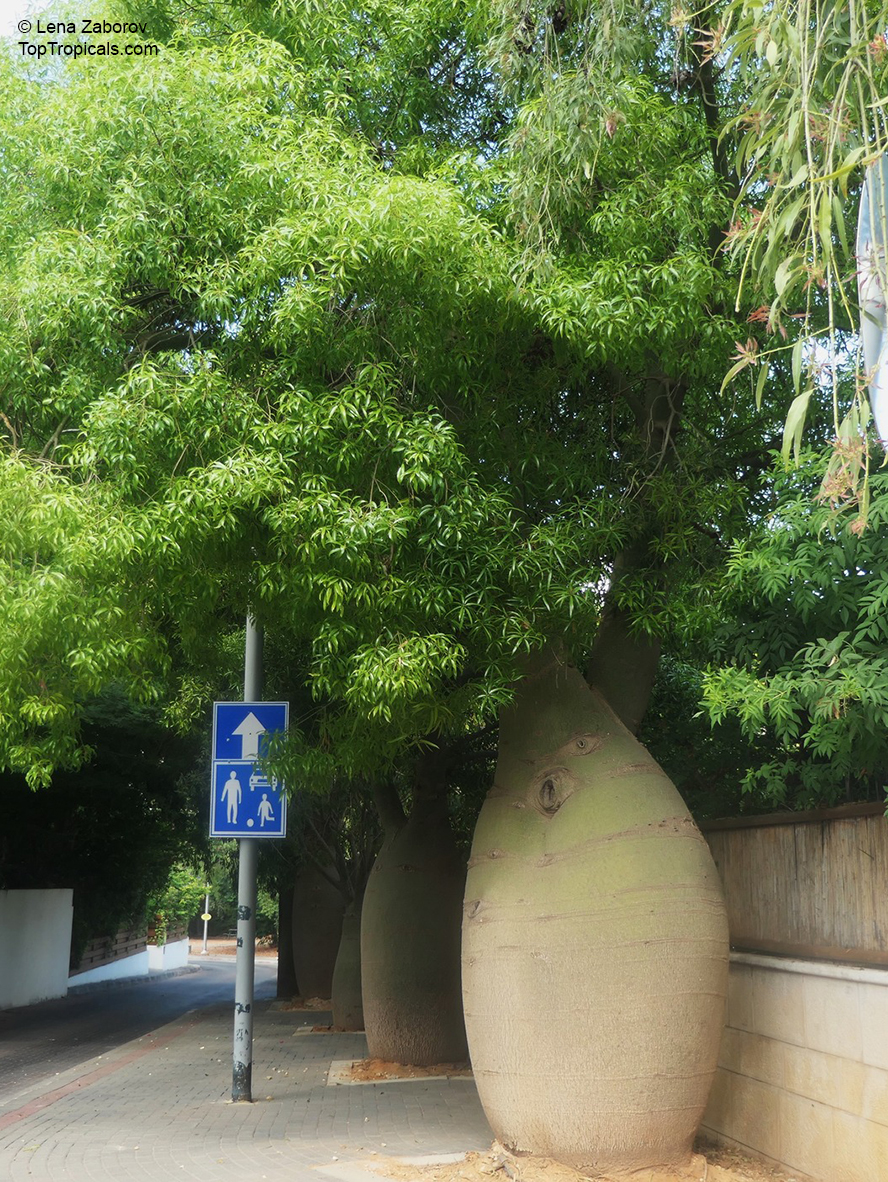
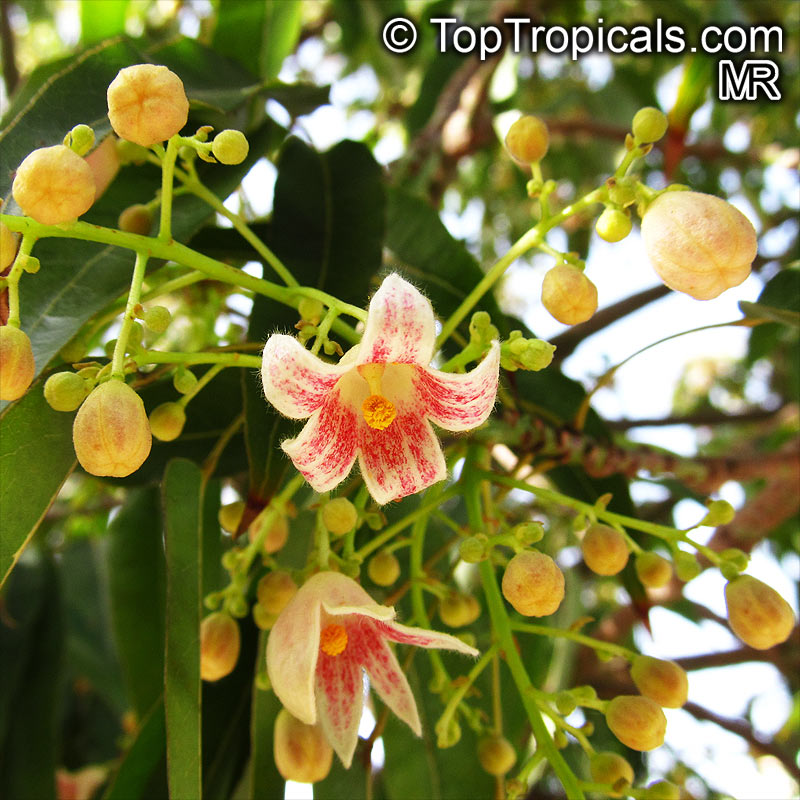
Botanical name: Brachychiton populneus
Common names: Bottle Tree, Kurrajong
Family: Malvaceae
Subfamily: Sterculioideae
Origin: Eastern Australia







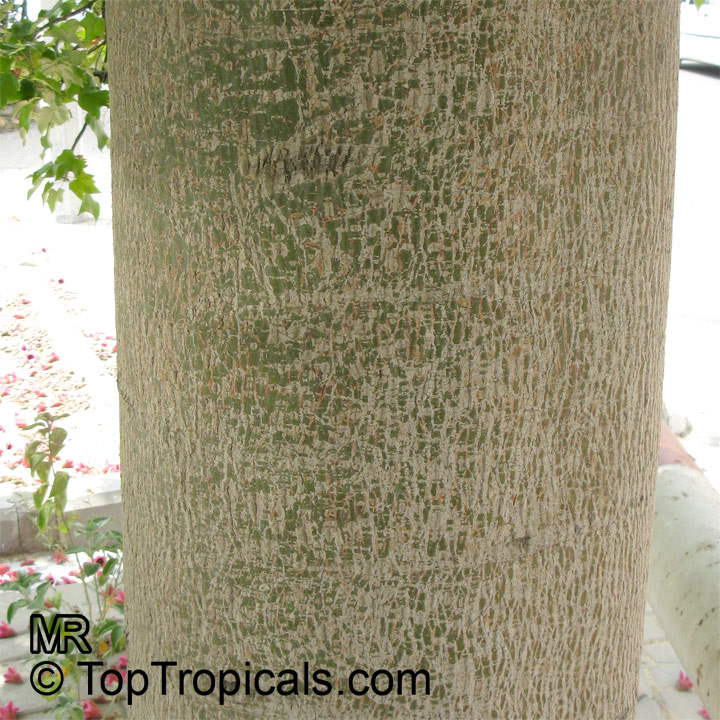
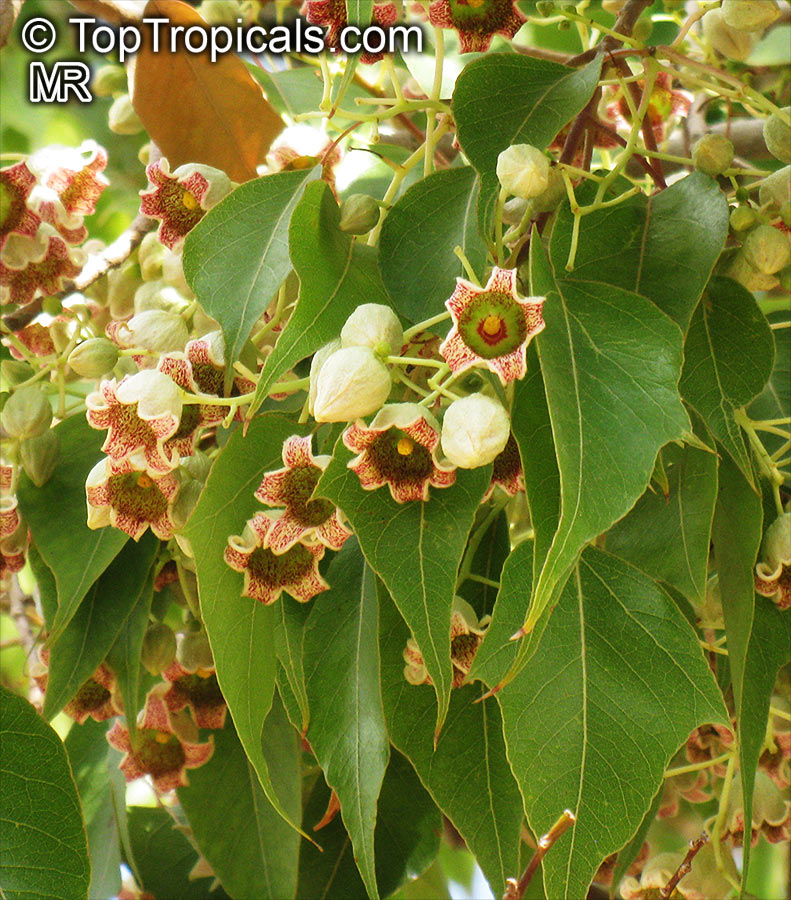
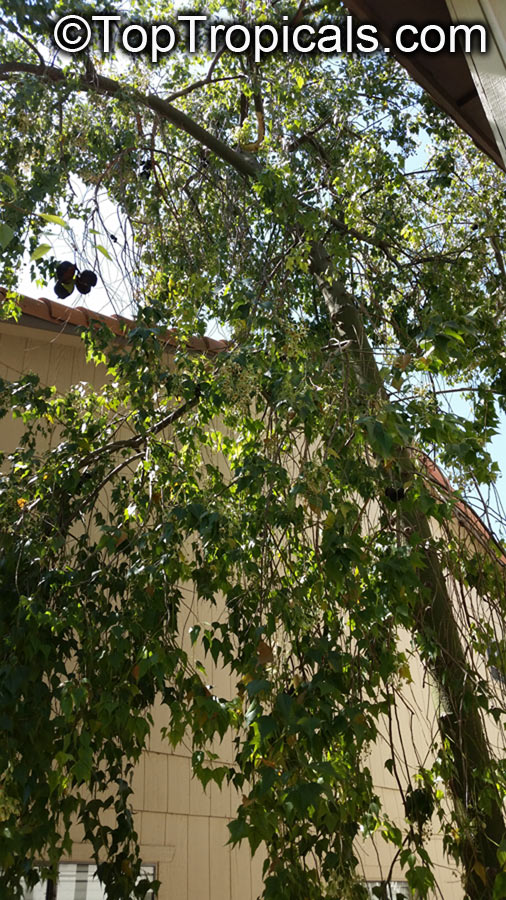
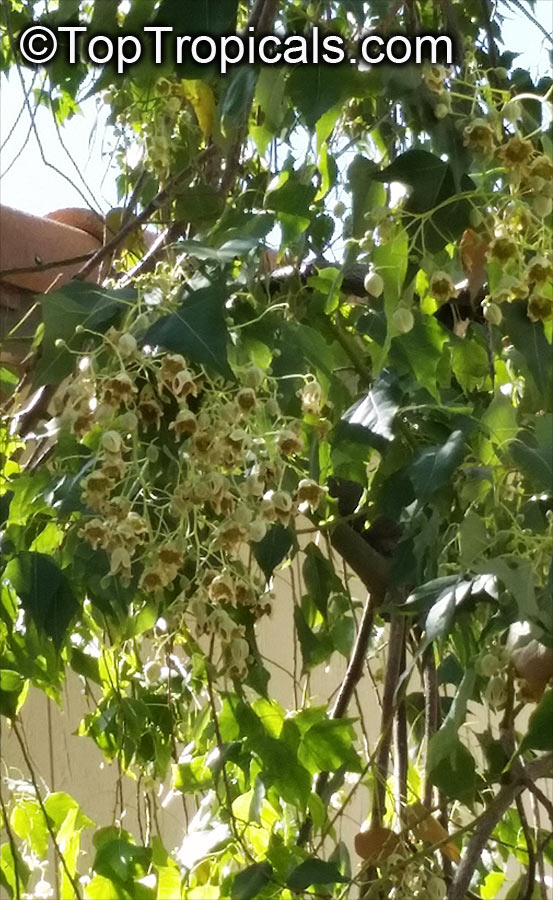
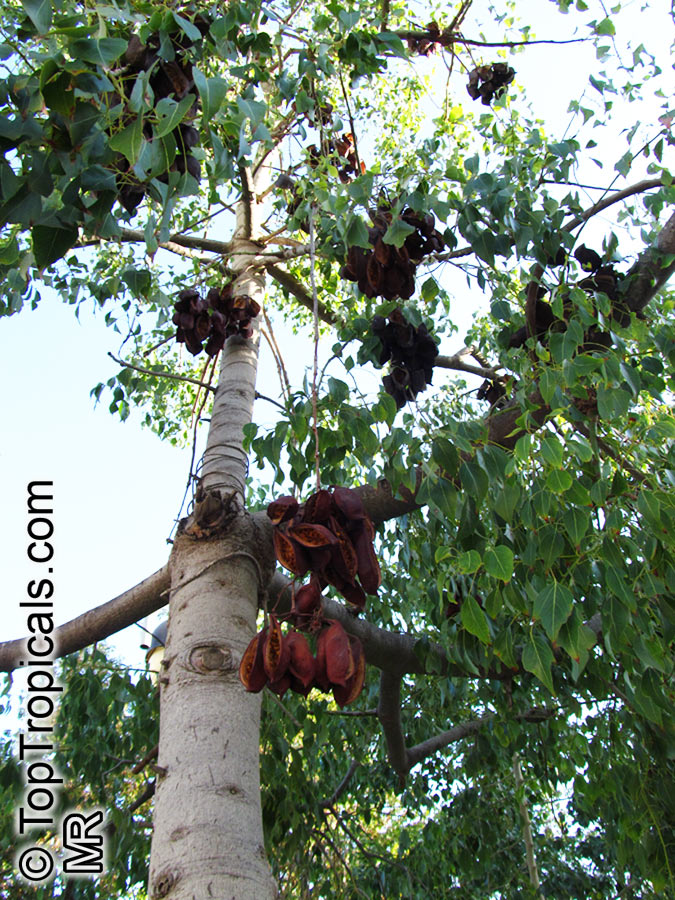
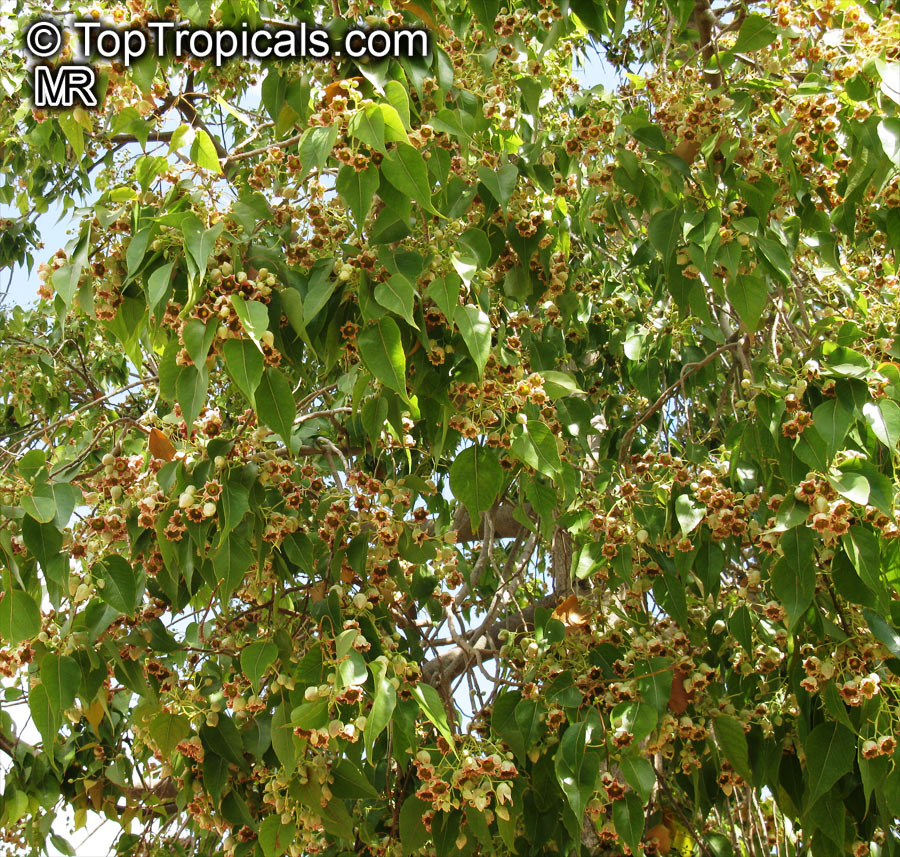
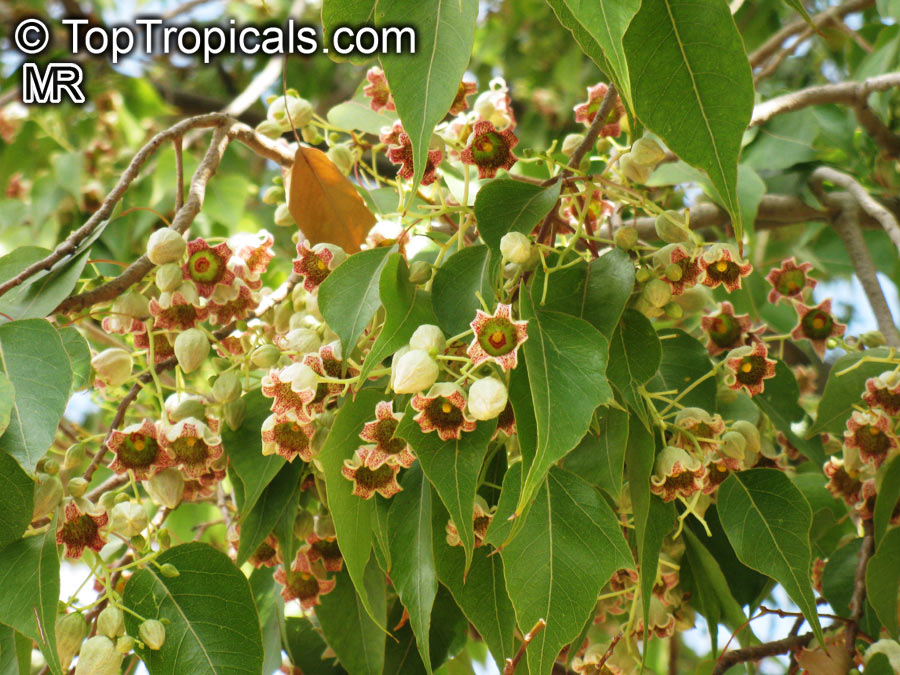
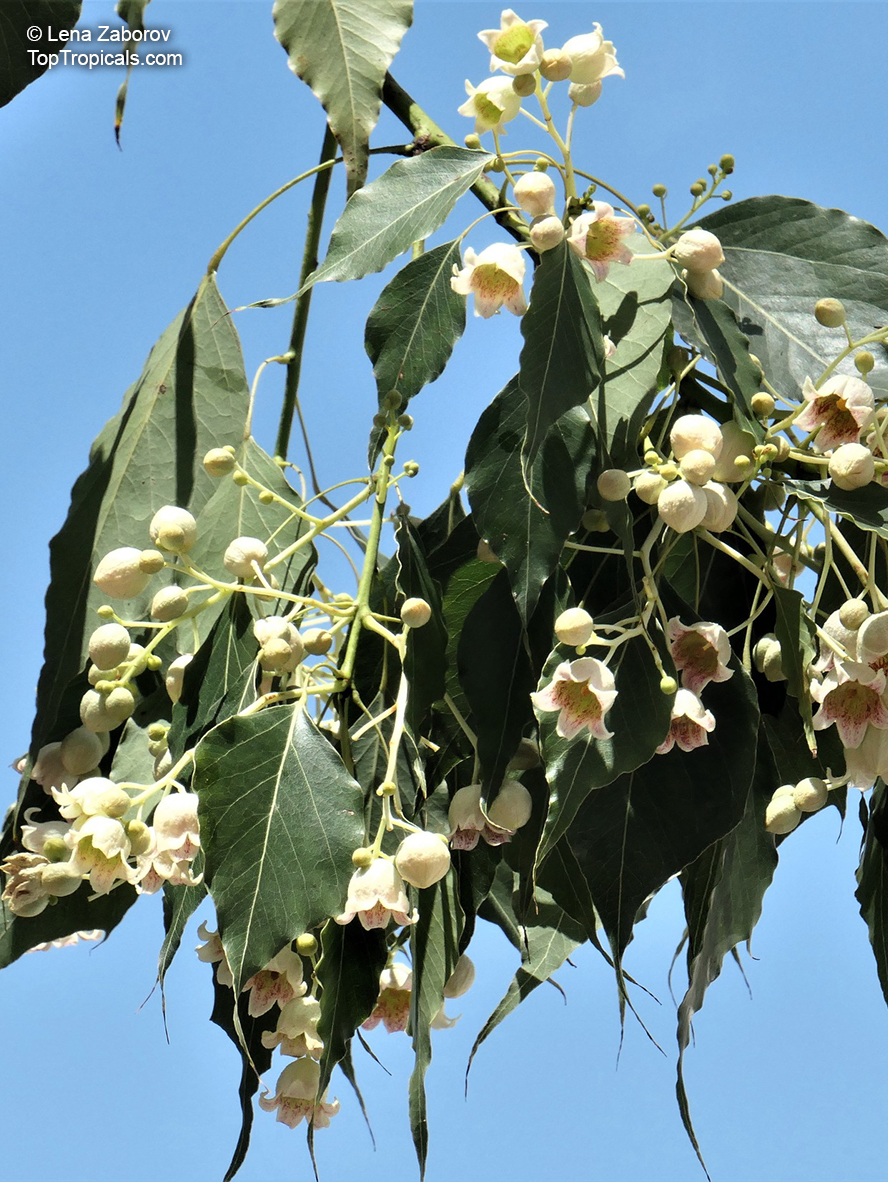
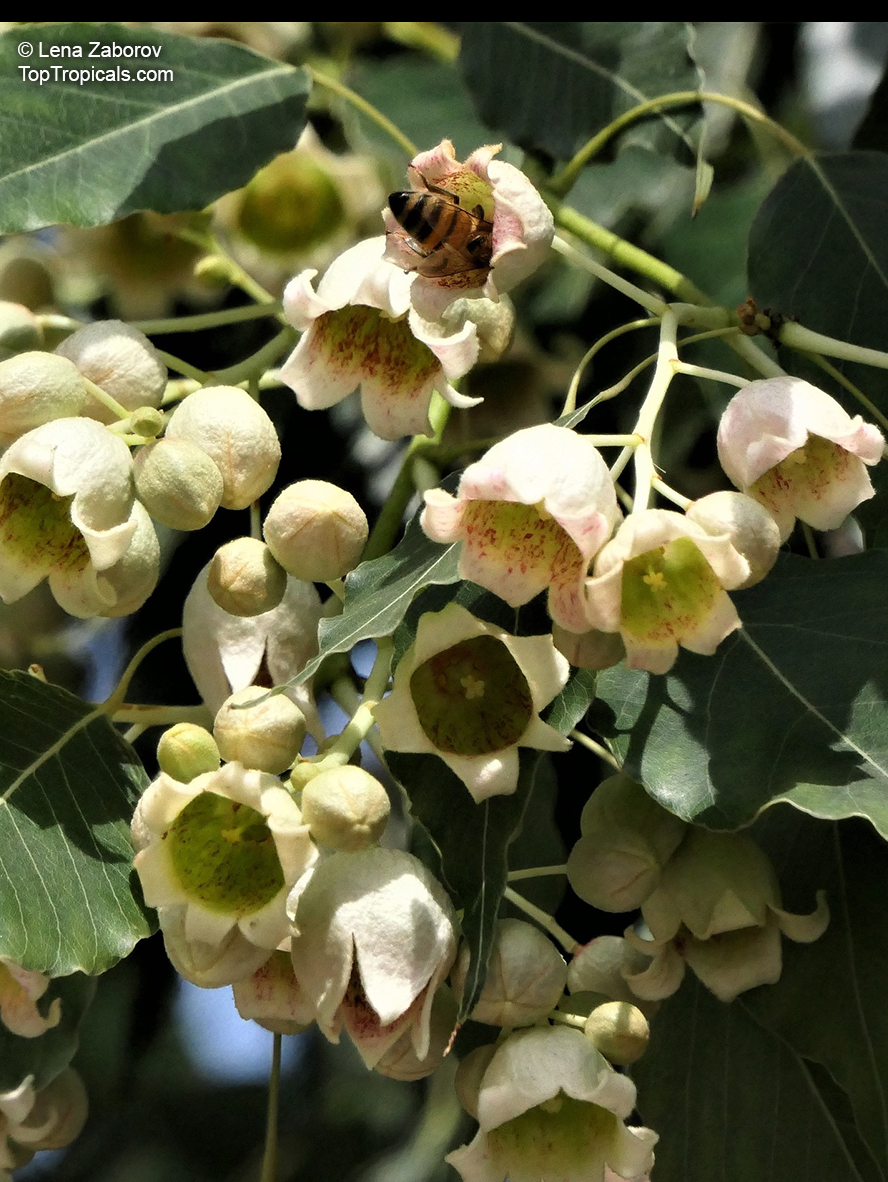
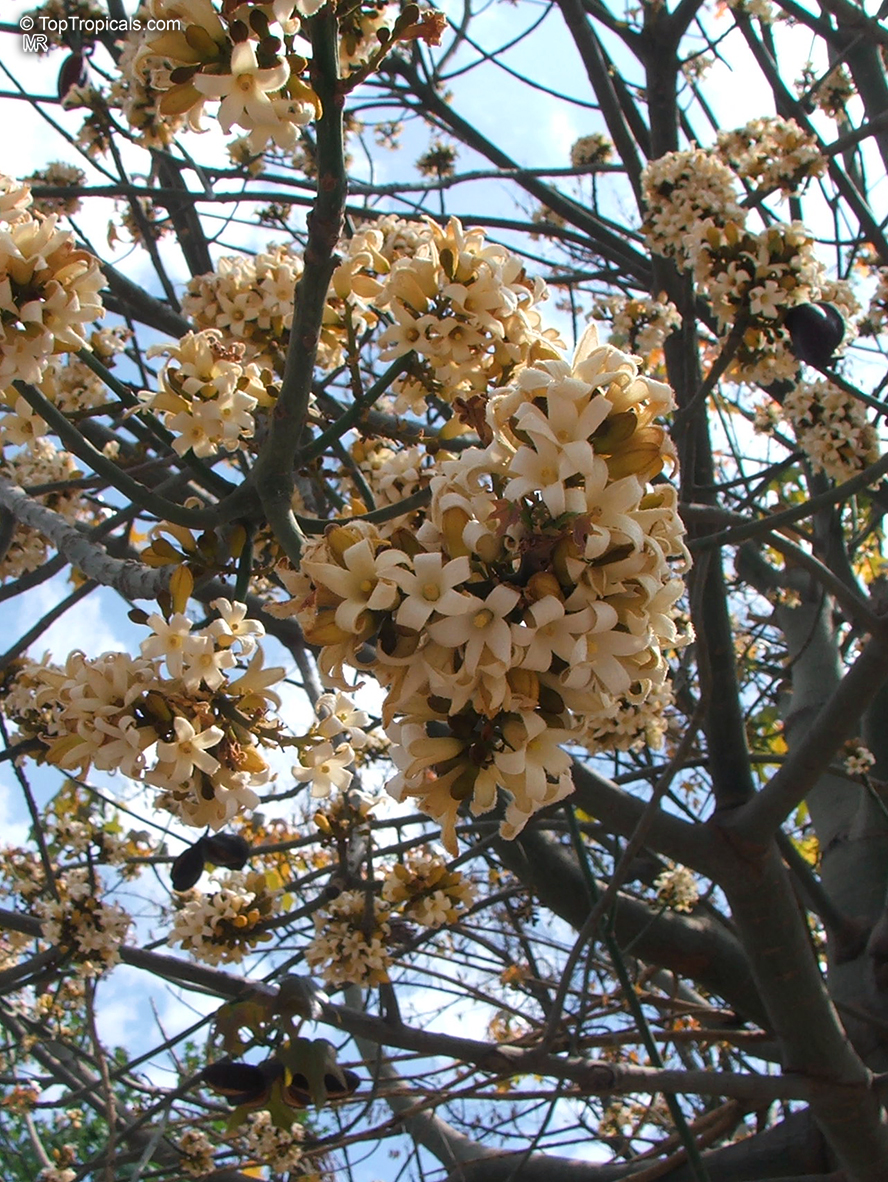
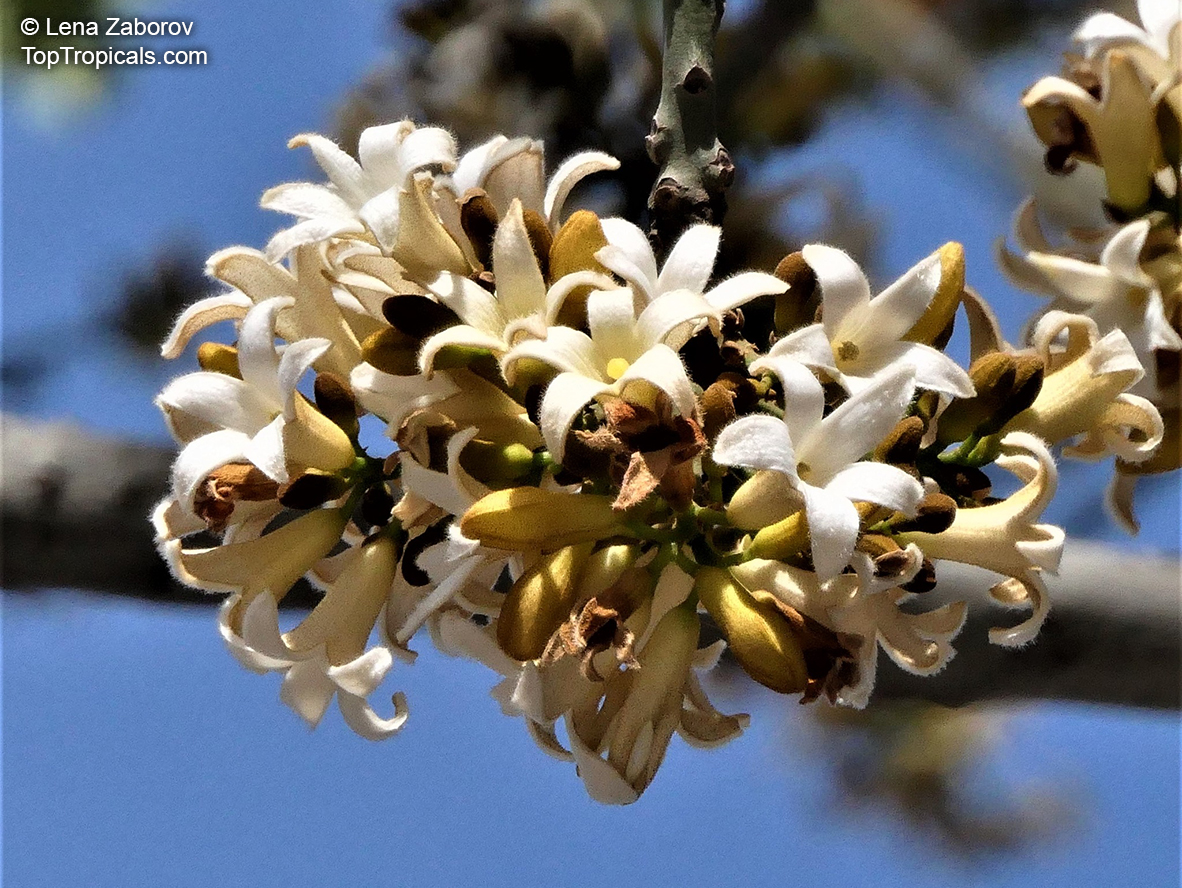
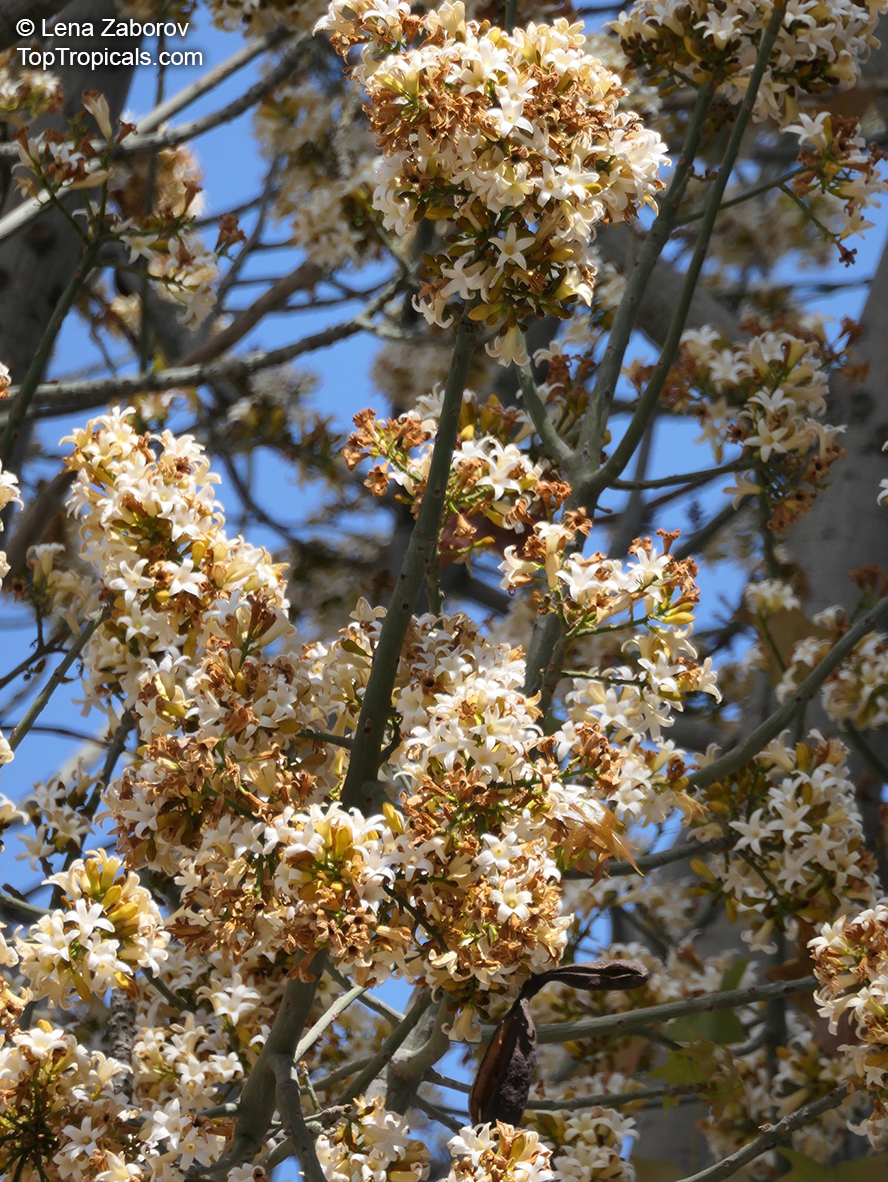
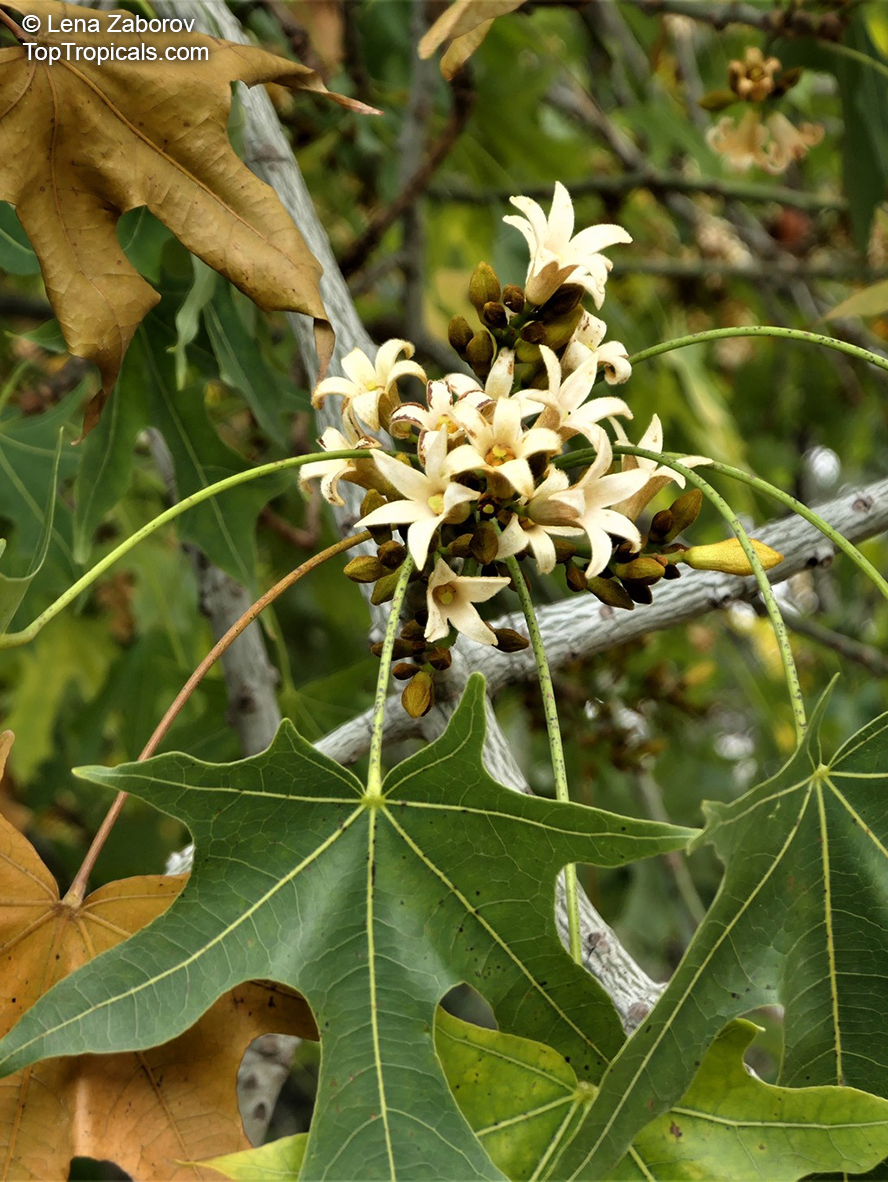
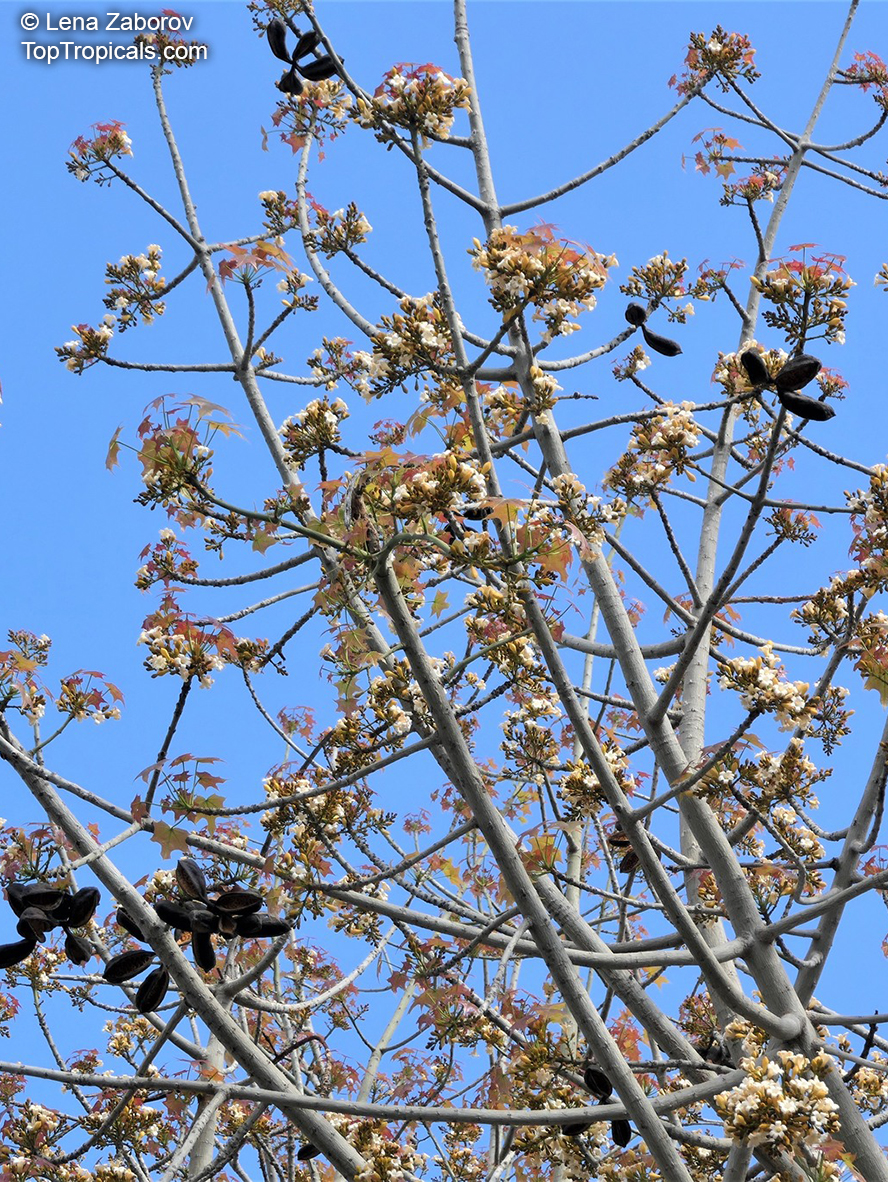
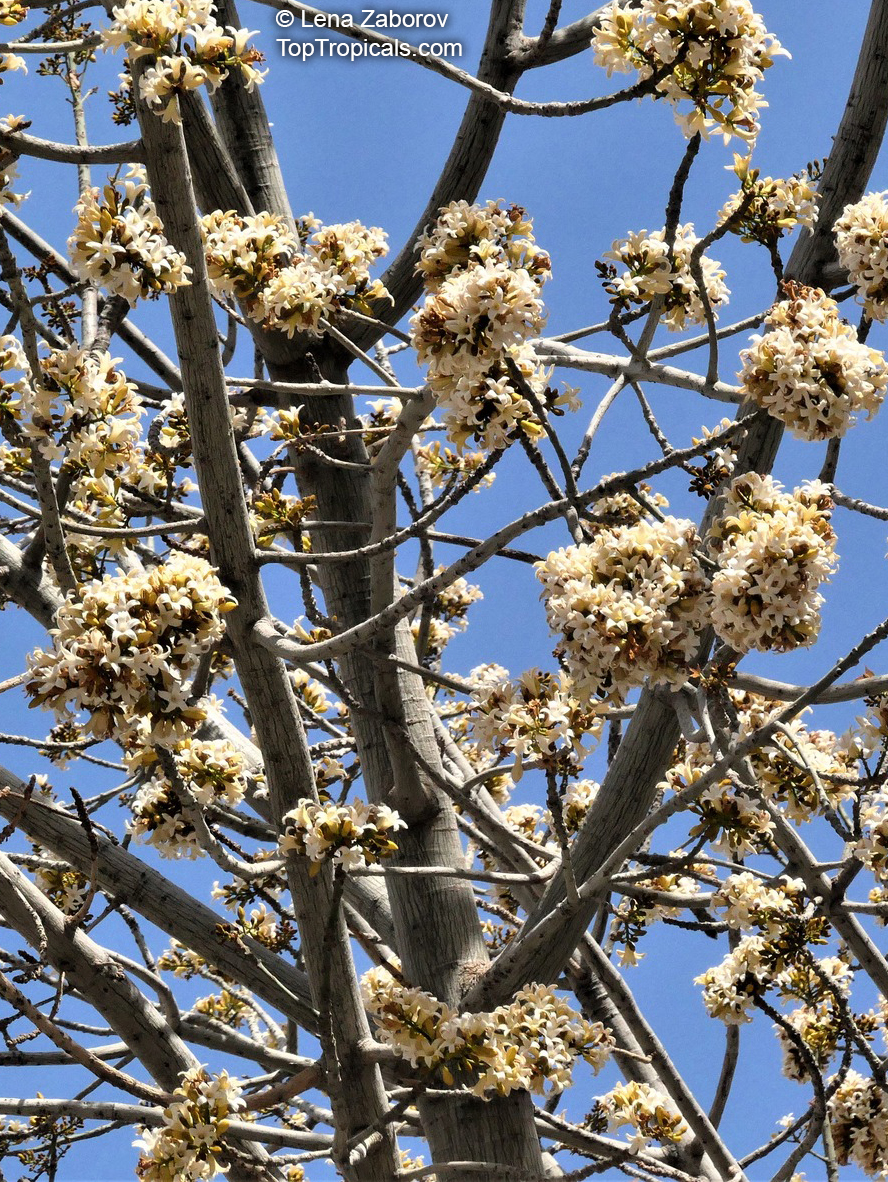
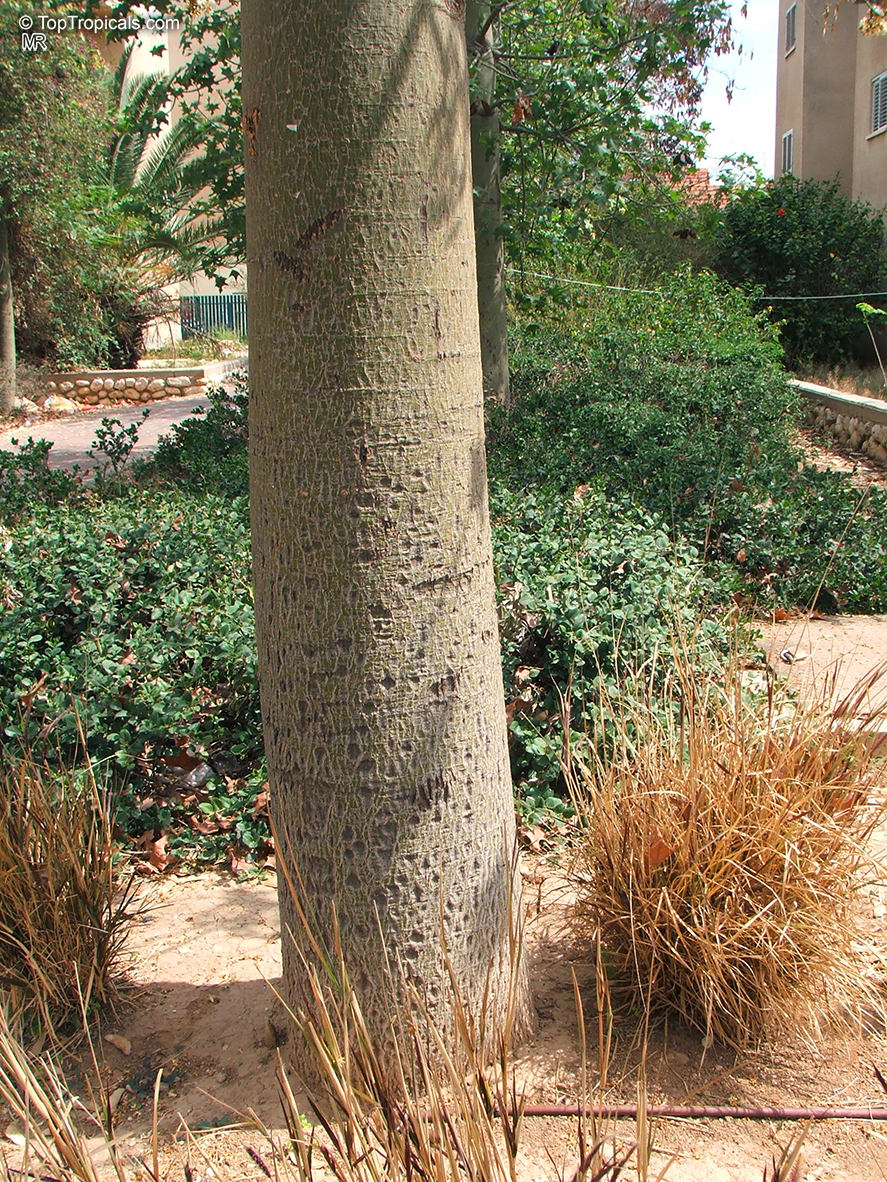
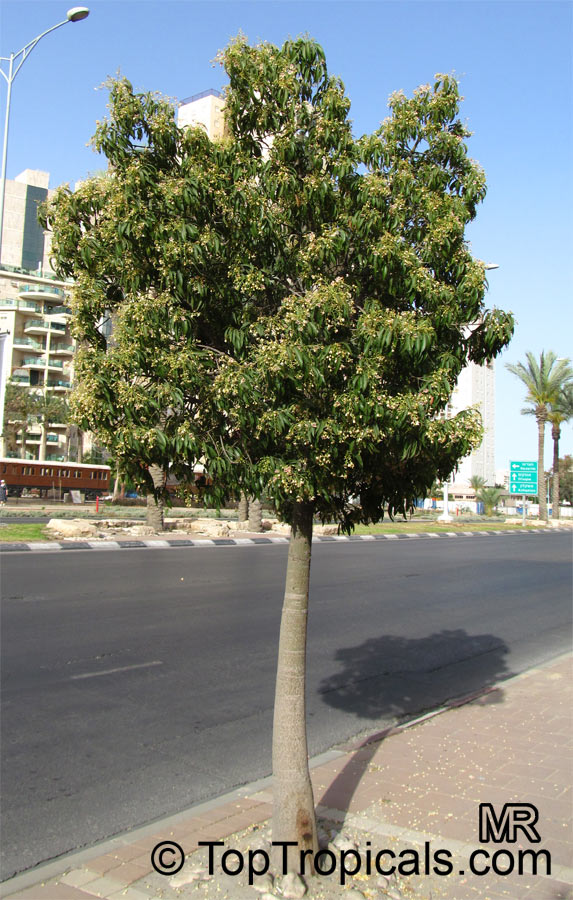
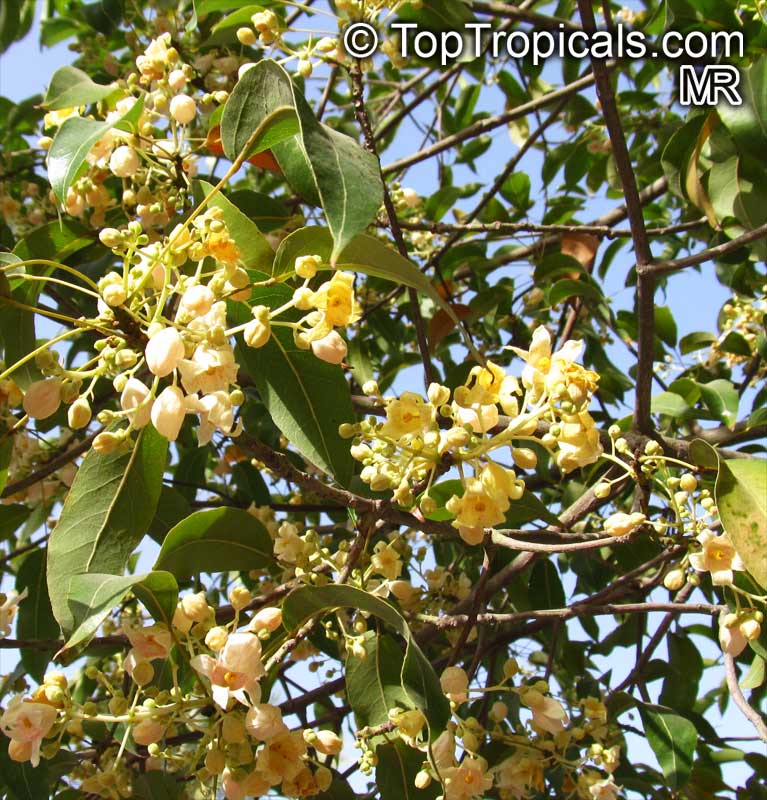
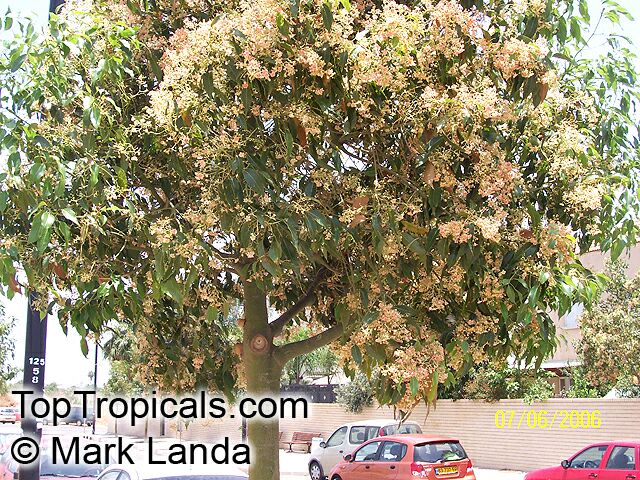
Grown successfully in USDA Zone: 9-11, the Brachychiton populneus (Bottle Tree) is a plant native to Eastern Australia. It can be used for bonsai, as it is a big tree, growing taller than 20 feet, and has attractive lobed leaves. The trunk is commonly swollen, as well as the taproot, giving an interesting bottle-like look to the tree. In addition to its aesthetic appeal, this species develops white or off-white, bell-shaped flowers with inner tubes that are streaked with purple-brown. Some hybrids can present pink or red blooms. The fruit of the Bottle Tree are woody and boat-shaped, surrounded by fine hairs that can cause skin and eye irritation, so care must be taken with them.
The Bottle Tree is an evergreen species and does best when grown in full sun, however it also tolerates some shade. It requires regular watering, but is quite resilient and tolerant of dry conditions. It is also easy to propagate from seed or from cuttings from desirable plants which can be grafted onto seedling rootstock. The transplantation must be done with care, protecting the swollen taproot from damage.
In cold regions, the Bottle Tree must be potted and taken inside during cold months. It is mature plant cold hardy at least to 30s F for a short time. The foliage is glossy-green and dense, making it a good option for street trees and to create shade as well as to provide a source of food for animals. The gum exudate is edible, and the swelled, carrot-like taproot is a nutritious vegetable. The species is also attractive to butterflies and hummingbirds, making it a nicely multi-functional plant.
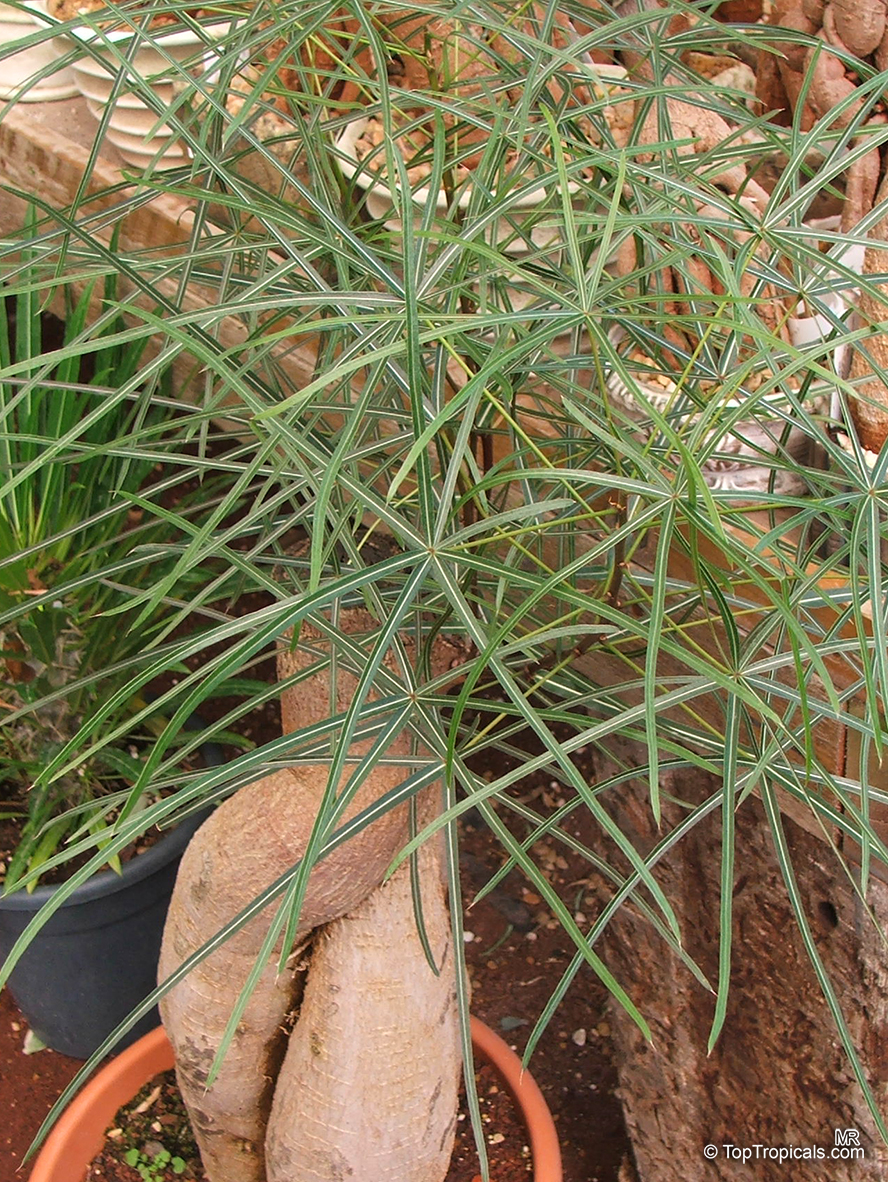
Botanical name: Brachychiton rupestris
Common name: Queensland Bottle Tree
Family: Malvaceae
Subfamily: Sterculioideae
Origin: Queensland (Australia)







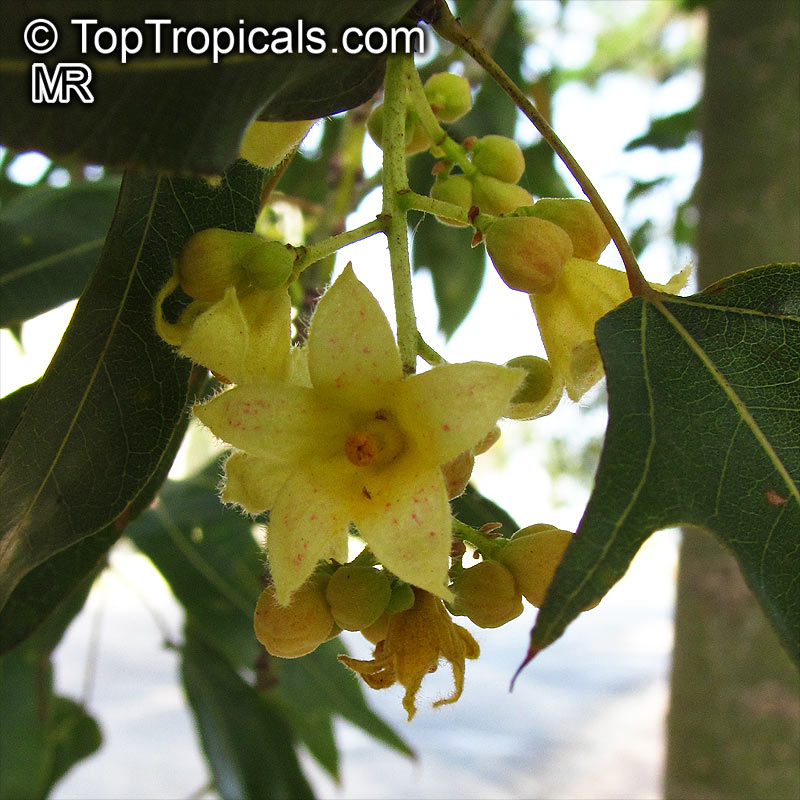
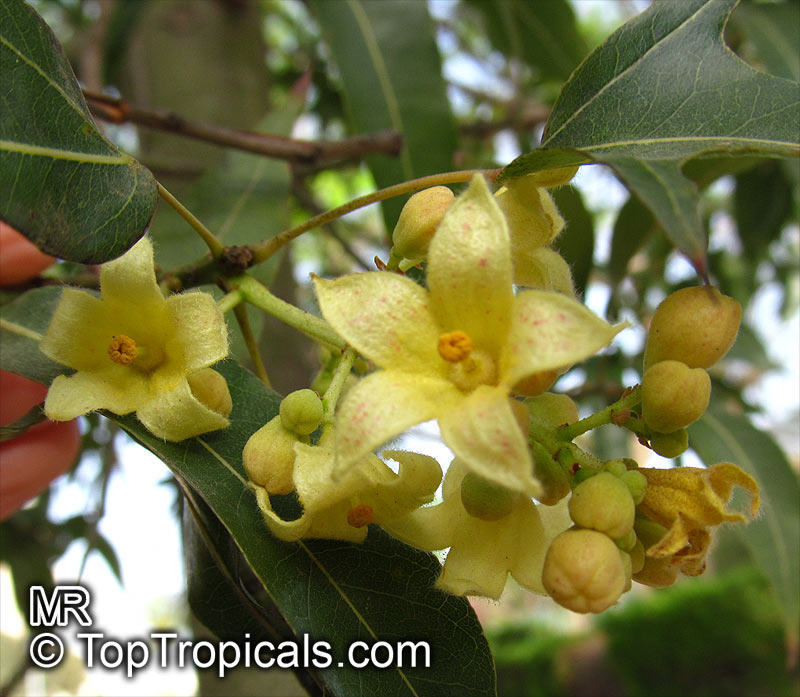
In cooler climates, Brachychiton rupestris can be grown in a pot if it is kept in a sunny position and watered regularly. The soil should be well drained and a slow release fertilizer applied in spring. If the temperature drops below zero, the pot can be moved to a sheltered area or moved indoors. The plant should be kept in a bright and sunny location, but sheltered from the wind. The pot should be watered regularly during the growing season and fertilized every few months. In winter, the plant should be kept dry and only watered occasionally. Pruning can be done to shape and maintain the size of the plant and to remove any dead or damaged branches. With careful attention, the bottle tree can be used as a Bonsai specimen. The bottle shaped trunk may start to be noticeable at around 5-8 years of age. The bell-shaped flowers are yellowish in clusters at the ends of the branches but are not especially conspicuous. The flowers are followed by seed capsules which contain many large seeds.
Overall, the Queensland Bottle Tree is an attractive, unusual and easy to grow plant.
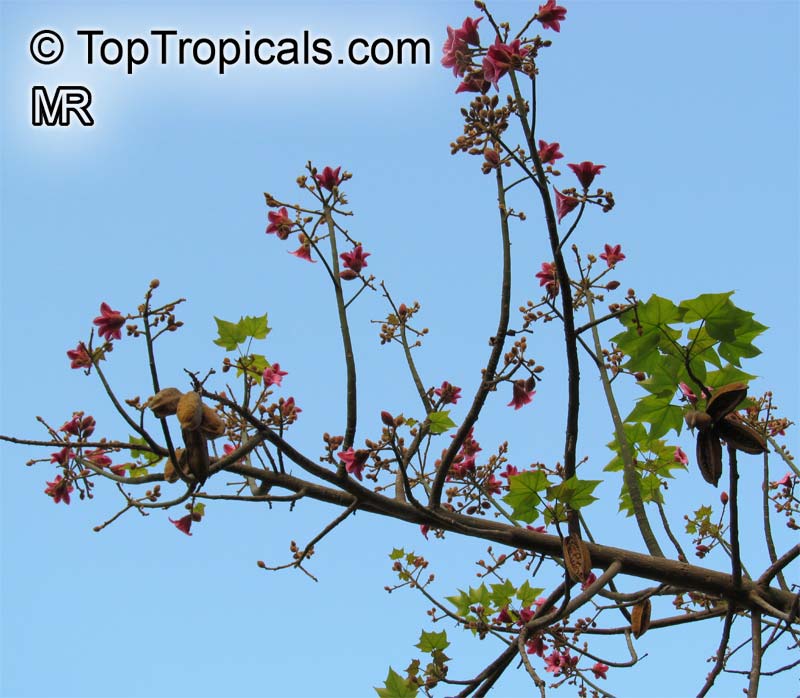
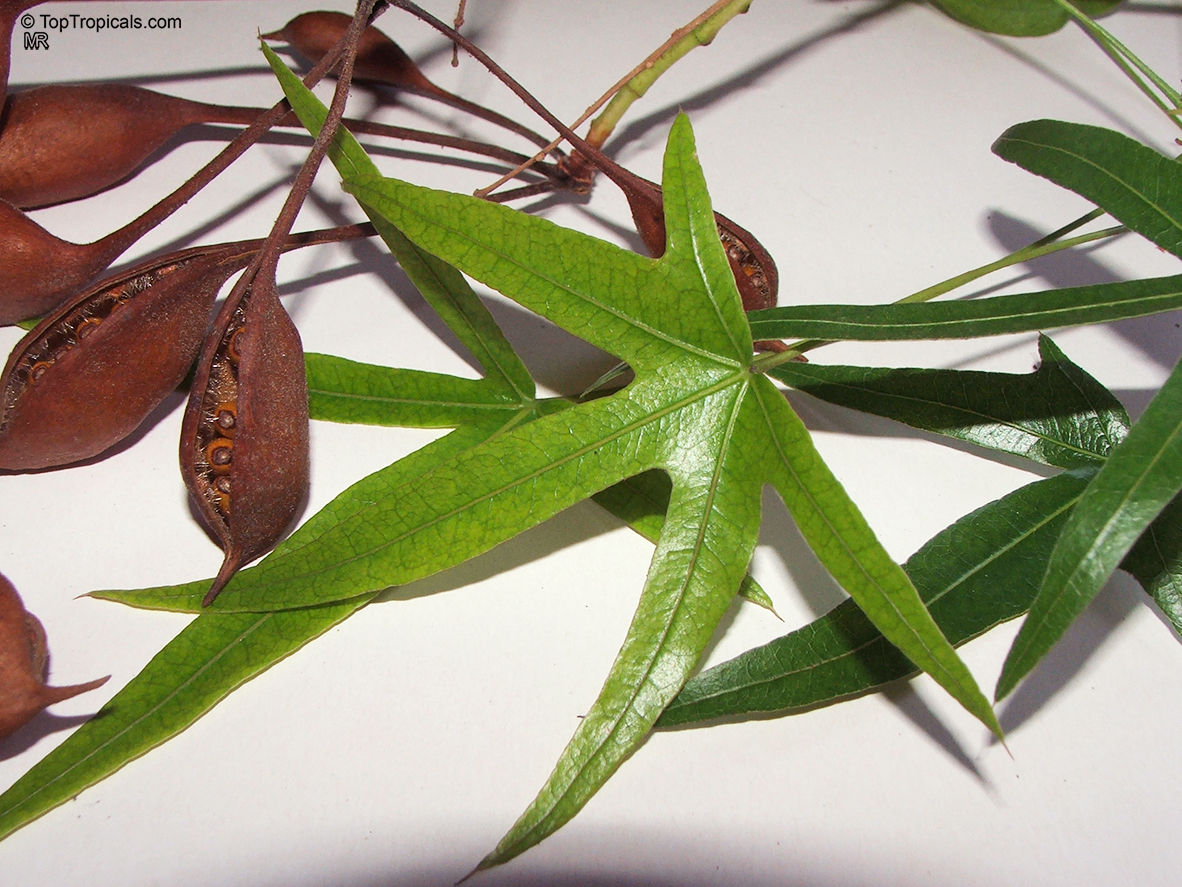
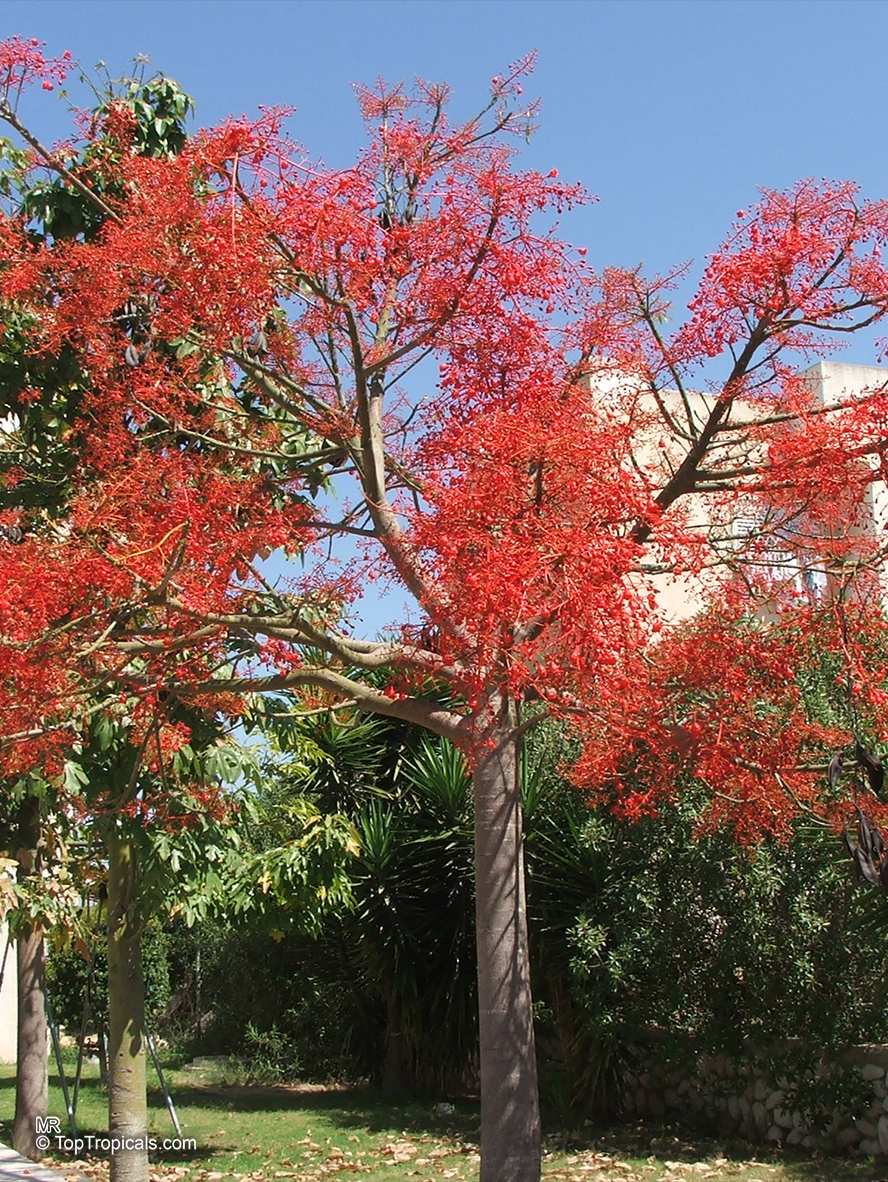
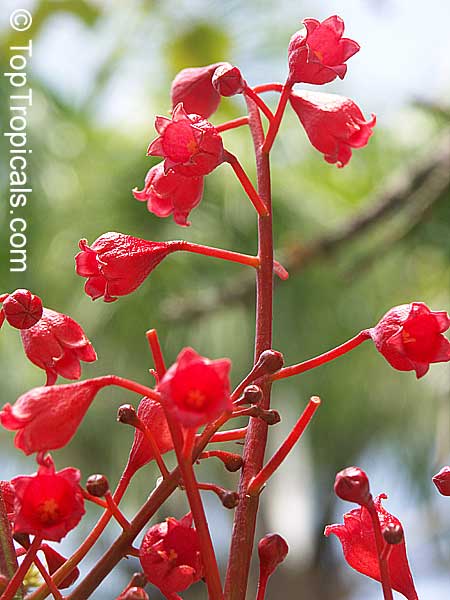
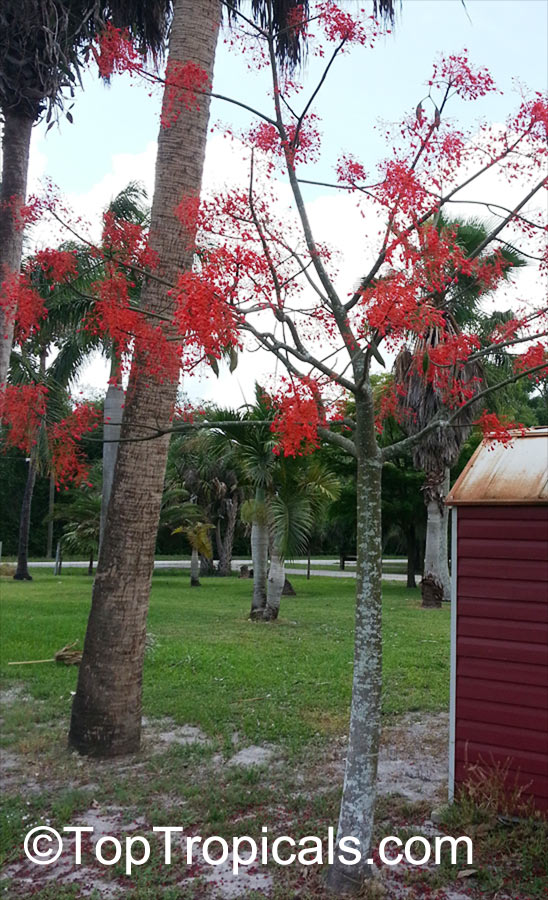
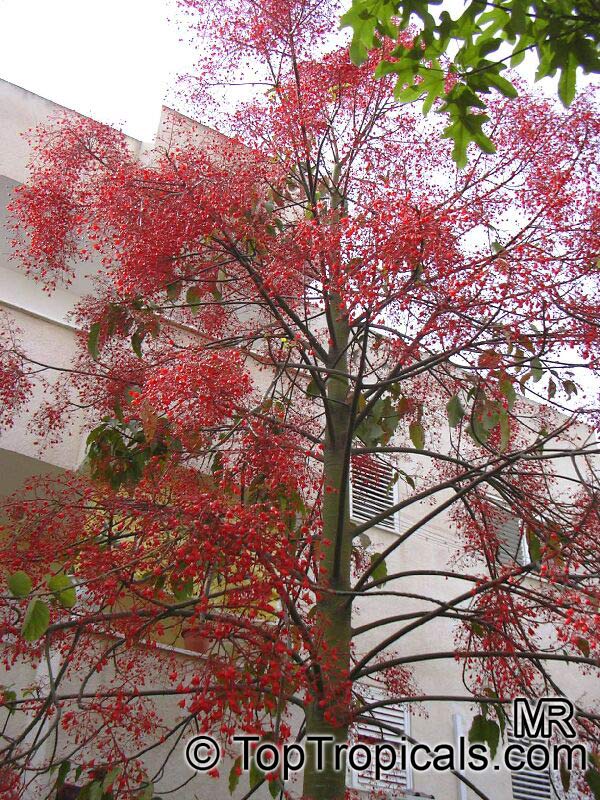
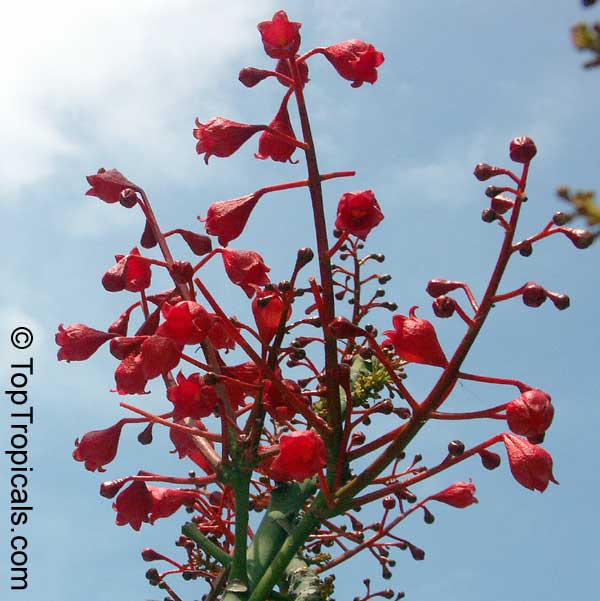
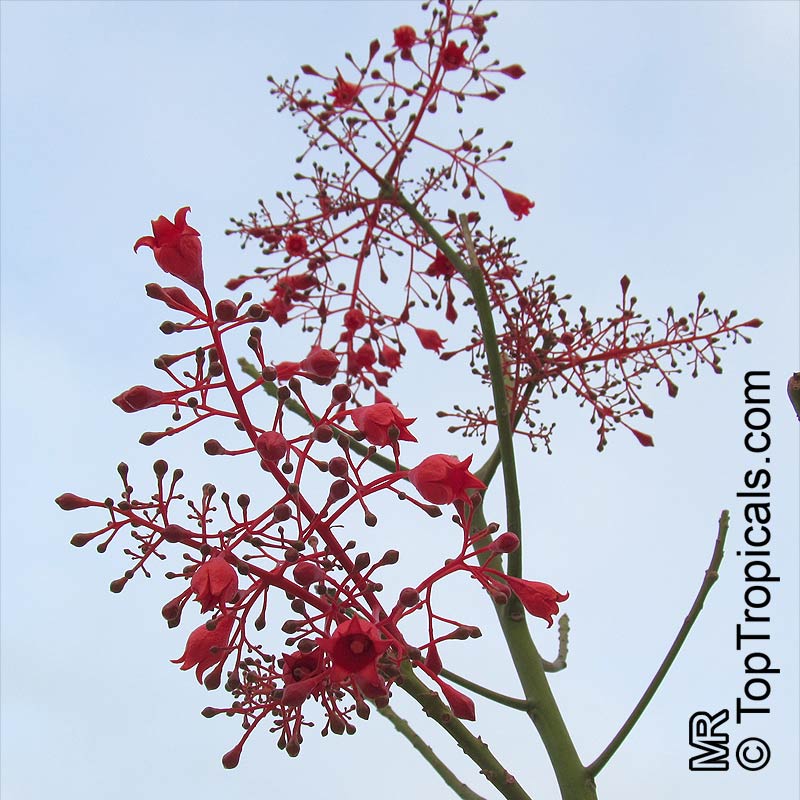
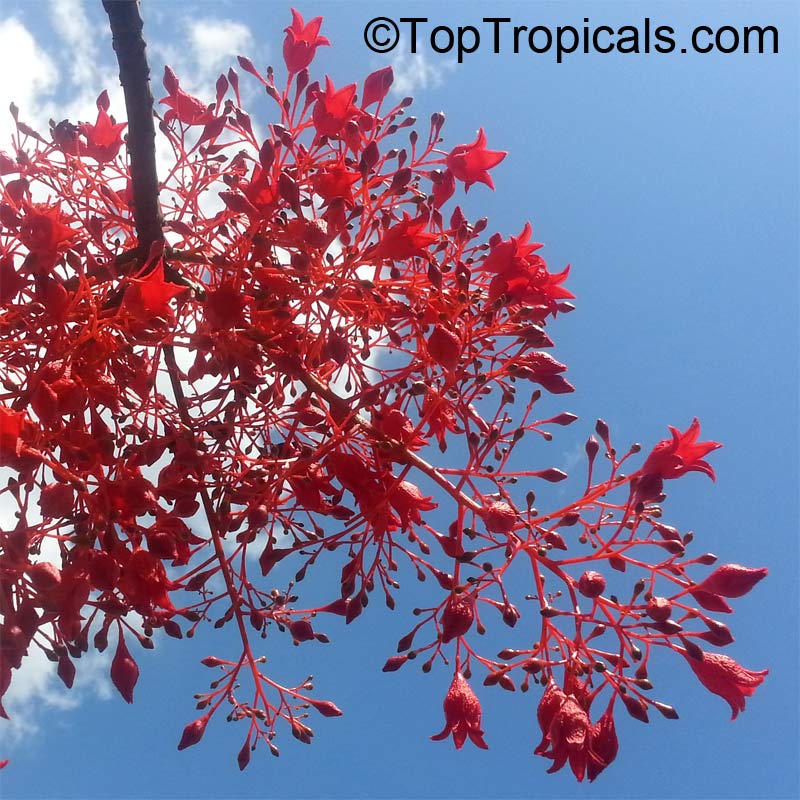
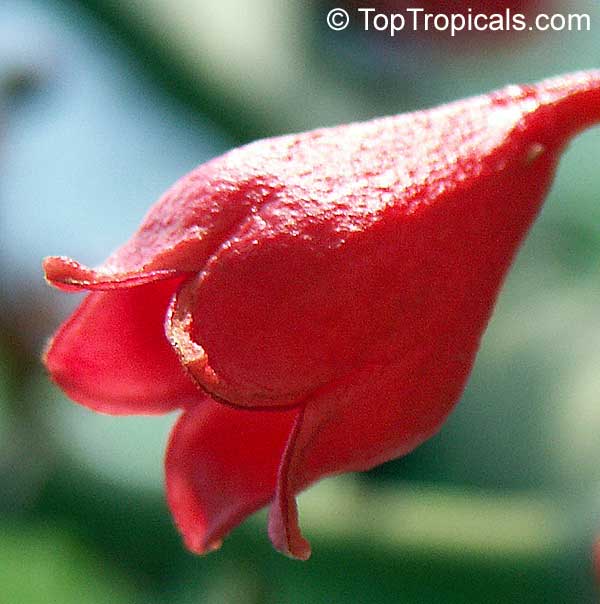
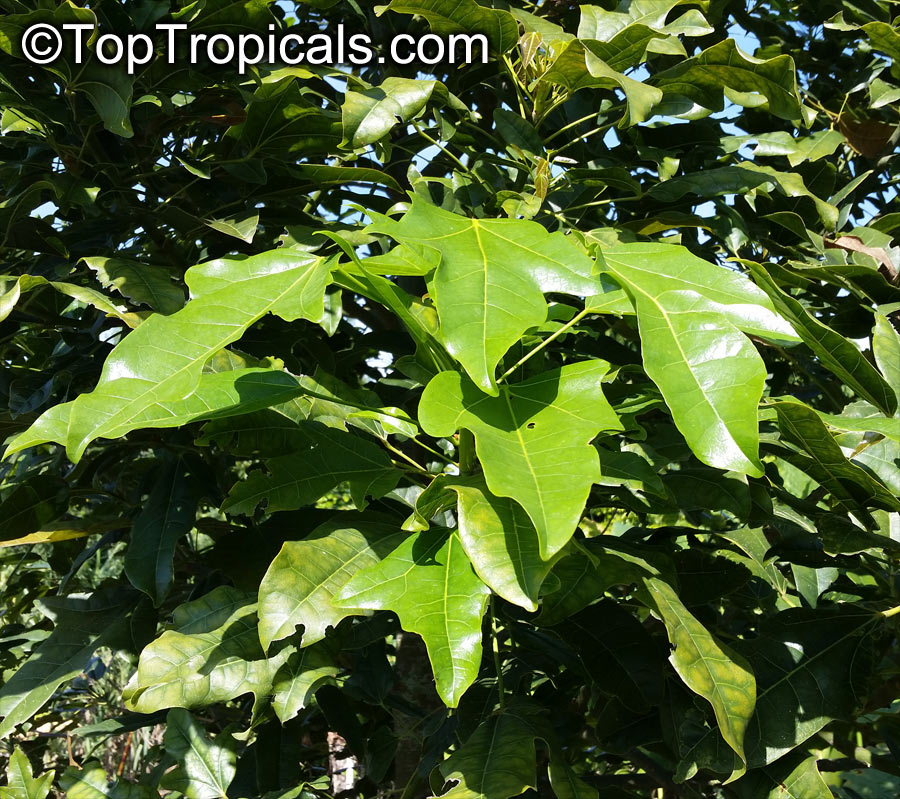
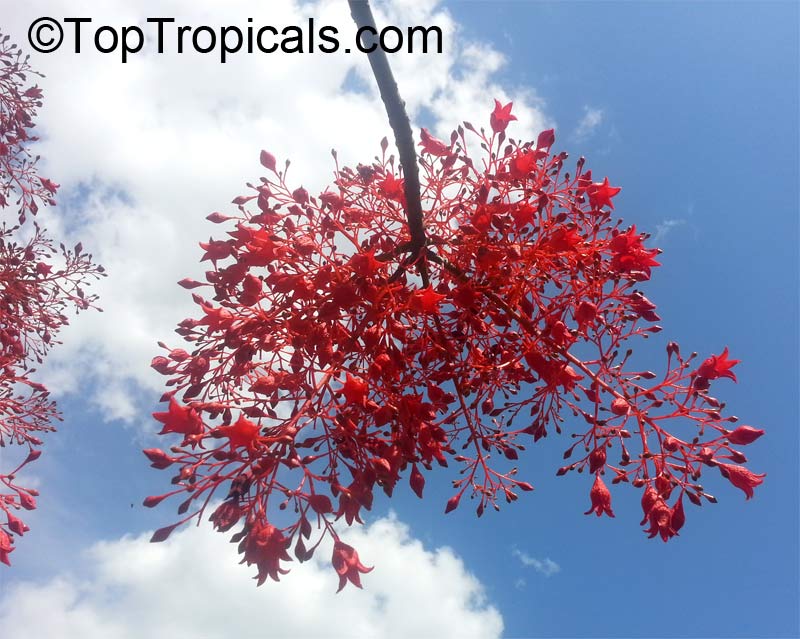
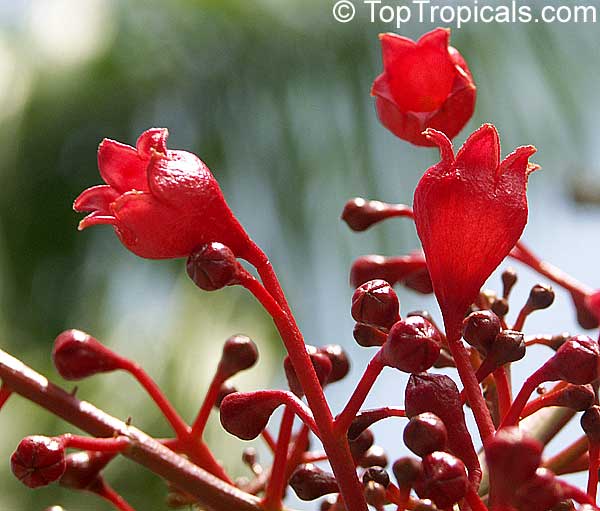
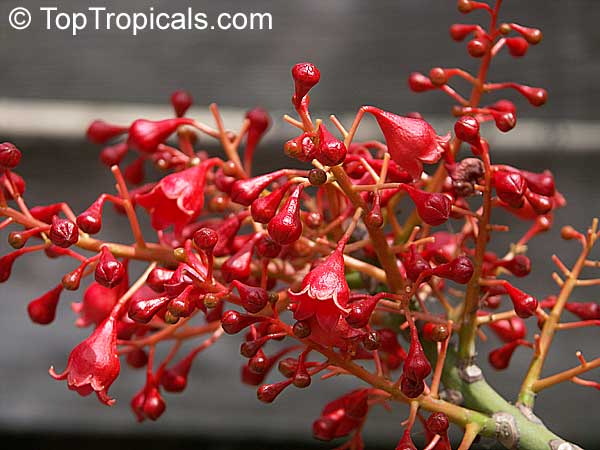
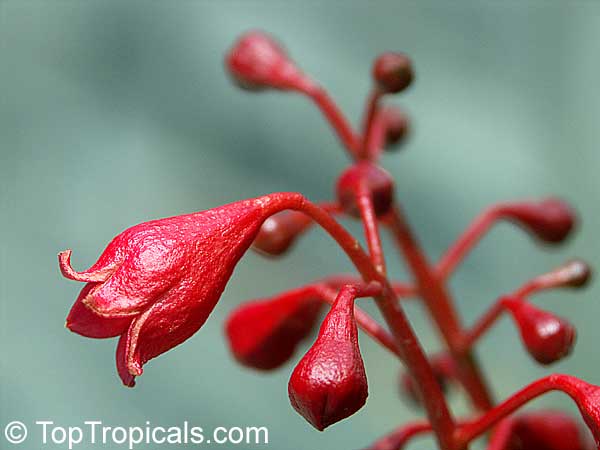
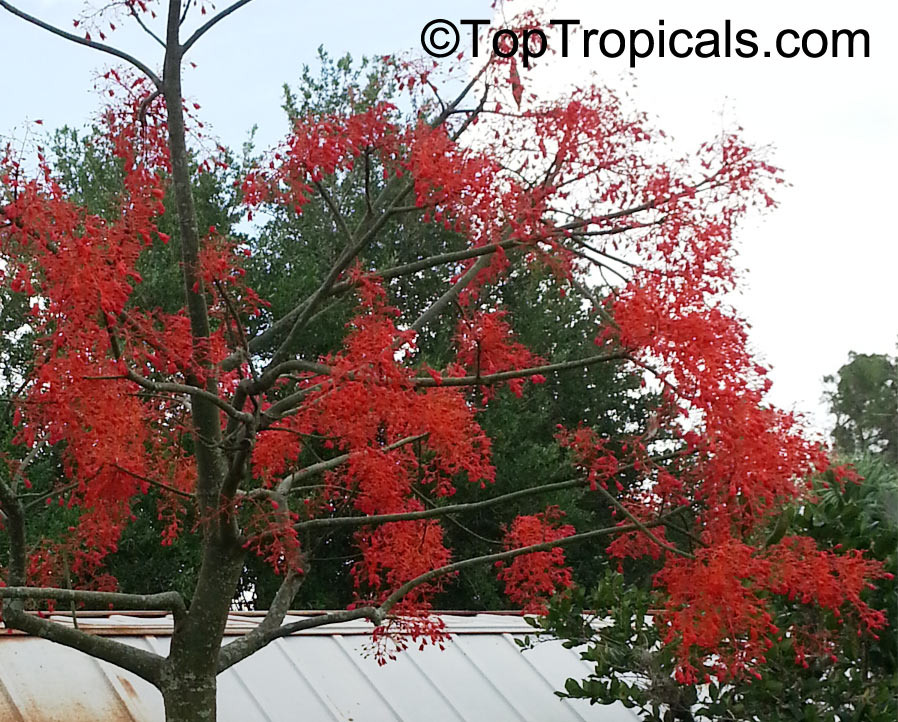
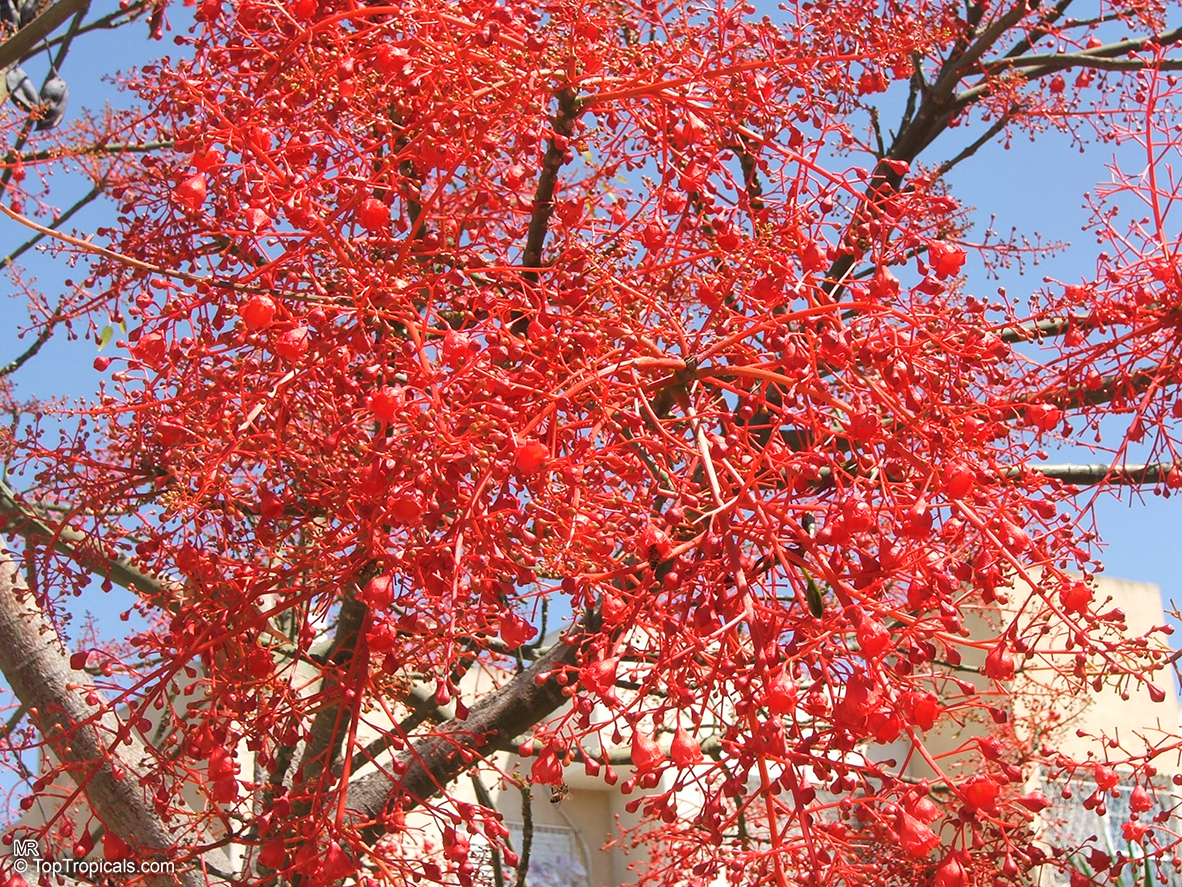
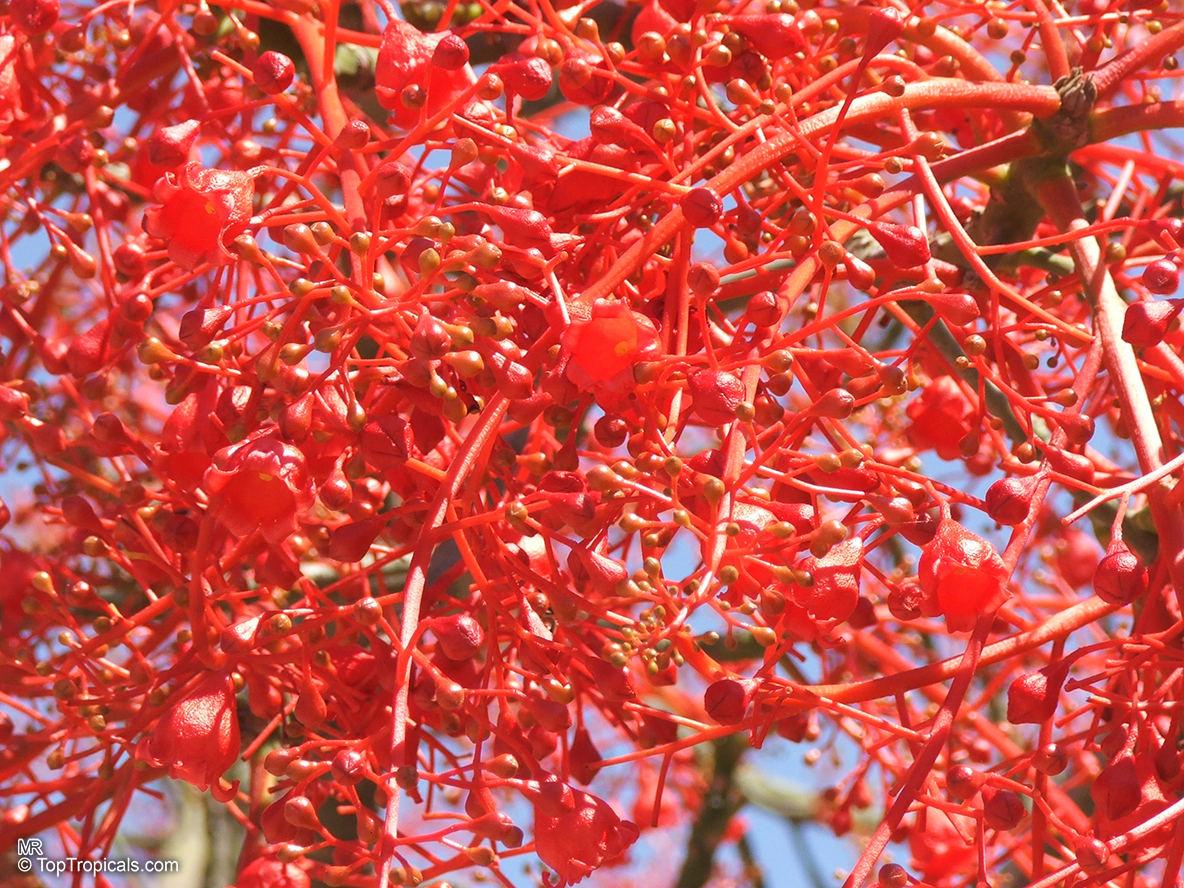
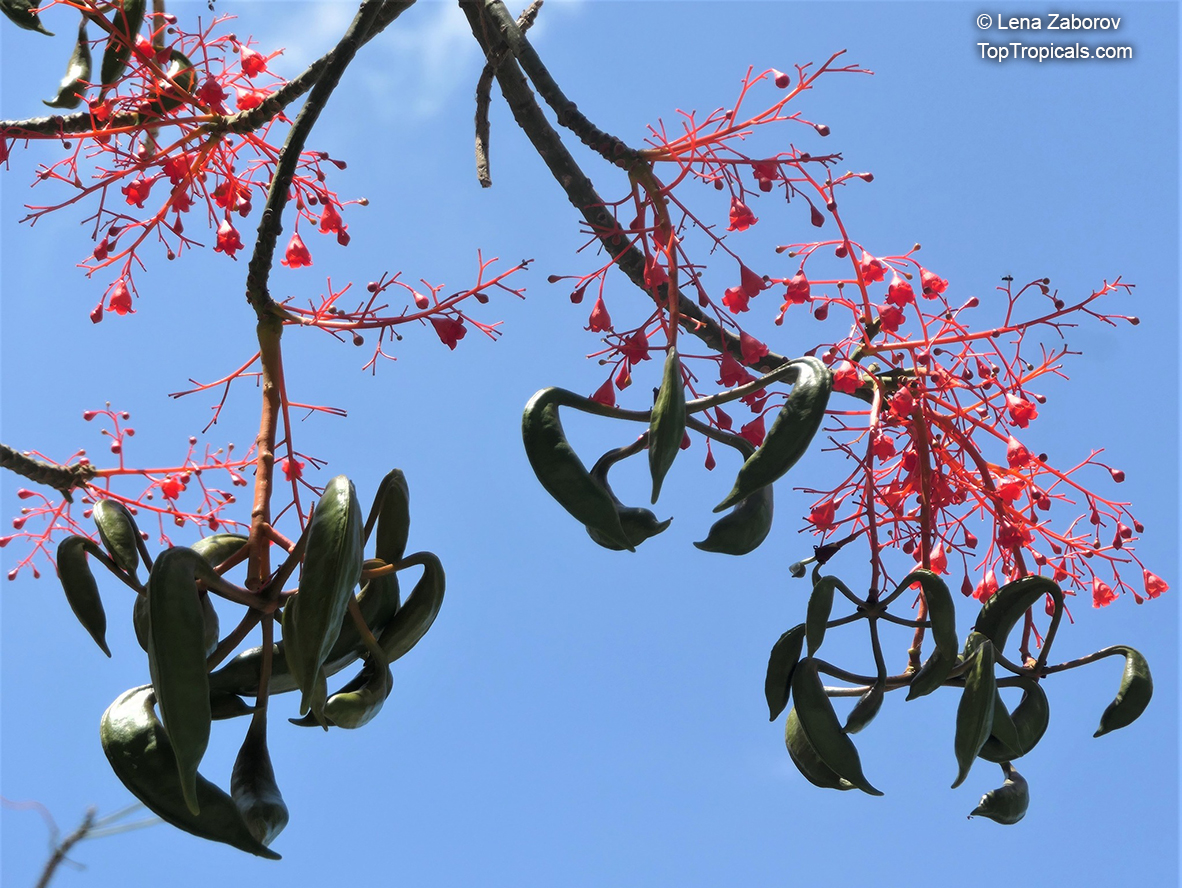
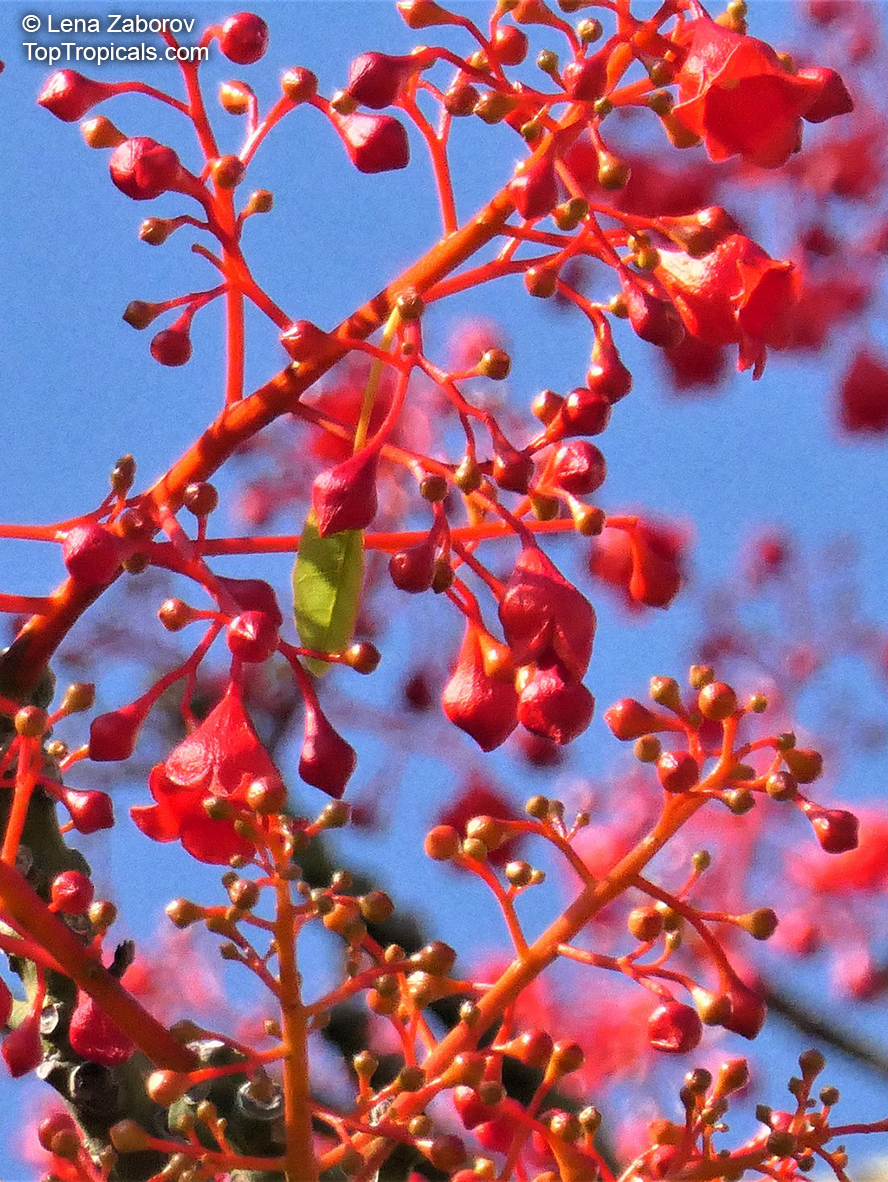
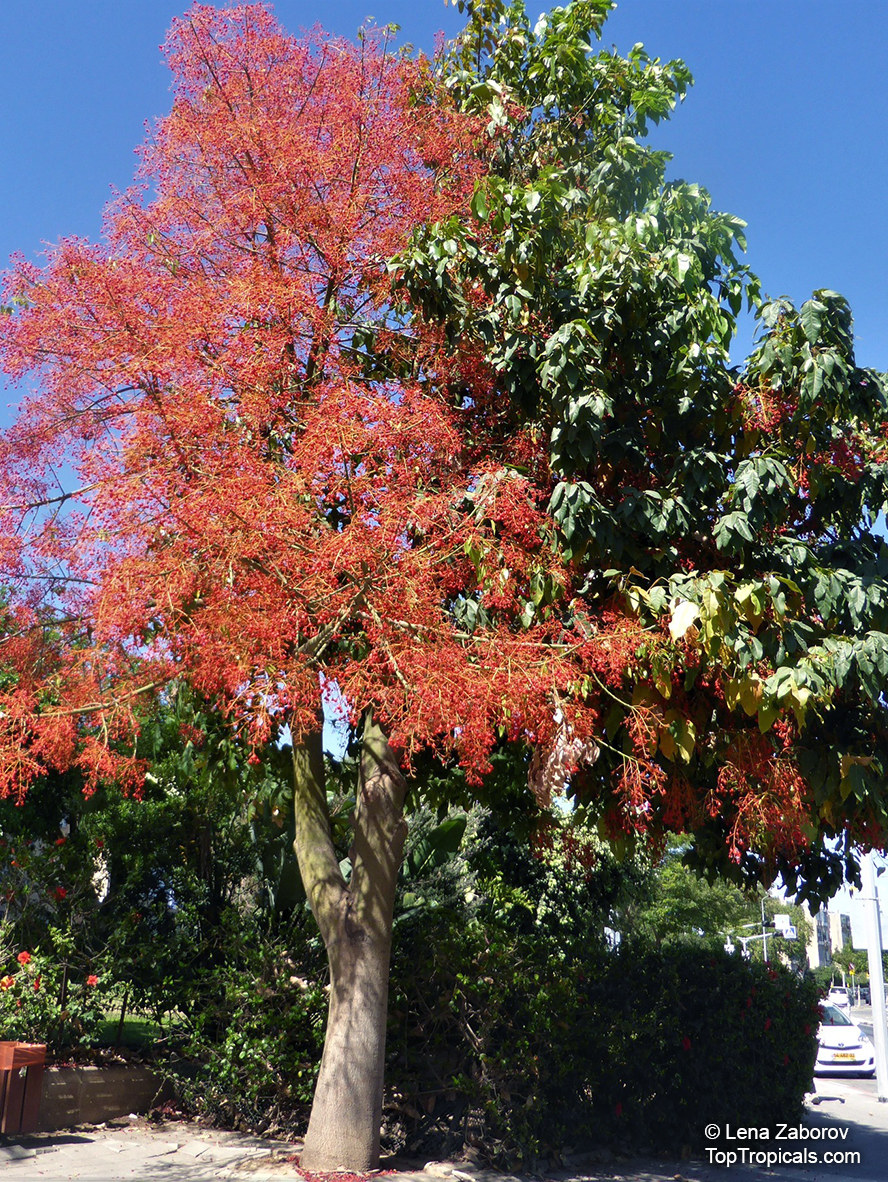
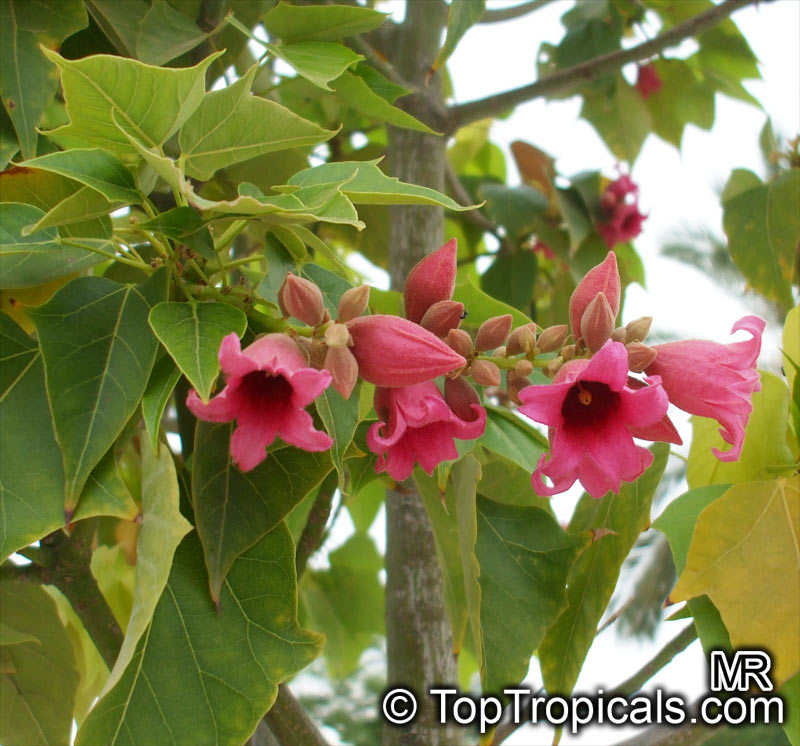
Botanical name: Brachychiton acerifolius
Common name: Flame Tree
Family: Malvaceae
Subfamily: Sterculioideae
Origin: Australia







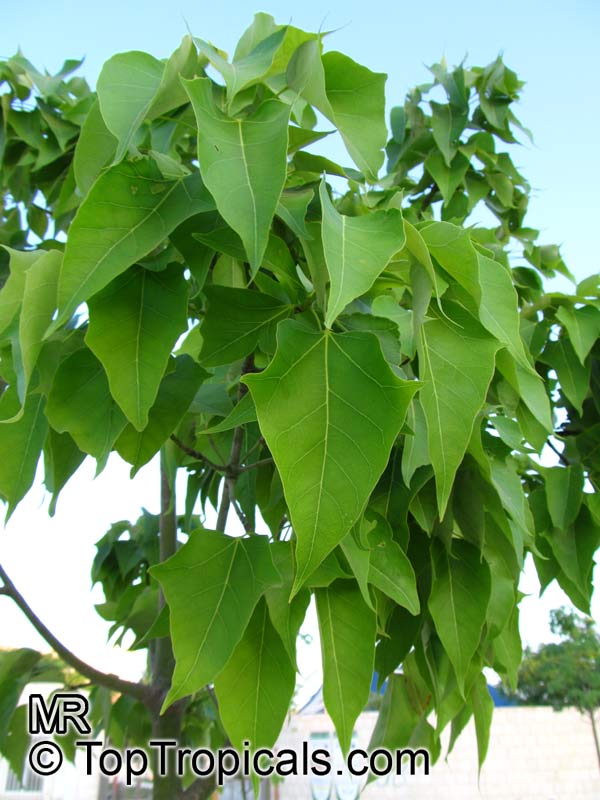
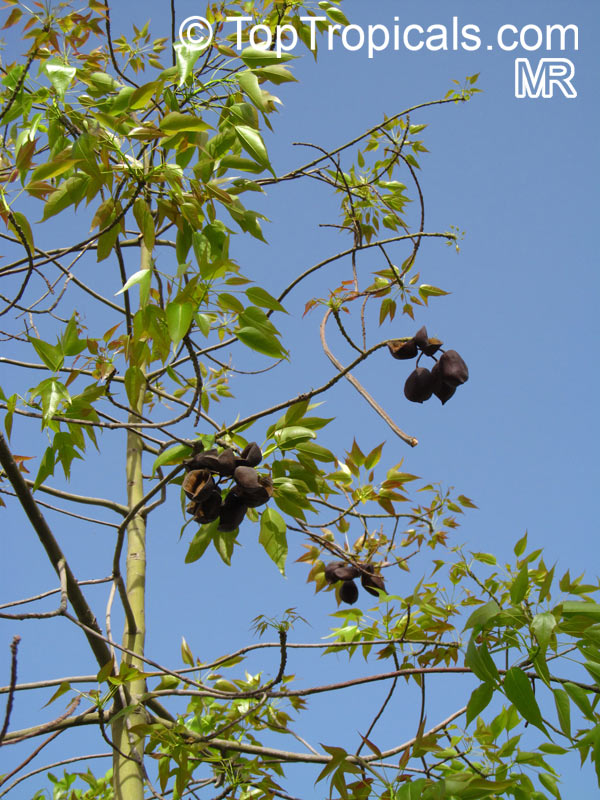
Rainforest tree. This spectacular Australian tree is often conical in shape with dark green glossy leaves, deeply lobed when young. The upper trunk is green. Bright red bell flowers occur when the tree is wholly or partly deciduous, and are followed by thick black pods. Very conspicuous in flower in gardens and in the rainforest.
Botanical names: Brachychiton australis, Sterculia trichosiphon
Common name: Broad Leaved Bottletree
Family: Malvaceae
Subfamily: Sterculioideae
Origin: Australia








A fast growing shade deciduous tree. Drought-tolerant; suitable for xeriscaping.
Botanical name: Brachychiton megaphyllus
Common name: Giant-leaved Kurrajong
Family: Malvaceae
Subfamily: Sterculioideae
Origin: Australia







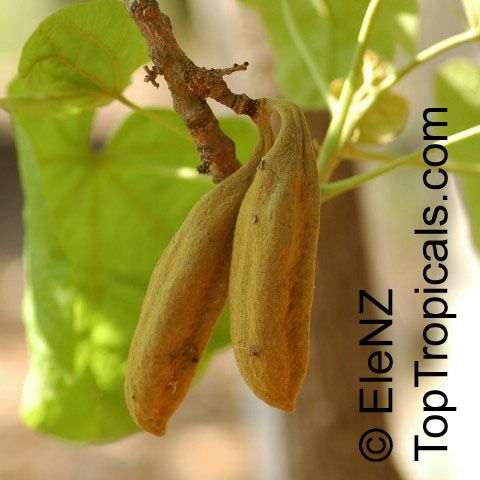
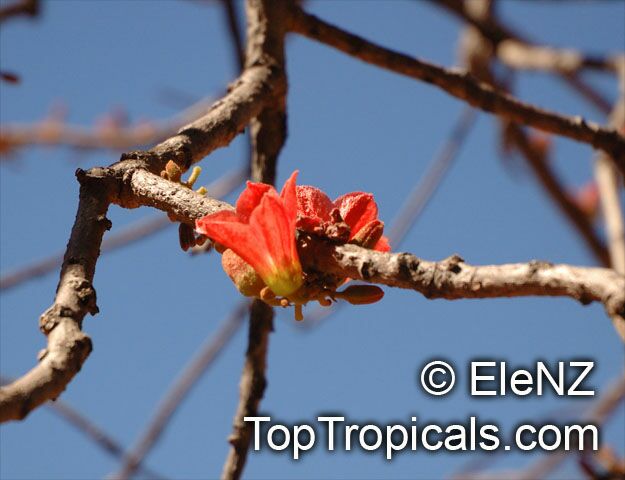
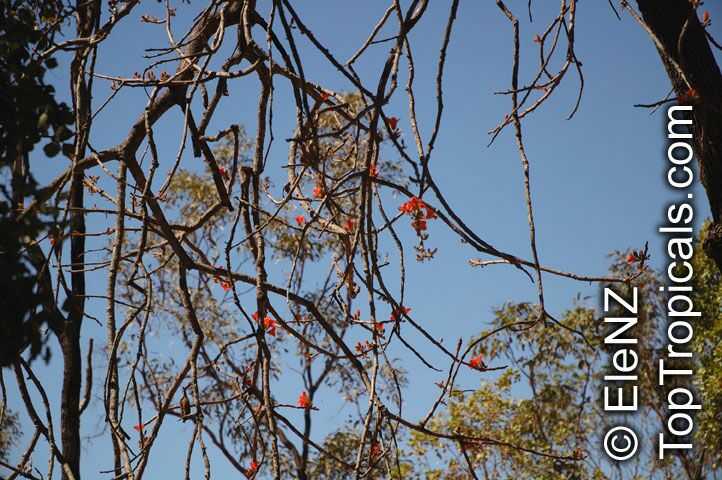
Botanical name: Brachychiton paradoxus
Common name: Red Kurrajong
Family: Malvaceae
Subfamily: Sterculioideae
Origin: Australia
Hardiness: 30°F





Botanical name: Brachychiton sp.
Common name: Bottle Tree
Family: Malvaceae
Origin: Australia
Hardiness: 30°F









Use link to repeat this search:
https://toptropicals.com/cgi-bin/garden_catalog/cat.cgi?find=Brachychiton&search_op=and&keyword_op=and&language=e&number=10
&no_change_lang=1&user=tt&sale=1&first=0























































































































