Neptunia oleracea (Water Mimosa)
Botanical name: Neptunia oleracea
Common name: Water Mimosa
Family: Fabaceae
Subfamily: Mimosoideae
Origin: South America






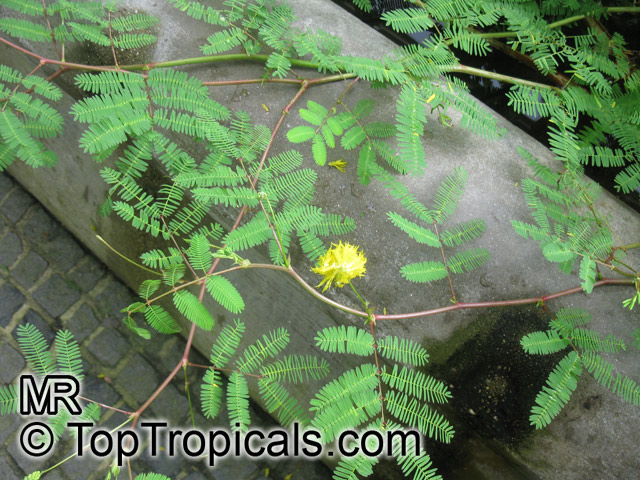
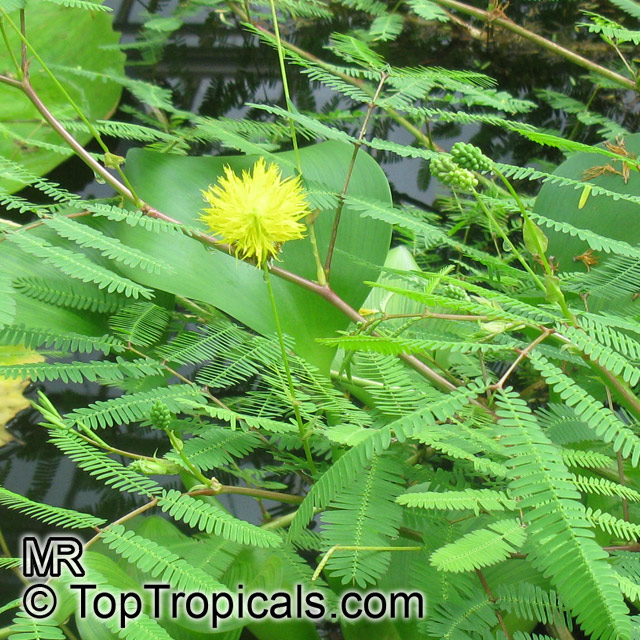
Native to South America, Neptunia oleracea is an invasive, fast-growing, small shrub with attractive yellow and orange flowers in USDA zones 9-11. It is found in ponds, streams, canals, and other bodies of water. It thrives in full or partial sun and grows best when partially or fully submerged, or if it can sit at the water's edge. For best results, a bog planted in moist, aquatic soil is recommended.
Neptunia oleracea is not just a lovely plant; it also has ethnomedical uses. The roots of the plant are used to treat dysentery, diarrhea, and other stomach ailments. The young leaves, shoot tips, and young pods can all be eaten, making them a suitable crop of vegetable in wet areas.
Fruit production of the plant is abundant. Each plant can produce up to 40 fruits in one season. The round fruit are bright yellow to orange in color, with a texture that is crispy like an apple. They can be eaten fresh, or processed for jams, jellies and other culinary uses. They are also used to made traditional medicines and are said to have a number of health benefits, such as enhanced strength, improved eyesight, and increased immunity.
Growing Neptunia oleracea in cold regions can be done with care. An established plant can withstand temperatures as low as 25F, but young plants will need to be pot-grown and brought indoors during winter. It should be planted in a container that is smaller than the root mass, about 8 inches deep, filled with moist aquatic soil and placed in bright indirect light. Care should also be taken to ensure the soil is kept damp, but not soggy. Turning the pot every week or so will also help the plant receive more even light exposure. To maintain healthy and abundant growth, the plant should be fertilized once per month during warmer months.


