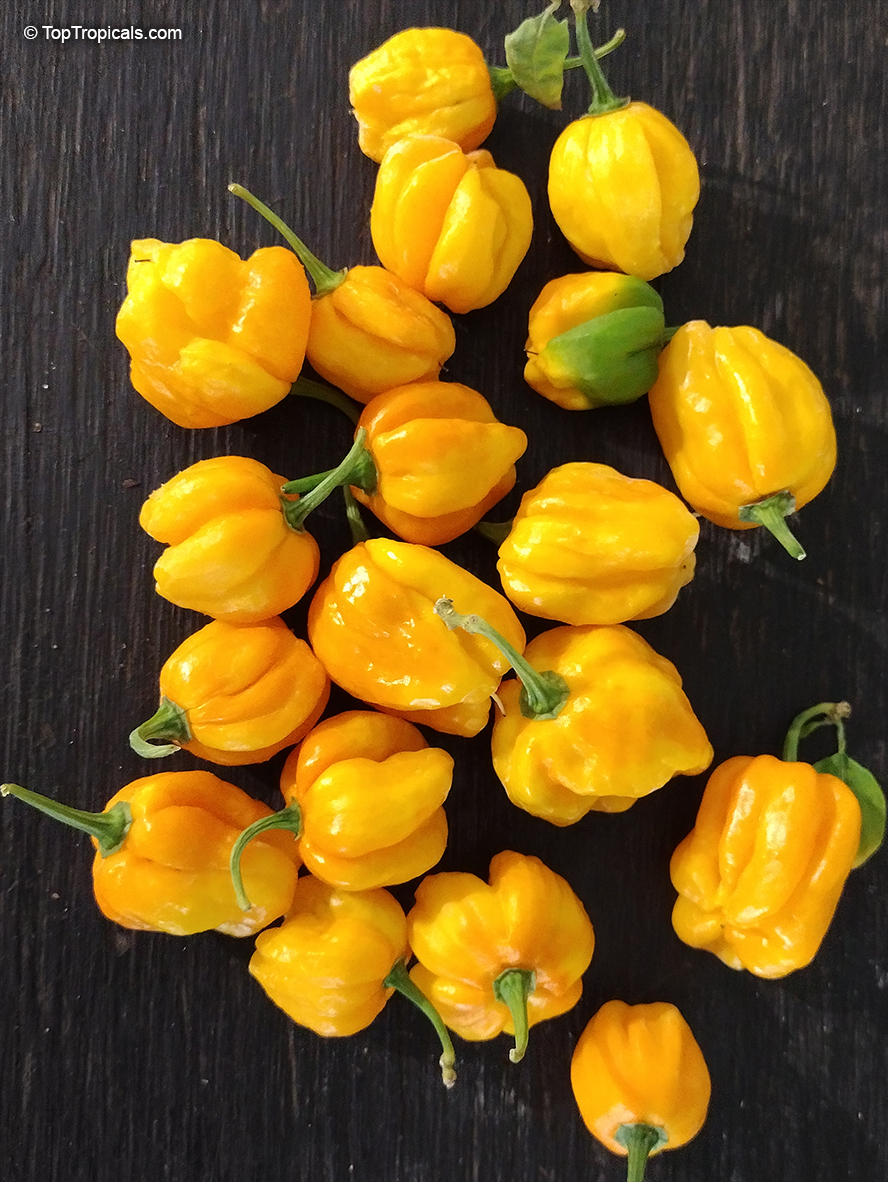
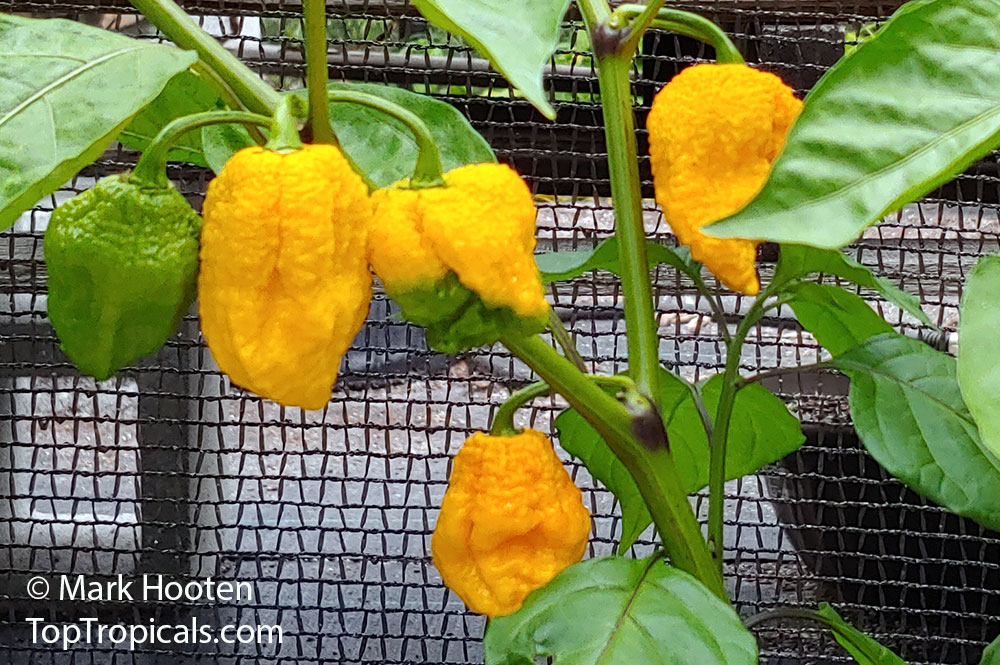
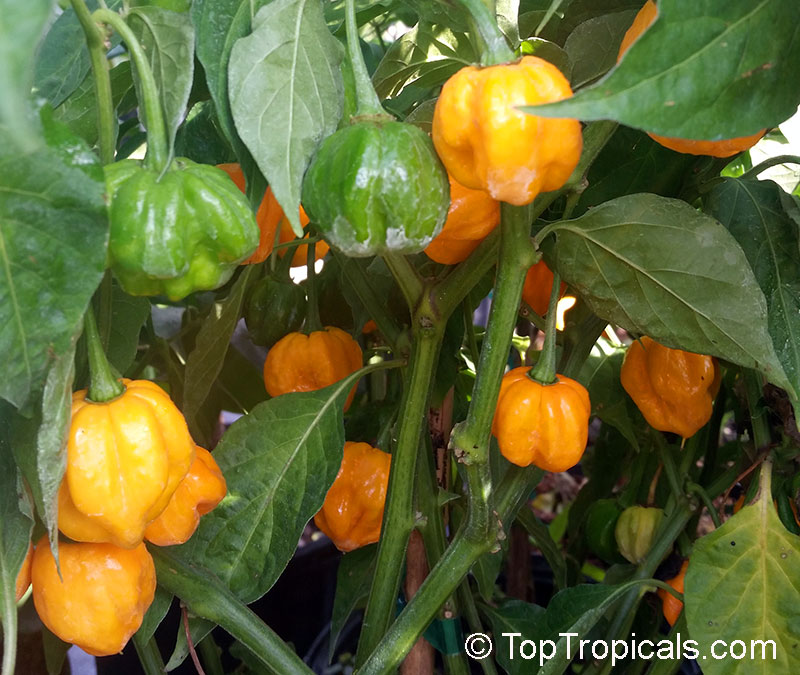
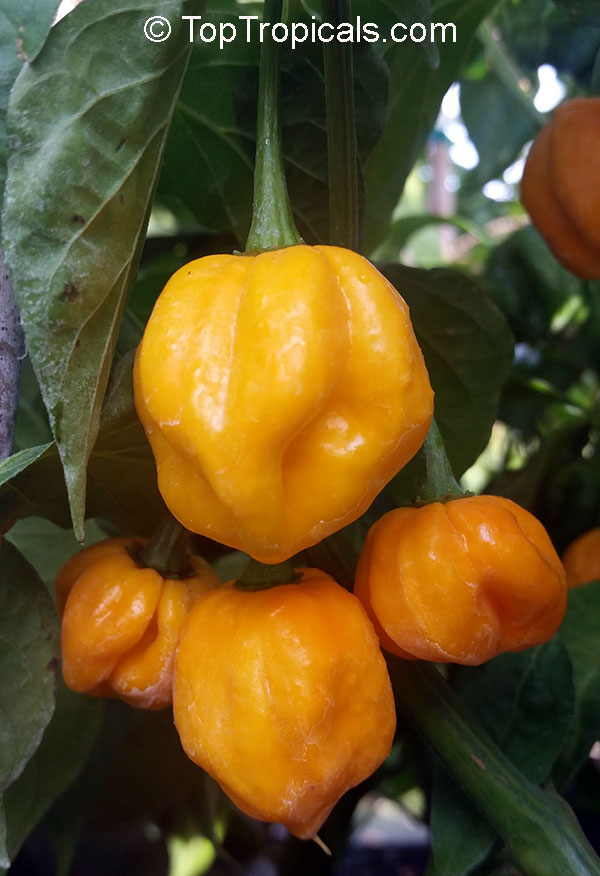
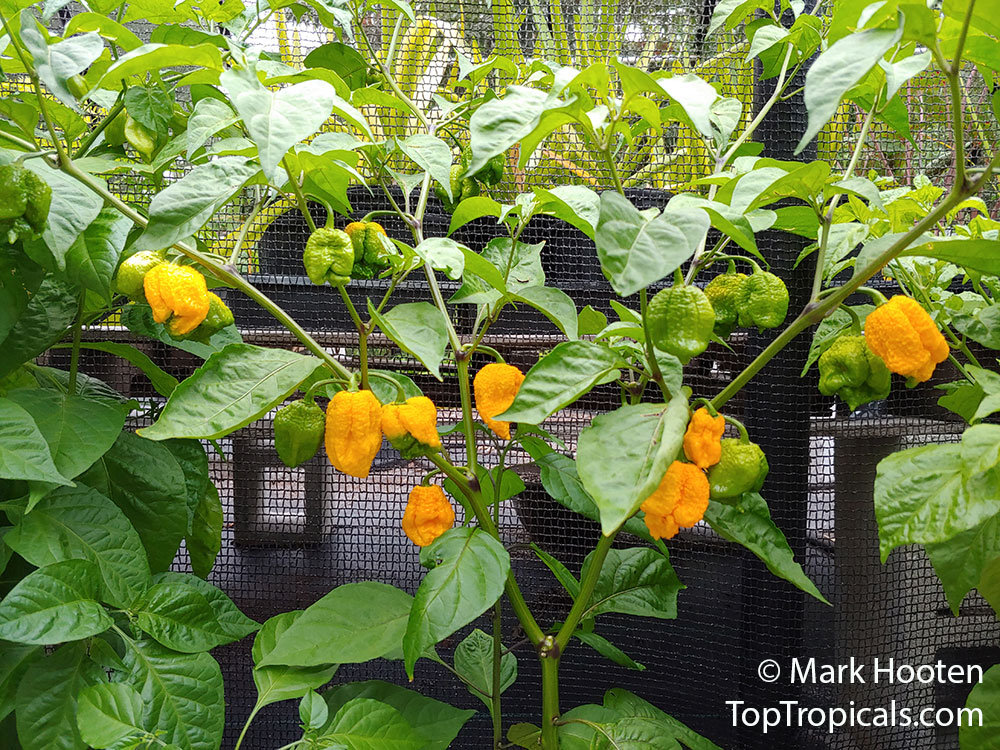
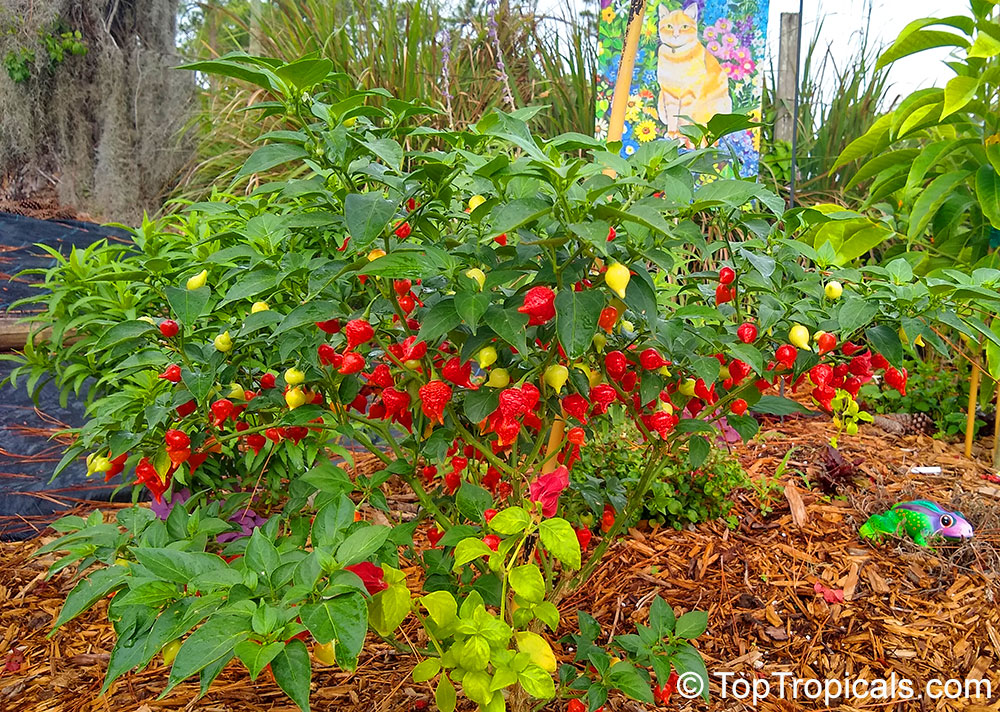
Capsicum chinense (Yellow Lantern Chili)
Botanical name: Capsicum chinense
Common name: Yellow Lantern Chili
Family: Solanaceae
Origin: Central America






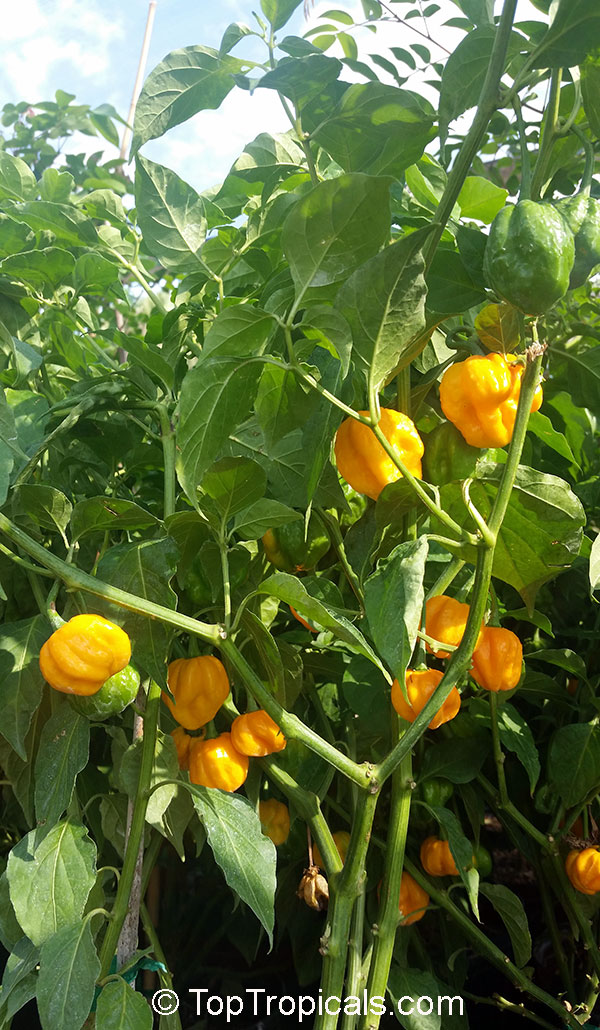
Capsicum chinense is a small shrub native to Central America that grows 2-5 ft tall. It thrives in full sun, but can tolerate some semi-shade. It produces white or off-white flowers which can be mildly irritating to the skin. This plant is a spice or herb and is cold hardy in USDA Zone 10 -12.
In cold regions, it is best to grow Capsicum chinense in pots. To do so, use a large pot with good quality soil that is well-drained and amended with organic matter such as compost. Add a layer of mulch on top of the soil to retain moisture and protect the roots in the winter. Place the pot in an area with at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day and water regularly, allowing the top inch of soil to dry out between waterings. Fertilize once a month during the growing season with a balanced fertilizer. For winter care, move the pot inside or to a sheltered area to prevent the roots from freezing. If temperatures drop below freezing, cover the pot with a blanket or other insulating material for added protection.
Capsicum chinense and its varieties have long been used in Yucatan and Caribbean cooking to add heat to traditional dishes. One well-known cultivar of this plant is the Carolina Reaper. The pepper is red and gnarled, with a bumpy texture and small pointed tail. In 2013, it was declared the hottest chili pepper in the world by Guinness World Records.
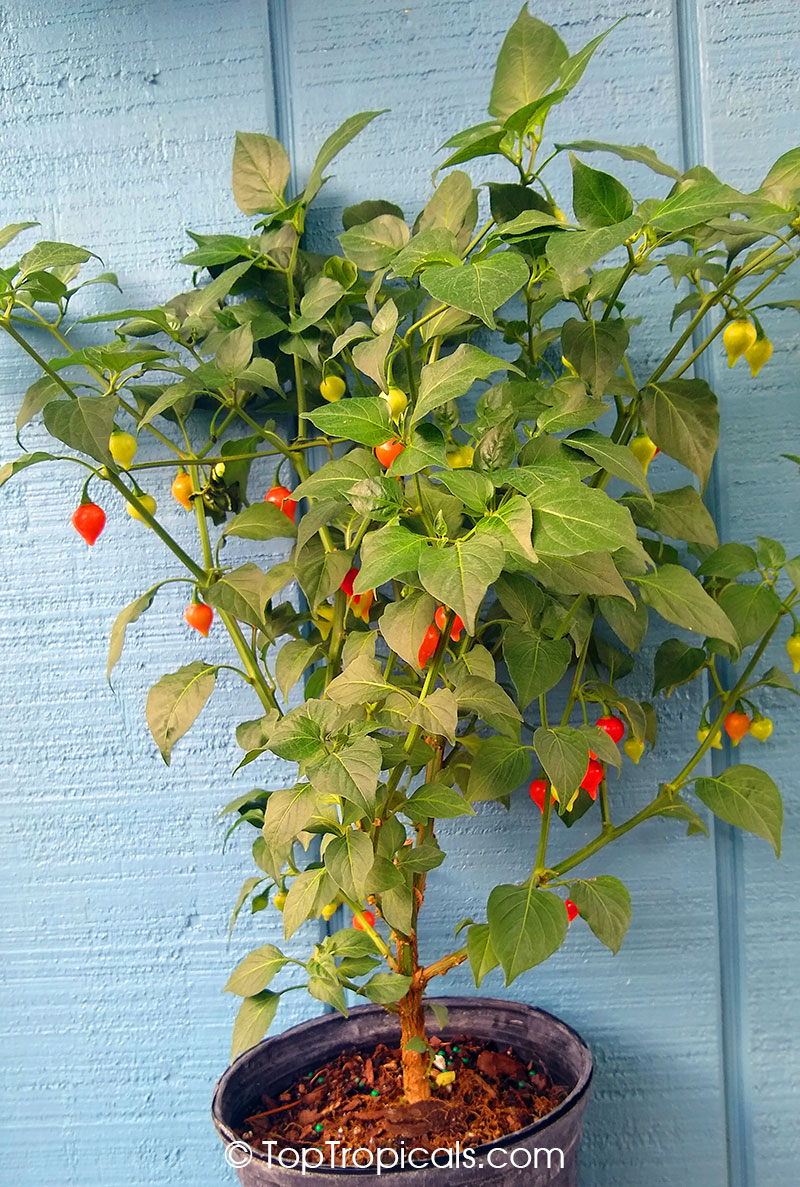
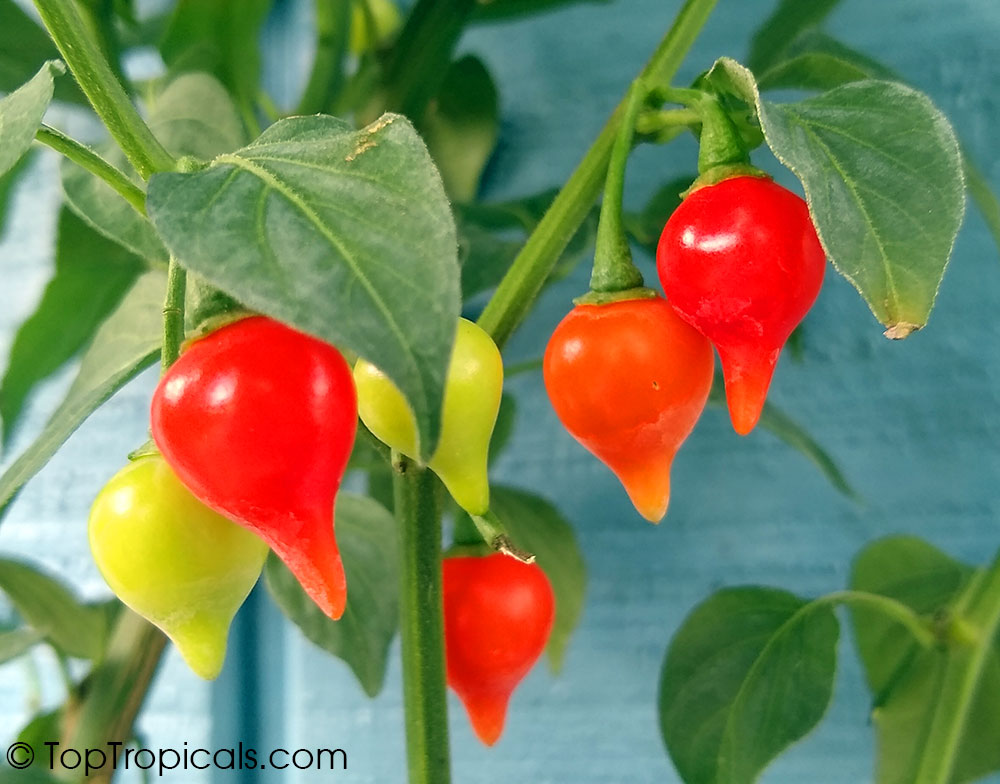
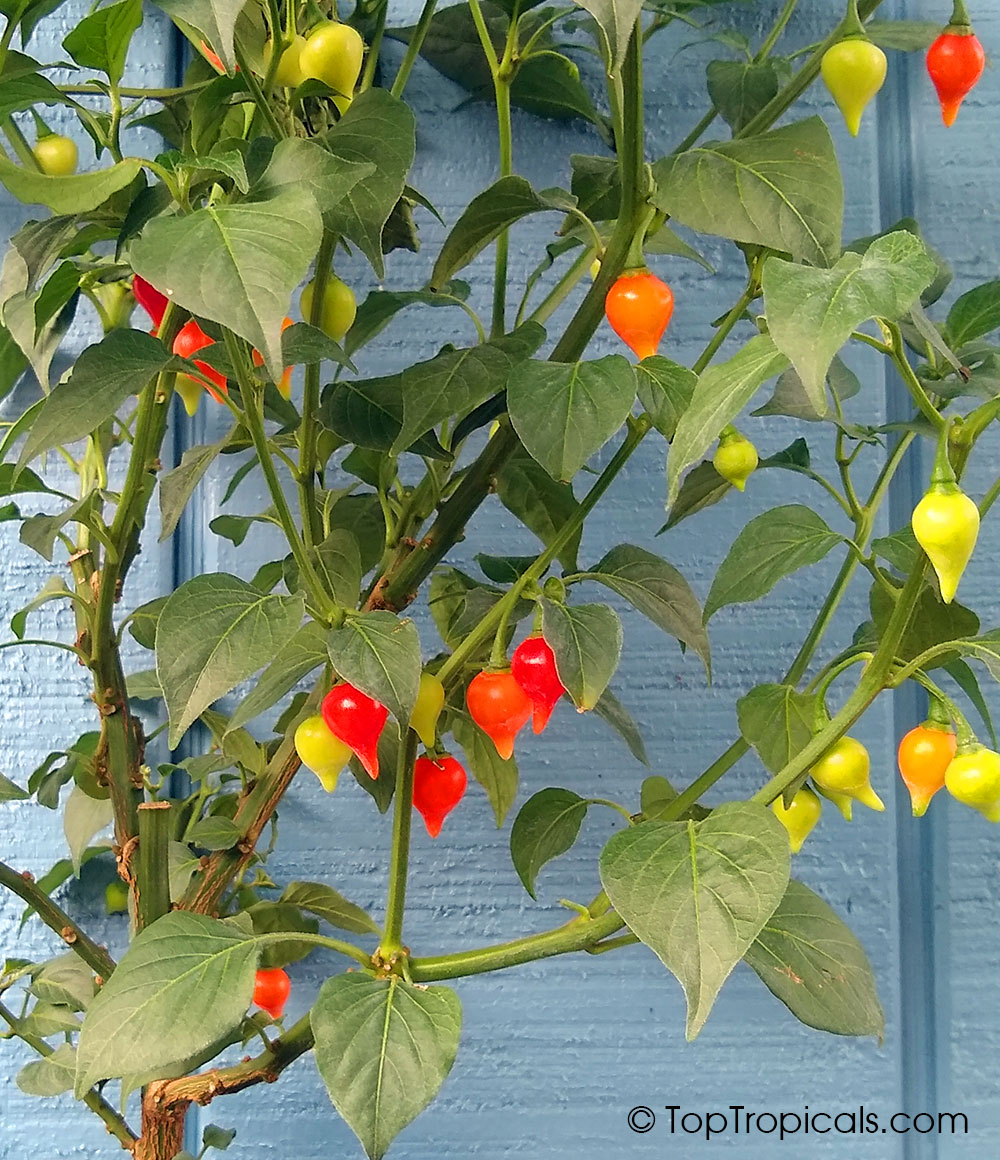
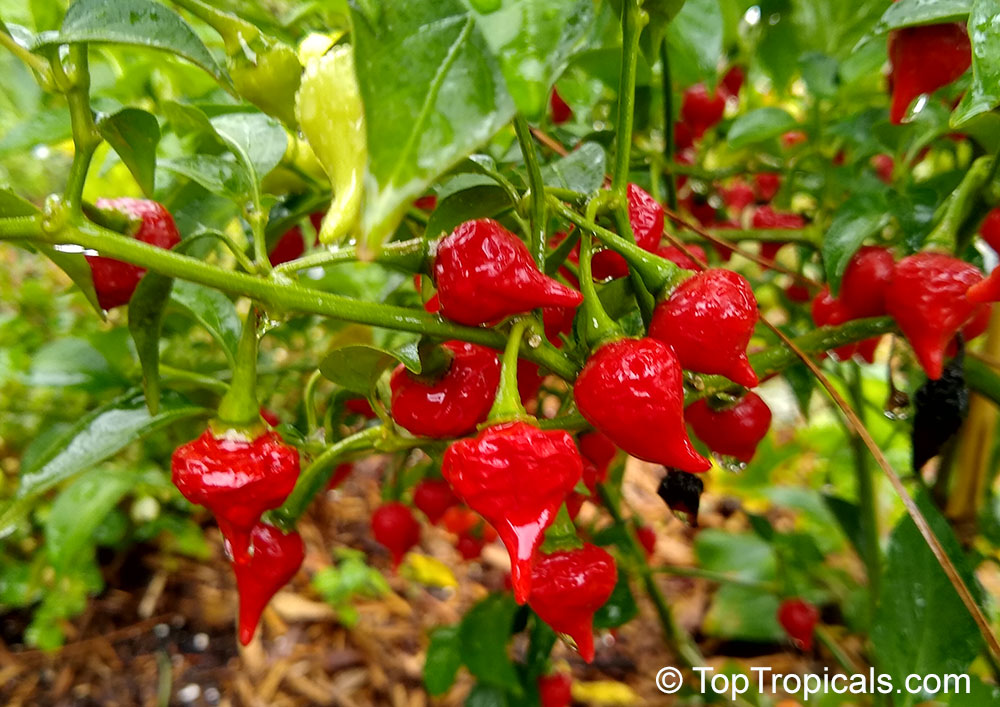
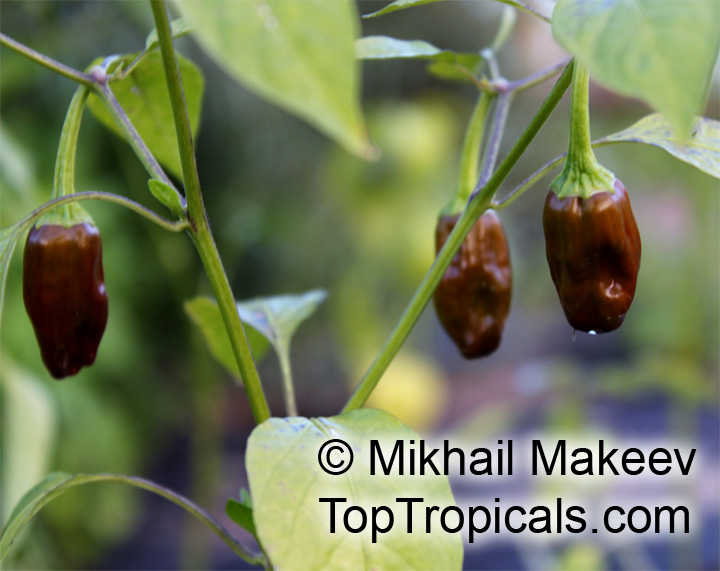
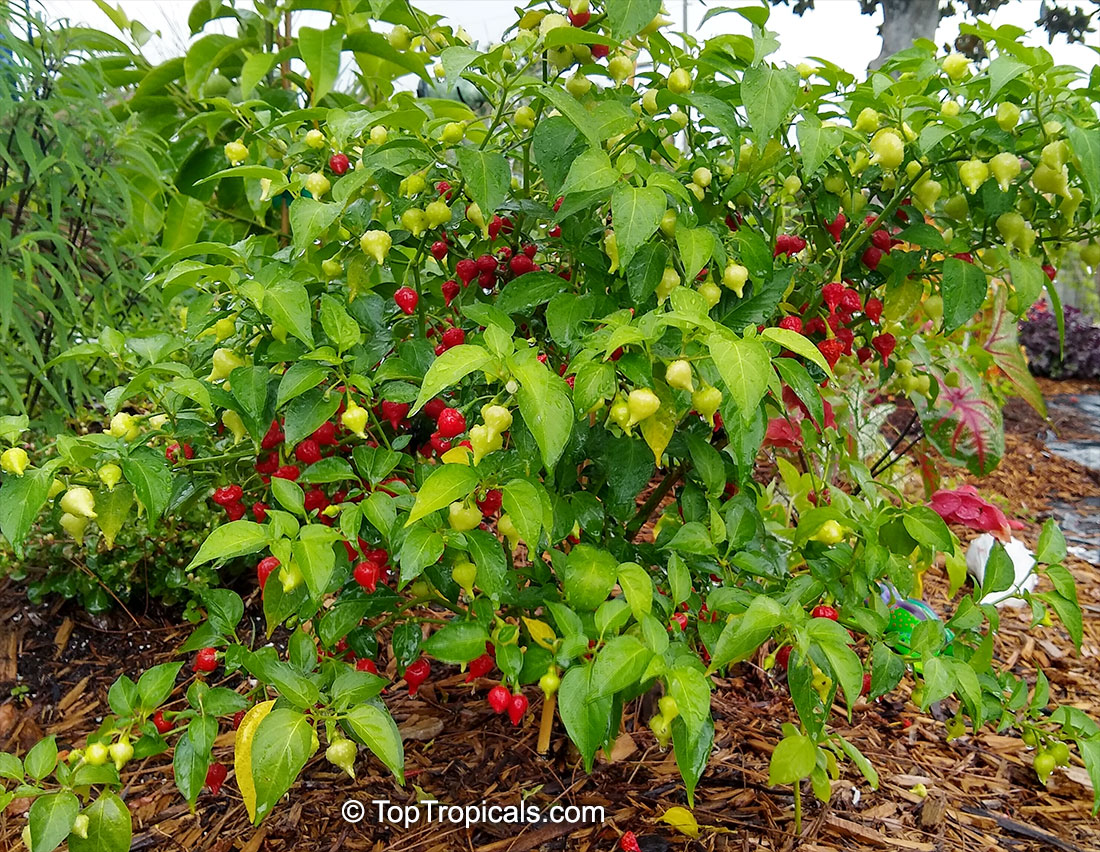
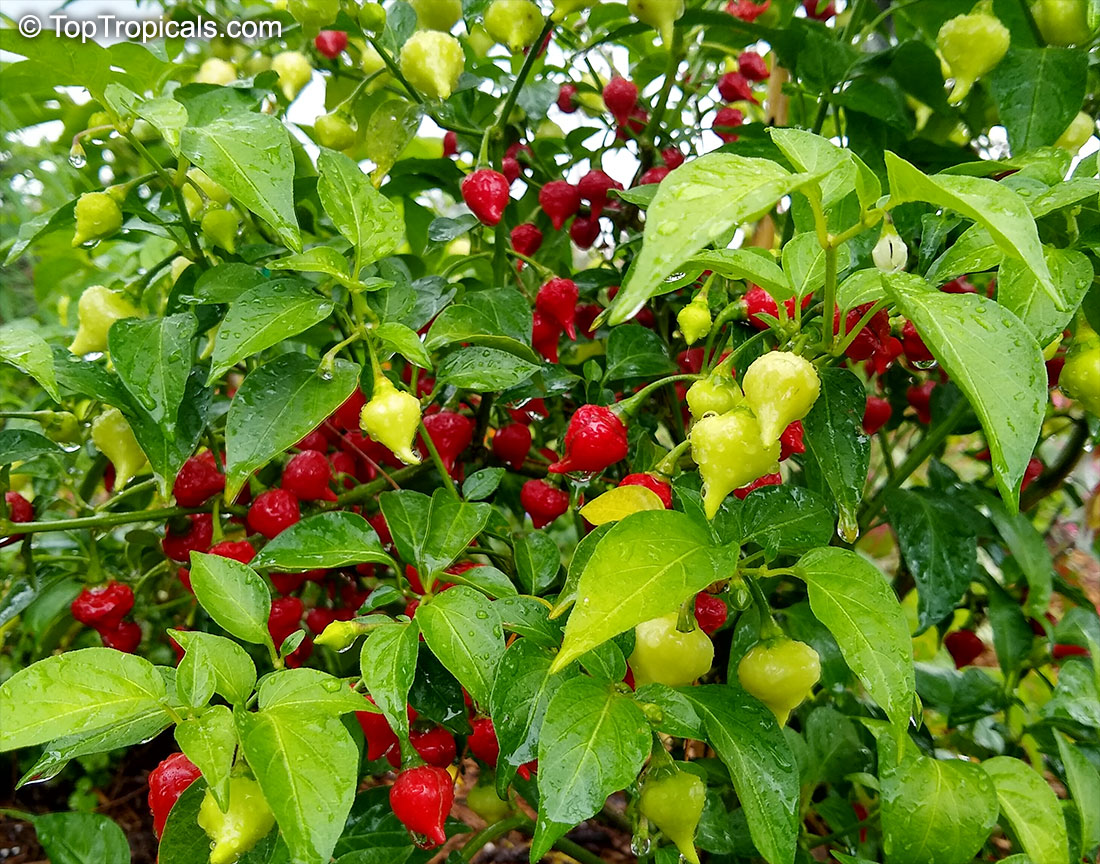
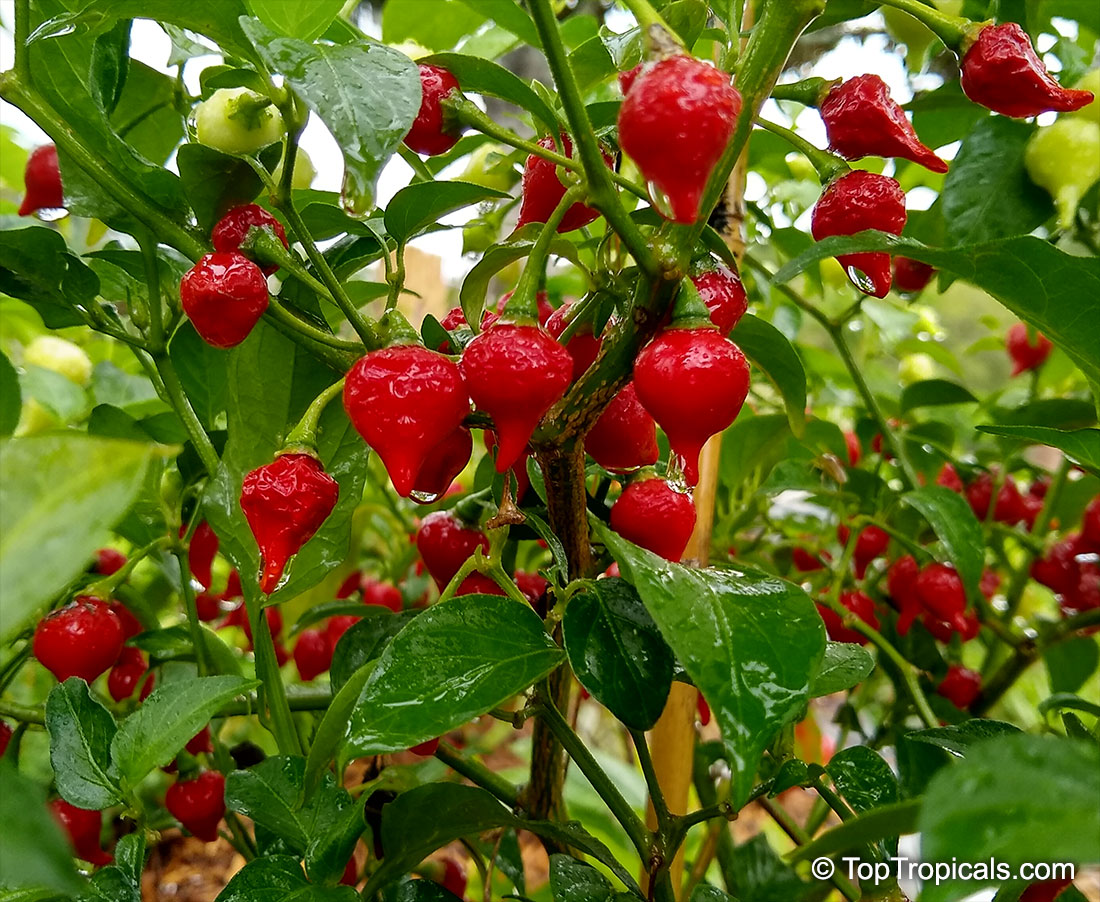
Another unique variety of Capsicum chinense is the Biquinho Pepper. This pepper is likely an ancient hybrid of Capsicum annuum and Capsicum chinense, and is native to an area of South America where Western Brazil and Eastern Peru meet. The small, bright orange to red fruits are known for their intense habanero flavor, although they typically have little or no heat. In recent years, the Biquinho Pepper has become popular in South America, especially in Rio, and is often pickled and served as a snack with caviar. It is also a great addition to salsas, guacamoles, and Bloody Marys.
Similar plants: Capsicum chinense (Yellow Lantern Chili)
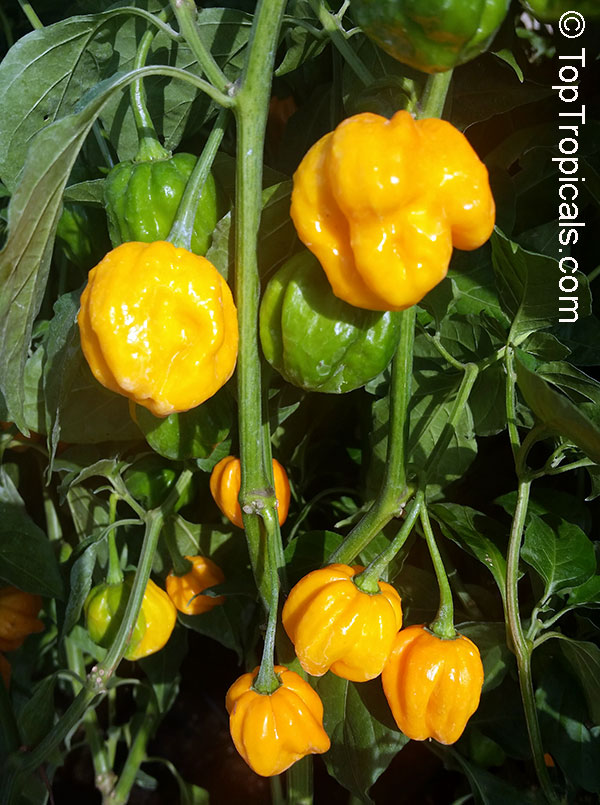
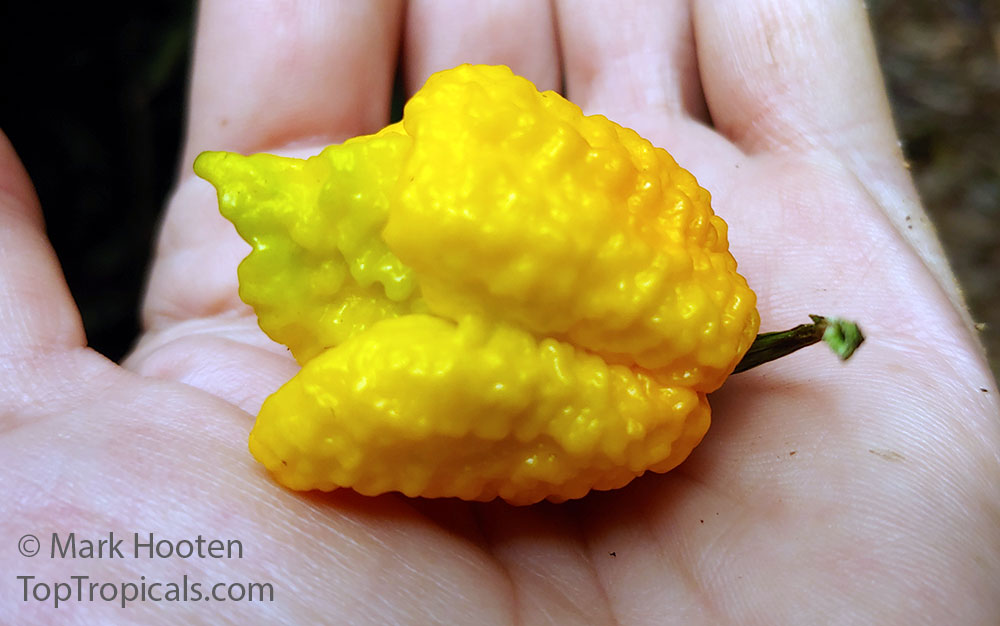
While of small size (something around an inch or so long), these oddly shaped bright orange to finally red fruits are prolifically produced along the branches of compact plants with small leaves.
What separates this variety from others is its unique flavor which packs quite a bang! Not because of its heat (because our strain has either no heat what-so-ever, or so little it is hard to even detect), but because of its intense fruity habanero flavor.
If one who knows that distinct habanero super fruit flavor (which is then normally followed by the heat blast), then tries a biquinho pepper, the flavor is so distinctly habanero that when the heat blast doesn
Shipped at customers risk, no replacements or refunds. Leaf drop possible. We guarantee healthy plant to be shipped and the best packaging. Express shipping optional.
Recommended Fertilizer: SUNSHINE C-Cibus - Crop Nutrition Booster
SUNSHINE-Honey - sugar booster
















 SUNSHINE C-Cibus (NPK 2-2-4) - Crop Booster for every watering.
SUNSHINE C-Cibus (NPK 2-2-4) - Crop Booster for every watering.  SUNSHINE C-Cibus (NPK 2-2-4) - Crop Booster for every watering.
SUNSHINE C-Cibus (NPK 2-2-4) - Crop Booster for every watering.