Momordica - Plant Encyclopedia Results
Top Tropicals Plant Encyclopedia
| Number of plants found: 5 |
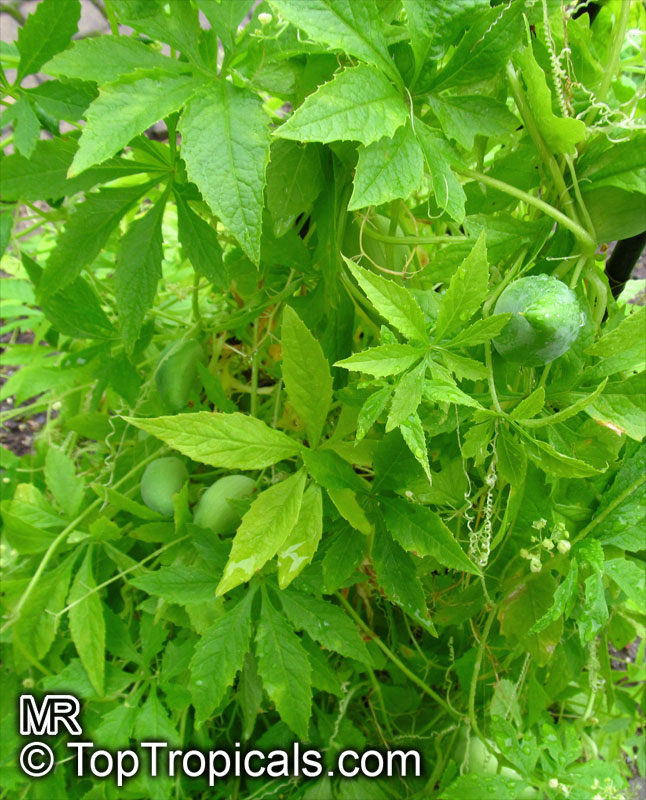
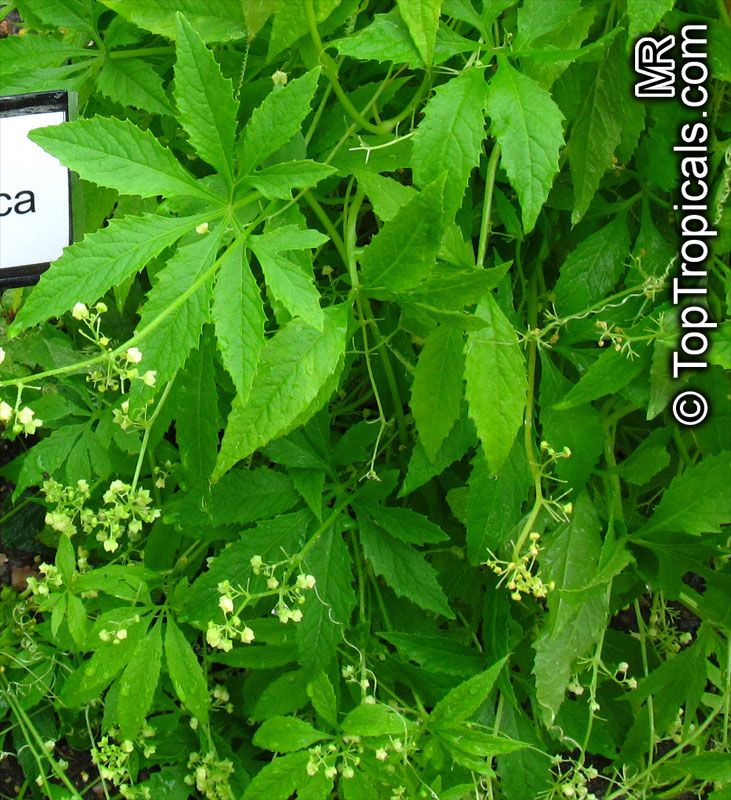
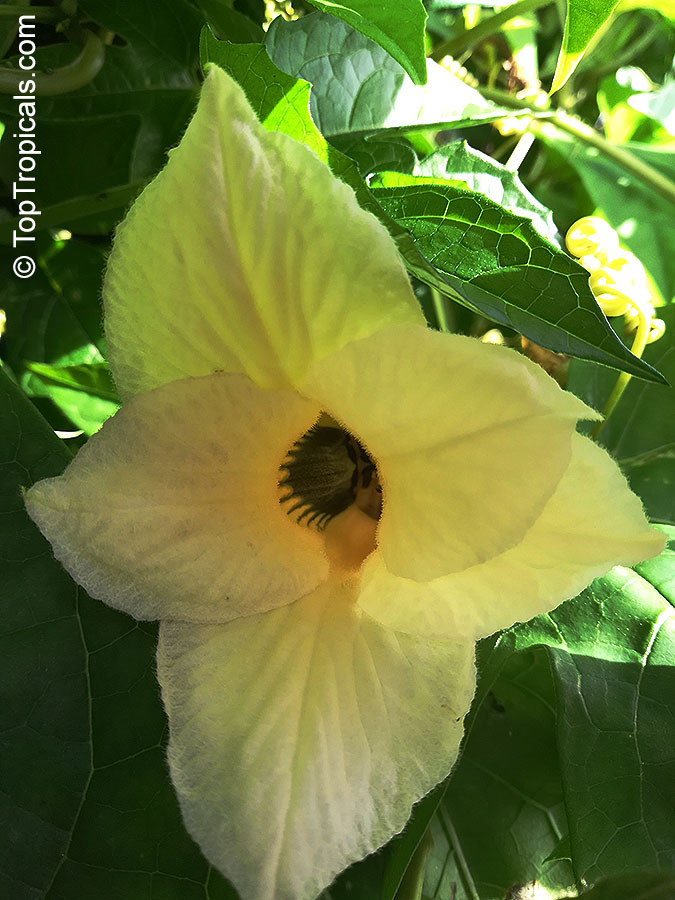
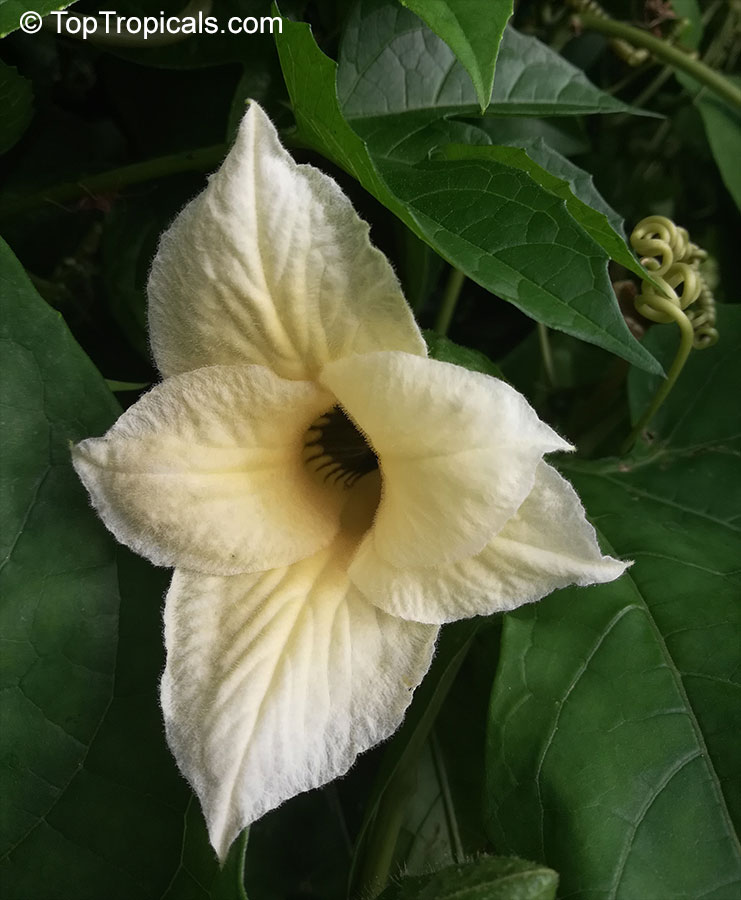
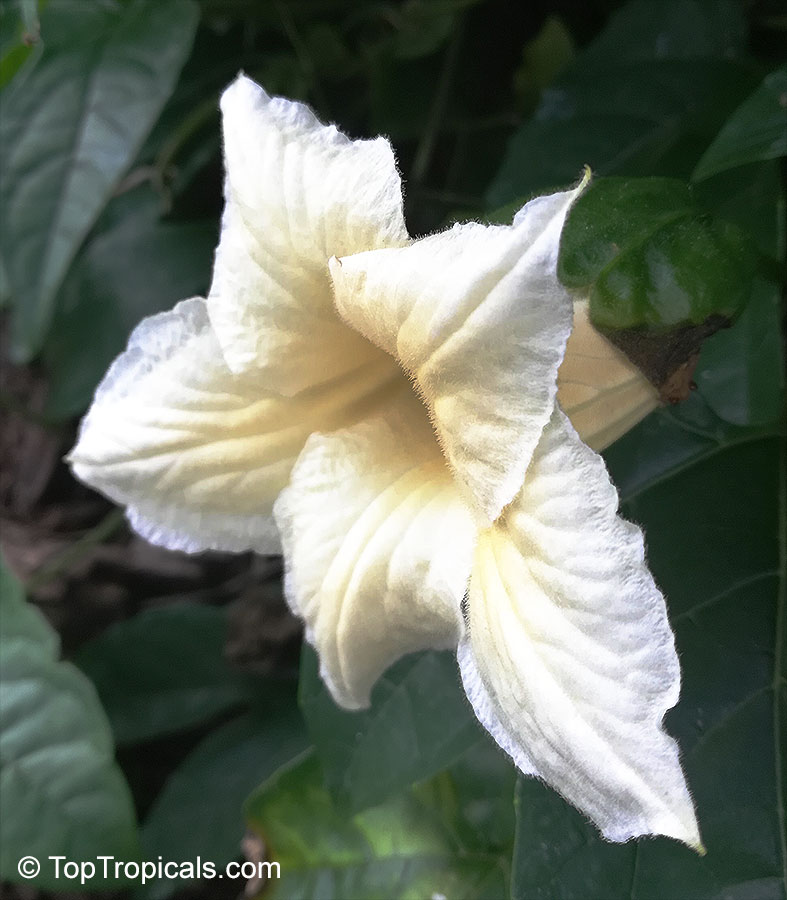
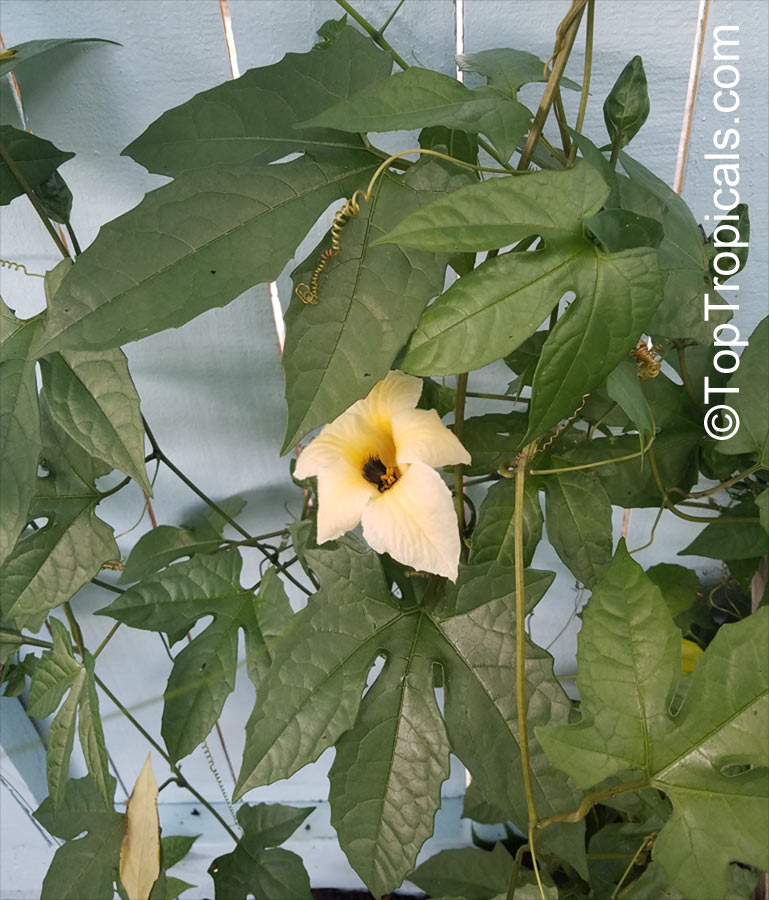
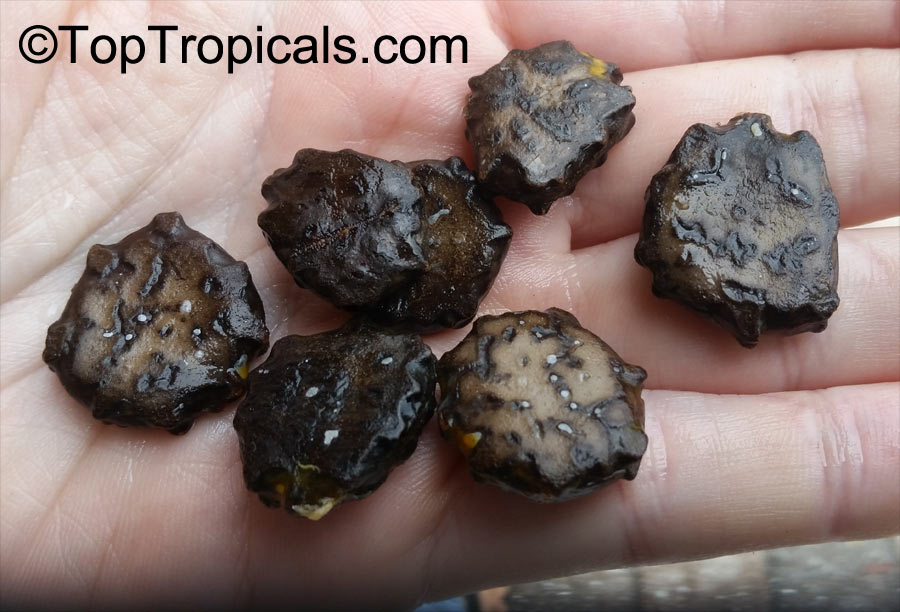
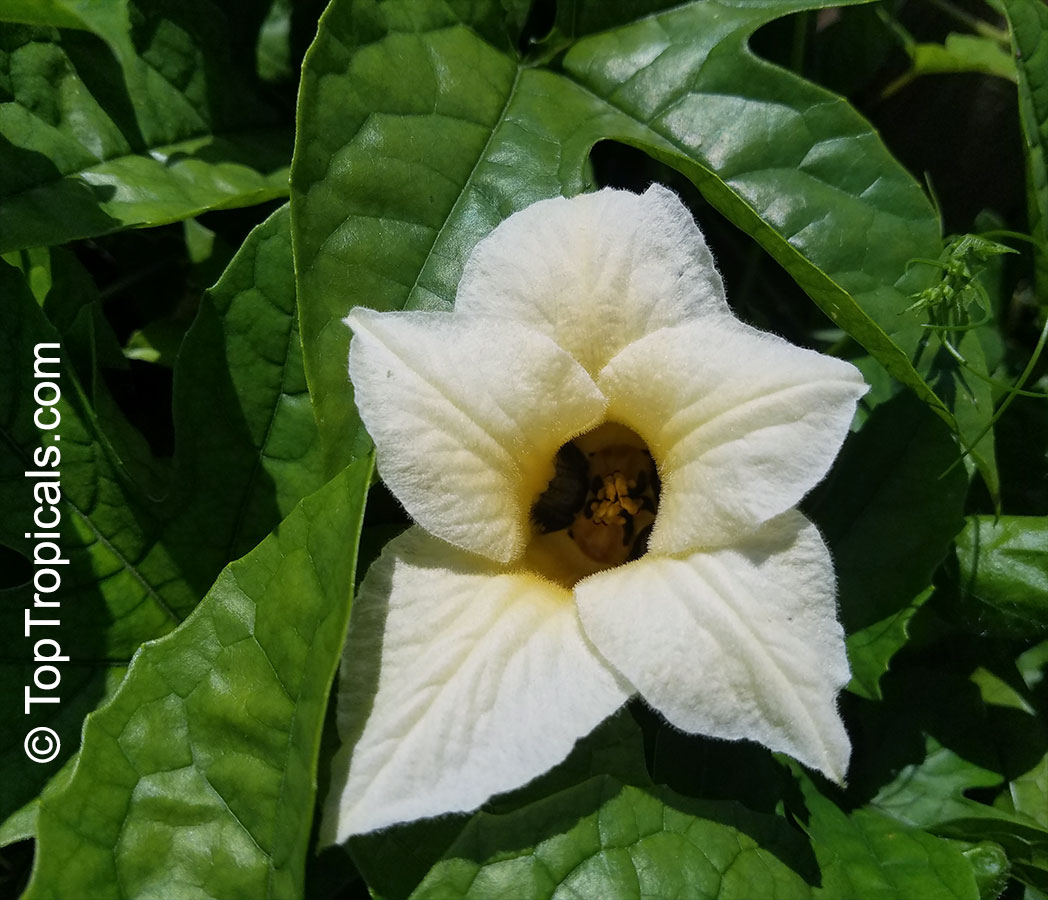
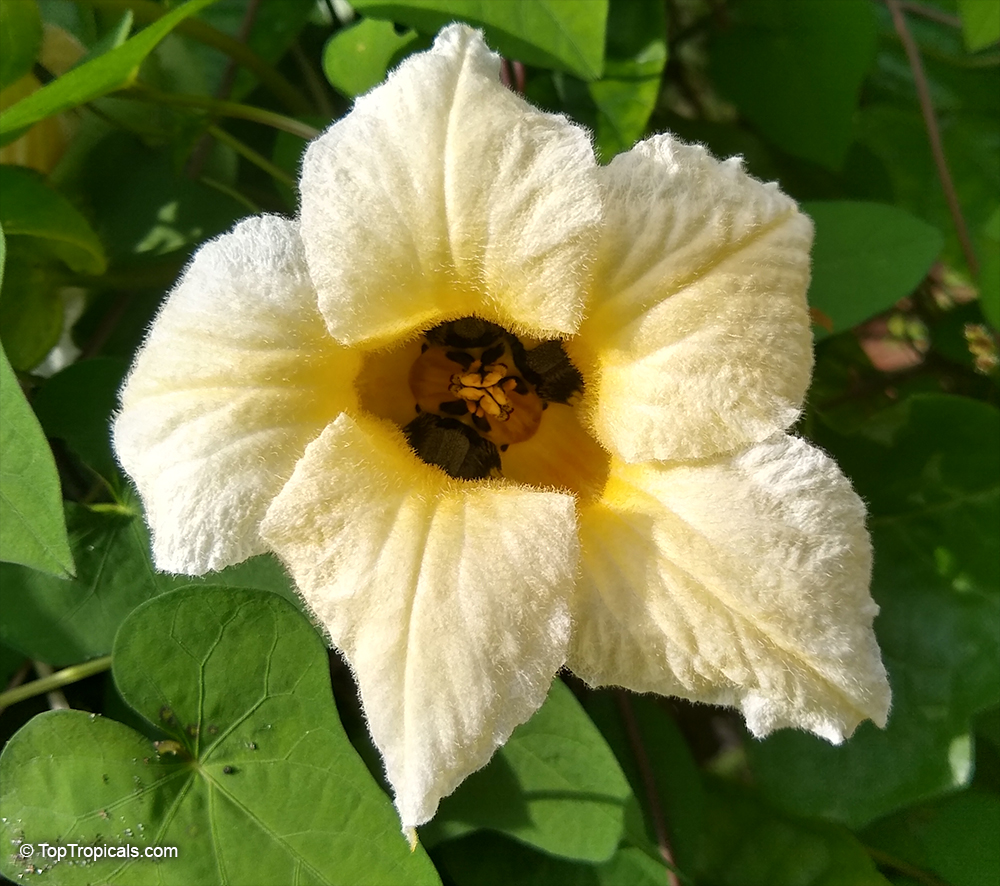
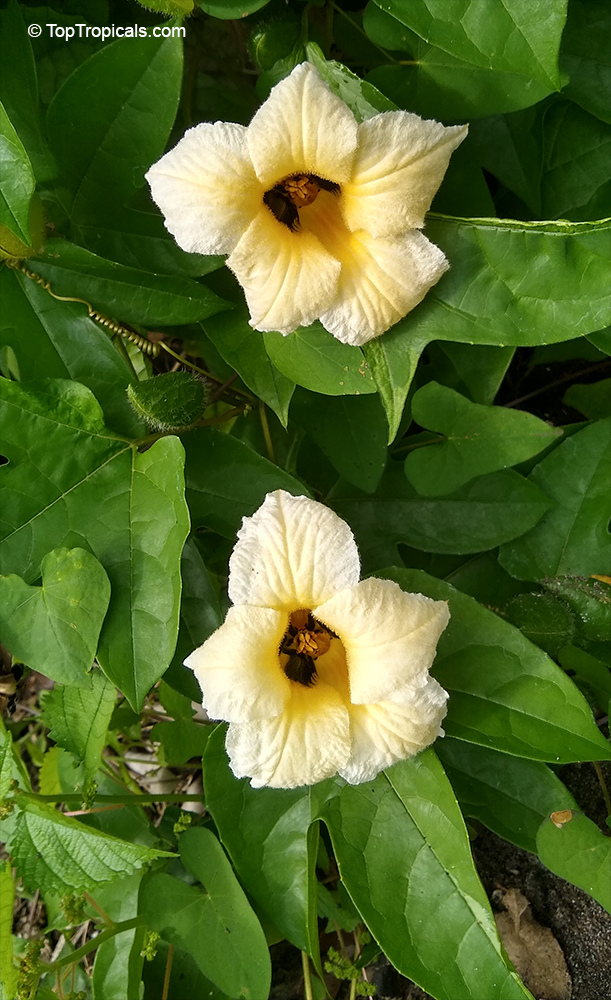
Botanical names: Cyclanthera pedata, Momordica pedata
Common names: Caigua, Wild Cucumber, Stuffing Cucumber
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Origin: South America









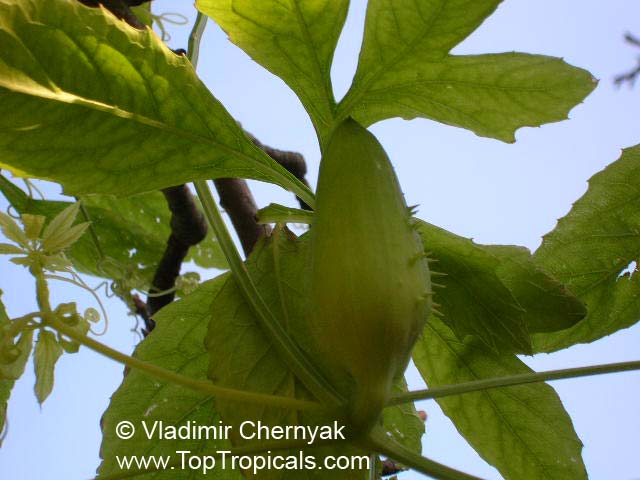
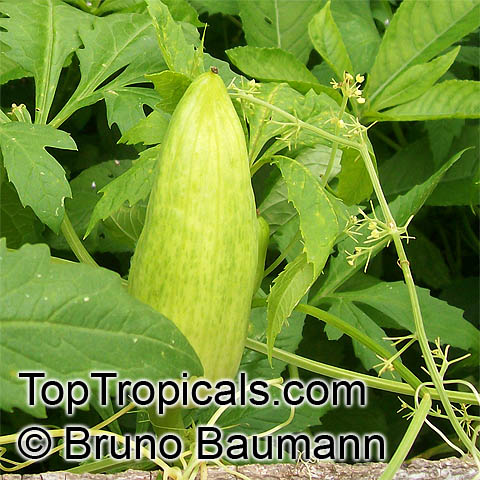
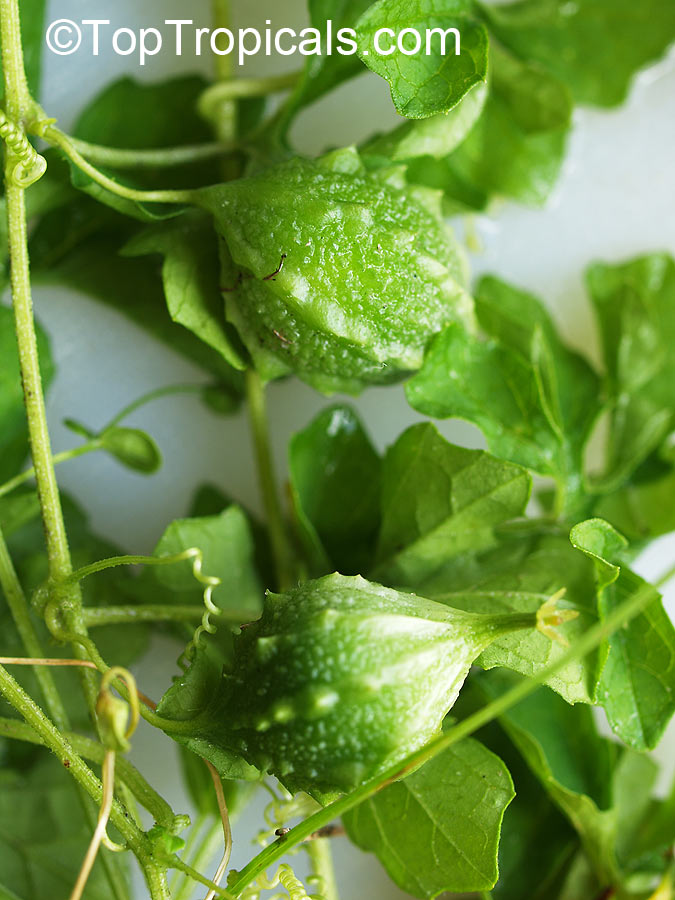
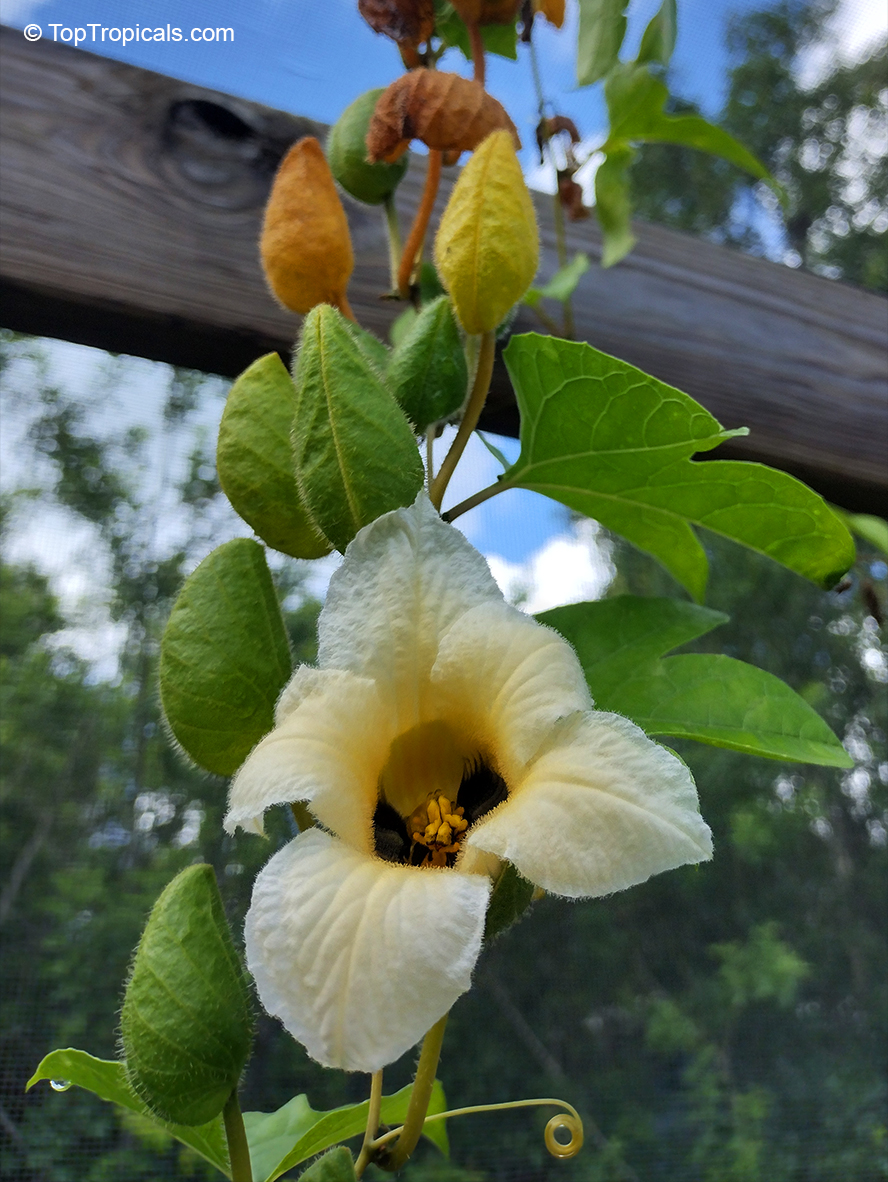
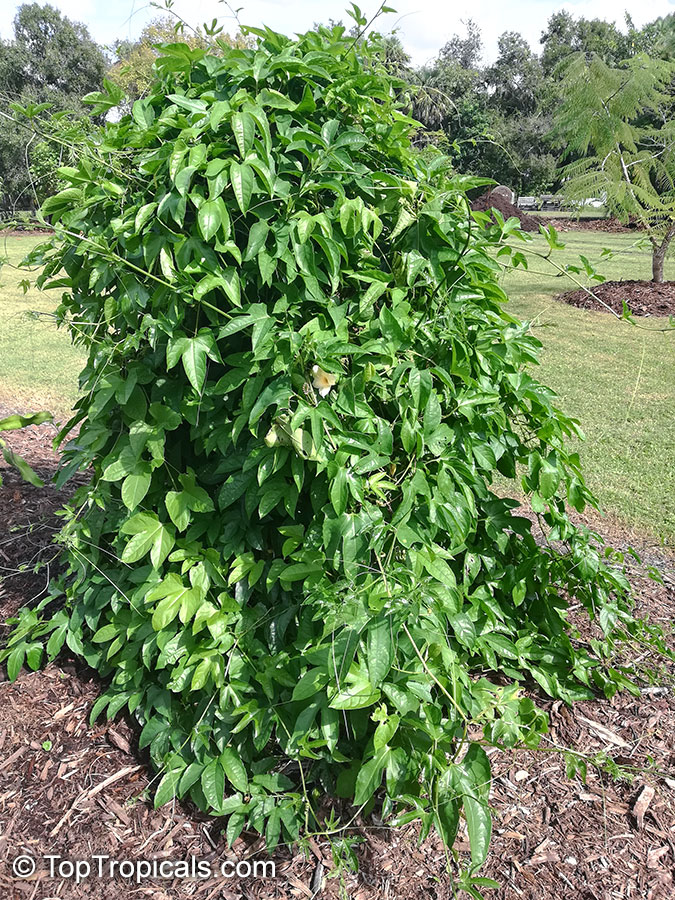
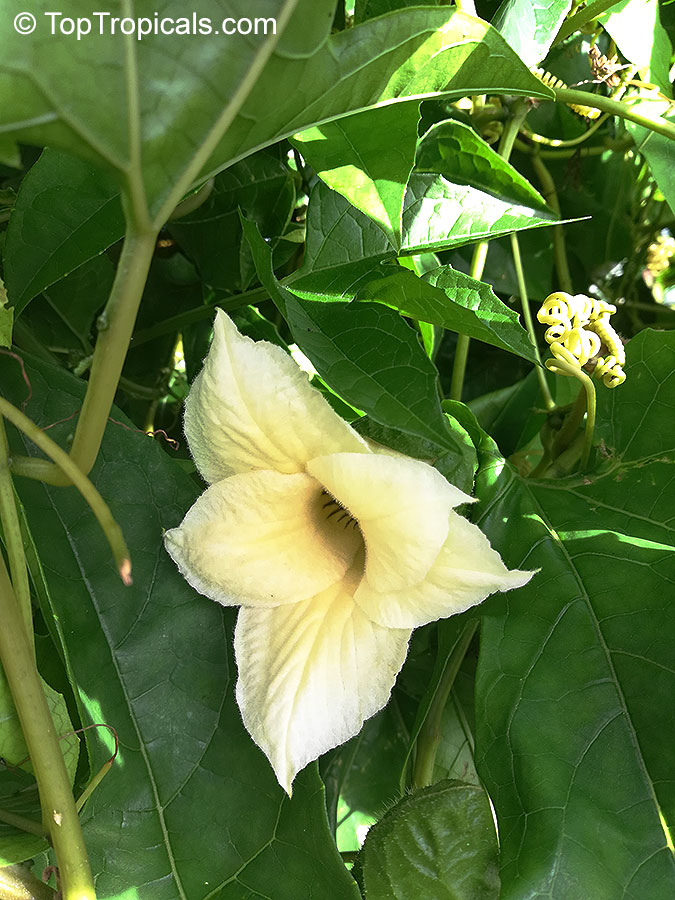
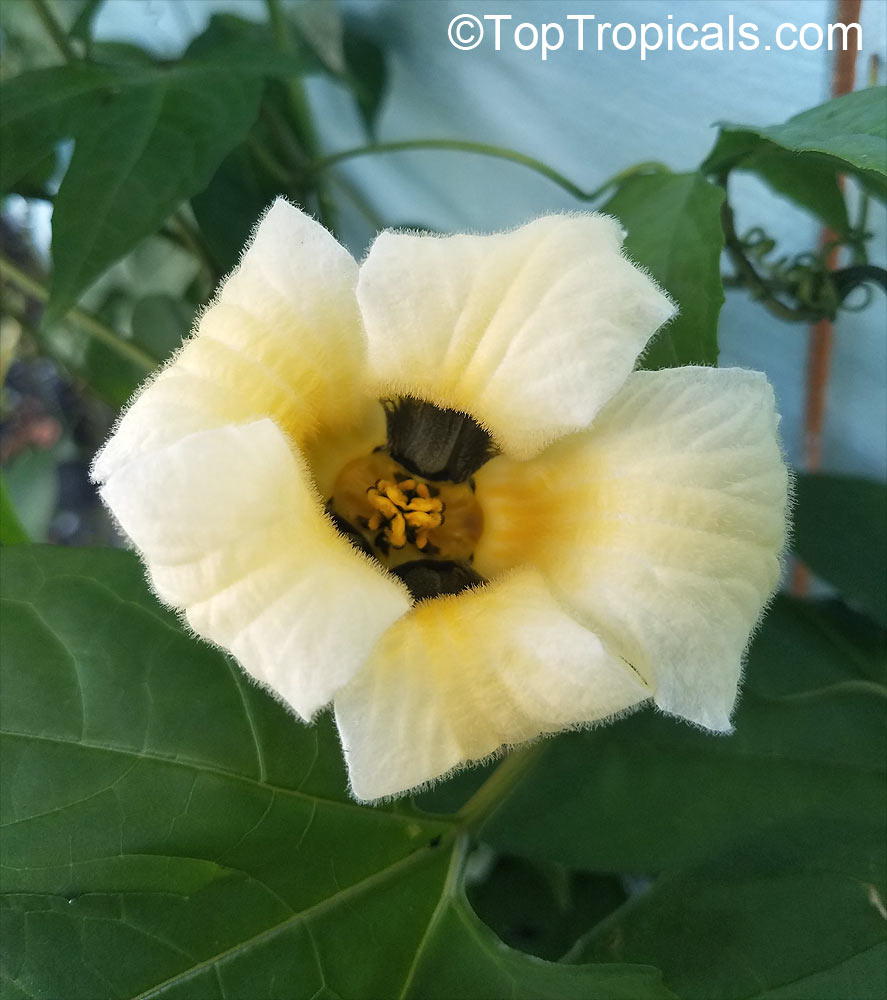
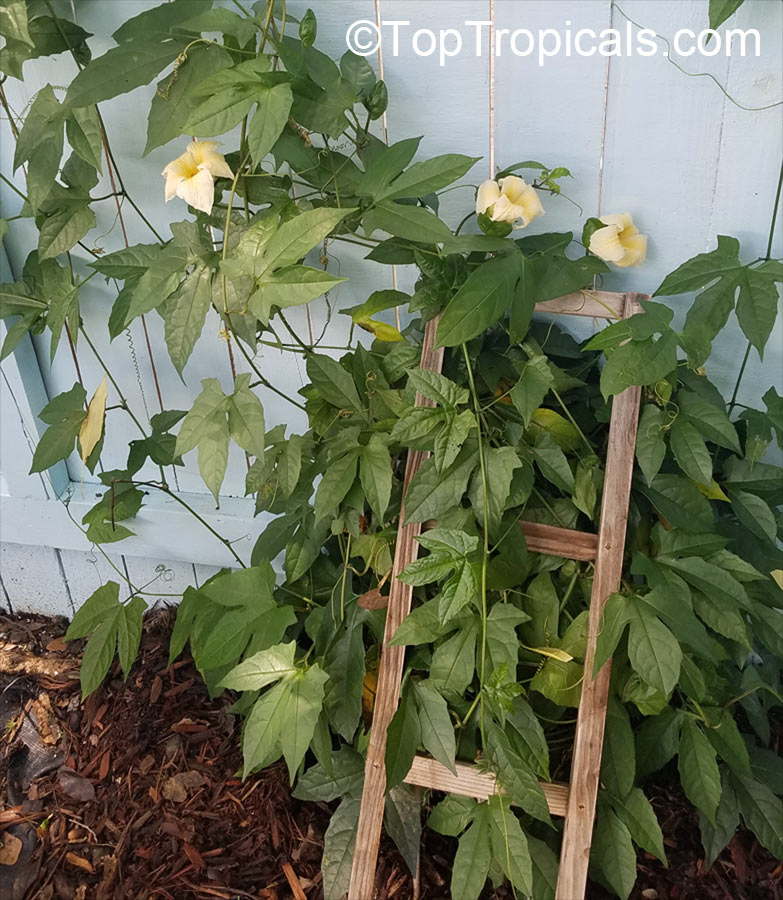
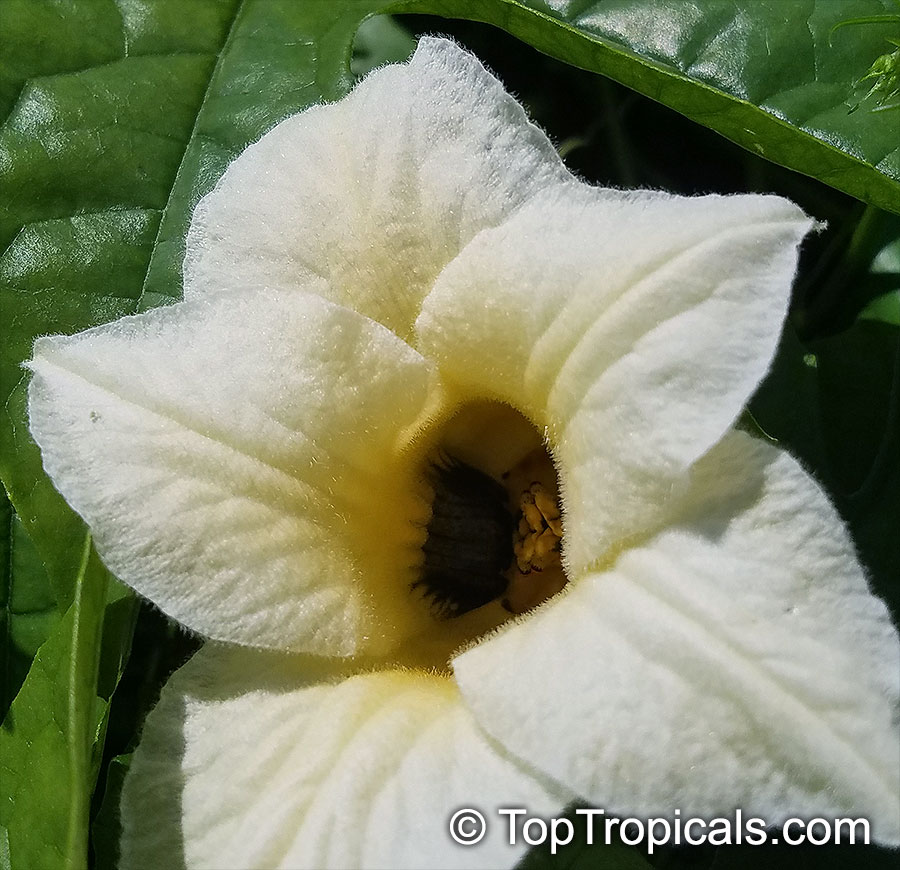
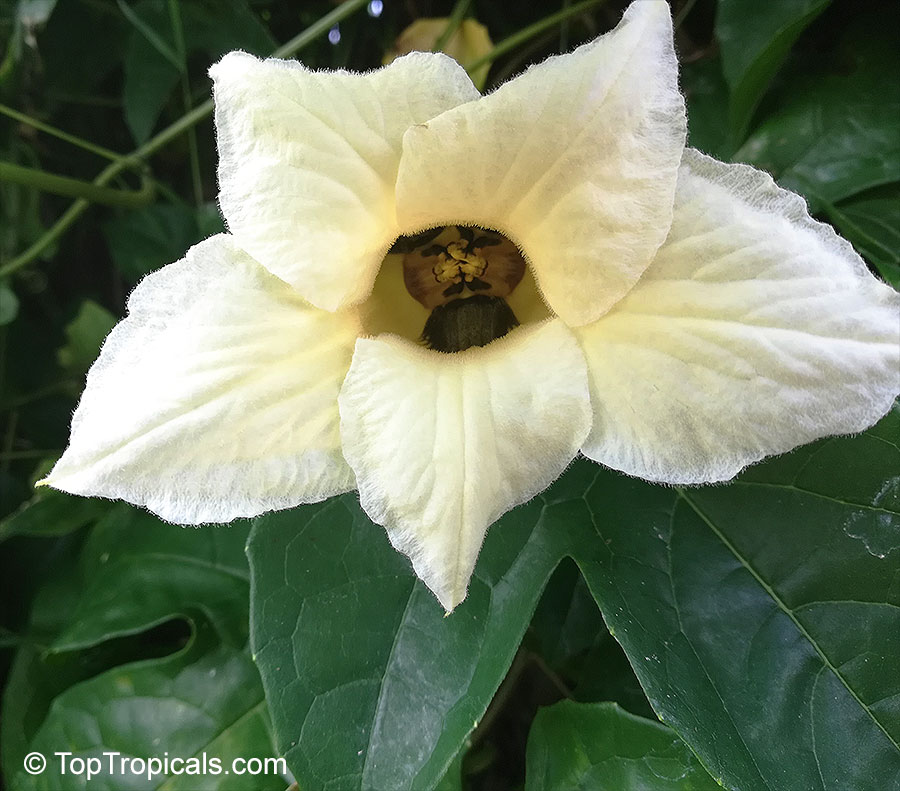
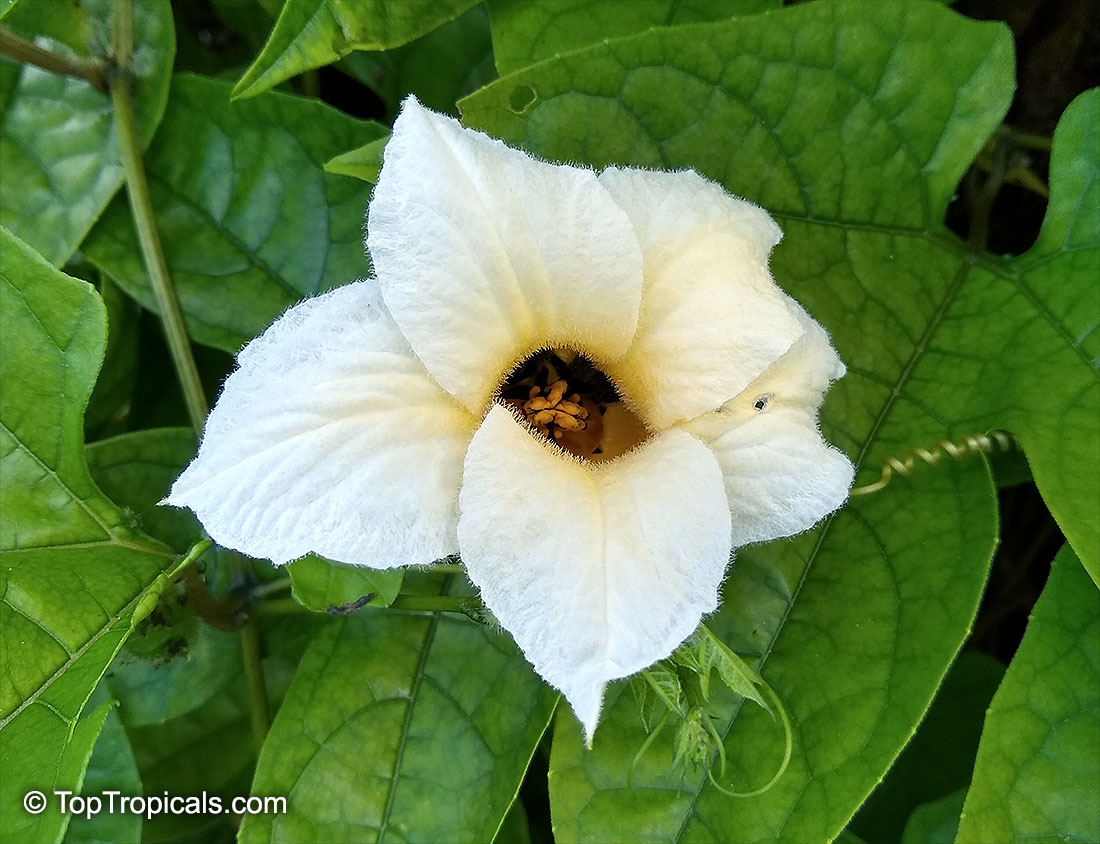
Cyclanthera pedata (Caigua) is a fast-growing vine or creeper that is native to South America. It thrives in full sun, with semi-shade in warmer climates. It can tolerate regular, moderate water and is an ethnomedical plant, used for many ailments. The Caigua produces white to off-white flowers, followed by small fruits. It is a versatile plant, with the leaves, flowers, young fruits and young shoots all edible; the mature fruit can be used in a dish similar to stuffed peppers.
This plant grows best in USDA Zone 6-10 and is fairly cold hardy, able to withstand temperatures at least to 30s F for a short period of time. When grown in a pot, it may need some protection from cold weather or frost. It can be grown in colder regions as an annual and is often seen in markets in Peru and Ecuador. If grown in a climate that suits it, the large mature fruits may produce up to 15 fruits per plant.
The fruit of the Caigua is rich in vitamins A, E and C and is also full of antioxidants and proteins. It can be eaten raw, pickled, boiled, or fried, and is often added to salads and sauces. It can also be used as a side dish, similar to a stuffed pepper, with ingredients like meat, fish, or cheese. Additionally, it is featured in popular Andean dishes, such as locro, a dish made using maize, pork, and caigua.
Overall, the Cyclanthera pedata is a versatile and healthy plant native to South America, with many nutritional benefits. Easily grown in warmer climates, the fruit of the caigua can be eaten in different ways, making it an interesting addition to any garden.
Botanical name: Momordica balsamina
Common name: Balsam Apple
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Origin: Tropical Africa







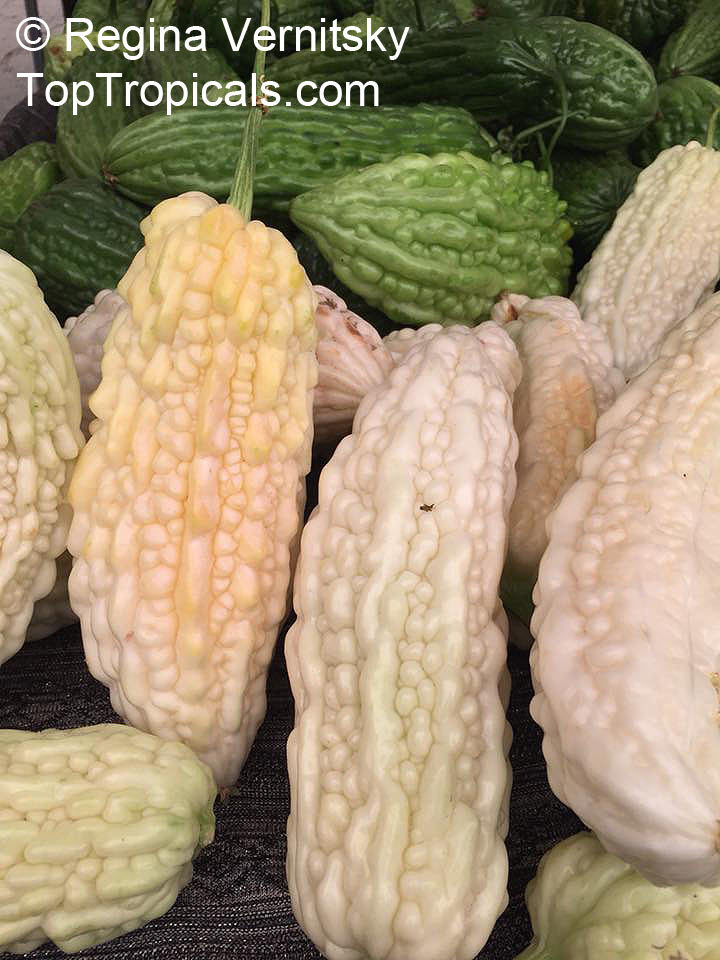
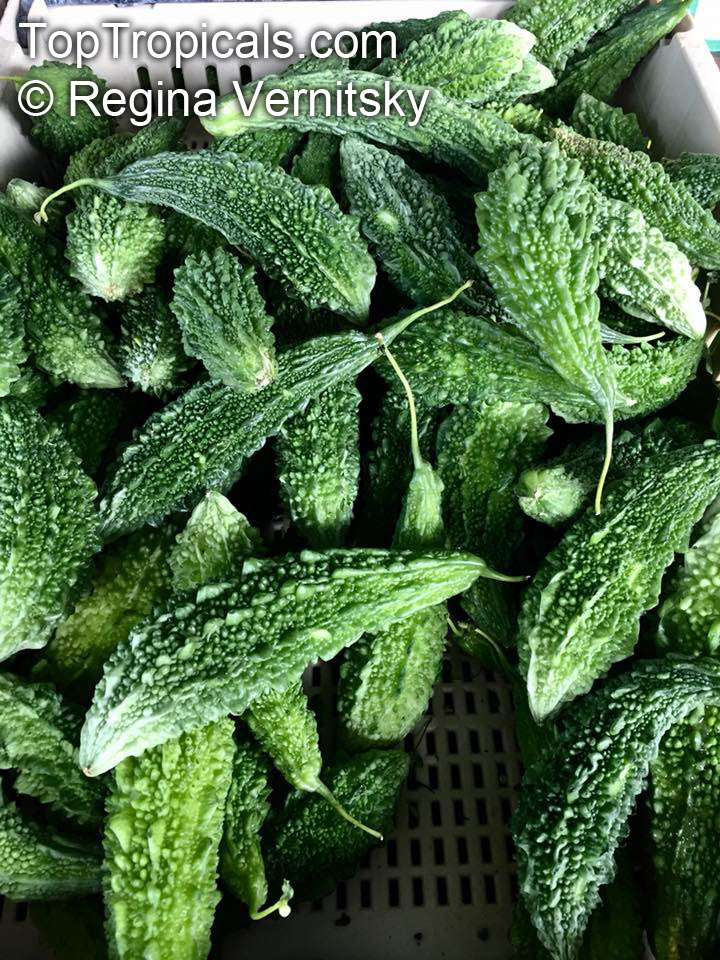
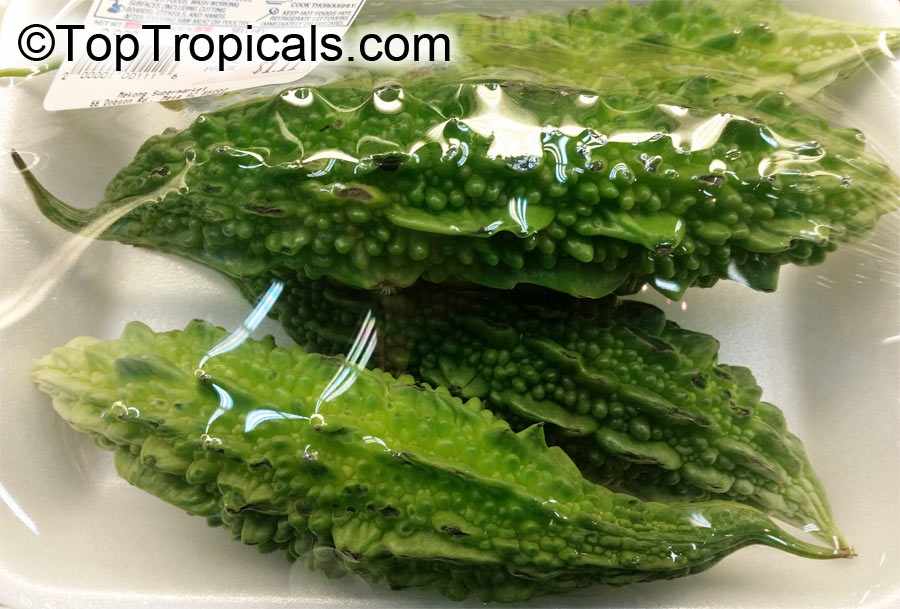
Botanical name: Momordica charantia
Common names: Bitter Melon, Balsam Apple, Balsam Pear, Karela
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Origin: SE Asia







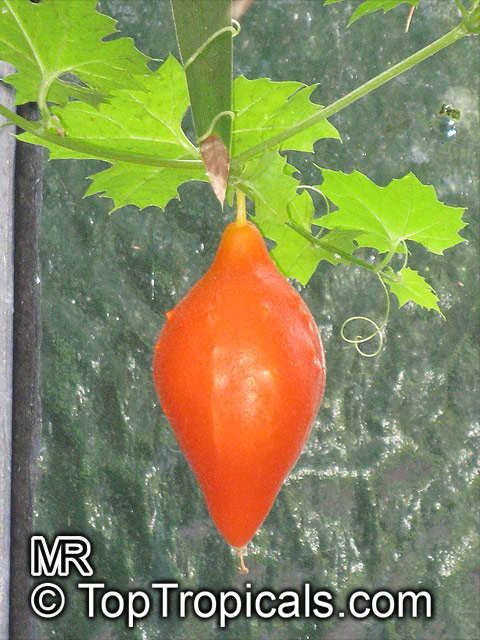
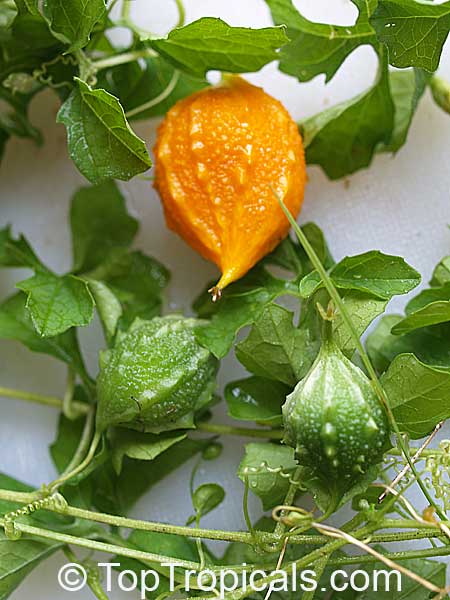
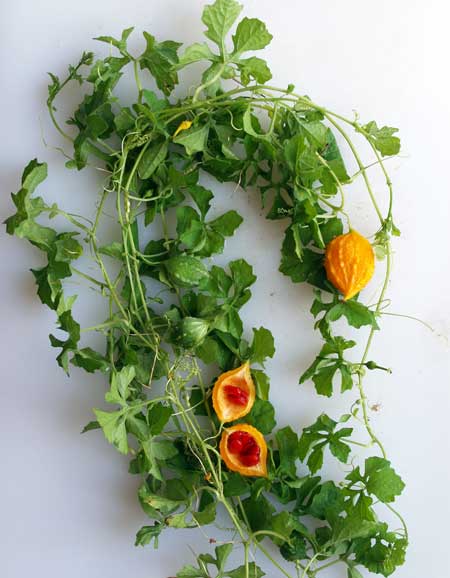
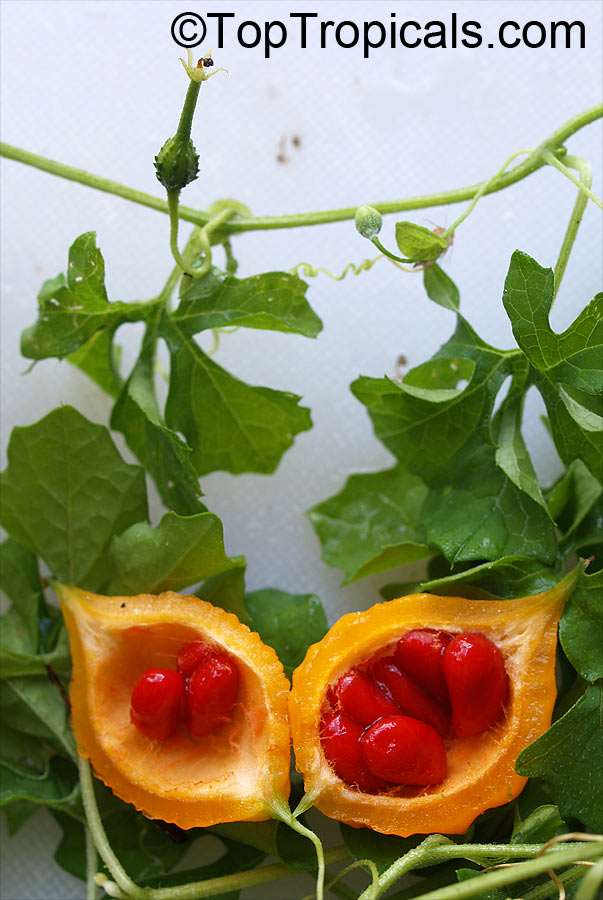
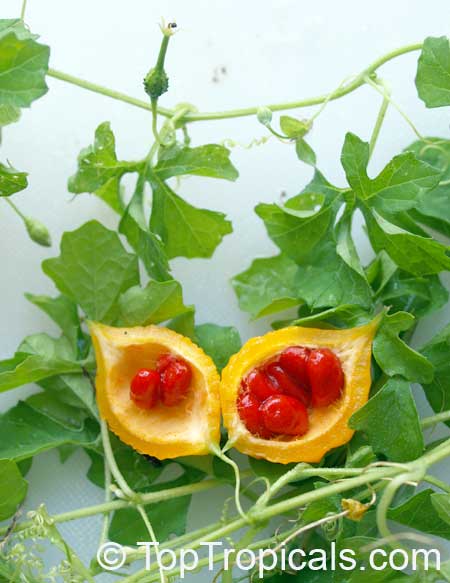
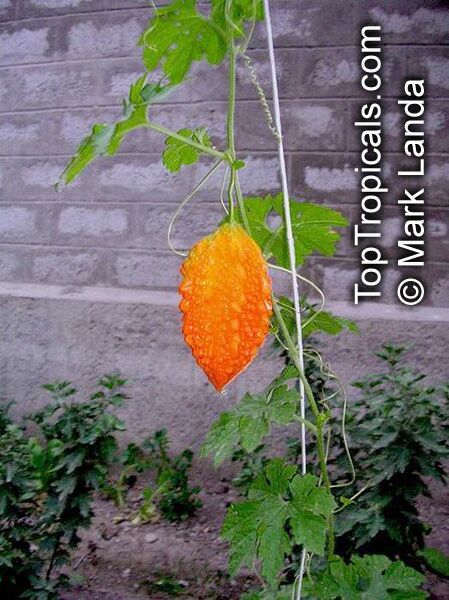
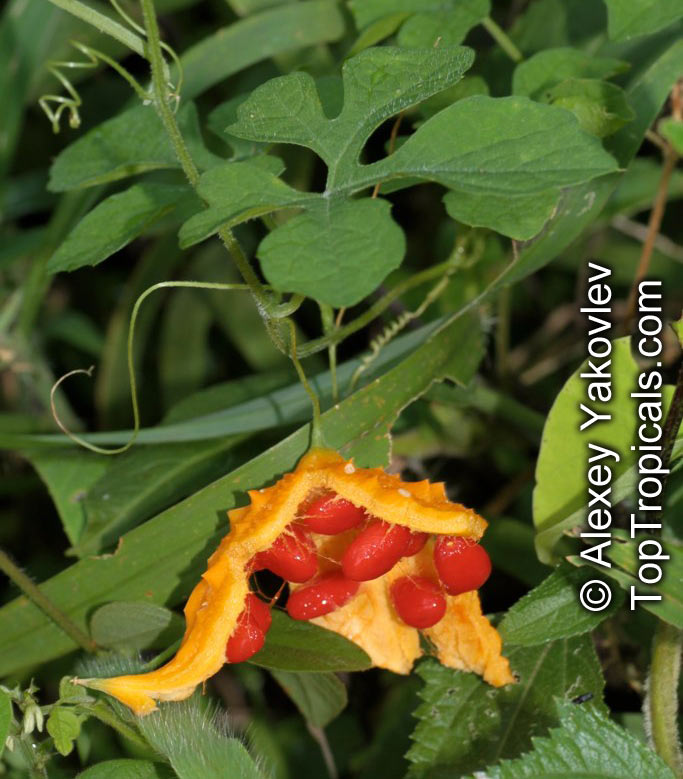
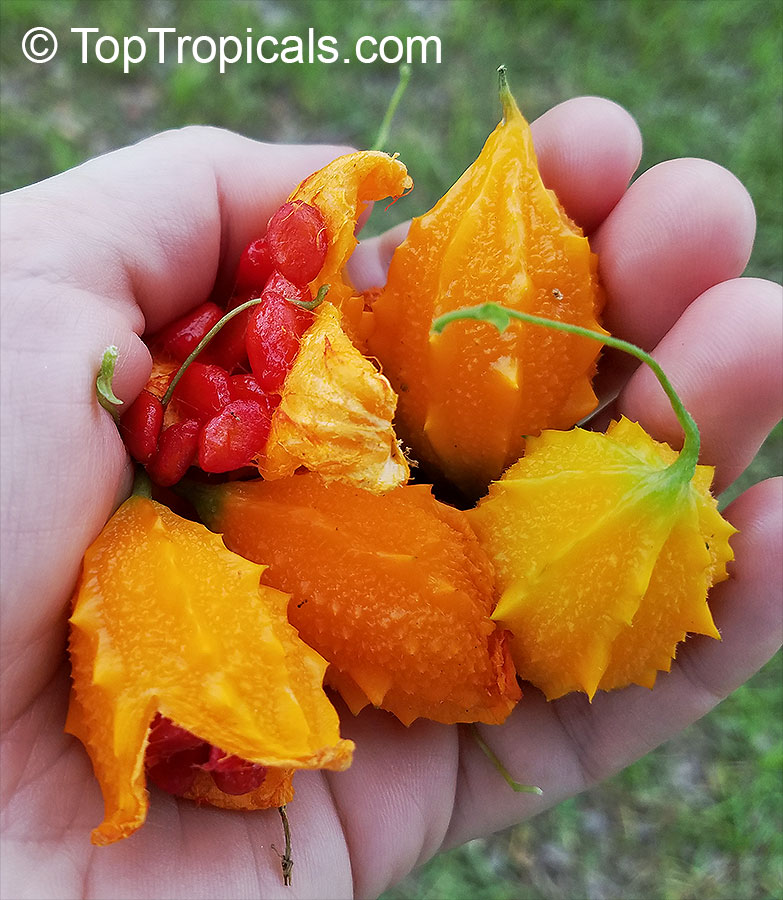
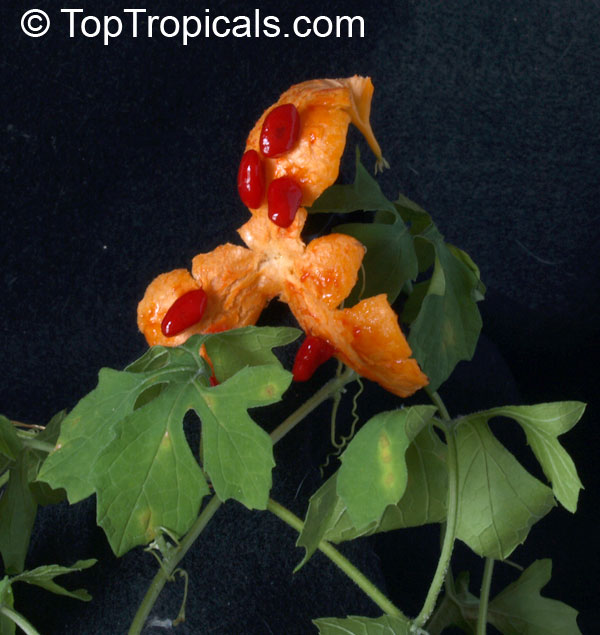
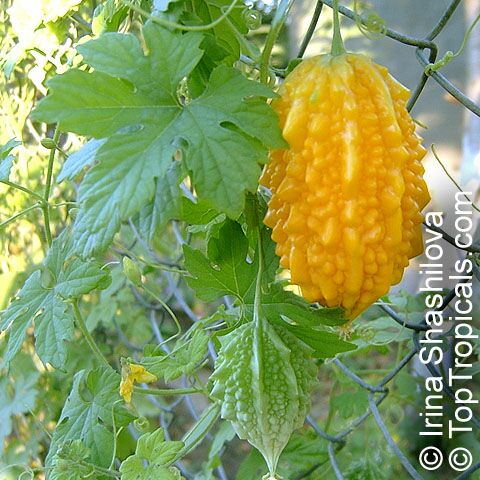
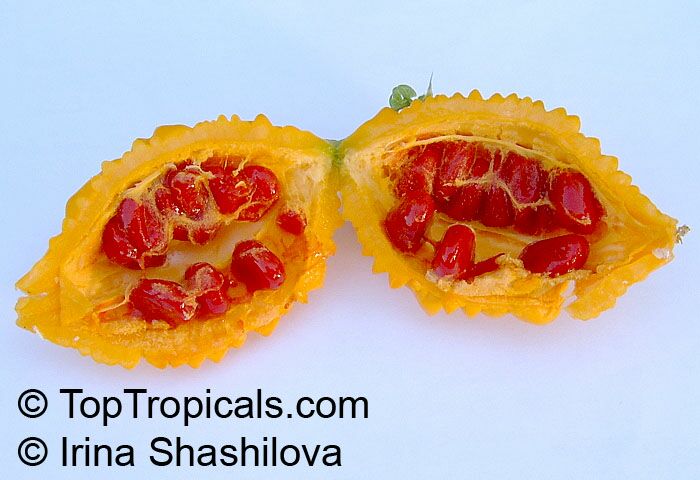
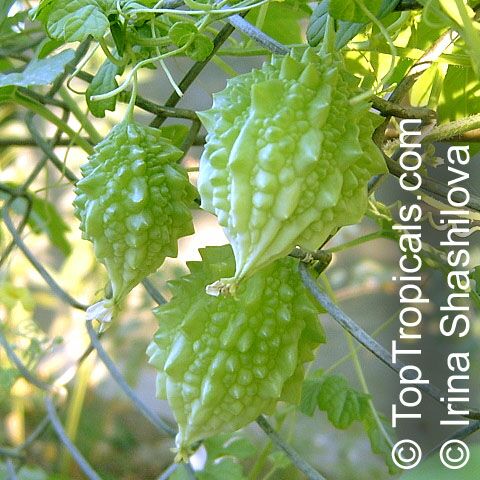
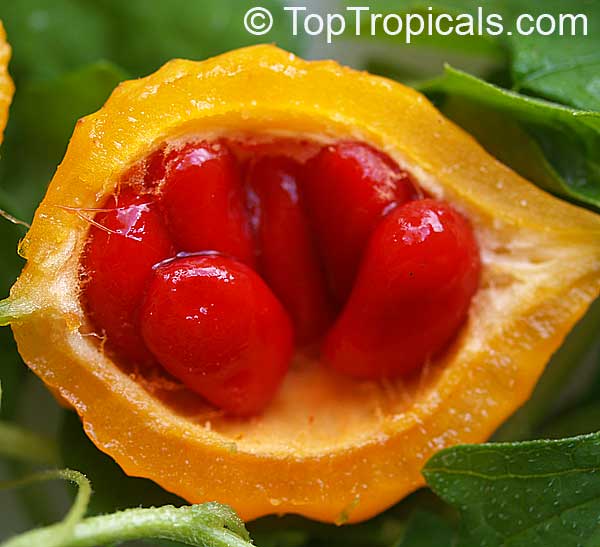
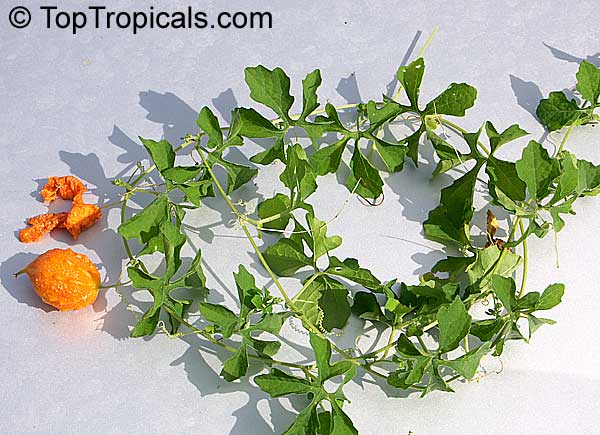
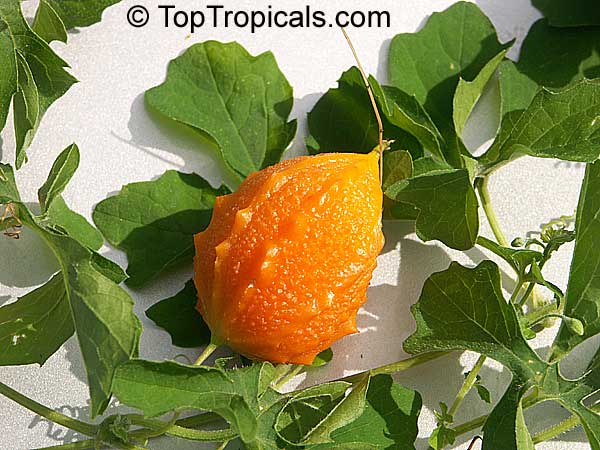
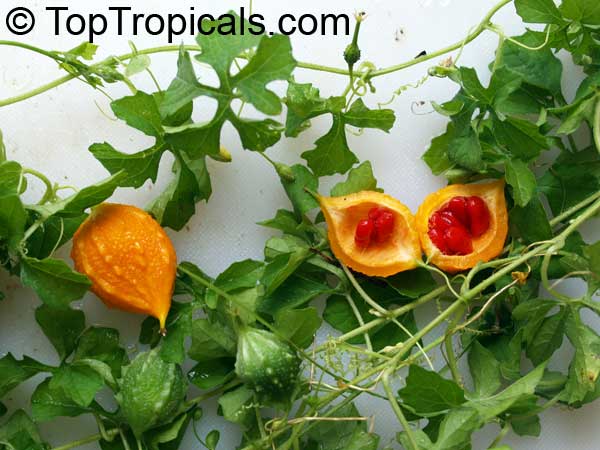
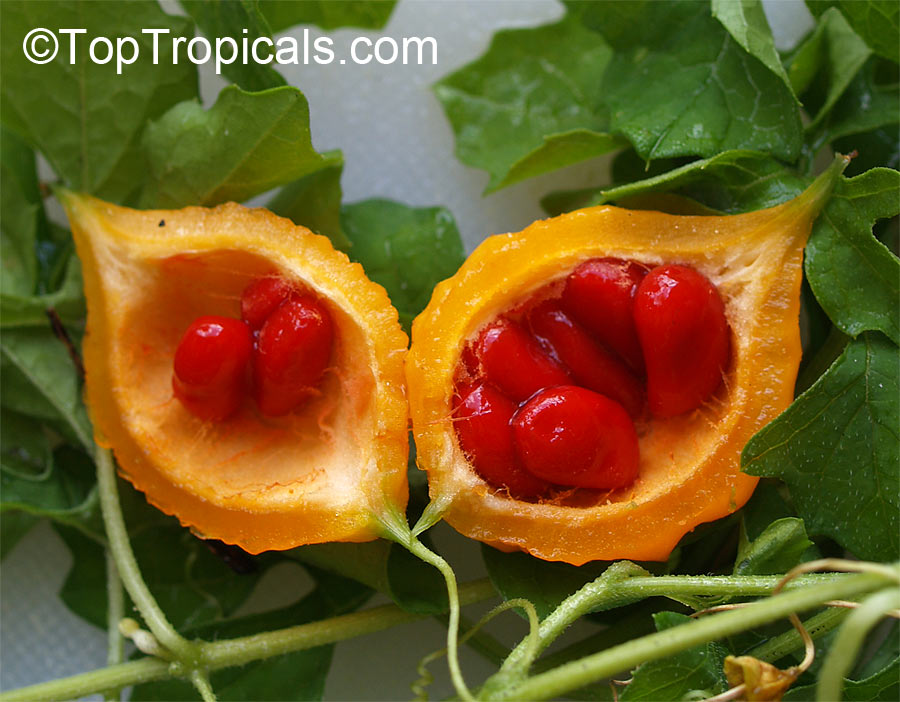
Momordica charantia is an annual and has a creeping or climbing stem. The fruit is broadly egg shaped, beaked, bumpy, ribbed, to 10 cm long and golden yellow to bright orange. At maturity the fruit breaks, bursting open along the 3 valves. The orange pulp contains bright red arils which enclose the seeds.
Momordica charantia has been used extensively in folk medicine as a remedy for diabetes. In Ayurveda, the fruit is considered as tonic, stomachic, stimulant, emetic, antibilous,laxative and alterative. The fruit is useful in gout, rheumatism and subacute cases of the spleen and liver diseases. It has also been shown to have hypoglycaemic properties (anti-diabetic) in animal as well as human studies.
Plant in rich moist soil, in frost free areas, since bitter melon is very sensitve to frost. Do not water too much.
In cooler climates start planting in pots 6 weeks before the frost free date; transplant when there is no more danger of frost.
Botanical names: Momordica cochinchinensis, Momordica macrophylla
Common names: Gac fruit, Spiny bitter-cucumber, Chinese bitter-cucumber
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Origin: SE Asia





Chinese bitter-cucumbers are yellow to reddish orange in color and have pale, firm flesh. The Indian is darker and thinner than the Chinese, while the Thai is white when immature. If left on the plant to ripen completely, the fruit bursts open. The light brown seeds are embedded in white, cottony flesh; but the seed coverings do taste pleasantly sweet and are often used as a condiment.
Momordica Cochinchinencis is a traditional medicinal plant in India, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, China, the Philippines, and the Caribbean, and has been used since early time. It was commonly grown in gardens and gave red fruit with red pulp. This plant is quite familiar to women; they know perfectly how to conserve such fruits and make use of them for various purposes such as cooking glutinous rice with fresh pulp, making dried pulp candy, jam, for the treatment of blur eyes, malnutrition as they contain active substances (now called pre-vitamin A).It is a good vegetable to hollow out and fill; but also delicious is curries, pickled, stir-fried, and salads; but it needs to be blanched before using as it cannot be eaten raw.
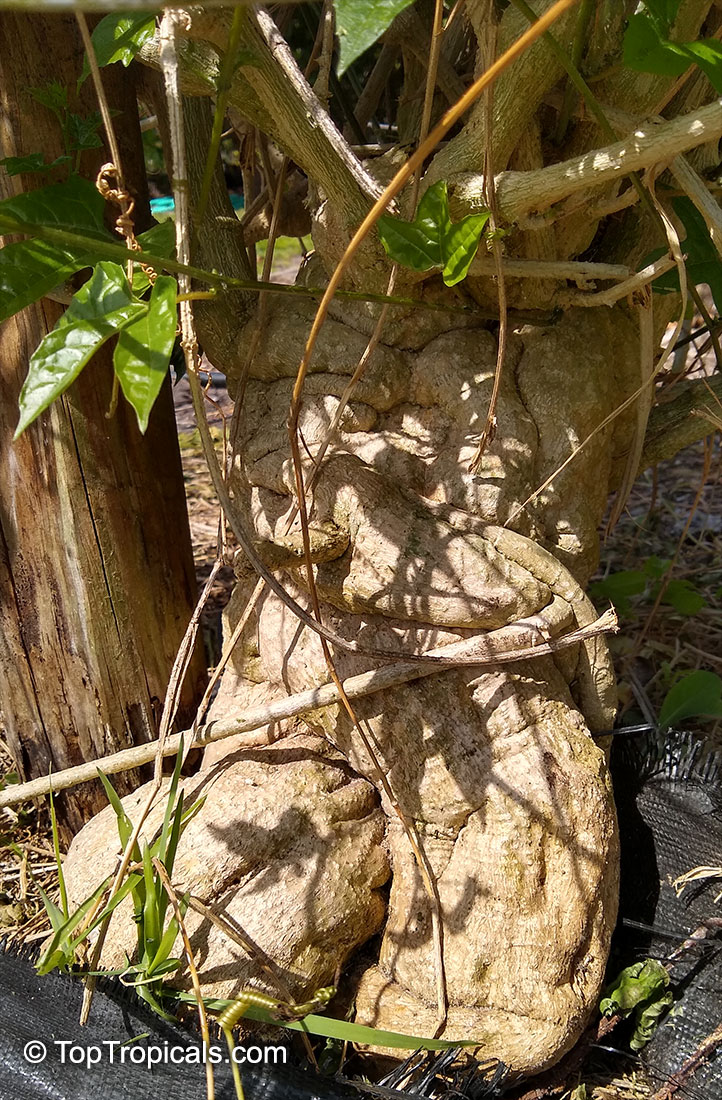
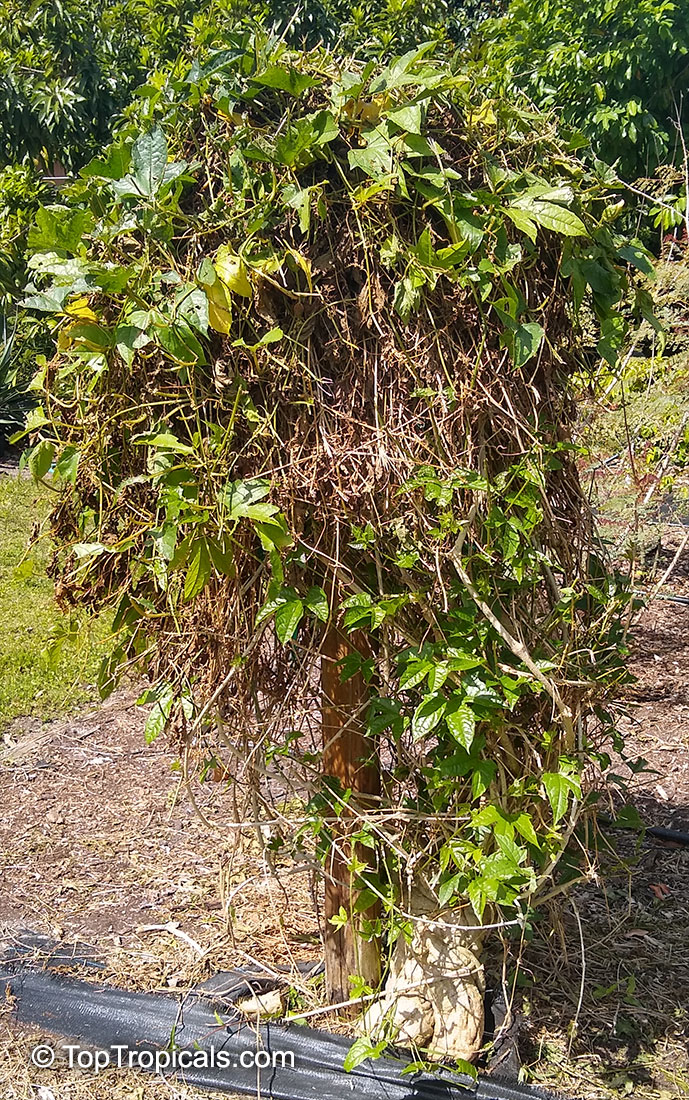
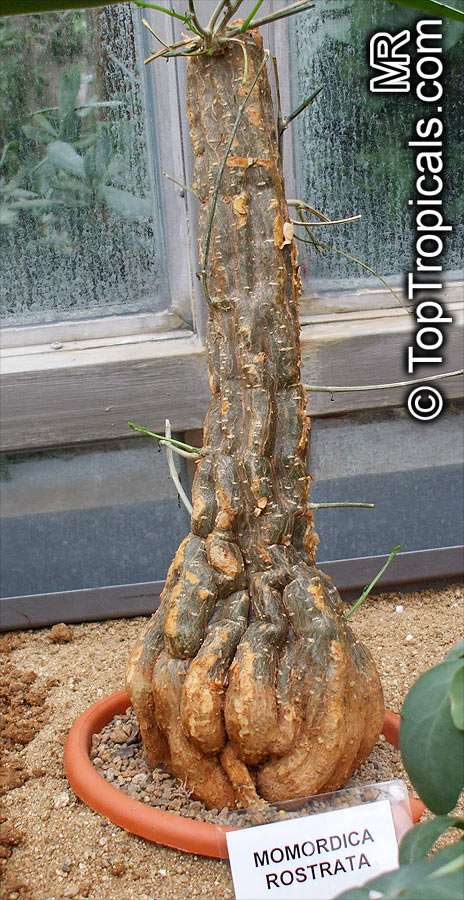
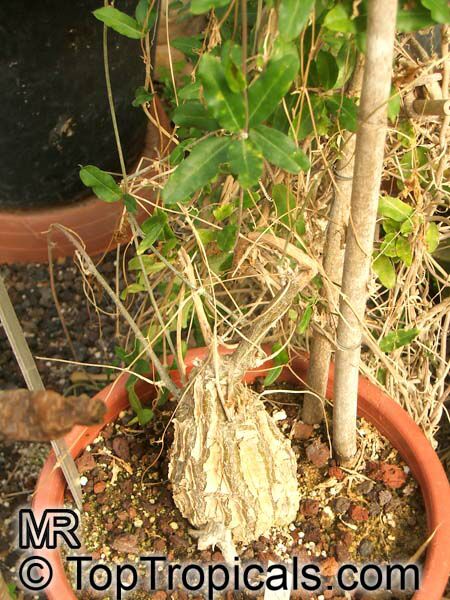
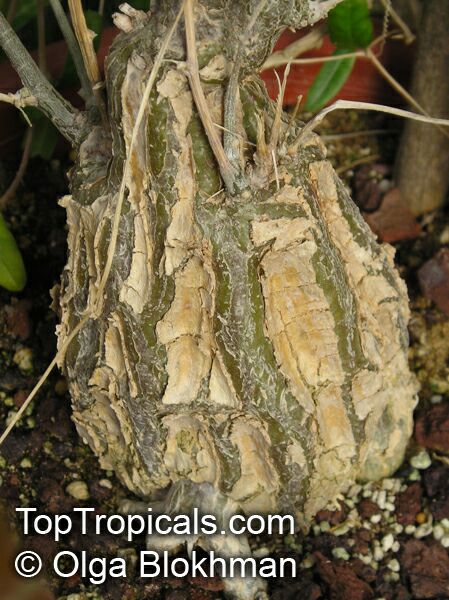
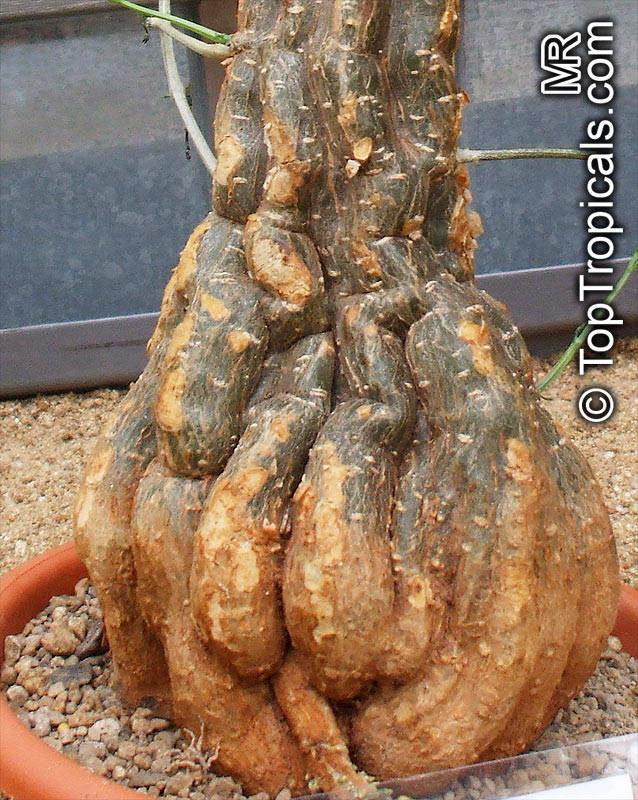
Botanical name: Momordica rostrata
Common name: Momordica
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Origin: East Africa



It prefers a well-drained soil, plenty of water in growth and some sun. The caudex will grow to 30 centimetres in diameter.
Use link to repeat this search:
https://toptropicals.com/cgi-bin/garden_catalog/cat.cgi?find=momordica&search_op=and&keyword_op=and&language=e&number=10
&no_change_lang=1&user=tt&sale=1&first=0




















































