Schinus terebinthifolius
Brazilian pepper-treeFamily: Anacardiaceae
Origin: Brazil








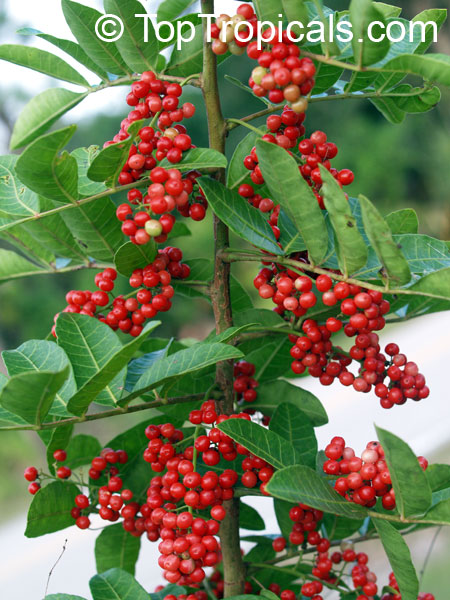
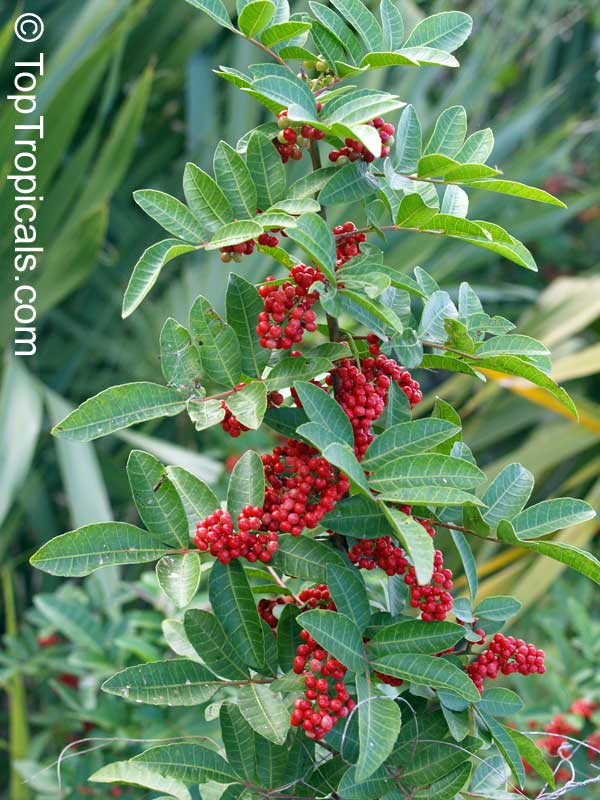
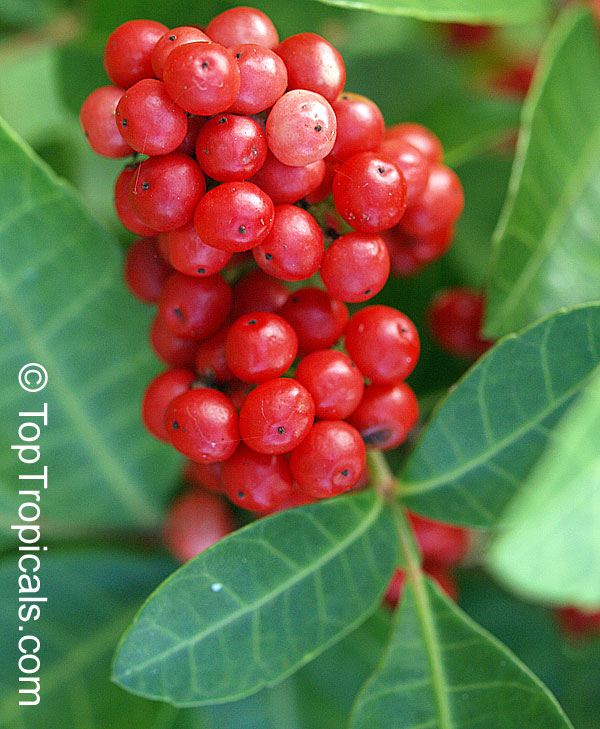
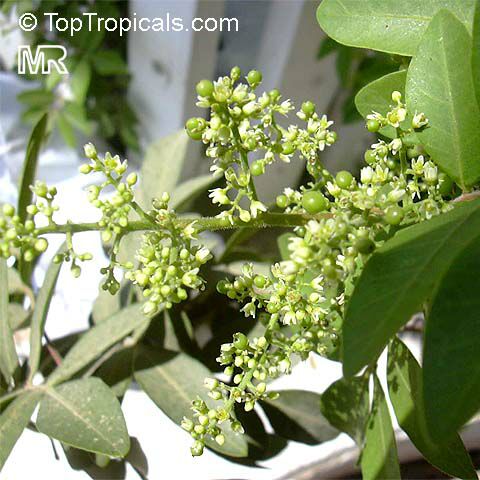
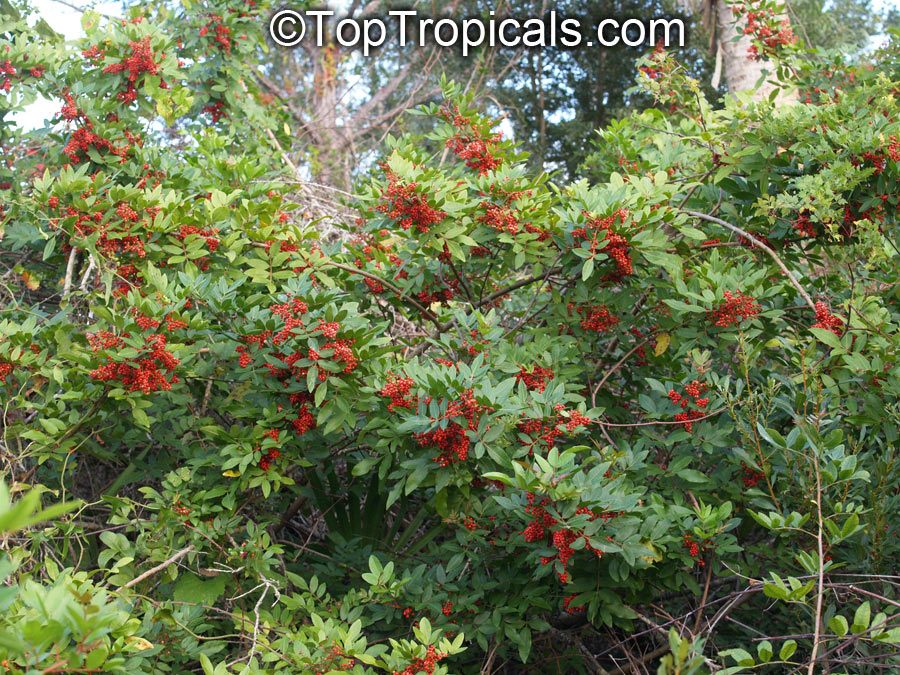
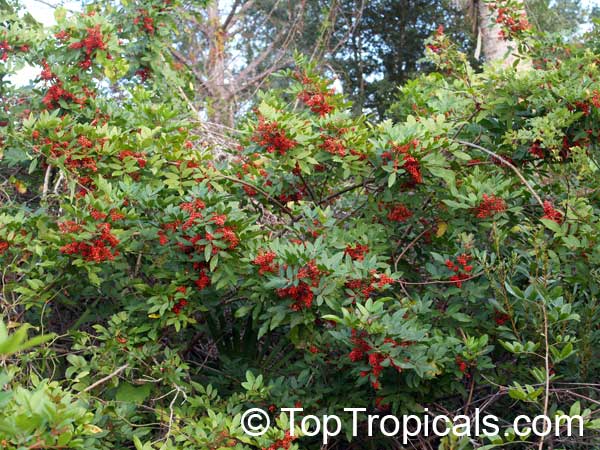
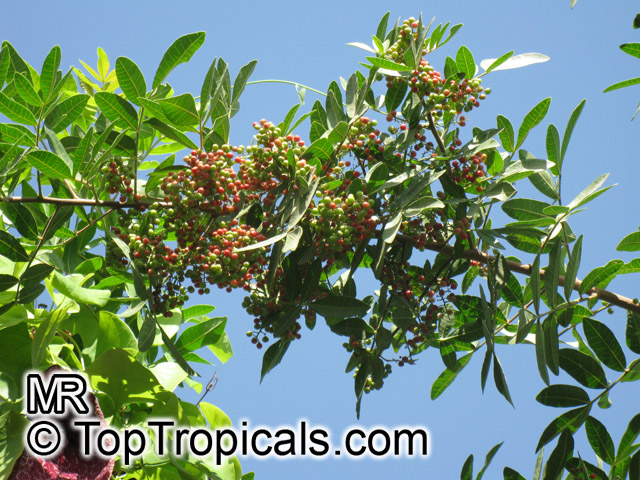
Brazilian pepper is a small tree, to 30 feet tall, with a short trunk usually hidden by dense intertwining branches. The leaves have a reddish, sometimes winged midrib. Leaves have 3 to 13 finely toothed leaflets which are 1 to 2 inches long. Leaves smell of turpentine when crushed. Numerous white or yellowish flowers are born on panicles and are insect pollinated. In Florida flowers are pollinated by a native syrphid fly. The tree is dioecious. The fruits are in clusters, glossy, green and juicy at first, becoming bright red. The red skin dries to become a papery shell surrounding the seed. Brazilian pepper is a beautiful evergreen with showy bright red berries that are used by South Floridians for Christmas decorations. Honey bees make honey from the flowers. The berries are a very important food source for wintering songbirds. Skin contact with leaves and the milky sap results in red, itching rashes and the tree's allergens also cause respiratory difficulties in many people. The leaves are aromatic and have a faint turpentine scent when crushed. The seeds have a peppery taste and are sometimes sold as "pink pepper". Fruit are used for producing red pepper but can be toxic if eaten in quantity. Since their peppery taste is much weaker than real peppercorns, they are mostly used for decorative purpose in dishes. Possession and cultivation of Brazilian pepper is illegal in Florida where the species is listed on the state's official Noxious Weeds List.
Similar plants:







